Module 2 Education Unit 3 Language in use课件(33张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Module 2 Education Unit 3 Language in use课件(33张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 284.0KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-05-19 17:12:25 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共35张PPT)
Module 2 Education
Unit 3 Language in use
代词、介词
一、代词
1. 定义:代词是代替名词或一句话的一种词类。大多数代词具有名词和形容词的功能。英语中的代词,按其意义、特征及在句中的作用分为十类。本模块主要讲解人称代词、物主代词、反身代词、指示代词、疑问代词和不定代词。
语法聚焦
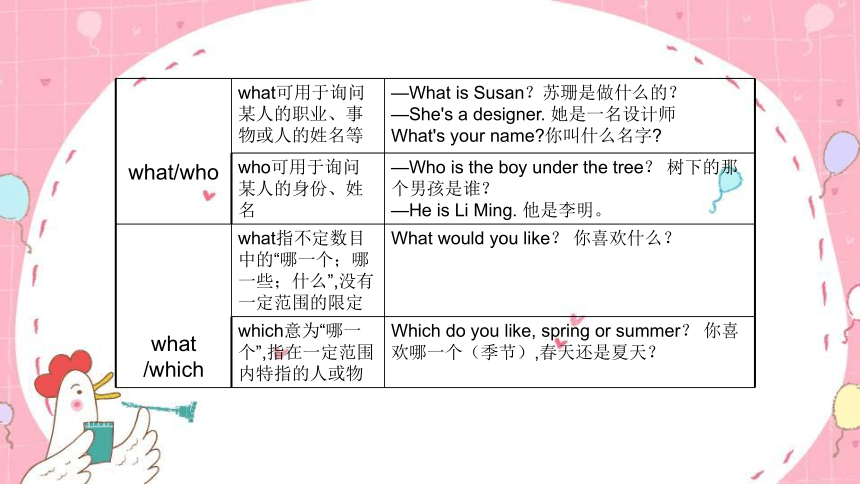
2.人称代词、物主代词及反身代词
人称代词 物主代词
反身代词
主格 宾格 形容词性 名词性
I me my mine myself
you (你) you your yours yourself
he him his his himself
she her her hers herself
it it its its itself
we us our ours ourselves
you (你们)
you your yours yourselves
they them their theirs
themselves
用法 举例
主格用来作主语 I like English. 我喜欢英语。
宾格用来作宾语、表语或主语
She told me a story yesterday. 她昨天给我讲了一个故事。
The girl in the photo is me. 照片里的女孩是我。
—Who's there 谁在那儿
—Only me. 只有我。
形容词性物主代词用来作定语,相当于一个形容词,置于名词之前
That's my computer.那是我的电脑。
名词性物主代词起名词的作用 —Whose ruler is this? 这是谁的尺子?
—It's mine. (mine=my ruler) 这是我的(尺子)。
反身代词作宾语,放于及物动词或介词之后 The girl is so old that she can look after herself. 这女孩岁数足够大,可以自己照顾自己。
反身代词作主语或宾语的同位语时起强调作用,可以放主语、宾语后,也可以放句末
I can do it myself. 我可以自己做。
附:形容词性物主代词+名词=名词性物主代词。如:
This isn't my dictionary, mine is over there. (mine=my dictionary)这不是我的字典,我的(字典)在那儿。
续表
用 法 举 例
指示代词在句中作主语、宾语、表语,也可以代替形容词作定语 This is my pen. 这是我的钢笔。→These are my pens. 这些是我的钢笔。(作主语)
These students will go hiking. 这些学生将去远足(作定语)
打电话时常用this指代“我”,用that指代“你” This is Mary speaking.Who is that 我是玛丽。你是谁
有时为了避免重复,可用that和those代替前面提到的名词 The population of China is much larger than that of Japan. 中国人口比日本人口多得多(that=the population)
除用作代词外,this和that都可用作副词,与形容词或副词连用,意为“这么;那么”,相当so Is it this/so hot every day 每天都这么热吗
3.指示代词
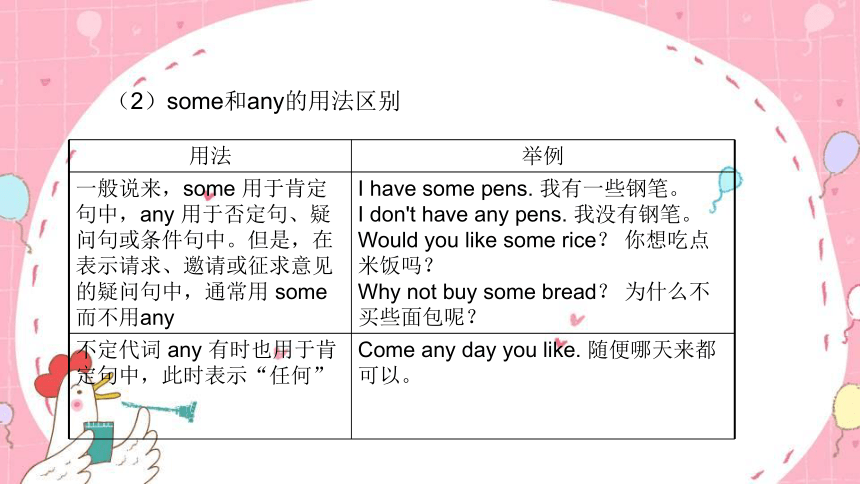
4.疑问代词
疑问代词指who, which, whom, whose, what, whoever, whichever, whomever, whatever等用于引导特殊疑问句的代词。常见的疑问代词的用法如下表:
疑问代词 主要用法 举 例
who 作主语、表语、宾语(作宾语时不能放在介词之后) Who wants to go with me? 谁想和我一起去?(作主语)
Who are you talking to? (此句中的who作介词的宾语,可用whom代替)你在跟谁说话?
