Unit 9 Human Biology Lesson 3 课件(共38张) 2024-2025学年高二英语北师版(2019)选择性必修3
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 9 Human Biology Lesson 3 课件(共38张) 2024-2025学年高二英语北师版(2019)选择性必修3 |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 7.7MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-05-01 20:11:16 | ||
图片预览





文档简介
(共38张PPT)
Unit 9 Human Biology
Lesson 3 Epidemics Explained
To read and talk about diseases;
To make and confirm guesses based on a general understanding;
To notice the organisationl structure of a passage;
To express and discuss ideas in a group setting;
To practice using phrasal verbs;
To search online for information and present findings to the class.
Learning objectives
What kinds of epidemics do you know
SARS (非典)
swine flu (猪流感)
avian/bird flu (禽流感)
EVD (埃博拉病毒)
…
Activate and share
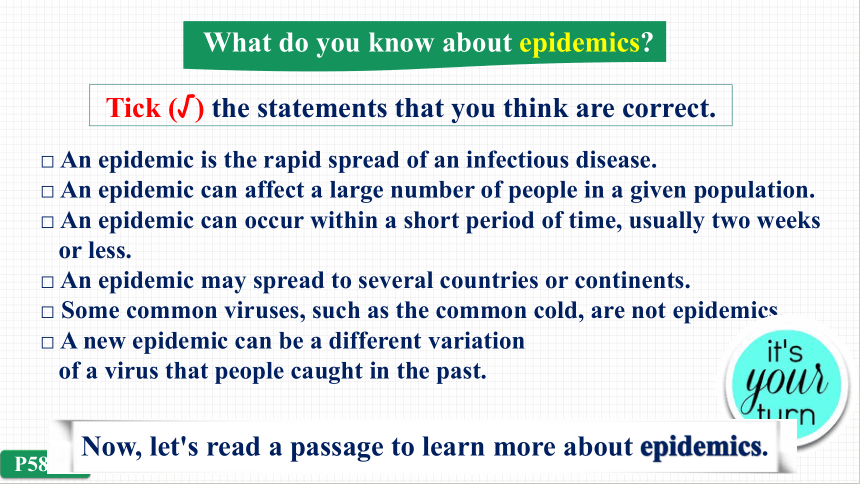
What do you know about epidemics
Tick (√) the statements that you think are correct.
□ An epidemic is the rapid spread of an infectious disease.
□ An epidemic can affect a large number of people in a given population.
□ An epidemic can occur within a short period of time, usually two weeks
or less.
□ An epidemic may spread to several countries or continents.
□ Some common viruses, such as the common cold, are not epidemics.
□ A new epidemic can be a different variation
of a virus that people caught in the past.
P58 1
Now, let's read a passage to learn more about epidemics.
Read the passage and answer the questions.
Task 1
What is an epidemic
How can a disease be classified as an epidemic
Circle all the epidemics mentioned in the passage.
P58 2
Read and explore
Check your answers.
What is an epidemic
How can a disease be classified as an epidemic
Circle all the epidemics mentioned in the passage.
bird flu
1918 Spanish Flu
The Black Death
SARS
Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
Bird Flu
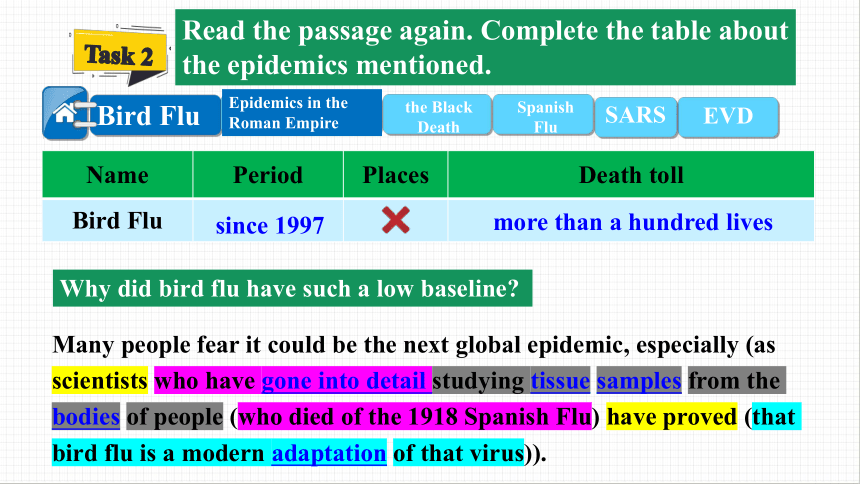
Name Period Places Death toll
Bird Flu
since 1997
more than a hundred lives
Many people fear it could be the next global epidemic, especially (as scientists who have gone into detail studying tissue samples from the bodies of people (who died of the 1918 Spanish Flu) have proved (that bird flu is a modern adaptation of that virus)).
