【2013中考英语夺分】专题十时态和语态
文档属性
| 名称 | 【2013中考英语夺分】专题十时态和语态 |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 415.3KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2013-02-27 22:04:05 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
课件39张PPT。语法互动(十) 时态和语态中考考点
1.动词的第三人称单数形式、过去式、过去分词和现在分词的构成。
2.动词的8种时态的基本结构及区别(了解过去将来时、过去完成时的基本用法)。
3.被动语态的构成及主动语态和被动语态的转换 。语法互动(十) 时态和语态考点一 动词的时态
初中阶段应掌握的时态共有八种,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、过去将来时、现在完成时和过去完成时。
1.一般现在时
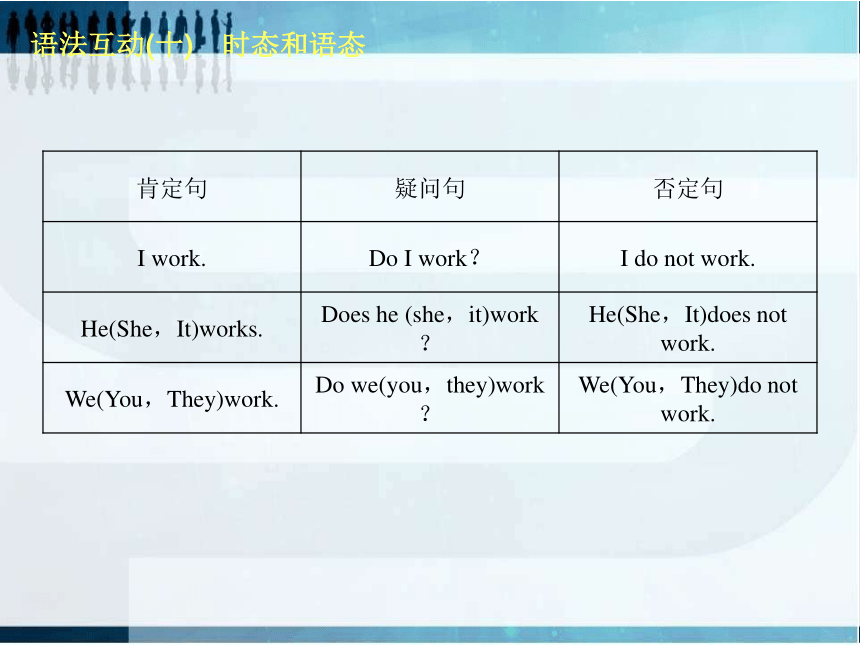
(1)结构:(以work为例)语法互动(十) 时态和语态语法互动(十) 时态和语态(2)用法:
①表示事实、现状、性质或经常的、习惯性的动作。常与seldom, often, usually, always, sometimes, today, every day, once a week, every five minutes, on Sundays等时间状语连用。如:
I go to school at seven every day.
我每天七点去上学。
②表示普遍真理。如:
The earth ______________ the sun.
地球绕着太阳转。语法互动(十) 时态和语态goes around ③表示在现在时间里所发生的一个动作。如:
Here comes the bus.
公共汽车来了。
④在时间和条件状语从句中代表一般将来时。如:
I'll go shopping with my mother if she ________ tomorrow.
如果明天我妈妈有空,我将和她去购物。
(3)动词的第三人称单数形式变化规则如下:
语法互动(十) 时态和语态is free 语法互动(十) 时态和语态①直接加-s。如:work—works。
②辅音字母+y结尾的词,先变y为i,再加-es。如:carry—carries; cry—cries; try—tries; study—studies。
③以s、x、o、ch、sh结尾的词加-es。如:wash—washes; teach—teaches; go—goes; pass—passes; fix—fixes。
④特殊:have—has。2.现在进行时
(1)结构: am/is/are+动词的-ing形式
(2)用法:
①表示目前发生(进行)的动作(不指状态),常用的时间状语有: now, at the moment 等。当有look, listen起提示作用时,后面的句子常用现在进行时。如:
Are you writing a letter to your friend now?
你现在正在给你朋友写信吗?
Listen! She __________ in the next room.
听!她正在隔壁唱歌。语法互动(十) 时态和语态is singing ②表示现阶段正在进行,而此刻不一定在进行的动作。如:
We _____________ trees these days.
这些日子我们在植树。
③表示位移的非延续性动词的进行时表示动作将要发生。此类词有come, go, leave, arrive, fly等,常与表示将来的时间状语连用。如:
They __________________ England tomorrow afternoon.
他们明天下午要去英国。
(3)现在分词的变化规则:语法互动(十) 时态和语态are planting are leaving for语法互动(十) 时态和语态①一般加-ing。如:play—playing。
②以不发音字母e结尾的,去e加-ing。如:
come—coming; make—making; live—living;
write—writing; take—taking。
③以重读闭音节结尾,末尾只有一个辅音字母的,先双写该辅音字母,再加-ing。如:
run—running; sit—sitting; begin—beginning; cut—cutting; stop—stopping; get—getting; swim—swimming; plan—planning。
④特殊:die—dying; lie—lying; tie—tying。3.一般将来时
(1)结构:助动词shall/will+动词原形
(2)用法:
①表示将要发生的动作或状态,常用的时间状语有: later(on), soon, in a month, next time, from now on, tomorrow等。如:
I shall be eighteen years old next year.
明年我18岁了。
②表示某种必然的趋势。如:
Fish ____________ without water.
离开水,鱼就会死。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态will die (3)注意:
① 在以第一人称作主语的问句中,常用 shall 表示提议和询问情况,在以第二人称作主语的句中,用will 表示请求。如:
Where shall we have lunch? 我们在哪里吃午饭?
②当主语是第一人称时,用will 表示意愿、决心、允诺、命令等。如:
I will give Xiaoming a good gift for his birthday.
我会在小明生日时送他一份好礼。
③在时间或条件状语从句中,一般用一般现在时代替一般将来时。如:
I ____________ Jim when he ______ there. 语法互动(十) 时态和语态will write to gets 当吉姆到达那里时,我将给他写信。
④“be going to+动词原形” 也可表示将来时。
a.表示主观意愿、打算等。如:
He's going to learn English next term.
下学期他打算学英语。
b.根据已有迹象能推测出可能要发生的情况。如:
Look at the black clouds!It __________ rain.
看那些乌云!马上要下雨了。
[提示] 表示位移的动词的进行时常表达将来之意,如: come, go, leave, fly, start, finish等。如:
She's flying to Australia next month.语法互动(十) 时态和语态is going to 下个月她将飞往澳大利亚。
4.一般过去时
表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。句中的谓语动词要变为过去式。
(1)句型结构:
①be动词型
I was a student last year. 去年我是名学生。
—Were you at home this morning?
今天早上你在家吗?
—Yes, I was./No, I wasn't.
是的,我在。/不,我不在。语法互动(十) 时态和语态②行为动词型
Tom ______ to Shanghai last year.
去年汤姆去了上海。
John __________ here last year.
去年约翰没有住在这里。
Did you see him just now? 你刚才看见他了吗?
(2)用法:
①主要表示过去的某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。如:His friend was at work yesterday.
