初中英语各大类词知识及考试要点学案
图片预览
文档简介
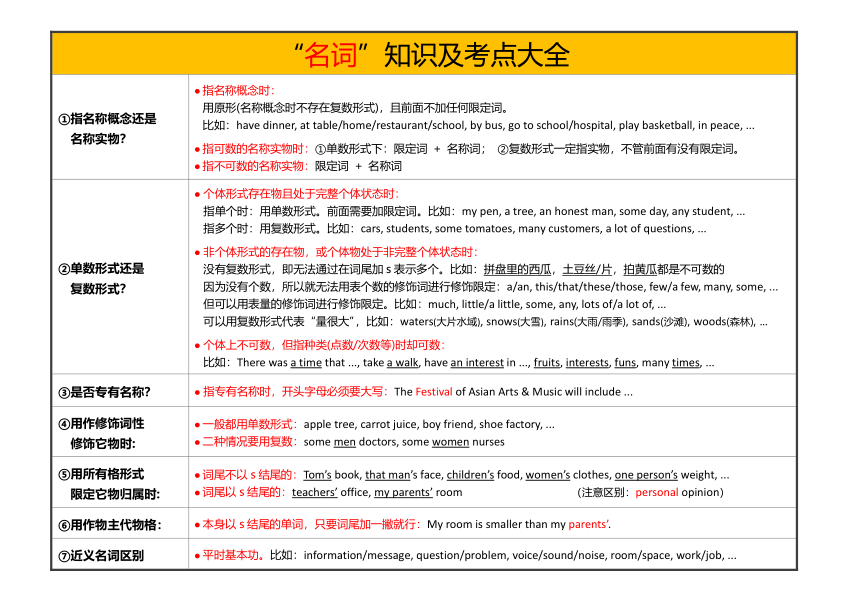
“名词”知识及考点大全
①指名称概念还是 名称实物? 指名称概念时: 用原形(名称概念时不存在复数形式),且前面不加任何限定词。 比如:have dinner, at table/home/restaurant/school, by bus, go to school/hospital, play basketball, in peace, ... 指可数的名称实物时:①单数形式下:限定词 + 名称词; ②复数形式一定指实物,不管前面有没有限定词。 指不可数的名称实物:限定词 + 名称词
②单数形式还是 复数形式? 个体形式存在物且处于完整个体状态时: 指单个时:用单数形式。前面需要加限定词。比如:my pen, a tree, an honest man, some day, any student, ... 指多个时:用复数形式。比如:cars, students, some tomatoes, many customers, a lot of questions, ... 非个体形式的存在物,或个体物处于非完整个体状态时: 没有复数形式,即无法通过在词尾加s表示多个。比如:拼盘里的西瓜,土豆丝/片,拍黄瓜都是不可数的 因为没有个数,所以就无法用表个数的修饰词进行修饰限定:a/an, this/that/these/those, few/a few, many, some, ... 但可以用表量的修饰词进行修饰限定。比如:much, little/a little, some, any, lots of/a lot of, ... 可以用复数形式代表“量很大”,比如:waters(大片水域), snows(大雪), rains(大雨/雨季), sands(沙滩), woods(森林), ... 个体上不可数,但指种类(点数/次数等)时却可数: 比如:There was a time that ..., take a walk, have an interest in ..., fruits, interests, funs, many times, ...
③是否专有名称? 指专有名称时,开头字母必须要大写:The Festival of Asian Arts & Music will include ...
④用作修饰词性 修饰它物时: 一般都用单数形式:apple tree, carrot juice, boy friend, shoe factory, ... 二种情况要用复数:some men doctors, some women nurses
⑤用所有格形式 限定它物归属时: 词尾不以s结尾的:Tom’s book, that man’s face, children’s food, women’s clothes, one person’s weight, ... 词尾以s结尾的:teachers’ office, my parents’ room (注意区别:personal opinion)
⑥用作物主代物格: 本身以s结尾的单词,只要词尾加一撇就行:My room is smaller than my parents’.
⑦近义名词区别 平时基本功。比如:information/message, question/problem, voice/sound/noise, room/space, work/job, ...
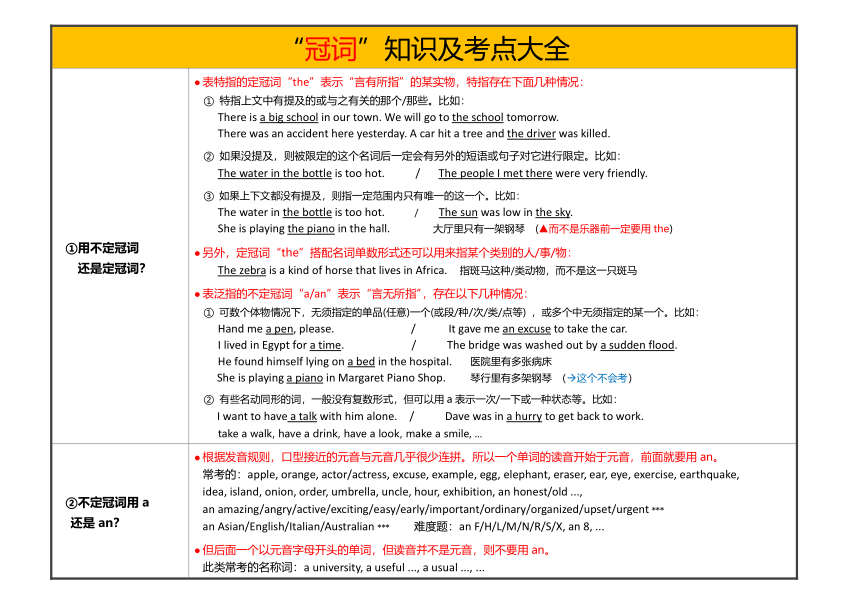
“冠词”知识及考点大全
①用不定冠词 还是定冠词? 表特指的定冠词“the”表示“言有所指”的某实物,特指存在下面几种情况: ① 特指上文中有提及的或与之有关的那个/那些。比如: There is a big school in our town. We will go to the school tomorrow. There was an accident here yesterday. A car hit a tree and the driver was killed. ② 如果没提及,则被限定的这个名词后一定会有另外的短语或句子对它进行限定。比如: The water in the bottle is too hot. / The people I met there were very friendly. ③ 如果上下文都没有提及,则指一定范围内只有唯一的这一个。比如: The water in the bottle is too hot. / The sun was low in the sky. She is playing the piano in the hall. 大厅里只有一架钢琴 (▲而不是乐器前一定要用the) 另外,定冠词“the”搭配名词单数形式还可以用来指某个类别的人/事/物: The zebra is a kind of horse that lives in Africa. 指斑马这种/类动物,而不是这一只斑马 表泛指的不定冠词“a/an”表示“言无所指”,存在以下几种情况: ① 可数个体物情况下,无须指定的单品(任意)一个(或段/种/次/类/点等) ,或多个中无须指定的某一个。比如: Hand me a pen, please. / It gave me an excuse to take the car. I lived in Egypt for a time. / The bridge was washed out by a sudden flood. He found himself lying on a bed in the hospital. 医院里有多张病床 She is playing a piano in Margaret Piano Shop. 琴行里有多架钢琴 (这个不会考) ② 有些名动同形的词,一般没有复数形式,但可以用a表示一次/一下或一种状态等。比如: I want to have a talk with him alone. / Dave was in a hurry to get back to work. take a walk, have a drink, have a look, make a smile, ...
