9A Unit 3 Teenage problems Integrated skills
文档属性
| 名称 | 9A Unit 3 Teenage problems Integrated skills |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 8.5MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2012-08-24 15:55:34 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共30张PPT)
英语
9A Unit 3 Integrated skills
吕燕
Chinese Maths English
Physics Chemistry
Politics History
PE Art Music
Computer Science
Subjects
Which subjects are you good at
Which subjects do you have problems with
Do you have any other problems
According to a survey, 30 million teenagers in China suffer from different kinds of problems with mood. 84℅ of the students interviewed suffer from bad feelings such as sadness, anxiety (焦虑)and depression(压抑) at times.
How can we deal with problems
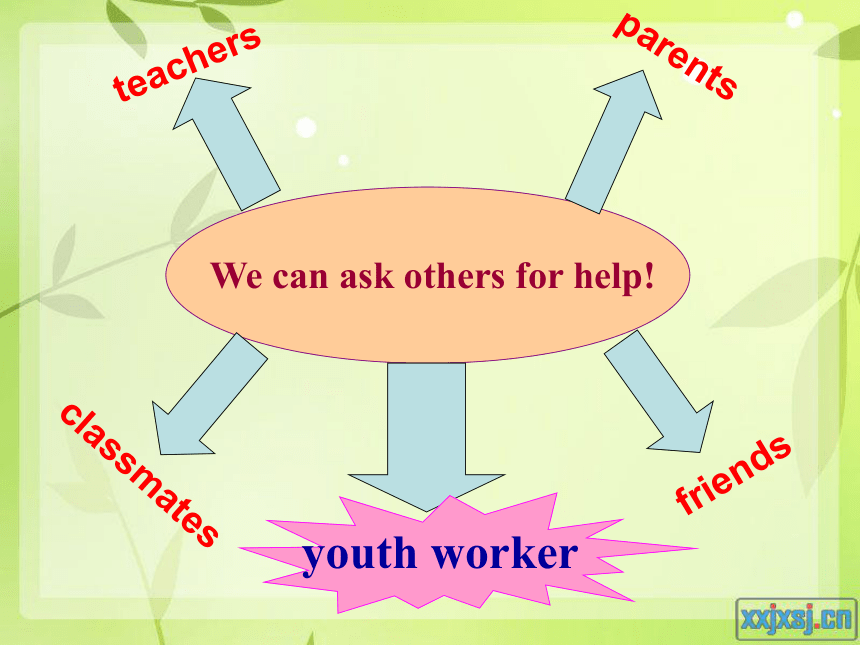
When we have problems , don’t keep worries to ourselves. Instead, we should ask others for help!
We can ask others for help!
parents
teachers
classmates
friends
youth worker
Sigmund Friend
youth worker
help teenagers solve problems
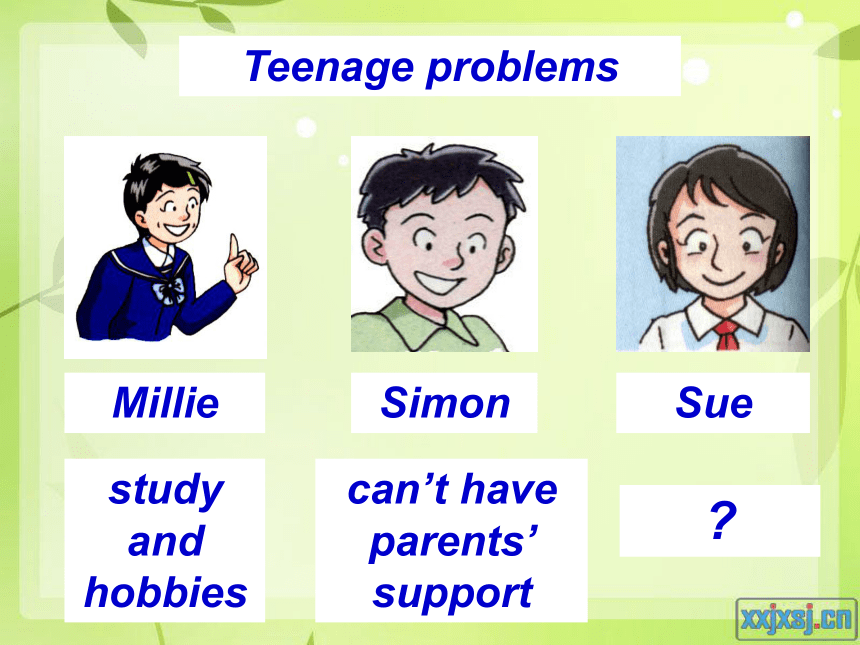
Teenage problems
Millie
Simon
study and hobbies
can’t have parents’ support
Sue
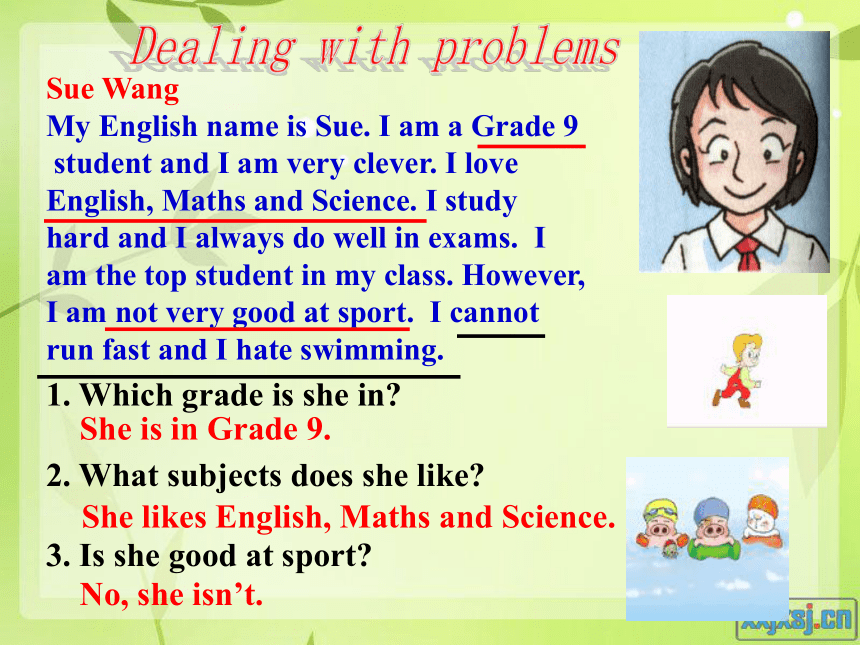
Sue Wang
My English name is Sue. I am a Grade 9
student and I am very clever. I love
English, Maths and Science. I study
hard and I always do well in exams. I
am the top student in my class. However,
I am not very good at sport. I cannot
run fast and I hate swimming.
1. Which grade is she in
2. What subjects does she like
3. Is she good at sport
She is in Grade 9.
