2022年中考语法复习四被动语态的运用,特殊疑问句综合,反义疑问句,祈使句,并与从句,主谓一致
文档属性
| 名称 | 2022年中考语法复习四被动语态的运用,特殊疑问句综合,反义疑问句,祈使句,并与从句,主谓一致 |  | |
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 200.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-01-21 19:46:03 | ||
图片预览



文档简介
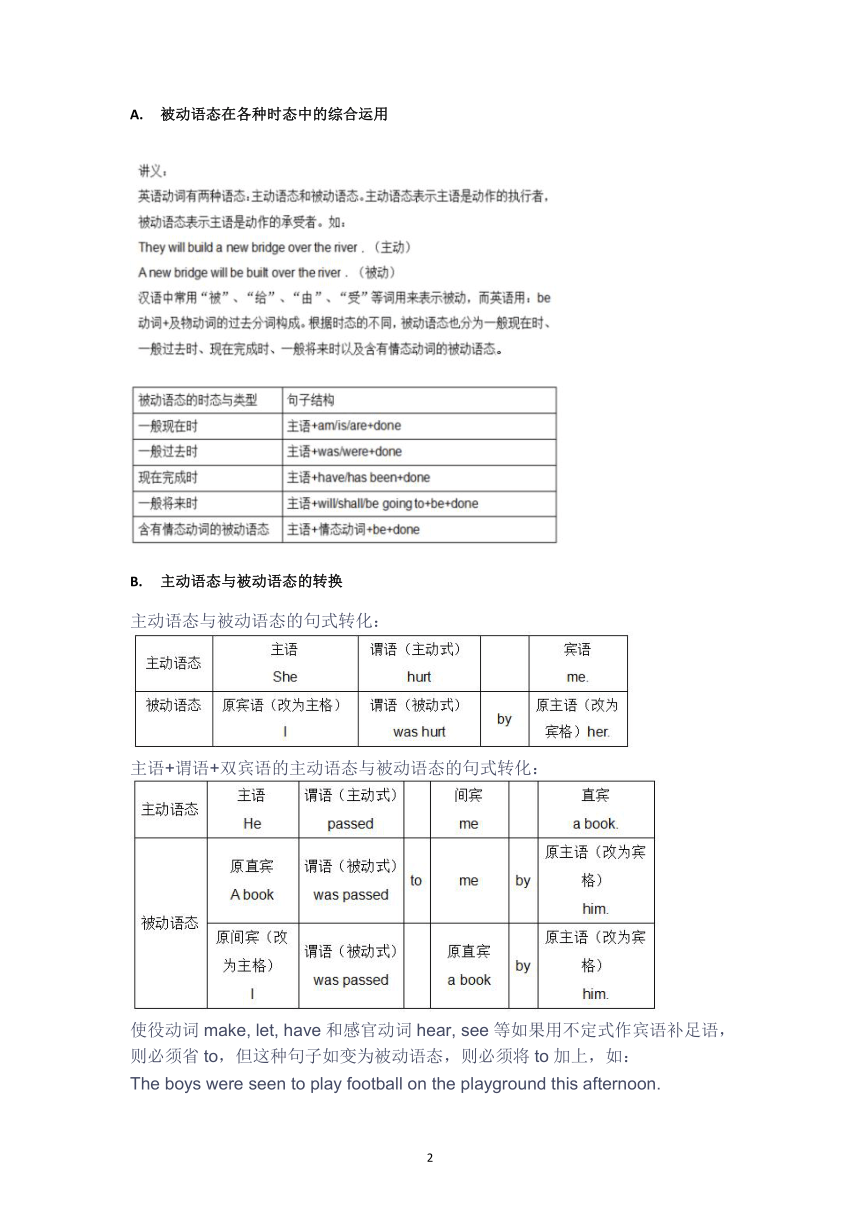
被动语态在各种时态中的综合运用
主动语态与被动语态的转换
时态和语态的综合运用
特殊疑问句用法:综合
反义疑问句:问句和答句
祈使句的综合用法
宾语从句的综合运用考查
主谓一致的常考点综合
被动语态在各种时态中的综合运用
主动语态与被动语态的转换
主动语态与被动语态的句式转化:
主语+谓语+双宾语的主动语态与被动语态的句式转化:
使役动词make, let, have和感官动词hear, see等如果用不定式作宾语补足语,则必须省to,但这种句子如变为被动语态,则必须将to加上,如:
The boys were seen to play football on the playground this afternoon.
