中考英语语法专题-代词教案(word版)
文档属性
| 名称 | 中考英语语法专题-代词教案(word版) |
|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 30.2KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-01-04 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览



文档简介
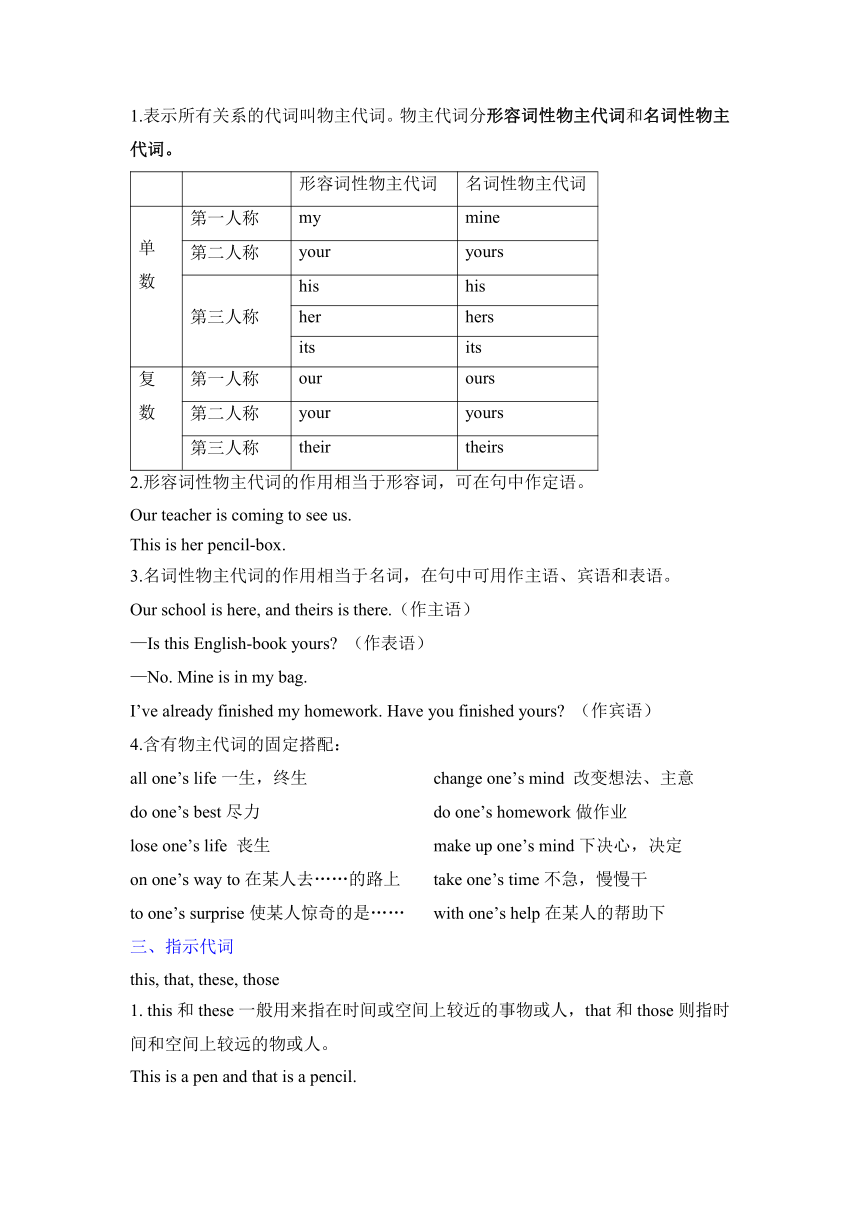
英语学科个性化教学辅导教案
学生 年级 上课地点 第 次授课
授课时间 年 月 日 星期 学科老师 班主任
教学课题 Lesson 03 代词
教学目标 人称代词,物主代词,反身代词等
教学重、难点 不定代词
教学内容
一、人称代词
1.人称代词的人称、数和格,如下表所示:
单数 复数
主格 宾格 主格 宾格
第一人称 I me we us
第二人称 you you you you
第三人称 he him
they
them
she her
it it
2.人称代词有主格和宾格之分。通常主格作主语,宾格作宾语。
I like table tennis. (作主语)
Do you know him (作宾语)
3.人称代词还可作表语,作表语时用宾格。
—Who is knocking at the door
—It’s me.
