Unit 13 We're trying to save the earth! SectionA (GrammarFocus-4c)课件 (共32张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 13 We're trying to save the earth! SectionA (GrammarFocus-4c)课件 (共32张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 837.3KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2021-12-31 19:09:46 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共32张PPT)
Section A (GF-4c)
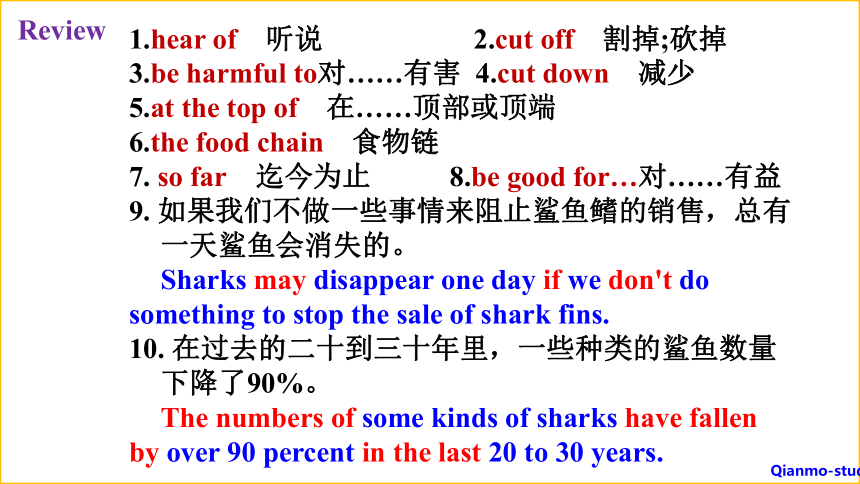
1.hear of 听说 2.cut off 割掉;砍掉
3.be harmful to对……有害 4.cut down 减少
5.at the top of 在……顶部或顶端
6.the food chain 食物链
7. so far 迄今为止 8.be good for…对……有益
9. 如果我们不做一些事情来阻止鲨鱼鳍的销售,总有一天鲨鱼会消失的。
Sharks may disappear one day if we don't do something to stop the sale of shark fins.
10. 在过去的二十到三十年里,一些种类的鲨鱼数量下降了90%。
The numbers of some kinds of sharks have fallen by over 90 percent in the last 20 to 30 years.
take part in
afford
turn off
reusable
pay for
take action
transportation
参加
v. 买的起;承担的起(后果)
关掉
adj. 可重复使用的
付费;付出代价
采取行动
n. 运输业;交通运输
Words Review
To review the use of The Present Continuous Tense,
passive voice, Present Perfect and Modal Verbs
Key words & phrases:
take part in ,afford, turn off, reusable, pay for, take action, transportation
Key sentences:
1.Have you ever taken part in an environmental project
2. We should help save the sharks.
1. We're trying to save the earth.
2. No scientific studies have shown that shark fins are good for health.
3. The air is badly polluted.
4.The river used to be so clean.
5. We should help save the sharks.
Grammar Focus
现在进行时
used to
被动语态
现在完成时
情态动词
现在进行时表示现在或现阶段正在进行或发生的动作。
Look! The two birds are flying away.
看,那两只鸟飞走了。
表示说话时正在进行的,目前正在发生的动作。
常带有表示目前时刻的时间状语, 如:now, at the (very) moment, for the time being, at present, 及Look! Listen! ...
We are not working on a farm these days.
这些天我们不在农场工作。
2)表示目前一段时间内正在进行,但说话时可能没有进行的动作。
现在进行时
① You are always changing your mind.
你总是主意不定。(太烦人了。)
② He is always helping others.
他总是帮助别人。(他真是个好人。)
He is leaving on Wednesday.
他将于周三离开。
3) 与always, constantly, forever, all the time等副词连用,表示动作反复或习惯。
此时句子常含有说话者的强烈情感在内。表达较强的“责备”或“表扬”之意。
4) 对于 come, go, leave, arrive, start 等表示位置移动的动词常可用进行时态表将来。
基本结构
① 肯定句: 主语 + am/is/are + V-ing...