whom who的宾格形式,作宾语 To whom are you talking? 你在跟谁说话?
whose who的所有格形式,作主语、表语、宾语或定语 Whose book is this? 这是谁的书?
what/who what可用于询问某人的职业、事物或人的姓名等 —What is Susan?苏珊是做什么的?
—She's a designer. 她是一名设计师
What's your name 你叫什么名字
who可用于询问某人的身份、姓名 —Who is the boy under the tree? 树下的那个男孩是谁?
—He is Li Ming. 他是李明。
what
/which what指不定数目中的“哪一个;哪一些;什么”,没有一定范围的限定 What would you like? 你喜欢什么?
which意为“哪一个”,指在一定范围内特指的人或物 Which do you like, spring or summer? 你喜欢哪一个(季节),春天还是夏天?
5.不定代词
英语中的不定代词有 all, each, both, either, neither, one, none, little, few, many, much, other, another, some, any, no, (a) few, (a) little, both, enough, every 等,以及由 some, any, no 和 every 构成的复合不定代词(即somebody, anyone, nothing 等)。
(1)指两者和三者的不定代词
用 法 举 例
有些不定代词意指两者(如both, either, neither,each),有些不定代词意指三者(如all, any, none, every)。其中:both与neither互为反义词,all与none相反。both,all都可作同位语,通常位于行为动词之前,be动词、助动词或情态动词之后。而each可单独使用,侧重个体;every则不能单独使用,且着重全体。在肯定句中用any通常表示“任一”,后接单数可数名词或不可数名词。此时any作形容词。表部分否定用all或both+not,表示全部否定用none或neither Both of my parents are doctors. 我的父母都是医生。
All of the students are interested in it. 所有的学生对此都很感兴趣。
There are flowers on each side of the street. 街道的两边都种着花。
There are trees on any/every side of the square. 广场的每一边都种有树。
He has two sons, neither of whom is rich. 他有两个儿子,他们都不富有。
He has three sons, none of whom is rich. 他有三个儿子,他们都不富有。
不定代词either与neither的用法区别:either指“两者中的任何一个”;neither指“两者中任何一个也不”,属于both的全部否定 There are mango trees on either side of the street. 街道两旁都有芒果树。(句中的either side=each
side=both sides)
Either of the answers is right. 两个答案中有一个对。
Neither of the answers is right. 两个答案都不对。
不定代词none与no one的用法区别:none既可指人也可指物,常暗示一定范围,因此通常与表范围的of短语连用;而no one(=nobody)只能指人,且不能与of短语连用;none与数量有关,可回答how many引导的疑问句,表示“一个也没有”;而no one表示“什么人也没有”,可回答who引导的疑问句 None of that money on the table is mine. 桌上的钱没有一分是我的。
No one (=Nobody) knows about it. 没有人了解此事。
—How many people are there in that room 那个房间里有几个人
—None.一个人也没有.
—Who was late today
今天谁迟到了
—No one.谁也没有迟到。
(2)some和any的用法区别
用法 举例
一般说来,some 用于肯定句中,any 用于否定句、疑问句或条件句中。但是,在表示请求、邀请或征求意见的疑问句中,通常用 some 而不用any I have some pens. 我有一些钢笔。
I don't have any pens. 我没有钢笔。
Would you like some rice? 你想吃点米饭吗?