4.人称代词在than之后与其他人或事物进行比较时,用主格和宾格都可以,但是注意意思差别。
He is older than me. = He is older than I (am).
He likes me better than she / her.
5.人称代词的排列顺序。
分三种情况:
复数人称代词we – you – they顺序;
单数人称代词you – he / she – I顺序;
当说的是不好的事情,如承担责任等 I用在最前面。
二、物主代词
1.表示所有关系的代词叫物主代词。物主代词分形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。
形容词性物主代词 名词性物主代词
单 数 第一人称 my mine
第二人称 your yours
第三人称 his his
her hers
its its
复 数 第一人称 our ours
第二人称 your yours
第三人称 their theirs
2.形容词性物主代词的作用相当于形容词,可在句中作定语。
Our teacher is coming to see us.
This is her pencil-box.
3.名词性物主代词的作用相当于名词,在句中可用作主语、宾语和表语。
Our school is here, and theirs is there.(作主语)
—Is this English-book yours (作表语)
—No. Mine is in my bag.
I’ve already finished my homework. Have you finished yours (作宾语)
4.含有物主代词的固定搭配:
all one’s life一生,终生 change one’s mind 改变想法、主意
do one’s best尽力 do one’s homework做作业
lose one’s life 丧生 make up one’s mind下决心,决定
on one’s way to在某人去……的路上 take one’s time不急,慢慢干
to one’s surprise使某人惊奇的是…… with one’s help在某人的帮助下
三、指示代词
this, that, these, those
1. this和these一般用来指在时间或空间上较近的事物或人,that和those则指时间和空间上较远的物或人。
This is a pen and that is a pencil.
We are busy these days.
In those days the workers had a hard time.
2.this在电话用语中代表自己,that则代表对方。
Hello! This is Mary. Is that Jack speaking
3.指代上文提到的事物一般用that或者those,有时也用this/these,指代下文要提到的事物常用this / these。
I had a cold. That’s why I didn’t come.
What I want to say is this: pronunciation is very important in learning English.
4.有时为了避免重复提到的名词,常可用that或those代替。
Television sets made in Beijing are just as good as those made in Shanghai.
5.习惯用法
this and that这样那样,各种事情 that is to say也就是说
Is that so 真的吗? That’s enough!够了!
四、反身代词
英语中用来表示“我自己”,“你自己”,“他自己”,“我们自己”,“你们自己”等意义的代词称为反身(自身)代词,第一和第二人称的反身代词由“形容词性物主代词+ self / selves”构成,第三人称的反身代词由“代词宾格+self / selves”构成。其形式如下:
第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
单数 myself yourself himself, herself, itself
复数 ourselves yourselves themselves
反身代词可以在句中作宾语,表语,同位语。
1.作宾语,表示动作的承受者就是动作的发出者,主语和宾语指同一个人或一些人。
He called himself a writer.
Would you please express yourself in English
2.作表语。
It doesn’t matter. I’ll be myself soon.
The girl in the news is myself.
3.作主语或宾语的同位语,表示亲自或本人。
I myself washed the clothes.(=I washed the clothes myself.)(作主语同位语)
You should ask the teacher himself.(作宾语同位语)
4.含有反身代词的固定搭配
all by oneself独自地、孤独地 enjoy oneself玩得开心,过得愉快
teach oneself自学 hurt oneself 伤到自己
dress oneself自己穿衣服 help oneself to…请随便吃……
say to oneself自言自语 leave one by oneself 把某人单独留下
behave oneself表现得体有礼貌
五、不定代词
不是指明代替任何特定名词的代词叫做不定代词,在句中可作主语、表语、宾语和定语。
1. some与any
some 和any 均表示“一些”,既可修饰可数名词,也可修饰不可数名词。some 用于肯定句,any用于否定句、疑问句、条件句;若疑问句表示请求、建议,用some不用any。
Some of the milk has gone bad.
I haven’t got any money on me.
