Unit3 A visit to Garden City 第2课时 语法知识及拓展 课件(共28张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit3 A visit to Garden City 第2课时 语法知识及拓展 课件(共28张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 481.8KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津上海版(试用本) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-03-09 17:53:22 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共28张PPT)
Lead in— 脑筋急转弯
Q:为什么黑人喜欢吃白色巧克力?
A:害怕咬到自己的手
沪教版 英语 六年级 第二学期
Snow and Ice Knowledge 冰雪知识
Alpine Skiing
沪教版 英语 六年级 第二学期
一、知识回顾
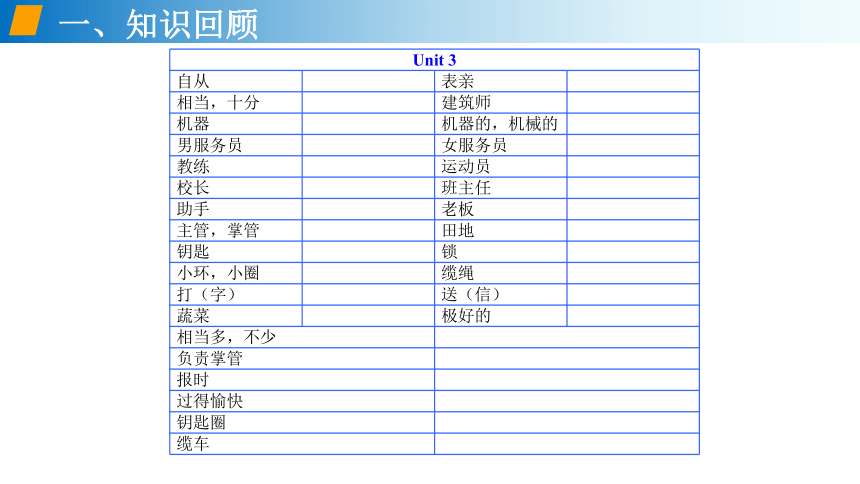
Unit 3 自从 表亲
相当,十分 建筑师
机器 机器的,机械的
男服务员 女服务员
教练 运动员
校长 班主任
助手 老板
主管,掌管 田地
钥匙 锁
小环,小圈 缆绳
打(字) 送(信)
蔬菜 极好的
相当多,不少 负责掌管 报时 过得愉快 钥匙圈 缆车 二、Important Sentences structures
1. Kitty's cousins, Lucy and Simon, have come to Garden City to visit the Li family.
基蒂的堂妹露西和堂弟西蒙到花园城市去拜访李先生一家人。
在这个句子中,现在完成时用于表示动作已经发生(但并不追究动作发生的具体时间),并对现在产生一定的影响(即目前露西和西蒙已经在Garden City了)。
I’ve lost my passport. 我把护照丢了。(其含义是:I can't find my passport now.)
-Where's Linda 琳达在哪儿呢?
-She’s gone to bed. 她去睡觉了。(其含义是:She is in bed now.)
We've bought a new car. 我们买了一辆新车。(其含义是:We have a new car and can use it now.)
2. How long has she been a teacher 她当老师多久了?
She has been a teacher since 1997. 她从1997年开始当老师的。
上述两个句子也使用了现在完成时。本例中的现在完成时用于表示某个动作发生的起点在过去,这个动作一直持续到现在,并还有可能持续下去。这样的句子通常会加上for或since引导的时间状语。如:
He has been a teacher here since 1981. 他自1981年起就在这儿当老师了。(可能还要继续在这儿教很多年)
I have't seen her for four years. 我有四年没见到她了。
【友情提示】 如果句子中的谓语表示持续的动作含义,现在完成时结构中的动词需使用持续性动词,而不可使用短暂性动词。试比较:
【正】 I have been in the club for three years. 我加入这个俱乐部已经有三年了。
【误】 I have joined the club for three years. (join是短暂性动词)
for和since是现在完成时中常见的两个引导时间状语的词。表示时间的for不能用于以all开头的短语前。如:
They've worked all day. 他们已干了整整一天。
总之,我们应当记住:for后接“时间段”,since后接“时间点”。
3. He catches thieves and helps keep the city safe. 他抓捕小偷、保卫城市的安全。
"keep+名词+形容词”的结构常用来表示‘使……保持某种状态”的意思。
We should try to keep the environment clean.
