2022届高考英语复习:状语从句详细讲解课件(64张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2022届高考英语复习:状语从句详细讲解课件(64张) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 417.4KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-04-05 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共64张PPT)
语法专题
主从复合句:状语从句
The Adverbial Clauses
一、基本概念
二、状语从句分类
三、各类状语从句重难点
四、考点与注意点汇总
1、状语
修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子,说明动作或状态特征的句子成分,叫做状语。通常由副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词或从句等担当。
2、状语从句
在主句中作状语的从句叫状语从句,主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语,状语从句在句中相当于副词做状语,因此又叫副词性从句。
一、基本概念
1.While I was walking along the street, I found many beautiful buildings ( )
2. Where there is a will, there is a way. ( )
3. Now that everybody is here, let’s begin our meeting. ( )
4. I’ll speak slowly so that you can understand me. ( )
5. So clever was he that he was able to work out all the difficult problems. ( )
6. As long as you don’t lose heart, you’ll succeed. ( )
7. Try as he might, he could not find a job. ( )
8. The old lady treats the boy as if he were his own son. ( )
9.He is taller than I am.( )
时间
地点
原因
目的
结果
★
例
句
导
入
★
条件
让步
方式
比较
二、状语从句分类
九种状语从句
时间状语从句
地点状语从句
原因状语从句
条件状语从句
让步状语从句
结果状语从句
目的状语从句
方式状语从句
比较状语从句
★归纳总结★
1、时间状语从句:when, while, as, before, after, since, by the time , till, until(直到…为止), not…until(直到…才), once , as soon as, the moment, the minute, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, hardly…when, scarcely…when, no sooner…than , every time, each time , the first/second…/last time
3、原因状语从句:because, since, as, for, now that(既然), in that(因为), considering/seeing/given (that) 考虑到…鉴于…
4、条件状语从句:if, unless, as (so) long as, on condition that(只要), in case,for fear that以免, providing/provided(that)
supposing ( that )假如
2、地点状语从句:where, wherever
各类状语从句常见的连接词
5、让步状语从句:although, though, as, even though/even if, while(虽然), no matter +which/what/when/where/who/how, whichever, wherever, whatever, whoever, whenever, however, whether…or…(不管…还是)
7、目的状语从句:so that, in order that, so as that
8、方式状语从句:as(按照), as if/as though
6、结果状语从句:so…that, such…that
9、比较状语从句:than, as…as, not so/as…as,
the +比较级…, the +比较级…
各类状语从句常见的连接词
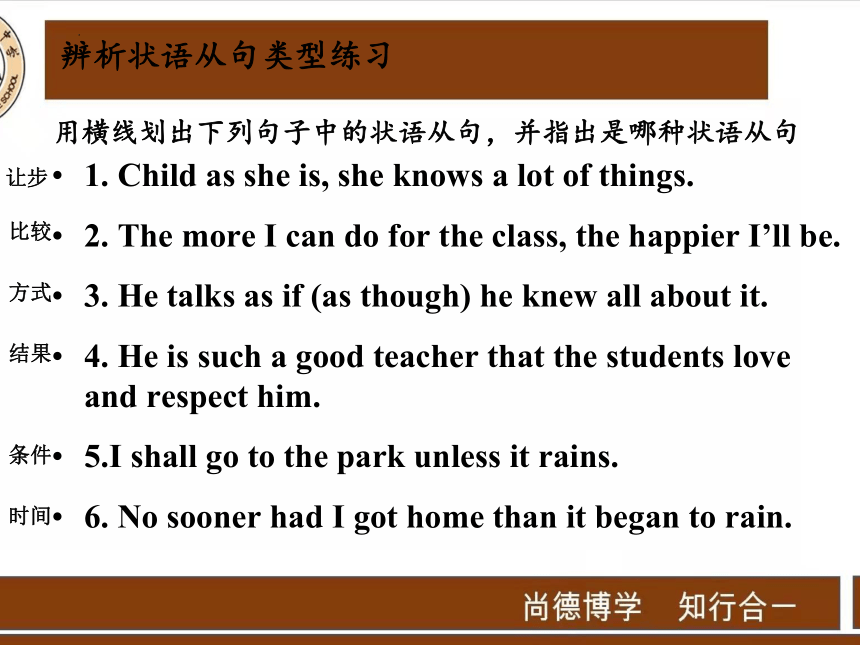
用横线划出下列句子中的状语从句,并指出是哪种状语从句
1. Child as she is, she knows a lot of things.
2. The more I can do for the class, the happier I’ll be.
3. He talks as if (as though) he knew all about it.
4. He is such a good teacher that the students love and respect him.
5.I shall go to the park unless it rains.
6. No sooner had I got home than it began to rain.
让步
比较
方式
结果
条件
时间
辨析状语从句类型练习
7. Where there is water, there is life.
8. He studied hard so that he could catch up with his classmates.
9. Since you are very busy, I won't trouble you.
10. Even if (though) I fail. I’ll never lose heart.
11. Once you begin the work, you must continue.
12. Although the sun was shining, it wasn’t very warm.
地点
目的
原因
让步
时间
让步
三、时间状语从句重难点
1、when, while, as引导时间状语从句
(1)when的用法
A. when引导时间状语从句既可指时间点,也可指时间段
(即:从句动词可以是短暂的也可是延续的)。
For example:
①When I lived there, I used to go to the seashore on Sundays.
② When he arrived in Shanghai , his mother met him at the station .
B. When 在下列句式中译为“就在那时,这时”,可以看成是并列句,这种用法的when一般位于句末。
For example:
① I was putting on my clothes when the telephone rang.
②我正要锁门,这时电话响了。
③我刚锁上门,这时电话响了。
was doing … when
was about to do…when
was on the point of doing … when
had done… when
(2)while的用法
A. while只能指一段时间,从句中的动词必须是延续性动词。强调某一段时间内主句动作发生,相当于during the time that....;从句常用进行时态。
For example:
①Please don’t talk so loud while others are working.
②My mother was cooking while I was doing my homework.
B. while作为并列连词,意为“而,却”,表示同类对比。
For example:
I like watching TV, while he likes reading.
C. while也可用来引导让步状语从句,意为“尽管,虽然”,相当于although
For example
While I admit that the problems are difficult , I don’t agree that they can’t be solved.
D. “ 只要 ” 条件状语
For example
While there is water, there exist life.
