L29-情态辅助动词二 初中英语词性句法新讲课件(共10张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | L29-情态辅助动词二 初中英语词性句法新讲课件(共10张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-04-11 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
(共10张PPT)
情态辅助动词二
Lesson 29:
授课人:曾老师
Will
I will check this letter for you, if you want.
How long will you be staying in Paris
He hopes from his very heart that he will win a prize.
Even if you won't tell me, I'll know anyway.
肯定:想要/将会/决心要
(主观意愿打算)
否定:不想/不会/不要
Will you tell me a story
Will you send my breakfast up, please
Will you (please)…
询问对方主观上愿不愿意
You'll do it this minute!
Will you be quiet
有时也可以用作相对委婉
的命令或要求
The train will depart at 7:30 a.m.
We hope it will be a commercial success.
It won’t rain tomorrow.
在猜测的情况下,偏向于
句中主语的意愿打算
Won't you have more rice
Why won't you help us
“否定+疑问”表建议责问
情态辅助动词:
Would
He said he would be here at eight o'clock.
She asked if I would do a help.
They told me that they probably wouldn’t come.
If you went to see him, he would be delighted. 较有可能
作为will的过去式,表述
相同的意思,但would
的强度相对要弱一点
It would be a shame to miss the beginning of the play.
She’d be a fool to accept it.
He’d always be the first to offer to help.
I wish you'd be quiet for a minute.
I’d say he was about fifty. (我估计)
I wouldn’t give you anything.
My car wouldn’t start this morning.
肯定:
将会/有可能/有意向…
较有可能的猜测
否定:
不愿意/没有可能
If I had seen the notice in time, I would have applied
for the job.
I wouldn't have any more to drink, if I were you.
用于假定(将有/没可能).
过去式有含与现在情况
相反之意
情态辅助动词:
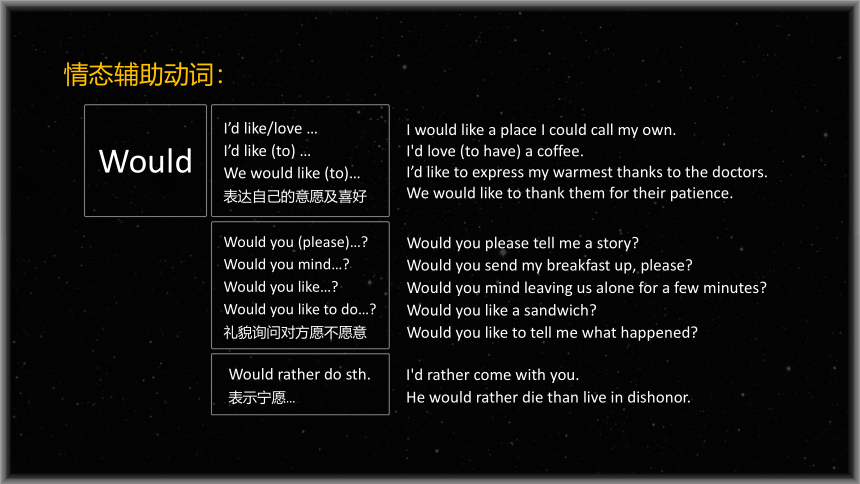
I would like a place I could call my own.
I'd love (to have) a coffee.
I’d like to express my warmest thanks to the doctors.
We would like to thank them for their patience.
I’d like/love …
I’d like (to) …
We would like (to)…
表达自己的意愿及喜好
Would you please tell me a story
Would you send my breakfast up, please
Would you mind leaving us alone for a few minutes
Would you like a sandwich
Would you like to tell me what happened
Would you (please)…
Would you mind…
Would you like…
Would you like to do…
礼貌询问对方愿不愿意
I'd rather come with you.
He would rather die than live in dishonor.
Would rather do sth.
表示宁愿…
情态辅助动词:
Would
Shall
I will come back, and I shall come back.
