人教新目标中考英语复习-- 连词和复合句(共有PPT111张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教新目标中考英语复习-- 连词和复合句(共有PPT111张) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 3.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-02-12 16:00:51 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共111张PPT)
第一编 语法专项突破
第十三讲 连词和复合句
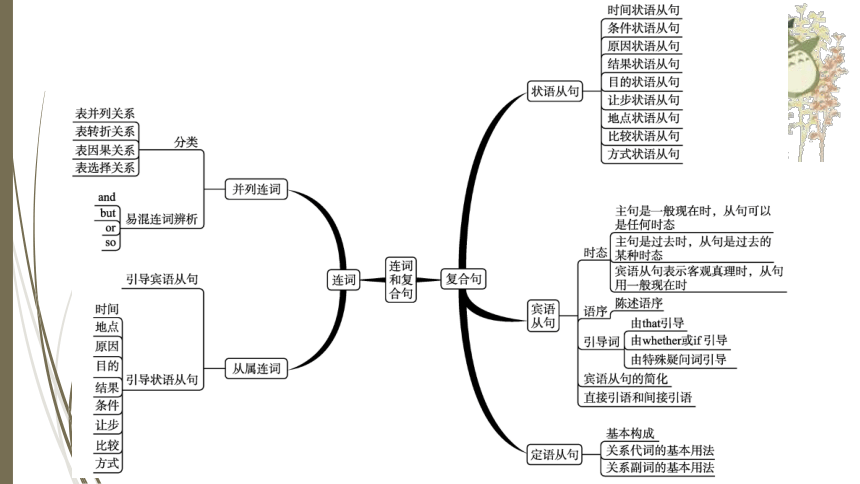
知识网络建构
考点探究突破
知识网络建构
考点一
考点二
考点探究突破
考点一
连词
连词是用于连接名词、短语或句子的虚词, 不单独做句子成分, 可分为并列连词和从属连词两类。
(一)并列连词
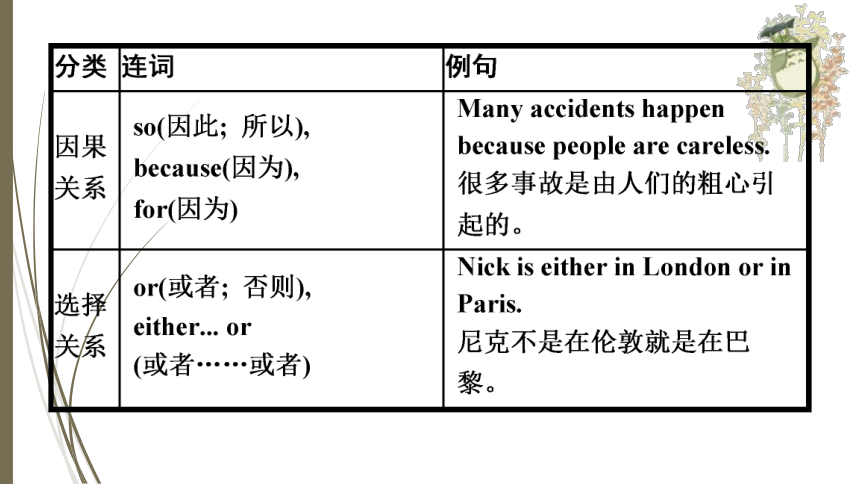
并列连词是指用来连接语法地位相同的单词、短语以及句子的连词。并列连词主要分为表示并列关系、转折关系、因果关系及选择关系的并列连词。
规律总结(1)and, but, or和so的区别
(2)否定句中两部分都有否定词时用and连接。如:
Bill has no brothers and no sisters.
=Bill has no brothers or sisters.
比尔没有兄弟姐妹。
(3)句中含有without时, 肯定句中用or, 否定句中用and。如:
We’ll die without air or water.
没有空气和水, 我们就会死亡。
We can’t live without air and water.
没有空气和水, 我们无法生存。
(4)and与or都可以与if引导的条件状语从句转换。如:
Get up quickly, or you’ll be late for school.
=If you don’t get up quickly, you’ll be late for school.
快点起床, 否则你上学会迟到。
Work hard, and you’ll get good grades.
=If you work hard, you’ll get good grades.
努力学习, 你会取得好成绩。
典例1Jenifer wants to go to that party very much all her best friends will go.
A.because B.so
C.unless D.while
解析:句意: 詹妮弗非常想去参加聚会, 因为她所有的好朋友都去。because“因为”, 故选A项。
答案:A
活学活用
(二)从属连词
1.引导宾语从句的从属连词that, if/whether
I know that the puppy is very clever.
我知道那条小狗很聪明。
We don’t know if/whether it will rain tomorrow.
我们不知道明天是否下雨。
2.引导状语从句的从属连词
典例2My family always go somewhere interesting the holiday begins.
A.as soon as B.so
C.so that D.even though
解析:句意: 我的家庭总是在假期一开始就去有趣的地方。as soon as“一……就……”。故选A项。
答案:A
活学活用
6.I enjoy fresh air so I always sleep with the window open
it is really cold.
A.unless B.when
C.if D.since
答案:A
解析:unless“如果不……”; when“当……时候”; if“如果”; since “自从……以来”。句意: 我喜欢新鲜空气, 因此如果不是很冷, 我总是开着窗户睡觉。故选A项。
7.—This dress is last year’s style.
