【高中英语语法大全】Lesson1 高中16种时态课件(共39张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 【高中英语语法大全】Lesson1 高中16种时态课件(共39张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2021-09-24 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共39张PPT)
Lesson
1
动词的时态
do
一般
进行
完成
完成进行
现在
过去
将来
过去将来
do
一般
进行
完成
完成进行
现在
do/does
am/is/are
doing
have/has
done
have/has
been
doing
过去
did
was/were
doing
had
done
had
been
doing
将来
will
do
will
be
doing
will
have
done
will
have
been
doing
过去将来
would
do
would
be
doing
would
have
done
would
have
been
doing
英语的16种时态列表(以do为例)[考纲要求掌握10种时态]
①表示习惯性、经常性或永久性的动作,常与often,usually,always,sometimes,once
a
week,frequently,
every
day/week/month等时间状语连用。
例如:He
often
goes
to
work
by
bus.
他经常乘公共汽车去上班。
②表示客观真理、科学事实、格言以及其他不受时间限制的客观存在的事实
(在主从复合句中,即使主句为一般过去时,从句也遵循此用法)。
例如:My
teacher
told
me
yesterday
that
the
earth
moves
around
the
sun.
我的老师昨天告诉我地球围绕太阳转。
③表示能力、特征或现时的情况或状态。
例如:She
lives
in
a
villa
at
the
foot
of
the
hill.
她住在山脚下的一幢别墅里。
1.
一般现在时(do/does)
④在时间状语从句、让步状语从句和条件状语从句中,用于代替一般将来时。
例如:I
will
tell
her
when
she
comes
tomorrow.
她明天来的时候我会告诉她的
⑤表示按时刻表或日程表将要发生的动作或事件,或者事先安排好的动作。有此用法的多为表示“方位移动”“开始/结束”等的短暂性动词(短语),如:
go,
come,
leave,
start,
begin,
arrive,
stop,
finish,
take
off等。
例如:The
train
leaves
at
six
tomorrow
morning.
火车明天早上六点出发。
1.
一般现在时(do/does)
练一练
1.
Look
at
the
timetable.
Hurry
up!
Flight
4026_______(take)
off
at
9:00.
2.
If
it
_______(rain)
tomorrow,
I
won't
go
to
school.
3.
When
fat
and
salt
_______
(remove)
from
food,the
food
tastes
as
if
it
is
missing
something.
takes
rains
are
removed
①表示此刻正在进行的动作或发生的事,常与now,
at
the
moment,
It's
+几点钟,look,
listen等词连用
。
例如:We
are
waiting
for
you.
我们正在等你。
②表示现阶段正在进行的动作或发生的事。有时与时间状语these
days等连用。例如:
Mr.
Green
is
writing
another
novel. 格林先生在写另一部小说。
(说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)
③表示某个按最近的计划或安排将要进行的动作,或表示即将开始或结束的动作。有此用法的动词(短语)有:go,
start,
begin,
leave,
arrive,
come,
return,
run
out等。
例如:I
am
leaving
for
Shanghai
the
day
after
tomorrow.
我打算后天前往上海。
2.
现在进行时(am/is/are+doing)
④常与always,
constantly,
forever
等词连用,表示反复发生的动作或持续存在的状态,往往带有说话人的主观色彩,表达满意、不满、厌恶等强烈的感彩。
例如:You
are
always
changing
your
mind.
你总是改变注意。
2.
现在进行时(am/is/are+doing)
不宜用现在进行时的常见动词
1.
表示感官的动词:feel,
look,
see,
hear,
sound,
taste,
smell等;
2.
表示情感的动词:like,
love,
hate,
fear,
prefer等;
3.
表示存在的动词:exist,
lie(位于),remain等;
4.
表示心理或思想的动词:agree,
hope,
wish,
believe,
understand,
know,
want,
need等;
5.
表示拥有或从属的动词:have,
posses,
own,
consist,
belong等。
①表示过去某个时间或某一段时间所发生的动作或存在的状态,常与yesterday,
last
week/month/year,
just
now,
the
other
day,
three
days
ago等时间状语连用。
例如:Where
did
you
go
just
now?
你刚才去哪儿了?
②表示过去一段时间内经常性或习惯性的动作。
【注】“used
to
+动词原形
”
表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,而现在已不再发生
例如:
When
I
was
a
child,
I
often
played
football
in
the
street.
当我小时候,我经常在街上踢足球。
He
used
to
go
to
work
by
bike.
他过去常骑自行车去上班。
3.
一般过去时(did)
③在表示时间、条件、让步等的状语从句中,用于代替过去将来时。
例如:We
would
not
leave
until
she
came
back.
直到她回来我们才会离开。
She
would
not
go
with
us
if
it
rained
the
next
day.
如果第二天下雨,她就不跟我们一起去。
④表示委婉语气。该用法通常仅限于hope,want,
think,
wonder等少数几个动词及情态动词could,would等。
例如:I
wondered
if
you
could
help
me.
我想知道你是否可以帮我。
Could
you
lend
me
your
bike?
你能借我你的自行车吗
⑤用于一些固定句型中表示虚拟语气,如:It
is
time
that
sb
did
sth.
(是某人做......的时候了),If
only
sb
did
sth(要是某人...就好了)
3.
一般过去时(did)
练一练
1.
Translated
fiction
sales
in
the
United
Kingdom
______(rise)
by
5.5
percent
last
year,
with
a
grwoing
demand
for
Chinese
titles,
said
Nielsen
Book
on
Wednesday.
2.
The
sun
was
setting
when
my
car
_______
(break)
down
near
a
remote
village.
3.
I
still
remember
visiting
a
friend
who’d
lived
here
for
five
years
and
I
________(shock)
when
I
learnt
she
hadn’t
cooked
once
in
all
that
time.
rose
broke
was
shocked
[解析]
此句型中的when意为at
that
time,
因此可判断此谓语应用一般过去时。同时此句也是一个特殊的句型:...was/were
doing...
when...
did...
①表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作或某一段时间内一直在进行的动作。
例如:What
were
you
doing
at
this
time
yesterday?
你昨天这个时间在做什么?
②表示过去的一个动作发生时另一个动作正在进行或表示过去的两个动作
同时进行。
例如:
When
I
came
home,
she
was
cooking
dinner.
当我到家时,她正在做饭。
He
was
reading
newspapers
while
I
was
studying.