She likes English, Maths and Science.
No, she isn’t.
Name: Sue Wang
Favourite subjects: English, (1) ______, Science
First problem: Not good at (2) ______--- cannot(3) ______
and (4)_______________
Advice: Just try (5)________ in PE lessons, enjoy
the (6)________
Second problem: Not have many (7)_______ --- classmates
(8)________ her and call her a bookworm
Advice: Talk to your (9)_________ when feeling
sad and share your (10) _______ with her;
(11) _________ attention to those students
who laugh at you and (12)__________
your schoolwork
maths
sport
run fast
hates swimming
Listening tips
Before listening, we can predict (预测) the missing information according to (根据) the information we have known and the context (上下文).
(在做听力之前,我们可以尝试根据已知的信息和
上下文语境来预测所缺内容)
e.g. _________________ attention to those students who laugh at you
Don’t pay any
/ Pay no
pay attention to
Name: Sue Wang
Favourite subjects: English, (1) ______, Science
First problem: Not good at (2) ______--- cannot(3) ______
and (4)_______________
Advice: Just try (5)________ in PE lessons, enjoy
the (6)________
Second problem: Not have many (7)_______ --- classmates
(8)________ her and call her a bookworm
Advice: Talk to your (9)_________ when feeling
sad and share your (10) _______ with her;
(11) _________ attention to those students
who laugh at you and (12)__________
your schoolwork
maths
sport
run fast
hates swimming
When we listen to long conversations or passages, we can try to make shorthand notes(速记) , such as writing down the key information (关键信息)or the first letter of a word.