While there is will, there is way.
E. 趁…的情况赶紧做, 否则来不及了
For example
Strike while the iron is hot.
趁热打铁。
(3)as的用法
A. as可用来引导时间状语,常可和when换用,但较强调主从句动作同时发生,意为“一边…一边”,引出伴随动作
For example:
She was doing her homework as she was listening to the music.
B. as还可说明两种正在发展或变化的情况,“随着...”的意思,表时间的推移。
For example:
①As time went by/With time ___ , I began to realize the importance
of learning.
② As I grow older, I become more interested in music.
C. as也可用来引导原因状语从句,意为“因为”
For example:
As she is free today, she would like to do some shopping.
D. as还可用来引导让步状语从句(用倒装结构),意为“尽管”。For example:
Tired as he was, he refused to take a rest.
2、before、after引导时间状语从句
(1)before和after表示的是两个时间或两个事件之间的先后关系;引导时间状语从句最基本的意思就是“在..之前”、“在…之后”;before从句的动作通常发生在主句动作之后,如果从句用过去时,主句一般要用过去完成时;after从句的动作通常发生在主句动作之前,如果主句用过去时,从句一般要用过去完成时。
For example
①在我们看到陆地前,我们已经航行四天四夜了。
We had sailed four days and four nights before we saw land.
②他在这家工厂工作十年以后就出国了。
After he had worked in the factory for ten years, he went abroad.
(2)before时间状语从句的特殊句式
主句包含表段时间的短语、且为肯定句常译成“…(之后)才”;
主句包含表段时间的短语、且为否定句常译成“…就”;
这样的句型有一般过去时、过去将来时、一般将来时三个时态。
A. It will be/+段时间+before…do…“还要过多久才…”
B. It was +时间段+before …did… (动作已发生)
C. It will not be long before…“不多久就会…”
D. It was not long before…“不多久就…了”
For example:
①再过两年他才大学毕业。
It will be two years before he graduates from the university.
②两年之后他才大学毕业。
It was two years before he graduated from the university.
③他不多久就会从大学毕业了。
It will not be long before he graduates from the university.
④他不多久就从大学毕业了。
It was not long before he graduated from the university.
3、until, till, not…until引导时间状语从句
(1)until/till从句用于肯定句时,主句的动词是延续性动作,表示“某动作一直延续到某时间点才停止”,译为“直到…为止”。
For example:我们一直在那里待到雨停了。
We stayed there until the rain stopped.
(2)until从句用于否定句时,主句的动词是短暂性动作,表示“某动作直到某时间才开始”,译为“直到… 才”。
For example:我们一直到雨停了才离开。
We didn’t leave until the rain stopped.
注意:till不可放在句首或用于强调句中, not…until句型中一般也不用till。
(3)用于强调句式“It is/ was not until ...that ...”
For example:
直到雨停了我们才离开。
It was not until the rain stopped that we left.
(4)not until放在句首时主句要进行部分倒装
For example:
我们一直到雨停了才离开。
Not until the rain stopped did we leave.
4、since引导时间状语从句
since从句一般要用非延续性动词did或动词have done,意为“自从…时起”,主句要用完成时态
For example:
He has worked in this city since he graduated from the college.
(1)since所引导从句如果用延续性或状态动词的一般过去时,所表示的就是动作或状态的完成或结束。
翻译:Since Tom lived in Nanjing, I have not heard from him.
自从Tom离开南京以后,我没有收到过他的信。
(2)作介词时,since后要接时间点,而不是时间段;
5、表示“一…就…”句型
(1)as soon as/ once
For example:
①我一到上海就会写信给你。
As soon as I arrive in Shanghai, I will write to you.
②你一旦开始这项工作,就必须继续下去。
Once you begin the work, you must continue.
★注意★
(1)在时间状语从句中,不能用将来时或过去将来时,而要用现在时或过去时代替将来时。
(2)once一般译为“一旦”,从句可以表示时间和条件两层含义。
(2)名词短语转变成连词:
the moment, the instant, the minute, the second
For example:
He came to the spot/ scene the moment he heard of the accident.
(3)副词转变成连词:
instantly, immediately, directly
For example:
They told me the news immediately they got the message.
(4)no sooner ...than , hardly/scarcely...when
A.意思:“一…就…”
B.时态:主句(no sooner/ hardly/ scarcely)用过去完成时,
从句(than/ when)用一般过去时。
C.倒装:结构中的否定词(no sooner/ hardly/ scarcely)放在句首时,主句(紧跟其后的句子)要倒装。
For example:
我刚到车站,火车就开走了。
I had no sooner got to the station than the train left.
句型转换(no sooner)置于句首:
No sooner had I got to the station than the train left.
(5)介词短语
upon/on doing sth./one’s + n.作时间状语,意为“一…就…”
For example:
美国学生一到来,我们就给他们热情地欢迎。
On arriving, we gave the American students a warm welcome.
句型转换:
On their arrival, we gave the American students a warm welcome.
6、一些含有time的名词短语
如the first /second/last time, every time, each time, next time, by the time等,也可引导时间状语从句。
For example:
①The first time I drove the car, I felt very nervous.
②Next time you come, please bring your composition.
③ By the time you graduate, we will have lived in Australia for one year.
四、地点状语从句重难点
1、where/wherever
Where指“在某个地方”,wherever指“在任何一个地方”;
可以放在主句前,也可以放在主句后。
For example:
①有志者事竟成/有水的地方就有生命。
Where there is a will, there is a way.
Where there is water, there is life.
②You should put the book where it was.
③ Wherever you go, you must obey the law.
2、where引导地点状语从句与定语从句的区别
For example:
一般而言,有工厂的地方空气都会被严重污染。
Generally, air will be heavily polluted in the places where there are factories.
Generally, air will be heavily polluted where there are factories.
定语从句:主句…表地点的名词+where…
place
状语从句:主句…+ where…
place
五、原因状语从句重难点
原因状语从句由because, as , since, now (that)(既然), in that(因为,多于口语中),seeing (that)(鉴于,由于),considering that(考虑到)等引导。
1、because
because用来回答why提出的问题,表示某件事发生的直接原因或理由,用于告知对方不知道的原因。在这几个连词中,它表示原因的语气最强,可用于强调句。
For example:
I came back late yesterday because I was on duty.
It was because I was on duty that I came back late yesterday.