我们应当尽力保持环境卫生。
Would you please keep your room tidy, Ben
本,你能不能让自己的房间保持整洁?
4. Aunt Betty works in a company in Beijing, doesn't she 贝蒂婶婶在北京的一家公司工作,不是吗?
这是一个反意疑问句。反意疑问句是英语四大问句之一,它是由一个陈述句加上一个短问句构成。反意疑问句的基本构成形式是:陈述句+逗号+助动词/be动词/情态动词(肯定或否定形式)+主语。
She often has lunch at school, doesn't she 她经常在学校吃午饭,不是吗?
You don't like sports, do you 你不喜欢体育运动,是吗?
5. A watch is used for telling the time. 手表是用来报时的。
We use a watch for telling the time. 我们用手表来报时。①
A watch is used for telling the time. 手表是用来报时的。②
(1)我们把句子①的结构称为“主动语态”,把句子②的结构称为“被动语态”。主动语态句的主语是动作的执行者,而被动语态句的主语是动作的承受者。被动语态的基本结构是“be+动词的过去分词”。be used for的结构表达“被用来……”的意思,后接动词的-ing形式。
Chopsticks are used for eating food. 筷子是用来吃饭的。
类似的用法还有be used by“被……使用”,be used as“被……用作”。
A knife is used for cutting things. 刀是用来切东西的。
The building was used as a shelter for homeless people.那座楼房用来收容无家可归的人。
(2) tell the time意为“报时”。
Little Mary can now tell the time. 小玛丽现在会认时间了。
6. A key ring is used for holding the keys. 钥匙圈是用来挂钥匙的。
hold有“拿着;抓住;夹着”的意思。hold在句中作及物动词时,有以下意义和用法:
(1) 握;抓住;拿住。如:She is holding up an umbrella. 她正打着伞。
He held me by the sleeve. 他抓着我的袖子。
Hold the line. (打电话用语)稍等/别挂断。
(2)容纳;装着。如:The hall can hold 1,000 people. 这个大厅能容纳1000人。
(3)拥有;占有。如:I held the job for two years. 这工作我干了两年。
(4)举行(会议等)。如:The Olympic Games are held every four years. 奥运会每四年举办一次。
(5)与hold相关的词组:
hold back意为“阻碍,阻止”。
hold on意为“等待,不要挂断电话”等。
hold up意为“举起;抬起,耽搁”。
7. Yesterday, we took the cable car to the top of a hill. 昨天,我们乘缆车去了山顶。
the top of意为“……的顶部”,常用于at the top of(在……的顶部)等短语中。
We can have a nice view from the top of the mountain. 从山顶上往下看,我们可以欣赏到不错的景色。
She is screaming at the top of her voice. 她正在声嘶力竭地尖叫。
Rewrite the sentences as required.
1. I have been to Beijing before. (改为否定句)I______ ______ to Beijing before.
2. My father has been a fireman for a few years. (改为一般疑问句)
___________your father a fireman for a few years
3. He had some bad habits for two years. (就划线部分提问)
___________ ___________ did he have some bad habits
4. I have learned English since 1998. (就划线部分提问)
____________ ___________ have you learned English
5. He got a lot of presents for his birthday. (保持原意不变)
He got quite____________ ___________ presents for his birthday.
1. haven't been 2. Has;been 3. How long 4.How long 5. a few
【随堂小练】
三、语法新课讲解
现在完成时
(1)表示过去发生的或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。如:
-Have you had your lunch yet 你吃过午饭了吗?
-Yes, I have. I've just had it. 是的,我刚吃过。(说明现在饱了。)
I have lost my pen. 我把钢笔弄丢了。(过去某时丢的,现在还没有找到。)
I have already watched the TV play. 我已经看过这部电视剧了。
-Have you found your lost pen yet 一你找到丢失的钢笔了吗?