我在学习时,他在看报。
③类比现在进行时,表示过去按计划、安排将要发生的动作,或与always,
constantly,
forever
等词连用,表达强烈的感彩。
4.
过去进行时(was/were+doing)
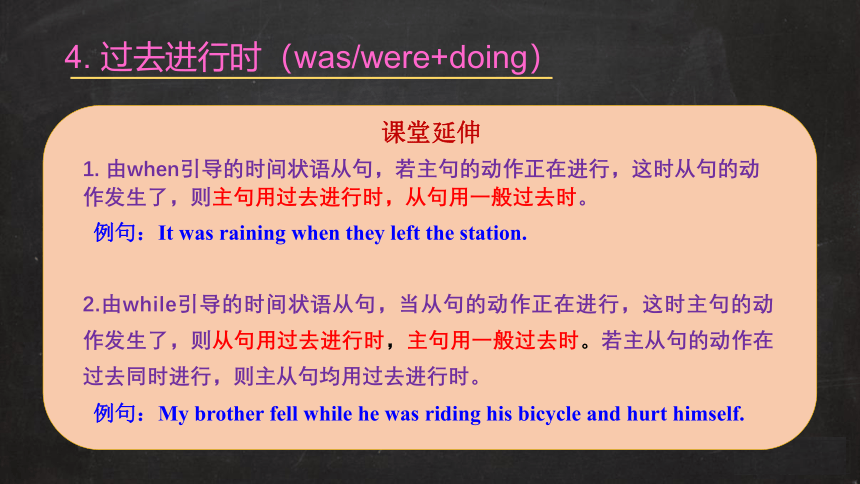
4.
过去进行时(was/were+doing)
课堂延伸
1.
由when引导的时间状语从句,若主句的动作正在进行,这时从句的动作发生了,则主句用过去进行时,从句用一般过去时。
例句:It
was
raining
when
they
left
the
station.
2.由while引导的时间状语从句,当从句的动作正在进行,这时主句的动作发生了,则从句用过去进行时,主句用一般过去时。若主从句的动作在过去同时进行,则主从句均用过去进行时。
例句:My
brother
fell
while
he
was
riding
his
bicycle
and
hurt
himself.
①表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示将来的时间状语tomorrow,next
week(year...),in
the
future,in+时间段,soon等连用。
【注】shall通常用于第一人称,will通常用于各种人称。
例如:He
will
graduate
from
college
next
year.
他明年将大学毕业。
We
shall
finish
our
work
as
quickly
as
possible.
我们会尽快完成工作。
②在时间状语从句、让步状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来
某些动词用现在进行时表示将来
5.
一般将来时(will/shall+do)
【典例】
Meanwhile,
as
the
construction
goes
on,
more
roads
________(build)
and
the
metro
system
will
be
expanded,
which
can
reduce
traffic
jams.
【答案】will
be
built。
形式
意义
例句
be
going
to
do
打算、计划、准备要做某事
What
are
you
going
to
do
tomorrow?
明天你打算干什么?
有迹象表明要发生的动作
It
looks
as
if
it
is
going
to
rain
看起来好像要下雨了。
be
to
do
按计划或安排要做某事
We
are
to
discuss
the
report
next
Saturday.
我们打算下周六讨论这个报告。
表示义务、命令、禁止等
You
are
to
hand
in
your
application
form
within
three
days.三天之内你必须递交你的申请表
表示注定要发生的事
Her
plan
is
to
be
a
failure.
她的计划注定要失败。
be
about
to
do/be
on
the
point
of
+n/doing
即将或正要做某事
He
is
about
to
leave
for
Beijing.
他正要前往北京。
一般将来时的其他表达形式
①表示将来某一时刻或某段时间内正在进行的或持续的动作。
例如:What
will
you
be
doing
at
this
time
next
Monday?
下周一的这个时候你将在做什么?
②表示将来被客观情况所决定的动作或者按照安排将要发生的动作。
例如:I'll
be
taking
my
holidays
soon.
我不久即将度假。
【注】shall通常用于第一人称,will通常用于各种人称。
6.
将来进行时(will/shall+be+doing)
【典例】
At
this
time
tomorrow
______
over
the
Atlantic.
A.
we're
going
to
fly
B.
we'll
be
flying
C.
we'll
fly
D.
we're
to
fly
【答案】at
this
time
tomorrow是将来进行时的标志词,选B。
时间
现在
过去
将来
一般过去时
一般现在时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
将来进行时
尝试将所学时态在时间轴上表示出来:
一般时往往用以叙述一个单纯的事实,时间可以很不具体。
而进行时强调动作发生的时刻点,描述性强,比较具体生动。
【注】(其中
would
用于各种人称,
should
常用于第一人称)。
①表示从过去的某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。它是一个相对的时态,即立足于过去某时,从过去的某一时间看即将发生的事情就要用这一时态。
例如:He
said
his
mother
would
buy
a
bike
for
him.
他说他的妈妈将会为他买个自行车。
②类比现在进行时,某些动词的过去进行时(如
go,come,
leave,start,
open,begin
等)也可用于表示过去将来。
③在时间和条件状语从句中,常用一般过去时来表示过去将来时(同一般现在时)
④其他表达形式:a.
was/were
going
to
do
b.
was/were
about
to
do
c.
was/were
to
do
7.
过去将来时(would/should+do)
时间
现在
过去
将来
一般过去时
一般现在时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
将来进行时
过去将来时在时间轴上如何表示呢?
过去将来时
过去将来时:必须保证时间的起点在过去,即从过去某时看,将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
【注】(其中
would
用于各种人称,
should
常用于第一人称)。
①表示在过去将来某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态,它应和表过去将来的时间
连用,也常用在间接引语中。
例如:Bruce
told
me
that
he
would
be
living
in
China
some
day.
布鲁斯告诉我将来有一天他会在中国居住。
He
called
me
in
New
York
to
let
me
know
what
time
he'd
be
arriving.
他打电话到纽约,告诉我他将到达的时间。
They
planned
they
would
be
building
another
big
and
modern
shopping
center
the
next
year.
他们计划第二年再建一家大型现代化购物中心。
8.
过去将来进行时(would/should+be+doing)
He
said
that
he
__________(watch)
TV
at
this
time
tomorrow
【答案】时间起点said为过去,从过去来看,将来的某一个时刻点
进行的动作,用过去将来进行时would
be
watching。
①表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果,强调的是这个影响或结果。通常与表示包括现在在内的时间副词just,already,
before,
yet,
never,
ever,recently,lately,twice等状语连用。
例如:
She
has
already
finished
the
work.
