初中英语语法大全——代词(共34张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 初中英语语法大全——代词(共34张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-04-10 10:23:54 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共34张PPT)
初中英语语法大全
代词
代词是代替名词或起名词作用的词,短语,分句或句子,因此,代词的使用必须和它所代替的词在人称、数和格上保持一致。代词本身的词义很弱,必须通过上下文来确定。大多数代词具有指代和修饰的功能。在英语中代词的使用极为广泛。正确运用代词可以使句子简洁、明快,但是如果使用不当也容易产生意义理解上的偏差。
一.人称代词
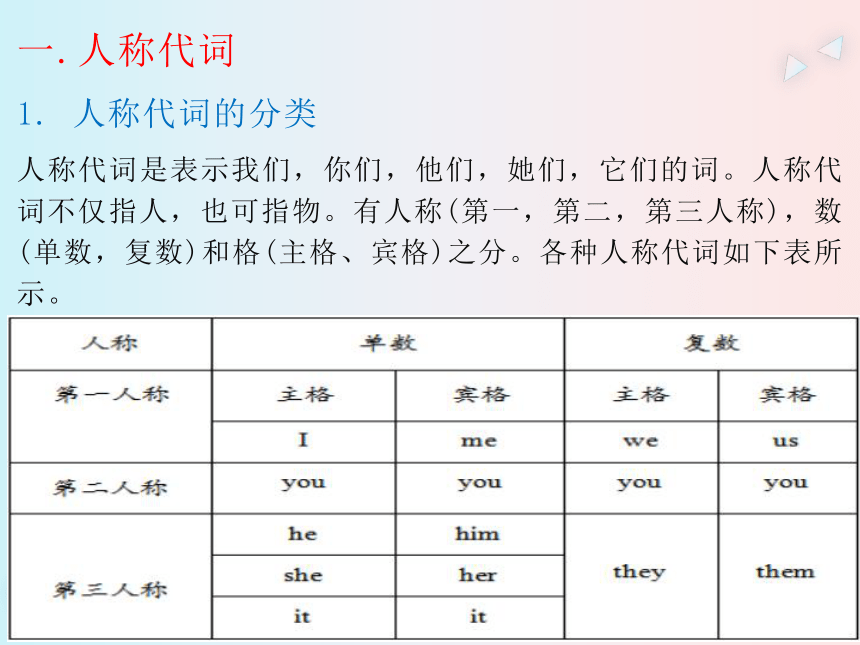
1. 人称代词的分类
人称代词是表示我们,你们,他们,她们,它们的词。人称代词不仅指人,也可指物。有人称(第一,第二,第三人称),数(单数,复数)和格(主格、宾格)之分。各种人称代词如下表所示。
2. 人称代词的句法功能
(1) 作主语
人称代词作主语时用主格
Look at the girl in the red skirt. She is my new classmate.
I can't say much for what you have done.
(2) 作宾语
作动词和介词的宾语时用宾格
Peter is my best friend.He often helps me with science.
It's a good habit of mood to read a few lines before going to bed.
(3) 作表语
作表语时用主格,但在口语中常用宾格
Who is knocking at the door? It's me/ I.
I saw at once it was her.
(4) 作同位语
Two students, he and I, was sent to buy some food and drink for the picnic.
The dinner was cooked by us girls.
3. 人称代词的用法
(1)并列人称的用法
A. 单数场合的排列顺序为: you+he/she+I
You, she and me all enjoy music.
You, Tom and I will go to Canada next month.
B. 负数场合的排列顺序为: we+you+they
We, you and they are to spare no effort to finish this work.
We, you and they are all Chinese.
(2) it的用法
A. 可用来代替上文提到过的事物
What do you think of the movie by Zhao Wei Terrific. I like it very much.
You have saved my life; I shall never forget it.
B. 用来指代时间、地点、距离、天气、温度等
It's seven o'clock now.
It's about five minutes' walk from my school to the park.
It's often rains in Nanjing in April.
C. 用来指代婴儿和不知身份,性别的人
Who is dancing in the classroom It must be Lily.
The baby is crying. It might be hungry.
D. 做形式主语或形式宾语
it可以代替不定式,动名词,从句等做形式主语或形式宾语,而把真正的主语和宾语置于句末。
It's hard work keeping the grass green at this time of year.