-No. I haven't found it yet. 一不,我还没有找到。
【友情提示】 already,yet常和现在完成时连用,already用于肯定句,可放在助动词之后、过去分词之前,也可放在句末。yet用在疑问句中意为“已经”,用在否定句中表示“还”,常放在句末。
(2)表示动作或状态在过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还要持续下去,常和for,since连用,表示持续的动作或状态多为延续性动词。如:
We have lived here since 2000.
自从2000年以来我们一直住在这里。(说明一直住在这里也许还会住下去。)
(3)现在完成时中经常使用的几个副词:
1) just意为“刚刚”,表示动作刚刚结束,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
He has just come back from Beijing. 他刚从北京回来。
2) ever意为“曾经”,用于疑问句或否定句中,放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
Have you ever been to Shanghai 你去过上海吗?
3) never意为“从来没有”,常与before连用,多放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
I have never travelled by plane before. 我以前从来没有乘飞机旅行过。
4) before意为“以前”,指过去不确定的某个时间,总是放在句末,不受句型的限制。如:
I haven’t heard of it before. 我以前从来没有听说过这件事。
5) since+时间点,for+时间段
I have been in Beijing for two years/since two years ago. 我在北京两年了。
(4)延续性动词与非延续性动词的用法
1) 现在完成时表示动作从过去某个时候开始一直持续到现在,与一段时间连用时应注意句中的谓语动词应是延续性动词,非延续性动词不可与一段时间连用。如:
我离开这所学校已八年了。
误:I've left this school for eight years.
正:I've been away from this school for eight years.
他借用我的词典已两天了。
误:He has borrowed my dictionary for two days.
正:He has kept my dictionary for two days.
不过,在否定句中非延续性动词可与一段时间连用。如:
I haven't gone to see him for several months. 我已经好几个月没去看他了。
2) 非延续性动词与一段时间连用时可采用下述三种方法:
a. 将非延续性动词转化为延续性动词
b. 将时间状语改为过去的时间,
并用一般过去时代替现在完成时。
c. 用句型“it is十一段时间+since从句
(从句中的谓语动词用非延续性动
词的一般过去式)”表示。如:
It is two years since the old man
died. 这个老人去世两年了。
非延续性动词 延续性动词
buy have
borrow keep
open be open
close be closed
begin/ start be on
come be here
go be away
finish be over
died be dead
catch a cold have a cold
put on wear
get up be up
wake up be awake
fall asleep be asleep
lose not have
join be(in)
leave be away from
arrive/ reach be
被动语态
一、被动语态的构成及用法
1. 被动语态的构成
(1)被动语态的基本结构为:be+动词的过去分词
(2)各种时态的主动、被动语态的结构如下表(以动词do为例):
时态 主动语态 被动语态 例句 主动语态 被动语态
一般现在时 do/does am/ is/ are+done We clean the classroom. The classroom is cleaned by bus.
一般过去时 did was/ were/+done He made the kite. The kite was made by him.
现在进行时 am/ is/ are +doing am/ is/ are+being done She is watering flowers. Flowers are being watered by her.
2. 被动语态的用法
在被动语态中,主语是动作的承受者,主要用于下列几种情况:
(1) 不知道动作的执行者是谁。如:
This watch is made in China. 这块手表是中国制造的。
(2) 没有必要指出动作的执行者是谁。如:
More trees should be planted every year. 每年都应该种更多的树。
(3) 需要强调或突出动作的承受者时。如:
Chinese is spoken by more and more people in the world. 世界上越来越多的人说汉语。(强调汉语的使用广泛)
(4) 句子的主语是动作的承受者。如:
Many houses were washed away by the flood. 许多房屋被洪水冲走了。
二、主动语态和被动语态的转换
1. 主动语态变为被动语态
(1)要将主动句里的宾语变为被动句中的主语,若主动句中的宾语是人称代词,要将宾格变成主格。
(2)把主动句中的主语变为被动句中的宾语,主格变成宾格,并由by引导。
(3)谓语动词变成相应的被动形式。
We asked him to sing an English song. (变为被动语态)→He was asked to sing an English song by us.