她已经完成了工作。
②表示过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还会持续下去的动作或状态。可以和表示从过去某一时刻延续到现在(包括现在在内)的一段时间的状语连用,如so
far,for+时间段,since+过去时间点
,up
to
now,
in
the
past
few
years,
these
years等
。
例如:She
has
learnt
English
for
3
years.
她学英语三年了
9.
现在完成时(have/has+done)
常用句型
①
It/This
is
the
first(second...)
time
+
(that)从句+
现在完成时
②
It/This
is
the
+
最高级
+
n
+
that从句+现在完成时
③
It
is/has
been
+
一段时间
+
since
+
从句(一般过去时)
考点一
非延续性动词(短语)leave,get
married,come,go,die,buy,borrow
等,在现在完成时的肯定句中不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,要进行相应的转换才能与表示一段时间的状语连用。
例如:The
man
died
for
4
years.
(×)
The
man
died
4
years
ago.
(√
)
The
man
has
been
dead
for
4
years.
(√
)
但在否定句中,一些非延续性动词可与表示一段时间的状语连用,表示过程或结果。
例如:I
haven't
bought
anything
for
a
year.
我一年没买任何东西了。
非延续性动词
延续性动词
非延续性动词的完成时
borrow
/
lend
keep
have
kept
buy
have
have
had
die
be
dead
have
been
dead
marry
/
get
married
be
married
have
been
married
open
be
open
have
been
open
close
be
closed
have
been
closed
leave
be
away
(from)
have
been
away
(from)
return
be
back
have
been
back
go
there
be
there
have
been
there
join
be
in/a
member
have
been
in(a
member)
常见非延续性动词与延续动词之间的转换:
考点二
have
been
(to)和have
gone
(to)的区别:
★
have
/
has
been
(to)
表示“曾经去过”某地,说话时此人很可能不在那里,已经回来。侧重指经历。
★
have
/
has
gone
(to)
表示某人“已经去了”某地,说话时此人在那里,或可能在路上,反正不在这里。
(不与时间段连用)
试比较:
He
has
been
to
Beijing.
他曾去过北京。
(人已回来,可能在这儿)
He
has
gone
to
Beijing.
他已经去了北京。
(人已走,不在这儿)
★
have
/
has
been
(in)
表示“某人已经在某地”,表示已经在某地待了多久,常与“for
+
时间段,
since
+
过去时间”等连用。
例如:He
has
been
in
the
Party
for
one
year.
他入党有一年了。
考点三
一般过去时与现在完成时之比较
1)过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯叙述过去的事情,强调动作;
现在完成时为过去发生的,强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。
试比较:
I
saw
this
film
yesterday.
(强调看的动作发生过了。)
I
have
seen
this
film.
(强调对现在的影响,电影的内容已经知道了。)
2)过去时常与具体的时间状语连用;
而现在完成时通常与模糊的时间状语连用,或无时间状语。
◎
一般过去时的时间状语有:yesterday,
last
week,…ago,
in1980,
just
now等。
◎
现在完成时的时间状语有:for+时间段,since+过去时间点,so
far,
up
to
now,
in
the
past/last
few
years,
recently等。
时间
现在
过去
将来
一般过去时
一般现在时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
将来进行时
请将现在完成时在时间轴上标出来:
过去将来时
现在完成时:起点在过去,止点在现在。
动作时间包含过去和现在
现在完成时
①表示在过去某一时刻或者某一动作之前已经完成的动作或状态,
时间定位是“过去的过去”。
例如:
I
had
learnt
5000
words
before
I
entered
the
university.
在我进入大学以前,我已经学了5000个词。
②表示从过去某一时刻
开始,一直持续到过去另一时刻的动作或状态,常与for,
by,
until,
before等构成的时间状语连用。
例如:By
then
he
had
learnt
English
for
3
years.
到那时,他已经学英语三年了。
③常用在told,
said,
knew,
heard,
thought等动词后的宾语从句中。
She
said
(that)
she
had
never
been
to
Paris.
她说她还没去过巴黎。
10.
过去完成时(had+done)
④在过去不同时间发生的两个动作中,发生在先,用过去完成时;发生在后,用一般过去时。
When
the
police
arrived,
the
thieves
had
run
away.
当警察到达的时候,小偷们已经跑了。
⑤表示意向的动词,如hope,
wish,
expect,
think,
intend,
mean,
suppose等,用过去完成时表达"原本打算做…,而实际未能…"
例如:We
had
intended
to
come
and
see
you.
我们本打算来看你。
10.
过去完成时(had+done)
常用句型
①
It/This
was
the
first(second...)
time
+
(that)
...had
done
②
It
was
+
一段时间
+
since
...had
done
③
主语+had
hardly/scarcely(no
sooner)+done+when(than)从句(一般过去时)
时间
现在
过去
将来
一般过去时
一般现在时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
将来进行时
请将过去完成时在时间轴上标出来:
过去将来时
过去完成时:起点在过去,止点也在过去。
动作发生在“过去的过去”
现在完成时
过去完成时
常用句型:
1、当某人正在做某事,这时发生了什么:
【sb.
be
doing
sth
when...】
例:I
was
doing
homework
when
my
mother
came
home.
2、当某人刚做完某事,这时发生了什么:
【sb.
had
just
done
sth
when...did...】
例:I
had
just
finished
my
report
when
someone
knocked
at
the
door.
3、当某人正要做某事,这时发生了什么:
【sb.
be
about
to
do
sth
when...】【be
on
the
point
of
doing
when...】
例:One
day,
I
was
about
to
do
some
shopping
when
he
telephoned
me.
①表示在将来某时/某动作之前已经完成的动作,并往往对将来某一时间产生影响或结果。常与时间状语“by/before
+将来的时间”等连用。
例如:By
this
time
tomorrow
you
will
have
arrived
in
Shenyang.
到明天
这个时候你就会到达沈阳了。
I
shall
have
finished
writing
the
article
by
the
end
of
this
week.
我将在本周末前写完这篇文章。
11.
将来完成时(will/shall
have
done)
【典例】By
the
time
Jane
gets
home,
her
aunt
_______
for
London
to
attend
a
meeting.
A.
will
leave
B.
leaves
C.
will
have
left
D.
left
【解析】by短语常与完成时连用,这里的gets
home是用现在时表将来,
实际上是指一个将来的时间,故主句用将来完成时。句意:到Jane到家
的时候,她的姑姑已经离开家去伦敦参加一个会议了。
①表示在过去将来某一时间或在此以前发生的动作。
例如:Andy
told
me
he
would
have
finished
it
by
9.