②不定冠词用a 还是an? 根据发音规则,口型接近的元音与元音几乎很少连拼。所以一个单词的读音开始于元音,前面就要用an。 常考的:apple, orange, actor/actress, excuse, example, egg, elephant, eraser, ear, eye, exercise, earthquake, idea, island, onion, order, umbrella, uncle, hour, exhibition, an honest/old ..., an amazing/angry/active/exciting/easy/early/important/ordinary/organized/upset/urgent *** an Asian/English/Italian/Australian *** 难度题:an F/H/L/M/N/R/S/X, an 8, ... 但后面一个以元音字母开头的单词,但读音并不是元音,则不要用an。 此类常考的名称词:a university, a useful ..., a usual ..., ...
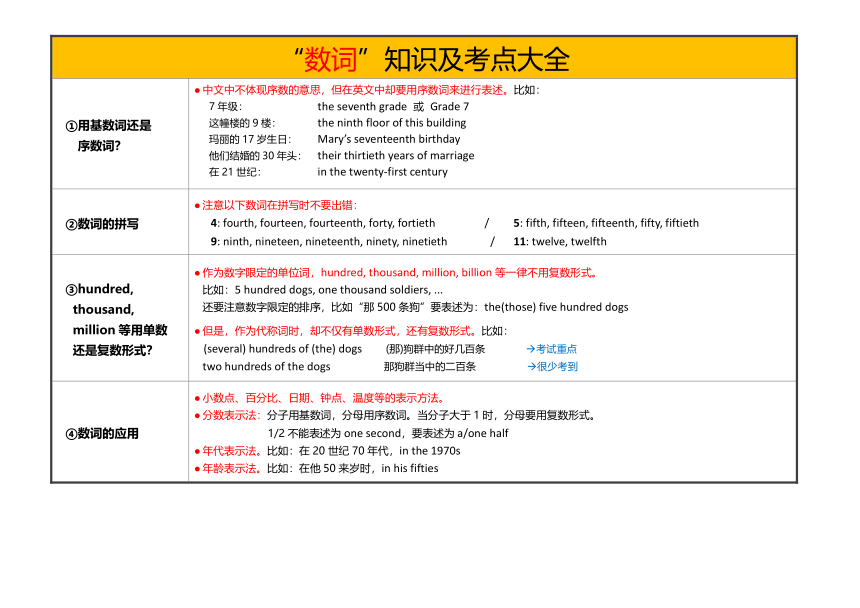
“数词”知识及考点大全
①用基数词还是 序数词? 中文中不体现序数的意思,但在英文中却要用序数词来进行表述。比如: 7年级: 这幢楼的9楼: 玛丽的17岁生日: 他们结婚的30年头: 在21世纪:the seventh grade 或 Grade 7 the ninth floor of this building Mary’s seventeenth birthday their thirtieth years of marriage in the twenty-first century
②数词的拼写 注意以下数词在拼写时不要出错: 4: fourth, fourteen, fourteenth, forty, fortieth / 5: fifth, fifteen, fifteenth, fifty, fiftieth 9: ninth, nineteen, nineteenth, ninety, ninetieth / 11: twelve, twelfth
③hundred, thousand, million等用单数 还是复数形式? 作为数字限定的单位词,hundred, thousand, million, billion等一律不用复数形式。 比如:5 hundred dogs, one thousand soldiers, ... 还要注意数字限定的排序,比如“那500条狗”要表述为:the(those) five hundred dogs 但是,作为代称词时,却不仅有单数形式,还有复数形式。比如: (several) hundreds of (the) dogs (那)狗群中的好几百条 考试重点 two hundreds of the dogs 那狗群当中的二百条 很少考到
④数词的应用 小数点、百分比、日期、钟点、温度等的表示方法。 分数表示法:分子用基数词,分母用序数词。当分子大于1时,分母要用复数形式。 1/2不能表述为one second,要表述为a/one half 年代表示法。比如:在20世纪70年代,in the 1970s 年龄表示法。比如:在他50来岁时,in his fifties
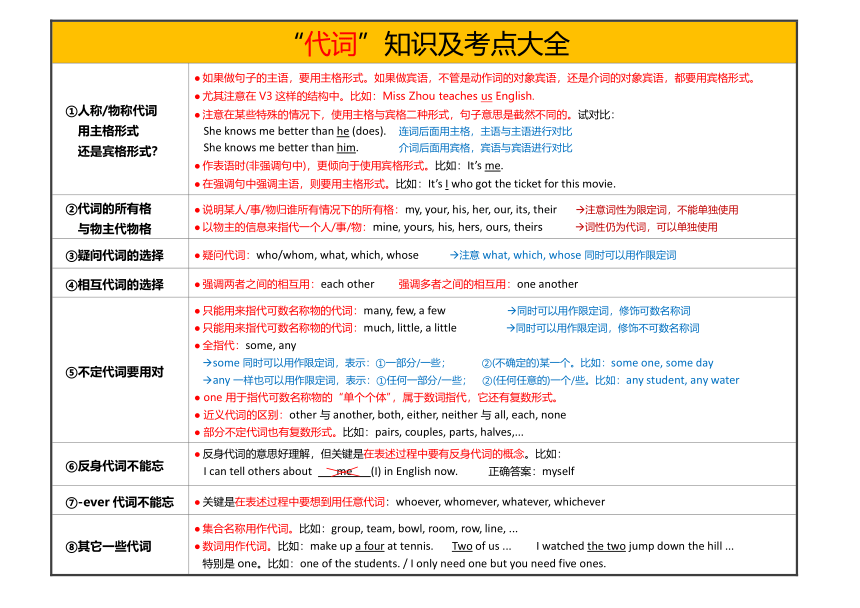
“代词”知识及考点大全
①人称/物称代词 用主格形式 还是宾格形式? 如果做句子的主语,要用主格形式。如果做宾语,不管是动作词的对象宾语,还是介词的对象宾语,都要用宾格形式。 尤其注意在V3这样的结构中。比如:Miss Zhou teaches us English. 注意在某些特殊的情况下,使用主格与宾格二种形式,句子意思是截然不同的。试对比: She knows me better than he (does). 连词后面用主格,主语与主语进行对比 She knows me better than him. 介词后面用宾格,宾语与宾语进行对比 作表语时(非强调句中),更倾向于使用宾格形式。比如:It’s me. 在强调句中强调主语,则要用主格形式。比如:It’s I who got the ticket for this movie.
②代词的所有格 与物主代物格 说明某人/事/物归谁所有情况下的所有格:my, your, his, her, our, its, their 注意词性为限定词,不能单独使用 以物主的信息来指代一个人/事/物:mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs 词性仍为代词,可以单独使用
③疑问代词的选择 疑问代词:who/whom, what, which, whose 注意what, which, whose同时可以用作限定词
④相互代词的选择 强调两者之间的相互用:each other 强调多者之间的相互用:one another
⑤不定代词要用对 只能用来指代可数名称物的代词:many, few, a few 同时可以用作限定词,修饰可数名称词 只能用来指代可数名称物的代词:much, little, a little 同时可以用作限定词,修饰不可数名称词 全指代:some, any some同时可以用作限定词,表示:①一部分/一些; ②(不确定的)某一个。比如:some one, some day any一样也可以用作限定词,表示:①任何一部分/一些; ②(任何任意的)一个/些。比如:any student, any water one用于指代可数名称物的“单个个体”,属于数词指代,它还有复数形式。 近义代词的区别:other与another, both, either, neither与all, each, none 部分不定代词也有复数形式。比如:pairs, couples, parts, halves,...
