高考英语语法完全讲解——虚拟语气(共23张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 高考英语语法完全讲解——虚拟语气(共23张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-04-08 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共23张PPT)
高考英语语法完全讲解
虚拟语气
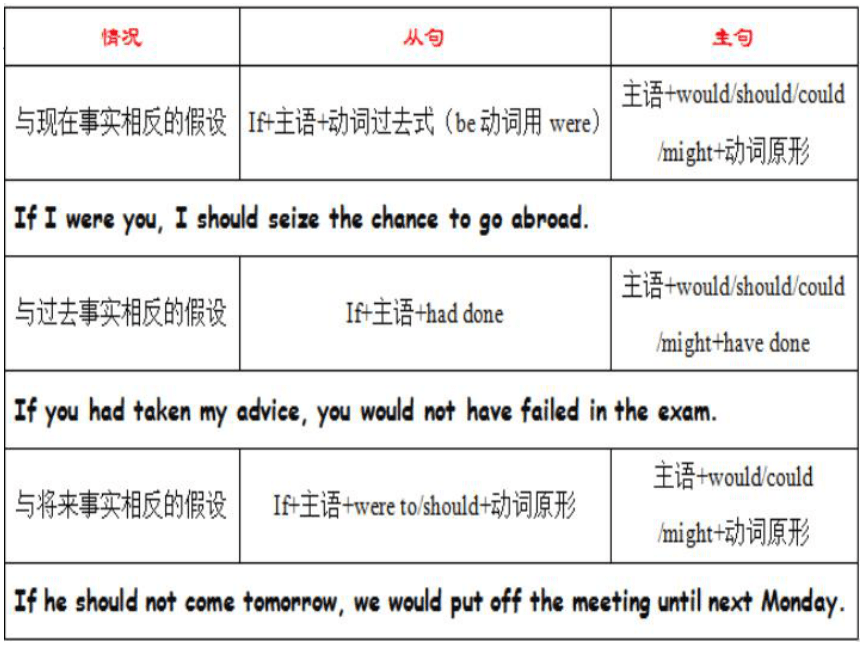
1、错综时间条件句
当条件状语从句表示的行为和主句表示的行为所发生的时间不一致时,被称为“错综时间条件句”,动词的形式要根据它所表示的时间作出相应的调整。
If you had followed my advice just now, you would be better now.
If it had rained last night, the ground would be wet now.
2、if省略句
当条件状语从句中谓语含有were, had, should时,可以省略if,将were, had, should提到从句句首,变为倒装句式。
If I were at school again, I would study harder.
—Were I at school again, I would study harder.
If you had come earlier, you would have caught the bus.
—Had you come earlier, you would have caught the bus.
If it should rain tomorrow, we would not go climbing.
—Should it rain tomorrow, we should not go climbing.
3、含蓄条件句
有时候为了表达的需要,在虚拟条件句中并不是总会出现if引导的条件句,而是通过其它手段来代替条件句,常见有with, without, or, otherwise, but, but for, but that等。
What would you do with a million dollars (=If you had a million dollars)
Without your help, we couldn’t have finished the work ahead of time.
=But for your help, ...
=If it hadn’t been for your help, ...
I was ill that day. Otherwise, I would have taken part in the sports meeting.
=If I hadn’t been ill that day, I would have taken part in the sports meeting.
I should have given you more help, but I was too busy.
=If I hadn’t been too busy, I should have given you more help.
1、wish后的宾语从句一般用虚拟语气,表示一种不可能实现的愿望。从句的谓语动词形式主要分为三类:(1)一般过去时(动作与wish同时发生);(2)过去完成时(动作先于wish发生);(3)would/could/might+动词原形(动作后于wish发生)。
I wish that I were a bird and could fly freely in the sky.
I wish I had met that film star yesterday.
I wish that I would fly to the moon one day in the future.
注:if only+句子=How I wish that+从句,表示“但愿……,如果……就好了”。
If only I were a flying bird!
=How I wish I were a flying bird!
If only I had seen the film!=How I wish I had seen the film!
2、用于表示建议、愿望、命令等动词后的宾语从句中,常见的动词有:suggest, advise, propose, recommend, insist, order, demand, require, request, desire, urge等,谓语动词用should +动词原形的形式,should通常省略。
He suggested that we (should) start off early the next day.
They insisted that the boy (should) go with them.