② 否定句: 主语 + am/is/are + not + V-ing...
③ 疑问句: Am/Is/Are + 主语 + V-ing...
V-ing变化规则
① 一般情况下,动词后直接加-ing
work-working buy-buying
②以不发音e结尾的动词,去掉e,加-ing
take – taking have — having
③以辅音字母+元音字母+辅音字母的重读闭音节结尾的动词,如果末尾只有一个辅音字母,双写辅音字母,然后加-ing
stop-stopping shop-shopping
④特殊变化
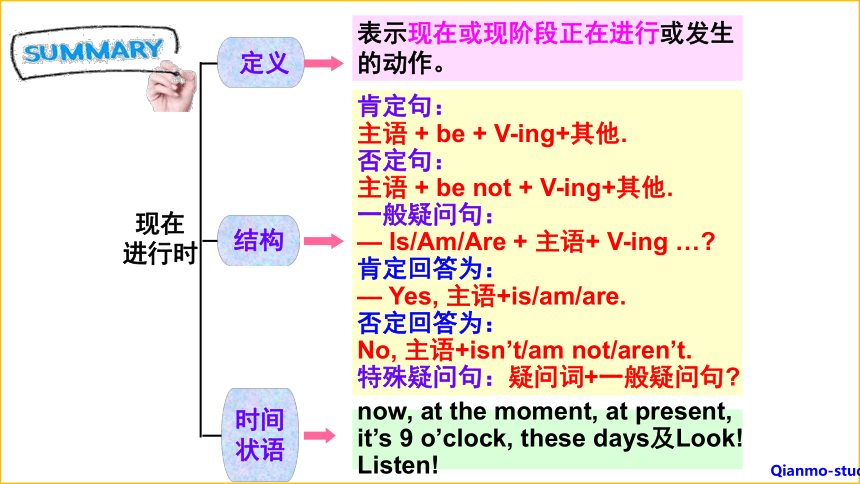
表示现在或现阶段正在进行或发生的动作。
now, at the moment, at present, it’s 9 o’clock, these days及Look! Listen!
现在
进行时
肯定句:
主语 + be + V-ing+其他.
否定句:
主语 + be not + V-ing+其他.
一般疑问句:
— Is/Am/Are + 主语+ V-ing …
肯定回答为:
— Yes, 主语+is/am/are.
否定回答为:
No, 主语+isn’t/am not/aren’t.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句
结构
定义
时间状语
1) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。
We have set up many new factories.
我们建立了许多新工厂。
2) 动作发生在过去,强调对现在的结果、 影响等。
Our city has already changed a great deal.
我们的城市已经发生了很大的变化。
(结果:现在城市面貌焕然一新)
现在完成时表示过去发生的动作与现在有关,指过去的动作对现在造成的影响、结果等。
现在完成时
3) 表示动作发生在过去,并且一直持续到现在,甚至还可能继续下去,句中使用持续性动词,且常有表示一段时间的时间状语。
① We haven't seen each other for ten years.
我们已经十年没见面了。
② I've been an English teacher for about 20 years.
