外研版必修2 Module 5 Newspapers and Magazines Grammar课件(45张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版必修2 Module 5 Newspapers and Magazines Grammar课件(45张ppt) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.7MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-01-28 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共45张PPT)
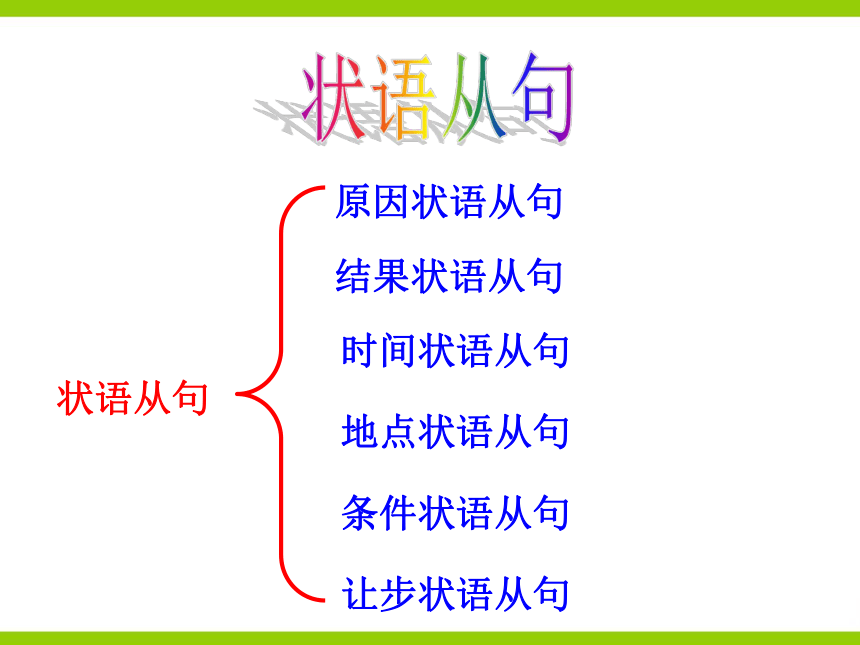
状语从句
原因状语从句
结果状语从句
时间状语从句
地点状语从句
条件状语从句
让步状语从句
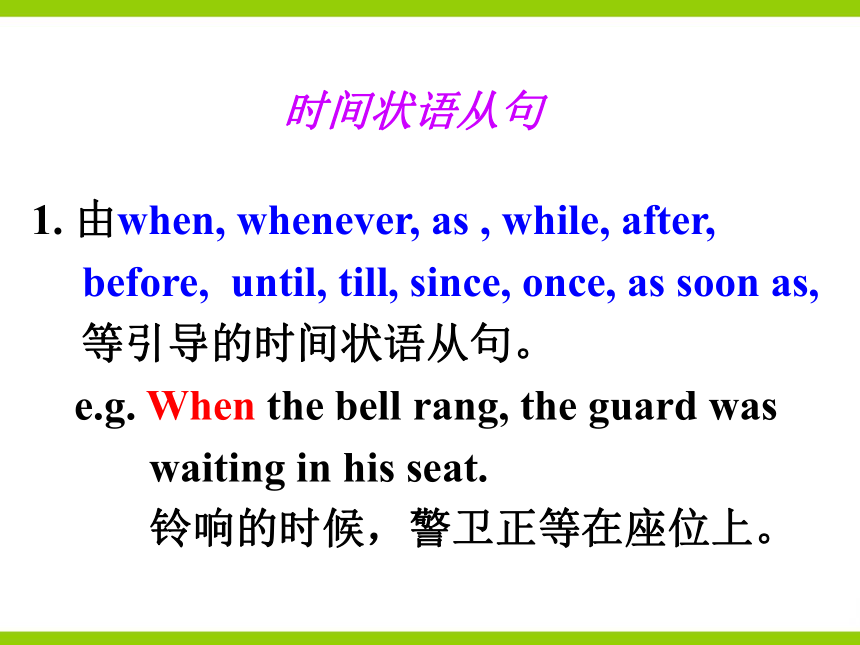
1. 由when, whenever, as , while, after, before, until, till, since, once, as soon as, 等引导的时间状语从句。
e.g. When the bell rang, the guard was
waiting in his seat.
铃响的时候,警卫正等在座位上。
时间状语从句
Three months went by before Jack realized it.
杰克意识到的时候三个月已经过去了。
I waited till he had finished his task.
我一直等到他完成了他的任务。
2. 由the minute, the moment, the instant, the day, the week, the year, the first time, any time, every time, each time, the last time, all the time, from the time, by the time, immediately, instantly, directly 等引导的时间状语从句。
e.g. I recognized you the minute I saw you.
我一见到你就认出了你。
He called on me the day he arrived.