⑥反身代词不能忘 反身代词的意思好理解,但关键是在表述过程中要有反身代词的概念。比如: I can tell others about me (I) in English now. 正确答案:myself
⑦-ever代词不能忘 关键是在表述过程中要想到用任意代词:whoever, whomever, whatever, whichever
⑧其它一些代词 集合名称用作代词。比如:group, team, bowl, room, row, line, ... 数词用作代词。比如:make up a four at tennis. Two of us ... I watched the two jump down the hill ... 特别是one。比如:one of the students. / I only need one but you need five ones.
“动词”知识及考点大全(一)
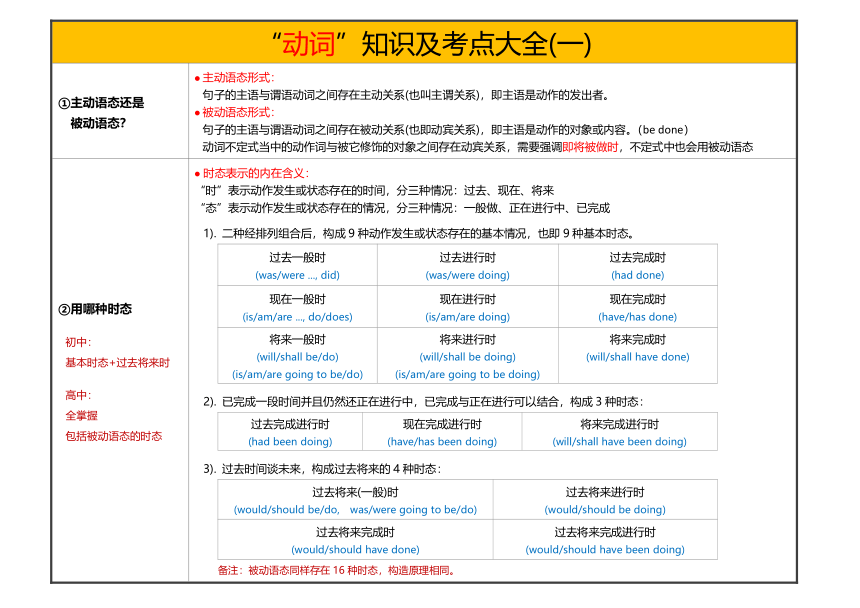
①主动语态还是 被动语态? 主动语态形式: 句子的主语与谓语动词之间存在主动关系(也叫主谓关系),即主语是动作的发出者。 被动语态形式: 句子的主语与谓语动词之间存在被动关系(也即动宾关系),即主语是动作的对象或内容。(be done) 动词不定式当中的动作词与被它修饰的对象之间存在动宾关系,需要强调即将被做时,不定式中也会用被动语态
②用哪种时态 初中: 基本时态+过去将来时 高中: 全掌握 包括被动语态的时态 时态表示的内在含义: “时”表示动作发生或状态存在的时间,分三种情况:过去、现在、将来 “态”表示动作发生或状态存在的情况,分三种情况:一般做、正在进行中、已完成 1). 二种经排列组合后,构成9种动作发生或状态存在的基本情况,也即9种基本时态。 过去一般时 (was/were ..., did)过去进行时 (was/were doing)过去完成时 (had done)现在一般时 (is/am/are ..., do/does)现在进行时 (is/am/are doing)现在完成时 (have/has done)将来一般时 (will/shall be/do) (is/am/are going to be/do)将来进行时 (will/shall be doing) (is/am/are going to be doing)将来完成时 (will/shall have done)
2). 已完成一段时间并且仍然还正在进行中,已完成与正在进行可以结合,构成3种时态: 过去完成进行时 (had been doing)现在完成进行时 (have/has been doing)将来完成进行时 (will/shall have been doing)
3). 过去时间谈未来,构成过去将来的4种时态: 过去将来(一般)时 (would/should be/do, was/were going to be/do)过去将来进行时 (would/should be doing)过去将来完成时 (would/should have done)过去将来完成进行时 (would/should have been doing)
备注:被动语态同样存在16种时态,构造原理相同。
“动词”知识及考点大全(二)
③三单(主谓一致原则) 一般现在时情况下:主语为第三人称单数时,谓语动词要用三单形式。 要用:is/was ..., has ..., does ... 第三人称单数还包括: 不可数名词、动名词的单数形式、不定式短语、主语从句、2及以上的纯数字都看作是单数 另外:一段时间或一个数额当作单个整体不看作多个数量时、“many a...”或“more than one…”修饰一个名词单数时、 “both…and…”连接二个名词时但指一个人时、“either...or...”或“neither…nor…”结构中后面这个是单数时。 其它情况: 有些集称名词就指群体,我们将它们看作是复数的。 有些集称名词,把它视为一个整体时是单数的,视为全体成员时是复数的。 “a number of ...”视为复数形式;“the number of ...”视为单数形式 “限定词+形容词”构成的名称,指可数名称物的多个时是复数的;指单个或不可数名称词时是单数的。 一般来说,“one of ...”后定从中,作为主语的引导词一般指复数。但“the only one of ...”后面定从,引导词视为复数。 主语有二物,且第一个为“a/an ...”,倒装句there be一般使用“is”(就近原则),介词短语倒装则使用“are”。
④动词的句职功能: 除非将动作词及其词组短语当作名称,否则它在句子当中只可以充当谓语。 不可以当作主语用。比如不可以说:Swim is my favourite. X 不可以当作宾语用。比如不可以说:I like swim. X 不可以当表语(或表述语)用,将is/am/are与do连在一起。比如不可以说: He is/was do ... X Is/Was he do ... X 一个句子或动词短语结构中,如果出现二个动作动词,要么用连词并列连接,要么将另外一个动词改成非谓语动词。 比如不可以说:go swim X 只能说成:go to swim, go swimming 见非谓语动词部分:动名词、不定式、现在分词、过去分词
“动词”知识及考点大全(三)
⑤一般助动词与情态 助动词后要用原形: 一般助动词do/does/did后要用动词原形 比如:They do know the secret. / Does he know the secret 绝大情态助动词后要用动词原形(除去have to do, ought to do) 比如:He can jump very high. / He may go with us. 其它几个类似于助动词的词后要用动词原形(除去used to do) 比如:Let’s help sweep the floor. / We’d better go now. / Kids would rather play than study.
⑥及物与不及物问题: 及物动词后可以直接跟宾语,但不及物动词则不可以。 区分及物与不及物最常考的有:arrive/reach/get, rise/raise/lift, go/enter, look/see, 不及物动词:agree, laugh 不定式短语作后置定语,如果其中的动作词为不及物动词,注意一定要搭配上合适的介词。 比如:They can’t find a room to live in. 定语从句限定一个名称词,如果其中的动作词为不及物动词,注意一定要搭配上合适的介词。 比如:They can’t find a room which they can live in. 就算是及物动词,但如果它跟被修饰的词不存在动宾关系,也要加上介词,以“介宾关系”来修饰说明该动作: 比如:Mr. Smith, from whom I have learned a lot, is a famous scientist. ..The driver was the man from whose room she had stolen the maps.