May I ask you some questions
Would you like some coffee
注意:
(1)some可放在单数名词前表达“某一”概念。
John, some student is waiting for you downstairs. 约翰,楼下有个人找你。
(2)any用于肯定句,含义为“任何” / “任何一个”。
You may choose any student to do the research.
2. few, a few, little, a little在用法上的区别
(1)用作形容词:
含义用法 表示肯定 表示否定
用于可数名词 a few虽少,但有几个 few不多,几乎没有
用于不可数名词 a little 虽少,但有一点 little不多,没有什么
I’m going to buy a few apples.
He has few friends.
There is only a little milk in the glass.
They had little money with them.
(2)a little和little也可以用作副词,a little = a bit = kind of 表示“有点,稍微”,little表示“很少”。
I’m a little hungry. (修饰形容词hungry)
Let him sleep a little. (修饰动词sleep)
Mary, go a little faster, please. (修饰副词比较级)
注意:
not a little / not a bit 的意思
I’m not a little tired. =I am very tired.
I’m not a bit tired. = I am not tired at all.
3. other, the other, another, others, the others
(1)other可以作形容词用,后面可以跟单数或复数名词,意思是“其他的、别的”, 注意和else的区别:
Where are his other books
I haven’t any other books except this one.
(2)other也可以用作代词,与冠词the连用构成“the other”, 表示两个人或物中的“另一个”。常与one搭配构成“one ..., the other ...”句型。
He has two brothers. One is 10 years old, the other is 5 years old.
She held a ruler in one hand and an exercise-book in the other.
(3)other作代词用时,可以有复数“others”,泛指“另外的人或物”。常与some搭配构成“some ...., others ...”句型。
Some went to the cinema, others went swimming.
This coat is too large. Show me some others, please.
(4)“the others”表示特指某范围内的“其他的人或物”。
We got home by 4 o’clock, but the others didn’t get back until 8 o’clock.
In our class only Tom is English, the others are Chinese.
(5)another作代词用,表示“另一个”;another也可以作形容词用,修饰后面的单数名词,意为“另一个”,还可以跟代词one。
I’m still hungry after I’ve had this cake. Please give me another.
You can see another ship in the sea, can’t you
Mary doesn’t want to buy this skirt. Would you please show her another one
4. every与each
(1)each 强调个体,every 强调全部,相当于all; every 可以和almost, nearly连用,而each 不能。
Almost every student in our class passed the English test yesterday.
(2)each指两个或两个以上中的每个,every指三个或者三个以上中的每个。
There are lots of trees on each side of the road.
(3)every可以用来表示“每隔”,each不行,经常用一下结构:
every +基数词+复数名词; every +序数词+单数名词
every other +单数名词,每隔; every few +复数名词,每隔几
He visited his uncle every few days.
Please write on every other line.请隔行写。
every other day每隔一天= every 2 days每2天
every second day每隔2天= every three days每3天
every third day每隔3天= every 4 days每四天
(4)every可以和not连用构成部分否定,而each无此用法。
(5)each可以直接做主语,可以和of 连用,也可以做同位语,every不行。
5. either, both, neither, all, none, any
either肯定含义,一般指二选一,做主语时谓语常用单数;
both肯定含义,二者都,做主语时用复数;
neither否定含义,做主语时谓语用单数;
all肯定含义,做主语时谓语单复数,要和all前面所指代的人或者物保持一致。
none,否定含义,做主语时,谓语动词用单复数均可,常与of 连用。
any,肯定含义,做主语时, 单复数均可,常与of 连用。
Neither answer is correct.
Neither of the two cars is mine.
None of the money is mine.
The headmaster refused to accept any of the three suggestions.
6. none, nobody / no one , nothing
(1)none既可指人也可以指物,常回答how many,how much引导的疑问句;no one / nobody 只能指人常回答who 引导的疑问句;nothing只能指物,常回答what引导的疑问句。
How much money do you have None.
What are you doing now Nothing.
Who is in the room No one. / Nobody.
(2)none后可以跟of 短语。
None of them knew about the plan.
7.any / every
(1)“any +名词”表示(三者或三者以上中的)任何一个;“every +名词”表示(三者或者三者以上中的每一个)。
I have many books, you can take any one.
