2022年中考英语复习课件16张被动语态&宾语从句
文档属性
| 名称 | 2022年中考英语复习课件16张被动语态&宾语从句 |

|
|
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 738.0KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2021-12-26 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览





文档简介
(共16张PPT)
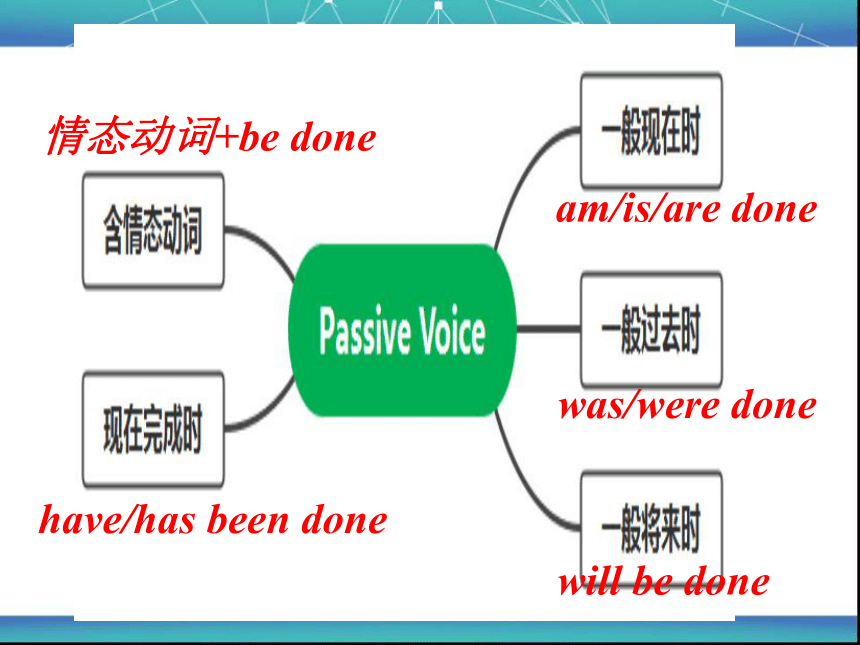
Passive Voice
被动语态
am/is/are done
was/were done
will be done
情态动词+be done
have/has been done
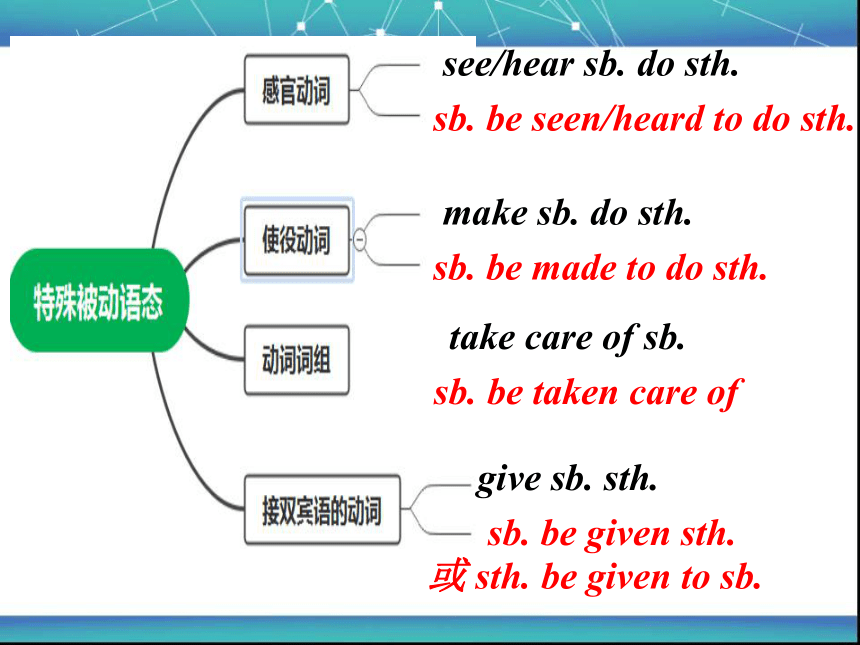
see/hear sb. do sth.
sb. be seen/heard to do sth.
make sb. do sth.
sb. be made to do sth.
give sb. sth.
sb. be given sth.
或 sth. be given to sb.
take care of sb.
sb. be taken care of
连系动词look, sound, smell, taste
open, write, sell, read, wash是
不及物动词,后有副词修饰
happen, take place
need /require /be worth +doing
Topic 1
最近你和父母针对“青少年该不该在周末与朋友外出”进行了讨论。 以“Should Teenagers Go out with Friends on Weekends ”
In my opinion, we teenagers should be allowed to go out with friends for fun on weekends, ...
Topic 2
假如你是班长,学期结束时你要给同学作简短的评价。你班的李华这个学期变化很大,根据提示写一篇简评。
过去 功课不好,常与同学争吵,垃圾扔的满地都是,课桌总是一团糟。
In the past, ... Rubbish was thrown all over the floor by him.
Topic 3
某软件公司为了开发一款适合中学生在课后学习英语的app,邀请你一起参与设计。根据下文提示,向公司介绍你的构思。
好处 1. 便于和同学一起学习;2.帮助学生扩大词汇量;3.有利于提高英语听力。
...Their English listening skills can be greatly improved.
Hot Topic
1. 熊孩子教育问题
2. 5G时代
3. 新冠疫情
Children should be educated to be polite from a young age.