—I think it still looks perfect it has gone out this year.
A.so that B.as if
C.even though D.ever since
答案:C
解析:句意: ——这件连衣裙是去年的样式。——我认为它仍然看起来很完美, 即使它今年过时了。so that“以至于”; as if “似乎, 好像”; even though“即使”; ever since“自从”。故选C项。
8.—Will you please give the dictionary to Jane
—Sure, I’ll give it to her she arrives here.
A.before B.until
C.because D.as soon as
答案:D
解析:句意: ——你可以把这本字典给简吗 ——可以。她一到这儿我就把它给她。before“在……之前”; until“直到……为止”; because“因为”; as soon as“一……就……”。故选D项。
考点二
复合句
英语句子按照结构分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
简单句是只有一套主谓结构的句子。并列句是由并列连词把两个或两个以上的简单句连接起来的句子。复合句是由一个主句和一个或者一个以上的从句构成的句子, 从句是主句的一个句子成分, 从属于主句。
初中英语教材中涉及的复合句主要有状语从句、宾语从句和定语从句。
(一)状语从句
状语从句在复合句中做状语, 修饰动词、形容词或副词, 可用来表示时间、条件、原因、结果、目的、让步、地点、比较、方式等含义。
1.时间状语从句
时间状语从句通常由when, while, as, before, after, since, as soon as, till/until等词引导。含有时间状语从句的复合句, 如果主句用一般将来时, 从句用一般现在时表示将来。
(1)when引导的从句表示主从句的动作同时发生或从句的动作发生在主句之后。如:
When he came back, his mother was reading a newspaper. 当他回来的时候, 他妈妈正在读报纸。
(2)while引导的从句表示“在……过程中”, 主从句的谓语动词所表示的动作同时发生。如:
My father was reading a newspaper while my mother was watching TV.
我爸爸在读报纸, 我妈妈在看电视。
(3)as表示“当……时候”, 往往可以和when互换。as还表示“一边……一边……”。如:
As we walked, we talked happily.
我们一边走一边高兴地交谈。
(4)before, after通常用来表示动作一前一后发生。如:
After he locked the door, he left.
他锁上门后就离开了。
He had finished his homework before his parents came back.
在父母回来前, 他就完成家庭作业了。
(5)由since引导的从句, 表示“自从……以来”, 从句常用一般过去时, 主句常用现在完成时。如:
He has made many friends since he came to China.
自从来到中国他已结交了许多朋友。
(6)as soon as引导的从句表示“一……就……”。till/until 引导的从句表示“直到”, 若主句中的谓语动词是非延续性的, 要用“not... until”。如:
I will write to you as soon as I get there.
我一到那儿就给你写信。
I waited until he came back. 我一直等到他回来。
I didn’t leave until he came back. 直到他回来我才离开。
2.条件状语从句
(1)条件状语从句常由if “如果, 假如”, unless“如果不, 除非”来引导, 如果表示将来, 从句要用一般现在时表示将来。如:
If it rains tomorrow, we’ll stay at home.
如果明天下雨, 我们将待在家里。
We won’t go to the party unless we are free.
除非我们有空, 否则我们将不去参加聚会。
(2)if还可以引导虚拟条件句, 表示与事实相反或不符。初中阶段常考与现在事实相反的情况。主句谓语动词用would+动词原形, 从句用一般过去时, be动词只用一种形式were。如:
If I were you, I wouldn’t do it like that.
如果我是你, 我就不会那样做。(我不可能是你)
If I had one million dollars, I would build a new school.
如果我有一百万美元, 我会建一所新学校。(我现在没有一百万美元)
3.原因状语从句
原因状语从句由because, since, as等引导。because 语气最强, 用来说明人所不知道的原因, 回答why提出的问题。当原因是显而易见的或已为人知的, 就用as或since。例如:
He didn’t catch the early bus because he got up late.
他没赶上早班公共汽车是因为他起晚了。
Since you know the answer, please tell me.
既然你知道答案, 请告诉我。
As you object, I’ll change the plan.
由于你反对, 我将改变计划。
4.结果状语从句
结果状语从句由so ... that或 such ... that引导。such修饰名词或名词词组; so修饰形容词或副词。常有以下几种句型:
(1)so+adj./adv.+that从句
It’s so cold that no one can play outside.
天太冷了, 没有人会在外面玩。
The problem is so hard that we can’t work it out.
这道题很难, 我们解答不出来。
(2)so+adj.+a/an+可数名词单数+that从句
It’s so heavy a box that I can’t carry it.
这个箱子太重了以至于我搬不动它。
(3)so+many/few/much/little+可数名词复数/不可数名词+that从句
There are so many books that we can’t choose which one to buy.
有如此多的书, 我们不知道要选哪一本了。
There is so little food that we must go out and buy some.
食物如此的少, 我们必须出去买点。
(4)such+a/an+adj.+可数名词单数+that从句
Mr. Green is such a good teacher that we all like him.
格林老师是位非常好的老师, 我们都喜欢他。
(5)such+adj.+可数名词复数/不可数名词+that从句
It is such nice weather that we’d better go out.