2、since, now that
since、now that常表示关系上的自然结果,特别用于原因已经清楚了的事情,说话人根据这个事实得出某一种结论。其语气比because要弱,一般译成“既然”,往往放在主句前。
For example:
Since you have known the secret, I needn’t say anything about it.
3、as
as常用于表示十分明显的原因,只是对主句的附带说明,重点放在主句上,语气较弱,常译成“由于”,可放在主句前或主句后。 For example:
As he didn’t know much English, he looked up the word in the dictionary .
4、for
for也可以表示原因,属并列连词,不是说明直接原因,而是对某种情况加以推断或解释,对前一分句进行附加说明;它引出的分句必须放在另一分句后。
For example:
门关着,屋子里肯定没人。
There must be no one in the house, for the door is closed.
5、seeing (that), considering (that), in that
这几个连词 和since, as 意义相似,他们都有“鉴于某个事实、原因是”的意思。
For example:
鉴于他病情严重,我们派人去请医生了。
Seeing that he was badly ill, we sent for the doctor .
六、条件状语从句重难点
由if, unless(if...not), so/as long as, supposing(that)(假设), provided/providing (that)(假若), in case(万一…, 以防…), on condition that(条件是...),so/as far as(就...而言)等引导
1、if/unless
if表示正面的条件,意为“如果”;
unless表示反面的条件,相当于(if…not),意为“除非,如果不”。
For example:
We won’t wait for him, if he doesn’t come before 12o’clock.
We won’t wait for him, unless he comes before 12o’clock.
2、 supposing(that), provided/providing (that),
on condition that, in case, so/as long as
这些连词词组意思相近,有“如果,假如,假设,在…条件下”等意义
For example:
①So long as you keep on trying, you will surely succeed.
②In case John comes, please tell him to wait.
3、as/so far as就…而言
For example:
So far as I know, the book will be published next month.
4、only if ﹠ if only
only if引导的从句用陈述语气,意为“只要”; if only引导的从句要用虚拟语气,意为“但愿…,要是…就好了”
For example:
①Only if you keep on trying, you will surely succeed.
②如果当初我们听取了你的建议就好了。
If only we had followed your advice!
If only …(要是…就好了)
与现在事实相反,从句中用一般过去时
与过去事实相反,从句中用过去完成时
与将来情况相反,从句中用could/would/might+动词原形
5、条件状语从句的虚拟
if引导的条件状语从句若与过去或现在事实不符,或对未来进行不可能的假设,就要用虚拟语气。
For example:
①如果有一天机器人掌控了世界,将不会再有友谊。
If Robots should control the world some day, here would be no friendship.
②如果考试中Tom能再仔细些,他就已经通过考试了。
If Tom had been more careful in the exam, he would have passed it already.
③如果我是一个老师,我会对我的学生很严格。
If I were a teacher, I would be strict with my students.
从句 主句
与现在相反 If +主语+动词过去式,主语+ should/would/could/might+动词原形
与过去相反 If +主语+had +过去分词,主语+should/would/could/might have+过去分词
If +主语+动词过去式,
与将来相反 If +主语+should+动词原形, 主语+should/would/could/might+动词原形
If +主语+were to+动词原形,
6、条件状语从句的省略与倒装
If引导的虚拟条件从句中谓语动词有were, had或should,可以把if省去,而把were,had或should移到主语前构成倒装。
If Tom had been more careful in the exam, he would have passed it already.
Had Tom been more careful in the exam , he would have passed it already.
七、目的状语从句重难点
由so that(以便), in order that(为了),for fear that(= in case)(以免),lest(以防)引导,谓语常含may, might, can, could, will, would, should等情态动词。从句往往放在主句之后,主从句之间不用任何标点符号。
1、so that/ in order that
For example:
① They worked harder than usual in order that they could finish the work ahead of time.
They worked harder than usual in order to finish the work ahead of time.
②The teacher raised his voice on purpose so that the students in the back could hear more clearly.
2、 lest/ for fear that/ in case
这些连词词组意思相近,意思是“以防、以免”;
lest从句一般用虚拟语气,形式“should+动词原形”或只用原形;
for fear that从句和in case从句一般用虚拟语气,但有时也可以用陈述语气。
For example:
①多穿点衣服,以免感冒。
Put on more clothes lest/ for fear that/ in case that you should catch a cold.
②他把相机准备好,万一看到适合拍照的东西。
He had his camera ready in case he saw something that would make a good picture.
八、结果状语从句重难点
常用的连词有so that,so ... that, such...that;
结果状语从句中一般无情态动词
1、so that,so ... that, such...that
For example:
①他们比往常更加努力工作,结果提前完成了工作。
They worked harder than usual, so that they finished the work ahead of time.
They worked hard enough to finish the work ahead of time.
②老师说话声音很大,因此后面的同学听得很清晰。
The teacher spoke so loud that the students in the back heard clearly.
2、 so/ such…that所用句式
A、 so + adj /adv + that从句
B、 so + adj +a/an+单[C]+ that从句
C、 so many/few +复[C]+ + that从句
D、 so much/little+[U]+ that从句
E、 such + adj +复[C] /[U]+ that从句
F、 such +a/an + adj + 单[C]+ + that从句
九、让步状语从句重难点
常用的连词有though, although, even though, even if, as, while, no matter wh-, wh-ever, whether…or(不管…还是)
1、though/ although
though, although这两个连词用法基本一样,只是前者口语化,后者较正式;
让步状语从句可以放在主句前或者主句后;
though还可作副词单独放在句尾,表示“然而,可是,不过”的意思。
For example:
I had a very good time although I didn’t know anybody at the party.
然而,我们有些不同之处。
We have some differences, though.
★注意★
连词引导让步状语从句不能与but连用,但可以与副词yet,still,nevertheless连用
2、 even if/ even though
常用以强调让步概念,有退一步设想的意思,“即使、纵使”;有时有假设含义,用于虚拟语气。
For example:
①即使明天下雨,我也要去。
I’ll go even if it rains tomorrow.
②即使我处在你的位置,我也不会接受这份工作。
Even if I were in your place, I wouldn’t take the job.
3、 while
while引导让步状语从句时置于主句前,与although,though相同
For example:
尽管我承认他的好成绩,但我依然感觉给他这个重要的职位不够明智。
While I admit his good points, I still feel it unwise to offer him this important position.