I was deeply moved by so many doctors, nurses and volunteers.
The new technology is used to keep us away from the danger.
5G will be widely used in the near future.
宾语从句的用法
连接词
宾语从句是由陈述句转化成的,连接词用that;(I know that she is a good student.)
宾语从句是由一般疑问句转化成的,连接词用if或whether;(I wonder if he can do it well.)
宾语从句是由特殊疑问句转化成的,连接词直接用特殊疑问词(如who, what, why, where, whose)做引导词,后面变为陈述语序。
( Do you know where the bookstore is )
语序
不管什么类型的宾语从句,总是用陈述句语序,即从句的连接词后是主语、谓语、宾语的语序。
I don’t know who wants to borrow these magazines.
我不知道谁想借这些杂志。
Excuse me, do you know where I can buy it
时态
主句和从句的时态须保持一致。如果主句为一般现在时,从句可根据需要选择各种时态;如果主句是一般过去时,从句只能用过去的某种时态(包括一般过去时、过去进行时、过去完成时、过去将来时等)。
I’m sorry to hear that your mother is ill.
听说你母亲病了,我很难过。
She didn’t know that Tom had left for Shanghai.
她不知道汤姆已去了上海。
1. 当宾语从句的内容是客观事实或科学真理时,不论主句是什么时态,从句都用一般现在时态。
2. 当主句谓语动词为think,suppose,guess, believe等, 并且主语为第一人称时,从句的否定词应转移为对主句谓语动词的否定, 即否定前移。
例如:
The teacher said (that) the earth goes around the sun.
I don't think I know you.
I don' t believe he will come.
3. “两副面孔”
if 和 when 等既能引导宾语从句,又能引导状语从句。因此,碰到此种情况要认真分析。当从句表示将来时,若引导的是宾语从句,它们的时态常用一般将来时;若引导的是状语从句,它们的时态常用一般现在时代替将来时。
If it rains tomorrow, I won’t come.(条件状语从句)
I don’t know if it will rain tomorrow. (宾语从句)
Passive Voice
被动语态
am/is/are done
was/were done
will be done
情态动词+be done
have/has been done
see/hear sb. do sth.
sb. be seen/heard to do sth.
make sb. do sth.
sb. be made to do sth.
give sb. sth.
sb. be given sth.
或 sth. be given to sb.
take care of sb.
sb. be taken care of
连系动词look, sound, smell, taste
open, write, sell, read, wash是
不及物动词,后有副词修饰
happen, take place
need /require /be worth +doing
Topic 1
最近你和父母针对“青少年该不该在周末与朋友外出”进行了讨论。 以“Should Teenagers Go out with Friends on Weekends ”
In my opinion, we teenagers should be allowed to go out with friends for fun on weekends, ...
Topic 2
假如你是班长,学期结束时你要给同学作简短的评价。你班的李华这个学期变化很大,根据提示写一篇简评。
过去 功课不好,常与同学争吵,垃圾扔的满地都是,课桌总是一团糟。
In the past, ... Rubbish was thrown all over the floor by him.
Topic 3
某软件公司为了开发一款适合中学生在课后学习英语的app,邀请你一起参与设计。根据下文提示,向公司介绍你的构思。
好处 1. 便于和同学一起学习;2.帮助学生扩大词汇量;3.有利于提高英语听力。
...Their English listening skills can be greatly improved.
Hot Topic
1. 熊孩子教育问题
2. 5G时代
3. 新冠疫情
Children should be educated to be polite from a young age.
I was deeply moved by so many doctors, nurses and volunteers.
The new technology is used to keep us away from the danger.
5G will be widely used in the near future.
宾语从句的用法
连接词
宾语从句是由陈述句转化成的,连接词用that;(I know that she is a good student.)
宾语从句是由一般疑问句转化成的,连接词用if或whether;(I wonder if he can do it well.)
宾语从句是由特殊疑问句转化成的,连接词直接用特殊疑问词(如who, what, why, where, whose)做引导词,后面变为陈述语序。
( Do you know where the bookstore is )
语序
不管什么类型的宾语从句,总是用陈述句语序,即从句的连接词后是主语、谓语、宾语的语序。
I don’t know who wants to borrow these magazines.
我不知道谁想借这些杂志。
Excuse me, do you know where I can buy it
时态
主句和从句的时态须保持一致。如果主句为一般现在时,从句可根据需要选择各种时态;如果主句是一般过去时,从句只能用过去的某种时态(包括一般过去时、过去进行时、过去完成时、过去将来时等)。
I’m sorry to hear that your mother is ill.
听说你母亲病了,我很难过。
She didn’t know that Tom had left for Shanghai.
她不知道汤姆已去了上海。
1. 当宾语从句的内容是客观事实或科学真理时,不论主句是什么时态,从句都用一般现在时态。
2. 当主句谓语动词为think,suppose,guess, believe等, 并且主语为第一人称时,从句的否定词应转移为对主句谓语动词的否定, 即否定前移。
例如:
The teacher said (that) the earth goes around the sun.
I don't think I know you.
I don' t believe he will come.
3. “两副面孔”
if 和 when 等既能引导宾语从句,又能引导状语从句。因此,碰到此种情况要认真分析。当从句表示将来时,若引导的是宾语从句,它们的时态常用一般将来时;若引导的是状语从句,它们的时态常用一般现在时代替将来时。
If it rains tomorrow, I won’t come.(条件状语从句)
I don’t know if it will rain tomorrow. (宾语从句)
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
