2013届高考英语一轮复习回扣语法课件 状语从句
文档属性
| 名称 | 2013届高考英语一轮复习回扣语法课件 状语从句 |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 310.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2013-01-03 22:19:12 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
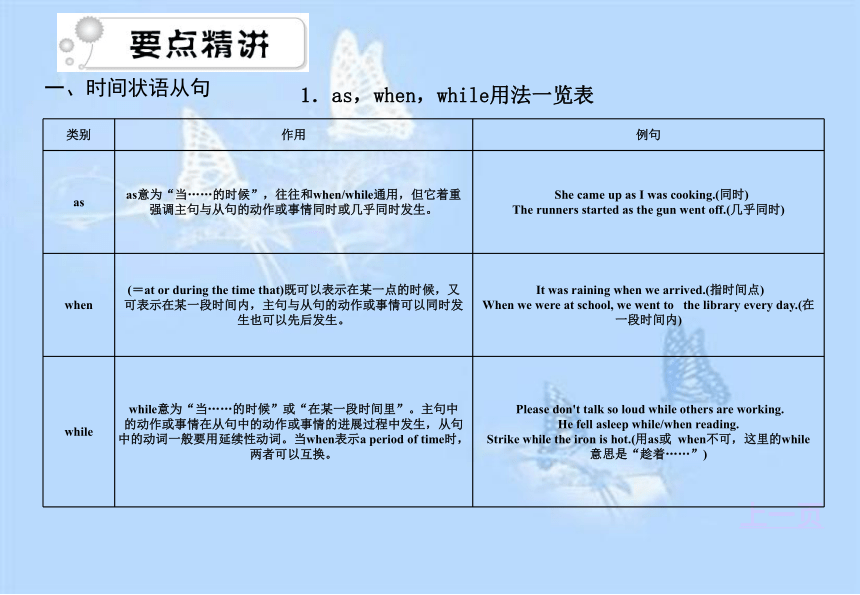
课件27张PPT。状语从句上一页一、时间状语从句
1.as,when,while用法一览表上一页2.引导时间状语从句的连接词除上述三者外还有:
(1)till, not...until..., until, before, since
He waited for his father until(till) it was twelve o'clock.
他等他父亲一直到12点钟。
Don't get off the bus until it has stopped.车停稳了再下车。
It will be five years before he returns from England.
要五年后他才会从英国回来 (2)hardly/scarcely...when, no sooner...than, as soon as, once表示“一……就”
We had hardly got/Hardly had we got into the country when it began to rain.我们一到这个国家就开始下雨。
No sooner had he arrived/He had no sooner arrived than she started complaining.
他一到她就开始抱怨。
As soon as I have finished it, I'll give you a call.
我一完成就给你打电话。
Once you show any fear, he will attack you.
一旦你表现出恐惧,他就会攻击你。上一页(3)directly, immediately, the moment, the minute that...表示“一……就”
Directly the teacher came in everyone was quiet.
老师一进来,大家就安静了下来。
I recognized her immediately I saw her.
我一看见她就认出她来了。
(4)each time, every time, by the time
Each time he came to my city, he would call on me.
他每次来我所在的城市都会来拜访我。上一页上一页表示未来的情况时,主句用将来时,从句用现在时。
She will go to her uncle's when she arrives in America.
当她到美国时,她将会去她叔叔家。二、让步状语从句
1.although与though可以引导让步状语从句,不能与but连用,但可以与yet连用。
Although they are poor,(yet) they are warm-hearted.
尽管他们穷,但却很热心。
2.even if或even though引导让步状语从句,表示“即使;纵然”,用来使人注意下文所强调内容的性质。
I'll get there even if (though) I have to sell my house to get enough money to go by air.
我会去那里的,即使我不得不卖掉房子来凑够钱乘飞机去。上一页上一页3.no matter+疑问词(who,what,where,how等)=who, what, where, how等+ever构成whoever,whatever,wherever,however等,表示“无论……”。
Don't trust him, no matter what/whatever he says.
不管他说什么,都不要相信他。
Whoever breaks the law will be published.