Why not buy some bread? 为什么不买些面包呢?
不定代词 any 有时也用于肯定句中,此时表示“任何” Come any day you like. 随便哪天来都可以。
(3)复合不定代词
复合不定代词是由some-,any-,no-,every-加上-one,-body,-thing,-where, -time所组成的不定代词。其用法如下表:
用法 举例
复合不定代词受定语(通常为形容词)修饰时,定语应放在它们后面 There is nothing wrong with the radio. 这部收音机没有毛病。
No one else loves you more than I do. 没有别的人比我更爱你。
指人的复合不定代词若用作主语,其谓语动词一般用单数,相应的人称代词和物主代词也用单数 he, him, his (不一定指男性)。但在非正式文体中常用复数代词 they, them, their Everyone knows this, doesn't he/don't they
人人都知道这一点,对吗
If anybody/anyone comes, ask him to wait. 要是有人来,让他等着。
指事物的复合不定代词若用作主语,谓语动词只能用单数,相应的人称代词也只能用it,而不用they
Everything is ready, isn't it? 一切都准备好了,是吗?
不定代词 anyone, everyone 等只能指人,不能指物,且其后一般不接
of 短语,若是指物或后接 of 短语,可用 any one, every one
any one of the boys孩子们当中的任
何一个
二、介词
1. 定义:介词表示名词、代词等与句中其他词的关系,在句中不能单独作句子成分。介词后面一般有名词、代词(如果是人称代词,则要用宾格)或相当于名词的其他词类、短语或从句作它的宾语,表示与其他成分的关系。介词和它的宾语构成介词词组,在句中作状语、表语、补语、定语或介词宾语。同时介词的用法也很灵活,同一个介词可以表达多种意义。介词可以分为时间介词、方位介词和方式介词等。
2.表示时间的介词(1)at, on, in
介词 用法 举例
at 用于具体的时刻 at seven o'clock;at half past two
on 主要用于具体的某一天或某一天的上午、下午或晚上,还用于具有某种特征的一个上午、下午或晚上 on Monday;
on Teachers' Day;
on August 8th, 2008;
on Monday morning/on the morning of Monday;
on a winter afternoon
in
用于世纪、年、季节、月 in the 21st century;
in 2010;
in spring;
in January
(2)五个表示延续时间的介词
类别 举例
by:在……之前;不迟于…… I must be at school by eight tomorrow morning. 我明天早晨八点前必须到校。
in:在……以后;在……时间内 He will be back in ten minutes. 他十分钟之后将会回来。
for:历时……之久;持续…… He has been a teacher for nine years. 他当老师已经9年了。
since:自从……以来;自……以后 I have lived here since ten years ago. 我已经在这儿住了10年了。
until:直到……才,用于否定句中,其前的谓语动词多为非延续性动词;用于肯定句中,其前的谓语动词要用延续性动词 We don't see any flowers until May. 直到五月我们才看到一些花。
You must stand here until the sun sets. 你必须站在这里直到太阳落山为止。
3.表方位、方式、运动方向的介词
(1)表示方位的介词
类别 要点
in,on,to in,on,to的后面均可加the再接方位名词
(east, south, west, north等)。用in表示“范围A在范围B之内”;用on表示“两个范围接壤并且相邻”;用to则表示“范围A在范围B的区域之外即相邻不接壤”(如中国和日本)
其他表示方位的常用介词 over:在……(垂直)的正上方
above:在……(不一定垂直)的上方
under:在……(垂直的)正下方
below:在……(不一定垂直)的下方
near:在……附近
next to:紧挨着
round/around:在……周围
by:在……旁边
(2)表示方式的介词
类别 举例
by+不带限定词的单数交通工具名词,意为“乘坐……” 海:by ship/boat/sea
陆:by bus/car/train/bike/taxi
空:by air/plane/spaceship
on/in+限定词+交通工具,意为“乘坐……” He goes to work on his bike/in his car. 他骑自行车/开车去上班。
on foot为固定短语,意为“步行” She goes to school on foot. =She walks to school. 她步行上学。
(3)表示运动方向的介词
类别 举例
across:从……表面穿过,通常表示由平面的一端到另一端(如马路、河流、桥梁等) Please be careful when you go across the road. 过马路时请小心。
through:从……内部穿过,即穿过一个空间(如洞、窗户、森林等) Look! The mosquito is trying to fly through the window. 看!蚊子正试图飞出窗户。
past和by:从旁边经过或路过 We often go past/by a bakery on our way to school. 上学路上我们经常路过一个面包店。
along和down:沿着 Walk along/down the street till the end.沿着街道直走到尽头。
4.其他重要的介词
类别 用法 举例
with 表示“和;同;与……;带着;随着” with my brother 跟我哥哥一起
with pleasure十分乐意
with best wishes致以美好的祝愿
speak with your mouth full 满嘴东西说话
a girl with sunglasses戴墨镜的女孩
表示“有着;具有” coffee with sugar and milk 加糖和牛奶的咖啡
a man with good manners一个很有礼貌的男士
表示“用;被;以” cut with a knife 用刀切开
in 表示“穿;戴”,后接衣服、颜色或鞋帽 He is in blue. 他穿着蓝色的衣服。
I know the man in a hat. 我认识那个戴帽子的男人。
表示“用”,后接语言或材料,表示手段或方法
等 How do you say that in English?那个用英语怎么说?