⑦行为动词还是 结果动词? 动作动词不要当结果动词用。比如不可以说:She listened that he was active about some business. X 有些动作词是强调动作行为的,如:look, watch, listen, … 有些动作词是强调动作结果的,如:see, meet, hear, …
“动词”知识及考点大全(四)
⑧延续性动作词还是 短暂性动作词? 延续性动作词可以跟一段时间连用(for ..., until ...): 比如说:I would like to stay here for two days. / I will stay here till 6 o’clock. I have borrowed this book and also have kept it for 10 days. 短暂性动作词不可以跟一段时间搭配连用: 比如不可以说:All the kids started to have dinner till 8 o’clock. X 但短暂性动作词的否定形式则可以延续,因此可以跟一段时间连用: 比如可以说: All the kids didn’t start to have dinner till 8 o’clock. 尤其是在完成时情况下,短暂性动作时不可以跟一段时间搭配连用: 比如可以说:I haven’t heard from my friend in Africa since he left. / I haven’t met him for a long time. 但不可以说: I have heard from my friend in Africa for a long time. X / I have met him for a long time. X 常见的短暂性动作词有: become, borrow, lend, buy, sell, join, open, die, close, start, begin, finish, come, reach, go, move, return, arrive, leave, marry, join, happen, meet, hear from, … 常考的: borrow, lend, buy, sell, join, marry, die, ...
⑨情态助动词 近义情态助动词的区别;情态助动词与动作动词的区别(need, dare) 情态助动词的否定。尤其是mustn’t 情态助动词用于虚拟语气。 高中阶段要求掌握
⑩近义动词及词组 的区别: 掌握单词的基本义,及其相关引申义: 常考的有:say/speak/talk/tell, spend/take/pay/cost, remember/remind, forget/leave, receive/accept, lie/lie/lay, attend/join/join in/take part in, send/post/deliver, find/find out/discover, make/produce, ... 在掌握动词基本义/引申义的基础上,结合介词与副词的基本义,用英文思维理解动词词组的基本义与引申义。 高频率使用的几个动作词:make, take, set, get, turn, give, go, ... 高频率使用的介词或副词:in, on, out, over, at, to, from, up, down, for, with, along, about, of, off, away, after, ... 当然,也可采用死记硬背的方式,尤其是那些与中文思维不太相同的表述。
⑾动词与介词或副词 的搭配问题
“形容词、副词”知识及考点大全
①用比较/最高级? 要注意是否要使用比较级或最高级,尤其是在隐性比较的情况下
②要用反义词吗? 特别要注意,在使用修饰词的时候是否该用反义词
③是否要后置? 修饰不定代词后置:something enough, anything important, /nothing more, someone else/here/there, what else, ... 表述性的形容词后置:people here/there, soldiers still alive, any way possible, ... 程度副词enough要放在被修饰词的后面:… good enough
④形容词还是副词? 形容词跟名称词发生关系,副词用来修饰说明动作词谓语或系表结构谓语 正确区分“系动动词 + 形容表述语”与“动作词谓语 + 修饰性状语副词”两种不同的结构 部分省略了介词的名词及其短语兼有副词:today, tomorrow, next year, here, there, ... 形容词及其短语/分词用作表述性状语 见非谓语动词部分,高中阶段要求掌握
⑤比较注意事项 A跟B群中任何一个人比较的时候,如果A属于B群中,要将自己排除在外。用any other(s) The more ..., the more ...结构 比较必须基于同物比较:The climate in Beijing is worse than that in Hangzhou. Salaries are higher here than those in my country. one of 后面的名称物一定要用复数形式。比如:one of the students
⑥形容词或短语 指代名称 限定词 + 形容词: 指单个:John is the shorter of the. / I don’t want the black pen. I want the blue. / the easiest of all / the first/second, ... 指一类:the rich/young/poor/honest, those wounded, … 也可以用复数形式:the youngs, some olds, Eight Strongs, those blacks, all the livings, … 单个形容词或分词指代名称:try to cash in big, than expected, as (what’s) reported/written/told, ... 形容词性与名称词性同形:Enough has been done ..., a car of my own, It’s my favourite., We are Chinese, ...
⑦副词特殊句式 so (形容词或副词原形)... that ...句式结构,注意区分:such (名词短语) that ... 感叹句“How + 形容词/副词原形”结构,“What+ 名词短语”结构:What good news! What fine weather!
⑧修饰不定式与 介词短语的副词 修饰介词短语:right in the room, high in the sky, badly in need of ..., shortly after us, deep in conversation with ..., ... 修饰不定式短语:... is just about to do, ... are likely to be expensive, ... came here just(only) to say goodbye ...
“非谓语词”知识及考点大全(一)
注意事项 使用动词现在分词,还是过去分词? 使用动名词,还是不定式短语? 使用不定式短语,还是分词?
①动名词 动名词的含义: ①动作对应的名称叫法(相当于这个动作行为)。比如:swimming指游泳这种动作行为 ②动作过程(相当于这件事)。比如:swimming指游泳这件事 ③部分动作会有结果产物。比如:building还可以指建筑物 句职功能: 做主语:Swimming is his hobby. / It is no use learning theory without practice. 使用it做形式主语 做表语或补足语:His hobby is swimming. We call it hiking. It is called hiking. (主补) 做动词宾语:I like swimming. 做介词宾语:She is afraid of going out at night alone. 介词后面必须要用动名词形式 做定语:a swimming pool (=a pool for swimming) a harming effect (= an effect about harming) 做同位语:He is looking for a job, repairing cars. 需要跟动名词做宾语的动词及词组: practice, enjoy, prefer, advise, suggest, consider, finish, mind, allow, avoid, appreciate, imagine, deny, complete, dislike, mention, resist, miss, forbid, risk, keep (on), can’t help, can’t stand, look forward to, pay attention to, give up, ... 动名词的逻辑主语一般用所有格。Thanks for your coming. Your calling back will be highly appreciated. 动名词的否定:前面直接加not. His not knowing English gets him a lot of trouble. 也有用no的:There is no denying the fact that he is diligent. No Parking.