The children were watched to sing that morning.
时态和语态的综合运用
时态和语态的综合运用
时态:
初中英语时态中常用的有8 种,它们是:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、现在完成时、过去进行时、过去完成时和过去将来时。
例如:Mr. Green has two children. (一般现在时)
Where did you go just now (一般过去时)
I'm going to do my homework this evening. (一般将来时)
Mr. Green is writing another novel.(现在进行时)
He has been in the League for three years. (现在完成时)
At this moment yesterday, I was packing for camping.(过去进行时)
I had been at the bus stop for 20 minutes when a bus finally came.(过去完成时)
She told me that she would go on a trip to Europe the next day.(过去将来时)
语态:
语态也是动词的一种形式,表示主语与谓语之间的关系。英语有两种语态:主动语态(active voice)和被动语态(passive voice)。主动语态表示主语是谓语动作的执行者,而被动语态则表示主语是谓语动作的承受者。被动语态是由“助动词be 加及物动词的过去分词”构成,如果有必要强调动作的执行者,动作执行者可以由“介词by”引出的短语表示。助动词be 随主语的人称、数、时态和语气的不同而变化。
例如:The classroom is cleaned by us every day.
The classroom was cleaned yesterday.
The classroom will be cleaned soon.
We told him that the classroom would be cleaned soon.
The classroom is being cleaned now.
The classroom looks tidy. It has been cleaned.
特殊疑问句用法:综合
特殊疑问句是指对不知道的事物或人作出提问,要求对方给出具体回答的疑问句。其句首要用疑问代词或疑问副词。回答时要根据具体情况作出回答,不用yes或no。句末多用降调。
特殊疑问句的结构为:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句?例如:
What is he doing over there
When do you go to school
Where is your school
How many pencils do you have
Who is he
注意:当特殊疑问词在句中作主语或作定语修饰主语时,句子用陈述句语序。例如:
Who is there
What is on the desk
Whose hat is lost
1. 由疑问词what构成的疑问句
What does your father do (询问职业)
What's the date today (询问日期)
What's three plus four (询问数量)
What colour is your new sweater (询问颜色)
What does your father look like (询问外貌)
2. 由疑问词how构成的疑问句
How do you feel (询问感受)
How do you go to school (询问方式)
How is the weather (询问天气)
How old is he (询问年龄)
How many books do you have (询问数量)
How much is the dress (询问价钱)
How about you (询问情况)
How far is it from here (询问距离)
3. 由疑问词when构成的疑问句
When is your birthday (询问日期)
4. 由疑问词where 构成的疑问句
Where are you going (询问去向)
Where is your teacher (询问地点)
5. 由疑问词why构成的疑问句
Why do you go to the grocery store (询问原因)
6. 由疑问词whose构成的疑问句
Whose coat is this (询问物主)
7. 由疑问词which构成的疑问句
Which way is south (询问方位)
Which is the first month of the year (询问月份)
反义疑问句:问句和答句
let’s 用shall,let sb,用will
注意:
1. 如果陈述句中出现never, seldom, hardly, scarcely, rarely, few, little, nobody, no one, nothing等含有否定意义的词时,反义疑问句用肯定式。
She seldom goes to the concert, does she 她很少去听音乐会,是吗?
2. 当陈述部分为there be句型时,反义疑问句用be (not) +there结构。
There is a book under the bed, isn't there 床下有一本书,不是吗?