She wrote the letter in pencil. 她用铅笔写了这封信。
表示境况、情绪、状态等 in trouble陷入困境
in danger处于危险中
in surprise惊讶地
in good health身体健康
表示“关于……;在……方面” I'm weak in maths. 我的数学不好。
against与for against表示“反对;违反;不利于”,其反义词为for,此时for表示“支持;
赞成” We are all against his idea. 我们都反对他的想法。
Are you for or against the plan?你是支持还是反对这个计划?
except与
besides except表示“除……外”,具有排他性质 We all went to see the film except Mr Wang. 除了王先生,我们都去看电影了。(王先生没去)
besides表示“除了……以外还有……”,具有附加性质 Besides Mr Wang, we also went to see the film. 除了王先生,我们也去看电影了。(王先生也去了)
一、根据句意及首字母或中文提示完成单词
1. Their new school is as beautiful as ________.
2. The ________(铃) is ringing. Let's go to the classroom.
3. Grace was ________(缺席) from school.
4. He has travelled to _________(日本) several times.
5. I think _________(社会的) life is a great tool.
yours
bell
absent
Japan
social
课堂小测
二、根据汉语意思完成句子,词数不限
6. 你最喜欢学校的什么?
________ do you like _________________ school
7. 她来中国三年了。
She ____________ China for three years.
8. 他骑自行车上学而不是乘公共汽车。
He rides to school __________________ a bus.
9. 你们玩得高兴吗?
Did you _______________________________________?
10. 我们学校的学生人数大约是600.
________________ students in our school is about 600.
What
most / best about
has been in
instead of taking
enjoy yourselves / have fun / have a good time
The number of
三、单项填空(语法专练)
( )11. I don't like _____ watch. I like _____.
A. me; your B. my; your
C. me; yours D. my; yours
( )12. —I'd like a ticket to The Sound of Music.
—Sorry, there is _____ left.
A. some B. none
C. any D. neither
( )13. The weather in London is different from _____ in Tianshui.
A. that B. one
C. it D. those
D
B
A
( )14. —When is Lang Lang's concert
—It's _____ three o'clock _____ the afternoon of December 18th.
A. at; in B. at; on
C. on; in D. in; on
( )15. —Who is your favourite singer, Mike
—TFBOYS. They are very _____ boys and girls.
A. proud of B. popular with
C. strict with D. worried about
B
B
读写综合
A. 信息归纳
请阅读下面这篇文章,根据所提供的信息,完成信息卡。
Woodlands Junior School
Hunt Road, Tonbridge, Kent, the UK
office@woodlands-junior.kent.sch.uk
Welcome to Woodlands Junior School. Our school is big and it has 380 students aged 7~11. However, it only had 108 students and four teachers when it was open on September 10th, 1964.
Main Teaching Building
As you can see, the school has a huge yard and next to it is the main teaching building. It is a two-storey building with twelve classrooms, six on each floor. In each classroom
there is a computer, an overhead projector (投影仪), and a smart whiteboard. It also has a small reading area with different kinds of books offered by the students.
Library
Our school library is used for all the reading classes weekly and at lunchtimes. The members of the reading club also meet here and do some reading after school.
School Hall
We have a fantastic school hall. It is used for gym, meetings and having lunch. It is the place where we hold many events, such as school plays, concerts, indoor games and so on.