2. 带双宾语的谓语动词变为被动语态
谓语动词带双宾语时,既可以将间接宾语转化成主语,也可以将直接宾语转化成主语。若将间接宾语转化成主语,则保留直接宾语;若将直接宾语转化成主语,则保留间接宾语,且在被保留的间接宾语前加上介词to或for。如:
She gave me a book.(变为被动语态)
I was given a book by her.(间接宾语me变为了主语)
A book was given to me by her.(直接宾语a book变为了主语)
3. 动词短语变为被动语态
许多由不及物动词和介词、副词构成的动词短语相当于及物动词,可以有宾语,也可以有被动语态。但是动词短语是一个不可分割的整体,在变为被动语态时,不可丢掉构成动词短语的介词或副词。
如:
We should speak to old men politely.(变为被动语态)
Old men should be spoken to politely.(to不可省略)
4. 带复合宾语的动词变为被动语态
宾语加上宾语补足语一起构成复合宾语。变为被动语态时,只把宾语变为被动句的主语,宾语补足语保留在原处,成为主语补足语。
如:
I heard Jane playing the piano in her room.(变为被动语态)
Jane was heard playing the piano in her room.
5. 变被动语态后动词形式的选择
主动句中在感官动词see,hear,watch,feel,notice等,及使役动词let,make,have等后跟省略to的不定式,
变为被动语态时,应加上不定式符号to。
如:
He makes the girl stay at home.(变为被动语态)→The girl is made to stay at home by him.
I.Fill in the blanks with the words in their proper forms.
1. How is your to the Science Museum (visit)
2. Tom's father is an . (engine)
3. cook food in a restaurant. (cook)
4. Washing can wash our clothes. (machine)
5. As we all know, were hard-working and creative in China. (farm)
6. This is my visit to Tokyo. (one)
7. deliver letters every morning to each door. (postman)
8. In our office we need a . (type)
9. Aunt Mary is a . She likes her job very much. (police)
10.Doctors can make sick people . (well)
【Keys】
I . 1. visit 2. engineer 3. Cooks 4. machines 5. farmers
6. first 7. Postmen 8. typist 9. policewoman 10. better
【随堂小练】
Read and choose the best answer.
( )1. — have you learnt English —Since 3 years ago.
A. How far B. How much C. How long D. How often
( )2. We've known each other more than seven years.
A. for B. since C. in D. at
( )3. Jane has lived here 1991. She has lived in Shanghai 19 years.
A. in; for B. since; for C. since; at D. in; since
( )4. He quite a few pictures since he was five years old.
A. has draw B. drew C. is drawing D. has drawn
( )5. My father in a travel agency since he school.
A. worked; left B. worked; has left C. works; leaves D. has worked; left
( )6. They go to school on foot every day, they
A. do B. don't C. are D. aren't
1.C 2. A 3.B 4.D 5.D 6. B
愿君皆有所获,皆有所得
Lead in— 脑筋急转弯
Q:为什么黑人喜欢吃白色巧克力?
A:害怕咬到自己的手
沪教版 英语 六年级 第二学期
Snow and Ice Knowledge 冰雪知识
Alpine Skiing
沪教版 英语 六年级 第二学期
一、知识回顾
Unit 3 自从 表亲
相当,十分 建筑师
机器 机器的,机械的
男服务员 女服务员
教练 运动员
校长 班主任
助手 老板
主管,掌管 田地
钥匙 锁
小环,小圈 缆绳
打(字) 送(信)
蔬菜 极好的
相当多,不少 负责掌管 报时 过得愉快 钥匙圈 缆车 二、Important Sentences structures
1. Kitty's cousins, Lucy and Simon, have come to Garden City to visit the Li family.
基蒂的堂妹露西和堂弟西蒙到花园城市去拜访李先生一家人。
在这个句子中,现在完成时用于表示动作已经发生(但并不追究动作发生的具体时间),并对现在产生一定的影响(即目前露西和西蒙已经在Garden City了)。
I’ve lost my passport. 我把护照丢了。(其含义是:I can't find my passport now.)
-Where's Linda 琳达在哪儿呢?
-She’s gone to bed. 她去睡觉了。(其含义是:She is in bed now.)
We've bought a new car. 我们买了一辆新车。(其含义是:We have a new car and can use it now.)