天气如此好, 我们最好出去走走。
5.目的状语从句
(1)目的状语从句由that, so that, in order that, so等引导, 谓语中常含有may/might/can/could/will/would等情态动词。如:
He studies hard in order that/so that he can catch up with their classmates.
他努力学习以便能赶上班里的其他同学。
Betty got up early so that she might catch the train.
贝蒂起得早, 以便能赶上火车。
(2)当从句与主句主语一致时, 常用so as to, in order to替换so that, in order that。如:
He ran fast so that he might arrive there on time.
=He ran fast so as to arrive there on time.
他快跑以便准时到达那里。
6.让步状语从句
让步状语从句表示某种对主句不利的条件或情况, 但从句所表示的这些不利因素并不能阻止主句动作的发生, 在这种条件下, 主句的情况依然存在。引导让步状语从句的连词有though/although“虽然”, even though“尽管”, whatever/no matter what“无论什么”, however/no matter how“无论怎样”, whoever/no matter who“无论谁”等, 但主句中不能再用but。如:
He didn’t turn on the lights, though it was dark inside.
虽然屋里很暗, 但他没开灯。
7.地点状语从句
引导地点状语从句的引导词有where, wherever, anywhere, everywhere, somewhere等。如:
Wherever you go, I will be with you.
无论你去哪儿, 我都和你在一起。
8.比较状语从句
常用的引导词有as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较)等。如:
Lucy is taller than me. 露西比我高。
9.方式状语从句
引导方式状语的常用引导词有as, as if等。如:
When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
入乡随俗。
典例3I looked through my test paper again and again
I wouldn’t make any mistakes.
A.so B.because
C.so that D.that
解析:句意: 我反复仔细浏览了我的试卷, 为了确保我不犯错误。so that引导目的状语从句。故选C项。
答案:C
活学活用
(二)宾语从句
宾语从句在复合句中充当宾语, 可以做谓语动词的宾语, 也可以做介词的宾语。
I don’t know where she has gone.
我不知道她去哪儿了。
This reminded me of what he had once promised me.
这使我想起他曾对我的承诺。
宾语从句的三要素是时态、语序和引导词。
1.宾语从句的时态
典例4I wonder next week. Please call me when they return.
A.when they will come back
B.when will they come back
C.when they come back
D.how will they come back
解析:宾语从句要用陈述语序, 再由宾语从句的时间状语是next week可知从句时态用一般将来时。故选A项。
答案:A
活学活用
15.—I wonder at 8: 00 last night.
—I was watching TV.
A.what were you doing
B.what did you do
C.what you were doing
D.what are you doing
答案:C
解析:宾语从句需用陈述语序, 由last night可知, 本句为一般过去时。故选C项。
16.Linda said that the train , so she couldn’t come.
A.left B.had left
C.leaving D.have left
答案:B
解析:当宾语从句的主句是过去时, 从句应用相应的过去时态。琳达说她不能来可知火车已经开走了, 故从句应用过去完成时。故选B项。
2.宾语从句的语序
宾语从句一律用陈述语序, 即主语在前, 谓语动词在后。如:
I don’t know whether he can pass the exam or not.
我不知道他是否能通过考试。
Could you tell me when Tom will come back
你能告诉我汤姆什么时候回来吗
典例5—Excuse me, but could you please tell me
—Sure.
A.where is the restroom
B.when the store opens
C.what time does it begin
D.how can I get to the library
解析:句意: ——打扰了, 你能告诉我商店什么时候开门吗 ——可以。宾语从句用陈述语序, 只有B项是陈述语序, 故选B项。
答案:B
活学活用
19.—Could you tell me for the meeting yesterday
—Because I got up late.
A.why did you late B.why you came late
C.why do you late D.why you come late
答案:B
解析:疑问句做宾语从句, 语序应用陈述语序, 且根据yesterday可确定时态为一般过去时, 故选B项。
20.I don’t know the charity show tomorrow. Can you tell me
A.when we start B.when did we start
C.when we will start D.when will we start
答案:C
解析:疑问句做宾语从句, 语序应用陈述语序; 主句时态为一般现在时, 从句的时态应根据具体的时间状语确定, 由tomorrow可判断时态应为一般将来时, 故选C项。
3.宾语从句的引导词
注意只能用whether不能用if的情况
典例6—Could you please tell me , Sonia
—It’s on the first Tuesday of May. We hold special parties and give teachers thank-you notes that day.
A.if you have Teachers’ Day in America
B.when Teachers’ Day is in America
C.what you do on Teachers’ Day
D.how do you show your thanks to your teachers
解析:在宾语从句中, 应该使用陈述语序, 故排除D项。根据答语“在五月的第一个星期二。我们在那天举行特殊的聚会并且给老师感谢信。”可知问句应该是询问时间, 故选B项。
答案:B
活学活用
4.宾语从句的简化
(1)当宾语从句的主语和主句的主语相同, 且主句的谓语动词是hope, wish, decide, agree, choose等时, 从句可简化为不定式结构。如:
I hope that I can receive your e-mail. =I hope to receive your e-mail. 我希望能收到你的电子邮件。
(2)当宾语从句的主语和主句的主语相同, 且主句的谓语动词是know, remember, forget, learn等时, 从句可简化为“疑问词+不定式”结构。如:
She doesn’t know what she should do next. =She doesn’t know what to do next.