他的朋友昨天在工作。
②表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常与often,always 等表示频度的时间状语连用。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态went didn't live We often went to work by bus last year.
去年我们经常乘公交车上班。
③和when 等引导的时间状语从句连用。如:
When he got home, he ______ a rest.
当他到家时,他休息了一会儿。
④常与表示过去的时间状语连用。这些状语有:ago, yesterday, last week, in the old days, when I was five years old, in 1995等。如:
We began our work ______________.
三小时前,我们开始工作。
(3)动词过去式的变化规则: 语法互动(十) 时态和语态had three hours ago 语法互动(十) 时态和语态5.现在完成时
(1)结构: have/has+动词的过去分词
(过去分词变化规则基本与过去式变化相同。有些特殊变化需单独记忆)
(2)用法:
①表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响和结果。有时与just, already, yet, recently, before,ever, never, twice, three times等时间状语连用。如:
I __________ the film already.
我已经看过这部电影了。(现在我知道电影的内容了。)语法互动(十) 时态和语态have seen ②表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。常与“since+时间点”,“for+时间段”,及how long, (ever)since, ever, before, so far, in the last/past few years, up to now, till now等时间状语连用。如:
We've planted thousands of trees in the past few years. 过去几年我们种了成千上万棵树。
So far there __________ no bad news.
到现在为止还没有什么坏消息。
(3)一般过去时与现在完成时的区别 语法互动(十) 时态和语态has been 一般过去时只强调在过去发生过某事或关注的是动作发生的时间、地点、方式等。而现在完成时则强调过去的动作对现在的影响,因此,若不强调某事对现在的影响就不用现在完成时。如:
I saw the movie yesterday.
我昨天看了这部电影。(强调电影是昨天看的)
I have already seen the film.
我已经看过这部电影了。(强调到现在为止看过这部电影了)
(4)延续性动词
在现在完成时中,如果有持续的时间状语,要把非延续性动词变为延续性动词。如: 语法互动(十) 时态和语态I have had the book for two days.
这本书我已经买了两天了。(用had,而不用bought)
I have been in Tokyo for two weeks.
我已经来东京两周了。(用been in,而不用come to)
语法互动(十) 时态和语态常用瞬间动词变延续性动词表
①have arrived at/in sp, got to/reached sp, come/gone/moved to sp→have been in sp
②have come/gone back, returned→have been back
③have come/gone out→have been out
④have become→have been
⑤have closed/opened→have been closed/open
⑥have got up→have been up
⑦have died→______________
⑧have left sp→__________________________
⑨have fallen asleep/gone to sleep→have been asleep语法互动(十) 时态和语态have been dead have been away from sp ⑩have finished/ended/completed→____________________
?have married→have been married
?have started/begun to do sth→have done sth
?have begun→______________
?have borrowed→______________
?have bought→have had
?have lost→haven't had
?have put on→have worn
?have caught/got a cold→have had a cold 语法互动(十) 时态和语态have been over have been on have kept ?have got to know→have known
?have gone to→have been in
have joined/taken part in the league/the Party/the army→have been a member of the league/the Party/the army, have been in the league/the Party/the army, have been the Party's member/the league member/the soldier
6.过去进行时
(1)结构: was/were+doing
(2)用法:
过去进行时主要表示过去某一时间点或某一段时间正在进行的动作。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态His father fell down while he __________ his bicycle and hurt himself.
他爸爸骑自行车时摔到了,并弄伤了自己。
(3)常用的时间状语: this morning, the whole morning, all day yesterday, from nine to ten, last evening, when, while。
(4)when和while的区别:
①引导时间状语从句时,while 连接的是时间段,后常接延续性动词;而when连接的既可以是延续性动词也可以是非延续性动词。如:
What was your father doing ________ your mother was cooking?你妈妈正在做饭时,你爸爸干什么呢?语法互动(十) 时态和语态was riding whileWhat was your mother doing ______ you came back?
当你回来时,你妈妈干什么呢?
②while可以连接两个并列的句子,而when不可以。如:
I was trying my best to finish my work while my sister was watching TV.
我当时正在尽力完成作业,而我的妹妹正在看电视。
③when可作特殊疑问词,对时间进行提问,while 不能。如:
When were you born?
你是什么时候出生的?语法互动(十) 时态和语态when 7.过去完成时
(1)结构: had+动词的过去分词
(2)用法:
①表示过去的某一时刻以前已经发生的动作或存在的状态,也就是“过去的过去”。常以by, before短语或when, before, after, until等引导的从句作为前提。如:
My teacher said she had never been to London.
我老师说过她从来没去过伦敦。
When the police arrived, the thieves ___________________.
警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态had run away
②表示从过去某一时刻开始一直延续到另一过去时刻的动作或状态。跟现在完成时一样,也常与 how long, for three days, before 等表示一段时间的状语连用。如:
When Jack arrived, he learned Mary _______________ for almost an hour. 当杰克到来时,他了解到玛丽已经离开差不多一个小时了。
8.过去将来时
(1)结构: would+动词原形或was/were+going to+动词原形。语法互动(十) 时态和语态had been away (2)用法:
表示从过去的某一时刻看,将要发生的动作。如:
His uncle said that _________________ a good harvest the next year.他叔叔说明年会有个好收成。
[提醒] 在由if引导的条件状语从句中,如果主句中用过去将来时,if从句中需用一般过去时代替过去将来时。如:
Amy said that she would go shopping if it didn't rain the next day. 艾米说如果明天不下雨,她就去购物。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态there would be 考点二 动词的被动语态
英语中的动词有两种语态: 主动语态和被动语态。
1.被动语态的构成: 助动词be+及物动词的过去分词
(1)一般现在时: 主语+am/is/are+动词的过去分词
(2)一般过去时: 主语+was/were+动词的过去分词
(3)一般将来时: 主语+will/shall/be going to+be+动词的过去分词。如:
A bridge will be built over the river.
人们将在这条河上建一座桥。
(4)现在进行时: 主语+am/is/are+being+动词的过去分词。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态A bridge is being built over the river.
人们正在这条河上建桥。
(5)现在完成时: 主语+have/has+been+动词的过去分词
(6)过去进行时: 主语+was/were+being+动词的过去分词
(7)过去完成时: 主语+had been+动词的过去分词
(8)过去将来时: 主语+would be+动词的过去分词
(9)含有情态动词的被动语态: 主语+情态动词+be+动词的过去分词。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态A bridge can be seen over the river.
人们能看到河上有座桥。
(10)在使役动词have, make, let以及感官动词see, find, watch, notice, hear, feel等后面作宾语补足语的不定式,在主动结构中不定式to要省略,但变为被动结构时,要加to。如:
Someone saw a stranger walk into the building.
被动结构为:
A stranger was seen_________ into the building.
有人看见一个陌生人走进了这座楼。
2.某些谓语动词的主动形式表示被动意义语法互动(十) 时态和语态to work(1)英语中有很多动词,如: break, catch, clean, drive, lock, open, sell, read, write, wash等,当它们被用作不及物动词来描述主语特征时,常用其主动形式表达被动意义,主语通常是物。如:
This kind of cloth ______________.