我当英语老师已经20年了。
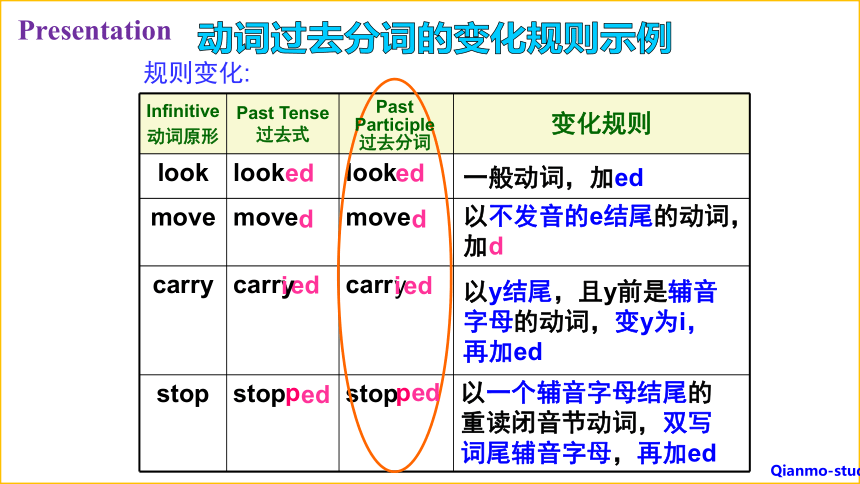
规则变化:
动词过去分词的变化规则示例
Infinitive 动词原形 Past Tense 过去式 变化规则
look look look
move move move
carry carr carr
stop stop stop
ed
ed
d
d
ed
ed
ed
ed
Past Participle
过去分词
一般动词,加ed
以不发音的e结尾的动词,加d
以y结尾,且y前是辅音字母的动词,变y为i,再加ed
以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词,双写词尾辅音字母,再加ed
y
i
y
i
p
p
Infinitive 动词原形 Past Tense 过去式 Past Participle
过去分词
cut cut cut
let let let
put put put
read read read
Infinitive 动词原形 Past Tense 过去式 Past Participle
过去分词
have had had
make made made
spend spent spent
tell told told
Infinitive 动词原形 Past Tense 过去式 Past Participle
过去分词
do did done
be was/were been
go went gone
see saw seen
不规则变化:
A-A-A型
(动词原形、过去式、过去分词都同形)
A-B-B型
(动词过去式、过去分词同形)
A-B-C型
(动词原形、过去式、过去分词都不同形)
I just my lunch.
我刚吃过午饭。(现在不饿)
一般过去时 vs 现在完成时①
I my lunch in the dining hall.
我是在餐厅吃的午饭。
一般过去时单纯描述过去发生的动作。
现在完成时表示过去发生的动作与现在有关,指过去的动作对现在造成的影响、结果等。
had
have had
Note 1
他离开上海已经3天了。
He has left Shanghai for three days.
He Shanghai for three days.
It three days since he left Shanghai.
Three days since he left Shanghai.
He Shanghai three days ago.
has been away from
is/has been
has passed
left
一般过去时 vs 现在完成时②
Note 2
短暂性动词的肯定式不能与表示一段
时间的for或since或how long等状语连用.
短暂性动词
现在完成时表示过去发生的动作与现在有关,指过去的动作对现在造成的影响、结果等。
already, yet, for+时间段, since+时间点
现在完成时
肯定句:
主语 + have/has + V-ed + 其他.
否定句:
主语 + haven't/hasn't + V-ed + 其他.
一般疑问句:
Have/Has + 主语 + V-ed + …?
肯定答语:
Yes, 主格代词 + have/has.
否定答语:
No, 主格代词 + haven't/hasn't.
特殊疑问句:
特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
结构
定义
标志词
被动语态表示主语是谓语动作的承受者,被动语态由“be + V-ed”构成。be随着主语人称和数以及时态的不同而变化。
It was made in Germany in 1681.
它于1681年在德国制造。
1. 不知道或没必要指出动作的执行者。
Chinese is spoken by more and more people in the world.
世界上越来越多的人说中文了。
2.强调动作的承受者。
被动语态
3. 动作的执行者有较长的修饰语。
The plan was supported by those who wished to have more chances to speak English.
该计划得到了那些希望有更多机会讲英语的人的支持。
4. 出于礼貌,不愿意说出动作执行者。
1) You are requested to attend the meeting.
请你参加会议。
2) I was told that you were not honest enough.
有人告诉我你不够诚实。
被动语态表示主语是谓语动作的承受者
谓语动词 be (not) + done (V-ed)
被动
语态
肯定句:
主语 + be + V-ed (+ by…).