3. 祈使句的反义疑问句通常都用will you;由Let's引导的祈使句,其反义疑问句部分用shall we 由Let us引导的祈使句,其反义疑问句部分用 will you
Let's play football, shall we 我们一起去踢足球吧,好吗?
Let us have a look at your book, will you 让我们看一眼你的书吧,好吗?
4. 肯定祈使句的反义疑问句用will you或won't you都行;否定的祈使句的反义疑问用will you。
Go to bed early, will/won't you 早点睡觉,好吗?
5. 对 I think/believe...+ 宾语从句的反义疑问时,是对宾语从句部分进行反问,故问句中助动词和主语与宾语从句保持一致。
I think he is right, isn't he 我认为他是对的,不是吗?
祈使句的综合用法
祈使句
一、祈使句的基本含义。
祈使句是指表示命令、请求、建议或劝告的句子。其主语you常省略,谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号或句号,读降调。
二、祈使句的结构。
1. 肯定的祈使句结构
(1) be+形容词/名词
Be a good boy.
Be patient.
(2) 动词原形+其他
Stand up, please.=Please stand up.
(3) let+宾语+动词原形+其他
Let me help you.
2. 否定的祈使句结构
(1) Don't+动词原形
Don't stand up.
(2) let引起的祈使句的否定形式有两种:
let开头的祈使句,如果后面跟第一、第三人称名词或代词的宾格,可在let前加Don't,也可在let后的宾语后面加not;如果以Let's开头的祈使句,必须在Let's后加not。
例:Don't let me go with her tomorrow. = Let me not go with her tomorrow.
不要让我明天跟她一起去。
Let's not tell her the true story.
我们别把真相告诉她。
(3) 用否定副词never构成,以加强否定含义
Never judge a person by looks.
(4) No+动词ing/名词,表示禁止
No parking here!
No photos!
注意:祈使句之后可用反义疑问句,多用will you,表示一种客气的语气。
Don't do that again, will you
在肯定的祈使句之后的反义疑问句既可以用will you, 也可以用won't you,表示提醒对方注意。
Tell me the truth, will/won't you
以Let's开头的祈使句,其反义疑问部分用shall we。
Let's try harder, shall we
以Let us开头的祈使句,其反义疑问部分用will you。
Let us go now, will you
三、祈使句的几种常见用法。
1. “祈使句+and/or+陈述句(一般将来时)”这一句型(祈使句表示条件),相当于if引导的条件句,整个句子可以改为if引导的条件状语从句。
(1)“祈使句+and+简单句”,and后简单句表示好的结果。
Hurry up, and you will catch the bus.
= If you hurry, you will catch the bus.
快点,你会赶上车。
(2)“祈使句+or+简单句”,or后简单句表示不理想的结果。
Study hard, or you will fail to pass the exam.
= If you don't study hard, you will fail to pass the exam.
努力学习,不然会考试不及格的。
2. 在含有if 引导的条件状语从句的主从复合句中,主句是祈使句,条件状语从句通常用一般现在时,即遵循“主祈从现”的原则。
If you are not strong enough, please don't take part in such an activity.
如果你不是很健壮,请不要参加这种活动。
宾语从句的综合运用考查
宾语从句是指一个句子放在动词、介词、形容词后面充当宾语的从句,其语序应用陈述语序。
在从句中,that只是一个引导词,没有意义,通常可以省略。whether/if, when, where, how, why等引导词的选择是由句子的意义决定的。如:
I'm glad (that) you are here with me.
He didn't tell me when we would start.
No one knows how he can get out of the trouble.
whether/if的意思均是“是否”,它们所引导的宾语从句,实际上是由一般疑问句演变而来的,从句要用陈述句语序。一般来说,在宾语从句中whether与if可以互换使用。但从句中有or not时只能与whether直接连用。如:
I wonder whether/if they will come to our party.
They ask me whether or not I have time to attend the party.