这种布料很好洗。
[注意] 主动语态表被动强调的是主语的特征,而被动语态则强调外界作用造成的影响。
试比较:
The door won't lock.(指门本身有毛病)语法互动(十) 时态和语态washes well The door won't be locked.(指不会有人来锁门,表示“门没有锁”是人的原因)
(2)表示“发生、进行”的不及物动词和短语,如:happen, last, take place, break out, come out, come about, come true, run out, give out, turn out等以主动形式表示被动意义。如:
How do the newspapers come out?
这些报纸是如何印刷出来的呢?
(3)系动词没有被动形式,但有些表示感受、感官的连系动词,如:feel, sound, taste, feel等在主系表结构中常以主动形式表示被动意义。如:
语法互动(十) 时态和语态Your reason sounds reasonable.
你的理由听起来很合理。
(4)下列结构中的v.-ing必须用主动形式表示被动意义:
①want(need, require, request)“需要”+v.-ing。但当这些动词后接不定式时,则必须用被动形式表示被动意义。如:
The bike needs mending.这辆自行车需要修理。
Our classroom needs to be cleaned.
我们的教室需要打扫。
②be worth doing sth值得做某事 如:
The book is well worth reading.
这本书很值得一读。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态考点过关
用所给词的适当形式填空
1.My father always ________(ride) his bike to work.
2.—What's he doing?
—He's ________ (wait) for his parents.
3.Everything ________(be) free in 100 years.
4.Last Sunday Jack __________ (not go) to the movie. He studied for the math test.
5.I ___________(keep) the book for two weeks.
6.They ____________(have) dinner at this time yesterday.
7.Our classroom ___________(clean) every day.语法互动(十) 时态和语态 rides waiting will be didn't go have kept were having is cleaned 8.Last month many volunteers ____________(send) to the poor village to help the old.
9.All the teachers will ___________ (invite) to the party.
10.These books must ________(put) in the bookcase.
11.He was made ________ (leave) his hometown.
12.This kind of watch ________(sell) well.
语法互动(十) 时态和语态were sent be invited be put to leave sells 谢谢合作 再见课件39张PPT。语法互动(十) 时态和语态中考考点
1.动词的第三人称单数形式、过去式、过去分词和现在分词的构成。
2.动词的8种时态的基本结构及区别(了解过去将来时、过去完成时的基本用法)。
3.被动语态的构成及主动语态和被动语态的转换 。语法互动(十) 时态和语态考点一 动词的时态
初中阶段应掌握的时态共有八种,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、过去将来时、现在完成时和过去完成时。
1.一般现在时
(1)结构:(以work为例)语法互动(十) 时态和语态语法互动(十) 时态和语态(2)用法:
①表示事实、现状、性质或经常的、习惯性的动作。常与seldom, often, usually, always, sometimes, today, every day, once a week, every five minutes, on Sundays等时间状语连用。如:
I go to school at seven every day.
我每天七点去上学。
②表示普遍真理。如:
The earth ______________ the sun.
地球绕着太阳转。语法互动(十) 时态和语态goes around ③表示在现在时间里所发生的一个动作。如:
Here comes the bus.
公共汽车来了。
④在时间和条件状语从句中代表一般将来时。如:
I'll go shopping with my mother if she ________ tomorrow.
如果明天我妈妈有空,我将和她去购物。
(3)动词的第三人称单数形式变化规则如下:
语法互动(十) 时态和语态is free 语法互动(十) 时态和语态2.现在进行时
(1)结构: am/is/are+动词的-ing形式
(2)用法:
①表示目前发生(进行)的动作(不指状态),常用的时间状语有: now, at the moment 等。当有look, listen起提示作用时,后面的句子常用现在进行时。如:
Are you writing a letter to your friend now?
你现在正在给你朋友写信吗?
Listen! She __________ in the next room.
听!她正在隔壁唱歌。语法互动(十) 时态和语态is singing ②表示现阶段正在进行,而此刻不一定在进行的动作。如:
We _____________ trees these days.
这些日子我们在植树。
③表示位移的非延续性动词的进行时表示动作将要发生。此类词有come, go, leave, arrive, fly等,常与表示将来的时间状语连用。如:
They __________________ England tomorrow afternoon.
他们明天下午要去英国。
(3)现在分词的变化规则:语法互动(十) 时态和语态are planting are leaving for语法互动(十) 时态和语态3.一般将来时
(1)结构:助动词shall/will+动词原形
(2)用法:
①表示将要发生的动作或状态,常用的时间状语有: later(on), soon, in a month, next time, from now on, tomorrow等。如:
I shall be eighteen years old next year.
明年我18岁了。
②表示某种必然的趋势。如:
Fish ____________ without water.
离开水,鱼就会死。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态will die (3)注意:
① 在以第一人称作主语的问句中,常用 shall 表示提议和询问情况,在以第二人称作主语的句中,用will 表示请求。如:
Where shall we have lunch? 我们在哪里吃午饭?
②当主语是第一人称时,用will 表示意愿、决心、允诺、命令等。如:
I will give Xiaoming a good gift for his birthday.
我会在小明生日时送他一份好礼。
③在时间或条件状语从句中,一般用一般现在时代替一般将来时。如:
I ____________ Jim when he ______ there. 语法互动(十) 时态和语态will write to gets 当吉姆到达那里时,我将给他写信。
④“be going to+动词原形” 也可表示将来时。
a.表示主观意愿、打算等。如:
He's going to learn English next term.
下学期他打算学英语。
b.根据已有迹象能推测出可能要发生的情况。如:
Look at the black clouds!It __________ rain.
看那些乌云!马上要下雨了。
[提示] 表示位移的动词的进行时常表达将来之意,如: come, go, leave, fly, start, finish等。如:
She's flying to Australia next month.语法互动(十) 时态和语态is going to 下个月她将飞往澳大利亚。
4.一般过去时
表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。句中的谓语动词要变为过去式。
(1)句型结构:
①be动词型
I was a student last year. 去年我是名学生。
—Were you at home this morning?
今天早上你在家吗?
—Yes, I was./No, I wasn't.
是的,我在。/不,我不在。语法互动(十) 时态和语态②行为动词型
Tom ______ to Shanghai last year.
去年汤姆去了上海。
John __________ here last year.
去年约翰没有住在这里。
Did you see him just now? 你刚才看见他了吗?
(2)用法:
①主要表示过去的某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。如:His friend was at work yesterday.
他的朋友昨天在工作。
②表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常与often,always 等表示频度的时间状语连用。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态went didn't live We often went to work by bus last year.
去年我们经常乘公交车上班。
③和when 等引导的时间状语从句连用。如:
When he got home, he ______ a rest.
当他到家时,他休息了一会儿。
④常与表示过去的时间状语连用。这些状语有:ago, yesterday, last week, in the old days, when I was five years old, in 1995等。如:
We began our work ______________.
三小时前,我们开始工作。
(3)动词过去式的变化规则: 语法互动(十) 时态和语态had three hours ago 语法互动(十) 时态和语态5.现在完成时
(1)结构: have/has+动词的过去分词
(过去分词变化规则基本与过去式变化相同。有些特殊变化需单独记忆)
(2)用法:
①表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响和结果。有时与just, already, yet, recently, before,ever, never, twice, three times等时间状语连用。如:
I __________ the film already.
