2021-2022学年外研版八年级下册英语Module 5 Cartoons讲义 (含答案)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2021-2022学年外研版八年级下册英语Module 5 Cartoons讲义 (含答案) |
|
|
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 279.9KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-04-15 16:05:38 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
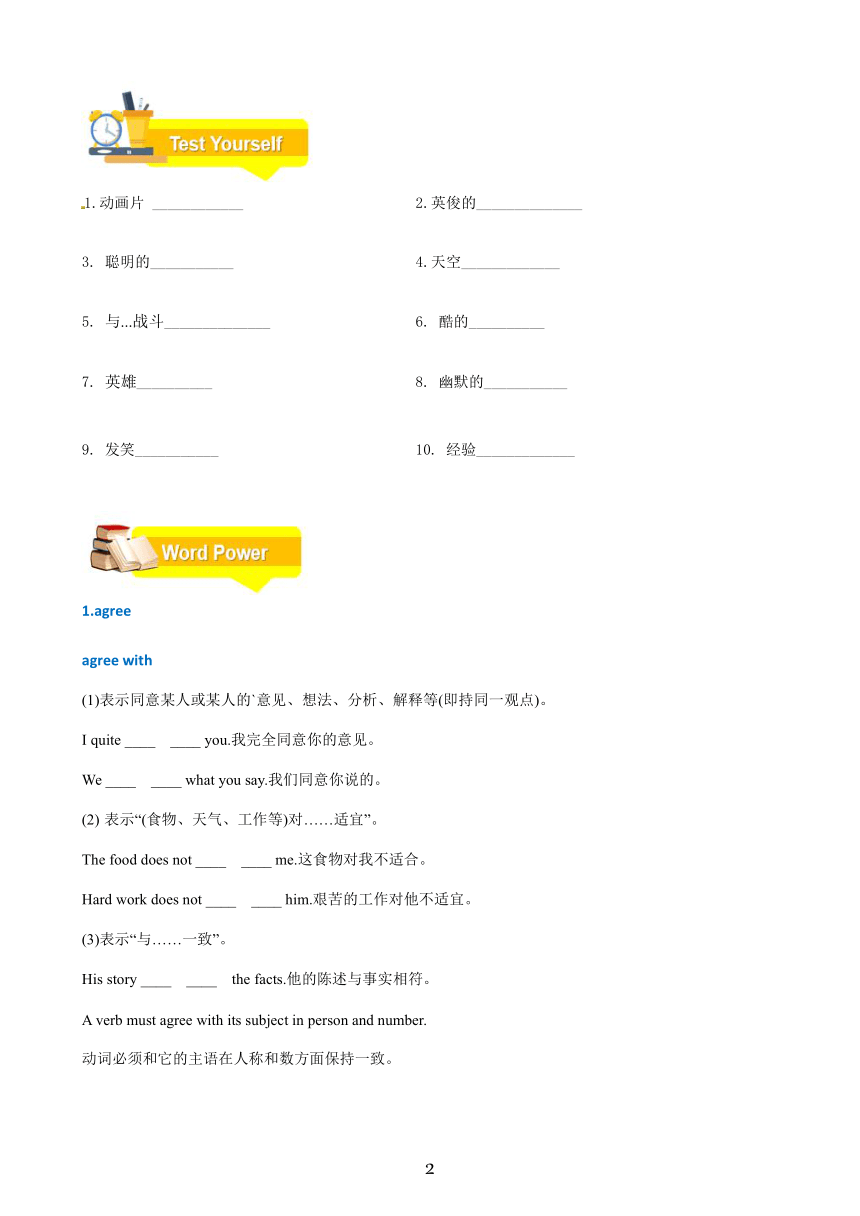
佛山外研版英语下册G8 Module 5 School-in
知识清单
词汇 词汇表单词 (必备) 名词:cartoon漫画,动画片 sky天空 hero英雄 lesson经验,教训,课程 schoolbag书包 mess脏乱 heaven天堂 artist艺术家 动词:laugh发笑 lead领导 expect期盼 invent发明 create创造;satisfy满足,使满意 形容词: handsome漂亮的,英俊的 smart聪明的 cool时髦的,凉爽的,酷的 humorous幽默的 orange-and-white橙白相间的 ugly丑陋的 clever聪明的 black-and-white黑白的 private私人得 副词: 代词: 连词:as当...时 兼词:1.fight与...战斗v.;战斗,斗争n. 2.copy一本/份n.;复制,复印v. 3.own自己的adj.;拥有v. 短语:1.can't help doing sth忍不住做某事 2.win the heart of sb.赢得某人得心 回收垃圾 4 4. 4.ea
佳句 I couldn't help laughing when I watch them. ...both of them have won the heart of young people all over the world. Fans have bought about 200 million copies of Tintin’s stories in more than fifty languages. It’s time to watch a cartoon. I don’t think we agree. Snoopy lives in his own private world.