任何触犯法律的人都要受到惩罚。
No matter how hard the work is, you'd better try to do it well.不管这个工作多么困难,你最好尽力做好。上一页4.as也可以引导让步状语从句,但从句要用倒装结构。
Child as(though) he is, he knows a lot.
尽管他是一个孩子,懂得却很多。
Much as I like it, I won't buy.
尽管我很喜欢,但我不会买。上一页三、原因状语从句
通常由because, for, as, since, now that, seeing(that), considering that等引导。
The woolly shrank because it was washed badly.
羊毛衣因洗得不得法而缩水。
Since(As) we've no money, we can't buy it.
由于我们没钱,我们无法购买它。
He could not have seen me, for I was not there.
他不可能见过我,因为我不在那里。上一页Now that you are here, you'd better stay.
你既然来了,最好还是留下吧(既来之,则安之)。
Seeing that it's raining outside, we'd better stay indoors.
既然外边在下雨,我们最好待在室内。
Considering (that) everybody is here, let's begin our discussion.
既然大家都到了,我们就开始讨论吧。上一页1.表示不知道的原因
(1)用because,即说话人认为听话人不知道,因此because从句是全句最重要的部分,通常它被置于主句之后。
You want to know why I'm leaving? I'm leaving because I'm full.你想知道我为什么想离开吗?我离开是因为我吃饱了。
(2)for虽然也表示不知道的原因,但其语气较because要弱得多,是可说可不说的话,它只能置于主句之后,这时,for是并列连词。如果不是因果关系,而是对前面主句的内容加以解释或推断时,只能用for。It's morning now, for the birds are singing.
现在应该是早晨了,因为鸟儿在歌唱。(很显然,鸟叫不可能是“现在已是早上”的原因。)
2.表示已经知道的原因
用as或since,即某种原因在说话人看来已经很明显,或已为听话人所熟悉,因此它是句中不很重要的部分。since要比as正式一些,它们通常被置于主句之前,但有时却相反。上一页Since (As) it is raining,you'd better take a taxi.
下雨了,你最好乘出租车。
Seeing all of the children already seated, he said,“Since everyone is here, let's start.”
看到所有的孩子都就座了,他说:“既然都到了,我们开始吧。”上一页3.只能使用because的情况
(1)在回答why的问句时
—Why did you leave so early?—你昨天怎么离开得那么早?
—Because I had a headache.——因为我头疼。
(2)用于强调句型时
It was because he was ill that he didn't go with us.
他是因为生病了才没跟我们一起去。
(3)被not否定时
You shouldn't get angry just because some people speak ill of you.你不要因为有人说你坏话就生气。上一页四、地点状语从句
通常由where, wherever等引导。
Make a mark wherever you have any questions.
在你有问题的地方做个记号。
Where there's plenty of sun and rain,the fields are green.
哪里阳光雨水充足,哪里的田野就绿油油的。上一页五、目的状语从句
通常由that, so that, in order that, in case, for fear that等引导。谓语动词常与may (might), can (could), should, will等情态动词连用,否则可能是结果状语从句,不可置于句首。
They stopped at Hangzhou in order that they could go around West Lake.他们在杭州停了下来,以便游览西湖。
Say it louder (so) that everyone can hear you.
大声说,以便大家都能听到你的声音。上一页You'd better take more clothes in case the weather is cold.
你最好多带些衣服以防天气太冷。
He wrote the name down for fear that he should forget it.
他把名字写下来以免他忘记了。
六、结果状语从句
通常由连词that, so that, so...that, such...that 引导。
so...that和such...that引导的结果状语从句都表示主句的动作或状态达到一定程度而引起的结果。上一页1.so是副词,用来修饰形容词、副词、分词或其他结构。such是形容词,用来修饰名词(可数或不可数名词)或名词短语,但名词被many, much, few, little(小)等修饰时要用so。
There were so many people in the room that we couldn't get in.屋里有这么多人以致于我们进不去。
So badly was he injured that he had to go to the hospital.
他伤得如此严重,不得不去医院。(so位于句首时,主句的语序须倒装)
He told us such a funny story that we all laughed.