我已经看过这部电影了。(现在我知道电影的内容了。)语法互动(十) 时态和语态have seen ②表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。常与“since+时间点”,“for+时间段”,及how long, (ever)since, ever, before, so far, in the last/past few years, up to now, till now等时间状语连用。如:
We've planted thousands of trees in the past few years. 过去几年我们种了成千上万棵树。
So far there __________ no bad news.
到现在为止还没有什么坏消息。
(3)一般过去时与现在完成时的区别 语法互动(十) 时态和语态has been 一般过去时只强调在过去发生过某事或关注的是动作发生的时间、地点、方式等。而现在完成时则强调过去的动作对现在的影响,因此,若不强调某事对现在的影响就不用现在完成时。如:
I saw the movie yesterday.
我昨天看了这部电影。(强调电影是昨天看的)
I have already seen the film.
我已经看过这部电影了。(强调到现在为止看过这部电影了)
(4)延续性动词
在现在完成时中,如果有持续的时间状语,要把非延续性动词变为延续性动词。如: 语法互动(十) 时态和语态I have had the book for two days.
这本书我已经买了两天了。(用had,而不用bought)
I have been in Tokyo for two weeks.
我已经来东京两周了。(用been in,而不用come to)
语法互动(十) 时态和语态常用瞬间动词变延续性动词表
①have arrived at/in sp, got to/reached sp, come/gone/moved to sp→have been in sp
②have come/gone back, returned→have been back
③have come/gone out→have been out
④have become→have been
⑤have closed/opened→have been closed/open
⑥have got up→have been up
⑦have died→______________
⑧have left sp→__________________________
⑨have fallen asleep/gone to sleep→have been asleep语法互动(十) 时态和语态have been dead have been away from sp ⑩have finished/ended/completed→____________________
?have married→have been married
?have started/begun to do sth→have done sth
?have begun→______________
?have borrowed→______________
?have bought→have had
?have lost→haven't had
?have put on→have worn
?have caught/got a cold→have had a cold 语法互动(十) 时态和语态have been over have been on have kept ?have got to know→have known
?have gone to→have been in
have joined/taken part in the league/the Party/the army→have been a member of the league/the Party/the army, have been in the league/the Party/the army, have been the Party's member/the league member/the soldier
6.过去进行时
(1)结构: was/were+doing
(2)用法:
过去进行时主要表示过去某一时间点或某一段时间正在进行的动作。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态His father fell down while he __________ his bicycle and hurt himself.
他爸爸骑自行车时摔到了,并弄伤了自己。
(3)常用的时间状语: this morning, the whole morning, all day yesterday, from nine to ten, last evening, when, while。
(4)when和while的区别:
①引导时间状语从句时,while 连接的是时间段,后常接延续性动词;而when连接的既可以是延续性动词也可以是非延续性动词。如:
What was your father doing ________ your mother was cooking?你妈妈正在做饭时,你爸爸干什么呢?语法互动(十) 时态和语态was riding whileWhat was your mother doing ______ you came back?
当你回来时,你妈妈干什么呢?
②while可以连接两个并列的句子,而when不可以。如:
I was trying my best to finish my work while my sister was watching TV.
我当时正在尽力完成作业,而我的妹妹正在看电视。
③when可作特殊疑问词,对时间进行提问,while 不能。如:
When were you born?
你是什么时候出生的?语法互动(十) 时态和语态when 7.过去完成时
(1)结构: had+动词的过去分词
(2)用法:
①表示过去的某一时刻以前已经发生的动作或存在的状态,也就是“过去的过去”。常以by, before短语或when, before, after, until等引导的从句作为前提。如:
My teacher said she had never been to London.
我老师说过她从来没去过伦敦。
When the police arrived, the thieves ___________________.
警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态had run away
②表示从过去某一时刻开始一直延续到另一过去时刻的动作或状态。跟现在完成时一样,也常与 how long, for three days, before 等表示一段时间的状语连用。如:
When Jack arrived, he learned Mary _______________ for almost an hour. 当杰克到来时,他了解到玛丽已经离开差不多一个小时了。
8.过去将来时
(1)结构: would+动词原形或was/were+going to+动词原形。语法互动(十) 时态和语态had been away (2)用法:
表示从过去的某一时刻看,将要发生的动作。如:
His uncle said that _________________ a good harvest the next year.他叔叔说明年会有个好收成。
[提醒] 在由if引导的条件状语从句中,如果主句中用过去将来时,if从句中需用一般过去时代替过去将来时。如:
Amy said that she would go shopping if it didn't rain the next day. 艾米说如果明天不下雨,她就去购物。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态there would be 考点二 动词的被动语态
英语中的动词有两种语态: 主动语态和被动语态。
1.被动语态的构成: 助动词be+及物动词的过去分词
(1)一般现在时: 主语+am/is/are+动词的过去分词
(2)一般过去时: 主语+was/were+动词的过去分词
(3)一般将来时: 主语+will/shall/be going to+be+动词的过去分词。如:
A bridge will be built over the river.
人们将在这条河上建一座桥。
(4)现在进行时: 主语+am/is/are+being+动词的过去分词。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态A bridge is being built over the river.
人们正在这条河上建桥。
(5)现在完成时: 主语+have/has+been+动词的过去分词
(6)过去进行时: 主语+was/were+being+动词的过去分词
(7)过去完成时: 主语+had been+动词的过去分词
(8)过去将来时: 主语+would be+动词的过去分词
(9)含有情态动词的被动语态: 主语+情态动词+be+动词的过去分词。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态A bridge can be seen over the river.
人们能看到河上有座桥。
(10)在使役动词have, make, let以及感官动词see, find, watch, notice, hear, feel等后面作宾语补足语的不定式,在主动结构中不定式to要省略,但变为被动结构时,要加to。如:
Someone saw a stranger walk into the building.
被动结构为:
A stranger was seen_________ into the building.
有人看见一个陌生人走进了这座楼。
2.某些谓语动词的主动形式表示被动意义语法互动(十) 时态和语态to work(1)英语中有很多动词,如: break, catch, clean, drive, lock, open, sell, read, write, wash等,当它们被用作不及物动词来描述主语特征时,常用其主动形式表达被动意义,主语通常是物。如:
This kind of cloth ______________.
这种布料很好洗。
[注意] 主动语态表被动强调的是主语的特征,而被动语态则强调外界作用造成的影响。
试比较:
The door won't lock.(指门本身有毛病)语法互动(十) 时态和语态washes well The door won't be locked.(指不会有人来锁门,表示“门没有锁”是人的原因)
(2)表示“发生、进行”的不及物动词和短语,如:happen, last, take place, break out, come out, come about, come true, run out, give out, turn out等以主动形式表示被动意义。如:
How do the newspapers come out?
这些报纸是如何印刷出来的呢?
(3)系动词没有被动形式,但有些表示感受、感官的连系动词,如:feel, sound, taste, feel等在主系表结构中常以主动形式表示被动意义。如:
语法互动(十) 时态和语态Your reason sounds reasonable.
你的理由听起来很合理。
(4)下列结构中的v.-ing必须用主动形式表示被动意义:
①want(need, require, request)“需要”+v.-ing。但当这些动词后接不定式时,则必须用被动形式表示被动意义。如:
The bike needs mending.这辆自行车需要修理。
Our classroom needs to be cleaned.