安迪告诉我他将在九点前完成。
The
football
team
would
have
arrived
by
6
o'clock.
足球队将于6点前到达。
②用于虚拟语气。
例如:If
you
had
not
helped
me,
I
wouldn't
have
succeeded.
如果你不帮我,我是不会成功的。
12.
过去将来完成时(would/should
have
done)
He
said
that
he
_________(read)
3
books
by
next
Friday.
【解析】根据语境said来看,时间的起点为过去,到将来的某一时间
之前要完成的动作,应用过去将来完成时,故为would
have
read.
①表示动作从过去某时开始一直持续到现在,并有可能持续下去。也可表示到目前为止的一段时间内动作时断时续、反复发生。这个时态通常多限于无限动词,如stay,
wait,
sit,
stand,
lie,
study,
live等,并常与all
this
time,
all
night,
all
the
morning等状语以及since(自从),during等引导的状语或从句连用。
例如:Tom
has
been
working
hard
since
the
new
term
began.
自新学期开始以来,汤姆一直在努力学习。
②有些不能用现在进行时态的动词,如be,love,know,see,hear等,同样也不能用现在完成进行时,而只能用现在完成时。
例如:I
have
not
seen
you
for
ages.
我好久没有见到你了。
13.
现在完成进行时(have/has+been+doing)
【典例】-Excuese
me,
which
movie
are
you
waiting
for?
-The
new
Star
Wars.
We
______(wait)
here
for
more
than
two
hours.
【解析】表示从过去开始一直等到现在,并且可能还会继续等,故用现在完成进行时have
been
waiting。
现在完成时与现在完成进行时的区别
用法
例句
区别1
现在完成进行时强调动作的未完成性
I
have
been
thinking
it
over.
我一直在仔细考虑这件事
现在完成时强调过去某个动作对现在造成的影响或产生的结果
I
have
thought
it
over.
我已经仔细考虑过这件事了。
区别2
现在完成进行时表示动作的反复性
Have
you
been
meeting
him
recently?
你最近经常见他吗?
现在完成时不表示动作的反复性
Have
you
met
him
recently?
你最近见过他吗?
区别3
现在完成进行时可以表示某种感彩
I
have
been
waiting
for
you
for
three
hours.
我已等了你三个小时。(暗含不满的语气)
现在完成时往往只说明一个事实、一种影响或结果,不带有感彩
I
have
waited
for
you
for
three
hours.
我已等了你三个小时。(说明一个事实)
①表示动作在过去某一时间之前开始,一直延续到过去这一时间。动作是否还会
继续下去,要由上下文决定。
例如:Bill
said
he
had
been
doing
experiments
those
days.
比尔说他那几天一直在做实验。
The
telephone
had
been
ringing
for
three
minutes
before
it
was
answered.
电话铃响了三分钟才有人接。
I
had
been
looking
for
my
bike
for
days
before
I
found
it.
我找了很多天才找到我的的车子。
14.
过去完成进行时(had+been+doing)
【典例】The
crazy
fans
_______(wait)
patiently
for
two
hours,
and
they
would
wait
till
the
movie
star
arrived.
【解析】从and后的分句可知电影明星还没有到,所以当时还在“等”,体现了进行时态;从主句的时间状语for
two
hours可知是过去完成时,由此可知用过去完成进行时。had
been
waiting
①表示动作从某一时间开始一直延续到将来某一时间。动作是否还会继续下去,要由上下文决定,常与表示将来某一时间的状语连用。
例如:In
another
month's
time,
Mr
Henry
will
have
been
teaching
here
for
exactly
thirty
years.
再过一个月,亨利先生将在这里从事教学三十年了。
I
shall
have
been
living
here
for
15
years
by
the
end
of
this
month.
到这月底,我就将在这里住够十五年了。
15.
将来完成进行时(will/shall
have
been
doing)
16.
过去将来完成进行时(would/should
have
been
doing)
①表示从过去某一时间开始一直延续到过去将来某一时间的动作。
例如:He
said
that
by
the
end
of
the
Spring
term
he
would
have
been
studying
English
for
three
years.
他说到了春季学期末,他将学了三年英语。
Exercise:
choose
the
best
answer
1.You
_______
television.
Why
not
do
something
more
active?
A.
always
watch
B.
are
always
watching
C.
have
always
watched
D.
have
always
been
watching
2.I
thought
I
_______
the
door,
but
it
is
still
open
A.
had
closed
B.
was
closing
C.
have
closed
D.
would
close
3.By
the
time
you
arrive
in
London,
we
_______
in
Europe
for
two
weeks.
A.
had
stayed
B.
shall
stay
C.
will
have
stayed
D.
have
been
staying
4.Shortly
after
we
______,
a
waiter
came
over
to
our
table
with
a
smile.
A.seated
B.were
seated
C.sat
ourselves
D.had
seated
B
A
C
B
Exercise:
choose
the
best
answer
5.
You
don't
need
to
describe
her.I
______
her
several
times.
A.
had
met
B.
have
met
C.
met
D.
meet
6.When
Jack
arrived,
he
learned
Mary_____for
about
an
hour.
A.had
gone
B.had
set
off
C.had
left
D.had
been
away
7.As
she
_______the
newspaper,
Granny________
asleep.
A.read;
was
falling
B.was
reading;
fell
C.was
reading;
was
flling
D.read;
fell
8.-
Oh,
it's
you?
I
didn't
recognize
you.
-
I
________
my
hair
cut,
and
I
_______
new
glass.
A.had;
was
wearing
B.have
had;
am
wearing
C.had;
wore
D.have
had;
wear
D
B
B
B
9.Someone
_______
my
book.I
______
for
it
for
the
last
ten
minutes
but
I
can't
see
it
anywhere.
A
took;
have
been
looking
B
has
taken;am
looking
C
took;
was
looking
D
has
taken;have
been
looking
10.After
driving
for
thirty
miles,
she
suddenly
realized
that
she______in
the
wrong
direction.
A.had
been
driving
B.has
been
driving
C.drove
D.had
driven
11.No
sooner_______
than
the
accident
happened.
A.
he
had
gone
B.
had
he
gone
C.
his
going
D.
he
went
12.Jane
can’t
attend
the
meeting
at
3
o’clock
this
afternoon
because
she
___________
a
class
at
that
time.
