2022届高考英语语法专题:时态和语态课件(30张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2022届高考英语语法专题:时态和语态课件(30张) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 777.7KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-04-06 11:06:36 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
(共30张PPT)
Part 1 时态和语态的概述
时态是谓语动词所表示的动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。
语态是指主语与谓语动词之间的关系,分为主谓关系(主动)和动宾关系(被动)。当说话者强调的是动作本身,且没有必要知道或不知道动作执行者是谁时,常使用被动语态。在被动语态中,句子的主语是动作的承受者。
Part 1 时态和语态的概述
Part 1 时态和语态的概述
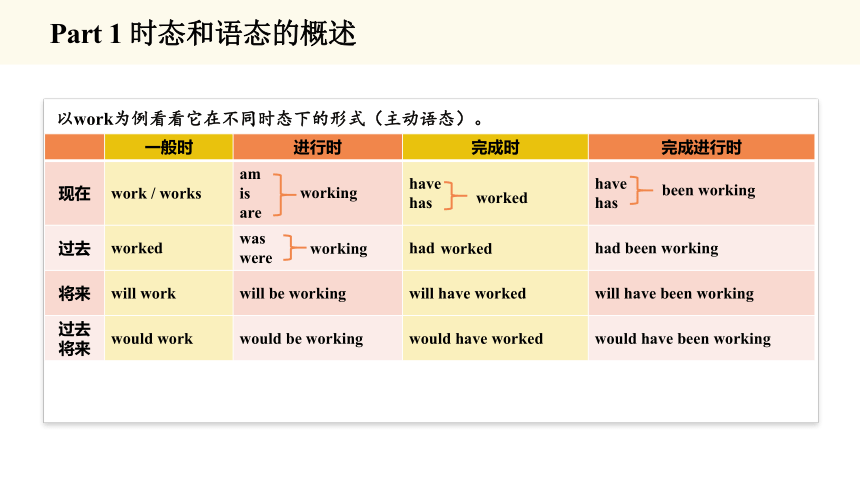
以work为例看看它在不同时态下的形式(主动语态)。
一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时
现在 work / works am is are have has have
has
过去 worked was were had had been working
将来 will work will be working will have worked will have been working
过去将来 would work would be working would have worked would have been working
working
working
worked
worked
been working
Part 1 时态和语态的概述
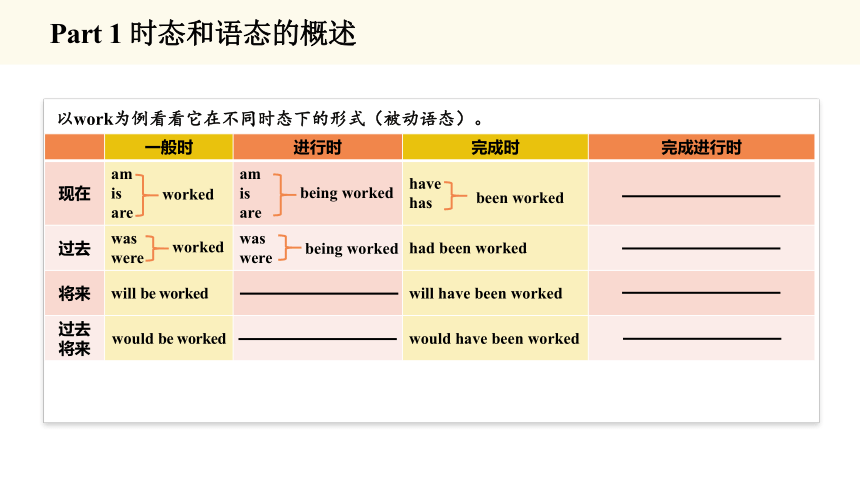
以work为例看看它在不同时态下的形式(被动语态)。
一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时
现在 am is are am is are have has
过去 was were was were had been worked
将来 will be worked will have been worked