2. How long has she been a teacher 她当老师多久了?
She has been a teacher since 1997. 她从1997年开始当老师的。
上述两个句子也使用了现在完成时。本例中的现在完成时用于表示某个动作发生的起点在过去,这个动作一直持续到现在,并还有可能持续下去。这样的句子通常会加上for或since引导的时间状语。如:
He has been a teacher here since 1981. 他自1981年起就在这儿当老师了。(可能还要继续在这儿教很多年)
I have't seen her for four years. 我有四年没见到她了。
【友情提示】 如果句子中的谓语表示持续的动作含义,现在完成时结构中的动词需使用持续性动词,而不可使用短暂性动词。试比较:
【正】 I have been in the club for three years. 我加入这个俱乐部已经有三年了。
【误】 I have joined the club for three years. (join是短暂性动词)
for和since是现在完成时中常见的两个引导时间状语的词。表示时间的for不能用于以all开头的短语前。如:
They've worked all day. 他们已干了整整一天。
总之,我们应当记住:for后接“时间段”,since后接“时间点”。
3. He catches thieves and helps keep the city safe. 他抓捕小偷、保卫城市的安全。
"keep+名词+形容词”的结构常用来表示‘使……保持某种状态”的意思。
We should try to keep the environment clean.
我们应当尽力保持环境卫生。
Would you please keep your room tidy, Ben
本,你能不能让自己的房间保持整洁?
4. Aunt Betty works in a company in Beijing, doesn't she 贝蒂婶婶在北京的一家公司工作,不是吗?
这是一个反意疑问句。反意疑问句是英语四大问句之一,它是由一个陈述句加上一个短问句构成。反意疑问句的基本构成形式是:陈述句+逗号+助动词/be动词/情态动词(肯定或否定形式)+主语。
She often has lunch at school, doesn't she 她经常在学校吃午饭,不是吗?
You don't like sports, do you 你不喜欢体育运动,是吗?
5. A watch is used for telling the time. 手表是用来报时的。
We use a watch for telling the time. 我们用手表来报时。①
A watch is used for telling the time. 手表是用来报时的。②
(1)我们把句子①的结构称为“主动语态”,把句子②的结构称为“被动语态”。主动语态句的主语是动作的执行者,而被动语态句的主语是动作的承受者。被动语态的基本结构是“be+动词的过去分词”。be used for的结构表达“被用来……”的意思,后接动词的-ing形式。
Chopsticks are used for eating food. 筷子是用来吃饭的。
类似的用法还有be used by“被……使用”,be used as“被……用作”。
A knife is used for cutting things. 刀是用来切东西的。
The building was used as a shelter for homeless people.那座楼房用来收容无家可归的人。
(2) tell the time意为“报时”。
Little Mary can now tell the time. 小玛丽现在会认时间了。
6. A key ring is used for holding the keys. 钥匙圈是用来挂钥匙的。
hold有“拿着;抓住;夹着”的意思。hold在句中作及物动词时,有以下意义和用法:
(1) 握;抓住;拿住。如:She is holding up an umbrella. 她正打着伞。
He held me by the sleeve. 他抓着我的袖子。
Hold the line. (打电话用语)稍等/别挂断。
(2)容纳;装着。如:The hall can hold 1,000 people. 这个大厅能容纳1000人。
(3)拥有;占有。如:I held the job for two years. 这工作我干了两年。
(4)举行(会议等)。如:The Olympic Games are held every four years. 奥运会每四年举办一次。
(5)与hold相关的词组:
hold back意为“阻碍,阻止”。
hold on意为“等待,不要挂断电话”等。
hold up意为“举起;抬起,耽搁”。
7. Yesterday, we took the cable car to the top of a hill. 昨天,我们乘缆车去了山顶。
the top of意为“……的顶部”,常用于at the top of(在……的顶部)等短语中。
We can have a nice view from the top of the mountain. 从山顶上往下看,我们可以欣赏到不错的景色。
She is screaming at the top of her voice. 她正在声嘶力竭地尖叫。
Rewrite the sentences as required.
1. I have been to Beijing before. (改为否定句)I______ ______ to Beijing before.
2. My father has been a fireman for a few years. (改为一般疑问句)
___________your father a fireman for a few years
3. He had some bad habits for two years. (就划线部分提问)
___________ ___________ did he have some bad habits
4. I have learned English since 1998. (就划线部分提问)
____________ ___________ have you learned English
5. He got a lot of presents for his birthday. (保持原意不变)
He got quite____________ ___________ presents for his birthday.