4、 whether…or (not)
whether…or (not)可以引导让步状语从句,提供两个对比的情况,意为“不管…”。
For example:
不管你是否相信,它都是真的。
Whether you believe it or nor, it is true.
6、 no matter+疑问词、疑问词+ever
For example:
①为了表示尊重,我们无论与谁握手,都常常将手套摘下。
To show our respect, we usually have to take off our gloves, whoever/ no matter who we are to shake hands with.
② 我会尊重任何尊重我的人。
I will show respect to whoever respects me.
who
what
no matter+ which
when
where
how
whoever
whatever
whichever
whenever
wherever
however
二者辨析
相同之处
在让步状语从句中可以相互替换
不同之处
后者能引导名词性从句
7、 as
as引导让步状语从句时,从句要用部分倒装语序。基本结构如下:
A、形容词/副词/名词+as+主+谓,主句…
B、动词+as+主+情态动词/助动词,主句…
★注★
作表语的单数名词放在句首时,该名词前不可加定冠词或者不定冠词
For example:
①他虽有耐心,但也不愿等三个小时。
Patient as he was, he was unwilling to wait for three hours.
②尽管我很尊重他,但却不同意他的建议。
Much as I respect him, I don’t agree to his advice.
③虽然他还是个孩子,但已经熟知了英语。
Child as he was, he had a good knowledge of English.
④尽管我尽可能地尝试了,但还是没能举起那块石头。
Try as I might, I couldn’t lift the stone.
8、 表让步的介词短语
For example:
① I had a very good time although I didn’t know anybody at the party.
I had a very good time despite the fact that I didn’t know anybody at the party.
②尽管我们竭尽全力保住这个学校,但政府还是决定把它关闭。
Despite all our efforts to save the school, the government decided to close it.
Although we tried our best to save the school, the government decided to close it.
A、despite
B、in spite of
C、despite the fact that
D、in spite of the fact that
十、方式状语从句重难点
常用的连词有as, as if, as though
1、as
引导方式状语从句,意为“按照,正如…”
For example:
①请按照我所讲的去做。
Please do it as I told you.
②他们严密地监视她,就好像猫盯着老鼠看。
They watched her closely as a cat watches a rat.
③入乡随俗。
When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
2、 as if/ as though
A、这两个连词意义相同,意为“好像,仿佛”;
B、可引导方式状语从句与表语从句;
C、当从句为(可能)符合事实的情况时,用陈述语气;
D、当从句不符合事实或与事实相反,用虚拟语气,具体如下:
For example:
①他待我如陌生人一样。
He treats me as if I were a stranger.
②他站在门口,好像在等谁似的。
He stood at the door as if he was waiting for someone.
as if/ as though …(好像,仿佛)
与现在事实相反,从句中用一般过去时
与过去事实相反,从句中用过去完成时
与将来情况相反,从句中用could/would+动词原形
十一、比较状语从句重难点
常用的连词有as…as, than, not so/ as…as, the same as…, the more…the more…
1、as+adj./adv.+as和not +so/as+adj./adv.+as
前者意为“和…一样”,表示肯定意义,为等量比较;
后者意为“不及…”,表示否定意义,为不等量比较
For example:
①他对音乐的了解就像我对画作的了解一样少。
He knows as little about music as I know about painting.
②他的舞姿不及他的妹妹优雅。
He dances not as gracefully as his sister (dances).
2、 than
表不同程度之比较,主句中用形容词或副词的比较级,意为“比…更”
For example:
①他今年比去年进步更大。
He has made greater progress this year than he did last year.
②我比他更了解你。
I know you better than he (knows you).
3、表比较的特殊结构
A、the+形容词或副词比较级…, the +形容词或副词比较级
B、A is to B what C is to D A对B而言就像C对D一样
For example:
①你工作越努力,取得地进步就越大。
The harder you work, the greater progress you will make.
②越快越好。The sooner, the better.
③Food is to men what oil is to machines.
食物之于人,犹如油之于机器。
十二、状语从句注意点
1、状语从句的省略问题
状语从句的省略常用在时间、条件、让步、方式、比较状语从句中,分两种情况:
A、当状语从句的主语是it,且谓语动词包含be动词的某种形式时,it和be可以省略掉
For example:
除非你不方便,否则你必须出席这次会议。
You must attend the meeting unless (it is) inconvenient to you.
B、当状语从句的主语和主句的主语一致,从句谓语动词包含be动词的某种形式时,从句主语和be可以省略掉.省略后从句常见的情形有:
连词+adj./n./prep. phrase/done/doing/to do
For example:
①他有空就去逛商店。
Whenever (she is ) free, she often goes shopping.
②他看上去很焦急,好像遇到了麻烦。
He looked anxious as if he was in trouble
While watching TV, _________.
A the doorbell rang
B the doorbell rings
C we heard the door bell ring
D we heard the doorbell rings
状语从句省略问题
2、状语从句的倒装问题
A、否定词开头:not until、hardly…when、no sooner…than(主句部分倒装)
B、so + adj./adv.开头(主句部分倒装)
C、as、though引导的让步状语从句(从句把需要强调部分提到主语前)
1、So difficult _____ it to live in an English-speaking country that I determined to learn English. (01 上海)
A. I have felt B. have I felt C. I did feel D. did I feel
2、Not until all the fish died in the river _____ how serious the pollution was.
A. did the villagers realize B. the villagers realized
C. the villagers did realize D. didn’t the villagers realize
选择题
D
A
3、状语从句的时态问题
A、在时间、条件状语从句中,用一般现在时、一般过去时表示一般将来时、过去将来时;
B、在since引导的时间状语从句中常用一般过去时、主句则常用现在完成时
The house will fall down soon if no one______(do)some quick repair work.
does
Goodbye!
对比训练与巩固
1. We were about to leave____ it began to
rain.
2. She thought I was talking about her son,
____, in fact, I was talking about my son.
3. Hardly had I finished my composition
____ the bell rang.
A. when B. while C. as D. during
对比训练 1
A
B
A
1. Child ____ she is, she know a lot.
2. He did the experiment ____ he was told.
3. The pianos in the other shop will be
cheaper, but not ____ good.
A. during B. as C. if D. though
对比训练 2
B
B
B
1. He would have a look at the bookstores
____ he went to town.
2. We decide to finish the work on time, ____
happens.
3. If we work with a strong will, we overcome
any difficulty, ____ great it is.