语法 区分一般现在时,一般过去时和现在完成时
1.动画片 ____________ 2.英俊的______________
3. 聪明的___________ 4.天空_____________
5. 与...战斗______________ 6. 酷的__________
7. 英雄__________ 8. 幽默的___________
9. 发笑___________ 10. 经验_____________
1.agree
agree with
(1)表示同意某人或某人的`意见、想法、分析、解释等(即持同一观点)。
I quite ____ ____ you.我完全同意你的意见。
We ____ ____ what you say.我们同意你说的。
表示“(食物、天气、工作等)对……适宜”。
The food does not ____ ____ me.这食物对我不适合。
Hard work does not ____ ____ him.艰苦的工作对他不适宜。
(3)表示“与……一致”。
His story ____ ____ the facts.他的陈述与事实相符。
A verb must agree with its subject in person and number.
动词必须和它的主语在人称和数方面保持一致。
agree to
(1)后接某些名词,表示同意或接受某事,尤其指别人提出的某事,有时可能是自己不喜欢的事。
He agree the plan(the date)。他同意了这个计划(日期)。
We ____ ____ their arrangement.我们同意了他们的安排。
I was forced to agree to it,but at heart I didn’t quite agree with it.我被迫答应,但内心不完全同意。
(2)后接动词原形(此时to是不定式符号)或动名词(一般有逻辑主语,此时to是介词)。
We agreed to leave early.我们同意早点出发。
She agreed to my going home.她同意我回去。
agree on /upon
(1)主要指双方通过协商而取得一致意见或达成协议。
Can we ____ ____ a price(a date) 我们能不能商定一个价格(日期)
Both sides agreed on these terms.双方都同意这些条件。
注:在正式文体中,有时可省略介词 on.
Can we agree a price(date)
后接动名词,表示同意做某事。
He agreed on helping us.他同意帮助我们。
注:与agree to do sth大致同义。所以上句也可说成:
He agreed to help us.
2.beat
充当beat的宾语的则是比赛,竞争的对手,即指人或球队的名词或代词
Our class beat Class One in the table tennis match yesterday.
辨析:beat和win
充当win 的宾语的是比赛、战争、奖品、金钱等名词,即race,match,game, competition,war,prize 之类的词;表示在某项活动或比赛中获胜。
Who won the game
助记点:win+比赛/活动,beat+对手
3.lesson
功课;课业;一节课,一课时 n.
I missed a lesson yesterday. 昨天我误了一节课。
课程
At the end of the class, we’ll invite someone to sum up the lesson.
本课结束之时,我们要请同学总结本课内容。
教训
Such a lesson should be treasured in our memories.
这样的宝贵教训应该铭记在心。
That accident taught them a lesson.
那次事故给了他们一个教训。
4.protect
>protect sb./sth. 保护某人/某物
He will protect me.他会保护我的。
We must protect the environment.我们必须保护环境。
> protect...from sth.保护….免受某事某物的侵害
They ___ the forest ___ fire.他们保护森林免受火灾。
The raincoat can___ you ___ the rain.这件雨衣能让你不被雨淋。
Her parents will protect her from bad men.她的父母会保护她,不被坏人伤害。
>protect sb. from doing sth.保护某人免于做某事的伤害
I will ___ you ___ ___ ___.我会保护你免受伤害。
I will protect myself from catching a cold.我会保护我自己不感冒。
.