她不知道下一步该做什么。
(3)动词seem后的宾语从句可用不定式(短语)来简化, 但句型要有适当的变化。通常将宾语从句的主语作为简化的句子的主语, seem(适当时态形式)做谓语。
It seems that football is very interesting.
=Football seems to be very interesting.
足球似乎非常有趣。
(4)宾语从句可以简化为名词或名词短语。
I don’t believe what Tom said. =I don’t believe Tom’s words.
我不相信汤姆所说的话。
典例7—Excuse me. Could you tell me get to the nearest post office
—Sorry, I am new here.
A.how can I B.how I could
C.how to D.what I can
解析:句意: ——打扰了, 你能告诉我如何到达最近的邮局吗 ——对不起, 我是新来的。当主句的主语和从句的主语一致时, 宾语从句可以用“疑问词+不定式”结构。故选C项。
答案:C
活学活用
28.It seems that he studies very hard. (改为同义句)
He seems very hard.
答案:to study
解析:It seems/seemed that... 句式进行同义句转换时, 需把that后的主语放在句首, 且seems/seemed后用动词不定式。
5.直接引语和间接引语
直接引用别人的话叫直接引语, 用引号引出。用自己的话转述别人的话叫间接引语, 不用引号。
直接引语变为间接引语需注意时态、语序、引导词、人称代词等几个方面的问题。具体地说:
(1)若直接引语为陈述句, 变为间接引语时要记住: 去掉引号加that, 人称变化要灵活, 时态向后退一步, 状语变化按规则。
She said,“My brother doesn’t want to go there.”
→She said that her brother didn’t want to go there.
(2)若直接引语为一般疑问句或反意疑问句, 变为间接引语时要记住: 去掉引号加if/whether, 陈述语序要记住, 时态、人称和状语, 小心变化别马虎。
I asked her,“Do you study English here ”
→I asked her if/whether she studied English there.
(3)若直接引语是特殊疑问句, 变为间接引语时要记住: 直接去引号, 陈述莫忘掉, 小心助动词, 丢它最重要。
“What do you want ” he asked me.
→He asked me what I wanted.
(4)若直接引语是祈使句, 变为间接引语时要记住: 去掉引号要加to, ask, order, tell须记住, 直接引语是否定, not加在to前面。
Mother said to him,“Please give me the book.”
→Mother told him to give her the book.
(5)对于人称代词的变化应遵循此口诀: 一主二宾三不变(即第一人称根据主语变, 第二人称根据宾语变, 第三人称无变化)。
Rose said,“I am having a surprise party for Lana on Friday night.”
→Rose said she was having a surprise party for Lana on Friday night.
(6)时态的变化
①主句是一般现在时(或一般将来时), 从句的时态不变。
②主句是一般过去时, 从句用相应的过去时态。
注意当直接引语是客观事实或谚语时, 变间接引语时时态不变。
(7)直接引语变为间接引语, 还应注意人称、时间和地点等词的变化, 具体情况如下:
典例8“Who is responsible for the food safety problem ” asked the reporter. (改为间接引语)
The reporter asked responsible for the food safety problem.
解析:由主句是一般过去时, 从句也用过去时, 且宾语从句是陈述语序, 可知答案为who was。
答案:who was
活学活用
32.“Jack, can you help with the dinner ” Jack’s mother asked. (改为间接引语)
Jack was asked he help with the dinner.
答案:if/whether; could
解析:由直接引语是一般疑问句故用if/whether引导, 再由主句的时态为一般过去时可知间接引语的时态也为相应的过去时态。故填if/whether; could。
三、定语从句
1.基本构成
(1)定义: 在复合句中做定语, 修饰主句中某一名词或代词的从句叫作定语从句。被定语从句修饰的词叫先行词, 通常位于定语从句之前。
(2)含有定语从句的复合句基本结构: 先行词+关系词+定语从句。
2.关系代词的基本用法
Do you know the girl who/that has won the first prize in the singing competition
你认识歌唱比赛中获得一等奖的那个女孩吗
(1)以下情况只用that不用which:
①先行词前有最高级或序数词修饰。
The Transformers Ⅲ is the greatest movie that I have ever seen.
《变形金刚Ⅲ》是我看过的最棒的一部电影。
The first gift that I got from Uncle Lin was a toy panda.
我从林叔叔那里得到的第一件礼物是一只玩具熊猫。
②先行词前有only, all, any, no, last, just, very等词修饰。
Miss Yu seems to be the only teacher that can help us now.
现在可以帮助我们的好像只有于老师了。
③先行词是something, anything, nothing, everything, little, few, many, all, none等。
Is there anything that I can do for you
我可以为你做点什么
④先行词既有人又有物。
I love the schools and teachers that give me happiness.
我喜爱给我带来欢乐的学校和老师。
(2)以下情况只用who/whom:
①先行词是anyone, anybody, one, ones, those等。
Anyone who breaks the law will be punished.
任何违法之人都将受到处罚。
②在there be结构中, 先行词指人时, 关系代词用who。
There are some boys who are playing basketball on the playground.
操场上有些男孩在打篮球。
(3)以下情况只用which不用that:
①引导词前有介词且先行词指物。
This is the house in which I’m living.
