2022年中考英语主从复合句(宾语从句,定语从句,状语从句)课件(96张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2022年中考英语主从复合句(宾语从句,定语从句,状语从句)课件(96张ppt) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 263.8KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2021-12-25 19:15:16 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共96张PPT)
复合句之宾语从句
句子的种类
根据作用分
A 陈述句:
B 疑问句
C 祈使句
D 感叹句
一般疑问句 特殊疑问句
选择疑问句 反意疑问句
what感叹句
How感叹句
肯定陈述句,否定陈述句
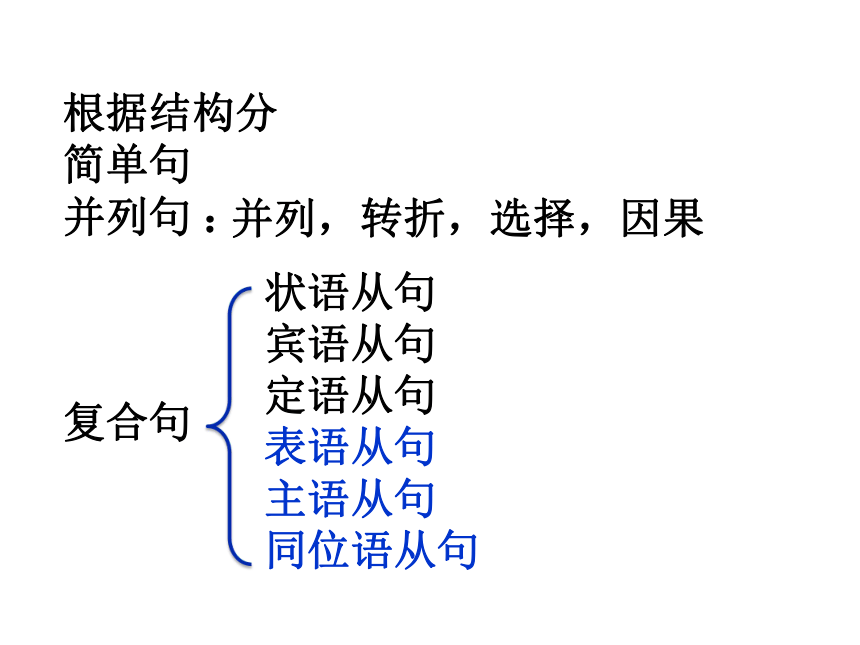
根据结构分
简单句
并列句 :
复合句
状语从句
宾语从句
定语从句
表语从句
主语从句
同位语从句
并列,转折,选择,因果
宾语从句的句法功能
1、作动词的宾语
Tell your son that watching TV too much is bad for his eyes.
2、作介词的宾语
It all depends on whether it will be fine tomorrow.
3、作系表结构的宾语
I am sure that he will come soon.
宾语从句
宾语从句考点
1. 时态
2. 连词(引导词)
3. 语序
1. 主句时态为现在
2. 主语时态为过去
3. 特殊情况
1. that
2. if/whether
3. 特殊疑问词
陈述句
1. that引导的宾语从句
由that引导的宾语从句表示陈述意义。从连
词that无实际意义,不在从句中充当任何成。
I don’t think (that) there will be time to do it.
我认为没有时间做这件事了。
Many people believe (that) robots will do
most our work.
许多人相信机器人会做我们的大部分工作。
2. whether/if引导的宾语从句
whether/if引导的从句大多由一般疑问句直
接引语变化而来。whether/if在从句中不作,
但含有“是否”之义,在句中不可省略。
I ask them whether/if they would win the match.
Do you care whether/if you win
He asked me whether/if Miss Li was a teacher.
只用whether不用if的情况
①引导介词后的宾语从句时。
It depends on whether it will snow tomorrow.
I am interested in whether he likes English.
②与or not连用时。
I asked your secretary whether she could come or not.
Let me know whether he has passed the exam or not.
④有些动词,如discuss, doubt等后的宾语从句常用whether引导。
We’re discussing whether we should group these three companies.
I doubt whether he will keep his promise.
⑤宾语从句前置,置于句首时。
Whether they can come here on time, we don’t know.
Whether they will join in the camp, I don’t care.
③与不定式连用时。
I really don’t know whether to accept or refuse.
Next Monday the teacher will tell us whether to have a test.
在这里要注意, whether to do 在句中做宾语,并不是宾语从句。
3、疑问词引导的宾语从句
宾语从句可以由连接代词what, who, whom,
whose, which等引导,它们在宾语从句中充当
主语、宾语、表语和定语等,因此不能省略。
宾语从句可由连接副when, where, how,
why等引导,它们在宾语从句中作状语,不可
以省略。
Do you know who will come this afternoon
连词作主语
I don’t know whom you should depend on.
连词作宾语
I don’t know what it is.
连词作表语
Could you tell me which gate we have to go to
连词作定语
I wonder whose bike it is.
连词作定语
He didn’t tell me when the traffic accident had taken place.
连词时间状语
Your coat looks very nice. Could you tell me where you bought it
连词作地点状语
It is hard work. I wonder how you finished it in two days.
连词作方式状语
Please explain why you are late again.
连词作原因状语
注意:
连接代词一般表示疑问,但what除了表示疑
问外,也可以表示陈述。
I don’t know what he did.
I believe what he told me.
1. Wang Hai told me_______(how/why) he didn’t go hiking yesterday afternoon.
2. Can you tell me_______(who/whom)else is going to be on duty today
3. She said_______(that/if)it wouldn’t matter much.
4. He always thinks________(how/who)he can do better.
5. I really don’t know _____________(how long/how soon)the bridge will be finished.
why
who
that
how
how soon
6. They don’t know ________(when/what)we are going hiking.
7. She wanted to know________(when/if)her coat would be ready the next day.
8. I was really surprised at________ (what/where) I saw.
9. I don’t know________(how/why) so many people are crowding round him.
10. Do you know_________(whose/who’s)shirt it is
when
if
what
why
whose
二、时态
宾语从句的时态
“宾从”时态怎么办?根据主句来判断;主句
现在,从随便;主句过去,从变换;“主从”动
词同发生,“过去进行”从句中;“宾从”动作先
发生,“过去完成”时态用;“宾从”动作后发
生,“过去将来”时态用;“宾从”表达是真理,
“一般现在”代“过去”。以上规则记心里,时态
呼应没问题。
主句现在,从随便
1. Mary says she _____________(come) back soon.
2. He says that he often ________ (play) football after school.
3. I hear that they _________________ (watch) a game now.
4. Do you know if he _____________(be) to Beijing ever
5. I don’t remember where he _________ (buy) the book yesterday.
will come
plays
are watching
has been
bought
主句过去,从变换
“主从”动词同发生,“过去进行”从句中;
He said that he was reading at that time.