否定句:
主语 + be + not + V-ed (+by…).
一般疑问句:
Be + 主语 + V-ed (+by…)
特殊疑问句:
疑问词 + be + 主语 + V-ed (+by…)
结构
定义
构成
时态 主动语态
一般现在时 do/does
一般过去时 did
一般将来时 will/shall/be going to + do
现在完成时 have/has done
现在进行时 am/is/are doing
过去进行时 was/were doing
被动语态
am/is/are + done
was/were + done
will/shall/be going to + be + done
have/has + been done
am/is/are + being done
was/were + being done
used to,“过去常常”,后面接动词原形,用来表示过去曾经的习惯或常有的行为而现在不再有,强调过去和现在的对比。
used to
构成
肯定句:
used to + 动词原形
否定句:
主语 + didn't use to…
一般疑问句:
Did+主语+use to do sth.
情态动词用来表示能力、应该、请求、推测等, 后接动词原形。情态动词(除have to以外)没有人称和数的变化。
情态动词
1.表示“能力”的情态动词。
1) — ________ your Australian friend eat with chopsticks
— Yes, but she can’t use them well.
A. Should B. Need C. Can D. Must
2) — Could your father play golf when he was young
— No, he ________. But he ________ play table tennis.
A. couldn’t; could B. needn’t; might
C. mustn’t; should D. shouldn’t; need
【考点点拨】
★情态动词can表示“能力”时,与be able to同义,其否定形式为can’t。can表示现在的能力,其过去式could表示过去的能力。
2.表示“应该”的情态动词。
1) — ________ we to finish our homework before noon
— Yes, you ________.
A. Need; can B. Have; do
C. Ought; ought to D. Should; must
2) You ________ study hard if you want to
be a scientist in the future.
A. may B. should
C. would D. could
【考点点拨】
★情态动词should和ought to都可表示
“应该”,但should侧重说话者主观的看法,而ought to更侧重客观情况。
★should的否定形式为shouldn’t,ought to的否定形式为oughtn’t to或ought not to。
1) — ________ I borrow your maths book
— Sure. Here you are.
A. Need B. Will
C. May D. Must
2) — Could I use your dictionary for a while
— Yes, of course you ________.
A. could B. can
C. will D. should
3.表示“请求;许可”的情态动词及其回答。
【考点点拨】
★情态动词may和can都可表示“请求;
许可”。may比can正式,could在表示“请求;许可” 时,语气更委婉。
★当“May / Can / Could I …”表示“请求;许可”时,肯定回答常用“Yes, please.” / “Certainly.”等,否定回答常用“No, you can’t / mustn’t.”等。
4. 考查表示“推测”的情态动词。
1) — I saw Lily in the supermarket this
morning.
— Oh, it ________ her. She moved to
Australia the day before yesterday.
A. can be B. must be
C. can’t be D. mustn’t be
2) After a long walk, the children ________
be very tired now.
A. will B. must
C. have to D. can
3) John ________ go with us tomorrow, but
he isn’t sure.
A. must B. can
C. need D. may
【考点点拨】
★may, can, must都可表“推测”,三者
的可能性依次递增。
★may和must表“推测”常用于肯定句中,can表“推测”常用于否定句和疑问句中。
5.考查need, must和have to的用法。
1) Jim, you ________ play with the knife.
You ________ hurt yourself.
A. won’t; can’t B. mustn’t; may
C. shouldn’t; must D. can’t; shouldn’t
2) — ________ I have to hand in my
homework now, Mr Zhang
— Yes, you do.
A. Do B. Can
C. May D. Must
3) — Must I get up before six o’clock
tomorrow morning, Dad
— No, you ________. Tomorrow is
Saturday. You may get up a little later.
A. mustn’t B. can’t
C. needn’t D. may not
4) It’s too late. We ________ go home, or
we’ll be blamed (责备).