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
the Black Death
EVD
Spanish Flu
SARS
Task 2
Read the passage again. Complete the table about the epidemics mentioned.
Why did bird flu have such a low baseline
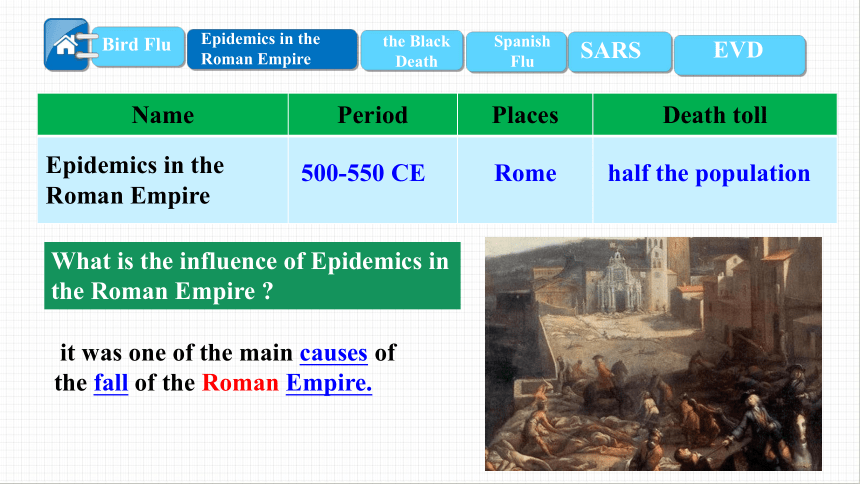
Name Period Places Death toll
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
500-550 CE
Rome
half the population
it was one of the main causes of the fall of the Roman Empire.
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
What is the influence of Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Name Period Places Death toll
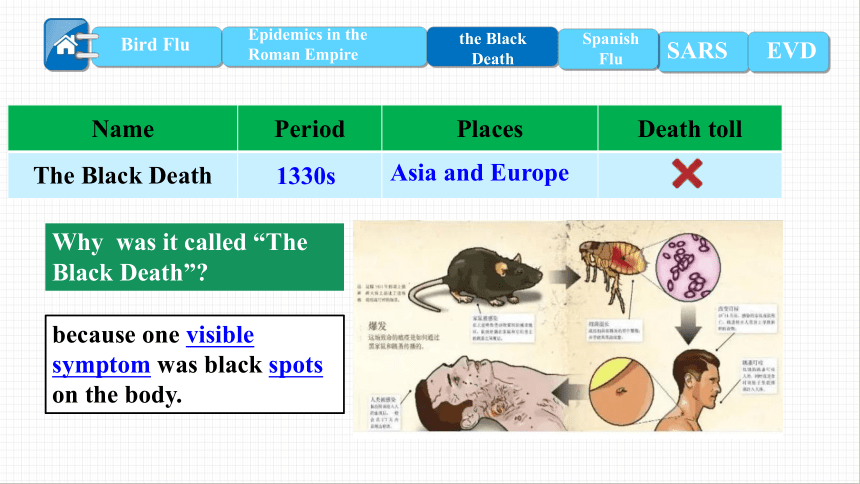
The Black Death
1330s
Asia and Europe
because one visible symptom was black spots on the body.
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
Why was it called “The Black Death”
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
Name Period Places Death toll
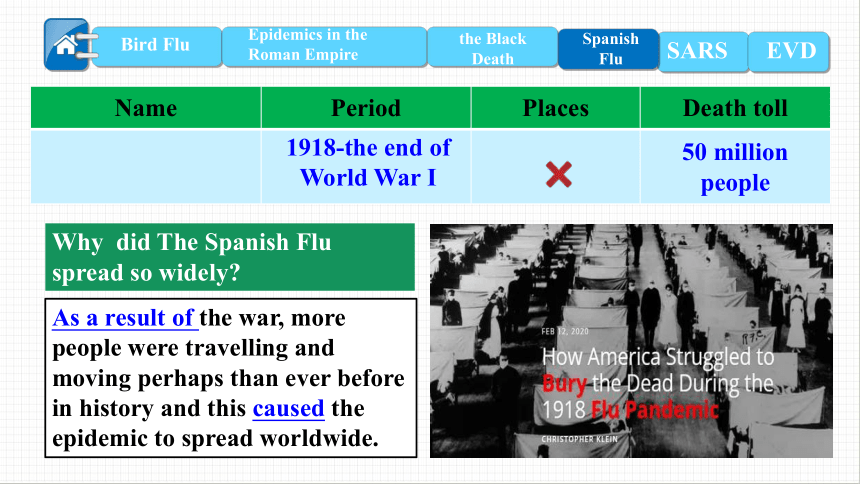
1918-the end of World War I
50 million people
As a result of the war, more people were travelling and moving perhaps than ever before in history and this caused the epidemic to spread worldwide.