宾语从句的时态
1. 当主句是一般现在时,其宾语从句的时态可以是任何适当的时态。所以,宾语从句的时态应根据实际情况而定。如:
She says (that) she works from Monday to Friday.
She says (that) she will leave a message on his desk.
2. 当主句的时态是一般过去时,其宾语从句的时态一般要用适当的过去时态。如:
He said (that) there were no classes yesterday afternoon.
He said (that) he was going to take care of the baby.
3. 当宾语从句表达客观真理和规律时,无论主句是何种时态,从句用一般现在时。如:
The teacher told us (that) nothing is difficult if we put our hearts into it.
He said (that) light travels much faster than sound.
主谓一致的常考点综合
主谓一致的重要考点
1. 在“not only+名词、代词等+ but (also)+名词、代词等”结构中,谓语动词的单、复数遵循“就近原则”,即和but (also)后的内容的数保持一致。
2. there be句型中be动词的单复数形式由后面挨近be动词的一项的单复数决定。
3. neither...nor/either...or用来连接两个主语时,谓语动词的单、复数遵循“就近原则”,即和nor/or后的内容的数保持一致。
4. as well as/along with/with/together with/like/besides/but连接两个名词作主语时,符合主谓一致的“就远原则”,谓语动词的数和前面的主语保持一致。
5. 表示路程、重量、数字、长度等的复数名词或短语作为一个整体作主语时,谓语动词通常用单数。
6. 分数/百分数+of+名词”结构作主语时,谓语动词的数与其中的名词的数保持一致。
7. all和both作主语时,谓语动词要用复数形式;neither作主语时,谓语动词用单数或者复数形式皆可;none作主语时,指代可数名词复数,谓语动词用单数或者复数形式皆可,指代不可数名词时,谓语动词用单数形式。
8. “the+形容词或由分词演变而来的形容词”表示“一类人”,其作主语时,谓语动词用复数形式。the +姓氏的复数,表示“某某一家人,夫妇”,谓语动词用复数形式。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
时态和语态的综合运用
特殊疑问句用法:综合
反义疑问句:问句和答句
祈使句的综合用法
宾语从句的综合运用考查
主谓一致的常考点综合
被动语态在各种时态中的综合运用
主动语态与被动语态的转换
主动语态与被动语态的句式转化:
主语+谓语+双宾语的主动语态与被动语态的句式转化:
使役动词make, let, have和感官动词hear, see等如果用不定式作宾语补足语,则必须省to,但这种句子如变为被动语态,则必须将to加上,如:
The boys were seen to play football on the playground this afternoon.
The children were watched to sing that morning.
时态和语态的综合运用
时态和语态的综合运用
时态:
初中英语时态中常用的有8 种,它们是:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、现在完成时、过去进行时、过去完成时和过去将来时。
例如:Mr. Green has two children. (一般现在时)
Where did you go just now (一般过去时)
I'm going to do my homework this evening. (一般将来时)
Mr. Green is writing another novel.(现在进行时)
He has been in the League for three years. (现在完成时)
At this moment yesterday, I was packing for camping.(过去进行时)
I had been at the bus stop for 20 minutes when a bus finally came.(过去完成时)
She told me that she would go on a trip to Europe the next day.(过去将来时)
语态:
语态也是动词的一种形式,表示主语与谓语之间的关系。英语有两种语态:主动语态(active voice)和被动语态(passive voice)。主动语态表示主语是谓语动作的执行者,而被动语态则表示主语是谓语动作的承受者。被动语态是由“助动词be 加及物动词的过去分词”构成,如果有必要强调动作的执行者,动作执行者可以由“介词by”引出的短语表示。助动词be 随主语的人称、数、时态和语气的不同而变化。
例如:The classroom is cleaned by us every day.
The classroom was cleaned yesterday.
The classroom will be cleaned soon.
We told him that the classroom would be cleaned soon.
The classroom is being cleaned now.
The classroom looks tidy. It has been cleaned.