Every student has to take the examination.
(2)“not +any”表示全部否定;“not +every”部分否定。
Not every child wants to be a film star.
8.复合不定代词
every, no, some, any + body / thing 构成。
(1)everything意为“每件事,一切事”可用于肯定句,否定句中。not everything(表示部分否定),并非每件东西。
I hope everything goes well.
(2)something意为“某事;某物”,常用语肯定句中,也可以用于征求对方意见的疑问句中。
Do you want anything to eat
(3)anything意为“任何事,任何东西”,一般用于疑问句或否定句中。not anything= nothing
Can you hear me anything
(4)nothing意为“没有什么;没有一件东西”
Tom saw nothing.
9.it, the one, one, that 辨析
one替代上文中出现的“同类”事物,但不是“同一”事物,所替代的名词必须是可数名词,泛指同类事物中的一个。
He bought many books and lent one to me.
the one替代前面的单数名词,表示特指。有时可以用that 代替(尤其在有后置定语的情况下)
The book on the desk is better than the one under the desk.
that替代上文出现的“同类”事物,所替代的名词可以是可数名词也可也是不可数名词,其后常跟介词短语作后置定语。
The weather here is better than that of Beijing.
it替代上文出现的“同一”事物,被替代的名词可以是可数也可以是不可数。
The weather here is cold and I don’t like it.
六、相互代词
表示相互关系的代词叫做相互代词。相互代词有each other 和one another两种形式。
相互代词可在句中作宾语,定语。作定语用时,相互代词用所有格形式。
We should learn from each other / one another. (作宾语)
Do you often write to each other / one another (作宾语)
We often borrow each other’s / one another’s books. (作定语)
The students corrected each other’s / one another’s mistakes in their homework. (作定语)
学生 年级 上课地点 第 次授课
授课时间 年 月 日 星期 学科老师 班主任
教学课题 Lesson 03 代词
教学目标 人称代词,物主代词,反身代词等
教学重、难点 不定代词
教学内容
一、人称代词
1.人称代词的人称、数和格,如下表所示:
单数 复数
主格 宾格 主格 宾格
第一人称 I me we us
第二人称 you you you you
第三人称 he him
they
them
she her
it it
2.人称代词有主格和宾格之分。通常主格作主语,宾格作宾语。
I like table tennis. (作主语)
Do you know him (作宾语)
3.人称代词还可作表语,作表语时用宾格。
—Who is knocking at the door
—It’s me.
4.人称代词在than之后与其他人或事物进行比较时,用主格和宾格都可以,但是注意意思差别。
He is older than me. = He is older than I (am).
He likes me better than she / her.
5.人称代词的排列顺序。
分三种情况:
复数人称代词we – you – they顺序;
单数人称代词you – he / she – I顺序;
当说的是不好的事情,如承担责任等 I用在最前面。
二、物主代词
1.表示所有关系的代词叫物主代词。物主代词分形容词性物主代词和名词性物主代词。
形容词性物主代词 名词性物主代词
单 数 第一人称 my mine
第二人称 your yours
第三人称 his his
her hers
its its
复 数 第一人称 our ours
第二人称 your yours
第三人称 their theirs
2.形容词性物主代词的作用相当于形容词,可在句中作定语。
Our teacher is coming to see us.
This is her pencil-box.
3.名词性物主代词的作用相当于名词,在句中可用作主语、宾语和表语。
Our school is here, and theirs is there.(作主语)
—Is this English-book yours (作表语)
—No. Mine is in my bag.
I’ve already finished my homework. Have you finished yours (作宾语)
4.含有物主代词的固定搭配:
all one’s life一生,终生 change one’s mind 改变想法、主意
do one’s best尽力 do one’s homework做作业
lose one’s life 丧生 make up one’s mind下决心,决定
on one’s way to在某人去……的路上 take one’s time不急,慢慢干
to one’s surprise使某人惊奇的是…… with one’s help在某人的帮助下
三、指示代词
this, that, these, those
1. this和these一般用来指在时间或空间上较近的事物或人,that和those则指时间和空间上较远的物或人。
This is a pen and that is a pencil.