4. I’ll give the book to ____ likes English.
A. whenever B. whoever
C. whatever D. however
对比训练 3
A
C
D
B
对比训练 4
1. If we work hard, we can overcome any
difficulty, no matter ____ great it is.
2. If we work hard, we can overcome any
difficulty, ____ great it is.
3. If we work hard, we can overcome any
difficulty, ____ difficulty it is.
4. If we work hard, we can overcome any
difficulty, no matter ____ difficulty it is.
A. what B. how C. however D. whatever
B
C
D
A
对比训练 5
1. It will be years ____ we meet again.
2. It is ten years ____ I came to this town.
3. It is ten years ago ____ I came to this town.
A. when B. that C. before D. since
C
D
B
对比训练 6
Go and get your coat. It is ____ you left it.
2. You are free to go ____ you like.
A. there B. where
C. wherever D. when
B
C
对比训练 7
1. The article is written in such easy English
____ all of us can read it.
2. The article is written in such easy English
____ all of us can read.
A. that B. which C. as D. so that
A
C
A
Practice makes perfect.
语法专题
主从复合句:状语从句
The Adverbial Clauses
一、基本概念
二、状语从句分类
三、各类状语从句重难点
四、考点与注意点汇总
1、状语
修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子,说明动作或状态特征的句子成分,叫做状语。通常由副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词或从句等担当。
2、状语从句
在主句中作状语的从句叫状语从句,主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语,状语从句在句中相当于副词做状语,因此又叫副词性从句。
一、基本概念
1.While I was walking along the street, I found many beautiful buildings ( )
2. Where there is a will, there is a way. ( )
3. Now that everybody is here, let’s begin our meeting. ( )
4. I’ll speak slowly so that you can understand me. ( )
5. So clever was he that he was able to work out all the difficult problems. ( )
6. As long as you don’t lose heart, you’ll succeed. ( )
7. Try as he might, he could not find a job. ( )
8. The old lady treats the boy as if he were his own son. ( )
9.He is taller than I am.( )
时间
地点
原因
目的
结果
★
例
句
导
入
★
条件
让步
方式
比较
二、状语从句分类
九种状语从句
时间状语从句
地点状语从句
原因状语从句
条件状语从句
让步状语从句
结果状语从句
目的状语从句
方式状语从句
比较状语从句
★归纳总结★
1、时间状语从句:when, while, as, before, after, since, by the time , till, until(直到…为止), not…until(直到…才), once , as soon as, the moment, the minute, the instant, immediately, directly, instantly, hardly…when, scarcely…when, no sooner…than , every time, each time , the first/second…/last time
3、原因状语从句:because, since, as, for, now that(既然), in that(因为), considering/seeing/given (that) 考虑到…鉴于…
4、条件状语从句:if, unless, as (so) long as, on condition that(只要), in case,for fear that以免, providing/provided(that)
supposing ( that )假如
2、地点状语从句:where, wherever
各类状语从句常见的连接词
5、让步状语从句:although, though, as, even though/even if, while(虽然), no matter +which/what/when/where/who/how, whichever, wherever, whatever, whoever, whenever, however, whether…or…(不管…还是)
7、目的状语从句:so that, in order that, so as that
8、方式状语从句:as(按照), as if/as though
6、结果状语从句:so…that, such…that
9、比较状语从句:than, as…as, not so/as…as,
the +比较级…, the +比较级…
各类状语从句常见的连接词
用横线划出下列句子中的状语从句,并指出是哪种状语从句
1. Child as she is, she knows a lot of things.
2. The more I can do for the class, the happier I’ll be.
3. He talks as if (as though) he knew all about it.
4. He is such a good teacher that the students love and respect him.
5.I shall go to the park unless it rains.
6. No sooner had I got home than it began to rain.
让步
比较
方式
结果
条件
时间
辨析状语从句类型练习
7. Where there is water, there is life.
8. He studied hard so that he could catch up with his classmates.
9. Since you are very busy, I won't trouble you.
10. Even if (though) I fail. I’ll never lose heart.
11. Once you begin the work, you must continue.
12. Although the sun was shining, it wasn’t very warm.
地点
目的
原因
让步
时间
让步
三、时间状语从句重难点
1、when, while, as引导时间状语从句
(1)when的用法
A. when引导时间状语从句既可指时间点,也可指时间段
(即:从句动词可以是短暂的也可是延续的)。
For example:
①When I lived there, I used to go to the seashore on Sundays.
② When he arrived in Shanghai , his mother met him at the station .
B. When 在下列句式中译为“就在那时,这时”,可以看成是并列句,这种用法的when一般位于句末。
For example:
① I was putting on my clothes when the telephone rang.
②我正要锁门,这时电话响了。
③我刚锁上门,这时电话响了。
was doing … when
was about to do…when
was on the point of doing … when
had done… when
(2)while的用法
A. while只能指一段时间,从句中的动词必须是延续性动词。强调某一段时间内主句动作发生,相当于during the time that....;从句常用进行时态。
For example:
①Please don’t talk so loud while others are working.
②My mother was cooking while I was doing my homework.
B. while作为并列连词,意为“而,却”,表示同类对比。
For example:
I like watching TV, while he likes reading.
C. while也可用来引导让步状语从句,意为“尽管,虽然”,相当于although
For example
While I admit that the problems are difficult , I don’t agree that they can’t be solved.
D. “ 只要 ” 条件状语
For example
While there is water, there exist life.
While there is will, there is way.
E. 趁…的情况赶紧做, 否则来不及了
For example
Strike while the iron is hot.
趁热打铁。
(3)as的用法
A. as可用来引导时间状语,常可和when换用,但较强调主从句动作同时发生,意为“一边…一边”,引出伴随动作
For example:
She was doing her homework as she was listening to the music.
B. as还可说明两种正在发展或变化的情况,“随着...”的意思,表时间的推移。
For example:
①As time went by/With time ___ , I began to realize the importance
of learning.
② As I grow older, I become more interested in music.
C. as也可用来引导原因状语从句,意为“因为”
For example:
As she is free today, she would like to do some shopping.
D. as还可用来引导让步状语从句(用倒装结构),意为“尽管”。For example:
Tired as he was, he refused to take a rest.