“宾从”动作先发生, “过去完成”时态用;
I told him that I had had dinner already.
“宾从”动作后发生,“过去将来”时态用;
We thought that we would meet him soon.
“宾从”表达是真理,“一般现在”代“过去”
The teacher said that the earth ______ (go) round the sun.
Everyone knew that there ______(be) sixty minutes in an hour.
goes
are
三、语序
所有从句中的语序都是陈述句语序,除倒装
句外。
1. Does her aunt live in Paris (I’m not sure)
I am not sure if her aunt lives in Paris.
2. Who will come to join us (Do you know)
Do you know who will come to join us
3. My son has a cold. (she said)
She said that her son had a cold.
注意一下句子的语序。
Who went Beijing with you
What is the matter with you
What is wrong with you
What happened to you
上面的句子语序都是陈述语序,Who和what
是句子的主语。
1. 当主句的谓语动词是know, learn, forget,
remember, decide, ask, tell, show, teach等后面带特
殊疑问句转化的宾语时,主从句的主语也须一致这时
从句可以简化成“疑问词+不定式结构”。
I don't know which sweater I should buy.
I don't know which sweater to buy.
Could you tell me how I can get to the park
Could you tell me how to get to the park
I haven’t decided whether I will go to the party.
I haven’t decided whether to go to the party.
2. 当句子满足一下条件,从句的否定往往体
现在主句中:
A: 主语是第一人称
B: 时态必须是一般现在时
C: 主句谓语动词表示观点,看法等词,如:
think, suppose, guess, believe, expect,
consider。
我认为我不会按时到达。
I think that I won’t arrive on time.
I don’t think that I will arrive on time.
I don't think that you can do it, _______________
We don't believe the news is true, ____________
He thinks English is very useful, _____________
He didn't think the news is true, _____________
We think we will win the game, ______________
I suppose father is sleeping, ______________
I don’t think you are right, ______________
can you
is it
doesn’t he
did he
won’t we
isn’t he
are you
3. 宾语从句中的虚拟语气
虚拟语气是一种动词形式,表示说话人的一
种愿望,假设,怀疑,猜测,建议等含义,虚
拟语气所表示的含义不是客观存在的事实。
建议 suggest 、advise、propose;
要求demand 、desire、request;
决定 decide; 命令 order、command、require; 坚决主张 insist;
等动词后跟宾语从句,用(should)+v
1. He suggested that we (should) meet at
8:00 in the morning.
2. Tom insists that the work (should) be
finished on time.
3. The boss ordered that all the employees
(should) work harder.
二、定语从句
在复合句中,修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫
定语从句。
在树下的那个女孩是我的妹妹。
The girl who is under the tree is my sister.
The girl is my sister. 主句
who is under the tree. 从句
The girl who is under the tree is my sister.
先行词
连词
从句
The girl who is under the tree is my sister.
The girl is my sister. 主句
who is under the tree. 从句
The girl who is under the tree is my sister.
先行词
连词
从句
连词的作用:
连接先行词和从句;
连词替代先行词;
连词在从句中充当句子成分;
定语从句的连词
先行词 主语 宾语 所有格
人 Who/that Whom/that Whose
事物 Which/that Which/that Whose
人+事物 that that
1. that
That 可以指人也可以指物,在定语从句中充
当主语、宾语。作宾语时可以省略。
Views _______ are entirely new may also be hard to accept.
We need a person ______ is right for the job.
The picture ________ we are studying was drawn by a fifteen-year-old student.
that
that
(that)
2. which
Which一般指物,在定语从句中作主语和宾
语。作宾语的关系代词which可以省略.
The river _________ runs through the center of the city was polluted seriously.
The house _________ I bought from a business is worth.
The story __________ he told was very popular.
which
which
(which)
3. who/whom
二者都用于指人。Who在定语从句中作主语、
宾语;whom在定语从句中作宾语。作宾语的关
系代词who,whom可以省略。
He is a great writer ______ won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2012.
e.g.: Her sister married a man ______________
she met on a plane.
who
(who/whom)
whom在定语从句中作介词的宾语,且介词提到whom前面时,不能用who代替:
The person ________________ you just talked to is Deep.
The person to ________ you just talked is Deep.
That is the classmate _______________ I study with.
That is the classmate ______________ I study.
who/whom
who
whom
who/whom
with whom
注:当先行词为one, ones, anyone 或those
时,这些不定代词往往指人,定语从句中的关
系代词用who。
God helps those who help themselves.
The ones who brake the laws will be
punished.
Anyone who wants to successful always has a
strong belief.
4. Whose
Whose可以指人也可以指物,在定语从句中
作定语,表示先行词和从句中名词之间是所属
关系。
Do you know the girl whose Japanese is excellent
I’d like a room whose window looks out over the sea.
1. Anyone ______ agrees with what I said may put up you hands.
2. April 1st is the day ________ is called April Fool’s Day in the west.
3. The family ________ had lost everything in a big fire got much help from their friends.
4. The house ________ we live in is very old.
5. Did you see the man _________I talked with just now?
who
which
that
that
whom
关系副词在定语从句中充当状语,一般不可
省略。常用的关系副词有when,where,why
等。选择哪一个关系副词要看其前面的先行。
关系副词 先行词 在从句中充当的成分
Where 表示地点的名词 地点状语
When 表示时间的名词 时间状语
Why Reason 原因状语
when引导定语从句
when指时间,在定语从句中作时间状语。它
的先行词通常为time,day,week等表示时间
的名词。
April the first is the day ________ people make fun of others.
I still remember the time _______ I first travelled by plane.
when
when
where引导的定语从句
where指地点,在定语从句中作状语。它的先行词常为place,house,country等表示地点的名词。
Last year my parents went to the farm ________ they worked 30years ago.
Keep the books in a place _________ you can find them easily.
where
where
why引导的定语从句
why指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语,它的先行词通常为reason。
I know the reason ________ she left you.
Please tell me the reason ________ she is crying so badly.
why
why
注:当先行词表示地点,时间,原因是,连接定语从句的关系词一定是关系副词吗?
I will never forget the days _______ we spent.
I don’t believe the reason _______ he told me.
That is the place _______ he called at last year.
This was the time _______ he arrived.
This is place _________he works.
Nobody knows the reason ______ he is late.
when
where
why
that
that
that
定语从句的注意事项:
一. 定语从句中的主谓一致。
The man who ______ (have) an umbrella in his hand ____ (be) my uncle.
The train which ______ just ______ (leave)is for Shenzhen.
The number of people that ________ (come) to visit this city each year ___________ (reach) one million.
has
is
has
left
come
reaches
当关系代词在从句中作主语时,从句谓语动词的单复数由先行词决定.