We are busy these days.
In those days the workers had a hard time.
2.this在电话用语中代表自己,that则代表对方。
Hello! This is Mary. Is that Jack speaking
3.指代上文提到的事物一般用that或者those,有时也用this/these,指代下文要提到的事物常用this / these。
I had a cold. That’s why I didn’t come.
What I want to say is this: pronunciation is very important in learning English.
4.有时为了避免重复提到的名词,常可用that或those代替。
Television sets made in Beijing are just as good as those made in Shanghai.
5.习惯用法
this and that这样那样,各种事情 that is to say也就是说
Is that so 真的吗? That’s enough!够了!
四、反身代词
英语中用来表示“我自己”,“你自己”,“他自己”,“我们自己”,“你们自己”等意义的代词称为反身(自身)代词,第一和第二人称的反身代词由“形容词性物主代词+ self / selves”构成,第三人称的反身代词由“代词宾格+self / selves”构成。其形式如下:
第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
单数 myself yourself himself, herself, itself
复数 ourselves yourselves themselves
反身代词可以在句中作宾语,表语,同位语。
1.作宾语,表示动作的承受者就是动作的发出者,主语和宾语指同一个人或一些人。
He called himself a writer.
Would you please express yourself in English
2.作表语。
It doesn’t matter. I’ll be myself soon.
The girl in the news is myself.
3.作主语或宾语的同位语,表示亲自或本人。
I myself washed the clothes.(=I washed the clothes myself.)(作主语同位语)
You should ask the teacher himself.(作宾语同位语)
4.含有反身代词的固定搭配
all by oneself独自地、孤独地 enjoy oneself玩得开心,过得愉快
teach oneself自学 hurt oneself 伤到自己
dress oneself自己穿衣服 help oneself to…请随便吃……
say to oneself自言自语 leave one by oneself 把某人单独留下
behave oneself表现得体有礼貌
五、不定代词
不是指明代替任何特定名词的代词叫做不定代词,在句中可作主语、表语、宾语和定语。
1. some与any
some 和any 均表示“一些”,既可修饰可数名词,也可修饰不可数名词。some 用于肯定句,any用于否定句、疑问句、条件句;若疑问句表示请求、建议,用some不用any。
Some of the milk has gone bad.
I haven’t got any money on me.
May I ask you some questions
Would you like some coffee
注意:
(1)some可放在单数名词前表达“某一”概念。
John, some student is waiting for you downstairs. 约翰,楼下有个人找你。
(2)any用于肯定句,含义为“任何” / “任何一个”。
You may choose any student to do the research.
2. few, a few, little, a little在用法上的区别
(1)用作形容词:
含义用法 表示肯定 表示否定
用于可数名词 a few虽少,但有几个 few不多,几乎没有
用于不可数名词 a little 虽少,但有一点 little不多,没有什么
I’m going to buy a few apples.
He has few friends.
There is only a little milk in the glass.
They had little money with them.
(2)a little和little也可以用作副词,a little = a bit = kind of 表示“有点,稍微”,little表示“很少”。
I’m a little hungry. (修饰形容词hungry)
Let him sleep a little. (修饰动词sleep)
Mary, go a little faster, please. (修饰副词比较级)
注意:
not a little / not a bit 的意思
I’m not a little tired. =I am very tired.
I’m not a bit tired. = I am not tired at all.
3. other, the other, another, others, the others
(1)other可以作形容词用,后面可以跟单数或复数名词,意思是“其他的、别的”, 注意和else的区别:
Where are his other books
I haven’t any other books except this one.
(2)other也可以用作代词,与冠词the连用构成“the other”, 表示两个人或物中的“另一个”。常与one搭配构成“one ..., the other ...”句型。
He has two brothers. One is 10 years old, the other is 5 years old.
She held a ruler in one hand and an exercise-book in the other.
(3)other作代词用时,可以有复数“others”,泛指“另外的人或物”。常与some搭配构成“some ...., others ...”句型。
Some went to the cinema, others went swimming.
This coat is too large. Show me some others, please.