Other Rooms
We have a well-equipped music room for music lessons, a computer room of thirty-two computers and a large staffroom for teachers to have a rest during lunchtimes.
Playgrounds
We are lucky to have two playgrounds. They are used by the students for ball games and track events(径赛项目). Our students enjoy themselves here after school every afternoon.
Information Card
The country which the school is in 1.
The opening date of the school 2.
The number of the classrooms on each floor 3.
The people who the staffroom is for 4.
The activities that the students can do on the playgrounds 5.
The UK.
September 10th, 1964.
Six / 6.
Teachers.
Ball games and track events.
B. 书面表达
当前,学生的学校生活多姿多彩,业余爱好也丰富多样。下图是我们对某所中学300名学生业余爱好的调查结果。请根据以下要求,用英语写一篇短文。
内容包括:
1. 调查结果;
2.你自己的爱好、选择的原因及带来的益处。
作文要求:
1. 不能照抄原文;不得在作文中出现学校的真实名称和学生的真实姓名。
2. 语句连贯,词数80个左右。作文的开头已经给出,不计入总词数。
【写作思路点拨】
第一步:描述某中学300名学生业余爱好的调查结果。参考句型:
1. Nearly half of ___ and a quarter of ___. A few ___.Few___.
2. _____ spend _____ doing _____.
3. _____ such as _____. As for _____.
第二步:个人选择的业余爱好,选择的原因及该爱好对本人的益处。参考句型:
_____ make sb. relaxed. _____ prefer doing_____.
第三步: 检查自己的写作。(1. 要求的2个内容都写到了吗?2. 是否有语法错误?)
Many students have hobbies. Here is the result of the survey about what 300 students usually do in their free time.
Nearly half the students like music,and a quarter of
them usually spend their time playing sports on weekends. Twenty percent enjoy reading books. A few students like collecting things they like,such as stamps,coins,and so on. Few students have other hobbies.
As for me,I prefer listening to music. Because it can give me pleasure when I'm unhappy and make me relaxed after hard study. Sometimes I listen to English songs. I can
learn English words or phrases from them. It really improves my English a lot.
Module 2 Education
Unit 3 Language in use
代词、介词
一、代词
1. 定义:代词是代替名词或一句话的一种词类。大多数代词具有名词和形容词的功能。英语中的代词,按其意义、特征及在句中的作用分为十类。本模块主要讲解人称代词、物主代词、反身代词、指示代词、疑问代词和不定代词。
语法聚焦
2.人称代词、物主代词及反身代词
人称代词 物主代词
反身代词
主格 宾格 形容词性 名词性
I me my mine myself
you (你) you your yours yourself
he him his his himself
she her her hers herself
it it its its itself
we us our ours ourselves
you (你们)
you your yours yourselves
they them their theirs
themselves
用法 举例
主格用来作主语 I like English. 我喜欢英语。
宾格用来作宾语、表语或主语
She told me a story yesterday. 她昨天给我讲了一个故事。
The girl in the photo is me. 照片里的女孩是我。
—Who's there 谁在那儿
—Only me. 只有我。
形容词性物主代词用来作定语,相当于一个形容词,置于名词之前
That's my computer.那是我的电脑。
名词性物主代词起名词的作用 —Whose ruler is this? 这是谁的尺子?
—It's mine. (mine=my ruler) 这是我的(尺子)。
反身代词作宾语,放于及物动词或介词之后 The girl is so old that she can look after herself. 这女孩岁数足够大,可以自己照顾自己。
反身代词作主语或宾语的同位语时起强调作用,可以放主语、宾语后,也可以放句末
I can do it myself. 我可以自己做。
附:形容词性物主代词+名词=名词性物主代词。如:
This isn't my dictionary, mine is over there. (mine=my dictionary)这不是我的字典,我的(字典)在那儿。
续表
用 法 举 例
指示代词在句中作主语、宾语、表语,也可以代替形容词作定语 This is my pen. 这是我的钢笔。→These are my pens. 这些是我的钢笔。(作主语)
These students will go hiking. 这些学生将去远足(作定语)
打电话时常用this指代“我”,用that指代“你” This is Mary speaking.Who is that 我是玛丽。你是谁
有时为了避免重复,可用that和those代替前面提到的名词 The population of China is much larger than that of Japan. 中国人口比日本人口多得多(that=the population)
除用作代词外,this和that都可用作副词,与形容词或副词连用,意为“这么;那么”,相当so Is it this/so hot every day 每天都这么热吗
3.指示代词
4.疑问代词
疑问代词指who, which, whom, whose, what, whoever, whichever, whomever, whatever等用于引导特殊疑问句的代词。常见的疑问代词的用法如下表:
疑问代词 主要用法 举 例
who 作主语、表语、宾语(作宾语时不能放在介词之后) Who wants to go with me? 谁想和我一起去?(作主语)
Who are you talking to? (此句中的who作介词的宾语,可用whom代替)你在跟谁说话?