“非谓语动词”知识及考点大全(二)
①不定式短语 不定式短语的含义: ①名称词性:“接下来要去做”的一个动作或一件事 ②名称表述词性:(属)接下来要去做的一个动作或一件事 ③名称限定词性:针对某个名称物,接下来要去怎么样的 ③动作修饰词性:a.表目的:目的为了接下去干嘛;b.表结果:结果导致下一个动作行为;c.表原因程度等等 句职功能: 做主语:To have a swim is a good idea. / It is important for you to learn English well. 使用it做形式主语 做宾语:He decided to buy a new car. / I want to have a swim now. 同位语:My wish to visit France finally comes true. 做表语:My wish is to visit France. / He is to cry. / seem to be impossible / appear to be a fine fellow 做补足语:带to:My neighbor invited me to join their party. / They are asked to live on campus. (主补) .不带to:Let’s go. / ... have me clean the room. (feel/hear/see/notice/have/let/make sb. do sth.) 做定语:The next train to arrive is from Washington. / I am looking for a room to live in. (注意搭配) 做状语:They came here just to say good bye. / Let’s go to have a drink. / We did what we could to help you. 需要跟不定式做宾语的动词: need, dare, seem, ask, wish, hope, plan, require, want, pretend, decide, choose, agree, refuse, promise, expect, prepare, become, afford, attempt, offer, swear, tend, demand, determine, hesitate, volunteer, manage, would like to do, make up one’s mind to do, ... 不定式与动名词做宾语的区别: try to do try doing like to do like doing fail to do fail doing go on to do go on doingstop to do stop doing forget to do forget doingremember to do remember doing regret to do regret doingused to do be used to doing be used to do
特殊表述结构中:too weak to do..., do nothing but do, have nothing to do but do, have no choice but to do, ... “特殊”不定式短语:how to do it, what to do, when to start, where to go, whether to leave or stay there, ... 不定式短语用在V4结构中,必须要用it指代:I have made it a rule to keep diaries. / ... take it for granted that ... 不定式的否定:前面直接加not. I was being so foolish not to follow your advice. 不定式的逻辑主语:It will be very easy for you to work it out. / It’s very kind of you to tell me the truth. 高中生还需要注意不定式当中的时态
“非谓语动词”知识及考点大全(三)
③现在分词 现在分词的含义: ①处于正在进行的状态中 比如:Stop! You are hurting me. 你正处于搞疼我的状态中 ②逻辑主语跟这个动作存在主谓关系 你把我搞疼 现在分词的句职功能: 做表语:He is crying in the car. 进行时结构,表示正处于做...的状态中 Growing all over the hills and around the lake are wild flowers of different colors. 表语提前倒装,用以强调 ◆系动动词+表语:seem interesting/exciting ... 宾语补足语:We found him crying in the car. / Can you hear her singing the song in the next room 主语补足语:He was often seen watching plants closely ... 做定语,前置:a developing country, a sleeping baby, a swimming girl (= a girl who is sleeping) 修饰不定代词后置:nothing interesting, ... 短语后置:the man standing there, ... 做状语:(While we were) Following our coach, we got on the coach. / Let’s go shopping. Being very tired, he still continued his working. / Having finished the work, the children went out to play. He stayed at home, (while) cleaning and washing. / Things get out of hand ..., putting her in the spotlight. ◆表述性状语,形容词性与副词性存在模糊性。这一点跟形容词做表述性状语同。 句转短语表述 比如:He returned from war, safe and sound. / Crusoe stared at the footprint, full of fear. 完成时结构下的现在分词:Having finished the work, the children went out to play. 现在分词的否定:Not being able to get the ticket, he left away. .Not having finished the homework, the children were not allowed to play football. 现在分词的逻辑主语用主格形式:I waiting for the bus, a bird fell on my head. Time permitting, we’ll do another two exercises. 现在分词等同于介词:Cassie went into the room, following her teacher. 要考虑逻辑关系,分清用现在分词还是过去分词 不考虑逻辑关系的:Generally speaking, the more you pay, the more you get. / She’s very active, considering her age. .I’ve got a three-day holiday including today. / It typically takes a day or two, depending on size.
“非谓语动词”知识及考点大全(四)
④过去分词 过去分词的含义: ①动作已经完成(强调动作性,与have搭配构成完成时) ②被怎么样(强调动作性,用于被动语态),主语跟这个动作存在动宾关系 ③处于已经被怎么样了的状态中(表述状态),逻辑主语跟这个动作存在动宾关系 过去分词的句职功能: 与have一起做谓语,表示已完成。比如:We have seen the film. 完成时结构 做表语:This novel was written by Hemingway. 被动语态结构,强调动作 We are interested in this story. / The window is broken. 被动语态结构,表述状态 Gone are the days when you could do anything you wanted. 表语提前倒装,用以强调 ◆系动动词+表语:get paid/married/annoyed/interested ..., feel comforted/disappointed ..., look worried/excited, ... 宾语补足语:She found her shoes stolen. / It isn’t worth having it repaired. / have my hair cut 主语补足语:One of her shoes was found stolen. 做定语,前置:a developed country, the wasted money (= the money which is wasted) ◆ the risen sun (无被动之意) 修饰不定代词后置:women married, ... 短语后置:the guests invited to this meeting, ... 做状语:(While we were) Followed by our coach, we got on the coach. When heated, the water changes into steam.. / Watched from the space, the earth seems very small. Caught in a heavy rain, he was all wet. / He stood there silently, moved to tears. 其它用法与现在分词同。
①指名称概念还是 名称实物? 指名称概念时: 用原形(名称概念时不存在复数形式),且前面不加任何限定词。 比如:have dinner, at table/home/restaurant/school, by bus, go to school/hospital, play basketball, in peace, ... 指可数的名称实物时:①单数形式下:限定词 + 名称词; ②复数形式一定指实物,不管前面有没有限定词。 指不可数的名称实物:限定词 + 名称词
②单数形式还是 复数形式? 个体形式存在物且处于完整个体状态时: 指单个时:用单数形式。前面需要加限定词。比如:my pen, a tree, an honest man, some day, any student, ... 指多个时:用复数形式。比如:cars, students, some tomatoes, many customers, a lot of questions, ... 非个体形式的存在物,或个体物处于非完整个体状态时: 没有复数形式,即无法通过在词尾加s表示多个。比如:拼盘里的西瓜,土豆丝/片,拍黄瓜都是不可数的 因为没有个数,所以就无法用表个数的修饰词进行修饰限定:a/an, this/that/these/those, few/a few, many, some, ... 但可以用表量的修饰词进行修饰限定。比如:much, little/a little, some, any, lots of/a lot of, ... 可以用复数形式代表“量很大”,比如:waters(大片水域), snows(大雪), rains(大雨/雨季), sands(沙滩), woods(森林), ... 个体上不可数,但指种类(点数/次数等)时却可数: 比如:There was a time that ..., take a walk, have an interest in ..., fruits, interests, funs, many times, ...
③是否专有名称? 指专有名称时,开头字母必须要大写:The Festival of Asian Arts & Music will include ...
④用作修饰词性 修饰它物时: 一般都用单数形式:apple tree, carrot juice, boy friend, shoe factory, ... 二种情况要用复数:some men doctors, some women nurses
⑤用所有格形式 限定它物归属时: 词尾不以s结尾的:Tom’s book, that man’s face, children’s food, women’s clothes, one person’s weight, ... 词尾以s结尾的:teachers’ office, my parents’ room (注意区别:personal opinion)
⑥用作物主代物格: 本身以s结尾的单词,只要词尾加一撇就行:My room is smaller than my parents’.
⑦近义名词区别 平时基本功。比如:information/message, question/problem, voice/sound/noise, room/space, work/job, ...