A. can B. may
C. might D. have to
【考点点拨】
★need作情态动词,意为“需要”,后接动词原形,常用于否定句、疑问句和条件句中。
★must意为“必须”,强调主观看法。
对must引导的一般疑问句,肯定回答常用“must”,否定回答常用needn’t或don’t have to。mustn’t意为“一定不要;禁止”。
★have to意为“ 不得不;必须”,强调
客观情况下需要做某事,有人称、数和时态的变化,变否定句和疑问句时需要借助助动词完成句型的变化。
Joe:_____you ever________ (take) part in an environmental project
Ken: Yes, I have. I _______(help) with a Clean-Up Day last year. It was __________(consider) the biggest clean-up project this city_____ ever ______(have).
Joe: How many people_______(take) part
Ken: I ________(think) more than 1,000 people _______ (come) to help out.
Joe: That's fantastic! I guess everyone in this city is _______(try) to improve the environment.
Ken: Yes, we can't afford to______ (wait) any longer to take action!
4a
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs in brackets.
Have
taken
helped
considered
had
had
took
think
came
trying
wait
People ___________ think that big things ___________ be done to save the earth. Many forget that saving the earth begins with small things. For example, you _______________save electricity by turning off the lights when you leave a room. You _________________ also use reusable bags instead of plastic bags. I think it’s a great idea that you now _________ pay for plastic bags in some stores. And instead of driving to school or work, you _______________ride your bike or walk. If it’s far, you ________ take the bus. All these small things ___________ add up and become big things that _______________improve the environment. Let’s take action now!
may/might
must/have to
can/should/could
have to
can/could
would/can/could
can/should/could
can/should/could
can/could
can would could have to should must may/might
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate modal verbs from the box.(P99)
4b
Homework
Memorize the summary
Recite Grammar Focus.
Finish the exercises on the students’ book.
Preview 1a-1e on page 101.
Section A (GF-4c)
1.hear of 听说 2.cut off 割掉;砍掉
3.be harmful to对……有害 4.cut down 减少
5.at the top of 在……顶部或顶端
6.the food chain 食物链
7. so far 迄今为止 8.be good for…对……有益
9. 如果我们不做一些事情来阻止鲨鱼鳍的销售,总有一天鲨鱼会消失的。
Sharks may disappear one day if we don't do something to stop the sale of shark fins.
10. 在过去的二十到三十年里,一些种类的鲨鱼数量下降了90%。
The numbers of some kinds of sharks have fallen by over 90 percent in the last 20 to 30 years.
take part in
afford
turn off
reusable
pay for
take action
transportation
参加
v. 买的起;承担的起(后果)
关掉
adj. 可重复使用的
付费;付出代价
采取行动
n. 运输业;交通运输
Words Review
To review the use of The Present Continuous Tense,
passive voice, Present Perfect and Modal Verbs
Key words & phrases:
take part in ,afford, turn off, reusable, pay for, take action, transportation
Key sentences:
1.Have you ever taken part in an environmental project
2. We should help save the sharks.
1. We're trying to save the earth.
2. No scientific studies have shown that shark fins are good for health.
3. The air is badly polluted.
4.The river used to be so clean.
5. We should help save the sharks.
Grammar Focus
现在进行时
used to
被动语态
现在完成时
情态动词
现在进行时表示现在或现阶段正在进行或发生的动作。
Look! The two birds are flying away.
看,那两只鸟飞走了。
表示说话时正在进行的,目前正在发生的动作。
常带有表示目前时刻的时间状语, 如:now, at the (very) moment, for the time being, at present, 及Look! Listen! ...
We are not working on a farm these days.
这些天我们不在农场工作。
2)表示目前一段时间内正在进行,但说话时可能没有进行的动作。
现在进行时
① You are always changing your mind.
你总是主意不定。(太烦人了。)
② He is always helping others.
他总是帮助别人。(他真是个好人。)
He is leaving on Wednesday.