他来的那一天就访问了我。
We were there the week it snowed so
heavily.
雪下得很大的那一周我们在那里。
3. 其中the minute, the moment, the instant, the second, 以及immediately, instantly, directly 表达的意思一样, 都是 “一……就……” 可替换。
e.g. You must show the gentleman in
immediately he comes.
You must show the gentleman in the minute /the moment/instantly he comes.
Translate the following sentences.
你一按按钮,灯就会亮。
他一出现,便一片沉寂。
The lamp will light instantly you press the button.
Directly he appeared there was dead silence.
4. 另外还要注意 hardly … when …,
scarcely … when …, no sooner …
than …的意义和用法。
“一……就……”。 通常hardly, scarcely, no sooner 位于句首, 后主句用had done,且倒装。而when, than 后面的从句用一般过去时。
e.g. Hardly/scarcely had I got home when
it started to rain.
我刚到家,就开始下雨了。
Hardly/Scarcely had I arrived when
he called me.
我刚到他就给我打电话了。
No sooner had I reached the station than the train left.
我们刚到火车站火车就走了。
5. when, while, as 引导的时间状语从句的
区别。
1) “当…...时”讲, when可以和延续性动词连用, 也可以和短暂性动词连用, 而while 和as只能和延续性动词连用。
e.g. Why do you want a new job when
you’ve got such a good one
Sorry, I was out when you called me.
Strike while the iron is hot.
The students took notes as they
listened.
get 为短暂性动词
call为短暂性动词
is为延续性动词
listen 为延续性动词
2) when 从句的谓语动词可以在主句动词之前或之后发生或同时发生。而while 和as 从句的动词必须是和主句的动词同时发生。
e.g. When he had finished his homework,
he took a rest.
When I got to the airport, the guests
had left.
had finished 先发生
got to 后发生
即当主从句动作同时发生, 且从句动作为延续性动词时, 三者可互换。
e.g. When/While/As she was making a phone call, I was writing a letter.
当她在打电话的时候,我在写信。
3) when 可以表示 “在那时”。
be about to do … when …
had done … when …
be doing … when …
e.g. I was about to go out when the phone rang.
我正打算出去这时电话响了。
I was on the point of reading books when someone knocked at the door.
我正在读书这时有人敲门。
4) as 可以表示 “因为” “作为” “随着”
“一边 …... 一边 ......”
e.g. As the time went on, the weather got worse.
随着时间的流失, 天气越来越糟了。
The little girl sang as she went.
小女孩边走边唱。
5) 在将来时的从句中常用when, 且从句必须用一般现在时。
e.g. You shall borrow the book when I
have finished reading it.
在我读完这本书后,你可以借阅。
6) when还用在表示 “一……就……”的句
型中。
e.g. Hardly/Scarcely had I entered my
room when the telephone rang.
我刚一走进房门,电话铃就响了。
7) while 还做并列连词 “然而” 表对比。和从属连词 “尽管” 的意思, 相当于though/ although。
e.g. While he is a little boy, he knows a
lot.
尽管他是一个小男孩,但懂得很多。
I’m working while my wife is
watching TV.
我正在工作而我妻子正在看电视。
–Was his father strict with him when
he was at school
– Yes. He had never praised him_____
he became one of top students in his
grade.
A. after B. unless C. until D. when
2. ____ you told me, I had no idea of it.
A. Until B. When C. While D. As
3. It was foolish of you to take a taxi____
you could easily walk there in 5
minutes.
A. before B. till C. so that D. when.
Underline the correct form of the verb.
1. When the astronauts returned/were
returning to Earth, they gave/were
giving a press conference.
2. While the fans waited/ were waiting in
the front of the hotel, the film star
arrived/was arriving at the back.
3. While I walked/was walking to school,
I met/was meeting an alien in the
street.
原因状语从句
1. 由because, as, since, now that 引导的原
因状语从句。
e.g. As the tree was a very small one, it
doesn’t take long to chop it down.
因为这是一棵很小的树,不需要很
长的时间就把它砍下来。
Since a lot of people make mistakes in
life, Mr. Smith wanted to give John a
chance.
既然许多人一生中都会犯错误,史密斯先生要给约翰一次改过的机会。
Now that all the guests have arrived,
let’s have dinner.
既然所有的客人都来了,我们吃饭吧。
2. 形容词glad, sorry, afraid, pleased , satisfied, proud delighted, 可接一个that引导的原因状语从句, 且that可省略。
e.g. I’m glad (that) you told me about it.
我很高兴你把这件事告诉了我。
I’m sorry (that) I haven’t done so
much as I should.
对不起,我没有做我该做的那么多。
I’m afraid (that) he hasn’t passed the exam.
恐怕他考试不及格了。
We feel proud (that) our country is getting stronger.