1. haven't been 2. Has;been 3. How long 4.How long 5. a few
【随堂小练】
三、语法新课讲解
现在完成时
(1)表示过去发生的或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。如:
-Have you had your lunch yet 你吃过午饭了吗?
-Yes, I have. I've just had it. 是的,我刚吃过。(说明现在饱了。)
I have lost my pen. 我把钢笔弄丢了。(过去某时丢的,现在还没有找到。)
I have already watched the TV play. 我已经看过这部电视剧了。
-Have you found your lost pen yet 一你找到丢失的钢笔了吗?
-No. I haven't found it yet. 一不,我还没有找到。
【友情提示】 already,yet常和现在完成时连用,already用于肯定句,可放在助动词之后、过去分词之前,也可放在句末。yet用在疑问句中意为“已经”,用在否定句中表示“还”,常放在句末。
(2)表示动作或状态在过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还要持续下去,常和for,since连用,表示持续的动作或状态多为延续性动词。如:
We have lived here since 2000.
自从2000年以来我们一直住在这里。(说明一直住在这里也许还会住下去。)
(3)现在完成时中经常使用的几个副词:
1) just意为“刚刚”,表示动作刚刚结束,常放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
He has just come back from Beijing. 他刚从北京回来。
2) ever意为“曾经”,用于疑问句或否定句中,放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
Have you ever been to Shanghai 你去过上海吗?
3) never意为“从来没有”,常与before连用,多放在助动词与过去分词之间。如:
I have never travelled by plane before. 我以前从来没有乘飞机旅行过。
4) before意为“以前”,指过去不确定的某个时间,总是放在句末,不受句型的限制。如:
I haven’t heard of it before. 我以前从来没有听说过这件事。
5) since+时间点,for+时间段
I have been in Beijing for two years/since two years ago. 我在北京两年了。
(4)延续性动词与非延续性动词的用法
1) 现在完成时表示动作从过去某个时候开始一直持续到现在,与一段时间连用时应注意句中的谓语动词应是延续性动词,非延续性动词不可与一段时间连用。如:
我离开这所学校已八年了。
误:I've left this school for eight years.
正:I've been away from this school for eight years.
他借用我的词典已两天了。
误:He has borrowed my dictionary for two days.
正:He has kept my dictionary for two days.
不过,在否定句中非延续性动词可与一段时间连用。如:
I haven't gone to see him for several months. 我已经好几个月没去看他了。
2) 非延续性动词与一段时间连用时可采用下述三种方法:
a. 将非延续性动词转化为延续性动词
b. 将时间状语改为过去的时间,
并用一般过去时代替现在完成时。
c. 用句型“it is十一段时间+since从句
(从句中的谓语动词用非延续性动
词的一般过去式)”表示。如:
It is two years since the old man
died. 这个老人去世两年了。
非延续性动词 延续性动词
buy have
borrow keep
open be open
close be closed
begin/ start be on
come be here
go be away
finish be over
died be dead
catch a cold have a cold
put on wear
get up be up
wake up be awake
fall asleep be asleep
lose not have
join be(in)
leave be away from
arrive/ reach be
被动语态
一、被动语态的构成及用法
1. 被动语态的构成
(1)被动语态的基本结构为:be+动词的过去分词
(2)各种时态的主动、被动语态的结构如下表(以动词do为例):
时态 主动语态 被动语态 例句 主动语态 被动语态
一般现在时 do/does am/ is/ are+done We clean the classroom. The classroom is cleaned by bus.
一般过去时 did was/ were/+done He made the kite. The kite was made by him.
现在进行时 am/ is/ are +doing am/ is/ are+being done She is watering flowers. Flowers are being watered by her.