这就是我住的房子。
②非限制性定语从句中。
He bought a new computer, which can work faster and better. 他买了台新电脑, 这台电脑可以工作得更快更好。
③先行词本身是that, those时。
What’s that which made so much noise just now
刚才发出这么多噪声的是什么
④—个句子中有两个定语从句时, 为避免重复, 一个用that, 另一个用which。
Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from the library which was newly open to us.
让我给你看看那本我刚刚从新开放的图书馆借来的小说。
典例9Sweet wormwood(青蒿) is a common plant in China. Tu Youyou is the woman used the plant’s special power to save millions of lives.
A.which B.who
C.whose D./
解析:句意: 青蒿在中国是一种普通的植物。屠呦呦是一个用这种植物的特殊能量救了无数人生命的女人。由先行词the woman可知, 此处的关系代词应该用who。故选B项。
答案:B
活学活用
36.The teacher is talking with Jane is strict us.
A.who; in B.that; about
C.which; with D.who; with
答案:D
解析:先行词为人时, 用who或that引导定语从句; be strict with sb.是固定短语, 意为“对某人要求严格”。故选D项。
3.关系副词的基本用法
典例10Have you been back to the place your ancestors lived, worked, studied and played
A.which B.where
C.that D.who
解析:定语从句的先行词是place, 且在句中做地点状语。句意: 你回到过你祖先生活、工作、学习和玩的地方吗
答案:B
活学活用
不要为这个世界而惊叹,
要让这个世界为你而惊叹!
第一编 语法专项突破
第十三讲 连词和复合句
知识网络建构
考点探究突破
知识网络建构
考点一
考点二
考点探究突破
考点一
连词
连词是用于连接名词、短语或句子的虚词, 不单独做句子成分, 可分为并列连词和从属连词两类。
(一)并列连词
并列连词是指用来连接语法地位相同的单词、短语以及句子的连词。并列连词主要分为表示并列关系、转折关系、因果关系及选择关系的并列连词。
规律总结(1)and, but, or和so的区别
(2)否定句中两部分都有否定词时用and连接。如:
Bill has no brothers and no sisters.
=Bill has no brothers or sisters.
比尔没有兄弟姐妹。
(3)句中含有without时, 肯定句中用or, 否定句中用and。如:
We’ll die without air or water.
没有空气和水, 我们就会死亡。
We can’t live without air and water.
没有空气和水, 我们无法生存。
(4)and与or都可以与if引导的条件状语从句转换。如:
Get up quickly, or you’ll be late for school.
=If you don’t get up quickly, you’ll be late for school.
快点起床, 否则你上学会迟到。
Work hard, and you’ll get good grades.
=If you work hard, you’ll get good grades.
努力学习, 你会取得好成绩。
典例1Jenifer wants to go to that party very much all her best friends will go.
A.because B.so
C.unless D.while
解析:句意: 詹妮弗非常想去参加聚会, 因为她所有的好朋友都去。because“因为”, 故选A项。
答案:A
活学活用
(二)从属连词
1.引导宾语从句的从属连词that, if/whether
I know that the puppy is very clever.
我知道那条小狗很聪明。
We don’t know if/whether it will rain tomorrow.
我们不知道明天是否下雨。
2.引导状语从句的从属连词
典例2My family always go somewhere interesting the holiday begins.
A.as soon as B.so
C.so that D.even though
解析:句意: 我的家庭总是在假期一开始就去有趣的地方。as soon as“一……就……”。故选A项。
答案:A
活学活用
6.I enjoy fresh air so I always sleep with the window open
it is really cold.
A.unless B.when
C.if D.since
答案:A
解析:unless“如果不……”; when“当……时候”; if“如果”; since “自从……以来”。句意: 我喜欢新鲜空气, 因此如果不是很冷, 我总是开着窗户睡觉。故选A项。
7.—This dress is last year’s style.
—I think it still looks perfect it has gone out this year.
A.so that B.as if
C.even though D.ever since
答案:C
解析:句意: ——这件连衣裙是去年的样式。——我认为它仍然看起来很完美, 即使它今年过时了。so that“以至于”; as if “似乎, 好像”; even though“即使”; ever since“自从”。故选C项。
8.—Will you please give the dictionary to Jane
—Sure, I’ll give it to her she arrives here.
A.before B.until
C.because D.as soon as
答案:D
解析:句意: ——你可以把这本字典给简吗 ——可以。她一到这儿我就把它给她。before“在……之前”; until“直到……为止”; because“因为”; as soon as“一……就……”。故选D项。
考点二
复合句
英语句子按照结构分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
简单句是只有一套主谓结构的句子。并列句是由并列连词把两个或两个以上的简单句连接起来的句子。复合句是由一个主句和一个或者一个以上的从句构成的句子, 从句是主句的一个句子成分, 从属于主句。
初中英语教材中涉及的复合句主要有状语从句、宾语从句和定语从句。
(一)状语从句
状语从句在复合句中做状语, 修饰动词、形容词或副词, 可用来表示时间、条件、原因、结果、目的、让步、地点、比较、方式等含义。
1.时间状语从句
时间状语从句通常由when, while, as, before, after, since, as soon as, till/until等词引导。含有时间状语从句的复合句, 如果主句用一般将来时, 从句用一般现在时表示将来。
(1)when引导的从句表示主从句的动作同时发生或从句的动作发生在主句之后。如:
When he came back, his mother was reading a newspaper. 当他回来的时候, 他妈妈正在读报纸。
(2)while引导的从句表示“在……过程中”, 主从句的谓语动词所表示的动作同时发生。如:
My father was reading a newspaper while my mother was watching TV.