他将于周三离开。
3) 与always, constantly, forever, all the time等副词连用,表示动作反复或习惯。
此时句子常含有说话者的强烈情感在内。表达较强的“责备”或“表扬”之意。
4) 对于 come, go, leave, arrive, start 等表示位置移动的动词常可用进行时态表将来。
基本结构
① 肯定句: 主语 + am/is/are + V-ing...
② 否定句: 主语 + am/is/are + not + V-ing...
③ 疑问句: Am/Is/Are + 主语 + V-ing...
V-ing变化规则
① 一般情况下,动词后直接加-ing
work-working buy-buying
②以不发音e结尾的动词,去掉e,加-ing
take – taking have — having
③以辅音字母+元音字母+辅音字母的重读闭音节结尾的动词,如果末尾只有一个辅音字母,双写辅音字母,然后加-ing
stop-stopping shop-shopping
④特殊变化
表示现在或现阶段正在进行或发生的动作。
now, at the moment, at present, it’s 9 o’clock, these days及Look! Listen!
现在
进行时
肯定句:
主语 + be + V-ing+其他.
否定句:
主语 + be not + V-ing+其他.
一般疑问句:
— Is/Am/Are + 主语+ V-ing …
肯定回答为:
— Yes, 主语+is/am/are.
否定回答为:
No, 主语+isn’t/am not/aren’t.
特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句
结构
定义
时间状语
1) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。
We have set up many new factories.
我们建立了许多新工厂。
2) 动作发生在过去,强调对现在的结果、 影响等。
Our city has already changed a great deal.
我们的城市已经发生了很大的变化。
(结果:现在城市面貌焕然一新)
现在完成时表示过去发生的动作与现在有关,指过去的动作对现在造成的影响、结果等。
现在完成时
3) 表示动作发生在过去,并且一直持续到现在,甚至还可能继续下去,句中使用持续性动词,且常有表示一段时间的时间状语。
① We haven't seen each other for ten years.
我们已经十年没见面了。
② I've been an English teacher for about 20 years.
我当英语老师已经20年了。
规则变化:
动词过去分词的变化规则示例
Infinitive 动词原形 Past Tense 过去式 变化规则
look look look
move move move
carry carr carr
stop stop stop
ed
ed
d
d
ed
ed
ed
ed
Past Participle
过去分词
一般动词,加ed
以不发音的e结尾的动词,加d
以y结尾,且y前是辅音字母的动词,变y为i,再加ed
以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词,双写词尾辅音字母,再加ed
y
i
y
i
p
p
Infinitive 动词原形 Past Tense 过去式 Past Participle
过去分词
cut cut cut
let let let
put put put
read read read
Infinitive 动词原形 Past Tense 过去式 Past Participle
过去分词
have had had
make made made
spend spent spent
tell told told
Infinitive 动词原形 Past Tense 过去式 Past Participle
过去分词
do did done
be was/were been
go went gone
see saw seen
不规则变化:
A-A-A型
(动词原形、过去式、过去分词都同形)
A-B-B型
(动词过去式、过去分词同形)
A-B-C型
(动词原形、过去式、过去分词都不同形)
I just my lunch.
我刚吃过午饭。(现在不饿)
一般过去时 vs 现在完成时①
I my lunch in the dining hall.
我是在餐厅吃的午饭。
一般过去时单纯描述过去发生的动作。
现在完成时表示过去发生的动作与现在有关,指过去的动作对现在造成的影响、结果等。
had
have had
Note 1
他离开上海已经3天了。
He has left Shanghai for three days.
He Shanghai for three days.
It three days since he left Shanghai.
Three days since he left Shanghai.
He Shanghai three days ago.
has been away from
is/has been
has passed
left
一般过去时 vs 现在完成时②
Note 2
短暂性动词的肯定式不能与表示一段
时间的for或since或how long等状语连用.