“冠词”知识及考点大全
①用不定冠词 还是定冠词? 表特指的定冠词“the”表示“言有所指”的某实物,特指存在下面几种情况: ① 特指上文中有提及的或与之有关的那个/那些。比如: There is a big school in our town. We will go to the school tomorrow. There was an accident here yesterday. A car hit a tree and the driver was killed. ② 如果没提及,则被限定的这个名词后一定会有另外的短语或句子对它进行限定。比如: The water in the bottle is too hot. / The people I met there were very friendly. ③ 如果上下文都没有提及,则指一定范围内只有唯一的这一个。比如: The water in the bottle is too hot. / The sun was low in the sky. She is playing the piano in the hall. 大厅里只有一架钢琴 (▲而不是乐器前一定要用the) 另外,定冠词“the”搭配名词单数形式还可以用来指某个类别的人/事/物: The zebra is a kind of horse that lives in Africa. 指斑马这种/类动物,而不是这一只斑马 表泛指的不定冠词“a/an”表示“言无所指”,存在以下几种情况: ① 可数个体物情况下,无须指定的单品(任意)一个(或段/种/次/类/点等) ,或多个中无须指定的某一个。比如: Hand me a pen, please. / It gave me an excuse to take the car. I lived in Egypt for a time. / The bridge was washed out by a sudden flood. He found himself lying on a bed in the hospital. 医院里有多张病床 She is playing a piano in Margaret Piano Shop. 琴行里有多架钢琴 (这个不会考) ② 有些名动同形的词,一般没有复数形式,但可以用a表示一次/一下或一种状态等。比如: I want to have a talk with him alone. / Dave was in a hurry to get back to work. take a walk, have a drink, have a look, make a smile, ...
②不定冠词用a 还是an? 根据发音规则,口型接近的元音与元音几乎很少连拼。所以一个单词的读音开始于元音,前面就要用an。 常考的:apple, orange, actor/actress, excuse, example, egg, elephant, eraser, ear, eye, exercise, earthquake, idea, island, onion, order, umbrella, uncle, hour, exhibition, an honest/old ..., an amazing/angry/active/exciting/easy/early/important/ordinary/organized/upset/urgent *** an Asian/English/Italian/Australian *** 难度题:an F/H/L/M/N/R/S/X, an 8, ... 但后面一个以元音字母开头的单词,但读音并不是元音,则不要用an。 此类常考的名称词:a university, a useful ..., a usual ..., ...
“数词”知识及考点大全
①用基数词还是 序数词? 中文中不体现序数的意思,但在英文中却要用序数词来进行表述。比如: 7年级: 这幢楼的9楼: 玛丽的17岁生日: 他们结婚的30年头: 在21世纪:the seventh grade 或 Grade 7 the ninth floor of this building Mary’s seventeenth birthday their thirtieth years of marriage in the twenty-first century
②数词的拼写 注意以下数词在拼写时不要出错: 4: fourth, fourteen, fourteenth, forty, fortieth / 5: fifth, fifteen, fifteenth, fifty, fiftieth 9: ninth, nineteen, nineteenth, ninety, ninetieth / 11: twelve, twelfth
③hundred, thousand, million等用单数 还是复数形式? 作为数字限定的单位词,hundred, thousand, million, billion等一律不用复数形式。 比如:5 hundred dogs, one thousand soldiers, ... 还要注意数字限定的排序,比如“那500条狗”要表述为:the(those) five hundred dogs 但是,作为代称词时,却不仅有单数形式,还有复数形式。比如: (several) hundreds of (the) dogs (那)狗群中的好几百条 考试重点 two hundreds of the dogs 那狗群当中的二百条 很少考到
④数词的应用 小数点、百分比、日期、钟点、温度等的表示方法。 分数表示法:分子用基数词,分母用序数词。当分子大于1时,分母要用复数形式。 1/2不能表述为one second,要表述为a/one half 年代表示法。比如:在20世纪70年代,in the 1970s 年龄表示法。比如:在他50来岁时,in his fifties
“代词”知识及考点大全
①人称/物称代词 用主格形式 还是宾格形式? 如果做句子的主语,要用主格形式。如果做宾语,不管是动作词的对象宾语,还是介词的对象宾语,都要用宾格形式。 尤其注意在V3这样的结构中。比如:Miss Zhou teaches us English. 注意在某些特殊的情况下,使用主格与宾格二种形式,句子意思是截然不同的。试对比: She knows me better than he (does). 连词后面用主格,主语与主语进行对比 She knows me better than him. 介词后面用宾格,宾语与宾语进行对比 作表语时(非强调句中),更倾向于使用宾格形式。比如:It’s me. 在强调句中强调主语,则要用主格形式。比如:It’s I who got the ticket for this movie.
②代词的所有格 与物主代物格 说明某人/事/物归谁所有情况下的所有格:my, your, his, her, our, its, their 注意词性为限定词,不能单独使用 以物主的信息来指代一个人/事/物:mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs 词性仍为代词,可以单独使用
③疑问代词的选择 疑问代词:who/whom, what, which, whose 注意what, which, whose同时可以用作限定词
④相互代词的选择 强调两者之间的相互用:each other 强调多者之间的相互用:one another
⑤不定代词要用对 只能用来指代可数名称物的代词:many, few, a few 同时可以用作限定词,修饰可数名称词 只能用来指代可数名称物的代词:much, little, a little 同时可以用作限定词,修饰不可数名称词 全指代:some, any some同时可以用作限定词,表示:①一部分/一些; ②(不确定的)某一个。比如:some one, some day any一样也可以用作限定词,表示:①任何一部分/一些; ②(任何任意的)一个/些。比如:any student, any water one用于指代可数名称物的“单个个体”,属于数词指代,它还有复数形式。 近义代词的区别:other与another, both, either, neither与all, each, none 部分不定代词也有复数形式。比如:pairs, couples, parts, halves,...
⑥反身代词不能忘 反身代词的意思好理解,但关键是在表述过程中要有反身代词的概念。比如: I can tell others about me (I) in English now. 正确答案:myself
⑦-ever代词不能忘 关键是在表述过程中要想到用任意代词:whoever, whomever, whatever, whichever
⑧其它一些代词 集合名称用作代词。比如:group, team, bowl, room, row, line, ... 数词用作代词。比如:make up a four at tennis. Two of us ... I watched the two jump down the hill ... 特别是one。比如:one of the students. / I only need one but you need five ones.