特殊疑问句用法:综合
特殊疑问句是指对不知道的事物或人作出提问,要求对方给出具体回答的疑问句。其句首要用疑问代词或疑问副词。回答时要根据具体情况作出回答,不用yes或no。句末多用降调。
特殊疑问句的结构为:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句?例如:
What is he doing over there
When do you go to school
Where is your school
How many pencils do you have
Who is he
注意:当特殊疑问词在句中作主语或作定语修饰主语时,句子用陈述句语序。例如:
Who is there
What is on the desk
Whose hat is lost
1. 由疑问词what构成的疑问句
What does your father do (询问职业)
What's the date today (询问日期)
What's three plus four (询问数量)
What colour is your new sweater (询问颜色)
What does your father look like (询问外貌)
2. 由疑问词how构成的疑问句
How do you feel (询问感受)
How do you go to school (询问方式)
How is the weather (询问天气)
How old is he (询问年龄)
How many books do you have (询问数量)
How much is the dress (询问价钱)
How about you (询问情况)
How far is it from here (询问距离)
3. 由疑问词when构成的疑问句
When is your birthday (询问日期)
4. 由疑问词where 构成的疑问句
Where are you going (询问去向)
Where is your teacher (询问地点)
5. 由疑问词why构成的疑问句
Why do you go to the grocery store (询问原因)
6. 由疑问词whose构成的疑问句
Whose coat is this (询问物主)
7. 由疑问词which构成的疑问句
Which way is south (询问方位)
Which is the first month of the year (询问月份)
反义疑问句:问句和答句
let’s 用shall,let sb,用will
注意:
1. 如果陈述句中出现never, seldom, hardly, scarcely, rarely, few, little, nobody, no one, nothing等含有否定意义的词时,反义疑问句用肯定式。
She seldom goes to the concert, does she 她很少去听音乐会,是吗?
2. 当陈述部分为there be句型时,反义疑问句用be (not) +there结构。
There is a book under the bed, isn't there 床下有一本书,不是吗?
3. 祈使句的反义疑问句通常都用will you;由Let's引导的祈使句,其反义疑问句部分用shall we 由Let us引导的祈使句,其反义疑问句部分用 will you
Let's play football, shall we 我们一起去踢足球吧,好吗?
Let us have a look at your book, will you 让我们看一眼你的书吧,好吗?
4. 肯定祈使句的反义疑问句用will you或won't you都行;否定的祈使句的反义疑问用will you。
Go to bed early, will/won't you 早点睡觉,好吗?
5. 对 I think/believe...+ 宾语从句的反义疑问时,是对宾语从句部分进行反问,故问句中助动词和主语与宾语从句保持一致。
I think he is right, isn't he 我认为他是对的,不是吗?
祈使句的综合用法
祈使句
一、祈使句的基本含义。
祈使句是指表示命令、请求、建议或劝告的句子。其主语you常省略,谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号或句号,读降调。
二、祈使句的结构。
1. 肯定的祈使句结构
(1) be+形容词/名词
Be a good boy.
Be patient.
(2) 动词原形+其他
Stand up, please.=Please stand up.
(3) let+宾语+动词原形+其他
Let me help you.
2. 否定的祈使句结构
(1) Don't+动词原形
Don't stand up.
(2) let引起的祈使句的否定形式有两种:
let开头的祈使句,如果后面跟第一、第三人称名词或代词的宾格,可在let前加Don't,也可在let后的宾语后面加not;如果以Let's开头的祈使句,必须在Let's后加not。
例:Don't let me go with her tomorrow. = Let me not go with her tomorrow.
不要让我明天跟她一起去。
Let's not tell her the true story.
我们别把真相告诉她。
(3) 用否定副词never构成,以加强否定含义
Never judge a person by looks.
(4) No+动词ing/名词,表示禁止
No parking here!
No photos!