我爸爸在读报纸, 我妈妈在看电视。
(3)as表示“当……时候”, 往往可以和when互换。as还表示“一边……一边……”。如:
As we walked, we talked happily.
我们一边走一边高兴地交谈。
(4)before, after通常用来表示动作一前一后发生。如:
After he locked the door, he left.
他锁上门后就离开了。
He had finished his homework before his parents came back.
在父母回来前, 他就完成家庭作业了。
(5)由since引导的从句, 表示“自从……以来”, 从句常用一般过去时, 主句常用现在完成时。如:
He has made many friends since he came to China.
自从来到中国他已结交了许多朋友。
(6)as soon as引导的从句表示“一……就……”。till/until 引导的从句表示“直到”, 若主句中的谓语动词是非延续性的, 要用“not... until”。如:
I will write to you as soon as I get there.
我一到那儿就给你写信。
I waited until he came back. 我一直等到他回来。
I didn’t leave until he came back. 直到他回来我才离开。
2.条件状语从句
(1)条件状语从句常由if “如果, 假如”, unless“如果不, 除非”来引导, 如果表示将来, 从句要用一般现在时表示将来。如:
If it rains tomorrow, we’ll stay at home.
如果明天下雨, 我们将待在家里。
We won’t go to the party unless we are free.
除非我们有空, 否则我们将不去参加聚会。
(2)if还可以引导虚拟条件句, 表示与事实相反或不符。初中阶段常考与现在事实相反的情况。主句谓语动词用would+动词原形, 从句用一般过去时, be动词只用一种形式were。如:
If I were you, I wouldn’t do it like that.
如果我是你, 我就不会那样做。(我不可能是你)
If I had one million dollars, I would build a new school.
如果我有一百万美元, 我会建一所新学校。(我现在没有一百万美元)
3.原因状语从句
原因状语从句由because, since, as等引导。because 语气最强, 用来说明人所不知道的原因, 回答why提出的问题。当原因是显而易见的或已为人知的, 就用as或since。例如:
He didn’t catch the early bus because he got up late.
他没赶上早班公共汽车是因为他起晚了。
Since you know the answer, please tell me.
既然你知道答案, 请告诉我。
As you object, I’ll change the plan.
由于你反对, 我将改变计划。
4.结果状语从句
结果状语从句由so ... that或 such ... that引导。such修饰名词或名词词组; so修饰形容词或副词。常有以下几种句型:
(1)so+adj./adv.+that从句
It’s so cold that no one can play outside.
天太冷了, 没有人会在外面玩。
The problem is so hard that we can’t work it out.
这道题很难, 我们解答不出来。
(2)so+adj.+a/an+可数名词单数+that从句
It’s so heavy a box that I can’t carry it.
这个箱子太重了以至于我搬不动它。
(3)so+many/few/much/little+可数名词复数/不可数名词+that从句
There are so many books that we can’t choose which one to buy.
有如此多的书, 我们不知道要选哪一本了。
There is so little food that we must go out and buy some.
食物如此的少, 我们必须出去买点。
(4)such+a/an+adj.+可数名词单数+that从句
Mr. Green is such a good teacher that we all like him.
格林老师是位非常好的老师, 我们都喜欢他。
(5)such+adj.+可数名词复数/不可数名词+that从句
It is such nice weather that we’d better go out.
天气如此好, 我们最好出去走走。
5.目的状语从句
(1)目的状语从句由that, so that, in order that, so等引导, 谓语中常含有may/might/can/could/will/would等情态动词。如:
He studies hard in order that/so that he can catch up with their classmates.
他努力学习以便能赶上班里的其他同学。
Betty got up early so that she might catch the train.
贝蒂起得早, 以便能赶上火车。
(2)当从句与主句主语一致时, 常用so as to, in order to替换so that, in order that。如:
He ran fast so that he might arrive there on time.
=He ran fast so as to arrive there on time.
他快跑以便准时到达那里。
6.让步状语从句
让步状语从句表示某种对主句不利的条件或情况, 但从句所表示的这些不利因素并不能阻止主句动作的发生, 在这种条件下, 主句的情况依然存在。引导让步状语从句的连词有though/although“虽然”, even though“尽管”, whatever/no matter what“无论什么”, however/no matter how“无论怎样”, whoever/no matter who“无论谁”等, 但主句中不能再用but。如:
He didn’t turn on the lights, though it was dark inside.
虽然屋里很暗, 但他没开灯。
7.地点状语从句
引导地点状语从句的引导词有where, wherever, anywhere, everywhere, somewhere等。如:
Wherever you go, I will be with you.
无论你去哪儿, 我都和你在一起。
8.比较状语从句
常用的引导词有as(同级比较), than(不同程度的比较)等。如:
Lucy is taller than me. 露西比我高。
9.方式状语从句
引导方式状语的常用引导词有as, as if等。如:
When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
入乡随俗。
典例3I looked through my test paper again and again
I wouldn’t make any mistakes.