A.
will
teach
B.
would
teach
C.
has
taught
D.
will
be
teaching
D
B
A
D
Thanks
for
listening
Lesson
1
动词的时态
do
一般
进行
完成
完成进行
现在
过去
将来
过去将来
do
一般
进行
完成
完成进行
现在
do/does
am/is/are
doing
have/has
done
have/has
been
doing
过去
did
was/were
doing
had
done
had
been
doing
将来
will
do
will
be
doing
will
have
done
will
have
been
doing
过去将来
would
do
would
be
doing
would
have
done
would
have
been
doing
英语的16种时态列表(以do为例)[考纲要求掌握10种时态]
①表示习惯性、经常性或永久性的动作,常与often,usually,always,sometimes,once
a
week,frequently,
every
day/week/month等时间状语连用。
例如:He
often
goes
to
work
by
bus.
他经常乘公共汽车去上班。
②表示客观真理、科学事实、格言以及其他不受时间限制的客观存在的事实
(在主从复合句中,即使主句为一般过去时,从句也遵循此用法)。
例如:My
teacher
told
me
yesterday
that
the
earth
moves
around
the
sun.
我的老师昨天告诉我地球围绕太阳转。
③表示能力、特征或现时的情况或状态。
例如:She
lives
in
a
villa
at
the
foot
of
the
hill.
她住在山脚下的一幢别墅里。
1.
一般现在时(do/does)
④在时间状语从句、让步状语从句和条件状语从句中,用于代替一般将来时。
例如:I
will
tell
her
when
she
comes
tomorrow.
她明天来的时候我会告诉她的
⑤表示按时刻表或日程表将要发生的动作或事件,或者事先安排好的动作。有此用法的多为表示“方位移动”“开始/结束”等的短暂性动词(短语),如:
go,
come,
leave,
start,
begin,
arrive,
stop,
finish,
take
off等。
例如:The
train
leaves
at
six
tomorrow
morning.
火车明天早上六点出发。
1.
一般现在时(do/does)
练一练
1.
Look
at
the
timetable.
Hurry
up!
Flight
4026_______(take)
off
at
9:00.
2.
If
it
_______(rain)
tomorrow,
I
won't
go
to
school.
3.
When
fat
and
salt
_______
(remove)
from
food,the
food
tastes
as
if
it
is
missing
something.
takes
rains
are
removed
①表示此刻正在进行的动作或发生的事,常与now,
at
the
moment,
It's
+几点钟,look,
listen等词连用
。
例如:We
are
waiting
for
you.
我们正在等你。
②表示现阶段正在进行的动作或发生的事。有时与时间状语these
days等连用。例如:
Mr.
Green
is
writing
another
novel. 格林先生在写另一部小说。
(说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)
③表示某个按最近的计划或安排将要进行的动作,或表示即将开始或结束的动作。有此用法的动词(短语)有:go,
start,
begin,
leave,
arrive,
come,
return,
run
out等。
例如:I
am
leaving
for
Shanghai
the
day
after
tomorrow.
我打算后天前往上海。
2.
现在进行时(am/is/are+doing)
④常与always,
constantly,
forever
等词连用,表示反复发生的动作或持续存在的状态,往往带有说话人的主观色彩,表达满意、不满、厌恶等强烈的感彩。
例如:You
are
always
changing
your
mind.
你总是改变注意。
2.
现在进行时(am/is/are+doing)
不宜用现在进行时的常见动词
1.
表示感官的动词:feel,
look,
see,
hear,
sound,
taste,
smell等;
2.
表示情感的动词:like,
love,
hate,
fear,
prefer等;
3.
表示存在的动词:exist,
lie(位于),remain等;
4.
表示心理或思想的动词:agree,
hope,
wish,
believe,
understand,
know,
want,
need等;
5.
表示拥有或从属的动词:have,
posses,
own,
consist,
belong等。
①表示过去某个时间或某一段时间所发生的动作或存在的状态,常与yesterday,
last
week/month/year,
just
now,
the
other
day,
three
days
ago等时间状语连用。
例如:Where
did
you
go
just
now?
你刚才去哪儿了?
②表示过去一段时间内经常性或习惯性的动作。
【注】“used
to
+动词原形
”
表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,而现在已不再发生
例如:
When
I
was
a
child,
I
often
played
football
in
the
street.
当我小时候,我经常在街上踢足球。
He
used
to
go
to
work
by
bike.
他过去常骑自行车去上班。
3.
一般过去时(did)
③在表示时间、条件、让步等的状语从句中,用于代替过去将来时。
例如:We
would
not
leave
until
she
came
back.
直到她回来我们才会离开。
She
would
not
go
with
us
if
it
rained
the
next
day.
如果第二天下雨,她就不跟我们一起去。
④表示委婉语气。该用法通常仅限于hope,want,
think,
wonder等少数几个动词及情态动词could,would等。
例如:I
wondered
if
you
could
help
me.
我想知道你是否可以帮我。
Could
you
lend
me
your
bike?
你能借我你的自行车吗
⑤用于一些固定句型中表示虚拟语气,如:It
is
time
that
sb
did
sth.
(是某人做......的时候了),If
only
sb
did
sth(要是某人...就好了)
3.
一般过去时(did)
练一练
1.
Translated
fiction
sales
in
the
United
Kingdom
______(rise)
by
5.5
percent
last
year,
with
a
grwoing
demand
for
Chinese
titles,
said
Nielsen
Book
on
Wednesday.
2.
The
sun
was
setting
when
my
car
_______
(break)
down
near
a
remote
village.
3.
I
still
remember
visiting
a
friend
who’d
lived
here
for
five
years
and
I
________(shock)
when
I
learnt
she
hadn’t
cooked
once
in
all
that
time.
rose
broke
was
shocked
[解析]
此句型中的when意为at
that
time,
因此可判断此谓语应用一般过去时。同时此句也是一个特殊的句型:...was/were
doing...
when...
did...
①表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作或某一段时间内一直在进行的动作。
例如:What
were
you
doing
at
this
time
yesterday?
你昨天这个时间在做什么?
②表示过去的一个动作发生时另一个动作正在进行或表示过去的两个动作
同时进行。
例如:
When
I
came
home,
she
was
cooking
dinner.
当我到家时,她正在做饭。
He
was
reading
newspapers
while
I
was
studying.