1.Why don’t we watch Spiderman
1.责备性建议:Why don't you do sth /Why not do sth 你为什么不做某事呢?
例如:___ ___ you ___ your parents =___ ___ ___ your parents 你为什么不问你的父母呢?
这两个句子在文章中也是可以句型转换的,第一句借助了助动词do,第二句没有,所以同学们在搭配句子的时候要留意了。
2.直接性建议:Let's+do sth咱们做某事吧。
例如:Let' go swimming.咱们去游泳吧。
注意了go+doing是固定搭配,此处的go swimming“去游泳”,常用的还有go shopping“去购物”。
遵循Let's+do sth的原则,句子中的动词原形是‘go’,切记不要改变动词原形的形式。
3. 委婉性建议:Shall we+do +sth 我们做某事好吗?/Would you mind+(not) doing sth 你介意(不)做某事吗?
例如:Shall we go shopping now 我们现在去购物好吗?
Shall用于第一人称,此处的第一人称是‘we’
4. 征求性建议:How/What about doing sth 做某事怎么样?
例如:___ ___ ___ basketball 打篮球怎么样?
about为介词,也是句子的固定搭配,所以其后要用动词的ing形式。How about=What about,同学们在日常学习中如果遇到句型转换,这两个句型就可以转换了。
5.劝告性意见:You'd better(not) do sth.你最好(不要)做某事。
例如:You'd better not swim now.你现在最好不要游泳。
该句型的否定是把not放在do的前面。
6.请求性建议:Would/Could you please (not) do sth 请你(不要)做某事好吗?
例如:___ ___ please ___ ___ me?请你等等我好吗?
2.Parents and children laugh together as the Monkey King makes a terrible mess in heaven.
as充当连接词conj
1.像...一样;依照;像
You ought to do as Paul tells you.你应按照保罗吩咐的做。
2.当...时
As she was leaving the room she remembered that book.她离开房间时想起了那本书。
3.随着
As the sun rose the fog dispersed.太阳一出来,雾随之消失。
4.因为
We didn't know what to do as we were just visiting there.
我们不知道该怎么办,因为当时我们仅仅在那里作访问。
as充当代词pron
1.(与such,the same,as等连用,引导关系从句)与...相同的事物(或人)
He has earned ___ ___ ___ ___I have.他赚的钱和我赚的一样多。
2.(引导从句,对前述内容作补充)本情况,该事实。
She has married again, as was expected.她已再婚,这是意料中的事。
as充当介词prep
1.作为,以...的身份
例如:He ___ ___ a tour guide.他作为导游工作。
2.当作
例如:She is a famous person ___ ___ ___.作为一个女演员,她很出名
3.像;如同
例如:The old woman ___ ___ ___ a young lady.这位老妇人打扮得像一位年轻人。
as充当副词adv
1.跟...一样地,同样地。
例如:I'm as tall as him 我和他一样高。
区分一般现在时,一般过去时和现在完成时
到目前为止,我们已经学过用多种时态来表达行为或状态。本模块重点复习一般现在时、
一般过去时和现在完成时。那么,如何区分这三种时态呢 下面我们以一种行为或状态为例,来看一下它们有什么不同。请看下面的句子:
(1)I often watch cartoon films.我经常看卡通片。
(2)I watched Spiderman last week.我上周看了《蜘蛛侠》。
(3)I have already watched Spiderman.I do not want to watch it again.
我已经看过《蜘蛛侠》了,不想再看了。
可以看出,(1)表示经常性、习惯性的动作,所以用一般现在时;(2)表示在过去某个时间发生的行为,用一般过去时(3)中发生的动作也是在过去,但是没有明确的表示过去的时间,并且本句强调的是结果,即“现在不想再看了”,所以用的是现在完成时。
一般现在时句型结构:
一般过去时句型结构:
现在完成时句型结构:
现在完成时
句型 结构
肯定句 主语+have/has+done+其他.
否定句 主语+have/has+not+done+其他.
一般疑问句 have/has+主语+done+其他?
特殊疑问句 Wh-+have/has+主语+done+其他?
一、用括号内单词的正确形式填空。
1.He often________(have) dinner at home.