A.so B.because
C.so that D.that
解析:句意: 我反复仔细浏览了我的试卷, 为了确保我不犯错误。so that引导目的状语从句。故选C项。
答案:C
活学活用
(二)宾语从句
宾语从句在复合句中充当宾语, 可以做谓语动词的宾语, 也可以做介词的宾语。
I don’t know where she has gone.
我不知道她去哪儿了。
This reminded me of what he had once promised me.
这使我想起他曾对我的承诺。
宾语从句的三要素是时态、语序和引导词。
1.宾语从句的时态
典例4I wonder next week. Please call me when they return.
A.when they will come back
B.when will they come back
C.when they come back
D.how will they come back
解析:宾语从句要用陈述语序, 再由宾语从句的时间状语是next week可知从句时态用一般将来时。故选A项。
答案:A
活学活用
15.—I wonder at 8: 00 last night.
—I was watching TV.
A.what were you doing
B.what did you do
C.what you were doing
D.what are you doing
答案:C
解析:宾语从句需用陈述语序, 由last night可知, 本句为一般过去时。故选C项。
16.Linda said that the train , so she couldn’t come.
A.left B.had left
C.leaving D.have left
答案:B
解析:当宾语从句的主句是过去时, 从句应用相应的过去时态。琳达说她不能来可知火车已经开走了, 故从句应用过去完成时。故选B项。
2.宾语从句的语序
宾语从句一律用陈述语序, 即主语在前, 谓语动词在后。如:
I don’t know whether he can pass the exam or not.
我不知道他是否能通过考试。
Could you tell me when Tom will come back
你能告诉我汤姆什么时候回来吗
典例5—Excuse me, but could you please tell me
—Sure.
A.where is the restroom
B.when the store opens
C.what time does it begin
D.how can I get to the library
解析:句意: ——打扰了, 你能告诉我商店什么时候开门吗 ——可以。宾语从句用陈述语序, 只有B项是陈述语序, 故选B项。
答案:B
活学活用
19.—Could you tell me for the meeting yesterday
—Because I got up late.
A.why did you late B.why you came late
C.why do you late D.why you come late
答案:B
解析:疑问句做宾语从句, 语序应用陈述语序, 且根据yesterday可确定时态为一般过去时, 故选B项。
20.I don’t know the charity show tomorrow. Can you tell me
A.when we start B.when did we start
C.when we will start D.when will we start
答案:C
解析:疑问句做宾语从句, 语序应用陈述语序; 主句时态为一般现在时, 从句的时态应根据具体的时间状语确定, 由tomorrow可判断时态应为一般将来时, 故选C项。
3.宾语从句的引导词
注意只能用whether不能用if的情况
典例6—Could you please tell me , Sonia
—It’s on the first Tuesday of May. We hold special parties and give teachers thank-you notes that day.
A.if you have Teachers’ Day in America
B.when Teachers’ Day is in America
C.what you do on Teachers’ Day
D.how do you show your thanks to your teachers
解析:在宾语从句中, 应该使用陈述语序, 故排除D项。根据答语“在五月的第一个星期二。我们在那天举行特殊的聚会并且给老师感谢信。”可知问句应该是询问时间, 故选B项。
答案:B
活学活用
4.宾语从句的简化
(1)当宾语从句的主语和主句的主语相同, 且主句的谓语动词是hope, wish, decide, agree, choose等时, 从句可简化为不定式结构。如:
I hope that I can receive your e-mail. =I hope to receive your e-mail. 我希望能收到你的电子邮件。
(2)当宾语从句的主语和主句的主语相同, 且主句的谓语动词是know, remember, forget, learn等时, 从句可简化为“疑问词+不定式”结构。如:
She doesn’t know what she should do next. =She doesn’t know what to do next.
她不知道下一步该做什么。
(3)动词seem后的宾语从句可用不定式(短语)来简化, 但句型要有适当的变化。通常将宾语从句的主语作为简化的句子的主语, seem(适当时态形式)做谓语。
It seems that football is very interesting.
=Football seems to be very interesting.
足球似乎非常有趣。
(4)宾语从句可以简化为名词或名词短语。
I don’t believe what Tom said. =I don’t believe Tom’s words.
我不相信汤姆所说的话。
典例7—Excuse me. Could you tell me get to the nearest post office
—Sorry, I am new here.
A.how can I B.how I could
C.how to D.what I can
解析:句意: ——打扰了, 你能告诉我如何到达最近的邮局吗 ——对不起, 我是新来的。当主句的主语和从句的主语一致时, 宾语从句可以用“疑问词+不定式”结构。故选C项。
答案:C
活学活用
28.It seems that he studies very hard. (改为同义句)
He seems very hard.
答案:to study
解析:It seems/seemed that... 句式进行同义句转换时, 需把that后的主语放在句首, 且seems/seemed后用动词不定式。
5.直接引语和间接引语
直接引用别人的话叫直接引语, 用引号引出。用自己的话转述别人的话叫间接引语, 不用引号。
直接引语变为间接引语需注意时态、语序、引导词、人称代词等几个方面的问题。具体地说:
(1)若直接引语为陈述句, 变为间接引语时要记住: 去掉引号加that, 人称变化要灵活, 时态向后退一步, 状语变化按规则。
She said,“My brother doesn’t want to go there.”