我在学习时,他在看报。
③类比现在进行时,表示过去按计划、安排将要发生的动作,或与always,
constantly,
forever
等词连用,表达强烈的感彩。
4.
过去进行时(was/were+doing)
4.
过去进行时(was/were+doing)
课堂延伸
1.
由when引导的时间状语从句,若主句的动作正在进行,这时从句的动作发生了,则主句用过去进行时,从句用一般过去时。
例句:It
was
raining
when
they
left
the
station.
2.由while引导的时间状语从句,当从句的动作正在进行,这时主句的动作发生了,则从句用过去进行时,主句用一般过去时。若主从句的动作在过去同时进行,则主从句均用过去进行时。
例句:My
brother
fell
while
he
was
riding
his
bicycle
and
hurt
himself.
①表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示将来的时间状语tomorrow,next
week(year...),in
the
future,in+时间段,soon等连用。
【注】shall通常用于第一人称,will通常用于各种人称。
例如:He
will
graduate
from
college
next
year.
他明年将大学毕业。
We
shall
finish
our
work
as
quickly
as
possible.
我们会尽快完成工作。
②在时间状语从句、让步状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来
某些动词用现在进行时表示将来
5.
一般将来时(will/shall+do)
【典例】
Meanwhile,
as
the
construction
goes
on,
more
roads
________(build)
and
the
metro
system
will
be
expanded,
which
can
reduce
traffic
jams.
【答案】will
be
built。
形式
意义
例句
be
going
to
do
打算、计划、准备要做某事
What
are
you
going
to
do
tomorrow?
明天你打算干什么?
有迹象表明要发生的动作
It
looks
as
if
it
is
going
to
rain
看起来好像要下雨了。
be
to
do
按计划或安排要做某事
We
are
to
discuss
the
report
next
Saturday.
我们打算下周六讨论这个报告。
表示义务、命令、禁止等
You
are
to
hand
in
your
application
form
within
three
days.三天之内你必须递交你的申请表
表示注定要发生的事
Her
plan
is
to
be
a
failure.
她的计划注定要失败。
be
about
to
do/be
on
the
point
of
+n/doing
即将或正要做某事
He
is
about
to
leave
for
Beijing.
他正要前往北京。
一般将来时的其他表达形式
①表示将来某一时刻或某段时间内正在进行的或持续的动作。
例如:What
will
you
be
doing
at
this
time
next
Monday?
下周一的这个时候你将在做什么?
②表示将来被客观情况所决定的动作或者按照安排将要发生的动作。
例如:I'll
be
taking
my
holidays
soon.
我不久即将度假。
【注】shall通常用于第一人称,will通常用于各种人称。
6.
将来进行时(will/shall+be+doing)
【典例】
At
this
time
tomorrow
______
over
the
Atlantic.
A.
we're
going
to
fly
B.
we'll
be
flying
C.
we'll
fly
D.
we're
to
fly
【答案】at
this
time
tomorrow是将来进行时的标志词,选B。
时间
现在
过去
将来
一般过去时
一般现在时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
将来进行时
尝试将所学时态在时间轴上表示出来:
一般时往往用以叙述一个单纯的事实,时间可以很不具体。
而进行时强调动作发生的时刻点,描述性强,比较具体生动。
【注】(其中
would
用于各种人称,
should
常用于第一人称)。
①表示从过去的某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。它是一个相对的时态,即立足于过去某时,从过去的某一时间看即将发生的事情就要用这一时态。
例如:He
said
his
mother
would
buy
a
bike
for
him.
他说他的妈妈将会为他买个自行车。
②类比现在进行时,某些动词的过去进行时(如
go,come,
leave,start,
open,begin
等)也可用于表示过去将来。
③在时间和条件状语从句中,常用一般过去时来表示过去将来时(同一般现在时)
④其他表达形式:a.
was/were
going
to
do
b.
was/were
about
to
do
c.
was/were
to
do
7.
过去将来时(would/should+do)
时间
现在
过去
将来
一般过去时
一般现在时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
将来进行时
过去将来时在时间轴上如何表示呢?
过去将来时
过去将来时:必须保证时间的起点在过去,即从过去某时看,将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
【注】(其中
would
用于各种人称,
should
常用于第一人称)。
①表示在过去将来某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态,它应和表过去将来的时间
连用,也常用在间接引语中。
例如:Bruce
told
me
that
he
would
be
living
in
China
some
day.
布鲁斯告诉我将来有一天他会在中国居住。
He
called
me
in
New
York
to
let
me
know
what
time
he'd
be
arriving.
他打电话到纽约,告诉我他将到达的时间。
They
planned
they
would
be
building
another
big
and
modern
shopping
center
the
next
year.
他们计划第二年再建一家大型现代化购物中心。
8.
过去将来进行时(would/should+be+doing)
He
said
that
he
__________(watch)
TV
at
this
time
tomorrow
【答案】时间起点said为过去,从过去来看,将来的某一个时刻点
进行的动作,用过去将来进行时would
be
watching。
①表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果,强调的是这个影响或结果。通常与表示包括现在在内的时间副词just,already,
before,
yet,
never,
ever,recently,lately,twice等状语连用。
例如:
She
has
already
finished
the
work.
她已经完成了工作。
②表示过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还会持续下去的动作或状态。可以和表示从过去某一时刻延续到现在(包括现在在内)的一段时间的状语连用,如so
far,for+时间段,since+过去时间点
,up
to
now,
in
the
past
few
years,
these
years等
。
例如:She
has
learnt
English
for
3
years.
她学英语三年了
9.
现在完成时(have/has+done)
常用句型
①
It/This
is
the
first(second...)
time
+
(that)从句+
现在完成时
②
It/This
is
the
+
最高级
+
n
+
that从句+现在完成时
③
It
is/has
been
+
一段时间
+
since
+
从句(一般过去时)
考点一
非延续性动词(短语)leave,get
married,come,go,die,buy,borrow
等,在现在完成时的肯定句中不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,要进行相应的转换才能与表示一段时间的状语连用。
例如:The
man
died
for
4
years.
(×)
The
man
died
4
years
ago.
(√
)
The
man
has
been
dead
for
4
years.
(√
)
但在否定句中,一些非延续性动词可与表示一段时间的状语连用,表示过程或结果。
例如:I
haven't
bought
anything
for
a
year.