Did you find it very interesting to play volleyball
二.物主代词
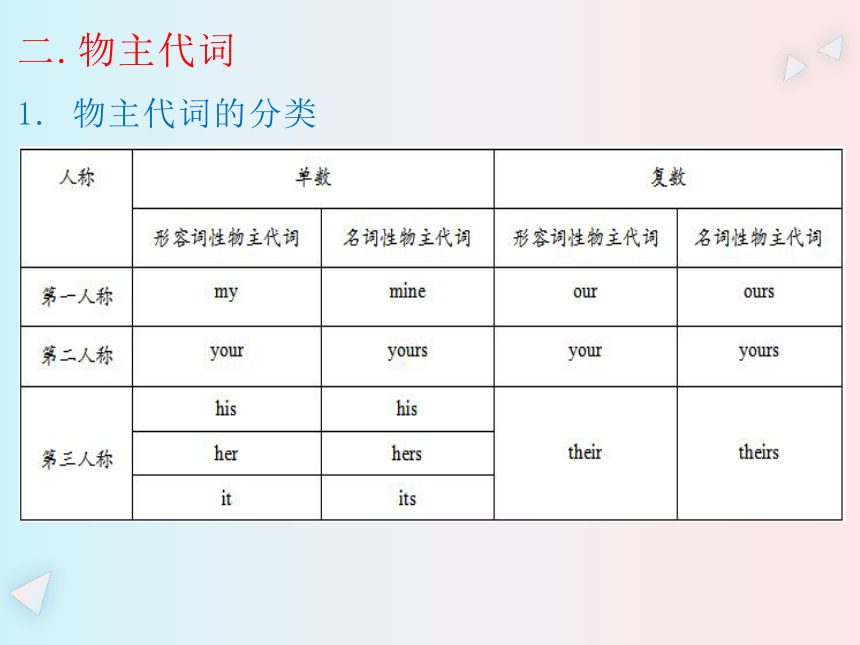
1. 物主代词的分类
2. 物主代词的用法
(1) 形容词性物主代词
形容词性物主代词相当于形容词,只能置于名词前作定语。
Their room is on the third floor.
The students are helping the old man clean his house now.
(2) 名词性物主代词
名词性物主代词,相当于“形容词性物主代词+名词”,其后不能接名词,句法功能与名词相同。
May I use your pen Yours works better.
If you don't have a dictionary on hand, you may use mine.
三. 反身代词
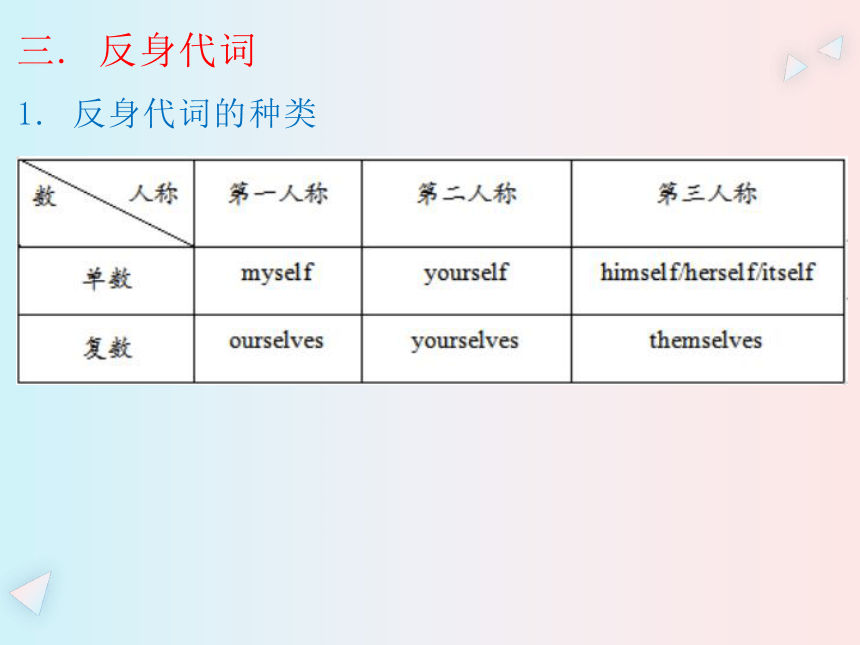
1. 反身代词的种类
2. 反身代词的句法功能
反身代词与它所指代的名词或代词形成互指关系,在人称和数上保持一致,可在句中作宾语、表语、同位语。
(1) 作宾语
反身代词作动词的宾语,表示动作的承受者,就是动作的执行者,也可用在介词后作宾语,与句子主语互指。
Boys, don't lose yourselves in playing. It's bad for your eyes to play computer games for long time.