→She said that her brother didn’t want to go there.
(2)若直接引语为一般疑问句或反意疑问句, 变为间接引语时要记住: 去掉引号加if/whether, 陈述语序要记住, 时态、人称和状语, 小心变化别马虎。
I asked her,“Do you study English here ”
→I asked her if/whether she studied English there.
(3)若直接引语是特殊疑问句, 变为间接引语时要记住: 直接去引号, 陈述莫忘掉, 小心助动词, 丢它最重要。
“What do you want ” he asked me.
→He asked me what I wanted.
(4)若直接引语是祈使句, 变为间接引语时要记住: 去掉引号要加to, ask, order, tell须记住, 直接引语是否定, not加在to前面。
Mother said to him,“Please give me the book.”
→Mother told him to give her the book.
(5)对于人称代词的变化应遵循此口诀: 一主二宾三不变(即第一人称根据主语变, 第二人称根据宾语变, 第三人称无变化)。
Rose said,“I am having a surprise party for Lana on Friday night.”
→Rose said she was having a surprise party for Lana on Friday night.
(6)时态的变化
①主句是一般现在时(或一般将来时), 从句的时态不变。
②主句是一般过去时, 从句用相应的过去时态。
注意当直接引语是客观事实或谚语时, 变间接引语时时态不变。
(7)直接引语变为间接引语, 还应注意人称、时间和地点等词的变化, 具体情况如下:
典例8“Who is responsible for the food safety problem ” asked the reporter. (改为间接引语)
The reporter asked responsible for the food safety problem.
解析:由主句是一般过去时, 从句也用过去时, 且宾语从句是陈述语序, 可知答案为who was。
答案:who was
活学活用
32.“Jack, can you help with the dinner ” Jack’s mother asked. (改为间接引语)
Jack was asked he help with the dinner.
答案:if/whether; could
解析:由直接引语是一般疑问句故用if/whether引导, 再由主句的时态为一般过去时可知间接引语的时态也为相应的过去时态。故填if/whether; could。
三、定语从句
1.基本构成
(1)定义: 在复合句中做定语, 修饰主句中某一名词或代词的从句叫作定语从句。被定语从句修饰的词叫先行词, 通常位于定语从句之前。
(2)含有定语从句的复合句基本结构: 先行词+关系词+定语从句。
2.关系代词的基本用法
Do you know the girl who/that has won the first prize in the singing competition
你认识歌唱比赛中获得一等奖的那个女孩吗
(1)以下情况只用that不用which:
①先行词前有最高级或序数词修饰。
The Transformers Ⅲ is the greatest movie that I have ever seen.
《变形金刚Ⅲ》是我看过的最棒的一部电影。
The first gift that I got from Uncle Lin was a toy panda.
我从林叔叔那里得到的第一件礼物是一只玩具熊猫。
②先行词前有only, all, any, no, last, just, very等词修饰。
Miss Yu seems to be the only teacher that can help us now.
现在可以帮助我们的好像只有于老师了。
③先行词是something, anything, nothing, everything, little, few, many, all, none等。
Is there anything that I can do for you
我可以为你做点什么
④先行词既有人又有物。
I love the schools and teachers that give me happiness.
我喜爱给我带来欢乐的学校和老师。
(2)以下情况只用who/whom:
①先行词是anyone, anybody, one, ones, those等。
Anyone who breaks the law will be punished.
任何违法之人都将受到处罚。
②在there be结构中, 先行词指人时, 关系代词用who。
There are some boys who are playing basketball on the playground.
操场上有些男孩在打篮球。
(3)以下情况只用which不用that:
①引导词前有介词且先行词指物。
This is the house in which I’m living.
这就是我住的房子。
②非限制性定语从句中。
He bought a new computer, which can work faster and better. 他买了台新电脑, 这台电脑可以工作得更快更好。
③先行词本身是that, those时。
What’s that which made so much noise just now
刚才发出这么多噪声的是什么
④—个句子中有两个定语从句时, 为避免重复, 一个用that, 另一个用which。
Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from the library which was newly open to us.
让我给你看看那本我刚刚从新开放的图书馆借来的小说。
典例9Sweet wormwood(青蒿) is a common plant in China. Tu Youyou is the woman used the plant’s special power to save millions of lives.
A.which B.who
C.whose D./
解析:句意: 青蒿在中国是一种普通的植物。屠呦呦是一个用这种植物的特殊能量救了无数人生命的女人。由先行词the woman可知, 此处的关系代词应该用who。故选B项。
答案:B
活学活用
36.The teacher is talking with Jane is strict us.
A.who; in B.that; about
C.which; with D.who; with
答案:D
解析:先行词为人时, 用who或that引导定语从句; be strict with sb.是固定短语, 意为“对某人要求严格”。故选D项。
3.关系副词的基本用法
典例10Have you been back to the place your ancestors lived, worked, studied and played
A.which B.where
C.that D.who
解析:定语从句的先行词是place, 且在句中做地点状语。句意: 你回到过你祖先生活、工作、学习和玩的地方吗
答案:B
活学活用
不要为这个世界而惊叹,
要让这个世界为你而惊叹!
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