“One of + 复数可数名词”充当先行词时,定语从句的谓语动词用复数形式;
“the only/very/right one of + 复数可数名词”充当先行词时,定语从句的谓语动词用单数形式。
Tom is one of the students who were awarded.
Tom is the only one of the students who was awarded.
二. 定语从句中只能用that作关系代词的情况。
Have you taken down everything that Mr. Li said
All that can be done has been done.
He stayed in the library and looked up some information that they needed.
1. 当先行词是everything, anything, nothing
(something 除外), all, none, few, little, some不定代
词时,或当先行词受every, any, all, some, no, little,
few, much等不定代词修饰时。
The first thing that my brother is going to do this afternoon is to study physics.
I have found the best way that could finish the test.
The first place that they visited in London was the Big Ben.
This is the best film that I have ever seen.
2. 先行词时序数词或者形容词最高级或者被
其修饰时.
He was watching the children and parcels that looked so strange.
Jack took photographs of the things and people that he was interested in.
hey talked about the persons and things that they remembered at school
3.先行词既有指人的名词又有指物的名词时。
This is the very dictionary that I want to buy.
After the fire in his house, the old car is the only thing that he owns.
This is the very dictionary that I want to buy.
4.当先行词被the very, the only, the same修饰时。
Who is the man that is standing by the gate
Which is the T-shirt that fits me most
Who is the person that is standing at the gate
Which is the bike that you lost
5. 当先行词前面有who, which等疑问代词时。
三. 在以下情况中关系代词只能用which/whom。
The school ________ he once studied in is very famous.
The school ___________ he once studied is very famous.
This is the boy __________ I played tennis with yesterday.
This is the boy _______________ I played tennis yesterday.
in which
where
whom
with whom
Great changes are taking place in the city ____________ they live.
Great changes are taking place in the city ____________ they live.
The reason _____________ he refused the invitation is quite clear.
The reason _____________ he refused the invitation is quite clear.
Shanghai is the city _____________ I was born.
Shanghai is the city _____________ I was born.
where
in which
why
for which
where
in which
四、当先行词本身就是that时,关系代词只能用which。
I don’t like that which he did.
What is that which is on the ground
状语从句
状语从句:在主从复合句中,充当状语的从句
叫做状语从句。
时间状语从句
原因状语从句
结果状语从句
目的状语从句
条件状语从句
让步状语从句
比较状语从句
状语从句
时间状语从句
连词(引导词)
1. when, while, as
2. until, till
3. before, after
4. since
5. hardly ... when …
no sooner … than …
as soon as
1. when, while, as
这三个词通常表示主句的动作和从句动作同
时发生,且常表示过去发生的动作。
when表示时间点或时间段
1. When he was a child, he always tried out some new ideas.
2. When we were having lunch, he arrived.
3. When she came into my room, I was just reading a book.
4. When he called me up, I arrived.
while 只能表示时间段
1. While my wife was reading the newspaper,
I was watching TV.
2. While Jim was mending his bike, Lin Tao came to see him.
3. While I was in Beijing, I visited many interesting places.
4. While Tom was in England, he learnt some English.
as 基本等同于when,可以表示时间点也可
表示时间段。
1. As we were talking on, he got more and more excited.
2. Just as he caught the ball, there was a tearing sound.
3. The students were taking notes as they were listening.
当主从句主语一致时,常表示一边 … , 一边… .
如果从句动作和主句动作同时发生,并且从
句动作为延续性动词 时,when,while,as
可以互换使用。
as, when 引导短暂性动作的动词
1. When /While /As we were dancing, a stranger
came in.
2. As / when I stopped my car, a man came up to me.
3. As the time went on,the weather got worse.
从句表示“随时间推移”连词能用as,不用when 或
while。
注: 当主从句动作发生有先后时,连词只能用
when。
当我到达车站时,火车已经离开了。
When I arrived at the station, the train had
left.
若动作发生在过去,根据动作的先后判断时态。
当他回来时,我会告诉你的。
When he comes back, I will let you know it.
若动作发生在将来,时态遵循主将从现。
2. until, till
肯定形式表示的意思是“做某事直至某 时”,动词必须是延续性的。
I slept till he called me up.
我一直睡到他给我打电话。
否定形式表达的意思是“直至某时才做某 事”, 动词常为非延续性动词。
I didn’t go to sleep until he called me up.
直到他给我打电话,我才去睡觉。
till,until的区别
I slept till he called me up.
I didn’t go to sleep until he called me up.
当主语表示肯定时,till和until可以互换,但
主语表示否定时,只能用until。
I slept till he called me up.
I didn’t go to sleep until he called me up.
until he called me up, I didn’t go to sleep.
until可用于句首,而till通常不用于句首
在not … until引导的时间状语从句中,可以
将not until 提至句首,句子发生倒转。
I didn’t go to sleep until he called me up.
I did not go to sleep until he called me up.
Not
until he called me up
did I go to sleep.
Not until the work is done will he go home.
He won’t go home until the work is done.
当not until 提至句首,主句倒装,从句不倒装。
3. before, after
before, after 连接主从句时,主从句的动作
有明显的先后顺序。如果动作发生在过去,注
意看下面的句子。
在我看完电视后,我就去睡觉了。
After I had watched TV, I went to bed.
在我睡觉前,我看完了电视。
Before I went to bed, I had watched TV.
After I had watched TV, I went to bed.
当after表示先后顺序时,after后的从句表示先
发生的动作,时态用过去完成时;主句则表示
后发生的动作,时态用一般过去时。
Before I went to bed, I had watched TV.
当before表示先后顺序时,before后的从句表
示后发生的动作,时态用一般过去时;主句则
表示先发生的动作,时态用过去完成时。
4. since
since 引导时间状语从句时态相对比较单一。
自从来到中国,他在中国生活了10年了。
Since he came to China, he has lived here for 10 years.
自她听到这个消息以来就一直不开兴。
He has been unhappy since he heard the news.
since 引导的时间状语从句,从句时态常用一般过去时,主句时态常用现在完成时。
since作为连词常见的句型结构。
It is 时间段 since 一般过去时从句
It has been 时间段 since一般过去时从句
自过去发生某事到现在有多长时间了。
自上次见到你已经有10年了。
It is 10 years since I met you last time.
It has been 10 years since I met you last time.
5. hardly … when…
no sooner … than…
as soon as
一个动作刚结束,另一个动作就发生了。
这个三个词所表示的动作常常有先后顺序。
Tom一吃完午饭就去玩游戏了。
As soon as Tom had had lunch, he played
games.
Tom had hardly had lunch when he played
games.
Tom had no sooner had lunch than he
played games.
他们一完成工作就去休息了。
They had no sooner finished the work than they took a rest.
They had hardly finished the work when they took a rest.
As soon as they had finished the work, they took a rest.