2、before、after引导时间状语从句
(1)before和after表示的是两个时间或两个事件之间的先后关系;引导时间状语从句最基本的意思就是“在..之前”、“在…之后”;before从句的动作通常发生在主句动作之后,如果从句用过去时,主句一般要用过去完成时;after从句的动作通常发生在主句动作之前,如果主句用过去时,从句一般要用过去完成时。
For example
①在我们看到陆地前,我们已经航行四天四夜了。
We had sailed four days and four nights before we saw land.
②他在这家工厂工作十年以后就出国了。
After he had worked in the factory for ten years, he went abroad.
(2)before时间状语从句的特殊句式
主句包含表段时间的短语、且为肯定句常译成“…(之后)才”;
主句包含表段时间的短语、且为否定句常译成“…就”;
这样的句型有一般过去时、过去将来时、一般将来时三个时态。
A. It will be/+段时间+before…do…“还要过多久才…”
B. It was +时间段+before …did… (动作已发生)
C. It will not be long before…“不多久就会…”
D. It was not long before…“不多久就…了”
For example:
①再过两年他才大学毕业。
It will be two years before he graduates from the university.
②两年之后他才大学毕业。
It was two years before he graduated from the university.
③他不多久就会从大学毕业了。
It will not be long before he graduates from the university.
④他不多久就从大学毕业了。
It was not long before he graduated from the university.
3、until, till, not…until引导时间状语从句
(1)until/till从句用于肯定句时,主句的动词是延续性动作,表示“某动作一直延续到某时间点才停止”,译为“直到…为止”。
For example:我们一直在那里待到雨停了。
We stayed there until the rain stopped.
(2)until从句用于否定句时,主句的动词是短暂性动作,表示“某动作直到某时间才开始”,译为“直到… 才”。
For example:我们一直到雨停了才离开。
We didn’t leave until the rain stopped.
注意:till不可放在句首或用于强调句中, not…until句型中一般也不用till。
(3)用于强调句式“It is/ was not until ...that ...”
For example:
直到雨停了我们才离开。
It was not until the rain stopped that we left.
(4)not until放在句首时主句要进行部分倒装
For example:
我们一直到雨停了才离开。
Not until the rain stopped did we leave.
4、since引导时间状语从句
since从句一般要用非延续性动词did或动词have done,意为“自从…时起”,主句要用完成时态
For example:
He has worked in this city since he graduated from the college.
(1)since所引导从句如果用延续性或状态动词的一般过去时,所表示的就是动作或状态的完成或结束。
翻译:Since Tom lived in Nanjing, I have not heard from him.
自从Tom离开南京以后,我没有收到过他的信。
(2)作介词时,since后要接时间点,而不是时间段;
5、表示“一…就…”句型
(1)as soon as/ once
For example:
①我一到上海就会写信给你。
As soon as I arrive in Shanghai, I will write to you.
②你一旦开始这项工作,就必须继续下去。
Once you begin the work, you must continue.
★注意★
(1)在时间状语从句中,不能用将来时或过去将来时,而要用现在时或过去时代替将来时。
(2)once一般译为“一旦”,从句可以表示时间和条件两层含义。
(2)名词短语转变成连词:
the moment, the instant, the minute, the second
For example:
He came to the spot/ scene the moment he heard of the accident.
(3)副词转变成连词:
instantly, immediately, directly
For example:
They told me the news immediately they got the message.
(4)no sooner ...than , hardly/scarcely...when
A.意思:“一…就…”
B.时态:主句(no sooner/ hardly/ scarcely)用过去完成时,
从句(than/ when)用一般过去时。
C.倒装:结构中的否定词(no sooner/ hardly/ scarcely)放在句首时,主句(紧跟其后的句子)要倒装。
For example:
我刚到车站,火车就开走了。
I had no sooner got to the station than the train left.
句型转换(no sooner)置于句首:
No sooner had I got to the station than the train left.
(5)介词短语
upon/on doing sth./one’s + n.作时间状语,意为“一…就…”
For example:
美国学生一到来,我们就给他们热情地欢迎。
On arriving, we gave the American students a warm welcome.
句型转换:
On their arrival, we gave the American students a warm welcome.
6、一些含有time的名词短语
如the first /second/last time, every time, each time, next time, by the time等,也可引导时间状语从句。
For example:
①The first time I drove the car, I felt very nervous.
②Next time you come, please bring your composition.
③ By the time you graduate, we will have lived in Australia for one year.
四、地点状语从句重难点
1、where/wherever
Where指“在某个地方”,wherever指“在任何一个地方”;
可以放在主句前,也可以放在主句后。
For example:
①有志者事竟成/有水的地方就有生命。
Where there is a will, there is a way.
Where there is water, there is life.
②You should put the book where it was.
③ Wherever you go, you must obey the law.
2、where引导地点状语从句与定语从句的区别
For example:
一般而言,有工厂的地方空气都会被严重污染。
Generally, air will be heavily polluted in the places where there are factories.
Generally, air will be heavily polluted where there are factories.
定语从句:主句…表地点的名词+where…
place
状语从句:主句…+ where…
place
五、原因状语从句重难点
原因状语从句由because, as , since, now (that)(既然), in that(因为,多于口语中),seeing (that)(鉴于,由于),considering that(考虑到)等引导。
1、because
because用来回答why提出的问题,表示某件事发生的直接原因或理由,用于告知对方不知道的原因。在这几个连词中,它表示原因的语气最强,可用于强调句。
For example:
I came back late yesterday because I was on duty.
It was because I was on duty that I came back late yesterday.
2、since, now that
since、now that常表示关系上的自然结果,特别用于原因已经清楚了的事情,说话人根据这个事实得出某一种结论。其语气比because要弱,一般译成“既然”,往往放在主句前。
For example:
Since you have known the secret, I needn’t say anything about it.
3、as
as常用于表示十分明显的原因,只是对主句的附带说明,重点放在主句上,语气较弱,常译成“由于”,可放在主句前或主句后。 For example:
As he didn’t know much English, he looked up the word in the dictionary .
4、for
for也可以表示原因,属并列连词,不是说明直接原因,而是对某种情况加以推断或解释,对前一分句进行附加说明;它引出的分句必须放在另一分句后。
For example:
门关着,屋子里肯定没人。
There must be no one in the house, for the door is closed.
5、seeing (that), considering (that), in that
这几个连词 和since, as 意义相似,他们都有“鉴于某个事实、原因是”的意思。
For example:
鉴于他病情严重,我们派人去请医生了。
Seeing that he was badly ill, we sent for the doctor .