我们的教室需要打扫。
②be worth doing sth值得做某事 如:
The book is well worth reading.
这本书很值得一读。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态考点过关
用所给词的适当形式填空
1.My father always ________(ride) his bike to work.
2.—What's he doing?
—He's ________ (wait) for his parents.
3.Everything ________(be) free in 100 years.
4.Last Sunday Jack __________ (not go) to the movie. He studied for the math test.
5.I ___________(keep) the book for two weeks.
6.They ____________(have) dinner at this time yesterday.
7.Our classroom ___________(clean) every day.语法互动(十) 时态和语态 rides waiting will be didn't go have kept were having is cleaned 8.Last month many volunteers ____________(send) to the poor village to help the old.
9.All the teachers will ___________ (invite) to the party.
10.These books must ________(put) in the bookcase.
11.He was made ________ (leave) his hometown.
12.This kind of watch ________(sell) well.
语法互动(十) 时态和语态were sent be invited be put to leave sells 谢谢合作 再见
1.动词的第三人称单数形式、过去式、过去分词和现在分词的构成。
2.动词的8种时态的基本结构及区别(了解过去将来时、过去完成时的基本用法)。
3.被动语态的构成及主动语态和被动语态的转换 。语法互动(十) 时态和语态考点一 动词的时态
初中阶段应掌握的时态共有八种,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、过去将来时、现在完成时和过去完成时。
1.一般现在时
(1)结构:(以work为例)语法互动(十) 时态和语态语法互动(十) 时态和语态(2)用法:
①表示事实、现状、性质或经常的、习惯性的动作。常与seldom, often, usually, always, sometimes, today, every day, once a week, every five minutes, on Sundays等时间状语连用。如:
I go to school at seven every day.
我每天七点去上学。
②表示普遍真理。如:
The earth ______________ the sun.
地球绕着太阳转。语法互动(十) 时态和语态goes around ③表示在现在时间里所发生的一个动作。如:
Here comes the bus.
公共汽车来了。
④在时间和条件状语从句中代表一般将来时。如:
I'll go shopping with my mother if she ________ tomorrow.
如果明天我妈妈有空,我将和她去购物。
(3)动词的第三人称单数形式变化规则如下:
语法互动(十) 时态和语态is free 语法互动(十) 时态和语态①直接加-s。如:work—works。
②辅音字母+y结尾的词,先变y为i,再加-es。如:carry—carries; cry—cries; try—tries; study—studies。
③以s、x、o、ch、sh结尾的词加-es。如:wash—washes; teach—teaches; go—goes; pass—passes; fix—fixes。
④特殊:have—has。2.现在进行时
(1)结构: am/is/are+动词的-ing形式
(2)用法:
①表示目前发生(进行)的动作(不指状态),常用的时间状语有: now, at the moment 等。当有look, listen起提示作用时,后面的句子常用现在进行时。如:
Are you writing a letter to your friend now?
你现在正在给你朋友写信吗?
Listen! She __________ in the next room.
听!她正在隔壁唱歌。语法互动(十) 时态和语态is singing ②表示现阶段正在进行,而此刻不一定在进行的动作。如:
We _____________ trees these days.
这些日子我们在植树。
③表示位移的非延续性动词的进行时表示动作将要发生。此类词有come, go, leave, arrive, fly等,常与表示将来的时间状语连用。如:
They __________________ England tomorrow afternoon.
他们明天下午要去英国。
(3)现在分词的变化规则:语法互动(十) 时态和语态are planting are leaving for语法互动(十) 时态和语态①一般加-ing。如:play—playing。
②以不发音字母e结尾的,去e加-ing。如:
come—coming; make—making; live—living;
write—writing; take—taking。
③以重读闭音节结尾,末尾只有一个辅音字母的,先双写该辅音字母,再加-ing。如:
run—running; sit—sitting; begin—beginning; cut—cutting; stop—stopping; get—getting; swim—swimming; plan—planning。
④特殊:die—dying; lie—lying; tie—tying。3.一般将来时
(1)结构:助动词shall/will+动词原形
(2)用法:
①表示将要发生的动作或状态,常用的时间状语有: later(on), soon, in a month, next time, from now on, tomorrow等。如:
I shall be eighteen years old next year.
明年我18岁了。
②表示某种必然的趋势。如:
Fish ____________ without water.
离开水,鱼就会死。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态will die (3)注意:
① 在以第一人称作主语的问句中,常用 shall 表示提议和询问情况,在以第二人称作主语的句中,用will 表示请求。如:
Where shall we have lunch? 我们在哪里吃午饭?
②当主语是第一人称时,用will 表示意愿、决心、允诺、命令等。如:
I will give Xiaoming a good gift for his birthday.
我会在小明生日时送他一份好礼。
③在时间或条件状语从句中,一般用一般现在时代替一般将来时。如:
I ____________ Jim when he ______ there. 语法互动(十) 时态和语态will write to gets 当吉姆到达那里时,我将给他写信。
④“be going to+动词原形” 也可表示将来时。
a.表示主观意愿、打算等。如:
He's going to learn English next term.
下学期他打算学英语。
b.根据已有迹象能推测出可能要发生的情况。如:
Look at the black clouds!It __________ rain.
看那些乌云!马上要下雨了。
[提示] 表示位移的动词的进行时常表达将来之意,如: come, go, leave, fly, start, finish等。如:
She's flying to Australia next month.语法互动(十) 时态和语态is going to 下个月她将飞往澳大利亚。
4.一般过去时
表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。句中的谓语动词要变为过去式。
(1)句型结构:
①be动词型
I was a student last year. 去年我是名学生。
—Were you at home this morning?
今天早上你在家吗?
—Yes, I was./No, I wasn't.
是的,我在。/不,我不在。语法互动(十) 时态和语态②行为动词型
Tom ______ to Shanghai last year.
去年汤姆去了上海。
John __________ here last year.
去年约翰没有住在这里。
Did you see him just now? 你刚才看见他了吗?
(2)用法:
①主要表示过去的某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。如:His friend was at work yesterday.
他的朋友昨天在工作。
②表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常与often,always 等表示频度的时间状语连用。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态went didn't live We often went to work by bus last year.
去年我们经常乘公交车上班。
③和when 等引导的时间状语从句连用。如:
When he got home, he ______ a rest.
当他到家时,他休息了一会儿。
④常与表示过去的时间状语连用。这些状语有:ago, yesterday, last week, in the old days, when I was five years old, in 1995等。如:
We began our work ______________.
三小时前,我们开始工作。
(3)动词过去式的变化规则: 语法互动(十) 时态和语态had three hours ago 语法互动(十) 时态和语态5.现在完成时
(1)结构: have/has+动词的过去分词
(过去分词变化规则基本与过去式变化相同。有些特殊变化需单独记忆)
(2)用法:
①表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响和结果。有时与just, already, yet, recently, before,ever, never, twice, three times等时间状语连用。如:
I __________ the film already.
我已经看过这部电影了。(现在我知道电影的内容了。)语法互动(十) 时态和语态have seen ②表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。常与“since+时间点”,“for+时间段”,及how long, (ever)since, ever, before, so far, in the last/past few years, up to now, till now等时间状语连用。如:
We've planted thousands of trees in the past few years. 过去几年我们种了成千上万棵树。
So far there __________ no bad news.