当hardly,no sooner 位于句首时,句子主句
发生半倒转。
They had no sooner finished the work than they took a rest.
They had hardly finished the work when they took a rest.
No sooner
had
they finished the work
than they took a rest.
Hardly
had
they finished the work
when they took a rest.
注:
以下连词需要注意的时态when, as, until, till,
before, after,as soon as当主从句的动作未发
生(发生在将来),时态常用主将从现。
当你遇到他时,他会告诉你真相。
When you meet him, he will tell you the truth.
随着夏天的到来,天气会越来越热。
As summer comes, it will be hotter and
hotter.
以下连词需要注意的时态when, as, until, till,
当主从句的动作表示经发生的动作时,主从句
时态常用主现从现。
每当我遇到Tom,他总是很开心。
When I meet Tom, he is always happy.
他每晚完成作业后才去睡觉。
He doesn’t go to bed until he finishes the work
every night.
原因状语从句、结果状语从句
在这两种状语从句中,主从句之间的关系表
示因果关系。有时这两种从句可以相互转化。
原因状语从句: 从句说明主句动作发生的原因。
because, as, since
because表示直接原因, 语气最强, 最适合回
答why引导的疑问句。
I do it because I like it.
We went by bus because it was cheaper.
since引导的原因状语从句一般放于主句之前
表示已知的、 显然的理由(通常被翻译成“既然
” ),语气比because弱。
Since you are free today, you had better help me with my mathematics.
Since you don't trust him, you should not employ him.
Since you are grown up, you should not rely on your parents.
as 引导原因状语从句时表示附带说明的“双
方已知的原因”,含有对比说明的意味, 语气
比since弱, 较为正式, 位置较为灵活(常放于
主句之前)。
As it is raining, you’d better take a taxi.
As you are tired, you had better rest.
I went to bed early, as I was exhausted.
for连接的是并列句,不是复合句。表示前后
句之间的关系是原因关系,只提供一些辅助性
的补充说明。
He could not have seen me, for I was not there.
He seldom goes out now, for he is very old.
what for也可以用来提问原因
结果状语从句:从句说明主句动作发生的结果。
so … that … (如此…以致…)
such … that …(如此…以致…)
They are such fine teachers that we all hold them in great respect.
He speaks so fast that no one can catch him.
1) so + 形/ 副+ that 从句
① The boy is so young that he can't go to school.
② He speaks so fast that no one can catch him.
2) so + many/few(+复名)+ that 从句
There are so many picture-story books that the boy won't leave.
3) so + much/ little(+ 不可数名词)+that 从句
He gave me so little time that it was impossible for me to finish the work on time.
4) so+ 形+ a/an+ 单名+ that 从句
It was so hot a day that they wanted to go swimming.
1) such+ a/an+ 形+单名+ that 从句
He is such a young boy that he can't go to school.
2) such+ 形+ 复名/不可数名词+ that 从句
① They are such fine teachers that we all hold them in great respect.
② It is such nice weather that I would like to go to the beach.
3) such a/an 单名 + that 从句
He is such a man that I don’t want to see him again.
4) such 可数复数/不可数 that 从句
He got such success that he was very excited.
两种状语从句之间的转化
He speaks so fast that no one can catch him.
Because he speaks so fast, no one can catch him.
It is such nice weather that I would like to go to the beach.
Because it is such nice weather, I would like to go to the beach.
Because the boy was tired, he fell asleep quickly.
The boy was so tired that he fell asleep quickly.
Because he made a stupid mistake, he could not forgive himself.
He made such a stupid mistake that he could not forgive himself.
原因状语从句和并列句的转化
He didn’t come to work because he had a
bad cold.
表示因果关系的并列连词:for(原因), so(结果)
He didn’t come to work, for he had a bad cold.
He had a bad cold, so he didn’t come to work.
结果状语从句和简单句的转化
so… that (从句为肯定句)
= … 形/副 + enough + (for sb.) to do sth.
He is so old that he can go to school alone.
= He is old enough to go to school alone.
The question is so easy that I can do it.
=The question is easy enough for me to do.
当主从句主句不一致时,为了说明to do 动作的发出者,常在to do 前for sb.
so… that (从句为否定句)
= … too + 形/副 + (for sb.) to do sth.
The problem is so hard that I can’t work it out.
=The problem is too hard for me to work out.
=The problem isn’t easy enough for me to work out.
让步状语从句:主从句关系表转折。
常用引导词:
although, though, even if, even though.
no matter+疑问词=疑问词-ever(无论…)
即便他不知道该如何解决这个问题,他还是尝试了。
Although he didn’t know how to solve the problem, he tried.
无论你去哪里,我都会找到你。
No matter where you go, I will find you.
Wherever you go, I will find you.
although/ though 不可与but连用(二者只选其一),但可与still / yet连用。
尽管他年龄大了,但依然很强壮。
Although / Though he is very old, he is still strong.
He is very old, but he is strong.
在时态上要保持一致。
无论发生什么,他都不在乎。
Whatever happened, he would not mind.
No matter what happened, he would not mind.
无论你是谁,都得遵守法律。
Whoever you are, you must keep the law.
No matter who you are, you must keep the law.
由wh-ever引导让步状语从句,时态常用主将从现等。
无论有多贵,我都会买。
No matter how it is expensive, I’ll take it.
No matter how expensive it is, I’ll take it.
However expensive it is, I’ll take it.
无论他跑得多快,都追不上汽车。
No matter how fast he runs, he can’t catch the car.
However fast he runs, he can’t catch the car.
条件状语从句
连词:if(如果), so/as long as(只要),
unless(如果不)
如果你按时到达的话,你就不会错过电影。
if you arrive on time, you will not miss the
film.
只要你坚持,你就会瘦下来。
As long as you persist, you will lose weight.
unless
unless
如果不 (if … not)
如果你不知道答案,你可以向我求助。
If you don’t know the answer, you can ask
me for help.
Unless you know the answer, you can ask me
for help.
条件状语从句注意事项
1. 主将从现的原则中,主句中的将来时只能
用will/shall, 不能用am/is/are going to do.
2. 在条件状语从句中,主从句表肯定时,可
以用any.
如果你有任何问题,你可以提问。
It you have any questions, you can ask.
这里any表示 “任何” 。
条件状语从句和并列句的转化
① 祈使句,and + 简单句(一般将来时)
= If you do sth, you’ll do sth.
用and引导的简单句常表示一个较好的结果。
Think hard , and you’ll find a good way.
= If you think hard, you’ll find a good way.
用心思考,你就会找个一个好方法。
② 祈使句,or +简单句(一般将来时)
= If you don’t do sth, you’ll do sth.
用or引导的简单句常表示一个不愉快或不理想的结果。
Hurry up, or you’ll be late.