短暂性动词
现在完成时表示过去发生的动作与现在有关,指过去的动作对现在造成的影响、结果等。
already, yet, for+时间段, since+时间点
现在完成时
肯定句:
主语 + have/has + V-ed + 其他.
否定句:
主语 + haven't/hasn't + V-ed + 其他.
一般疑问句:
Have/Has + 主语 + V-ed + …?
肯定答语:
Yes, 主格代词 + have/has.
否定答语:
No, 主格代词 + haven't/hasn't.
特殊疑问句:
特殊疑问词+一般疑问句
结构
定义
标志词
被动语态表示主语是谓语动作的承受者,被动语态由“be + V-ed”构成。be随着主语人称和数以及时态的不同而变化。
It was made in Germany in 1681.
它于1681年在德国制造。
1. 不知道或没必要指出动作的执行者。
Chinese is spoken by more and more people in the world.
世界上越来越多的人说中文了。
2.强调动作的承受者。
被动语态
3. 动作的执行者有较长的修饰语。
The plan was supported by those who wished to have more chances to speak English.
该计划得到了那些希望有更多机会讲英语的人的支持。
4. 出于礼貌,不愿意说出动作执行者。
1) You are requested to attend the meeting.
请你参加会议。
2) I was told that you were not honest enough.
有人告诉我你不够诚实。
被动语态表示主语是谓语动作的承受者
谓语动词 be (not) + done (V-ed)
被动
语态
肯定句:
主语 + be + V-ed (+ by…).
否定句:
主语 + be + not + V-ed (+by…).
一般疑问句:
Be + 主语 + V-ed (+by…)
特殊疑问句:
疑问词 + be + 主语 + V-ed (+by…)
结构
定义
构成
时态 主动语态
一般现在时 do/does
一般过去时 did
一般将来时 will/shall/be going to + do
现在完成时 have/has done
现在进行时 am/is/are doing
过去进行时 was/were doing
被动语态
am/is/are + done
was/were + done
will/shall/be going to + be + done
have/has + been done
am/is/are + being done
was/were + being done
used to,“过去常常”,后面接动词原形,用来表示过去曾经的习惯或常有的行为而现在不再有,强调过去和现在的对比。
used to
构成
肯定句:
used to + 动词原形
否定句:
主语 + didn't use to…
一般疑问句:
Did+主语+use to do sth.
情态动词用来表示能力、应该、请求、推测等, 后接动词原形。情态动词(除have to以外)没有人称和数的变化。
情态动词
1.表示“能力”的情态动词。
1) — ________ your Australian friend eat with chopsticks
— Yes, but she can’t use them well.
A. Should B. Need C. Can D. Must
2) — Could your father play golf when he was young
— No, he ________. But he ________ play table tennis.
A. couldn’t; could B. needn’t; might
C. mustn’t; should D. shouldn’t; need
【考点点拨】
★情态动词can表示“能力”时,与be able to同义,其否定形式为can’t。can表示现在的能力,其过去式could表示过去的能力。
2.表示“应该”的情态动词。
1) — ________ we to finish our homework before noon
— Yes, you ________.
A. Need; can B. Have; do
C. Ought; ought to D. Should; must
2) You ________ study hard if you want to
be a scientist in the future.
A. may B. should
C. would D. could
【考点点拨】
★情态动词should和ought to都可表示
“应该”,但should侧重说话者主观的看法,而ought to更侧重客观情况。
★should的否定形式为shouldn’t,ought to的否定形式为oughtn’t to或ought not to。
1) — ________ I borrow your maths book
— Sure. Here you are.
A. Need B. Will
C. May D. Must
2) — Could I use your dictionary for a while
— Yes, of course you ________.
A. could B. can
C. will D. should
3.表示“请求;许可”的情态动词及其回答。
【考点点拨】
★情态动词may和can都可表示“请求;
许可”。may比can正式,could在表示“请求;许可” 时,语气更委婉。
★当“May / Can / Could I …”表示“请求;许可”时,肯定回答常用“Yes, please.” / “Certainly.”等,否定回答常用“No, you can’t / mustn’t.”等。
4. 考查表示“推测”的情态动词。
1) — I saw Lily in the supermarket this
morning.