(当我们听较长的对话或短文时,可以尝试速记,如记录关键信息或单词首字母)
e.g. I’m good at English, Maths and Science, but I’m not good at sport.
I’m good at English, ______ and Science,
but I’m not good at _____.
M
s
aths
port
Name: Sue Wang
Favourite subjects: English, (1) ______, Science
First problem: Not good at (2) _____--- cannot(3) _______
and (4)______________
Advice: Just try (5)________ in PE lessons, enjoy
the (6)________
Second problem: Not have many (7)_______ --- classmates
(8)________ her and call her a bookworm
Advice: Talk to your (9)_________ when feeling
sad and share your (10) ________ with her;
(11) _________ attention to those students
who laugh at you and (12)___________
your schoolwork
Maths
sport
run fast
hates swimming
your best
exercise
friends
best friend
problems
Pay no
be proud of
laugh at
A bookworm is someone who
spends a lot of
time reading books.
bookworm
Sue is the __________in her class at Beijing Sunshine
Secondary School. Her favourite subjects are ________
_________ and _________.
Sue does well in exams, but she still has some problems.
She is not very good at sport. She _________________
and _______________. Also, her classmates call her a
___________ . This makes her feel sad.
top student
English
maths
science
cannot run fast
hates swimming
bookworm
I told her what to do in PE lessons. She should just
_______________ and ______________________.
I also told her not to ______________________ the
students who laugh at her.
Now, Sue seems much happier than before. She still
finds sport difficult for her ,but now she can talk to
her best friend Betty when she feels sad and _______
_____________ with her. She is also______________
her school work.
try her best
enjoy the exercise
pay any attention to
share
her problems
proud of
Miss Pei —youth worker of our school
A: I’ve got a problem. I’m very worried.
B: I’m sorry to hear that. What’s the problem
A: … Can you help me
B: Why don’t you…
A: That’s a good idea. Thanks for listening to
my problems and giving me your advice.
B: My pleasure. That’s what friends are for.
A: student who has a problem
B: volunteer student
Offering help and giving advice
Why don’t you … / Why not…
I think it’s a good idea to…
How / What about…
Maybe you should…
You’d better…
Asking for help/advice
Can you help me
What should I do
Can you tell me what I should do
Could you give me some advice
Sharing problems and giving advice
Sentence Patterns
Everyone has problems from time to time. When we have problems, we can ask others for help. When other people have problems, we should also help them and give them some advice.
Some listening tips.
How to ask others for advice and how to give others advice.
Memorize the useful sentences we learned in this class.
2. Practise the conversation after class.
英语
9A Unit 3 Integrated skills
吕燕
Chinese Maths English
Physics Chemistry
Politics History
PE Art Music
Computer Science
Subjects
Which subjects are you good at
Which subjects do you have problems with
Do you have any other problems
According to a survey, 30 million teenagers in China suffer from different kinds of problems with mood. 84℅ of the students interviewed suffer from bad feelings such as sadness, anxiety (焦虑)and depression(压抑) at times.
How can we deal with problems
When we have problems , don’t keep worries to ourselves. Instead, we should ask others for help!
We can ask others for help!
parents
teachers
classmates
friends
youth worker
Sigmund Friend
youth worker
help teenagers solve problems
Teenage problems
Millie
Simon
study and hobbies
can’t have parents’ support
Sue
Sue Wang
My English name is Sue. I am a Grade 9
student and I am very clever. I love
English, Maths and Science. I study
hard and I always do well in exams. I
am the top student in my class. However,
I am not very good at sport. I cannot
run fast and I hate swimming.
1. Which grade is she in
2. What subjects does she like
3. Is she good at sport
She is in Grade 9.
She likes English, Maths and Science.