= If you don’t hurry (up), you’ll be late.
快一点,不然你就要迟到了。
目的状语从句
从句表示主句动作的目的。
so that…
in order that…
为的是…,为了…
我们在线上上课是为了保护自己。
We have classes on line so that we can protect ourselves.
在目的状语从句中,从句中常会出现情态动词,
且要注意主从句的时态要保持一致。
目的状语从句考点:
1.在目的状语从句中,从句中常会出现情态动
词,且要注意主从句的时态要保持一致。
到跟前来以便我能看到你。
Come closer so that I can see you.
我租了一艘小船为了我能去钓鱼。
I hired a boat so that I could go fishing.
说清楚一点,他们也许就可以懂了。
Speak clearly so that they may understand you.
We used the computer in order that we
might save time.
We used the computer in order to save time.
I lent him £ 50 in order that he might go
for a holiday.
I lent him £ 50 for him to go for a holiday.
We will tell you everything about it soon in
order that you can not be cheated.
We will tell you everything about it soon for
you in order not to be cheated.
复合句之宾语从句
句子的种类
根据作用分
A 陈述句:
B 疑问句
C 祈使句
D 感叹句
一般疑问句 特殊疑问句
选择疑问句 反意疑问句
what感叹句
How感叹句
肯定陈述句,否定陈述句
根据结构分
简单句
并列句 :
复合句
状语从句
宾语从句
定语从句
表语从句
主语从句
同位语从句
并列,转折,选择,因果
宾语从句的句法功能
1、作动词的宾语
Tell your son that watching TV too much is bad for his eyes.
2、作介词的宾语
It all depends on whether it will be fine tomorrow.
3、作系表结构的宾语
I am sure that he will come soon.
宾语从句
宾语从句考点
1. 时态
2. 连词(引导词)
3. 语序
1. 主句时态为现在
2. 主语时态为过去
3. 特殊情况
1. that
2. if/whether
3. 特殊疑问词
陈述句
1. that引导的宾语从句
由that引导的宾语从句表示陈述意义。从连
词that无实际意义,不在从句中充当任何成。
I don’t think (that) there will be time to do it.
我认为没有时间做这件事了。
Many people believe (that) robots will do
most our work.
许多人相信机器人会做我们的大部分工作。
2. whether/if引导的宾语从句
whether/if引导的从句大多由一般疑问句直
接引语变化而来。whether/if在从句中不作,
但含有“是否”之义,在句中不可省略。
I ask them whether/if they would win the match.
Do you care whether/if you win
He asked me whether/if Miss Li was a teacher.
只用whether不用if的情况
①引导介词后的宾语从句时。
It depends on whether it will snow tomorrow.
I am interested in whether he likes English.
②与or not连用时。
I asked your secretary whether she could come or not.
Let me know whether he has passed the exam or not.
④有些动词,如discuss, doubt等后的宾语从句常用whether引导。
We’re discussing whether we should group these three companies.
I doubt whether he will keep his promise.
⑤宾语从句前置,置于句首时。
Whether they can come here on time, we don’t know.
Whether they will join in the camp, I don’t care.
③与不定式连用时。
I really don’t know whether to accept or refuse.
Next Monday the teacher will tell us whether to have a test.
在这里要注意, whether to do 在句中做宾语,并不是宾语从句。
3、疑问词引导的宾语从句
宾语从句可以由连接代词what, who, whom,
whose, which等引导,它们在宾语从句中充当
主语、宾语、表语和定语等,因此不能省略。
宾语从句可由连接副when, where, how,
why等引导,它们在宾语从句中作状语,不可
以省略。
Do you know who will come this afternoon
连词作主语
I don’t know whom you should depend on.
连词作宾语
I don’t know what it is.
连词作表语
Could you tell me which gate we have to go to
连词作定语
I wonder whose bike it is.
连词作定语
He didn’t tell me when the traffic accident had taken place.
连词时间状语
Your coat looks very nice. Could you tell me where you bought it
连词作地点状语
It is hard work. I wonder how you finished it in two days.
连词作方式状语
Please explain why you are late again.
连词作原因状语
注意:
连接代词一般表示疑问,但what除了表示疑
问外,也可以表示陈述。
I don’t know what he did.
I believe what he told me.
1. Wang Hai told me_______(how/why) he didn’t go hiking yesterday afternoon.
2. Can you tell me_______(who/whom)else is going to be on duty today
3. She said_______(that/if)it wouldn’t matter much.
4. He always thinks________(how/who)he can do better.
5. I really don’t know _____________(how long/how soon)the bridge will be finished.
why
who
that
how
how soon
6. They don’t know ________(when/what)we are going hiking.
7. She wanted to know________(when/if)her coat would be ready the next day.
8. I was really surprised at________ (what/where) I saw.
9. I don’t know________(how/why) so many people are crowding round him.
10. Do you know_________(whose/who’s)shirt it is
when
if
what
why
whose
二、时态
宾语从句的时态
“宾从”时态怎么办?根据主句来判断;主句
现在,从随便;主句过去,从变换;“主从”动
词同发生,“过去进行”从句中;“宾从”动作先
发生,“过去完成”时态用;“宾从”动作后发
生,“过去将来”时态用;“宾从”表达是真理,
“一般现在”代“过去”。以上规则记心里,时态
呼应没问题。
主句现在,从随便
1. Mary says she _____________(come) back soon.
2. He says that he often ________ (play) football after school.
3. I hear that they _________________ (watch) a game now.
4. Do you know if he _____________(be) to Beijing ever
5. I don’t remember where he _________ (buy) the book yesterday.
will come
plays
are watching
has been
bought
主句过去,从变换
“主从”动词同发生,“过去进行”从句中;
He said that he was reading at that time.
“宾从”动作先发生, “过去完成”时态用;
I told him that I had had dinner already.
“宾从”动作后发生,“过去将来”时态用;
We thought that we would meet him soon.
“宾从”表达是真理,“一般现在”代“过去”
The teacher said that the earth ______ (go) round the sun.
Everyone knew that there ______(be) sixty minutes in an hour.
goes
are
三、语序
所有从句中的语序都是陈述句语序,除倒装
句外。
1. Does her aunt live in Paris (I’m not sure)
I am not sure if her aunt lives in Paris.
2. Who will come to join us (Do you know)
Do you know who will come to join us
3. My son has a cold. (she said)
She said that her son had a cold.
注意一下句子的语序。
Who went Beijing with you
What is the matter with you
What is wrong with you
What happened to you
上面的句子语序都是陈述语序,Who和what
是句子的主语。
1. 当主句的谓语动词是know, learn, forget,
remember, decide, ask, tell, show, teach等后面带特
殊疑问句转化的宾语时,主从句的主语也须一致这时
从句可以简化成“疑问词+不定式结构”。
I don't know which sweater I should buy.