“动词”知识及考点大全(一)
①主动语态还是 被动语态? 主动语态形式: 句子的主语与谓语动词之间存在主动关系(也叫主谓关系),即主语是动作的发出者。 被动语态形式: 句子的主语与谓语动词之间存在被动关系(也即动宾关系),即主语是动作的对象或内容。(be done) 动词不定式当中的动作词与被它修饰的对象之间存在动宾关系,需要强调即将被做时,不定式中也会用被动语态
②用哪种时态 初中: 基本时态+过去将来时 高中: 全掌握 包括被动语态的时态 时态表示的内在含义: “时”表示动作发生或状态存在的时间,分三种情况:过去、现在、将来 “态”表示动作发生或状态存在的情况,分三种情况:一般做、正在进行中、已完成 1). 二种经排列组合后,构成9种动作发生或状态存在的基本情况,也即9种基本时态。 过去一般时 (was/were ..., did)过去进行时 (was/were doing)过去完成时 (had done)现在一般时 (is/am/are ..., do/does)现在进行时 (is/am/are doing)现在完成时 (have/has done)将来一般时 (will/shall be/do) (is/am/are going to be/do)将来进行时 (will/shall be doing) (is/am/are going to be doing)将来完成时 (will/shall have done)
2). 已完成一段时间并且仍然还正在进行中,已完成与正在进行可以结合,构成3种时态: 过去完成进行时 (had been doing)现在完成进行时 (have/has been doing)将来完成进行时 (will/shall have been doing)
3). 过去时间谈未来,构成过去将来的4种时态: 过去将来(一般)时 (would/should be/do, was/were going to be/do)过去将来进行时 (would/should be doing)过去将来完成时 (would/should have done)过去将来完成进行时 (would/should have been doing)
备注:被动语态同样存在16种时态,构造原理相同。
“动词”知识及考点大全(二)
③三单(主谓一致原则) 一般现在时情况下:主语为第三人称单数时,谓语动词要用三单形式。 要用:is/was ..., has ..., does ... 第三人称单数还包括: 不可数名词、动名词的单数形式、不定式短语、主语从句、2及以上的纯数字都看作是单数 另外:一段时间或一个数额当作单个整体不看作多个数量时、“many a...”或“more than one…”修饰一个名词单数时、 “both…and…”连接二个名词时但指一个人时、“either...or...”或“neither…nor…”结构中后面这个是单数时。 其它情况: 有些集称名词就指群体,我们将它们看作是复数的。 有些集称名词,把它视为一个整体时是单数的,视为全体成员时是复数的。 “a number of ...”视为复数形式;“the number of ...”视为单数形式 “限定词+形容词”构成的名称,指可数名称物的多个时是复数的;指单个或不可数名称词时是单数的。 一般来说,“one of ...”后定从中,作为主语的引导词一般指复数。但“the only one of ...”后面定从,引导词视为复数。 主语有二物,且第一个为“a/an ...”,倒装句there be一般使用“is”(就近原则),介词短语倒装则使用“are”。
④动词的句职功能: 除非将动作词及其词组短语当作名称,否则它在句子当中只可以充当谓语。 不可以当作主语用。比如不可以说:Swim is my favourite. X 不可以当作宾语用。比如不可以说:I like swim. X 不可以当表语(或表述语)用,将is/am/are与do连在一起。比如不可以说: He is/was do ... X Is/Was he do ... X 一个句子或动词短语结构中,如果出现二个动作动词,要么用连词并列连接,要么将另外一个动词改成非谓语动词。 比如不可以说:go swim X 只能说成:go to swim, go swimming 见非谓语动词部分:动名词、不定式、现在分词、过去分词
“动词”知识及考点大全(三)
⑤一般助动词与情态 助动词后要用原形: 一般助动词do/does/did后要用动词原形 比如:They do know the secret. / Does he know the secret 绝大情态助动词后要用动词原形(除去have to do, ought to do) 比如:He can jump very high. / He may go with us. 其它几个类似于助动词的词后要用动词原形(除去used to do) 比如:Let’s help sweep the floor. / We’d better go now. / Kids would rather play than study.
⑥及物与不及物问题: 及物动词后可以直接跟宾语,但不及物动词则不可以。 区分及物与不及物最常考的有:arrive/reach/get, rise/raise/lift, go/enter, look/see, 不及物动词:agree, laugh 不定式短语作后置定语,如果其中的动作词为不及物动词,注意一定要搭配上合适的介词。 比如:They can’t find a room to live in. 定语从句限定一个名称词,如果其中的动作词为不及物动词,注意一定要搭配上合适的介词。 比如:They can’t find a room which they can live in. 就算是及物动词,但如果它跟被修饰的词不存在动宾关系,也要加上介词,以“介宾关系”来修饰说明该动作: 比如:Mr. Smith, from whom I have learned a lot, is a famous scientist. ..The driver was the man from whose room she had stolen the maps.
⑦行为动词还是 结果动词? 动作动词不要当结果动词用。比如不可以说:She listened that he was active about some business. X 有些动作词是强调动作行为的,如:look, watch, listen, … 有些动作词是强调动作结果的,如:see, meet, hear, …
“动词”知识及考点大全(四)
⑧延续性动作词还是 短暂性动作词? 延续性动作词可以跟一段时间连用(for ..., until ...): 比如说:I would like to stay here for two days. / I will stay here till 6 o’clock. I have borrowed this book and also have kept it for 10 days. 短暂性动作词不可以跟一段时间搭配连用: 比如不可以说:All the kids started to have dinner till 8 o’clock. X 但短暂性动作词的否定形式则可以延续,因此可以跟一段时间连用: 比如可以说: All the kids didn’t start to have dinner till 8 o’clock. 尤其是在完成时情况下,短暂性动作时不可以跟一段时间搭配连用: 比如可以说:I haven’t heard from my friend in Africa since he left. / I haven’t met him for a long time. 但不可以说: I have heard from my friend in Africa for a long time. X / I have met him for a long time. X 常见的短暂性动作词有: become, borrow, lend, buy, sell, join, open, die, close, start, begin, finish, come, reach, go, move, return, arrive, leave, marry, join, happen, meet, hear from, … 常考的: borrow, lend, buy, sell, join, marry, die, ...
⑨情态助动词 近义情态助动词的区别;情态助动词与动作动词的区别(need, dare) 情态助动词的否定。尤其是mustn’t 情态助动词用于虚拟语气。 高中阶段要求掌握
⑩近义动词及词组 的区别: 掌握单词的基本义,及其相关引申义: 常考的有:say/speak/talk/tell, spend/take/pay/cost, remember/remind, forget/leave, receive/accept, lie/lie/lay, attend/join/join in/take part in, send/post/deliver, find/find out/discover, make/produce, ... 在掌握动词基本义/引申义的基础上,结合介词与副词的基本义,用英文思维理解动词词组的基本义与引申义。 高频率使用的几个动作词:make, take, set, get, turn, give, go, ... 高频率使用的介词或副词:in, on, out, over, at, to, from, up, down, for, with, along, about, of, off, away, after, ... 当然,也可采用死记硬背的方式,尤其是那些与中文思维不太相同的表述。
⑾动词与介词或副词 的搭配问题
“形容词、副词”知识及考点大全
①用比较/最高级? 要注意是否要使用比较级或最高级,尤其是在隐性比较的情况下
②要用反义词吗? 特别要注意,在使用修饰词的时候是否该用反义词
③是否要后置? 修饰不定代词后置:something enough, anything important, /nothing more, someone else/here/there, what else, ... 表述性的形容词后置:people here/there, soldiers still alive, any way possible, ... 程度副词enough要放在被修饰词的后面:… good enough
④形容词还是副词? 形容词跟名称词发生关系,副词用来修饰说明动作词谓语或系表结构谓语 正确区分“系动动词 + 形容表述语”与“动作词谓语 + 修饰性状语副词”两种不同的结构 部分省略了介词的名词及其短语兼有副词:today, tomorrow, next year, here, there, ... 形容词及其短语/分词用作表述性状语 见非谓语动词部分,高中阶段要求掌握
⑤比较注意事项 A跟B群中任何一个人比较的时候,如果A属于B群中,要将自己排除在外。用any other(s) The more ..., the more ...结构 比较必须基于同物比较:The climate in Beijing is worse than that in Hangzhou. Salaries are higher here than those in my country. one of 后面的名称物一定要用复数形式。比如:one of the students
⑥形容词或短语 指代名称 限定词 + 形容词: 指单个:John is the shorter of the. / I don’t want the black pen. I want the blue. / the easiest of all / the first/second, ... 指一类:the rich/young/poor/honest, those wounded, … 也可以用复数形式:the youngs, some olds, Eight Strongs, those blacks, all the livings, … 单个形容词或分词指代名称:try to cash in big, than expected, as (what’s) reported/written/told, ... 形容词性与名称词性同形:Enough has been done ..., a car of my own, It’s my favourite., We are Chinese, ...