到现在为止还没有什么坏消息。
(3)一般过去时与现在完成时的区别 语法互动(十) 时态和语态has been 一般过去时只强调在过去发生过某事或关注的是动作发生的时间、地点、方式等。而现在完成时则强调过去的动作对现在的影响,因此,若不强调某事对现在的影响就不用现在完成时。如:
I saw the movie yesterday.
我昨天看了这部电影。(强调电影是昨天看的)
I have already seen the film.
我已经看过这部电影了。(强调到现在为止看过这部电影了)
(4)延续性动词
在现在完成时中,如果有持续的时间状语,要把非延续性动词变为延续性动词。如: 语法互动(十) 时态和语态I have had the book for two days.
这本书我已经买了两天了。(用had,而不用bought)
I have been in Tokyo for two weeks.
我已经来东京两周了。(用been in,而不用come to)
语法互动(十) 时态和语态常用瞬间动词变延续性动词表
①have arrived at/in sp, got to/reached sp, come/gone/moved to sp→have been in sp
②have come/gone back, returned→have been back
③have come/gone out→have been out
④have become→have been
⑤have closed/opened→have been closed/open
⑥have got up→have been up
⑦have died→______________
⑧have left sp→__________________________
⑨have fallen asleep/gone to sleep→have been asleep语法互动(十) 时态和语态have been dead have been away from sp ⑩have finished/ended/completed→____________________
?have married→have been married
?have started/begun to do sth→have done sth
?have begun→______________
?have borrowed→______________
?have bought→have had
?have lost→haven't had
?have put on→have worn
?have caught/got a cold→have had a cold 语法互动(十) 时态和语态have been over have been on have kept ?have got to know→have known
?have gone to→have been in
have joined/taken part in the league/the Party/the army→have been a member of the league/the Party/the army, have been in the league/the Party/the army, have been the Party's member/the league member/the soldier
6.过去进行时
(1)结构: was/were+doing
(2)用法:
过去进行时主要表示过去某一时间点或某一段时间正在进行的动作。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态His father fell down while he __________ his bicycle and hurt himself.
他爸爸骑自行车时摔到了,并弄伤了自己。
(3)常用的时间状语: this morning, the whole morning, all day yesterday, from nine to ten, last evening, when, while。
(4)when和while的区别:
①引导时间状语从句时,while 连接的是时间段,后常接延续性动词;而when连接的既可以是延续性动词也可以是非延续性动词。如:
What was your father doing ________ your mother was cooking?你妈妈正在做饭时,你爸爸干什么呢?语法互动(十) 时态和语态was riding whileWhat was your mother doing ______ you came back?
当你回来时,你妈妈干什么呢?
②while可以连接两个并列的句子,而when不可以。如:
I was trying my best to finish my work while my sister was watching TV.
我当时正在尽力完成作业,而我的妹妹正在看电视。
③when可作特殊疑问词,对时间进行提问,while 不能。如:
When were you born?
你是什么时候出生的?语法互动(十) 时态和语态when 7.过去完成时
(1)结构: had+动词的过去分词
(2)用法:
①表示过去的某一时刻以前已经发生的动作或存在的状态,也就是“过去的过去”。常以by, before短语或when, before, after, until等引导的从句作为前提。如:
My teacher said she had never been to London.
我老师说过她从来没去过伦敦。
When the police arrived, the thieves ___________________.
警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态had run away
②表示从过去某一时刻开始一直延续到另一过去时刻的动作或状态。跟现在完成时一样,也常与 how long, for three days, before 等表示一段时间的状语连用。如:
When Jack arrived, he learned Mary _______________ for almost an hour. 当杰克到来时,他了解到玛丽已经离开差不多一个小时了。
8.过去将来时
(1)结构: would+动词原形或was/were+going to+动词原形。语法互动(十) 时态和语态had been away (2)用法:
表示从过去的某一时刻看,将要发生的动作。如:
His uncle said that _________________ a good harvest the next year.他叔叔说明年会有个好收成。
[提醒] 在由if引导的条件状语从句中,如果主句中用过去将来时,if从句中需用一般过去时代替过去将来时。如:
Amy said that she would go shopping if it didn't rain the next day. 艾米说如果明天不下雨,她就去购物。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态there would be 考点二 动词的被动语态
英语中的动词有两种语态: 主动语态和被动语态。
1.被动语态的构成: 助动词be+及物动词的过去分词
(1)一般现在时: 主语+am/is/are+动词的过去分词
(2)一般过去时: 主语+was/were+动词的过去分词
(3)一般将来时: 主语+will/shall/be going to+be+动词的过去分词。如:
A bridge will be built over the river.
人们将在这条河上建一座桥。
(4)现在进行时: 主语+am/is/are+being+动词的过去分词。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态A bridge is being built over the river.
人们正在这条河上建桥。
(5)现在完成时: 主语+have/has+been+动词的过去分词
(6)过去进行时: 主语+was/were+being+动词的过去分词
(7)过去完成时: 主语+had been+动词的过去分词
(8)过去将来时: 主语+would be+动词的过去分词
(9)含有情态动词的被动语态: 主语+情态动词+be+动词的过去分词。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态A bridge can be seen over the river.
人们能看到河上有座桥。
(10)在使役动词have, make, let以及感官动词see, find, watch, notice, hear, feel等后面作宾语补足语的不定式,在主动结构中不定式to要省略,但变为被动结构时,要加to。如:
Someone saw a stranger walk into the building.
被动结构为:
A stranger was seen_________ into the building.
有人看见一个陌生人走进了这座楼。
2.某些谓语动词的主动形式表示被动意义语法互动(十) 时态和语态to work(1)英语中有很多动词,如: break, catch, clean, drive, lock, open, sell, read, write, wash等,当它们被用作不及物动词来描述主语特征时,常用其主动形式表达被动意义,主语通常是物。如:
This kind of cloth ______________.
这种布料很好洗。
[注意] 主动语态表被动强调的是主语的特征,而被动语态则强调外界作用造成的影响。
试比较:
The door won't lock.(指门本身有毛病)语法互动(十) 时态和语态washes well The door won't be locked.(指不会有人来锁门,表示“门没有锁”是人的原因)
(2)表示“发生、进行”的不及物动词和短语,如:happen, last, take place, break out, come out, come about, come true, run out, give out, turn out等以主动形式表示被动意义。如:
How do the newspapers come out?
这些报纸是如何印刷出来的呢?
(3)系动词没有被动形式,但有些表示感受、感官的连系动词,如:feel, sound, taste, feel等在主系表结构中常以主动形式表示被动意义。如:
语法互动(十) 时态和语态Your reason sounds reasonable.
你的理由听起来很合理。
(4)下列结构中的v.-ing必须用主动形式表示被动意义:
①want(need, require, request)“需要”+v.-ing。但当这些动词后接不定式时,则必须用被动形式表示被动意义。如:
The bike needs mending.这辆自行车需要修理。
Our classroom needs to be cleaned.
我们的教室需要打扫。
②be worth doing sth值得做某事 如:
The book is well worth reading.