I don't know which sweater to buy.
Could you tell me how I can get to the park
Could you tell me how to get to the park
I haven’t decided whether I will go to the party.
I haven’t decided whether to go to the party.
2. 当句子满足一下条件,从句的否定往往体
现在主句中:
A: 主语是第一人称
B: 时态必须是一般现在时
C: 主句谓语动词表示观点,看法等词,如:
think, suppose, guess, believe, expect,
consider。
我认为我不会按时到达。
I think that I won’t arrive on time.
I don’t think that I will arrive on time.
I don't think that you can do it, _______________
We don't believe the news is true, ____________
He thinks English is very useful, _____________
He didn't think the news is true, _____________
We think we will win the game, ______________
I suppose father is sleeping, ______________
I don’t think you are right, ______________
can you
is it
doesn’t he
did he
won’t we
isn’t he
are you
3. 宾语从句中的虚拟语气
虚拟语气是一种动词形式,表示说话人的一
种愿望,假设,怀疑,猜测,建议等含义,虚
拟语气所表示的含义不是客观存在的事实。
建议 suggest 、advise、propose;
要求demand 、desire、request;
决定 decide; 命令 order、command、require; 坚决主张 insist;
等动词后跟宾语从句,用(should)+v
1. He suggested that we (should) meet at
8:00 in the morning.
2. Tom insists that the work (should) be
finished on time.
3. The boss ordered that all the employees
(should) work harder.
二、定语从句
在复合句中,修饰某一名词或代词的从句叫
定语从句。
在树下的那个女孩是我的妹妹。
The girl who is under the tree is my sister.
The girl is my sister. 主句
who is under the tree. 从句
The girl who is under the tree is my sister.
先行词
连词
从句
The girl who is under the tree is my sister.
The girl is my sister. 主句
who is under the tree. 从句
The girl who is under the tree is my sister.
先行词
连词
从句
连词的作用:
连接先行词和从句;
连词替代先行词;
连词在从句中充当句子成分;
定语从句的连词
先行词 主语 宾语 所有格
人 Who/that Whom/that Whose
事物 Which/that Which/that Whose
人+事物 that that
1. that
That 可以指人也可以指物,在定语从句中充
当主语、宾语。作宾语时可以省略。
Views _______ are entirely new may also be hard to accept.
We need a person ______ is right for the job.
The picture ________ we are studying was drawn by a fifteen-year-old student.
that
that
(that)
2. which
Which一般指物,在定语从句中作主语和宾
语。作宾语的关系代词which可以省略.
The river _________ runs through the center of the city was polluted seriously.
The house _________ I bought from a business is worth.
The story __________ he told was very popular.
which
which
(which)
3. who/whom
二者都用于指人。Who在定语从句中作主语、
宾语;whom在定语从句中作宾语。作宾语的关
系代词who,whom可以省略。
He is a great writer ______ won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2012.
e.g.: Her sister married a man ______________
she met on a plane.
who
(who/whom)
whom在定语从句中作介词的宾语,且介词提到whom前面时,不能用who代替:
The person ________________ you just talked to is Deep.
The person to ________ you just talked is Deep.
That is the classmate _______________ I study with.
That is the classmate ______________ I study.
who/whom
who
whom
who/whom
with whom
注:当先行词为one, ones, anyone 或those
时,这些不定代词往往指人,定语从句中的关
系代词用who。
God helps those who help themselves.
The ones who brake the laws will be
punished.
Anyone who wants to successful always has a
strong belief.
4. Whose
Whose可以指人也可以指物,在定语从句中
作定语,表示先行词和从句中名词之间是所属
关系。
Do you know the girl whose Japanese is excellent
I’d like a room whose window looks out over the sea.
1. Anyone ______ agrees with what I said may put up you hands.
2. April 1st is the day ________ is called April Fool’s Day in the west.
3. The family ________ had lost everything in a big fire got much help from their friends.
4. The house ________ we live in is very old.
5. Did you see the man _________I talked with just now?
who
which
that
that
whom
关系副词在定语从句中充当状语,一般不可
省略。常用的关系副词有when,where,why
等。选择哪一个关系副词要看其前面的先行。
关系副词 先行词 在从句中充当的成分
Where 表示地点的名词 地点状语
When 表示时间的名词 时间状语
Why Reason 原因状语
when引导定语从句
when指时间,在定语从句中作时间状语。它
的先行词通常为time,day,week等表示时间
的名词。
April the first is the day ________ people make fun of others.
I still remember the time _______ I first travelled by plane.
when
when
where引导的定语从句
where指地点,在定语从句中作状语。它的先行词常为place,house,country等表示地点的名词。
Last year my parents went to the farm ________ they worked 30years ago.
Keep the books in a place _________ you can find them easily.
where
where
why引导的定语从句
why指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语,它的先行词通常为reason。
I know the reason ________ she left you.
Please tell me the reason ________ she is crying so badly.
why
why
注:当先行词表示地点,时间,原因是,连接定语从句的关系词一定是关系副词吗?
I will never forget the days _______ we spent.
I don’t believe the reason _______ he told me.
That is the place _______ he called at last year.
This was the time _______ he arrived.
This is place _________he works.
Nobody knows the reason ______ he is late.
when
where
why
that
that
that
定语从句的注意事项:
一. 定语从句中的主谓一致。
The man who ______ (have) an umbrella in his hand ____ (be) my uncle.
The train which ______ just ______ (leave)is for Shenzhen.
The number of people that ________ (come) to visit this city each year ___________ (reach) one million.
has
is
has
left
come
reaches
当关系代词在从句中作主语时,从句谓语动词的单复数由先行词决定.
“One of + 复数可数名词”充当先行词时,定语从句的谓语动词用复数形式;
“the only/very/right one of + 复数可数名词”充当先行词时,定语从句的谓语动词用单数形式。
Tom is one of the students who were awarded.
Tom is the only one of the students who was awarded.
二. 定语从句中只能用that作关系代词的情况。
Have you taken down everything that Mr. Li said
All that can be done has been done.
He stayed in the library and looked up some information that they needed.
1. 当先行词是everything, anything, nothing
(something 除外), all, none, few, little, some不定代
词时,或当先行词受every, any, all, some, no, little,
few, much等不定代词修饰时。
The first thing that my brother is going to do this afternoon is to study physics.
I have found the best way that could finish the test.
The first place that they visited in London was the Big Ben.
This is the best film that I have ever seen.
2. 先行词时序数词或者形容词最高级或者被
其修饰时.
He was watching the children and parcels that looked so strange.
Jack took photographs of the things and people that he was interested in.
hey talked about the persons and things that they remembered at school
3.先行词既有指人的名词又有指物的名词时。
This is the very dictionary that I want to buy.