2. ___she_____(write)a letter to her aunt yet Yes, she______.
3.She________(write)it the day before yesterday.
4.--______you_____(find) your knife yet ---Not yet.
4.He_________(go) to school at nine yesterday
5.______they_______(like) computer games
6. Tom and Mary_____(come) to China last month.
7.I________(sing) the English song before.
8.I___ never____(see) him before.
二、按照要求改写句子
1.Daniel watches TV every evening.(改为一般疑问句)
2.I do my homework every day.(改为否定句)
3. She likes milk.(划线提问)
4. Amy likes playing computer games.(改为一般疑问句)
5.We have ever read this book.
否定句:
答案:
cartoon 2.handsome 3.smart 4.sky 5.fight 6.cool 7.hero 8.humorous
laugh 10.lesson
agree with agree with agree with agree with agrees with agreed to agree on
protected from protect from protect from getting hurt
Why don't ask Why not ask How about playing Would you wait for
as much money as works as as a actress was dressed as
一.1.has Has written has wrote Have found went Do like came have sung have seen
二.1.Does Daniel watch TV every evening
2.I don’t do my homework every day.
3.What does she like
4.Does Amy like playing computer games
5.We haven’t read this book.
3
6
6
知识清单
词汇 词汇表单词 (必备) 名词:cartoon漫画,动画片 sky天空 hero英雄 lesson经验,教训,课程 schoolbag书包 mess脏乱 heaven天堂 artist艺术家 动词:laugh发笑 lead领导 expect期盼 invent发明 create创造;satisfy满足,使满意 形容词: handsome漂亮的,英俊的 smart聪明的 cool时髦的,凉爽的,酷的 humorous幽默的 orange-and-white橙白相间的 ugly丑陋的 clever聪明的 black-and-white黑白的 private私人得 副词: 代词: 连词:as当...时 兼词:1.fight与...战斗v.;战斗,斗争n. 2.copy一本/份n.;复制,复印v. 3.own自己的adj.;拥有v. 短语:1.can't help doing sth忍不住做某事 2.win the heart of sb.赢得某人得心 回收垃圾 4 4. 4.ea
佳句 I couldn't help laughing when I watch them. ...both of them have won the heart of young people all over the world. Fans have bought about 200 million copies of Tintin’s stories in more than fifty languages. It’s time to watch a cartoon. I don’t think we agree. Snoopy lives in his own private world.
语法 区分一般现在时,一般过去时和现在完成时
1.动画片 ____________ 2.英俊的______________
3. 聪明的___________ 4.天空_____________
5. 与...战斗______________ 6. 酷的__________
7. 英雄__________ 8. 幽默的___________
9. 发笑___________ 10. 经验_____________
1.agree
agree with
(1)表示同意某人或某人的`意见、想法、分析、解释等(即持同一观点)。
I quite ____ ____ you.我完全同意你的意见。
We ____ ____ what you say.我们同意你说的。
表示“(食物、天气、工作等)对……适宜”。
The food does not ____ ____ me.这食物对我不适合。
Hard work does not ____ ____ him.艰苦的工作对他不适宜。
(3)表示“与……一致”。
His story ____ ____ the facts.他的陈述与事实相符。
A verb must agree with its subject in person and number.
动词必须和它的主语在人称和数方面保持一致。
agree to
(1)后接某些名词,表示同意或接受某事,尤其指别人提出的某事,有时可能是自己不喜欢的事。
He agree the plan(the date)。他同意了这个计划(日期)。
We ____ ____ their arrangement.我们同意了他们的安排。
I was forced to agree to it,but at heart I didn’t quite agree with it.我被迫答应,但内心不完全同意。
(2)后接动词原形(此时to是不定式符号)或动名词(一般有逻辑主语,此时to是介词)。
We agreed to leave early.我们同意早点出发。
She agreed to my going home.她同意我回去。
agree on /upon
(1)主要指双方通过协商而取得一致意见或达成协议。
Can we ____ ____ a price(a date) 我们能不能商定一个价格(日期)
Both sides agreed on these terms.双方都同意这些条件。
注:在正式文体中,有时可省略介词 on.