用于表示建议、愿望、命令等动词后的宾语从句中,常见的动词有:suggest, advise, propose, recommend, insist, order, demand, require, request, desire, urge等,谓语动词用should +动词原形的形式,should通常省略。
He suggested that we (should) start off early the next day.
They insisted that the boy (should) go with them.
3、在would rather后的宾语从句中也用虚拟语气,用过去时表示对现在或者将来情况的虚拟,用过去完成时表示对过去情况的虚拟。
I would rather they hadn’t heard of the news yesterday.
Itisdesired/suggested/proposed/recommended/necessary/essential/important/strange/natural/a pity/a shame+that从句,从句谓语动词用“should +动词原形”的形式,should通常省略。
It is suggested that the meeting (should) be put off till next week.
It is a pity that he (should) be badly ill.
用于主句从句中
在suggestion, advice, proposal, order, plan, idea, desire, request, demand等名词后的表语从句和同位语从句中要用虚拟语气,从句谓语动词用“should +动词原形”的形式,should通常省略。
My idea is that we (should) think it over before accepting it.
We all agreed to his suggestion that we (should) go to Dalian for sightseeing.
用于表语从句和同位语从句中
在It is (high/about) time that...句型中,定语从句的谓语动词一般用过去时,或用“should+动词原形”(其中should不可以省略),该句型表示“该……”,用来表示提议。
It is time that you went to school.
It is time that the children should have lunch.
1、在as if/though“好像、似乎”引导的方式状语从句中,如果表达虚假的事实,需要用虚拟语气,从句用一般过去时表示与现在事实的相反;用过去完成时表示与过去事实的相反;用过去将来时表示与将来事实的相反。
He looks as if he were an artist.
They spoke English fluently as if they had learned English for many years.
特别提醒:
as if/though也可以表示真实的情况,这时用真实语气。
Look at the dark clouds in the sky. It looks as if it is going to rain soon.
2、在lest/for fear that“以防”引导的目的状语从句中,从句谓语动词用“should +动词原形”的形式,should通常省略。
He got up early lest(for fear that)he should miss the first train.
在考查虚拟语气时,在同一个语境中会牵扯到真实情况和虚拟情况,真实情况的时态使用为如何表达虚拟情况提供了依据,尤其在含蓄虚拟语气中。具体说来,如果真实情况用的是现在时态,那么接下来所使用的虚拟语气就是对现在情况的虚拟;同理,如果真实情况用的是过去时态,那么虚拟语气应该是对过去情况的虚拟。
would/could/might/should +动词原形+ but+现在时陈述句
→表示同现在事实相反的假设
We would arrive earlier but the car breaks down.
(If the car didn't break down, we would arrive earlier.)
would/could/might/should have +过去分词+ but+过去时陈述句
→表示同过去事实相反的假设
We would have arrived earlier but the car broke down.
(If the car hadn't broken down, we would have arrived earlier.)
现在时陈述句+otherwise/or+would/could/might/should +动词原形
→表示同现在事实相反的假设
The car breaks down otherwise we would arrive earlier.
(If the car didn't break down, we would arrive earlier.)
过去时陈述句+otherwise/or+would/could/might/should have +过去分词
→表示同过去事实相反的假设
The car broke down otherwise we would have arrived earlier.
(If the car hadn't broken down, we would have arrived earlier.)
高考英语语法完全讲解
虚拟语气
1、错综时间条件句
当条件状语从句表示的行为和主句表示的行为所发生的时间不一致时,被称为“错综时间条件句”,动词的形式要根据它所表示的时间作出相应的调整。
If you had followed my advice just now, you would be better now.
If it had rained last night, the ground would be wet now.
2、if省略句
当条件状语从句中谓语含有were, had, should时,可以省略if,将were, had, should提到从句句首,变为倒装句式。
If I were at school again, I would study harder.
—Were I at school again, I would study harder.
If you had come earlier, you would have caught the bus.
—Had you come earlier, you would have caught the bus.
If it should rain tomorrow, we would not go climbing.
—Should it rain tomorrow, we should not go climbing.
3、含蓄条件句
有时候为了表达的需要,在虚拟条件句中并不是总会出现if引导的条件句,而是通过其它手段来代替条件句,常见有with, without, or, otherwise, but, but for, but that等。
What would you do with a million dollars (=If you had a million dollars)
Without your help, we couldn’t have finished the work ahead of time.
=But for your help, ...
=If it hadn’t been for your help, ...
I was ill that day. Otherwise, I would have taken part in the sports meeting.