After the fire in his house, the old car is the only thing that he owns.
This is the very dictionary that I want to buy.
4.当先行词被the very, the only, the same修饰时。
Who is the man that is standing by the gate
Which is the T-shirt that fits me most
Who is the person that is standing at the gate
Which is the bike that you lost
5. 当先行词前面有who, which等疑问代词时。
三. 在以下情况中关系代词只能用which/whom。
The school ________ he once studied in is very famous.
The school ___________ he once studied is very famous.
This is the boy __________ I played tennis with yesterday.
This is the boy _______________ I played tennis yesterday.
in which
where
whom
with whom
Great changes are taking place in the city ____________ they live.
Great changes are taking place in the city ____________ they live.
The reason _____________ he refused the invitation is quite clear.
The reason _____________ he refused the invitation is quite clear.
Shanghai is the city _____________ I was born.
Shanghai is the city _____________ I was born.
where
in which
why
for which
where
in which
四、当先行词本身就是that时,关系代词只能用which。
I don’t like that which he did.
What is that which is on the ground
状语从句
状语从句:在主从复合句中,充当状语的从句
叫做状语从句。
时间状语从句
原因状语从句
结果状语从句
目的状语从句
条件状语从句
让步状语从句
比较状语从句
状语从句
时间状语从句
连词(引导词)
1. when, while, as
2. until, till
3. before, after
4. since
5. hardly ... when …
no sooner … than …
as soon as
1. when, while, as
这三个词通常表示主句的动作和从句动作同
时发生,且常表示过去发生的动作。
when表示时间点或时间段
1. When he was a child, he always tried out some new ideas.
2. When we were having lunch, he arrived.
3. When she came into my room, I was just reading a book.
4. When he called me up, I arrived.
while 只能表示时间段
1. While my wife was reading the newspaper,
I was watching TV.
2. While Jim was mending his bike, Lin Tao came to see him.
3. While I was in Beijing, I visited many interesting places.
4. While Tom was in England, he learnt some English.
as 基本等同于when,可以表示时间点也可
表示时间段。
1. As we were talking on, he got more and more excited.
2. Just as he caught the ball, there was a tearing sound.
3. The students were taking notes as they were listening.
当主从句主语一致时,常表示一边 … , 一边… .
如果从句动作和主句动作同时发生,并且从
句动作为延续性动词 时,when,while,as
可以互换使用。
as, when 引导短暂性动作的动词
1. When /While /As we were dancing, a stranger
came in.
2. As / when I stopped my car, a man came up to me.
3. As the time went on,the weather got worse.
从句表示“随时间推移”连词能用as,不用when 或
while。
注: 当主从句动作发生有先后时,连词只能用
when。
当我到达车站时,火车已经离开了。
When I arrived at the station, the train had
left.
若动作发生在过去,根据动作的先后判断时态。
当他回来时,我会告诉你的。
When he comes back, I will let you know it.
若动作发生在将来,时态遵循主将从现。
2. until, till
肯定形式表示的意思是“做某事直至某 时”,动词必须是延续性的。
I slept till he called me up.
我一直睡到他给我打电话。
否定形式表达的意思是“直至某时才做某 事”, 动词常为非延续性动词。
I didn’t go to sleep until he called me up.
直到他给我打电话,我才去睡觉。
till,until的区别
I slept till he called me up.
I didn’t go to sleep until he called me up.
当主语表示肯定时,till和until可以互换,但
主语表示否定时,只能用until。
I slept till he called me up.
I didn’t go to sleep until he called me up.
until he called me up, I didn’t go to sleep.
until可用于句首,而till通常不用于句首
在not … until引导的时间状语从句中,可以
将not until 提至句首,句子发生倒转。
I didn’t go to sleep until he called me up.
I did not go to sleep until he called me up.
Not
until he called me up
did I go to sleep.
Not until the work is done will he go home.
He won’t go home until the work is done.
当not until 提至句首,主句倒装,从句不倒装。
3. before, after
before, after 连接主从句时,主从句的动作
有明显的先后顺序。如果动作发生在过去,注
意看下面的句子。
在我看完电视后,我就去睡觉了。
After I had watched TV, I went to bed.
在我睡觉前,我看完了电视。
Before I went to bed, I had watched TV.
After I had watched TV, I went to bed.
当after表示先后顺序时,after后的从句表示先
发生的动作,时态用过去完成时;主句则表示
后发生的动作,时态用一般过去时。
Before I went to bed, I had watched TV.
当before表示先后顺序时,before后的从句表
示后发生的动作,时态用一般过去时;主句则
表示先发生的动作,时态用过去完成时。
4. since
since 引导时间状语从句时态相对比较单一。
自从来到中国,他在中国生活了10年了。
Since he came to China, he has lived here for 10 years.
自她听到这个消息以来就一直不开兴。
He has been unhappy since he heard the news.
since 引导的时间状语从句,从句时态常用一般过去时,主句时态常用现在完成时。
since作为连词常见的句型结构。
It is 时间段 since 一般过去时从句
It has been 时间段 since一般过去时从句
自过去发生某事到现在有多长时间了。
自上次见到你已经有10年了。
It is 10 years since I met you last time.
It has been 10 years since I met you last time.
5. hardly … when…
no sooner … than…
as soon as
一个动作刚结束,另一个动作就发生了。
这个三个词所表示的动作常常有先后顺序。
Tom一吃完午饭就去玩游戏了。
As soon as Tom had had lunch, he played
games.
Tom had hardly had lunch when he played
games.
Tom had no sooner had lunch than he
played games.
他们一完成工作就去休息了。
They had no sooner finished the work than they took a rest.
They had hardly finished the work when they took a rest.
As soon as they had finished the work, they took a rest.
当hardly,no sooner 位于句首时,句子主句
发生半倒转。
They had no sooner finished the work than they took a rest.
They had hardly finished the work when they took a rest.
No sooner
had
they finished the work
than they took a rest.
Hardly
had
they finished the work
when they took a rest.
注:
以下连词需要注意的时态when, as, until, till,
before, after,as soon as当主从句的动作未发
生(发生在将来),时态常用主将从现。
当你遇到他时,他会告诉你真相。
When you meet him, he will tell you the truth.
随着夏天的到来,天气会越来越热。
As summer comes, it will be hotter and
hotter.
以下连词需要注意的时态when, as, until, till,
当主从句的动作表示经发生的动作时,主从句
时态常用主现从现。
每当我遇到Tom,他总是很开心。
When I meet Tom, he is always happy.
他每晚完成作业后才去睡觉。
He doesn’t go to bed until he finishes the work
every night.