这本书很值得一读。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态考点过关
用所给词的适当形式填空
1.My father always ________(ride) his bike to work.
2.—What's he doing?
—He's ________ (wait) for his parents.
3.Everything ________(be) free in 100 years.
4.Last Sunday Jack __________ (not go) to the movie. He studied for the math test.
5.I ___________(keep) the book for two weeks.
6.They ____________(have) dinner at this time yesterday.
7.Our classroom ___________(clean) every day.语法互动(十) 时态和语态 rides waiting will be didn't go have kept were having is cleaned 8.Last month many volunteers ____________(send) to the poor village to help the old.
9.All the teachers will ___________ (invite) to the party.
10.These books must ________(put) in the bookcase.
11.He was made ________ (leave) his hometown.
12.This kind of watch ________(sell) well.
语法互动(十) 时态和语态were sent be invited be put to leave sells 谢谢合作 再见课件39张PPT。语法互动(十) 时态和语态中考考点
1.动词的第三人称单数形式、过去式、过去分词和现在分词的构成。
2.动词的8种时态的基本结构及区别(了解过去将来时、过去完成时的基本用法)。
3.被动语态的构成及主动语态和被动语态的转换 。语法互动(十) 时态和语态考点一 动词的时态
初中阶段应掌握的时态共有八种,即一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、过去将来时、现在完成时和过去完成时。
1.一般现在时
(1)结构:(以work为例)语法互动(十) 时态和语态语法互动(十) 时态和语态(2)用法:
①表示事实、现状、性质或经常的、习惯性的动作。常与seldom, often, usually, always, sometimes, today, every day, once a week, every five minutes, on Sundays等时间状语连用。如:
I go to school at seven every day.
我每天七点去上学。
②表示普遍真理。如:
The earth ______________ the sun.
地球绕着太阳转。语法互动(十) 时态和语态goes around ③表示在现在时间里所发生的一个动作。如:
Here comes the bus.
公共汽车来了。
④在时间和条件状语从句中代表一般将来时。如:
I'll go shopping with my mother if she ________ tomorrow.
如果明天我妈妈有空,我将和她去购物。
(3)动词的第三人称单数形式变化规则如下:
语法互动(十) 时态和语态is free 语法互动(十) 时态和语态2.现在进行时
(1)结构: am/is/are+动词的-ing形式
(2)用法:
①表示目前发生(进行)的动作(不指状态),常用的时间状语有: now, at the moment 等。当有look, listen起提示作用时,后面的句子常用现在进行时。如:
Are you writing a letter to your friend now?
你现在正在给你朋友写信吗?
Listen! She __________ in the next room.
听!她正在隔壁唱歌。语法互动(十) 时态和语态is singing ②表示现阶段正在进行,而此刻不一定在进行的动作。如:
We _____________ trees these days.
这些日子我们在植树。
③表示位移的非延续性动词的进行时表示动作将要发生。此类词有come, go, leave, arrive, fly等,常与表示将来的时间状语连用。如:
They __________________ England tomorrow afternoon.
他们明天下午要去英国。
(3)现在分词的变化规则:语法互动(十) 时态和语态are planting are leaving for语法互动(十) 时态和语态3.一般将来时
(1)结构:助动词shall/will+动词原形
(2)用法:
①表示将要发生的动作或状态,常用的时间状语有: later(on), soon, in a month, next time, from now on, tomorrow等。如:
I shall be eighteen years old next year.
明年我18岁了。
②表示某种必然的趋势。如:
Fish ____________ without water.
离开水,鱼就会死。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态will die (3)注意:
① 在以第一人称作主语的问句中,常用 shall 表示提议和询问情况,在以第二人称作主语的句中,用will 表示请求。如:
Where shall we have lunch? 我们在哪里吃午饭?
②当主语是第一人称时,用will 表示意愿、决心、允诺、命令等。如:
I will give Xiaoming a good gift for his birthday.
我会在小明生日时送他一份好礼。
③在时间或条件状语从句中,一般用一般现在时代替一般将来时。如:
I ____________ Jim when he ______ there. 语法互动(十) 时态和语态will write to gets 当吉姆到达那里时,我将给他写信。
④“be going to+动词原形” 也可表示将来时。
a.表示主观意愿、打算等。如:
He's going to learn English next term.
下学期他打算学英语。
b.根据已有迹象能推测出可能要发生的情况。如:
Look at the black clouds!It __________ rain.
看那些乌云!马上要下雨了。
[提示] 表示位移的动词的进行时常表达将来之意,如: come, go, leave, fly, start, finish等。如:
She's flying to Australia next month.语法互动(十) 时态和语态is going to 下个月她将飞往澳大利亚。
4.一般过去时
表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。句中的谓语动词要变为过去式。
(1)句型结构:
①be动词型
I was a student last year. 去年我是名学生。
—Were you at home this morning?
今天早上你在家吗?
—Yes, I was./No, I wasn't.
是的,我在。/不,我不在。语法互动(十) 时态和语态②行为动词型
Tom ______ to Shanghai last year.
去年汤姆去了上海。
John __________ here last year.
去年约翰没有住在这里。
Did you see him just now? 你刚才看见他了吗?
(2)用法:
①主要表示过去的某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态。如:His friend was at work yesterday.
他的朋友昨天在工作。
②表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常与often,always 等表示频度的时间状语连用。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态went didn't live We often went to work by bus last year.
去年我们经常乘公交车上班。
③和when 等引导的时间状语从句连用。如:
When he got home, he ______ a rest.
当他到家时,他休息了一会儿。
④常与表示过去的时间状语连用。这些状语有:ago, yesterday, last week, in the old days, when I was five years old, in 1995等。如:
We began our work ______________.
三小时前,我们开始工作。
(3)动词过去式的变化规则: 语法互动(十) 时态和语态had three hours ago 语法互动(十) 时态和语态5.现在完成时
(1)结构: have/has+动词的过去分词
(过去分词变化规则基本与过去式变化相同。有些特殊变化需单独记忆)
(2)用法:
①表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响和结果。有时与just, already, yet, recently, before,ever, never, twice, three times等时间状语连用。如:
I __________ the film already.
我已经看过这部电影了。(现在我知道电影的内容了。)语法互动(十) 时态和语态have seen ②表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。常与“since+时间点”,“for+时间段”,及how long, (ever)since, ever, before, so far, in the last/past few years, up to now, till now等时间状语连用。如:
We've planted thousands of trees in the past few years. 过去几年我们种了成千上万棵树。
So far there __________ no bad news.
到现在为止还没有什么坏消息。
(3)一般过去时与现在完成时的区别 语法互动(十) 时态和语态has been 一般过去时只强调在过去发生过某事或关注的是动作发生的时间、地点、方式等。而现在完成时则强调过去的动作对现在的影响,因此,若不强调某事对现在的影响就不用现在完成时。如:
I saw the movie yesterday.
我昨天看了这部电影。(强调电影是昨天看的)
I have already seen the film.
我已经看过这部电影了。(强调到现在为止看过这部电影了)
(4)延续性动词
在现在完成时中,如果有持续的时间状语,要把非延续性动词变为延续性动词。如: 语法互动(十) 时态和语态I have had the book for two days.
这本书我已经买了两天了。(用had,而不用bought)
I have been in Tokyo for two weeks.