Very important for us to learn how to learn by ourselves.
(2) 作表语
在be, feel, look, seem等系动词后作表语,表示身体和精神所处的状态。
After a few days of rest, He was more himself again.
He doesn't seem himself today.
(3) 作同位语
作宾语和主语的同位语,起加强语气的作用,表示“亲自、本身、本人”。
The story itself is good, only he did not tell it well.
I spoke to the headmaster himself.
四. 相互代词
相互代词表示相互关系的代词。主要有each other和one another, 意为“相互,互相”。each other 主要用于两者之间,one another要用于三者或三者以上。在现代英语中,each other也可以用于三者或三者以上之间。其用法如下:
1. 相互代词作宾语
We often help each other/ one another when we are in trouble.
He put all his books beside each other/ one another.
2. 相互代词作定语
相互代词的所有格用作定语,表示所属关系。
We said hello to one another's/ each other's family.
We usually meet in one another's house.
五. 指示代词
指示代词是用来指代或标记人或事物的代词,表示这个/些,那个/些。常用的指示代词有this, that, these, those。指示代词的用法如下:
1. 指示代词的基本用法
(1) this/ these表示在时间上或空间上较近的人或物。that/ those表示在时间上或空间上较远的人或物。
This is my new pen pal.
I like these flowers very much.
That is a lovely boy.
In those days the workers had a hard time.
(2) that还可以指上文提到的事物,this指下文中将要提到的事物。
I had a bad cold. That was why I didn't go to school.
Please remember this: No pains, No gains.
(3) 打电话时,常用this指自己,that指对方。
This is Allen. Who's that speaking
Hello, this is Mary. Who's that This is Tom.
2. that和those作替代词的用法
为了避免重复,that可指代前面提到的单数可数名词和不可数名词,those可代替复数可数可数名词,其后总有修饰。
In summer in Beijing is cooler than that in Shanghai.
Television sets made in Beijing are just as good as those made in Shanghai.
六. 不定代词
1.some, any
(1) 表示“一些”时,some和any既可以修饰可数名词,也可以修饰不可数名词。一般来说,some常用于肯定句中,而any常用于否定句和疑问句中。
He asked for tea, so I gave him some.
There is not any water in the bottle.
Is there any reason for changing the plan
(2) some用于疑问句时,表建议请求,邀请等,并希望得到对方的肯定回答。
Would you buy me some stamps when you pass the post office
Can I have some coffee with sugar
2. all, both
(1) all和both都意为“都”。all指三者或三者以上的人或物; both则指两个人或物。
They were only two paintings for sale and he bought both.
We should protect the beautiful flowers on both sides of the street.
All of them have now become writers.
All was quiet in the street outside.
Both men and women are not of the same character.
3. one
(1) 可以用来代替单数可数名词,表示泛指意义;ones用来代替复数可数名词。
I've been looking for map but I can't find one.
There are twenty old tables in our classroom. Our teacher wants to buy ten new ones.
(2) one, it和that的区别
one可指代单数可数名词,指上文出现过的同一类事物。替代同一类人或事物时,其前面必须有如the, some, all等限定词,同一类人或事物的复数用ones。it可代替单数可数词,指同一个,不能带任何修饰语。that可代替前面提到过的单数可数名词或者不可数名词,他表示同一类而不是同一个,其后面常带有修饰语。
Which jacket would you like, this one or that one
I can't find my hat, I don't know where I put it.
The population of China is larger than that in India.
4. either,neither
(1) either表示“两者中的任何一个”,做主语时,谓语动词常用单数形式,起其后可接of短语。
You can come on Saturday or Sunday. Either is OK for me.
We can't care much for what to eat. Either of the two will do.
(2) neither 表示“两者都不”,做主语时,谓语动词常用单数形式,其后可接of短语。
We have red and yellow T-shirts. Which color do you like
Oh, neither. I think blue will be OK.
Neither of them wants to speak to him about this matter.
5. none, no one
(1) none意为“三者或三者以上都不”,指代人或物,既可指代复数可数名词,也可指代不可数名词,可与of连用。替代复数可数名词做主语时,谓语动词用单、复数均可。常用来回答以how many/ how much提出的特殊疑问句。
How much money do you have --- None.
I need some paper, but there is none at hand.
(2) no one意为“没有一个人”,常指人,仅用于指代单数可数名词,常用来回答以who提出的特殊疑问句。
Who is absent from class today No one, sir.
No one knows all of it.