过去将来 would be worked would have been worked
being worked
being worked
been worked
worked
worked
Part 2 一般时
Part 2 一般时
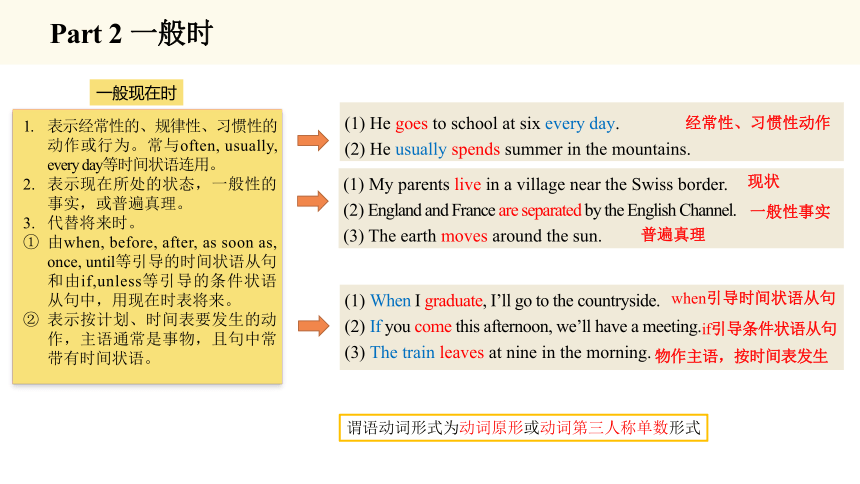
一般现在时
表示经常性的、规律性、习惯性的动作或行为。常与often, usually, every day等时间状语连用。
表示现在所处的状态,一般性的事实,或普遍真理。
代替将来时。
由when, before, after, as soon as, once, until等引导的时间状语从句和由if,unless等引导的条件状语从句中,用现在时表将来。
表示按计划、时间表要发生的动作,主语通常是事物,且句中常带有时间状语。
(1) He goes to school at six every day.
(2) He usually spends summer in the mountains.
(1) My parents live in a village near the Swiss border.
(2) England and France are separated by the English Channel.
(3) The earth moves around the sun.
经常性、习惯性动作
现状
一般性事实
普遍真理
(1) When I graduate, I’ll go to the countryside.
(2) If you come this afternoon, we’ll have a meeting.
(3) The train leaves at nine in the morning.
when引导时间状语从句
if引导条件状语从句
物作主语,按时间表发生
谓语动词形式为动词原形或动词第三人称单数形式
Part 2 一般时
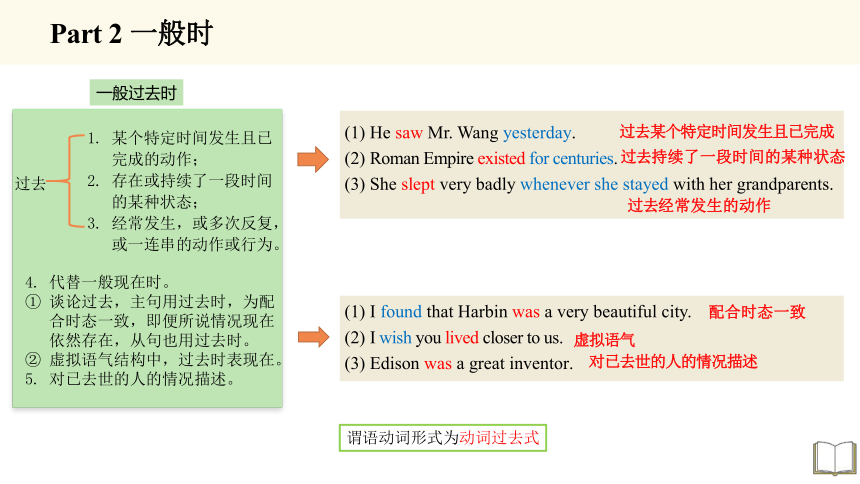
一般过去时
(1) He saw Mr. Wang yesterday.
(2) Roman Empire existed for centuries.
(3) She slept very badly whenever she stayed with her grandparents.
过去某个特定时间发生且已完成
(1) I found that Harbin was a very beautiful city.
(2) I wish you lived closer to us.
(3) Edison was a great inventor.