他讲了个如此有趣的故事,以致于我们都笑了。上一页2.such修饰单数可数名词且名词前有形容词时,可用so替换such,冠词与形容词交换位置,构成“so+adj.+a (an)+名词”。
上面的句子可写成:
He told us so funny a story that we all laughed.
他讲了个如此有趣的故事,以致于我们都笑了。上一页七、条件状语从句
1.通常由if, unless,as(so) long as, in case (that) 等连词引导。
If he is not in the office, he must be out for lunch.
如果他不在办公室,那他一定出去吃午饭了。
I'll lend it to you as long as you handle it with care.
只要你小心使用,我会借给你。
In case anything important happens, please call me up.
万一发生了什么重要事情,请打电话给我。上一页2.if only常表示愿望或未实现的条件,尤用于感叹句。表示“但愿;要是……就好了”。
If only he arrives in time! 但愿他及时到达!
If only I had met him earlier!要是能早遇见他就好了!
3.由on condition (that);provided (that);providing (that);supposing (that)等引导的条件状语从句。
You can go swimming on condition that you don't go too far from the river bank.只要不离河岸太远你就能下去游泳。
I'll go providing (provided that) my wages are paid.上一页如果发了工资我就去。
Supposing it rains tomorrow, what shall we do?
假设明天下雨我们做什么?
4.条件状语从句中的省略情况:
在条件状语从句中,如果条件状语从句的主语同主句主语一致或是无人称代词,从句的谓语动词是be时,可将从句的主语和动词be一起省略。
If (I am) invited, I'll go.如果被邀请,我就去。
If (it is) important, I'll write this article.
如果重要,我就写这篇作文。上一页八、方式状语从句
通常由as, as if, as though引导。
You must do the exercise as I show you.
你必须按我给你展示的方式做练习。
I'll do as I'm told to.我将按别人告诉我的方式做。
as if, as though 引导的状语从句,多描述非现实情况,应用虚拟语气,但口语中也有用陈述语气的。
He walked as if he were(was) drunk.
他走起路来就像喝醉了似的。
He walked slowly as if(though) he had hurt his leg.
他慢慢地走好像腿受伤了。上一页上一页九、比较状语从句
通常由as...as, not so(as)...as, than等引导。
His brother is as handsome as he (him).
他的哥哥和他一样帅。
The film was not so(as) good as I had expected.
这部电影比我期望得差。
He swims faster than any other student in his class.
他比班里其他任何同学都游得快。 1.as和than引导的比较状语从句常常省去与主句中相同 的部分,只留下相比较的部分。
She looks far older than she is.她看上去比实际年龄大好多。
It's generally more expensive to travel by plane than by train.
一般乘飞机旅行比乘火车要贵得多。上一页2. 比较状语从句中应注意被比较内容的一致。
The weather here is hotter than that(=the weather) in your hometown.
不能说:The weather here is hotter than your hometown.
此句中所比较的对象主体是weather,而than所引出的被比较对象是your hometown,这样被比较的内容不一致。上一页
1.as,when,while用法一览表上一页2.引导时间状语从句的连接词除上述三者外还有:
(1)till, not...until..., until, before, since
He waited for his father until(till) it was twelve o'clock.
他等他父亲一直到12点钟。
Don't get off the bus until it has stopped.车停稳了再下车。
It will be five years before he returns from England.
要五年后他才会从英国回来 (2)hardly/scarcely...when, no sooner...than, as soon as, once表示“一……就”
We had hardly got/Hardly had we got into the country when it began to rain.我们一到这个国家就开始下雨。
No sooner had he arrived/He had no sooner arrived than she started complaining.
他一到她就开始抱怨。
As soon as I have finished it, I'll give you a call.
我一完成就给你打电话。
Once you show any fear, he will attack you.
一旦你表现出恐惧,他就会攻击你。上一页(3)directly, immediately, the moment, the minute that...表示“一……就”
Directly the teacher came in everyone was quiet.
老师一进来,大家就安静了下来。
I recognized her immediately I saw her.