Why did The Spanish Flu spread so widely
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
Name Period Places
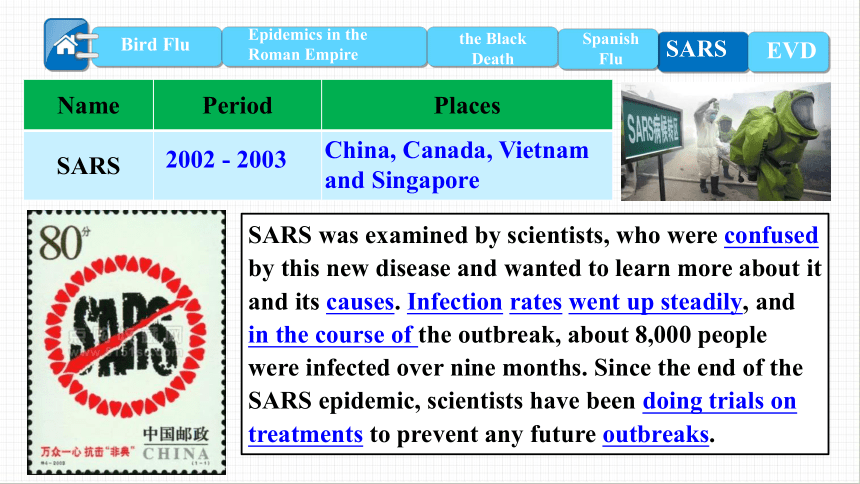
SARS
2002 - 2003
China, Canada, Vietnam and Singapore
SARS was examined by scientists, who were confused by this new disease and wanted to learn more about it and its causes. Infection rates went up steadily, and in the course of the outbreak, about 8,000 people were infected over nine months. Since the end of the SARS epidemic, scientists have been doing trials on treatments to prevent any future outbreaks.
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
Name Period Places Death toll
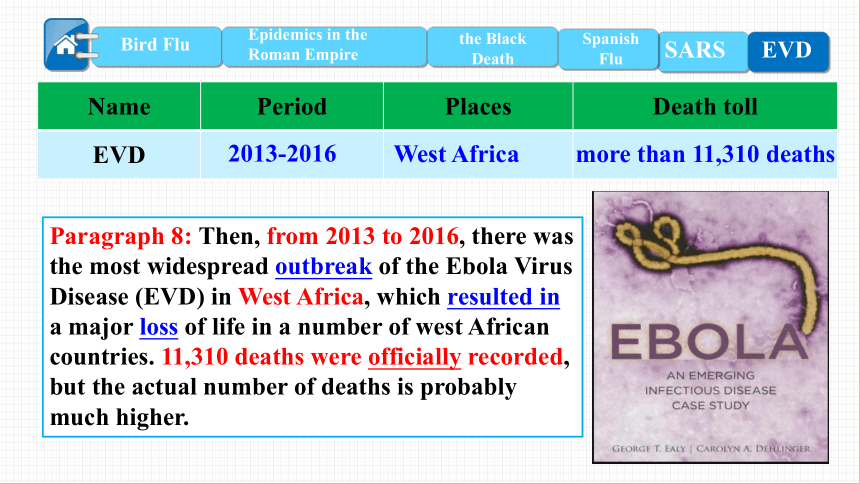
EVD
2013-2016
West Africa
more than 11,310 deaths
Paragraph 8: Then, from 2013 to 2016, there was the most widespread outbreak of the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in West Africa, which resulted in a major loss of life in a number of west African countries. 11,310 deaths were officially recorded, but the actual number of deaths is probably much higher.
Task 3
□ when epidemics started □ definition
□ examples of epidemics □ when it ended
□ treatments □ possible causes of epidemics
□ baseline number of deaths of epidemics
□ possible solutions
P60 4
Tick (√) the aspects of information that are mentioned in the passage.