配合时态一致
过去
某个特定时间发生且已完成的动作;
存在或持续了一段时间的某种状态;
经常发生,或多次反复,或一连串的动作或行为。
过去持续了一段时间的某种状态
虚拟语气
代替一般现在时。
谈论过去,主句用过去时,为配合时态一致,即便所说情况现在依然存在,从句也用过去时。
虚拟语气结构中,过去时表现在。
对已去世的人的情况描述。
对已去世的人的情况描述
过去经常发生的动作
谓语动词形式为动词过去式
Part 2 一般时
一般将来时
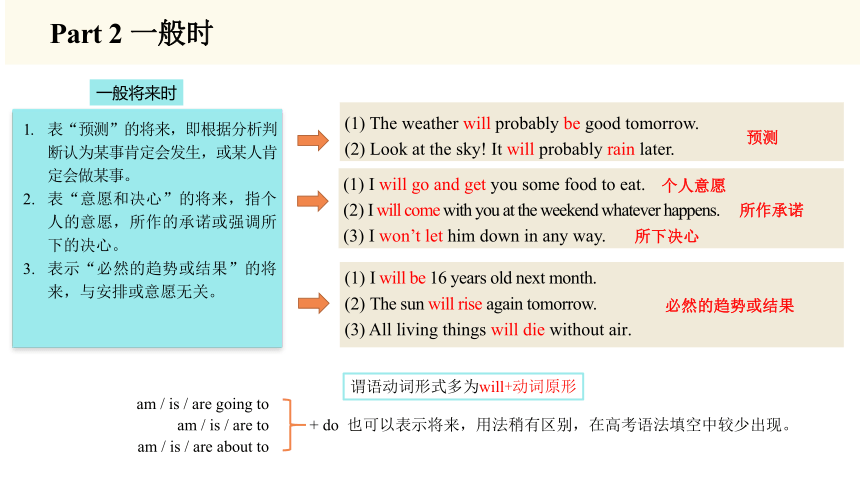
表“预测”的将来,即根据分析判断认为某事肯定会发生,或某人肯定会做某事。
表“意愿和决心”的将来,指个人的意愿,所作的承诺或强调所下的决心。
表示“必然的趋势或结果”的将来,与安排或意愿无关。
(1) The weather will probably be good tomorrow.
(2) Look at the sky! It will probably rain later.
(1) I will go and get you some food to eat.
(2) I will come with you at the weekend whatever happens.
(3) I won’t let him down in any way.
预测
个人意愿
所作承诺
所下决心
(1) I will be 16 years old next month.
(2) The sun will rise again tomorrow.
(3) All living things will die without air.
am / is / are going to
am / is / are to
am / is / are about to
+ do 也可以表示将来,用法稍有区别,在高考语法填空中较少出现。
谓语动词形式多为will+动词原形
必然的趋势或结果
Part 2 一般时
过去将来时
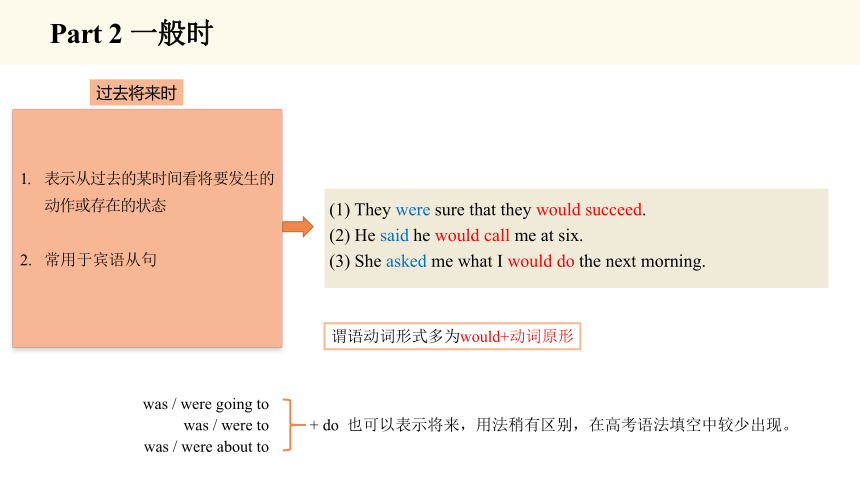
表示从过去的某时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态
常用于宾语从句
(1) They were sure that they would succeed.
(2) He said he would call me at six.