6. other, the other, others, the others和another
(1) other意为“另外的”,只能作定语,常与复数可数名词和不可数名词连用。
I suggested a camping holiday, but Jane had other ideas.
Other people may not think that way.
They have no other place to go.
(2) the other意为“两者中的另一个”,常与one连用,构成"one...the other..."结构。
I have two brothers. One is a salesman, and the other is an engineer.
Hold it in this hand, not the other hand.
(3) others泛指"别的人或物",相当于"other+复数可数名词",常构成“some...others...”结构。
Some boys are playing basketball, and others are playing soccer.
Some people like tea, others like coffee and others like milk.
(4) the others特指“其余所有的人或物”,相当于“the other+ 复数可数名词”。
Three of us remain here and all the others go to the next room.
Some students swept the floor, and the others cleaned the windows.
(5) another表示“三者或三者以上中的任何一个”,一般修饰或代替单数可数名词。常用于“another+数词+复数可数名词”结构,相当于“数词+more/other+复数可数名词”,表示在原有的基础上需要更多数量的东西。
Could we see each other at nine o'clock tomorrow morning
Sorry. Let's make it another time.
They need another two hours to finish this work.
We will have to wait another three weeks for the results.
7. many, much
(1) many和much都表示“许多,大量”。many只修饰复数可数名词,much是修饰不可数名词。
My cousins have collected stamps for two years, they have many stamps from different countries.
It's a small car,doesn't use much fuel.
(2) too many和too much都表示“太多”,too many修饰复数可数名词,too much修饰不可数名词。much too表示“实在太”,修饰形容词或副词。
There are too many mistakes in your homework.
I have too much work to do.
I'm afraid that this cap is much too big for me.
8. few, a few, little, a little
I have been to Beijing a few times.
He has written many books, but few of them are good.
Please add a little sugar to the coffee.
There is little news about this movie star in this paper. Where can I get some
七. 疑问代词
1. who, whom的用法
两者都意为"谁",用来指人,其中who可做主语,宾语和表语,whom只用作宾语。在介词后作宾语只能用whom, 而不能用who。
Who is that man over there He's my uncle.
Who are you writing to
To whom did you speak on the playground
2. whose的用法
whose意为"谁的",既可置于名词前作定语,也可单独使用,作主语和表语。
Whose dictionary is this
They are good at math, but whose is the best
Whose are those flowers
3. which的用法
which意为"哪一个,哪一些",可用来指代人或物在句中作主语,宾语和定语。它与who及what的不同在于which一般有特定的选择范围,而who和what则没有。
Which would you like to choose to live in, Chengdu, Beijing or Shanghai Chengdu, I think.
Which T- shirt do you like better, the red one or the blue one I prefer the red one.
4. what的用法
what意为"什么"可单独使用,也可放在名词前,既可以指代或修饰单数可数名词,也可以指代或修饰复数可数名词。在句中作主语,宾语,表语,定语。
What makes you love your hometown so much
What are your reasons for leaving
初中英语语法大全
代词
代词是代替名词或起名词作用的词,短语,分句或句子,因此,代词的使用必须和它所代替的词在人称、数和格上保持一致。代词本身的词义很弱,必须通过上下文来确定。大多数代词具有指代和修饰的功能。在英语中代词的使用极为广泛。正确运用代词可以使句子简洁、明快,但是如果使用不当也容易产生意义理解上的偏差。
一.人称代词
1. 人称代词的分类
人称代词是表示我们,你们,他们,她们,它们的词。人称代词不仅指人,也可指物。有人称(第一,第二,第三人称),数(单数,复数)和格(主格、宾格)之分。各种人称代词如下表所示。
2. 人称代词的句法功能
(1) 作主语
人称代词作主语时用主格
Look at the girl in the red skirt. She is my new classmate.
I can't say much for what you have done.
(2) 作宾语
作动词和介词的宾语时用宾格
Peter is my best friend.He often helps me with science.
It's a good habit of mood to read a few lines before going to bed.
(3) 作表语
作表语时用主格,但在口语中常用宾格
Who is knocking at the door? It's me/ I.
I saw at once it was her.
(4) 作同位语
Two students, he and I, was sent to buy some food and drink for the picnic.
The dinner was cooked by us girls.
3. 人称代词的用法
(1)并列人称的用法
A. 单数场合的排列顺序为: you+he/she+I
You, she and me all enjoy music.
You, Tom and I will go to Canada next month.
B. 负数场合的排列顺序为: we+you+they
We, you and they are to spare no effort to finish this work.
We, you and they are all Chinese.