Part 3(Para.9)
Basic information about epidemics: definition, cause, difference
Epidemics in history (Examples)
Measures to fight against epidemics
1) Bird Flu (since 1997)
2) Epidemics in the Roman
Empire (500-550 CE)
3) The Black Death (1330s)
4) The Spanish Flu (near the end of World War I)
5) The SARS (2002-2003)
6) EVD (2013-2016)
time order
Use a diagram to demonstrate in a logical way how they are organised.
Part 1(Para.1-2 )
Part 2(Para.3-8 )
Task 4
Discuss the questions.
1. What are the main features of an epidemic
Give at least two examples to illustrate your points.
2. What should different countries do to prevent outbreaks of epidemics in the future Why
3. What does the title mean to you
What does the writer want to convey in the passage
4. Who do you think the passage is written to
P60 5
1. What are the main features of an epidemic
Give at least two examples to illustrate your points.
Countries will need to work together to do this because teamwork among nations across the globe can save lives.
This is a good example of building a community with shared future for mankind.
2. What should different countries do to prevent
outbreaks of epidemics in the future Why
The title means that the passage will explain questions about epidemics.
The author wants to convey the information that we are always on our way to find an explanation to epidemics so as to find cure. It also implies that epidemics occurred naturally and inevitably. We can only explain it, and cannot prevent it or stop it completely now.
3. What does the title mean to you
What does the writer want to convey in the passage
This is a popular science article. It is more likely to be written for people who is interested in this topic or who has a lot of questions or misunderstanding of epidemics.
4. Who do you think the passage is written to
P61 6
Task 5
Complete these sentences in your own words.
1. Epidemics can be caused by …
2. Diseases can only be officially classified as epidemics when …
3. The Spanish Flu spread worldwide because …
4. Since the end of the SARS epidemic, scientists …
5. Countries need to work together to conduct thorough and
systematic research because …
Epidemics can be caused by a virus being carried into an area, or changes in the way people live.
Diseases can only be officially classified as epidemics when a baseline number of people have died from the disease.
The Spanish Flu spread worldwide because soldiers and other people were moving and travelling around the world after World War I.
Since the end of the SARS epidemic, scientists have been doing experiments on treatments to prevent further outbreaks.
Countries need to work together to conduct thorough and systematic research because teamwork among nations across the globe can save lives.
An
Epidemics
Definition
An infectious disease that rapidly spreads to 1. ____________________
within a short period of time.
Causes
* A virus 2. _____________________
* 3. _________ in the way people live
(increase the chances to infect with
viruses)
Examples
Classification
When 4. ________________________ have occurred from the disease.
Measures
* 9. ____________________________
______________ on epidemics.
* Countries 10. _____________ to do
the research.
Name
Period
Places
Death toll
Bird flu
1997~now
Over 100
An epidemic in the Roman Empire
500~550 CE
The Roman Empire
Up to 5. __________
_________________
The Black Death
In the 1330s
Asia & Europe
The Spanish Flu
In 1918
All over the world
Up to 6. ________
SARS
7. _________
China&Canada&Vietnam&Singapore
About 8,000
EVD
2013 ~ 2016
8. ____________________
11,310 or more
a large number of people
being carried into an area
Changes
a certain number of deaths
50% of the area's population
50 million
2002~2003
West African countries
Do thorough and systematic medical research
work together
Complete the graphic organiser and then retell the text according to it.
An epidemic is an 1.________________ that rapidly spreads to large numbers of people within a short period of time. Epidemics can be caused by several different factors. Each disease can only officially be classified as an epidemic once a certain number of 2.______ have occurred from the disease.
3._________ first appeared in 1997 and it has taken over one hundred lives ever since. Many people fear it could be the next global epidemic, because scientists have proved that bird flu is a modern adaptation of the 1918 Spanish Flu. One of the earliest epidemics on record happened between about
4._______________ in the Roman Empire. It is estimated that up to 50% of the area's population died from the epidemic.
Complete the summary using the information in the article.
infectious disease
deaths
Bird Flu
500 and 550 CE
Then, in the 1330s, this epidemic happened in 5._____ again. It spread rapidly to Europe and became known as 6.___________ ______. In 1918, the Spanish Flu struck and killed more people than World War I did. Having killed up to 50 million people in 18 months, the Spanish Flu is believed to have been the most severe epidemic in history. The 7._______ epidemic began in 2002 in Guangdong and lasted until 2003. From 2013 to 2016, the 8._________________ attacked west African countries. The virus was extremely infectious and the survival rate was low.