— Oh, it ________ her. She moved to
Australia the day before yesterday.
A. can be B. must be
C. can’t be D. mustn’t be
2) After a long walk, the children ________
be very tired now.
A. will B. must
C. have to D. can
3) John ________ go with us tomorrow, but
he isn’t sure.
A. must B. can
C. need D. may
【考点点拨】
★may, can, must都可表“推测”,三者
的可能性依次递增。
★may和must表“推测”常用于肯定句中,can表“推测”常用于否定句和疑问句中。
5.考查need, must和have to的用法。
1) Jim, you ________ play with the knife.
You ________ hurt yourself.
A. won’t; can’t B. mustn’t; may
C. shouldn’t; must D. can’t; shouldn’t
2) — ________ I have to hand in my
homework now, Mr Zhang
— Yes, you do.
A. Do B. Can
C. May D. Must
3) — Must I get up before six o’clock
tomorrow morning, Dad
— No, you ________. Tomorrow is
Saturday. You may get up a little later.
A. mustn’t B. can’t
C. needn’t D. may not
4) It’s too late. We ________ go home, or
we’ll be blamed (责备).
A. can B. may
C. might D. have to
【考点点拨】
★need作情态动词,意为“需要”,后接动词原形,常用于否定句、疑问句和条件句中。
★must意为“必须”,强调主观看法。
对must引导的一般疑问句,肯定回答常用“must”,否定回答常用needn’t或don’t have to。mustn’t意为“一定不要;禁止”。
★have to意为“ 不得不;必须”,强调
客观情况下需要做某事,有人称、数和时态的变化,变否定句和疑问句时需要借助助动词完成句型的变化。
Joe:_____you ever________ (take) part in an environmental project
Ken: Yes, I have. I _______(help) with a Clean-Up Day last year. It was __________(consider) the biggest clean-up project this city_____ ever ______(have).
Joe: How many people_______(take) part
Ken: I ________(think) more than 1,000 people _______ (come) to help out.
Joe: That's fantastic! I guess everyone in this city is _______(try) to improve the environment.
Ken: Yes, we can't afford to______ (wait) any longer to take action!
4a
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs in brackets.
Have
taken
helped
considered
had
had
took
think
came
trying
wait
People ___________ think that big things ___________ be done to save the earth. Many forget that saving the earth begins with small things. For example, you _______________save electricity by turning off the lights when you leave a room. You _________________ also use reusable bags instead of plastic bags. I think it’s a great idea that you now _________ pay for plastic bags in some stores. And instead of driving to school or work, you _______________ride your bike or walk. If it’s far, you ________ take the bus. All these small things ___________ add up and become big things that _______________improve the environment. Let’s take action now!
may/might
must/have to
can/should/could
have to
can/could
would/can/could
can/should/could
can/should/could
can/could
can would could have to should must may/might
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate modal verbs from the box.(P99)
4b
Homework
Memorize the summary
Recite Grammar Focus.
Finish the exercises on the students’ book.
Preview 1a-1e on page 101.
同课章节目录
- Unit 1 How can we become good learners.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 2 I think that mooncakes are delicious!
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 3 Could you please tell me where the restroom
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 4 I used to be afraid of the dark.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 5 What are the shirts made of?
- Section A
- Section B
- Review of Units 1-5
- Unit 6 When was it invented?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 7 Teenagers should be allowed to choose their
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 8 It must belong to Carla.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 9 I like music that I can dance to.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 10 You're supposed to shake hands.
- Section A
- Section B
- Review of Units 6-10
- Unit 11 Sad movies make me cry.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 12 Life is full of the unexpected
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 13 We're trying to save the earth!
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 14 I remember meeting all of you in Grade 7.
- Section A
- Section B
- Review of Units 11-14