六、条件状语从句重难点
由if, unless(if...not), so/as long as, supposing(that)(假设), provided/providing (that)(假若), in case(万一…, 以防…), on condition that(条件是...),so/as far as(就...而言)等引导
1、if/unless
if表示正面的条件,意为“如果”;
unless表示反面的条件,相当于(if…not),意为“除非,如果不”。
For example:
We won’t wait for him, if he doesn’t come before 12o’clock.
We won’t wait for him, unless he comes before 12o’clock.
2、 supposing(that), provided/providing (that),
on condition that, in case, so/as long as
这些连词词组意思相近,有“如果,假如,假设,在…条件下”等意义
For example:
①So long as you keep on trying, you will surely succeed.
②In case John comes, please tell him to wait.
3、as/so far as就…而言
For example:
So far as I know, the book will be published next month.
4、only if ﹠ if only
only if引导的从句用陈述语气,意为“只要”; if only引导的从句要用虚拟语气,意为“但愿…,要是…就好了”
For example:
①Only if you keep on trying, you will surely succeed.
②如果当初我们听取了你的建议就好了。
If only we had followed your advice!
If only …(要是…就好了)
与现在事实相反,从句中用一般过去时
与过去事实相反,从句中用过去完成时
与将来情况相反,从句中用could/would/might+动词原形
5、条件状语从句的虚拟
if引导的条件状语从句若与过去或现在事实不符,或对未来进行不可能的假设,就要用虚拟语气。
For example:
①如果有一天机器人掌控了世界,将不会再有友谊。
If Robots should control the world some day, here would be no friendship.
②如果考试中Tom能再仔细些,他就已经通过考试了。
If Tom had been more careful in the exam, he would have passed it already.
③如果我是一个老师,我会对我的学生很严格。
If I were a teacher, I would be strict with my students.
从句 主句
与现在相反 If +主语+动词过去式,主语+ should/would/could/might+动词原形
与过去相反 If +主语+had +过去分词,主语+should/would/could/might have+过去分词
If +主语+动词过去式,
与将来相反 If +主语+should+动词原形, 主语+should/would/could/might+动词原形
If +主语+were to+动词原形,
6、条件状语从句的省略与倒装
If引导的虚拟条件从句中谓语动词有were, had或should,可以把if省去,而把were,had或should移到主语前构成倒装。
If Tom had been more careful in the exam, he would have passed it already.
Had Tom been more careful in the exam , he would have passed it already.
七、目的状语从句重难点
由so that(以便), in order that(为了),for fear that(= in case)(以免),lest(以防)引导,谓语常含may, might, can, could, will, would, should等情态动词。从句往往放在主句之后,主从句之间不用任何标点符号。
1、so that/ in order that
For example:
① They worked harder than usual in order that they could finish the work ahead of time.
They worked harder than usual in order to finish the work ahead of time.
②The teacher raised his voice on purpose so that the students in the back could hear more clearly.
2、 lest/ for fear that/ in case
这些连词词组意思相近,意思是“以防、以免”;
lest从句一般用虚拟语气,形式“should+动词原形”或只用原形;
for fear that从句和in case从句一般用虚拟语气,但有时也可以用陈述语气。
For example:
①多穿点衣服,以免感冒。
Put on more clothes lest/ for fear that/ in case that you should catch a cold.
②他把相机准备好,万一看到适合拍照的东西。
He had his camera ready in case he saw something that would make a good picture.
八、结果状语从句重难点
常用的连词有so that,so ... that, such...that;
结果状语从句中一般无情态动词
1、so that,so ... that, such...that
For example:
①他们比往常更加努力工作,结果提前完成了工作。
They worked harder than usual, so that they finished the work ahead of time.
They worked hard enough to finish the work ahead of time.
②老师说话声音很大,因此后面的同学听得很清晰。
The teacher spoke so loud that the students in the back heard clearly.
2、 so/ such…that所用句式
A、 so + adj /adv + that从句
B、 so + adj +a/an+单[C]+ that从句
C、 so many/few +复[C]+ + that从句
D、 so much/little+[U]+ that从句
E、 such + adj +复[C] /[U]+ that从句
F、 such +a/an + adj + 单[C]+ + that从句
九、让步状语从句重难点
常用的连词有though, although, even though, even if, as, while, no matter wh-, wh-ever, whether…or(不管…还是)
1、though/ although
though, although这两个连词用法基本一样,只是前者口语化,后者较正式;
让步状语从句可以放在主句前或者主句后;
though还可作副词单独放在句尾,表示“然而,可是,不过”的意思。
For example:
I had a very good time although I didn’t know anybody at the party.
然而,我们有些不同之处。
We have some differences, though.
★注意★
连词引导让步状语从句不能与but连用,但可以与副词yet,still,nevertheless连用
2、 even if/ even though
常用以强调让步概念,有退一步设想的意思,“即使、纵使”;有时有假设含义,用于虚拟语气。
For example:
①即使明天下雨,我也要去。
I’ll go even if it rains tomorrow.
②即使我处在你的位置,我也不会接受这份工作。
Even if I were in your place, I wouldn’t take the job.
3、 while
while引导让步状语从句时置于主句前,与although,though相同
For example:
尽管我承认他的好成绩,但我依然感觉给他这个重要的职位不够明智。
While I admit his good points, I still feel it unwise to offer him this important position.
4、 whether…or (not)
whether…or (not)可以引导让步状语从句,提供两个对比的情况,意为“不管…”。
For example:
不管你是否相信,它都是真的。
Whether you believe it or nor, it is true.
6、 no matter+疑问词、疑问词+ever
For example:
①为了表示尊重,我们无论与谁握手,都常常将手套摘下。
To show our respect, we usually have to take off our gloves, whoever/ no matter who we are to shake hands with.
② 我会尊重任何尊重我的人。
I will show respect to whoever respects me.
who
what
no matter+ which
when
where
how
whoever
whatever
whichever
whenever
wherever
however
二者辨析
相同之处
在让步状语从句中可以相互替换
不同之处
后者能引导名词性从句
7、 as
as引导让步状语从句时,从句要用部分倒装语序。基本结构如下:
A、形容词/副词/名词+as+主+谓,主句…
B、动词+as+主+情态动词/助动词,主句…
★注★
作表语的单数名词放在句首时,该名词前不可加定冠词或者不定冠词
For example:
①他虽有耐心,但也不愿等三个小时。
Patient as he was, he was unwilling to wait for three hours.