=If I hadn’t been ill that day, I would have taken part in the sports meeting.
I should have given you more help, but I was too busy.
=If I hadn’t been too busy, I should have given you more help.
1、wish后的宾语从句一般用虚拟语气,表示一种不可能实现的愿望。从句的谓语动词形式主要分为三类:(1)一般过去时(动作与wish同时发生);(2)过去完成时(动作先于wish发生);(3)would/could/might+动词原形(动作后于wish发生)。
I wish that I were a bird and could fly freely in the sky.
I wish I had met that film star yesterday.
I wish that I would fly to the moon one day in the future.
注:if only+句子=How I wish that+从句,表示“但愿……,如果……就好了”。
If only I were a flying bird!
=How I wish I were a flying bird!
If only I had seen the film!=How I wish I had seen the film!
2、用于表示建议、愿望、命令等动词后的宾语从句中,常见的动词有:suggest, advise, propose, recommend, insist, order, demand, require, request, desire, urge等,谓语动词用should +动词原形的形式,should通常省略。
He suggested that we (should) start off early the next day.
They insisted that the boy (should) go with them.
用于表示建议、愿望、命令等动词后的宾语从句中,常见的动词有:suggest, advise, propose, recommend, insist, order, demand, require, request, desire, urge等,谓语动词用should +动词原形的形式,should通常省略。
He suggested that we (should) start off early the next day.
They insisted that the boy (should) go with them.
3、在would rather后的宾语从句中也用虚拟语气,用过去时表示对现在或者将来情况的虚拟,用过去完成时表示对过去情况的虚拟。
I would rather they hadn’t heard of the news yesterday.
Itisdesired/suggested/proposed/recommended/necessary/essential/important/strange/natural/a pity/a shame+that从句,从句谓语动词用“should +动词原形”的形式,should通常省略。
It is suggested that the meeting (should) be put off till next week.
It is a pity that he (should) be badly ill.
用于主句从句中
在suggestion, advice, proposal, order, plan, idea, desire, request, demand等名词后的表语从句和同位语从句中要用虚拟语气,从句谓语动词用“should +动词原形”的形式,should通常省略。
My idea is that we (should) think it over before accepting it.
We all agreed to his suggestion that we (should) go to Dalian for sightseeing.
用于表语从句和同位语从句中
在It is (high/about) time that...句型中,定语从句的谓语动词一般用过去时,或用“should+动词原形”(其中should不可以省略),该句型表示“该……”,用来表示提议。
It is time that you went to school.
It is time that the children should have lunch.
1、在as if/though“好像、似乎”引导的方式状语从句中,如果表达虚假的事实,需要用虚拟语气,从句用一般过去时表示与现在事实的相反;用过去完成时表示与过去事实的相反;用过去将来时表示与将来事实的相反。
He looks as if he were an artist.
They spoke English fluently as if they had learned English for many years.
特别提醒:
as if/though也可以表示真实的情况,这时用真实语气。
Look at the dark clouds in the sky. It looks as if it is going to rain soon.
2、在lest/for fear that“以防”引导的目的状语从句中,从句谓语动词用“should +动词原形”的形式,should通常省略。
He got up early lest(for fear that)he should miss the first train.
在考查虚拟语气时,在同一个语境中会牵扯到真实情况和虚拟情况,真实情况的时态使用为如何表达虚拟情况提供了依据,尤其在含蓄虚拟语气中。具体说来,如果真实情况用的是现在时态,那么接下来所使用的虚拟语气就是对现在情况的虚拟;同理,如果真实情况用的是过去时态,那么虚拟语气应该是对过去情况的虚拟。
would/could/might/should +动词原形+ but+现在时陈述句
→表示同现在事实相反的假设
We would arrive earlier but the car breaks down.
(If the car didn't break down, we would arrive earlier.)
would/could/might/should have +过去分词+ but+过去时陈述句
→表示同过去事实相反的假设
We would have arrived earlier but the car broke down.
(If the car hadn't broken down, we would have arrived earlier.)
现在时陈述句+otherwise/or+would/could/might/should +动词原形
→表示同现在事实相反的假设
The car breaks down otherwise we would arrive earlier.
(If the car didn't break down, we would arrive earlier.)
过去时陈述句+otherwise/or+would/could/might/should have +过去分词
→表示同过去事实相反的假设
The car broke down otherwise we would have arrived earlier.
(If the car hadn't broken down, we would have arrived earlier.)