(3) She asked me what I would do the next morning.
was / were going to
was / were to
was / were about to
+ do 也可以表示将来,用法稍有区别,在高考语法填空中较少出现。
谓语动词形式多为would+动词原形
Part 2 一般时
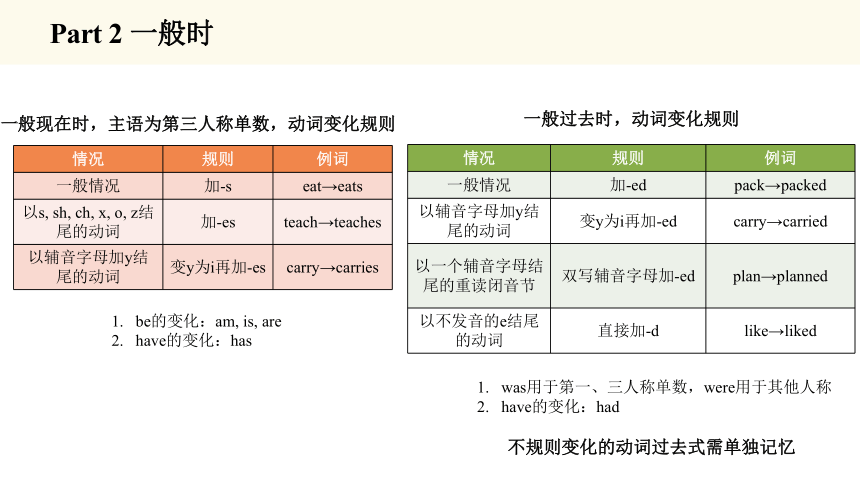
情况 规则 例词
一般情况 加-s eat→eats
以s, sh, ch, x, o, z结尾的动词 加-es teach→teaches
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词 变y为i再加-es carry→carries
情况 规则 例词
一般情况 加-ed pack→packed
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词 变y为i再加-ed carry→carried
以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节 双写辅音字母加-ed plan→planned
以不发音的e结尾的动词 直接加-d like→liked
一般现在时,主语为第三人称单数,动词变化规则
一般过去时,动词变化规则
be的变化:am, is, are
have的变化:has
was用于第一、三人称单数,were用于其他人称
have的变化:had
不规则变化的动词过去式需单独记忆
Part 2 一般时
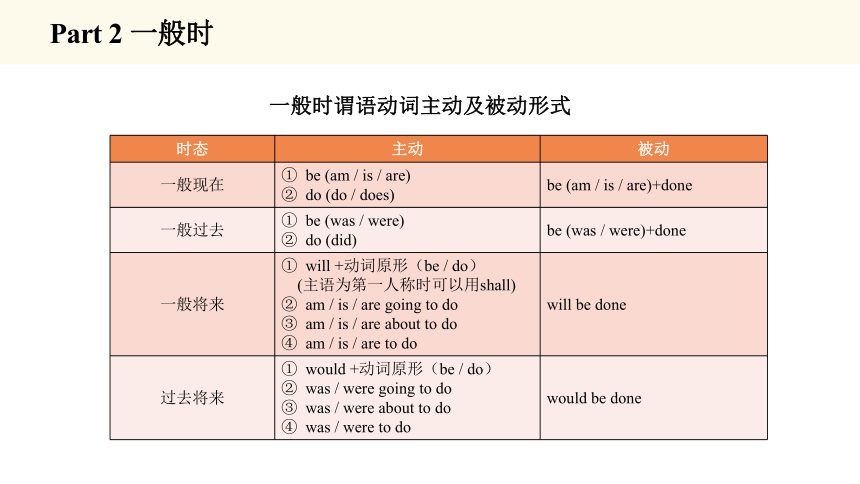
时态 主动 被动
一般现在 be (am / is / are) do (do / does) be (am / is / are)+done
一般过去 be (was / were) do (did) be (was / were)+done
一般将来 will +动词原形(be / do) (主语为第一人称时可以用shall) am / is / are going to do am / is / are about to do am / is / are to do will be done
过去将来 would +动词原形(be / do) was / were going to do was / were about to do was / were to do would be done
一般时谓语动词主动及被动形式
Part 3 进行时
Part 3 进行时
现在进行时
表示说话时正在进行中的动作,或目前正在不断变化的情况。
表示某个特定时间段内正在进行或反复进行的事情,常与these/those days, this/that week等时间状语连用。
表示赞赏、厌恶、遗憾等情绪,常与always, continually, constantly, forever, all the time等连用。
(1) Please don’t make so much noise. I am working.