⑦副词特殊句式 so (形容词或副词原形)... that ...句式结构,注意区分:such (名词短语) that ... 感叹句“How + 形容词/副词原形”结构,“What+ 名词短语”结构:What good news! What fine weather!
⑧修饰不定式与 介词短语的副词 修饰介词短语:right in the room, high in the sky, badly in need of ..., shortly after us, deep in conversation with ..., ... 修饰不定式短语:... is just about to do, ... are likely to be expensive, ... came here just(only) to say goodbye ...
“非谓语词”知识及考点大全(一)
注意事项 使用动词现在分词,还是过去分词? 使用动名词,还是不定式短语? 使用不定式短语,还是分词?
①动名词 动名词的含义: ①动作对应的名称叫法(相当于这个动作行为)。比如:swimming指游泳这种动作行为 ②动作过程(相当于这件事)。比如:swimming指游泳这件事 ③部分动作会有结果产物。比如:building还可以指建筑物 句职功能: 做主语:Swimming is his hobby. / It is no use learning theory without practice. 使用it做形式主语 做表语或补足语:His hobby is swimming. We call it hiking. It is called hiking. (主补) 做动词宾语:I like swimming. 做介词宾语:She is afraid of going out at night alone. 介词后面必须要用动名词形式 做定语:a swimming pool (=a pool for swimming) a harming effect (= an effect about harming) 做同位语:He is looking for a job, repairing cars. 需要跟动名词做宾语的动词及词组: practice, enjoy, prefer, advise, suggest, consider, finish, mind, allow, avoid, appreciate, imagine, deny, complete, dislike, mention, resist, miss, forbid, risk, keep (on), can’t help, can’t stand, look forward to, pay attention to, give up, ... 动名词的逻辑主语一般用所有格。Thanks for your coming. Your calling back will be highly appreciated. 动名词的否定:前面直接加not. His not knowing English gets him a lot of trouble. 也有用no的:There is no denying the fact that he is diligent. No Parking.
“非谓语动词”知识及考点大全(二)
①不定式短语 不定式短语的含义: ①名称词性:“接下来要去做”的一个动作或一件事 ②名称表述词性:(属)接下来要去做的一个动作或一件事 ③名称限定词性:针对某个名称物,接下来要去怎么样的 ③动作修饰词性:a.表目的:目的为了接下去干嘛;b.表结果:结果导致下一个动作行为;c.表原因程度等等 句职功能: 做主语:To have a swim is a good idea. / It is important for you to learn English well. 使用it做形式主语 做宾语:He decided to buy a new car. / I want to have a swim now. 同位语:My wish to visit France finally comes true. 做表语:My wish is to visit France. / He is to cry. / seem to be impossible / appear to be a fine fellow 做补足语:带to:My neighbor invited me to join their party. / They are asked to live on campus. (主补) .不带to:Let’s go. / ... have me clean the room. (feel/hear/see/notice/have/let/make sb. do sth.) 做定语:The next train to arrive is from Washington. / I am looking for a room to live in. (注意搭配) 做状语:They came here just to say good bye. / Let’s go to have a drink. / We did what we could to help you. 需要跟不定式做宾语的动词: need, dare, seem, ask, wish, hope, plan, require, want, pretend, decide, choose, agree, refuse, promise, expect, prepare, become, afford, attempt, offer, swear, tend, demand, determine, hesitate, volunteer, manage, would like to do, make up one’s mind to do, ... 不定式与动名词做宾语的区别: try to do try doing like to do like doing fail to do fail doing go on to do go on doingstop to do stop doing forget to do forget doingremember to do remember doing regret to do regret doingused to do be used to doing be used to do
特殊表述结构中:too weak to do..., do nothing but do, have nothing to do but do, have no choice but to do, ... “特殊”不定式短语:how to do it, what to do, when to start, where to go, whether to leave or stay there, ... 不定式短语用在V4结构中,必须要用it指代:I have made it a rule to keep diaries. / ... take it for granted that ... 不定式的否定:前面直接加not. I was being so foolish not to follow your advice. 不定式的逻辑主语:It will be very easy for you to work it out. / It’s very kind of you to tell me the truth. 高中生还需要注意不定式当中的时态
“非谓语动词”知识及考点大全(三)
③现在分词 现在分词的含义: ①处于正在进行的状态中 比如:Stop! You are hurting me. 你正处于搞疼我的状态中 ②逻辑主语跟这个动作存在主谓关系 你把我搞疼 现在分词的句职功能: 做表语:He is crying in the car. 进行时结构,表示正处于做...的状态中 Growing all over the hills and around the lake are wild flowers of different colors. 表语提前倒装,用以强调 ◆系动动词+表语:seem interesting/exciting ... 宾语补足语:We found him crying in the car. / Can you hear her singing the song in the next room 主语补足语:He was often seen watching plants closely ... 做定语,前置:a developing country, a sleeping baby, a swimming girl (= a girl who is sleeping) 修饰不定代词后置:nothing interesting, ... 短语后置:the man standing there, ... 做状语:(While we were) Following our coach, we got on the coach. / Let’s go shopping. Being very tired, he still continued his working. / Having finished the work, the children went out to play. He stayed at home, (while) cleaning and washing. / Things get out of hand ..., putting her in the spotlight. ◆表述性状语,形容词性与副词性存在模糊性。这一点跟形容词做表述性状语同。 句转短语表述 比如:He returned from war, safe and sound. / Crusoe stared at the footprint, full of fear. 完成时结构下的现在分词:Having finished the work, the children went out to play. 现在分词的否定:Not being able to get the ticket, he left away. .Not having finished the homework, the children were not allowed to play football. 现在分词的逻辑主语用主格形式:I waiting for the bus, a bird fell on my head. Time permitting, we’ll do another two exercises. 现在分词等同于介词:Cassie went into the room, following her teacher. 要考虑逻辑关系,分清用现在分词还是过去分词 不考虑逻辑关系的:Generally speaking, the more you pay, the more you get. / She’s very active, considering her age. .I’ve got a three-day holiday including today. / It typically takes a day or two, depending on size.
“非谓语动词”知识及考点大全(四)
④过去分词 过去分词的含义: ①动作已经完成(强调动作性,与have搭配构成完成时) ②被怎么样(强调动作性,用于被动语态),主语跟这个动作存在动宾关系 ③处于已经被怎么样了的状态中(表述状态),逻辑主语跟这个动作存在动宾关系 过去分词的句职功能: 与have一起做谓语,表示已完成。比如:We have seen the film. 完成时结构 做表语:This novel was written by Hemingway. 被动语态结构,强调动作 We are interested in this story. / The window is broken. 被动语态结构,表述状态 Gone are the days when you could do anything you wanted. 表语提前倒装,用以强调 ◆系动动词+表语:get paid/married/annoyed/interested ..., feel comforted/disappointed ..., look worried/excited, ... 宾语补足语:She found her shoes stolen. / It isn’t worth having it repaired. / have my hair cut 主语补足语:One of her shoes was found stolen. 做定语,前置:a developed country, the wasted money (= the money which is wasted) ◆ the risen sun (无被动之意) 修饰不定代词后置:women married, ... 短语后置:the guests invited to this meeting, ... 做状语:(While we were) Followed by our coach, we got on the coach. When heated, the water changes into steam.. / Watched from the space, the earth seems very small. Caught in a heavy rain, he was all wet. / He stood there silently, moved to tears. 其它用法与现在分词同。
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