Countries will need to 9._____________ to do thorough and systematic medical research on epidemics to get at the 10.______ and come up with cures.
Asia
“The Black
Death”
SARS
Ebola Virus Disease
work together
causes
Search online and find some information about epidemics in China or Asia.Report your information to the class.
Coronavirus emerged in December 2019.
Coronavirus can be spread from person to person.
COVID-19 symptoms include:
Cough; Sore throat; Fever or chills; Tiredness;
Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing …
To prevent infection and to slow transmission of
COVID-19, do the following:
Wash your hands regularly;
Cover your coughs and sneezes;
Wear a mask in public places …
P61 8
Express yourself
Phrasal verbs are verbs that are made up of two or three words. They can be either transitive (they have an object) or intransitive (they have no object).
短语动词是由两三个单词组成的动词,可以是及物的(带宾语)也可以是不及物的(不带宾语)。
Phrasal verbs can be complex as many can look similar but have very different meanings.
e.g. take on, take over, take down.
短语动词比较复杂,很多短语形式相似意思却不同。
Transitive (及物动词短语)
She made us take down all the posters.
Intransitive (不及物动词短语)
I get up early even at the weekend.
Focus on language: Phrasal Verbs (2)
Some phrasal verbs can be separated by the noun whereas others cannot.
有的短语动词中可以插入名词,有的则不能。
可插入名词的短语动词:
I forgot to turn off my computer when I left the office. / I forgot to turn my computer off when I left the office.
He threw away his notebook, accidentally. /
He threw his notebook away, accidentally.
不可拆分的短语动词:
I came across an interesting article in the newspaper.
I'm looking forward to spending time with my sister.
学习短语动词的困难在于,没有规则确定短语动词是及物或不及物,可拆分或不可拆分,必须逐一学习。
Verb Examples
go away, around, with, without, against, under, over, for, in for, through, through with, off …
get over, through, in, into, on with, down, at, down with, out of, away from, along, along with …
come along, with, over, into, out, out with, by, down with, on, across …
短语动词
及物
不及物
e.g. take down
e.g. get up
可拆分
不可拆分
e.g. turn off
e.g. come across
Choose prepositions or adverbs in the box to make phrasal verbs with the three verbs in the Word Builder.
Phrasal Verbs (2)
(The prepositions and adverbs may be used more than once.)
go ________________________________
get ________________________________
come ______________________________
Word Builder
at into over up with through under up away
at, over, through, away
at, into, over, through, up, away
at, into, over, up with, up, away
P61 7
go相关短语 go at
go over
go through
go away
拼命干;卖力干
攻击某人
仔细检查(或审查、查阅)某事
反复研究;仔细琢磨
经历,经受(尤指苦难或艰难时期)
翻阅;翻找;整理
通读;彻查
获准,经过程序
离开
get相关短语 get at
get into
get over
get through
get up
get away
触及;够得着;抓住
查明;弄清楚
从事;致力于
获准(入学);被录取
养成某种习惯;习惯于
(使)陷入,达到
从(不快或疾病中)恢复过来
克服,战胜(问题、困难)
完成(任务);干完(工作等)
消耗;用完
使理解;使明白
用电话联系上
通过(考试)
起床
起立;站起来
离开;脱身
(使)逃跑;(使)逃脱
come相关短语 come at
come into
come over
come up with
come up
come away
扑向(某人)
(用某方法)考虑,思考
继承,得到(遗产)
(在某种情形下)是重要的
(尤指到某人家中)短暂造访
想出,提出(计划、想法等)
设法拿出(所需钱款)
被提及;被讨论
长出地面;破土而出
发生
升起
即将发生(或出现、到来)
分离;脱离
(带着某种感觉或印象)离开
1. The medical expert asked a few questions to try to _________ the truth.
2. Books on epidemics __________ the medicine section of the store.
3. During this course, we'll __________ the main causes of bird flu.
4. It took him a week to __________ the flu.
Use the phrasal verbs to complete the following sentences.
go at, over, through, away
get at, into, over, through, up, away
come at, into, over, up with, up, away
come at
go under
go over
get over
5. Has your headache ________ yet
6. The price of this drug has ________ twenty cents since August.
7. Are you willing to stand by him and help him ___________ this difficult time
8. Jordan has ____________ some creative ideas for helping the sick.
go at, over, through, away
get at, into, over, through, up, away
come at, into, over, up with, up, away
get over
gone up
go through
come up with
1. classify … as
2. get through
3. get over
4. get at sth.