(2) More people are moving to the cities, so the cities are getting larger.
(1) We are making model planes these days.
(2) I’m feeding the neighbour’s cat this week.
(3) I’m hearing a lot of good news about you.
(1) She is always complaining.
(2) He is forever finding fault with me.
(3) You are always thinking of others first.
谓语动词形式为be (am / is / are)+doing
Part 3 进行时
过去进行时
表示过去某一时刻、某一阶段正在进行的动作。
常和一般过去时一起使用,描述一个动作进行过程中另一个动作发生。
也能与always, constantly, continually, forever等连用表达某种感彩。
(1) In 2011 he was studying in a university.
(2) During my training I was earning a lot less than my wife.
(1) He was reading a novel when I came in.
(2) When the telephone rang, I was watching TV.
(1) My brother was always losing his keys.
(2) My sister was always late for school.
谓语动词形式为 be (was / were)+doing
Part 3 进行时
将来进行时
表示将来某个特定时间要进行的动作。
表示早已安排将来要做的或预订会发生的事,往往指难以改变。
(1) What will you be doing this time tomorrow
(2) When I get home, you will probably be watching television.
(1) He will be staying with us again next year.
(2) I will be meeting her over Christmas vacation.
谓语动词形式多为will / shall+be+doing
Part 3 进行时
情况 规则 例词
一般情况 加-ing eat→eating
以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词 双写结尾的辅音字母加-ing sit→sitting
以不发音的e结尾的动词 去掉结尾的e再加-ing hate→hating
write→writing
现在分词的变化规则
时态 主动 被动
现在进行 be (am / is / are)+doing be (am / is / are)+being+done
过去进行 be (was / were)+doing be (was / were)+being+done
将来进行 will +be+doing (主语为第一人称时可以用shall)
进行时谓语动词主动及被动形式
下列动词不用于进行时
感觉类(look, smell, feel, taste, see, hear)
情感类(like, love, prefer, admire, hate, fear, adore)
心态类(wish, hope, want, need, believe, understand, forget, agree, know )
状态类(appear, lie (位于), remain, belong to, have)
Part 4 完成时
Part 4 完成时
现在完成时
表示一个动作开始于过去,持续到现在。常与for和since,so far,up to now,in the past / last few days / years,recently等连用。
表示动作在说话之前已完成,但对现在有影响。句中常没有具体的时间状语。
在“It / This is +the+序数词 / 最高级 / only+名词”之后的从句中谓语动词常用现在完成时。
(1) In the past few years, great changes have taken place.
(2) He has written 8 books so far.
(3) Up to now, everything has been successful.
(1) He has gone to Beijing.
(2) I have lost my wallet.
(3) He has already obtained a scholarship.
(1) It is the best film that I’ve ever seen.
(2) It is the first time that I’ve seen such a wonderful building.
(3) It is the only book that he has written.
谓语动词形式为have / has+done
过去完成时
一件事情发生在过去,而另外一件事情先于它发生(即表“过去的过去”),那么发生在前的动作要用过去完成时。
表示从过去某一时间开始,一直延续到过去的另一时间的动作,常用的时间状语有:by / until / before / by the end of +表过去的某一时间。
Hardly / Scarcely / Barely+过去完成时(倒装)+when +句子(过去时)
No sooner +过去完成时(倒装)+than +句子(过去时)
It was / had been +一段时间+since从句(过去完成时)
(1) She had learned some English before she came to the institute.
(2) He said that he had been abroad for 3 years.
(1) By then he had learned English for 3 years.
(2) Until then he had known nothing about it yet.
(3) By the end of last year, they had treated over 10,000 patients.
(1) Hardly had we arrived when she started complaining.
(2) No sooner had he arrived than he began to complain.
(3) It was ten years since we had had such a wonderful time.
谓语动词形式为had+done
Part 4 完成时
将来完成时
表示将来某时刻前某动作已完成,或预计将已完成。常用时间状语为“by+将来的某个时间”。
(1) By the time of next week, they will have reached the destination.
(2) A new type of computer will have been manufactured within the
next years.