我们很自豪我们的国家越来越壮大。
原因状语从句中应注意的问题
as, because, for, since 的区别
1) as作为从属连词引导原因状语从句时,语气不如because 强烈。从句常放在句首, 说明原因, 主句则说明结果。
2) because 引导从句时, 语气最强, 直接回答why的问句。引导的句子是语意中心所在, 一般在句后。
3) for作为并列连词,多用于书面语中,表示原因, 语气最弱, 往往含对所作论述提供情况或补充说明之意。它引导的句子一般在主句之后。
4) since表示原因是双方已知道的。
Complete the sentences using the
correct punctuation.
the story is in the newspaper/everyone
believes it is true (since)
Since the story is in the newspaper,
everyone believes it is true.
2. he was the first Chinese person to
travel in space/he is a national
hero (as)
As he was the first Chinese person
to travel in space, he is a national
hero.
3. I have a telescope/I can look at the stars (now that)
Now that I have a telescope, I can look at the stars.
4. Wu’s parents were born in China/he
was able to speak to Yang in Chinese
(as)
As Wu’s parents were born in China,
he was able to speak to Yang in
Chinese.
1. He found it increasingly difficult to read, _____ his eyesight was beginning to fail.
A. though B. for
C. but D. so
2. – Did you return Fred’s call
– I didn’t need to _____ I’ll see him tomorrow.
A. though B. unless C. when D. because
3. Jenny was very sad over the loss of the photos she had shot at Canada, _____ this was a memory she especially treasured.
A. as B. if
C. when D. where
4. Animals suffered at the hands of Man _____ they were destroyed by people to make way for agricultural land to provide food for more people.
A. in which B. for which
C. so that D. in that
5. I hope you’ve got your own car, _____ if you haven’t we may have to hire one.
A. because B. so that
C. ever since D. when
6. _____ you’ve got a chance, you might as well make full use of it.
A. Now that
B. After
C. Although
D. As soon as
Revise what we learned in this class and finish exercises 1- 4 on page 91.
状语从句
原因状语从句
结果状语从句
时间状语从句
地点状语从句
条件状语从句
让步状语从句
1. 由when, whenever, as , while, after, before, until, till, since, once, as soon as, 等引导的时间状语从句。
e.g. When the bell rang, the guard was
waiting in his seat.
铃响的时候,警卫正等在座位上。
时间状语从句
Three months went by before Jack realized it.
杰克意识到的时候三个月已经过去了。
I waited till he had finished his task.
我一直等到他完成了他的任务。
2. 由the minute, the moment, the instant, the day, the week, the year, the first time, any time, every time, each time, the last time, all the time, from the time, by the time, immediately, instantly, directly 等引导的时间状语从句。
e.g. I recognized you the minute I saw you.
我一见到你就认出了你。
He called on me the day he arrived.
他来的那一天就访问了我。
We were there the week it snowed so
heavily.
雪下得很大的那一周我们在那里。
3. 其中the minute, the moment, the instant, the second, 以及immediately, instantly, directly 表达的意思一样, 都是 “一……就……” 可替换。
e.g. You must show the gentleman in
immediately he comes.
You must show the gentleman in the minute /the moment/instantly he comes.
Translate the following sentences.
你一按按钮,灯就会亮。
他一出现,便一片沉寂。
The lamp will light instantly you press the button.
Directly he appeared there was dead silence.
4. 另外还要注意 hardly … when …,
scarcely … when …, no sooner …
than …的意义和用法。
“一……就……”。 通常hardly, scarcely, no sooner 位于句首, 后主句用had done,且倒装。而when, than 后面的从句用一般过去时。
e.g. Hardly/scarcely had I got home when
it started to rain.
我刚到家,就开始下雨了。
Hardly/Scarcely had I arrived when
he called me.
我刚到他就给我打电话了。
No sooner had I reached the station than the train left.
我们刚到火车站火车就走了。
5. when, while, as 引导的时间状语从句的
区别。
1) “当…...时”讲, when可以和延续性动词连用, 也可以和短暂性动词连用, 而while 和as只能和延续性动词连用。
e.g. Why do you want a new job when
you’ve got such a good one
Sorry, I was out when you called me.
Strike while the iron is hot.
The students took notes as they
listened.
get 为短暂性动词
call为短暂性动词
is为延续性动词
listen 为延续性动词
2) when 从句的谓语动词可以在主句动词之前或之后发生或同时发生。而while 和as 从句的动词必须是和主句的动词同时发生。
e.g. When he had finished his homework,
he took a rest.
When I got to the airport, the guests
had left.
had finished 先发生
got to 后发生
即当主从句动作同时发生, 且从句动作为延续性动词时, 三者可互换。
e.g. When/While/As she was making a phone call, I was writing a letter.