(2) it的用法
A. 可用来代替上文提到过的事物
What do you think of the movie by Zhao Wei Terrific. I like it very much.
You have saved my life; I shall never forget it.
B. 用来指代时间、地点、距离、天气、温度等
It's seven o'clock now.
It's about five minutes' walk from my school to the park.
It's often rains in Nanjing in April.
C. 用来指代婴儿和不知身份,性别的人
Who is dancing in the classroom It must be Lily.
The baby is crying. It might be hungry.
D. 做形式主语或形式宾语
it可以代替不定式,动名词,从句等做形式主语或形式宾语,而把真正的主语和宾语置于句末。
It's hard work keeping the grass green at this time of year.
Did you find it very interesting to play volleyball
二.物主代词
1. 物主代词的分类
2. 物主代词的用法
(1) 形容词性物主代词
形容词性物主代词相当于形容词,只能置于名词前作定语。
Their room is on the third floor.
The students are helping the old man clean his house now.
(2) 名词性物主代词
名词性物主代词,相当于“形容词性物主代词+名词”,其后不能接名词,句法功能与名词相同。
May I use your pen Yours works better.
If you don't have a dictionary on hand, you may use mine.
三. 反身代词
1. 反身代词的种类
2. 反身代词的句法功能
反身代词与它所指代的名词或代词形成互指关系,在人称和数上保持一致,可在句中作宾语、表语、同位语。
(1) 作宾语
反身代词作动词的宾语,表示动作的承受者,就是动作的执行者,也可用在介词后作宾语,与句子主语互指。
Boys, don't lose yourselves in playing. It's bad for your eyes to play computer games for long time.
Very important for us to learn how to learn by ourselves.
(2) 作表语
在be, feel, look, seem等系动词后作表语,表示身体和精神所处的状态。
After a few days of rest, He was more himself again.
He doesn't seem himself today.
(3) 作同位语
作宾语和主语的同位语,起加强语气的作用,表示“亲自、本身、本人”。
The story itself is good, only he did not tell it well.
I spoke to the headmaster himself.
四. 相互代词
相互代词表示相互关系的代词。主要有each other和one another, 意为“相互,互相”。each other 主要用于两者之间,one another要用于三者或三者以上。在现代英语中,each other也可以用于三者或三者以上之间。其用法如下:
1. 相互代词作宾语
We often help each other/ one another when we are in trouble.
He put all his books beside each other/ one another.
2. 相互代词作定语
相互代词的所有格用作定语,表示所属关系。
We said hello to one another's/ each other's family.
We usually meet in one another's house.
五. 指示代词
指示代词是用来指代或标记人或事物的代词,表示这个/些,那个/些。常用的指示代词有this, that, these, those。指示代词的用法如下:
1. 指示代词的基本用法
(1) this/ these表示在时间上或空间上较近的人或物。that/ those表示在时间上或空间上较远的人或物。
This is my new pen pal.
I like these flowers very much.
That is a lovely boy.
In those days the workers had a hard time.
(2) that还可以指上文提到的事物,this指下文中将要提到的事物。
I had a bad cold. That was why I didn't go to school.
Please remember this: No pains, No gains.
(3) 打电话时,常用this指自己,that指对方。
This is Allen. Who's that speaking
Hello, this is Mary. Who's that This is Tom.
2. that和those作替代词的用法
为了避免重复,that可指代前面提到的单数可数名词和不可数名词,those可代替复数可数可数名词,其后总有修饰。
In summer in Beijing is cooler than that in Shanghai.
Television sets made in Beijing are just as good as those made in Shanghai.
六. 不定代词
1.some, any
(1) 表示“一些”时,some和any既可以修饰可数名词,也可以修饰不可数名词。一般来说,some常用于肯定句中,而any常用于否定句和疑问句中。
He asked for tea, so I gave him some.
There is not any water in the bottle.
Is there any reason for changing the plan
(2) some用于疑问句时,表建议请求,邀请等,并希望得到对方的肯定回答。
Would you buy me some stamps when you pass the post office
Can I have some coffee with sugar
2. all, both
(1) all和both都意为“都”。all指三者或三者以上的人或物; both则指两个人或物。
They were only two paintings for sale and he bought both.
We should protect the beautiful flowers on both sides of the street.
All of them have now become writers.
All was quiet in the street outside.
Both men and women are not of the same character.
3. one
(1) 可以用来代替单数可数名词,表示泛指意义;ones用来代替复数可数名词。
I've been looking for map but I can't find one.
There are twenty old tables in our classroom. Our teacher wants to buy ten new ones.