5. come up with
6. as soon as possible
将……归类为;将……界定为
度过,熬过(困难或不快的时期)
从(不快或疾病中)恢复过来
获悉;了解;查明;发现
尽快
想出;提出
1. Can you introduce epidemic briefly to others
2. Have you had a better knowledge of epidemics
3. Do you know how a disease can be classified as an epidemic
4. Do you know how to use phrasal verbs
Self-evaluation
Please write a short passage to introduce epidemics from different aspects to others. Pay attention to the structure of your writing.
Homework
Unit 9 Human Biology
Lesson 3 Epidemics Explained
To read and talk about diseases;
To make and confirm guesses based on a general understanding;
To notice the organisationl structure of a passage;
To express and discuss ideas in a group setting;
To practice using phrasal verbs;
To search online for information and present findings to the class.
Learning objectives
What kinds of epidemics do you know
SARS (非典)
swine flu (猪流感)
avian/bird flu (禽流感)
EVD (埃博拉病毒)
…
Activate and share
What do you know about epidemics
Tick (√) the statements that you think are correct.
□ An epidemic is the rapid spread of an infectious disease.
□ An epidemic can affect a large number of people in a given population.
□ An epidemic can occur within a short period of time, usually two weeks
or less.
□ An epidemic may spread to several countries or continents.
□ Some common viruses, such as the common cold, are not epidemics.
□ A new epidemic can be a different variation
of a virus that people caught in the past.
P58 1
Now, let's read a passage to learn more about epidemics.
Read the passage and answer the questions.
Task 1
What is an epidemic
How can a disease be classified as an epidemic
Circle all the epidemics mentioned in the passage.
P58 2
Read and explore
Check your answers.
What is an epidemic
How can a disease be classified as an epidemic
Circle all the epidemics mentioned in the passage.
bird flu
1918 Spanish Flu
The Black Death
SARS
Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
Bird Flu
Name Period Places Death toll
Bird Flu
since 1997
more than a hundred lives
Many people fear it could be the next global epidemic, especially (as scientists who have gone into detail studying tissue samples from the bodies of people (who died of the 1918 Spanish Flu) have proved (that bird flu is a modern adaptation of that virus)).
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
the Black Death
EVD
Spanish Flu
SARS
Task 2
Read the passage again. Complete the table about the epidemics mentioned.
Why did bird flu have such a low baseline
Name Period Places Death toll
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
500-550 CE
Rome
half the population
it was one of the main causes of the fall of the Roman Empire.
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
What is the influence of Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Name Period Places Death toll
The Black Death
1330s
Asia and Europe
because one visible symptom was black spots on the body.
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
Why was it called “The Black Death”
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
Name Period Places Death toll
1918-the end of World War I
50 million people
As a result of the war, more people were travelling and moving perhaps than ever before in history and this caused the epidemic to spread worldwide.
Why did The Spanish Flu spread so widely
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
Name Period Places
SARS
2002 - 2003
China, Canada, Vietnam and Singapore
SARS was examined by scientists, who were confused by this new disease and wanted to learn more about it and its causes. Infection rates went up steadily, and in the course of the outbreak, about 8,000 people were infected over nine months. Since the end of the SARS epidemic, scientists have been doing trials on treatments to prevent any future outbreaks.
Bird Flu
the Black Death
SARS
EVD
Epidemics in the Roman Empire
Spanish Flu
Name Period Places Death toll
EVD
2013-2016
West Africa
more than 11,310 deaths
Paragraph 8: Then, from 2013 to 2016, there was the most widespread outbreak of the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in West Africa, which resulted in a major loss of life in a number of west African countries. 11,310 deaths were officially recorded, but the actual number of deaths is probably much higher.
Task 3
□ when epidemics started □ definition
□ examples of epidemics □ when it ended
□ treatments □ possible causes of epidemics
□ baseline number of deaths of epidemics
□ possible solutions
P60 4
Tick (√) the aspects of information that are mentioned in the passage.
Part 3(Para.9)
Basic information about epidemics: definition, cause, difference
Epidemics in history (Examples)
Measures to fight against epidemics
1) Bird Flu (since 1997)
2) Epidemics in the Roman
Empire (500-550 CE)
3) The Black Death (1330s)
4) The Spanish Flu (near the end of World War I)
5) The SARS (2002-2003)
6) EVD (2013-2016)
time order
Use a diagram to demonstrate in a logical way how they are organised.
Part 1(Para.1-2 )
Part 2(Para.3-8 )
Task 4
Discuss the questions.