(3) When we get there, they will probably have left.
谓语动词形式为will have done
Part 4 完成时
现在完成进行时
动作发生在过去,持续到现在且现在还在进行
现在完成进行时是现在完成时和现在进行时的组合,因此它既具备现在完成时的特征,又具备现在进行时的特征。
(1) He has been learning English for 6 years.
(2) It has been raining for 3 days.
(3) Helen has been spending a lot of time at the club lately.
谓语动词形式为have / has+been+doing
Part 4 完成时
完成时谓语动词主动及被动形式
时态 主动 被动
现在完成 have / has done have / has been done
过去完成 had done had been done
将来完成 will have done will have been done
现在完成进行 have been doing
瞬间性动词用于现在完成时且与表示一段时间的时间状语连用时,需在谓语动词、时
态或句型方面作相应的变化。
如:
借:borrow→have kept 买:buy→have had 感冒:catch a cold→have had a cold
参加:join→have been in 死:die→have been dead 开始:start→be on
入睡:fall asleep→have been asleep 病倒:fall ill→have been / felt ill
结婚:marry→have been married 离开:leave→have been away
Part 4 完成时
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
一、AAA型(原形→原形→原形)
二、ABA型(原形→过去式→原形)
三、ABC型
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
三、ABC型
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
三、ABC型
四、ABB型
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
四、ABB型
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
四、ABB型
五、AAB型
六、有两种形式
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
六、有两种形式
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
六、有两种形式
七、情态动词
谢谢观看
Part 1 时态和语态的概述
时态是谓语动词所表示的动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。
语态是指主语与谓语动词之间的关系,分为主谓关系(主动)和动宾关系(被动)。当说话者强调的是动作本身,且没有必要知道或不知道动作执行者是谁时,常使用被动语态。在被动语态中,句子的主语是动作的承受者。
Part 1 时态和语态的概述
Part 1 时态和语态的概述
以work为例看看它在不同时态下的形式(主动语态)。
一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时
现在 work / works am is are have has have
has
过去 worked was were had had been working
将来 will work will be working will have worked will have been working
过去将来 would work would be working would have worked would have been working
working
working
worked
worked
been working
Part 1 时态和语态的概述
以work为例看看它在不同时态下的形式(被动语态)。
一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时
现在 am is are am is are have has
过去 was were was were had been worked
将来 will be worked will have been worked
过去将来 would be worked would have been worked
being worked
being worked
been worked
worked
worked
Part 2 一般时
Part 2 一般时
一般现在时
表示经常性的、规律性、习惯性的动作或行为。常与often, usually, every day等时间状语连用。
表示现在所处的状态,一般性的事实,或普遍真理。
代替将来时。
由when, before, after, as soon as, once, until等引导的时间状语从句和由if,unless等引导的条件状语从句中,用现在时表将来。
表示按计划、时间表要发生的动作,主语通常是事物,且句中常带有时间状语。
(1) He goes to school at six every day.
(2) He usually spends summer in the mountains.
(1) My parents live in a village near the Swiss border.
(2) England and France are separated by the English Channel.
(3) The earth moves around the sun.
经常性、习惯性动作
现状
一般性事实
普遍真理
(1) When I graduate, I’ll go to the countryside.
(2) If you come this afternoon, we’ll have a meeting.
(3) The train leaves at nine in the morning.
when引导时间状语从句
if引导条件状语从句
物作主语,按时间表发生
谓语动词形式为动词原形或动词第三人称单数形式
Part 2 一般时
一般过去时
(1) He saw Mr. Wang yesterday.
(2) Roman Empire existed for centuries.
(3) She slept very badly whenever she stayed with her grandparents.
过去某个特定时间发生且已完成
(1) I found that Harbin was a very beautiful city.
(2) I wish you lived closer to us.
(3) Edison was a great inventor.