(2) one, it和that的区别
one可指代单数可数名词,指上文出现过的同一类事物。替代同一类人或事物时,其前面必须有如the, some, all等限定词,同一类人或事物的复数用ones。it可代替单数可数词,指同一个,不能带任何修饰语。that可代替前面提到过的单数可数名词或者不可数名词,他表示同一类而不是同一个,其后面常带有修饰语。
Which jacket would you like, this one or that one
I can't find my hat, I don't know where I put it.
The population of China is larger than that in India.
4. either,neither
(1) either表示“两者中的任何一个”,做主语时,谓语动词常用单数形式,起其后可接of短语。
You can come on Saturday or Sunday. Either is OK for me.
We can't care much for what to eat. Either of the two will do.
(2) neither 表示“两者都不”,做主语时,谓语动词常用单数形式,其后可接of短语。
We have red and yellow T-shirts. Which color do you like
Oh, neither. I think blue will be OK.
Neither of them wants to speak to him about this matter.
5. none, no one
(1) none意为“三者或三者以上都不”,指代人或物,既可指代复数可数名词,也可指代不可数名词,可与of连用。替代复数可数名词做主语时,谓语动词用单、复数均可。常用来回答以how many/ how much提出的特殊疑问句。
How much money do you have --- None.
I need some paper, but there is none at hand.
(2) no one意为“没有一个人”,常指人,仅用于指代单数可数名词,常用来回答以who提出的特殊疑问句。
Who is absent from class today No one, sir.
No one knows all of it.
6. other, the other, others, the others和another
(1) other意为“另外的”,只能作定语,常与复数可数名词和不可数名词连用。
I suggested a camping holiday, but Jane had other ideas.
Other people may not think that way.
They have no other place to go.
(2) the other意为“两者中的另一个”,常与one连用,构成"one...the other..."结构。
I have two brothers. One is a salesman, and the other is an engineer.
Hold it in this hand, not the other hand.
(3) others泛指"别的人或物",相当于"other+复数可数名词",常构成“some...others...”结构。
Some boys are playing basketball, and others are playing soccer.
Some people like tea, others like coffee and others like milk.
(4) the others特指“其余所有的人或物”,相当于“the other+ 复数可数名词”。
Three of us remain here and all the others go to the next room.
Some students swept the floor, and the others cleaned the windows.
(5) another表示“三者或三者以上中的任何一个”,一般修饰或代替单数可数名词。常用于“another+数词+复数可数名词”结构,相当于“数词+more/other+复数可数名词”,表示在原有的基础上需要更多数量的东西。
Could we see each other at nine o'clock tomorrow morning
Sorry. Let's make it another time.
They need another two hours to finish this work.
We will have to wait another three weeks for the results.
7. many, much
(1) many和much都表示“许多,大量”。many只修饰复数可数名词,much是修饰不可数名词。
My cousins have collected stamps for two years, they have many stamps from different countries.
It's a small car,doesn't use much fuel.
(2) too many和too much都表示“太多”,too many修饰复数可数名词,too much修饰不可数名词。much too表示“实在太”,修饰形容词或副词。
There are too many mistakes in your homework.
I have too much work to do.
I'm afraid that this cap is much too big for me.
8. few, a few, little, a little
I have been to Beijing a few times.
He has written many books, but few of them are good.
Please add a little sugar to the coffee.
There is little news about this movie star in this paper. Where can I get some
七. 疑问代词
1. who, whom的用法
两者都意为"谁",用来指人,其中who可做主语,宾语和表语,whom只用作宾语。在介词后作宾语只能用whom, 而不能用who。
Who is that man over there He's my uncle.
Who are you writing to
To whom did you speak on the playground
2. whose的用法
whose意为"谁的",既可置于名词前作定语,也可单独使用,作主语和表语。
Whose dictionary is this
They are good at math, but whose is the best
Whose are those flowers
3. which的用法
which意为"哪一个,哪一些",可用来指代人或物在句中作主语,宾语和定语。它与who及what的不同在于which一般有特定的选择范围,而who和what则没有。
Which would you like to choose to live in, Chengdu, Beijing or Shanghai Chengdu, I think.
Which T- shirt do you like better, the red one or the blue one I prefer the red one.
4. what的用法
what意为"什么"可单独使用,也可放在名词前,既可以指代或修饰单数可数名词,也可以指代或修饰复数可数名词。在句中作主语,宾语,表语,定语。
What makes you love your hometown so much
What are your reasons for leaving
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