我一年没买任何东西了。
非延续性动词
延续性动词
非延续性动词的完成时
borrow
/
lend
keep
have
kept
buy
have
have
had
die
be
dead
have
been
dead
marry
/
get
married
be
married
have
been
married
open
be
open
have
been
open
close
be
closed
have
been
closed
leave
be
away
(from)
have
been
away
(from)
return
be
back
have
been
back
go
there
be
there
have
been
there
join
be
in/a
member
have
been
in(a
member)
常见非延续性动词与延续动词之间的转换:
考点二
have
been
(to)和have
gone
(to)的区别:
★
have
/
has
been
(to)
表示“曾经去过”某地,说话时此人很可能不在那里,已经回来。侧重指经历。
★
have
/
has
gone
(to)
表示某人“已经去了”某地,说话时此人在那里,或可能在路上,反正不在这里。
(不与时间段连用)
试比较:
He
has
been
to
Beijing.
他曾去过北京。
(人已回来,可能在这儿)
He
has
gone
to
Beijing.
他已经去了北京。
(人已走,不在这儿)
★
have
/
has
been
(in)
表示“某人已经在某地”,表示已经在某地待了多久,常与“for
+
时间段,
since
+
过去时间”等连用。
例如:He
has
been
in
the
Party
for
one
year.
他入党有一年了。
考点三
一般过去时与现在完成时之比较
1)过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯叙述过去的事情,强调动作;
现在完成时为过去发生的,强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。
试比较:
I
saw
this
film
yesterday.
(强调看的动作发生过了。)
I
have
seen
this
film.
(强调对现在的影响,电影的内容已经知道了。)
2)过去时常与具体的时间状语连用;
而现在完成时通常与模糊的时间状语连用,或无时间状语。
◎
一般过去时的时间状语有:yesterday,
last
week,…ago,
in1980,
just
now等。
◎
现在完成时的时间状语有:for+时间段,since+过去时间点,so
far,
up
to
now,
in
the
past/last
few
years,
recently等。
时间
现在
过去
将来
一般过去时
一般现在时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
将来进行时
请将现在完成时在时间轴上标出来:
过去将来时
现在完成时:起点在过去,止点在现在。
动作时间包含过去和现在
现在完成时
①表示在过去某一时刻或者某一动作之前已经完成的动作或状态,
时间定位是“过去的过去”。
例如:
I
had
learnt
5000
words
before
I
entered
the
university.
在我进入大学以前,我已经学了5000个词。
②表示从过去某一时刻
开始,一直持续到过去另一时刻的动作或状态,常与for,
by,
until,
before等构成的时间状语连用。
例如:By
then
he
had
learnt
English
for
3
years.
到那时,他已经学英语三年了。
③常用在told,
said,
knew,
heard,
thought等动词后的宾语从句中。
She
said
(that)
she
had
never
been
to
Paris.
她说她还没去过巴黎。
10.
过去完成时(had+done)
④在过去不同时间发生的两个动作中,发生在先,用过去完成时;发生在后,用一般过去时。
When
the
police
arrived,
the
thieves
had
run
away.
当警察到达的时候,小偷们已经跑了。
⑤表示意向的动词,如hope,
wish,
expect,
think,
intend,
mean,
suppose等,用过去完成时表达"原本打算做…,而实际未能…"
例如:We
had
intended
to
come
and
see
you.
我们本打算来看你。
10.
过去完成时(had+done)
常用句型
①
It/This
was
the
first(second...)
time
+
(that)
...had
done
②
It
was
+
一段时间
+
since
...had
done
③
主语+had
hardly/scarcely(no
sooner)+done+when(than)从句(一般过去时)
时间
现在
过去
将来
一般过去时
一般现在时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
将来进行时
请将过去完成时在时间轴上标出来:
过去将来时
过去完成时:起点在过去,止点也在过去。
动作发生在“过去的过去”
现在完成时
过去完成时
常用句型:
1、当某人正在做某事,这时发生了什么:
【sb.
be
doing
sth
when...】
例:I
was
doing
homework
when
my
mother
came
home.
2、当某人刚做完某事,这时发生了什么:
【sb.
had
just
done
sth
when...did...】
例:I
had
just
finished
my
report
when
someone
knocked
at
the
door.
3、当某人正要做某事,这时发生了什么:
【sb.
be
about
to
do
sth
when...】【be
on
the
point
of
doing
when...】
例:One
day,
I
was
about
to
do
some
shopping
when
he
telephoned
me.
①表示在将来某时/某动作之前已经完成的动作,并往往对将来某一时间产生影响或结果。常与时间状语“by/before
+将来的时间”等连用。
例如:By
this
time
tomorrow
you
will
have
arrived
in
Shenyang.
到明天
这个时候你就会到达沈阳了。
I
shall
have
finished
writing
the
article
by
the
end
of
this
week.
我将在本周末前写完这篇文章。
11.
将来完成时(will/shall
have
done)
【典例】By
the
time
Jane
gets
home,
her
aunt
_______
for
London
to
attend
a
meeting.
A.
will
leave
B.
leaves
C.
will
have
left
D.
left
【解析】by短语常与完成时连用,这里的gets
home是用现在时表将来,
实际上是指一个将来的时间,故主句用将来完成时。句意:到Jane到家
的时候,她的姑姑已经离开家去伦敦参加一个会议了。
①表示在过去将来某一时间或在此以前发生的动作。
例如:Andy
told
me
he
would
have
finished
it
by
9.
安迪告诉我他将在九点前完成。
The
football
team
would
have
arrived
by
6
o'clock.
足球队将于6点前到达。
②用于虚拟语气。
例如:If
you
had
not
helped
me,
I
wouldn't
have
succeeded.
如果你不帮我,我是不会成功的。
12.
过去将来完成时(would/should
have
done)
He
said
that
he
_________(read)
3
books
by
next
Friday.
【解析】根据语境said来看,时间的起点为过去,到将来的某一时间
之前要完成的动作,应用过去将来完成时,故为would
have
read.
①表示动作从过去某时开始一直持续到现在,并有可能持续下去。也可表示到目前为止的一段时间内动作时断时续、反复发生。这个时态通常多限于无限动词,如stay,
wait,
sit,
stand,
lie,
study,
live等,并常与all
this
time,
all
night,
all
the
morning等状语以及since(自从),during等引导的状语或从句连用。
例如:Tom
has
been
working
hard
since
the
new
term
began.
自新学期开始以来,汤姆一直在努力学习。
②有些不能用现在进行时态的动词,如be,love,know,see,hear等,同样也不能用现在完成进行时,而只能用现在完成时。
例如:I
have
not
seen
you
for
ages.