我一看见她就认出她来了。
(4)each time, every time, by the time
Each time he came to my city, he would call on me.
他每次来我所在的城市都会来拜访我。上一页上一页表示未来的情况时,主句用将来时,从句用现在时。
She will go to her uncle's when she arrives in America.
当她到美国时,她将会去她叔叔家。二、让步状语从句
1.although与though可以引导让步状语从句,不能与but连用,但可以与yet连用。
Although they are poor,(yet) they are warm-hearted.
尽管他们穷,但却很热心。
2.even if或even though引导让步状语从句,表示“即使;纵然”,用来使人注意下文所强调内容的性质。
I'll get there even if (though) I have to sell my house to get enough money to go by air.
我会去那里的,即使我不得不卖掉房子来凑够钱乘飞机去。上一页上一页3.no matter+疑问词(who,what,where,how等)=who, what, where, how等+ever构成whoever,whatever,wherever,however等,表示“无论……”。
Don't trust him, no matter what/whatever he says.
不管他说什么,都不要相信他。
Whoever breaks the law will be published.
任何触犯法律的人都要受到惩罚。
No matter how hard the work is, you'd better try to do it well.不管这个工作多么困难,你最好尽力做好。上一页4.as也可以引导让步状语从句,但从句要用倒装结构。
Child as(though) he is, he knows a lot.
尽管他是一个孩子,懂得却很多。
Much as I like it, I won't buy.
尽管我很喜欢,但我不会买。上一页三、原因状语从句
通常由because, for, as, since, now that, seeing(that), considering that等引导。
The woolly shrank because it was washed badly.
羊毛衣因洗得不得法而缩水。
Since(As) we've no money, we can't buy it.
由于我们没钱,我们无法购买它。
He could not have seen me, for I was not there.
他不可能见过我,因为我不在那里。上一页Now that you are here, you'd better stay.
你既然来了,最好还是留下吧(既来之,则安之)。
Seeing that it's raining outside, we'd better stay indoors.
既然外边在下雨,我们最好待在室内。
Considering (that) everybody is here, let's begin our discussion.
既然大家都到了,我们就开始讨论吧。上一页1.表示不知道的原因
(1)用because,即说话人认为听话人不知道,因此because从句是全句最重要的部分,通常它被置于主句之后。
You want to know why I'm leaving? I'm leaving because I'm full.你想知道我为什么想离开吗?我离开是因为我吃饱了。
(2)for虽然也表示不知道的原因,但其语气较because要弱得多,是可说可不说的话,它只能置于主句之后,这时,for是并列连词。如果不是因果关系,而是对前面主句的内容加以解释或推断时,只能用for。It's morning now, for the birds are singing.
现在应该是早晨了,因为鸟儿在歌唱。(很显然,鸟叫不可能是“现在已是早上”的原因。)
2.表示已经知道的原因
用as或since,即某种原因在说话人看来已经很明显,或已为听话人所熟悉,因此它是句中不很重要的部分。since要比as正式一些,它们通常被置于主句之前,但有时却相反。上一页Since (As) it is raining,you'd better take a taxi.
下雨了,你最好乘出租车。
Seeing all of the children already seated, he said,“Since everyone is here, let's start.”
看到所有的孩子都就座了,他说:“既然都到了,我们开始吧。”上一页3.只能使用because的情况
(1)在回答why的问句时
—Why did you leave so early?—你昨天怎么离开得那么早?
—Because I had a headache.——因为我头疼。
(2)用于强调句型时
It was because he was ill that he didn't go with us.
他是因为生病了才没跟我们一起去。
(3)被not否定时
You shouldn't get angry just because some people speak ill of you.你不要因为有人说你坏话就生气。上一页四、地点状语从句
通常由where, wherever等引导。
Make a mark wherever you have any questions.
在你有问题的地方做个记号。
Where there's plenty of sun and rain,the fields are green.
哪里阳光雨水充足,哪里的田野就绿油油的。上一页五、目的状语从句
通常由that, so that, in order that, in case, for fear that等引导。谓语动词常与may (might), can (could), should, will等情态动词连用,否则可能是结果状语从句,不可置于句首。
They stopped at Hangzhou in order that they could go around West Lake.他们在杭州停了下来,以便游览西湖。
Say it louder (so) that everyone can hear you.