当她在打电话的时候,我在写信。
3) when 可以表示 “在那时”。
be about to do … when …
had done … when …
be doing … when …
e.g. I was about to go out when the phone rang.
我正打算出去这时电话响了。
I was on the point of reading books when someone knocked at the door.
我正在读书这时有人敲门。
4) as 可以表示 “因为” “作为” “随着”
“一边 …... 一边 ......”
e.g. As the time went on, the weather got worse.
随着时间的流失, 天气越来越糟了。
The little girl sang as she went.
小女孩边走边唱。
5) 在将来时的从句中常用when, 且从句必须用一般现在时。
e.g. You shall borrow the book when I
have finished reading it.
在我读完这本书后,你可以借阅。
6) when还用在表示 “一……就……”的句
型中。
e.g. Hardly/Scarcely had I entered my
room when the telephone rang.
我刚一走进房门,电话铃就响了。
7) while 还做并列连词 “然而” 表对比。和从属连词 “尽管” 的意思, 相当于though/ although。
e.g. While he is a little boy, he knows a
lot.
尽管他是一个小男孩,但懂得很多。
I’m working while my wife is
watching TV.
我正在工作而我妻子正在看电视。
–Was his father strict with him when
he was at school
– Yes. He had never praised him_____
he became one of top students in his
grade.
A. after B. unless C. until D. when
2. ____ you told me, I had no idea of it.
A. Until B. When C. While D. As
3. It was foolish of you to take a taxi____
you could easily walk there in 5
minutes.
A. before B. till C. so that D. when.
Underline the correct form of the verb.
1. When the astronauts returned/were
returning to Earth, they gave/were
giving a press conference.
2. While the fans waited/ were waiting in
the front of the hotel, the film star
arrived/was arriving at the back.
3. While I walked/was walking to school,
I met/was meeting an alien in the
street.
原因状语从句
1. 由because, as, since, now that 引导的原
因状语从句。
e.g. As the tree was a very small one, it
doesn’t take long to chop it down.
因为这是一棵很小的树,不需要很
长的时间就把它砍下来。
Since a lot of people make mistakes in
life, Mr. Smith wanted to give John a
chance.
既然许多人一生中都会犯错误,史密斯先生要给约翰一次改过的机会。
Now that all the guests have arrived,
let’s have dinner.
既然所有的客人都来了,我们吃饭吧。
2. 形容词glad, sorry, afraid, pleased , satisfied, proud delighted, 可接一个that引导的原因状语从句, 且that可省略。
e.g. I’m glad (that) you told me about it.
我很高兴你把这件事告诉了我。
I’m sorry (that) I haven’t done so
much as I should.
对不起,我没有做我该做的那么多。
I’m afraid (that) he hasn’t passed the exam.
恐怕他考试不及格了。
We feel proud (that) our country is getting stronger.
我们很自豪我们的国家越来越壮大。
原因状语从句中应注意的问题
as, because, for, since 的区别
1) as作为从属连词引导原因状语从句时,语气不如because 强烈。从句常放在句首, 说明原因, 主句则说明结果。
2) because 引导从句时, 语气最强, 直接回答why的问句。引导的句子是语意中心所在, 一般在句后。
3) for作为并列连词,多用于书面语中,表示原因, 语气最弱, 往往含对所作论述提供情况或补充说明之意。它引导的句子一般在主句之后。
4) since表示原因是双方已知道的。
Complete the sentences using the
correct punctuation.
the story is in the newspaper/everyone
believes it is true (since)
Since the story is in the newspaper,
everyone believes it is true.
2. he was the first Chinese person to
travel in space/he is a national
hero (as)
As he was the first Chinese person
to travel in space, he is a national
hero.
3. I have a telescope/I can look at the stars (now that)
Now that I have a telescope, I can look at the stars.
4. Wu’s parents were born in China/he
was able to speak to Yang in Chinese
(as)
As Wu’s parents were born in China,
he was able to speak to Yang in
Chinese.
1. He found it increasingly difficult to read, _____ his eyesight was beginning to fail.
A. though B. for
C. but D. so
2. – Did you return Fred’s call
– I didn’t need to _____ I’ll see him tomorrow.
A. though B. unless C. when D. because
3. Jenny was very sad over the loss of the photos she had shot at Canada, _____ this was a memory she especially treasured.
A. as B. if
C. when D. where
4. Animals suffered at the hands of Man _____ they were destroyed by people to make way for agricultural land to provide food for more people.
A. in which B. for which
C. so that D. in that
5. I hope you’ve got your own car, _____ if you haven’t we may have to hire one.
A. because B. so that
C. ever since D. when
6. _____ you’ve got a chance, you might as well make full use of it.
A. Now that
B. After
C. Although
D. As soon as
Revise what we learned in this class and finish exercises 1- 4 on page 91.