1. What are the main features of an epidemic
Give at least two examples to illustrate your points.
2. What should different countries do to prevent outbreaks of epidemics in the future Why
3. What does the title mean to you
What does the writer want to convey in the passage
4. Who do you think the passage is written to
P60 5
1. What are the main features of an epidemic
Give at least two examples to illustrate your points.
Countries will need to work together to do this because teamwork among nations across the globe can save lives.
This is a good example of building a community with shared future for mankind.
2. What should different countries do to prevent
outbreaks of epidemics in the future Why
The title means that the passage will explain questions about epidemics.
The author wants to convey the information that we are always on our way to find an explanation to epidemics so as to find cure. It also implies that epidemics occurred naturally and inevitably. We can only explain it, and cannot prevent it or stop it completely now.
3. What does the title mean to you
What does the writer want to convey in the passage
This is a popular science article. It is more likely to be written for people who is interested in this topic or who has a lot of questions or misunderstanding of epidemics.
4. Who do you think the passage is written to
P61 6
Task 5
Complete these sentences in your own words.
1. Epidemics can be caused by …
2. Diseases can only be officially classified as epidemics when …
3. The Spanish Flu spread worldwide because …
4. Since the end of the SARS epidemic, scientists …
5. Countries need to work together to conduct thorough and
systematic research because …
Epidemics can be caused by a virus being carried into an area, or changes in the way people live.
Diseases can only be officially classified as epidemics when a baseline number of people have died from the disease.
The Spanish Flu spread worldwide because soldiers and other people were moving and travelling around the world after World War I.
Since the end of the SARS epidemic, scientists have been doing experiments on treatments to prevent further outbreaks.
Countries need to work together to conduct thorough and systematic research because teamwork among nations across the globe can save lives.
An
Epidemics
Definition
An infectious disease that rapidly spreads to 1. ____________________
within a short period of time.
Causes
* A virus 2. _____________________
* 3. _________ in the way people live
(increase the chances to infect with
viruses)
Examples
Classification
When 4. ________________________ have occurred from the disease.
Measures
* 9. ____________________________
______________ on epidemics.
* Countries 10. _____________ to do
the research.
Name
Period
Places
Death toll
Bird flu
1997~now
Over 100
An epidemic in the Roman Empire
500~550 CE
The Roman Empire
Up to 5. __________
_________________
The Black Death
In the 1330s
Asia & Europe
The Spanish Flu
In 1918
All over the world
Up to 6. ________
SARS
7. _________
China&Canada&Vietnam&Singapore
About 8,000
EVD
2013 ~ 2016
8. ____________________
11,310 or more
a large number of people
being carried into an area
Changes
a certain number of deaths
50% of the area's population
50 million
2002~2003
West African countries
Do thorough and systematic medical research
work together
Complete the graphic organiser and then retell the text according to it.
An epidemic is an 1.________________ that rapidly spreads to large numbers of people within a short period of time. Epidemics can be caused by several different factors. Each disease can only officially be classified as an epidemic once a certain number of 2.______ have occurred from the disease.
3._________ first appeared in 1997 and it has taken over one hundred lives ever since. Many people fear it could be the next global epidemic, because scientists have proved that bird flu is a modern adaptation of the 1918 Spanish Flu. One of the earliest epidemics on record happened between about
4._______________ in the Roman Empire. It is estimated that up to 50% of the area's population died from the epidemic.
Complete the summary using the information in the article.
infectious disease
deaths
Bird Flu
500 and 550 CE
Then, in the 1330s, this epidemic happened in 5._____ again. It spread rapidly to Europe and became known as 6.___________ ______. In 1918, the Spanish Flu struck and killed more people than World War I did. Having killed up to 50 million people in 18 months, the Spanish Flu is believed to have been the most severe epidemic in history. The 7._______ epidemic began in 2002 in Guangdong and lasted until 2003. From 2013 to 2016, the 8._________________ attacked west African countries. The virus was extremely infectious and the survival rate was low.
Countries will need to 9._____________ to do thorough and systematic medical research on epidemics to get at the 10.______ and come up with cures.
Asia
“The Black
Death”
SARS
Ebola Virus Disease
work together
causes
Search online and find some information about epidemics in China or Asia.Report your information to the class.
Coronavirus emerged in December 2019.
Coronavirus can be spread from person to person.