注意:祈使句之后可用反义疑问句,多用will you,表示一种客气的语气。
Don't do that again, will you
在肯定的祈使句之后的反义疑问句既可以用will you, 也可以用won't you,表示提醒对方注意。
Tell me the truth, will/won't you
以Let's开头的祈使句,其反义疑问部分用shall we。
Let's try harder, shall we
以Let us开头的祈使句,其反义疑问部分用will you。
Let us go now, will you
三、祈使句的几种常见用法。
1. “祈使句+and/or+陈述句(一般将来时)”这一句型(祈使句表示条件),相当于if引导的条件句,整个句子可以改为if引导的条件状语从句。
(1)“祈使句+and+简单句”,and后简单句表示好的结果。
Hurry up, and you will catch the bus.
= If you hurry, you will catch the bus.
快点,你会赶上车。
(2)“祈使句+or+简单句”,or后简单句表示不理想的结果。
Study hard, or you will fail to pass the exam.
= If you don't study hard, you will fail to pass the exam.
努力学习,不然会考试不及格的。
2. 在含有if 引导的条件状语从句的主从复合句中,主句是祈使句,条件状语从句通常用一般现在时,即遵循“主祈从现”的原则。
If you are not strong enough, please don't take part in such an activity.
如果你不是很健壮,请不要参加这种活动。
宾语从句的综合运用考查
宾语从句是指一个句子放在动词、介词、形容词后面充当宾语的从句,其语序应用陈述语序。
在从句中,that只是一个引导词,没有意义,通常可以省略。whether/if, when, where, how, why等引导词的选择是由句子的意义决定的。如:
I'm glad (that) you are here with me.
He didn't tell me when we would start.
No one knows how he can get out of the trouble.
whether/if的意思均是“是否”,它们所引导的宾语从句,实际上是由一般疑问句演变而来的,从句要用陈述句语序。一般来说,在宾语从句中whether与if可以互换使用。但从句中有or not时只能与whether直接连用。如:
I wonder whether/if they will come to our party.
They ask me whether or not I have time to attend the party.
宾语从句的时态
1. 当主句是一般现在时,其宾语从句的时态可以是任何适当的时态。所以,宾语从句的时态应根据实际情况而定。如:
She says (that) she works from Monday to Friday.
She says (that) she will leave a message on his desk.
2. 当主句的时态是一般过去时,其宾语从句的时态一般要用适当的过去时态。如:
He said (that) there were no classes yesterday afternoon.
He said (that) he was going to take care of the baby.
3. 当宾语从句表达客观真理和规律时,无论主句是何种时态,从句用一般现在时。如:
The teacher told us (that) nothing is difficult if we put our hearts into it.
He said (that) light travels much faster than sound.
主谓一致的常考点综合
主谓一致的重要考点
1. 在“not only+名词、代词等+ but (also)+名词、代词等”结构中,谓语动词的单、复数遵循“就近原则”,即和but (also)后的内容的数保持一致。
2. there be句型中be动词的单复数形式由后面挨近be动词的一项的单复数决定。
3. neither...nor/either...or用来连接两个主语时,谓语动词的单、复数遵循“就近原则”,即和nor/or后的内容的数保持一致。
4. as well as/along with/with/together with/like/besides/but连接两个名词作主语时,符合主谓一致的“就远原则”,谓语动词的数和前面的主语保持一致。
5. 表示路程、重量、数字、长度等的复数名词或短语作为一个整体作主语时,谓语动词通常用单数。
6. 分数/百分数+of+名词”结构作主语时,谓语动词的数与其中的名词的数保持一致。
7. all和both作主语时,谓语动词要用复数形式;neither作主语时,谓语动词用单数或者复数形式皆可;none作主语时,指代可数名词复数,谓语动词用单数或者复数形式皆可,指代不可数名词时,谓语动词用单数形式。
8. “the+形容词或由分词演变而来的形容词”表示“一类人”,其作主语时,谓语动词用复数形式。the +姓氏的复数,表示“某某一家人,夫妇”,谓语动词用复数形式。
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