2. 被动语态的用法
在被动语态中,主语是动作的承受者,主要用于下列几种情况:
(1) 不知道动作的执行者是谁。如:
This watch is made in China. 这块手表是中国制造的。
(2) 没有必要指出动作的执行者是谁。如:
More trees should be planted every year. 每年都应该种更多的树。
(3) 需要强调或突出动作的承受者时。如:
Chinese is spoken by more and more people in the world. 世界上越来越多的人说汉语。(强调汉语的使用广泛)
(4) 句子的主语是动作的承受者。如:
Many houses were washed away by the flood. 许多房屋被洪水冲走了。
二、主动语态和被动语态的转换
1. 主动语态变为被动语态
(1)要将主动句里的宾语变为被动句中的主语,若主动句中的宾语是人称代词,要将宾格变成主格。
(2)把主动句中的主语变为被动句中的宾语,主格变成宾格,并由by引导。
(3)谓语动词变成相应的被动形式。
We asked him to sing an English song. (变为被动语态)→He was asked to sing an English song by us.
2. 带双宾语的谓语动词变为被动语态
谓语动词带双宾语时,既可以将间接宾语转化成主语,也可以将直接宾语转化成主语。若将间接宾语转化成主语,则保留直接宾语;若将直接宾语转化成主语,则保留间接宾语,且在被保留的间接宾语前加上介词to或for。如:
She gave me a book.(变为被动语态)
I was given a book by her.(间接宾语me变为了主语)
A book was given to me by her.(直接宾语a book变为了主语)
3. 动词短语变为被动语态
许多由不及物动词和介词、副词构成的动词短语相当于及物动词,可以有宾语,也可以有被动语态。但是动词短语是一个不可分割的整体,在变为被动语态时,不可丢掉构成动词短语的介词或副词。
如:
We should speak to old men politely.(变为被动语态)
Old men should be spoken to politely.(to不可省略)
4. 带复合宾语的动词变为被动语态
宾语加上宾语补足语一起构成复合宾语。变为被动语态时,只把宾语变为被动句的主语,宾语补足语保留在原处,成为主语补足语。
如:
I heard Jane playing the piano in her room.(变为被动语态)
Jane was heard playing the piano in her room.
5. 变被动语态后动词形式的选择
主动句中在感官动词see,hear,watch,feel,notice等,及使役动词let,make,have等后跟省略to的不定式,
变为被动语态时,应加上不定式符号to。
如:
He makes the girl stay at home.(变为被动语态)→The girl is made to stay at home by him.
I.Fill in the blanks with the words in their proper forms.
1. How is your to the Science Museum (visit)
2. Tom's father is an . (engine)
3. cook food in a restaurant. (cook)
4. Washing can wash our clothes. (machine)
5. As we all know, were hard-working and creative in China. (farm)
6. This is my visit to Tokyo. (one)
7. deliver letters every morning to each door. (postman)
8. In our office we need a . (type)
9. Aunt Mary is a . She likes her job very much. (police)
10.Doctors can make sick people . (well)
【Keys】
I . 1. visit 2. engineer 3. Cooks 4. machines 5. farmers
6. first 7. Postmen 8. typist 9. policewoman 10. better
【随堂小练】
Read and choose the best answer.
( )1. — have you learnt English —Since 3 years ago.
A. How far B. How much C. How long D. How often
( )2. We've known each other more than seven years.
A. for B. since C. in D. at
( )3. Jane has lived here 1991. She has lived in Shanghai 19 years.
A. in; for B. since; for C. since; at D. in; since
( )4. He quite a few pictures since he was five years old.
A. has draw B. drew C. is drawing D. has drawn
( )5. My father in a travel agency since he school.
A. worked; left B. worked; has left C. works; leaves D. has worked; left
( )6. They go to school on foot every day, they
A. do B. don't C. are D. aren't
1.C 2. A 3.B 4.D 5.D 6. B
愿君皆有所获,皆有所得
同课章节目录
- Module 1 Garden City and its neighbours
- Unit 1 Writing a travel guide
- Unit 2 Going to see a film
- Unit 3 A visit to Garden City
- Module 2 Better future
- Unit 4 Let's go shopping
- Unit 5 What can we learn from others?
- Unit 6 Hard work for a better life
- Unit 7 in the future
- Module 3 The natural elements
- Unit 8 A more enjoyable school life
- Unit 9 The wind is blowing
- Unit 10 Water Festival
- Unit 11 Electricity