配合时态一致
过去
某个特定时间发生且已完成的动作;
存在或持续了一段时间的某种状态;
经常发生,或多次反复,或一连串的动作或行为。
过去持续了一段时间的某种状态
虚拟语气
代替一般现在时。
谈论过去,主句用过去时,为配合时态一致,即便所说情况现在依然存在,从句也用过去时。
虚拟语气结构中,过去时表现在。
对已去世的人的情况描述。
对已去世的人的情况描述
过去经常发生的动作
谓语动词形式为动词过去式
Part 2 一般时
一般将来时
表“预测”的将来,即根据分析判断认为某事肯定会发生,或某人肯定会做某事。
表“意愿和决心”的将来,指个人的意愿,所作的承诺或强调所下的决心。
表示“必然的趋势或结果”的将来,与安排或意愿无关。
(1) The weather will probably be good tomorrow.
(2) Look at the sky! It will probably rain later.
(1) I will go and get you some food to eat.
(2) I will come with you at the weekend whatever happens.
(3) I won’t let him down in any way.
预测
个人意愿
所作承诺
所下决心
(1) I will be 16 years old next month.
(2) The sun will rise again tomorrow.
(3) All living things will die without air.
am / is / are going to
am / is / are to
am / is / are about to
+ do 也可以表示将来,用法稍有区别,在高考语法填空中较少出现。
谓语动词形式多为will+动词原形
必然的趋势或结果
Part 2 一般时
过去将来时
表示从过去的某时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态
常用于宾语从句
(1) They were sure that they would succeed.
(2) He said he would call me at six.
(3) She asked me what I would do the next morning.
was / were going to
was / were to
was / were about to
+ do 也可以表示将来,用法稍有区别,在高考语法填空中较少出现。
谓语动词形式多为would+动词原形
Part 2 一般时
情况 规则 例词
一般情况 加-s eat→eats
以s, sh, ch, x, o, z结尾的动词 加-es teach→teaches
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词 变y为i再加-es carry→carries
情况 规则 例词
一般情况 加-ed pack→packed
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词 变y为i再加-ed carry→carried
以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节 双写辅音字母加-ed plan→planned
以不发音的e结尾的动词 直接加-d like→liked
一般现在时,主语为第三人称单数,动词变化规则
一般过去时,动词变化规则
be的变化:am, is, are
have的变化:has
was用于第一、三人称单数,were用于其他人称
have的变化:had
不规则变化的动词过去式需单独记忆
Part 2 一般时
时态 主动 被动
一般现在 be (am / is / are) do (do / does) be (am / is / are)+done
一般过去 be (was / were) do (did) be (was / were)+done
一般将来 will +动词原形(be / do) (主语为第一人称时可以用shall) am / is / are going to do am / is / are about to do am / is / are to do will be done
过去将来 would +动词原形(be / do) was / were going to do was / were about to do was / were to do would be done
一般时谓语动词主动及被动形式
Part 3 进行时
Part 3 进行时
现在进行时
表示说话时正在进行中的动作,或目前正在不断变化的情况。
表示某个特定时间段内正在进行或反复进行的事情,常与these/those days, this/that week等时间状语连用。
表示赞赏、厌恶、遗憾等情绪,常与always, continually, constantly, forever, all the time等连用。
(1) Please don’t make so much noise. I am working.
(2) More people are moving to the cities, so the cities are getting larger.
(1) We are making model planes these days.
(2) I’m feeding the neighbour’s cat this week.
(3) I’m hearing a lot of good news about you.
(1) She is always complaining.
(2) He is forever finding fault with me.
(3) You are always thinking of others first.
谓语动词形式为be (am / is / are)+doing
Part 3 进行时
过去进行时
表示过去某一时刻、某一阶段正在进行的动作。
常和一般过去时一起使用,描述一个动作进行过程中另一个动作发生。
也能与always, constantly, continually, forever等连用表达某种感彩。
(1) In 2011 he was studying in a university.
(2) During my training I was earning a lot less than my wife.
(1) He was reading a novel when I came in.
(2) When the telephone rang, I was watching TV.
(1) My brother was always losing his keys.
(2) My sister was always late for school.
谓语动词形式为 be (was / were)+doing
Part 3 进行时
将来进行时
表示将来某个特定时间要进行的动作。
表示早已安排将来要做的或预订会发生的事,往往指难以改变。
(1) What will you be doing this time tomorrow
(2) When I get home, you will probably be watching television.
(1) He will be staying with us again next year.
(2) I will be meeting her over Christmas vacation.