②尽管我很尊重他,但却不同意他的建议。
Much as I respect him, I don’t agree to his advice.
③虽然他还是个孩子,但已经熟知了英语。
Child as he was, he had a good knowledge of English.
④尽管我尽可能地尝试了,但还是没能举起那块石头。
Try as I might, I couldn’t lift the stone.
8、 表让步的介词短语
For example:
① I had a very good time although I didn’t know anybody at the party.
I had a very good time despite the fact that I didn’t know anybody at the party.
②尽管我们竭尽全力保住这个学校,但政府还是决定把它关闭。
Despite all our efforts to save the school, the government decided to close it.
Although we tried our best to save the school, the government decided to close it.
A、despite
B、in spite of
C、despite the fact that
D、in spite of the fact that
十、方式状语从句重难点
常用的连词有as, as if, as though
1、as
引导方式状语从句,意为“按照,正如…”
For example:
①请按照我所讲的去做。
Please do it as I told you.
②他们严密地监视她,就好像猫盯着老鼠看。
They watched her closely as a cat watches a rat.
③入乡随俗。
When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
2、 as if/ as though
A、这两个连词意义相同,意为“好像,仿佛”;
B、可引导方式状语从句与表语从句;
C、当从句为(可能)符合事实的情况时,用陈述语气;
D、当从句不符合事实或与事实相反,用虚拟语气,具体如下:
For example:
①他待我如陌生人一样。
He treats me as if I were a stranger.
②他站在门口,好像在等谁似的。
He stood at the door as if he was waiting for someone.
as if/ as though …(好像,仿佛)
与现在事实相反,从句中用一般过去时
与过去事实相反,从句中用过去完成时
与将来情况相反,从句中用could/would+动词原形
十一、比较状语从句重难点
常用的连词有as…as, than, not so/ as…as, the same as…, the more…the more…
1、as+adj./adv.+as和not +so/as+adj./adv.+as
前者意为“和…一样”,表示肯定意义,为等量比较;
后者意为“不及…”,表示否定意义,为不等量比较
For example:
①他对音乐的了解就像我对画作的了解一样少。
He knows as little about music as I know about painting.
②他的舞姿不及他的妹妹优雅。
He dances not as gracefully as his sister (dances).
2、 than
表不同程度之比较,主句中用形容词或副词的比较级,意为“比…更”
For example:
①他今年比去年进步更大。
He has made greater progress this year than he did last year.
②我比他更了解你。
I know you better than he (knows you).
3、表比较的特殊结构
A、the+形容词或副词比较级…, the +形容词或副词比较级
B、A is to B what C is to D A对B而言就像C对D一样
For example:
①你工作越努力,取得地进步就越大。
The harder you work, the greater progress you will make.
②越快越好。The sooner, the better.
③Food is to men what oil is to machines.
食物之于人,犹如油之于机器。
十二、状语从句注意点
1、状语从句的省略问题
状语从句的省略常用在时间、条件、让步、方式、比较状语从句中,分两种情况:
A、当状语从句的主语是it,且谓语动词包含be动词的某种形式时,it和be可以省略掉
For example:
除非你不方便,否则你必须出席这次会议。
You must attend the meeting unless (it is) inconvenient to you.
B、当状语从句的主语和主句的主语一致,从句谓语动词包含be动词的某种形式时,从句主语和be可以省略掉.省略后从句常见的情形有:
连词+adj./n./prep. phrase/done/doing/to do
For example:
①他有空就去逛商店。
Whenever (she is ) free, she often goes shopping.
②他看上去很焦急,好像遇到了麻烦。
He looked anxious as if he was in trouble
While watching TV, _________.
A the doorbell rang
B the doorbell rings
C we heard the door bell ring
D we heard the doorbell rings
状语从句省略问题
2、状语从句的倒装问题
A、否定词开头:not until、hardly…when、no sooner…than(主句部分倒装)
B、so + adj./adv.开头(主句部分倒装)
C、as、though引导的让步状语从句(从句把需要强调部分提到主语前)
1、So difficult _____ it to live in an English-speaking country that I determined to learn English. (01 上海)
A. I have felt B. have I felt C. I did feel D. did I feel
2、Not until all the fish died in the river _____ how serious the pollution was.
A. did the villagers realize B. the villagers realized
C. the villagers did realize D. didn’t the villagers realize
选择题
D
A
3、状语从句的时态问题
A、在时间、条件状语从句中,用一般现在时、一般过去时表示一般将来时、过去将来时;
B、在since引导的时间状语从句中常用一般过去时、主句则常用现在完成时
The house will fall down soon if no one______(do)some quick repair work.
does
Goodbye!
对比训练与巩固
1. We were about to leave____ it began to
rain.
2. She thought I was talking about her son,
____, in fact, I was talking about my son.
3. Hardly had I finished my composition
____ the bell rang.
A. when B. while C. as D. during
对比训练 1
A
B
A
1. Child ____ she is, she know a lot.
2. He did the experiment ____ he was told.
3. The pianos in the other shop will be
cheaper, but not ____ good.
A. during B. as C. if D. though
对比训练 2
B
B
B
1. He would have a look at the bookstores
____ he went to town.
2. We decide to finish the work on time, ____
happens.
3. If we work with a strong will, we overcome
any difficulty, ____ great it is.
4. I’ll give the book to ____ likes English.
A. whenever B. whoever
C. whatever D. however
对比训练 3
A
C
D
B
对比训练 4
1. If we work hard, we can overcome any
difficulty, no matter ____ great it is.
2. If we work hard, we can overcome any
difficulty, ____ great it is.
3. If we work hard, we can overcome any
difficulty, ____ difficulty it is.
4. If we work hard, we can overcome any
difficulty, no matter ____ difficulty it is.
A. what B. how C. however D. whatever
B
C
D
A
对比训练 5
1. It will be years ____ we meet again.
2. It is ten years ____ I came to this town.
3. It is ten years ago ____ I came to this town.
A. when B. that C. before D. since
C
D
B
对比训练 6
Go and get your coat. It is ____ you left it.
2. You are free to go ____ you like.
A. there B. where
C. wherever D. when
B
C
对比训练 7
1. The article is written in such easy English
____ all of us can read it.
2. The article is written in such easy English
____ all of us can read.
A. that B. which C. as D. so that
A
C
A
Practice makes perfect.