This time next week I shall be in Scotland.
I intend that he shall be a physician.
You shall not make this speech.
No matter how you say, he shall not come back!
肯定:应该/应当
(较强的主观意愿)
否定:不应该/不可能…
Shall I telephone her and ask her to come here
Shall we take your message to her
Shall I/We…
询问对方我(们) 该不该…
情态辅助动词:
Should
She said she should know it by now.
I should probably go now.
So we should be arriving in Mexico right on time.
You should say ‘excuse me’ when you step on somebody's foot.
可以作为shall的过去式,
也可以作为独立的情态助
动词用。肯定表示应该,
否定则不应该
He should have been more careful.
I should have written the notes in the opposite order.
If I had your help, I should succeed.
用于假定 (本该…)
过去式有含与现情况相
反之意
情态辅助动词:
have to
Nurses have to wear a uniform.
You haven't got to go there with me.
肯定:必须/不得不(外因)
否定:不必/不用
ought to
I ought to give up smoking.
You've got a good wife. You ought to take care of her.
肯定:应该/应当(客观)
否定:不必/不用
“This ought to be fun.” He told Alex, eyes gleaming.
应该/可能(客观猜测)
情态辅助动词:
1. Can、May 的区别:
表示同意允许时:
肯定行的时候会说:You can …, 或其它表示同意的词,比如“OK, no problem.”
基本行的时候会说:You may …
“May I … ”与 “Can I … ” 意思基本相同:前者指“可不可以”,后者指“能不能”。
2. Must、Should、Have/has to、Ought to 的区别:
表示命令建议时:
主观意愿中带有命令含义的时候会说:You must …
主观意愿中带有建议含义的时候会说:You should …
客观因素引起的“不得不”要说:You have to …
客观因素引起的“得要”要说:You ought to …
3. Mustn’t、Shouldn’t、Can’t、May not 的区别:
表示不可以时:
绝对不行的时候会说:You mustn’t …
不应该这么做的时候会说:You shouldn’t …
不允许这么做的时候会说:You can’t …
不可以这么做的时候会说:You may not …,(you can’t…语气更强)
4. Will、Be going to 的区别:
表示将来的动作时:
主观意愿较强的时候会说:It will rain tomorrow.
He will fly to Chicago next Tuesday.
客观原因条件的时候会说:It is going to rain tomorrow.
The meeting is going to begin.
5. Will、Shall 的区别:
表示意愿打算时:
意愿较强时用shall, 一般意愿时用will, 比如:I will come back, and I shall come back.
6. Will、Would、May、Might 的区别:
很肯定的情况用will, 比如:The train will come soon.
较肯定的情况用would, 比如:The train would come soon.
有可能的情况用may, 比如:The train may come soon.
也许有可能的情况用might, 比如:The train might come soon.
情态辅助动词二
Lesson 29:
授课人:曾老师
Will
I will check this letter for you, if you want.
How long will you be staying in Paris
He hopes from his very heart that he will win a prize.
Even if you won't tell me, I'll know anyway.
肯定:想要/将会/决心要
(主观意愿打算)
否定:不想/不会/不要
Will you tell me a story
Will you send my breakfast up, please
Will you (please)…
询问对方主观上愿不愿意
You'll do it this minute!
Will you be quiet
有时也可以用作相对委婉
的命令或要求
The train will depart at 7:30 a.m.
We hope it will be a commercial success.
It won’t rain tomorrow.
在猜测的情况下,偏向于
句中主语的意愿打算
Won't you have more rice
Why won't you help us
“否定+疑问”表建议责问
情态辅助动词:
Would
He said he would be here at eight o'clock.
She asked if I would do a help.
They told me that they probably wouldn’t come.
If you went to see him, he would be delighted. 较有可能
作为will的过去式,表述
相同的意思,但would
的强度相对要弱一点
It would be a shame to miss the beginning of the play.
She’d be a fool to accept it.
He’d always be the first to offer to help.