No, she isn’t.
Name: Sue Wang
Favourite subjects: English, (1) ______, Science
First problem: Not good at (2) ______--- cannot(3) ______
and (4)_______________
Advice: Just try (5)________ in PE lessons, enjoy
the (6)________
Second problem: Not have many (7)_______ --- classmates
(8)________ her and call her a bookworm
Advice: Talk to your (9)_________ when feeling
sad and share your (10) _______ with her;
(11) _________ attention to those students
who laugh at you and (12)__________
your schoolwork
maths
sport
run fast
hates swimming
Listening tips
Before listening, we can predict (预测) the missing information according to (根据) the information we have known and the context (上下文).
(在做听力之前,我们可以尝试根据已知的信息和
上下文语境来预测所缺内容)
e.g. _________________ attention to those students who laugh at you
Don’t pay any
/ Pay no
pay attention to
Name: Sue Wang
Favourite subjects: English, (1) ______, Science
First problem: Not good at (2) ______--- cannot(3) ______
and (4)_______________
Advice: Just try (5)________ in PE lessons, enjoy
the (6)________
Second problem: Not have many (7)_______ --- classmates
(8)________ her and call her a bookworm
Advice: Talk to your (9)_________ when feeling
sad and share your (10) _______ with her;
(11) _________ attention to those students
who laugh at you and (12)__________
your schoolwork
maths
sport
run fast
hates swimming
When we listen to long conversations or passages, we can try to make shorthand notes(速记) , such as writing down the key information (关键信息)or the first letter of a word.
(当我们听较长的对话或短文时,可以尝试速记,如记录关键信息或单词首字母)
e.g. I’m good at English, Maths and Science, but I’m not good at sport.
I’m good at English, ______ and Science,
but I’m not good at _____.
M
s
aths
port
Name: Sue Wang
Favourite subjects: English, (1) ______, Science
First problem: Not good at (2) _____--- cannot(3) _______
and (4)______________
Advice: Just try (5)________ in PE lessons, enjoy
the (6)________
Second problem: Not have many (7)_______ --- classmates
(8)________ her and call her a bookworm
Advice: Talk to your (9)_________ when feeling
sad and share your (10) ________ with her;
(11) _________ attention to those students
who laugh at you and (12)___________
your schoolwork
Maths
sport
run fast
hates swimming
your best
exercise
friends
best friend
problems
Pay no
be proud of
laugh at
A bookworm is someone who
spends a lot of
time reading books.
bookworm
Sue is the __________in her class at Beijing Sunshine
Secondary School. Her favourite subjects are ________
_________ and _________.
Sue does well in exams, but she still has some problems.
She is not very good at sport. She _________________
and _______________. Also, her classmates call her a
___________ . This makes her feel sad.
top student
English
maths
science
cannot run fast
hates swimming
bookworm
I told her what to do in PE lessons. She should just
_______________ and ______________________.
I also told her not to ______________________ the
students who laugh at her.
Now, Sue seems much happier than before. She still
finds sport difficult for her ,but now she can talk to
her best friend Betty when she feels sad and _______
_____________ with her. She is also______________
her school work.
try her best
enjoy the exercise
pay any attention to
share
her problems
proud of
Miss Pei —youth worker of our school
A: I’ve got a problem. I’m very worried.
B: I’m sorry to hear that. What’s the problem
A: … Can you help me
B: Why don’t you…
A: That’s a good idea. Thanks for listening to
my problems and giving me your advice.
B: My pleasure. That’s what friends are for.
A: student who has a problem
B: volunteer student
Offering help and giving advice
Why don’t you … / Why not…
I think it’s a good idea to…
How / What about…
Maybe you should…
You’d better…
Asking for help/advice
Can you help me
What should I do
Can you tell me what I should do
Could you give me some advice
Sharing problems and giving advice
Sentence Patterns
Everyone has problems from time to time. When we have problems, we can ask others for help. When other people have problems, we should also help them and give them some advice.
Some listening tips.
How to ask others for advice and how to give others advice.
Memorize the useful sentences we learned in this class.
2. Practise the conversation after class.