我好久没有见到你了。
13.
现在完成进行时(have/has+been+doing)
【典例】-Excuese
me,
which
movie
are
you
waiting
for?
-The
new
Star
Wars.
We
______(wait)
here
for
more
than
two
hours.
【解析】表示从过去开始一直等到现在,并且可能还会继续等,故用现在完成进行时have
been
waiting。
现在完成时与现在完成进行时的区别
用法
例句
区别1
现在完成进行时强调动作的未完成性
I
have
been
thinking
it
over.
我一直在仔细考虑这件事
现在完成时强调过去某个动作对现在造成的影响或产生的结果
I
have
thought
it
over.
我已经仔细考虑过这件事了。
区别2
现在完成进行时表示动作的反复性
Have
you
been
meeting
him
recently?
你最近经常见他吗?
现在完成时不表示动作的反复性
Have
you
met
him
recently?
你最近见过他吗?
区别3
现在完成进行时可以表示某种感彩
I
have
been
waiting
for
you
for
three
hours.
我已等了你三个小时。(暗含不满的语气)
现在完成时往往只说明一个事实、一种影响或结果,不带有感彩
I
have
waited
for
you
for
three
hours.
我已等了你三个小时。(说明一个事实)
①表示动作在过去某一时间之前开始,一直延续到过去这一时间。动作是否还会
继续下去,要由上下文决定。
例如:Bill
said
he
had
been
doing
experiments
those
days.
比尔说他那几天一直在做实验。
The
telephone
had
been
ringing
for
three
minutes
before
it
was
answered.
电话铃响了三分钟才有人接。
I
had
been
looking
for
my
bike
for
days
before
I
found
it.
我找了很多天才找到我的的车子。
14.
过去完成进行时(had+been+doing)
【典例】The
crazy
fans
_______(wait)
patiently
for
two
hours,
and
they
would
wait
till
the
movie
star
arrived.
【解析】从and后的分句可知电影明星还没有到,所以当时还在“等”,体现了进行时态;从主句的时间状语for
two
hours可知是过去完成时,由此可知用过去完成进行时。had
been
waiting
①表示动作从某一时间开始一直延续到将来某一时间。动作是否还会继续下去,要由上下文决定,常与表示将来某一时间的状语连用。
例如:In
another
month's
time,
Mr
Henry
will
have
been
teaching
here
for
exactly
thirty
years.
再过一个月,亨利先生将在这里从事教学三十年了。
I
shall
have
been
living
here
for
15
years
by
the
end
of
this
month.
到这月底,我就将在这里住够十五年了。
15.
将来完成进行时(will/shall
have
been
doing)
16.
过去将来完成进行时(would/should
have
been
doing)
①表示从过去某一时间开始一直延续到过去将来某一时间的动作。
例如:He
said
that
by
the
end
of
the
Spring
term
he
would
have
been
studying
English
for
three
years.
他说到了春季学期末,他将学了三年英语。
Exercise:
choose
the
best
answer
1.You
_______
television.
Why
not
do
something
more
active?
A.
always
watch
B.
are
always
watching
C.
have
always
watched
D.
have
always
been
watching
2.I
thought
I
_______
the
door,
but
it
is
still
open
A.
had
closed
B.
was
closing
C.
have
closed
D.
would
close
3.By
the
time
you
arrive
in
London,
we
_______
in
Europe
for
two
weeks.
A.
had
stayed
B.
shall
stay
C.
will
have
stayed
D.
have
been
staying
4.Shortly
after
we
______,
a
waiter
came
over
to
our
table
with
a
smile.
A.seated
B.were
seated
C.sat
ourselves
D.had
seated
B
A
C
B
Exercise:
choose
the
best
answer
5.
You
don't
need
to
describe
her.I
______
her
several
times.
A.
had
met
B.
have
met
C.
met
D.
meet
6.When
Jack
arrived,
he
learned
Mary_____for
about
an
hour.
A.had
gone
B.had
set
off
C.had
left
D.had
been
away
7.As
she
_______the
newspaper,
Granny________
asleep.
A.read;
was
falling
B.was
reading;
fell
C.was
reading;
was
flling
D.read;
fell
8.-
Oh,
it's
you?
I
didn't
recognize
you.
-
I
________
my
hair
cut,
and
I
_______
new
glass.
A.had;
was
wearing
B.have
had;
am
wearing
C.had;
wore
D.have
had;
wear
D
B
B
B
9.Someone
_______
my
book.I
______
for
it
for
the
last
ten
minutes
but
I
can't
see
it
anywhere.
A
took;
have
been
looking
B
has
taken;am
looking
C
took;
was
looking
D
has
taken;have
been
looking
10.After
driving
for
thirty
miles,
she
suddenly
realized
that
she______in
the
wrong
direction.
A.had
been
driving
B.has
been
driving
C.drove
D.had
driven
11.No
sooner_______
than
the
accident
happened.
A.
he
had
gone
B.
had
he
gone
C.
his
going
D.
he
went
12.Jane
can’t
attend
the
meeting
at
3
o’clock
this
afternoon
because
she
___________
a
class
at
that
time.
A.
will
teach
B.
would
teach
C.
has
taught
D.
will
be
teaching
D
B
A
D
Thanks
for
listening
同课章节目录
- 名词
- 动词/动词短语
- 一般现在时及其被动式
- 一般过去时及其被动式
- 现在进行时及其被动式
- 过去进行时及其被动式
- 将来进行时及其被动式
- 现在完成时及其被动式
- 过去完成时及其被动式
- 一般将来时及其被动式
- 过去将来时及其被动式
- 现在完成进行时及其被动式
- 将来完成时及其被动式
- 副词
- 介词/介词短语
- 连词/连接词
- 数词/量词
- 冠词
- 形容词
- 非谓语动词
- 句型
- 简单句与并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 倒装与省略
- 强调句
- 虚拟语气
- 插入语
- 固定句型
- 祈使句/感叹句
- 疑问句/反义疑问句
- 非限制性定语从句
- 句型转换
- 定语从句
- 表语从句
- 宾语从句
- 主语从句
- 动词时态与语态
- 虚拟语气与情态动词
- 主谓一致
- 独立主格结构、with的复合结构
- 情态动词
- 状语从句
- 定语从句
- 特殊句式
- 交际用语
- 代词/不定代词
- 名词性从句
- 同位语从句
- 表语从句
- 宾语从句
- 主语从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 构词法(word formation)