I wish you'd be quiet for a minute.
I’d say he was about fifty. (我估计)
I wouldn’t give you anything.
My car wouldn’t start this morning.
肯定:
将会/有可能/有意向…
较有可能的猜测
否定:
不愿意/没有可能
If I had seen the notice in time, I would have applied
for the job.
I wouldn't have any more to drink, if I were you.
用于假定(将有/没可能).
过去式有含与现在情况
相反之意
情态辅助动词:
I would like a place I could call my own.
I'd love (to have) a coffee.
I’d like to express my warmest thanks to the doctors.
We would like to thank them for their patience.
I’d like/love …
I’d like (to) …
We would like (to)…
表达自己的意愿及喜好
Would you please tell me a story
Would you send my breakfast up, please
Would you mind leaving us alone for a few minutes
Would you like a sandwich
Would you like to tell me what happened
Would you (please)…
Would you mind…
Would you like…
Would you like to do…
礼貌询问对方愿不愿意
I'd rather come with you.
He would rather die than live in dishonor.
Would rather do sth.
表示宁愿…
情态辅助动词:
Would
Shall
I will come back, and I shall come back.
This time next week I shall be in Scotland.
I intend that he shall be a physician.
You shall not make this speech.
No matter how you say, he shall not come back!
肯定:应该/应当
(较强的主观意愿)
否定:不应该/不可能…
Shall I telephone her and ask her to come here
Shall we take your message to her
Shall I/We…
询问对方我(们) 该不该…
情态辅助动词:
Should
She said she should know it by now.
I should probably go now.
So we should be arriving in Mexico right on time.
You should say ‘excuse me’ when you step on somebody's foot.
可以作为shall的过去式,
也可以作为独立的情态助
动词用。肯定表示应该,
否定则不应该
He should have been more careful.
I should have written the notes in the opposite order.
If I had your help, I should succeed.
用于假定 (本该…)
过去式有含与现情况相
反之意
情态辅助动词:
have to
Nurses have to wear a uniform.
You haven't got to go there with me.
肯定:必须/不得不(外因)
否定:不必/不用
ought to
I ought to give up smoking.
You've got a good wife. You ought to take care of her.
肯定:应该/应当(客观)
否定:不必/不用
“This ought to be fun.” He told Alex, eyes gleaming.
应该/可能(客观猜测)
情态辅助动词:
1. Can、May 的区别:
表示同意允许时:
肯定行的时候会说:You can …, 或其它表示同意的词,比如“OK, no problem.”
基本行的时候会说:You may …
“May I … ”与 “Can I … ” 意思基本相同:前者指“可不可以”,后者指“能不能”。
2. Must、Should、Have/has to、Ought to 的区别:
表示命令建议时:
主观意愿中带有命令含义的时候会说:You must …
主观意愿中带有建议含义的时候会说:You should …
客观因素引起的“不得不”要说:You have to …
客观因素引起的“得要”要说:You ought to …
3. Mustn’t、Shouldn’t、Can’t、May not 的区别:
表示不可以时:
绝对不行的时候会说:You mustn’t …
不应该这么做的时候会说:You shouldn’t …
不允许这么做的时候会说:You can’t …
不可以这么做的时候会说:You may not …,(you can’t…语气更强)
4. Will、Be going to 的区别:
表示将来的动作时:
主观意愿较强的时候会说:It will rain tomorrow.
He will fly to Chicago next Tuesday.
客观原因条件的时候会说:It is going to rain tomorrow.
The meeting is going to begin.
5. Will、Shall 的区别:
表示意愿打算时:
意愿较强时用shall, 一般意愿时用will, 比如:I will come back, and I shall come back.
6. Will、Would、May、Might 的区别:
很肯定的情况用will, 比如:The train will come soon.
较肯定的情况用would, 比如:The train would come soon.
有可能的情况用may, 比如:The train may come soon.
也许有可能的情况用might, 比如:The train might come soon.
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