COVID-19 symptoms include:
Cough; Sore throat; Fever or chills; Tiredness;
Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing …
To prevent infection and to slow transmission of
COVID-19, do the following:
Wash your hands regularly;
Cover your coughs and sneezes;
Wear a mask in public places …
P61 8
Express yourself
Phrasal verbs are verbs that are made up of two or three words. They can be either transitive (they have an object) or intransitive (they have no object).
短语动词是由两三个单词组成的动词,可以是及物的(带宾语)也可以是不及物的(不带宾语)。
Phrasal verbs can be complex as many can look similar but have very different meanings.
e.g. take on, take over, take down.
短语动词比较复杂,很多短语形式相似意思却不同。
Transitive (及物动词短语)
She made us take down all the posters.
Intransitive (不及物动词短语)
I get up early even at the weekend.
Focus on language: Phrasal Verbs (2)
Some phrasal verbs can be separated by the noun whereas others cannot.
有的短语动词中可以插入名词,有的则不能。
可插入名词的短语动词:
I forgot to turn off my computer when I left the office. / I forgot to turn my computer off when I left the office.
He threw away his notebook, accidentally. /
He threw his notebook away, accidentally.
不可拆分的短语动词:
I came across an interesting article in the newspaper.
I'm looking forward to spending time with my sister.
学习短语动词的困难在于,没有规则确定短语动词是及物或不及物,可拆分或不可拆分,必须逐一学习。
Verb Examples
go away, around, with, without, against, under, over, for, in for, through, through with, off …
get over, through, in, into, on with, down, at, down with, out of, away from, along, along with …
come along, with, over, into, out, out with, by, down with, on, across …
短语动词
及物
不及物
e.g. take down
e.g. get up
可拆分
不可拆分
e.g. turn off
e.g. come across
Choose prepositions or adverbs in the box to make phrasal verbs with the three verbs in the Word Builder.
Phrasal Verbs (2)
(The prepositions and adverbs may be used more than once.)
go ________________________________
get ________________________________
come ______________________________
Word Builder
at into over up with through under up away
at, over, through, away
at, into, over, through, up, away
at, into, over, up with, up, away
P61 7
go相关短语 go at
go over
go through
go away
拼命干;卖力干
攻击某人
仔细检查(或审查、查阅)某事
反复研究;仔细琢磨
经历,经受(尤指苦难或艰难时期)
翻阅;翻找;整理
通读;彻查
获准,经过程序
离开
get相关短语 get at
get into
get over
get through
get up
get away
触及;够得着;抓住
查明;弄清楚
从事;致力于
获准(入学);被录取
养成某种习惯;习惯于
(使)陷入,达到
从(不快或疾病中)恢复过来
克服,战胜(问题、困难)
完成(任务);干完(工作等)
消耗;用完
使理解;使明白
用电话联系上
通过(考试)
起床
起立;站起来
离开;脱身
(使)逃跑;(使)逃脱
come相关短语 come at
come into
come over
come up with
come up
come away
扑向(某人)
(用某方法)考虑,思考
继承,得到(遗产)
(在某种情形下)是重要的
(尤指到某人家中)短暂造访
想出,提出(计划、想法等)
设法拿出(所需钱款)
被提及;被讨论
长出地面;破土而出
发生
升起
即将发生(或出现、到来)
分离;脱离
(带着某种感觉或印象)离开
1. The medical expert asked a few questions to try to _________ the truth.
2. Books on epidemics __________ the medicine section of the store.
3. During this course, we'll __________ the main causes of bird flu.
4. It took him a week to __________ the flu.
Use the phrasal verbs to complete the following sentences.
go at, over, through, away
get at, into, over, through, up, away
come at, into, over, up with, up, away
come at
go under
go over
get over
5. Has your headache ________ yet
6. The price of this drug has ________ twenty cents since August.
7. Are you willing to stand by him and help him ___________ this difficult time
8. Jordan has ____________ some creative ideas for helping the sick.
go at, over, through, away
get at, into, over, through, up, away
come at, into, over, up with, up, away
get over
gone up
go through
come up with
1. classify … as
2. get through
3. get over
4. get at sth.
5. come up with
6. as soon as possible
将……归类为;将……界定为
度过,熬过(困难或不快的时期)
从(不快或疾病中)恢复过来
获悉;了解;查明;发现
尽快
想出;提出
1. Can you introduce epidemic briefly to others
2. Have you had a better knowledge of epidemics
3. Do you know how a disease can be classified as an epidemic
4. Do you know how to use phrasal verbs
Self-evaluation
Please write a short passage to introduce epidemics from different aspects to others. Pay attention to the structure of your writing.
Homework