谓语动词形式多为will / shall+be+doing
Part 3 进行时
情况 规则 例词
一般情况 加-ing eat→eating
以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词 双写结尾的辅音字母加-ing sit→sitting
以不发音的e结尾的动词 去掉结尾的e再加-ing hate→hating
write→writing
现在分词的变化规则
时态 主动 被动
现在进行 be (am / is / are)+doing be (am / is / are)+being+done
过去进行 be (was / were)+doing be (was / were)+being+done
将来进行 will +be+doing (主语为第一人称时可以用shall)
进行时谓语动词主动及被动形式
下列动词不用于进行时
感觉类(look, smell, feel, taste, see, hear)
情感类(like, love, prefer, admire, hate, fear, adore)
心态类(wish, hope, want, need, believe, understand, forget, agree, know )
状态类(appear, lie (位于), remain, belong to, have)
Part 4 完成时
Part 4 完成时
现在完成时
表示一个动作开始于过去,持续到现在。常与for和since,so far,up to now,in the past / last few days / years,recently等连用。
表示动作在说话之前已完成,但对现在有影响。句中常没有具体的时间状语。
在“It / This is +the+序数词 / 最高级 / only+名词”之后的从句中谓语动词常用现在完成时。
(1) In the past few years, great changes have taken place.
(2) He has written 8 books so far.
(3) Up to now, everything has been successful.
(1) He has gone to Beijing.
(2) I have lost my wallet.
(3) He has already obtained a scholarship.
(1) It is the best film that I’ve ever seen.
(2) It is the first time that I’ve seen such a wonderful building.
(3) It is the only book that he has written.
谓语动词形式为have / has+done
过去完成时
一件事情发生在过去,而另外一件事情先于它发生(即表“过去的过去”),那么发生在前的动作要用过去完成时。
表示从过去某一时间开始,一直延续到过去的另一时间的动作,常用的时间状语有:by / until / before / by the end of +表过去的某一时间。
Hardly / Scarcely / Barely+过去完成时(倒装)+when +句子(过去时)
No sooner +过去完成时(倒装)+than +句子(过去时)
It was / had been +一段时间+since从句(过去完成时)
(1) She had learned some English before she came to the institute.
(2) He said that he had been abroad for 3 years.
(1) By then he had learned English for 3 years.
(2) Until then he had known nothing about it yet.
(3) By the end of last year, they had treated over 10,000 patients.
(1) Hardly had we arrived when she started complaining.
(2) No sooner had he arrived than he began to complain.
(3) It was ten years since we had had such a wonderful time.
谓语动词形式为had+done
Part 4 完成时
将来完成时
表示将来某时刻前某动作已完成,或预计将已完成。常用时间状语为“by+将来的某个时间”。
(1) By the time of next week, they will have reached the destination.
(2) A new type of computer will have been manufactured within the
next years.
(3) When we get there, they will probably have left.
谓语动词形式为will have done
Part 4 完成时
现在完成进行时
动作发生在过去,持续到现在且现在还在进行
现在完成进行时是现在完成时和现在进行时的组合,因此它既具备现在完成时的特征,又具备现在进行时的特征。
(1) He has been learning English for 6 years.
(2) It has been raining for 3 days.
(3) Helen has been spending a lot of time at the club lately.
谓语动词形式为have / has+been+doing
Part 4 完成时
完成时谓语动词主动及被动形式
时态 主动 被动
现在完成 have / has done have / has been done
过去完成 had done had been done
将来完成 will have done will have been done
现在完成进行 have been doing
瞬间性动词用于现在完成时且与表示一段时间的时间状语连用时,需在谓语动词、时
态或句型方面作相应的变化。
如:
借:borrow→have kept 买:buy→have had 感冒:catch a cold→have had a cold
参加:join→have been in 死:die→have been dead 开始:start→be on
入睡:fall asleep→have been asleep 病倒:fall ill→have been / felt ill
结婚:marry→have been married 离开:leave→have been away
Part 4 完成时
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
一、AAA型(原形→原形→原形)
二、ABA型(原形→过去式→原形)
三、ABC型
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
三、ABC型
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
三、ABC型
四、ABB型
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
四、ABB型
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
四、ABB型
五、AAB型
六、有两种形式
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
六、有两种形式
Part 5 不规则动词归类记忆表
六、有两种形式
七、情态动词
谢谢观看