Can we agree a price(date)
后接动名词,表示同意做某事。
He agreed on helping us.他同意帮助我们。
注:与agree to do sth大致同义。所以上句也可说成:
He agreed to help us.
2.beat
充当beat的宾语的则是比赛,竞争的对手,即指人或球队的名词或代词
Our class beat Class One in the table tennis match yesterday.
辨析:beat和win
充当win 的宾语的是比赛、战争、奖品、金钱等名词,即race,match,game, competition,war,prize 之类的词;表示在某项活动或比赛中获胜。
Who won the game
助记点:win+比赛/活动,beat+对手
3.lesson
功课;课业;一节课,一课时 n.
I missed a lesson yesterday. 昨天我误了一节课。
课程
At the end of the class, we’ll invite someone to sum up the lesson.
本课结束之时,我们要请同学总结本课内容。
教训
Such a lesson should be treasured in our memories.
这样的宝贵教训应该铭记在心。
That accident taught them a lesson.
那次事故给了他们一个教训。
4.protect
>protect sb./sth. 保护某人/某物
He will protect me.他会保护我的。
We must protect the environment.我们必须保护环境。
> protect...from sth.保护….免受某事某物的侵害
They ___ the forest ___ fire.他们保护森林免受火灾。
The raincoat can___ you ___ the rain.这件雨衣能让你不被雨淋。
Her parents will protect her from bad men.她的父母会保护她,不被坏人伤害。
>protect sb. from doing sth.保护某人免于做某事的伤害
I will ___ you ___ ___ ___.我会保护你免受伤害。
I will protect myself from catching a cold.我会保护我自己不感冒。
.
1.Why don’t we watch Spiderman
1.责备性建议:Why don't you do sth /Why not do sth 你为什么不做某事呢?
例如:___ ___ you ___ your parents =___ ___ ___ your parents 你为什么不问你的父母呢?
这两个句子在文章中也是可以句型转换的,第一句借助了助动词do,第二句没有,所以同学们在搭配句子的时候要留意了。
2.直接性建议:Let's+do sth咱们做某事吧。
例如:Let' go swimming.咱们去游泳吧。
注意了go+doing是固定搭配,此处的go swimming“去游泳”,常用的还有go shopping“去购物”。
遵循Let's+do sth的原则,句子中的动词原形是‘go’,切记不要改变动词原形的形式。
3. 委婉性建议:Shall we+do +sth 我们做某事好吗?/Would you mind+(not) doing sth 你介意(不)做某事吗?
例如:Shall we go shopping now 我们现在去购物好吗?
Shall用于第一人称,此处的第一人称是‘we’
4. 征求性建议:How/What about doing sth 做某事怎么样?
例如:___ ___ ___ basketball 打篮球怎么样?
about为介词,也是句子的固定搭配,所以其后要用动词的ing形式。How about=What about,同学们在日常学习中如果遇到句型转换,这两个句型就可以转换了。
5.劝告性意见:You'd better(not) do sth.你最好(不要)做某事。
例如:You'd better not swim now.你现在最好不要游泳。
该句型的否定是把not放在do的前面。
6.请求性建议:Would/Could you please (not) do sth 请你(不要)做某事好吗?
例如:___ ___ please ___ ___ me?请你等等我好吗?
2.Parents and children laugh together as the Monkey King makes a terrible mess in heaven.
as充当连接词conj
1.像...一样;依照;像
You ought to do as Paul tells you.你应按照保罗吩咐的做。
2.当...时
As she was leaving the room she remembered that book.她离开房间时想起了那本书。
3.随着
As the sun rose the fog dispersed.太阳一出来,雾随之消失。
4.因为
We didn't know what to do as we were just visiting there.