我已经来东京两周了。(用been in,而不用come to)
语法互动(十) 时态和语态常用瞬间动词变延续性动词表
①have arrived at/in sp, got to/reached sp, come/gone/moved to sp→have been in sp
②have come/gone back, returned→have been back
③have come/gone out→have been out
④have become→have been
⑤have closed/opened→have been closed/open
⑥have got up→have been up
⑦have died→______________
⑧have left sp→__________________________
⑨have fallen asleep/gone to sleep→have been asleep语法互动(十) 时态和语态have been dead have been away from sp ⑩have finished/ended/completed→____________________
?have married→have been married
?have started/begun to do sth→have done sth
?have begun→______________
?have borrowed→______________
?have bought→have had
?have lost→haven't had
?have put on→have worn
?have caught/got a cold→have had a cold 语法互动(十) 时态和语态have been over have been on have kept ?have got to know→have known
?have gone to→have been in
have joined/taken part in the league/the Party/the army→have been a member of the league/the Party/the army, have been in the league/the Party/the army, have been the Party's member/the league member/the soldier
6.过去进行时
(1)结构: was/were+doing
(2)用法:
过去进行时主要表示过去某一时间点或某一段时间正在进行的动作。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态His father fell down while he __________ his bicycle and hurt himself.
他爸爸骑自行车时摔到了,并弄伤了自己。
(3)常用的时间状语: this morning, the whole morning, all day yesterday, from nine to ten, last evening, when, while。
(4)when和while的区别:
①引导时间状语从句时,while 连接的是时间段,后常接延续性动词;而when连接的既可以是延续性动词也可以是非延续性动词。如:
What was your father doing ________ your mother was cooking?你妈妈正在做饭时,你爸爸干什么呢?语法互动(十) 时态和语态was riding whileWhat was your mother doing ______ you came back?
当你回来时,你妈妈干什么呢?
②while可以连接两个并列的句子,而when不可以。如:
I was trying my best to finish my work while my sister was watching TV.
我当时正在尽力完成作业,而我的妹妹正在看电视。
③when可作特殊疑问词,对时间进行提问,while 不能。如:
When were you born?
你是什么时候出生的?语法互动(十) 时态和语态when 7.过去完成时
(1)结构: had+动词的过去分词
(2)用法:
①表示过去的某一时刻以前已经发生的动作或存在的状态,也就是“过去的过去”。常以by, before短语或when, before, after, until等引导的从句作为前提。如:
My teacher said she had never been to London.
我老师说过她从来没去过伦敦。
When the police arrived, the thieves ___________________.
警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态had run away
②表示从过去某一时刻开始一直延续到另一过去时刻的动作或状态。跟现在完成时一样,也常与 how long, for three days, before 等表示一段时间的状语连用。如:
When Jack arrived, he learned Mary _______________ for almost an hour. 当杰克到来时,他了解到玛丽已经离开差不多一个小时了。
8.过去将来时
(1)结构: would+动词原形或was/were+going to+动词原形。语法互动(十) 时态和语态had been away (2)用法:
表示从过去的某一时刻看,将要发生的动作。如:
His uncle said that _________________ a good harvest the next year.他叔叔说明年会有个好收成。
[提醒] 在由if引导的条件状语从句中,如果主句中用过去将来时,if从句中需用一般过去时代替过去将来时。如:
Amy said that she would go shopping if it didn't rain the next day. 艾米说如果明天不下雨,她就去购物。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态there would be 考点二 动词的被动语态
英语中的动词有两种语态: 主动语态和被动语态。
1.被动语态的构成: 助动词be+及物动词的过去分词
(1)一般现在时: 主语+am/is/are+动词的过去分词
(2)一般过去时: 主语+was/were+动词的过去分词
(3)一般将来时: 主语+will/shall/be going to+be+动词的过去分词。如:
A bridge will be built over the river.
人们将在这条河上建一座桥。
(4)现在进行时: 主语+am/is/are+being+动词的过去分词。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态A bridge is being built over the river.
人们正在这条河上建桥。
(5)现在完成时: 主语+have/has+been+动词的过去分词
(6)过去进行时: 主语+was/were+being+动词的过去分词
(7)过去完成时: 主语+had been+动词的过去分词
(8)过去将来时: 主语+would be+动词的过去分词
(9)含有情态动词的被动语态: 主语+情态动词+be+动词的过去分词。如:语法互动(十) 时态和语态A bridge can be seen over the river.
人们能看到河上有座桥。
(10)在使役动词have, make, let以及感官动词see, find, watch, notice, hear, feel等后面作宾语补足语的不定式,在主动结构中不定式to要省略,但变为被动结构时,要加to。如:
Someone saw a stranger walk into the building.
被动结构为:
A stranger was seen_________ into the building.
有人看见一个陌生人走进了这座楼。
2.某些谓语动词的主动形式表示被动意义语法互动(十) 时态和语态to work(1)英语中有很多动词,如: break, catch, clean, drive, lock, open, sell, read, write, wash等,当它们被用作不及物动词来描述主语特征时,常用其主动形式表达被动意义,主语通常是物。如:
This kind of cloth ______________.
这种布料很好洗。
[注意] 主动语态表被动强调的是主语的特征,而被动语态则强调外界作用造成的影响。
试比较:
The door won't lock.(指门本身有毛病)语法互动(十) 时态和语态washes well The door won't be locked.(指不会有人来锁门,表示“门没有锁”是人的原因)
(2)表示“发生、进行”的不及物动词和短语,如:happen, last, take place, break out, come out, come about, come true, run out, give out, turn out等以主动形式表示被动意义。如:
How do the newspapers come out?
这些报纸是如何印刷出来的呢?
(3)系动词没有被动形式,但有些表示感受、感官的连系动词,如:feel, sound, taste, feel等在主系表结构中常以主动形式表示被动意义。如:
语法互动(十) 时态和语态Your reason sounds reasonable.
你的理由听起来很合理。
(4)下列结构中的v.-ing必须用主动形式表示被动意义:
①want(need, require, request)“需要”+v.-ing。但当这些动词后接不定式时,则必须用被动形式表示被动意义。如:
The bike needs mending.这辆自行车需要修理。
Our classroom needs to be cleaned.
我们的教室需要打扫。
②be worth doing sth值得做某事 如:
The book is well worth reading.
这本书很值得一读。 语法互动(十) 时态和语态考点过关
用所给词的适当形式填空
1.My father always ________(ride) his bike to work.
2.—What's he doing?
—He's ________ (wait) for his parents.
3.Everything ________(be) free in 100 years.
4.Last Sunday Jack __________ (not go) to the movie. He studied for the math test.
5.I ___________(keep) the book for two weeks.
6.They ____________(have) dinner at this time yesterday.
7.Our classroom ___________(clean) every day.语法互动(十) 时态和语态 rides waiting will be didn't go have kept were having is cleaned 8.Last month many volunteers ____________(send) to the poor village to help the old.
9.All the teachers will ___________ (invite) to the party.
10.These books must ________(put) in the bookcase.
11.He was made ________ (leave) his hometown.
12.This kind of watch ________(sell) well.
语法互动(十) 时态和语态were sent be invited be put to leave sells 谢谢合作 再见
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