大声说,以便大家都能听到你的声音。上一页You'd better take more clothes in case the weather is cold.
你最好多带些衣服以防天气太冷。
He wrote the name down for fear that he should forget it.
他把名字写下来以免他忘记了。
六、结果状语从句
通常由连词that, so that, so...that, such...that 引导。
so...that和such...that引导的结果状语从句都表示主句的动作或状态达到一定程度而引起的结果。上一页1.so是副词,用来修饰形容词、副词、分词或其他结构。such是形容词,用来修饰名词(可数或不可数名词)或名词短语,但名词被many, much, few, little(小)等修饰时要用so。
There were so many people in the room that we couldn't get in.屋里有这么多人以致于我们进不去。
So badly was he injured that he had to go to the hospital.
他伤得如此严重,不得不去医院。(so位于句首时,主句的语序须倒装)
He told us such a funny story that we all laughed.
他讲了个如此有趣的故事,以致于我们都笑了。上一页2.such修饰单数可数名词且名词前有形容词时,可用so替换such,冠词与形容词交换位置,构成“so+adj.+a (an)+名词”。
上面的句子可写成:
He told us so funny a story that we all laughed.
他讲了个如此有趣的故事,以致于我们都笑了。上一页七、条件状语从句
1.通常由if, unless,as(so) long as, in case (that) 等连词引导。
If he is not in the office, he must be out for lunch.
如果他不在办公室,那他一定出去吃午饭了。
I'll lend it to you as long as you handle it with care.
只要你小心使用,我会借给你。
In case anything important happens, please call me up.
万一发生了什么重要事情,请打电话给我。上一页2.if only常表示愿望或未实现的条件,尤用于感叹句。表示“但愿;要是……就好了”。
If only he arrives in time! 但愿他及时到达!
If only I had met him earlier!要是能早遇见他就好了!
3.由on condition (that);provided (that);providing (that);supposing (that)等引导的条件状语从句。
You can go swimming on condition that you don't go too far from the river bank.只要不离河岸太远你就能下去游泳。
I'll go providing (provided that) my wages are paid.上一页如果发了工资我就去。
Supposing it rains tomorrow, what shall we do?
假设明天下雨我们做什么?
4.条件状语从句中的省略情况:
在条件状语从句中,如果条件状语从句的主语同主句主语一致或是无人称代词,从句的谓语动词是be时,可将从句的主语和动词be一起省略。
If (I am) invited, I'll go.如果被邀请,我就去。
If (it is) important, I'll write this article.
如果重要,我就写这篇作文。上一页八、方式状语从句
通常由as, as if, as though引导。
You must do the exercise as I show you.
你必须按我给你展示的方式做练习。
I'll do as I'm told to.我将按别人告诉我的方式做。
as if, as though 引导的状语从句,多描述非现实情况,应用虚拟语气,但口语中也有用陈述语气的。
He walked as if he were(was) drunk.
他走起路来就像喝醉了似的。
He walked slowly as if(though) he had hurt his leg.
他慢慢地走好像腿受伤了。上一页上一页九、比较状语从句
通常由as...as, not so(as)...as, than等引导。
His brother is as handsome as he (him).
他的哥哥和他一样帅。
The film was not so(as) good as I had expected.
这部电影比我期望得差。
He swims faster than any other student in his class.
他比班里其他任何同学都游得快。 1.as和than引导的比较状语从句常常省去与主句中相同 的部分,只留下相比较的部分。
She looks far older than she is.她看上去比实际年龄大好多。
It's generally more expensive to travel by plane than by train.
一般乘飞机旅行比乘火车要贵得多。上一页2. 比较状语从句中应注意被比较内容的一致。
The weather here is hotter than that(=the weather) in your hometown.
不能说:The weather here is hotter than your hometown.
此句中所比较的对象主体是weather,而than所引出的被比较对象是your hometown,这样被比较的内容不一致。上一页