我们不知道该怎么办,因为当时我们仅仅在那里作访问。
as充当代词pron
1.(与such,the same,as等连用,引导关系从句)与...相同的事物(或人)
He has earned ___ ___ ___ ___I have.他赚的钱和我赚的一样多。
2.(引导从句,对前述内容作补充)本情况,该事实。
She has married again, as was expected.她已再婚,这是意料中的事。
as充当介词prep
1.作为,以...的身份
例如:He ___ ___ a tour guide.他作为导游工作。
2.当作
例如:She is a famous person ___ ___ ___.作为一个女演员,她很出名
3.像;如同
例如:The old woman ___ ___ ___ a young lady.这位老妇人打扮得像一位年轻人。
as充当副词adv
1.跟...一样地,同样地。
例如:I'm as tall as him 我和他一样高。
区分一般现在时,一般过去时和现在完成时
到目前为止,我们已经学过用多种时态来表达行为或状态。本模块重点复习一般现在时、
一般过去时和现在完成时。那么,如何区分这三种时态呢 下面我们以一种行为或状态为例,来看一下它们有什么不同。请看下面的句子:
(1)I often watch cartoon films.我经常看卡通片。
(2)I watched Spiderman last week.我上周看了《蜘蛛侠》。
(3)I have already watched Spiderman.I do not want to watch it again.
我已经看过《蜘蛛侠》了,不想再看了。
可以看出,(1)表示经常性、习惯性的动作,所以用一般现在时;(2)表示在过去某个时间发生的行为,用一般过去时(3)中发生的动作也是在过去,但是没有明确的表示过去的时间,并且本句强调的是结果,即“现在不想再看了”,所以用的是现在完成时。
一般现在时句型结构:
一般过去时句型结构:
现在完成时句型结构:
现在完成时
句型 结构
肯定句 主语+have/has+done+其他.
否定句 主语+have/has+not+done+其他.
一般疑问句 have/has+主语+done+其他?
特殊疑问句 Wh-+have/has+主语+done+其他?
一、用括号内单词的正确形式填空。
1.He often________(have) dinner at home.
2. ___she_____(write)a letter to her aunt yet Yes, she______.
3.She________(write)it the day before yesterday.
4.--______you_____(find) your knife yet ---Not yet.
4.He_________(go) to school at nine yesterday
5.______they_______(like) computer games
6. Tom and Mary_____(come) to China last month.
7.I________(sing) the English song before.
8.I___ never____(see) him before.
二、按照要求改写句子
1.Daniel watches TV every evening.(改为一般疑问句)
2.I do my homework every day.(改为否定句)
3. She likes milk.(划线提问)
4. Amy likes playing computer games.(改为一般疑问句)
5.We have ever read this book.
否定句:
答案:
cartoon 2.handsome 3.smart 4.sky 5.fight 6.cool 7.hero 8.humorous
laugh 10.lesson
agree with agree with agree with agree with agrees with agreed to agree on
protected from protect from protect from getting hurt
Why don't ask Why not ask How about playing Would you wait for
as much money as works as as a actress was dressed as
一.1.has Has written has wrote Have found went Do like came have sung have seen
二.1.Does Daniel watch TV every evening
2.I don’t do my homework every day.
3.What does she like
4.Does Amy like playing computer games
5.We haven’t read this book.
3
6
6
同课章节目录
- Module 1 Feelings and impressions
- Unit 1 It smells delicious.
- Unit 2 I feel nervous when I speak Chinese .
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 2 Experiences
- Unit 1 I've also entered lots of speaking competi
- Unit 2 They have seen the Pyramids.
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 3 Journey to space
- Unit 1 Has it arrived yet?
- Unit 2 We have not found life on any other planet
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 4 Seeing the docto
- Unit 1 I haven't done much exercise since I got m
- Unit 2 We have played football for a year now
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 5 Cartoons
- Unit 1 It's time to watch a cartoon.
- Unit 2 Tintin has been popular for over eighty yea
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Revision module A
- Module 6 Hobbies
- Unit 1 Do you collect anything ?
- Unit 2 Hobbies can make you grow as a person.
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 7 Summer in Los Angeles
- Unit 1 Please write to me and send me some photos
- Unit 2 Fill out a form and come to learn English
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 8 Time off
- Unit 1 I can hardly believe we are in the city ce
- Unit 2 We thought somebody was moving about
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 9 Friendship
- Unit 1 Could I ask if you've mentioned this to he
- Unit 2 I believe that the world is what you think
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 10 On the radio
- Unit 1 I hope that you can join us one day
- Unit 2 It seemed that they were speaking to me in
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Revision module B