(4)“the others”表示特指某范围内的“其他的人或物”。
We got home by 4 o’clock, but the others didn’t get back until 8 o’clock.
In our class only Tom is English, the others are Chinese.
(5)another作代词用,表示“另一个”;another也可以作形容词用,修饰后面的单数名词,意为“另一个”,还可以跟代词one。
I’m still hungry after I’ve had this cake. Please give me another.
You can see another ship in the sea, can’t you
Mary doesn’t want to buy this skirt. Would you please show her another one
4. every与each
(1)each 强调个体,every 强调全部,相当于all; every 可以和almost, nearly连用,而each 不能。
Almost every student in our class passed the English test yesterday.
(2)each指两个或两个以上中的每个,every指三个或者三个以上中的每个。
There are lots of trees on each side of the road.
(3)every可以用来表示“每隔”,each不行,经常用一下结构:
every +基数词+复数名词; every +序数词+单数名词
every other +单数名词,每隔; every few +复数名词,每隔几
He visited his uncle every few days.
Please write on every other line.请隔行写。
every other day每隔一天= every 2 days每2天
every second day每隔2天= every three days每3天
every third day每隔3天= every 4 days每四天
(4)every可以和not连用构成部分否定,而each无此用法。
(5)each可以直接做主语,可以和of 连用,也可以做同位语,every不行。
5. either, both, neither, all, none, any
either肯定含义,一般指二选一,做主语时谓语常用单数;
both肯定含义,二者都,做主语时用复数;
neither否定含义,做主语时谓语用单数;
all肯定含义,做主语时谓语单复数,要和all前面所指代的人或者物保持一致。
none,否定含义,做主语时,谓语动词用单复数均可,常与of 连用。
any,肯定含义,做主语时, 单复数均可,常与of 连用。
Neither answer is correct.
Neither of the two cars is mine.
None of the money is mine.
The headmaster refused to accept any of the three suggestions.
6. none, nobody / no one , nothing
(1)none既可指人也可以指物,常回答how many,how much引导的疑问句;no one / nobody 只能指人常回答who 引导的疑问句;nothing只能指物,常回答what引导的疑问句。
How much money do you have None.
What are you doing now Nothing.
Who is in the room No one. / Nobody.
(2)none后可以跟of 短语。
None of them knew about the plan.
7.any / every
(1)“any +名词”表示(三者或三者以上中的)任何一个;“every +名词”表示(三者或者三者以上中的每一个)。
I have many books, you can take any one.
Every student has to take the examination.
(2)“not +any”表示全部否定;“not +every”部分否定。
Not every child wants to be a film star.
8.复合不定代词
every, no, some, any + body / thing 构成。
(1)everything意为“每件事,一切事”可用于肯定句,否定句中。not everything(表示部分否定),并非每件东西。
I hope everything goes well.
(2)something意为“某事;某物”,常用语肯定句中,也可以用于征求对方意见的疑问句中。
Do you want anything to eat
(3)anything意为“任何事,任何东西”,一般用于疑问句或否定句中。not anything= nothing
Can you hear me anything
(4)nothing意为“没有什么;没有一件东西”
Tom saw nothing.
9.it, the one, one, that 辨析
one替代上文中出现的“同类”事物,但不是“同一”事物,所替代的名词必须是可数名词,泛指同类事物中的一个。
He bought many books and lent one to me.
the one替代前面的单数名词,表示特指。有时可以用that 代替(尤其在有后置定语的情况下)
The book on the desk is better than the one under the desk.
that替代上文出现的“同类”事物,所替代的名词可以是可数名词也可也是不可数名词,其后常跟介词短语作后置定语。
The weather here is better than that of Beijing.
it替代上文出现的“同一”事物,被替代的名词可以是可数也可以是不可数。
The weather here is cold and I don’t like it.
六、相互代词
表示相互关系的代词叫做相互代词。相互代词有each other 和one another两种形式。
相互代词可在句中作宾语,定语。作定语用时,相互代词用所有格形式。
We should learn from each other / one another. (作宾语)
Do you often write to each other / one another (作宾语)
We often borrow each other’s / one another’s books. (作定语)
The students corrected each other’s / one another’s mistakes in their homework. (作定语)
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