原因状语从句、结果状语从句
在这两种状语从句中,主从句之间的关系表
示因果关系。有时这两种从句可以相互转化。
原因状语从句: 从句说明主句动作发生的原因。
because, as, since
because表示直接原因, 语气最强, 最适合回
答why引导的疑问句。
I do it because I like it.
We went by bus because it was cheaper.
since引导的原因状语从句一般放于主句之前
表示已知的、 显然的理由(通常被翻译成“既然
” ),语气比because弱。
Since you are free today, you had better help me with my mathematics.
Since you don't trust him, you should not employ him.
Since you are grown up, you should not rely on your parents.
as 引导原因状语从句时表示附带说明的“双
方已知的原因”,含有对比说明的意味, 语气
比since弱, 较为正式, 位置较为灵活(常放于
主句之前)。
As it is raining, you’d better take a taxi.
As you are tired, you had better rest.
I went to bed early, as I was exhausted.
for连接的是并列句,不是复合句。表示前后
句之间的关系是原因关系,只提供一些辅助性
的补充说明。
He could not have seen me, for I was not there.
He seldom goes out now, for he is very old.
what for也可以用来提问原因
结果状语从句:从句说明主句动作发生的结果。
so … that … (如此…以致…)
such … that …(如此…以致…)
They are such fine teachers that we all hold them in great respect.
He speaks so fast that no one can catch him.
1) so + 形/ 副+ that 从句
① The boy is so young that he can't go to school.
② He speaks so fast that no one can catch him.
2) so + many/few(+复名)+ that 从句
There are so many picture-story books that the boy won't leave.
3) so + much/ little(+ 不可数名词)+that 从句
He gave me so little time that it was impossible for me to finish the work on time.
4) so+ 形+ a/an+ 单名+ that 从句
It was so hot a day that they wanted to go swimming.
1) such+ a/an+ 形+单名+ that 从句
He is such a young boy that he can't go to school.
2) such+ 形+ 复名/不可数名词+ that 从句
① They are such fine teachers that we all hold them in great respect.
② It is such nice weather that I would like to go to the beach.
3) such a/an 单名 + that 从句
He is such a man that I don’t want to see him again.
4) such 可数复数/不可数 that 从句
He got such success that he was very excited.
两种状语从句之间的转化
He speaks so fast that no one can catch him.
Because he speaks so fast, no one can catch him.
It is such nice weather that I would like to go to the beach.
Because it is such nice weather, I would like to go to the beach.
Because the boy was tired, he fell asleep quickly.
The boy was so tired that he fell asleep quickly.
Because he made a stupid mistake, he could not forgive himself.
He made such a stupid mistake that he could not forgive himself.
原因状语从句和并列句的转化
He didn’t come to work because he had a
bad cold.
表示因果关系的并列连词:for(原因), so(结果)
He didn’t come to work, for he had a bad cold.
He had a bad cold, so he didn’t come to work.
结果状语从句和简单句的转化
so… that (从句为肯定句)
= … 形/副 + enough + (for sb.) to do sth.
He is so old that he can go to school alone.
= He is old enough to go to school alone.
The question is so easy that I can do it.
=The question is easy enough for me to do.
当主从句主句不一致时,为了说明to do 动作的发出者,常在to do 前for sb.
so… that (从句为否定句)
= … too + 形/副 + (for sb.) to do sth.
The problem is so hard that I can’t work it out.
=The problem is too hard for me to work out.
=The problem isn’t easy enough for me to work out.
让步状语从句:主从句关系表转折。
常用引导词:
although, though, even if, even though.
no matter+疑问词=疑问词-ever(无论…)
即便他不知道该如何解决这个问题,他还是尝试了。
Although he didn’t know how to solve the problem, he tried.
无论你去哪里,我都会找到你。
No matter where you go, I will find you.
Wherever you go, I will find you.
although/ though 不可与but连用(二者只选其一),但可与still / yet连用。
尽管他年龄大了,但依然很强壮。
Although / Though he is very old, he is still strong.
He is very old, but he is strong.
在时态上要保持一致。
无论发生什么,他都不在乎。
Whatever happened, he would not mind.
No matter what happened, he would not mind.
无论你是谁,都得遵守法律。
Whoever you are, you must keep the law.
No matter who you are, you must keep the law.
由wh-ever引导让步状语从句,时态常用主将从现等。
无论有多贵,我都会买。
No matter how it is expensive, I’ll take it.
No matter how expensive it is, I’ll take it.
However expensive it is, I’ll take it.
无论他跑得多快,都追不上汽车。
No matter how fast he runs, he can’t catch the car.
However fast he runs, he can’t catch the car.
条件状语从句
连词:if(如果), so/as long as(只要),
unless(如果不)
如果你按时到达的话,你就不会错过电影。
if you arrive on time, you will not miss the
film.
只要你坚持,你就会瘦下来。
As long as you persist, you will lose weight.
unless
unless
如果不 (if … not)
如果你不知道答案,你可以向我求助。
If you don’t know the answer, you can ask
me for help.
Unless you know the answer, you can ask me
for help.
条件状语从句注意事项
1. 主将从现的原则中,主句中的将来时只能
用will/shall, 不能用am/is/are going to do.
2. 在条件状语从句中,主从句表肯定时,可
以用any.
如果你有任何问题,你可以提问。
It you have any questions, you can ask.
这里any表示 “任何” 。
条件状语从句和并列句的转化
① 祈使句,and + 简单句(一般将来时)
= If you do sth, you’ll do sth.
用and引导的简单句常表示一个较好的结果。
Think hard , and you’ll find a good way.
= If you think hard, you’ll find a good way.
用心思考,你就会找个一个好方法。
② 祈使句,or +简单句(一般将来时)
= If you don’t do sth, you’ll do sth.
用or引导的简单句常表示一个不愉快或不理想的结果。
Hurry up, or you’ll be late.
= If you don’t hurry (up), you’ll be late.
快一点,不然你就要迟到了。
目的状语从句
从句表示主句动作的目的。
so that…
in order that…
为的是…,为了…
我们在线上上课是为了保护自己。
We have classes on line so that we can protect ourselves.
在目的状语从句中,从句中常会出现情态动词,
且要注意主从句的时态要保持一致。
目的状语从句考点:
1.在目的状语从句中,从句中常会出现情态动
词,且要注意主从句的时态要保持一致。
到跟前来以便我能看到你。
Come closer so that I can see you.
我租了一艘小船为了我能去钓鱼。
I hired a boat so that I could go fishing.
说清楚一点,他们也许就可以懂了。
Speak clearly so that they may understand you.
We used the computer in order that we
might save time.
We used the computer in order to save time.
I lent him £ 50 in order that he might go
for a holiday.
I lent him £ 50 for him to go for a holiday.
We will tell you everything about it soon in
order that you can not be cheated.
We will tell you everything about it soon for
you in order not to be cheated.
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