whom who的宾格形式,作宾语 To whom are you talking? 你在跟谁说话?
whose who的所有格形式,作主语、表语、宾语或定语 Whose book is this? 这是谁的书?
what/who what可用于询问某人的职业、事物或人的姓名等 —What is Susan?苏珊是做什么的?
—She's a designer. 她是一名设计师
What's your name 你叫什么名字
who可用于询问某人的身份、姓名 —Who is the boy under the tree? 树下的那个男孩是谁?
—He is Li Ming. 他是李明。
what
/which what指不定数目中的“哪一个;哪一些;什么”,没有一定范围的限定 What would you like? 你喜欢什么?
which意为“哪一个”,指在一定范围内特指的人或物 Which do you like, spring or summer? 你喜欢哪一个(季节),春天还是夏天?
5.不定代词
英语中的不定代词有 all, each, both, either, neither, one, none, little, few, many, much, other, another, some, any, no, (a) few, (a) little, both, enough, every 等,以及由 some, any, no 和 every 构成的复合不定代词(即somebody, anyone, nothing 等)。
(1)指两者和三者的不定代词
用 法 举 例
有些不定代词意指两者(如both, either, neither,each),有些不定代词意指三者(如all, any, none, every)。其中:both与neither互为反义词,all与none相反。both,all都可作同位语,通常位于行为动词之前,be动词、助动词或情态动词之后。而each可单独使用,侧重个体;every则不能单独使用,且着重全体。在肯定句中用any通常表示“任一”,后接单数可数名词或不可数名词。此时any作形容词。表部分否定用all或both+not,表示全部否定用none或neither Both of my parents are doctors. 我的父母都是医生。
All of the students are interested in it. 所有的学生对此都很感兴趣。
There are flowers on each side of the street. 街道的两边都种着花。
There are trees on any/every side of the square. 广场的每一边都种有树。
He has two sons, neither of whom is rich. 他有两个儿子,他们都不富有。
He has three sons, none of whom is rich. 他有三个儿子,他们都不富有。
不定代词either与neither的用法区别:either指“两者中的任何一个”;neither指“两者中任何一个也不”,属于both的全部否定 There are mango trees on either side of the street. 街道两旁都有芒果树。(句中的either side=each
side=both sides)
Either of the answers is right. 两个答案中有一个对。
Neither of the answers is right. 两个答案都不对。
不定代词none与no one的用法区别:none既可指人也可指物,常暗示一定范围,因此通常与表范围的of短语连用;而no one(=nobody)只能指人,且不能与of短语连用;none与数量有关,可回答how many引导的疑问句,表示“一个也没有”;而no one表示“什么人也没有”,可回答who引导的疑问句 None of that money on the table is mine. 桌上的钱没有一分是我的。
No one (=Nobody) knows about it. 没有人了解此事。
—How many people are there in that room 那个房间里有几个人
—None.一个人也没有.
—Who was late today
今天谁迟到了
—No one.谁也没有迟到。
(2)some和any的用法区别
用法 举例
一般说来,some 用于肯定句中,any 用于否定句、疑问句或条件句中。但是,在表示请求、邀请或征求意见的疑问句中,通常用 some 而不用any I have some pens. 我有一些钢笔。
I don't have any pens. 我没有钢笔。
Would you like some rice? 你想吃点米饭吗?
Why not buy some bread? 为什么不买些面包呢?
不定代词 any 有时也用于肯定句中,此时表示“任何” Come any day you like. 随便哪天来都可以。
(3)复合不定代词
复合不定代词是由some-,any-,no-,every-加上-one,-body,-thing,-where, -time所组成的不定代词。其用法如下表:
用法 举例
复合不定代词受定语(通常为形容词)修饰时,定语应放在它们后面 There is nothing wrong with the radio. 这部收音机没有毛病。
No one else loves you more than I do. 没有别的人比我更爱你。
指人的复合不定代词若用作主语,其谓语动词一般用单数,相应的人称代词和物主代词也用单数 he, him, his (不一定指男性)。但在非正式文体中常用复数代词 they, them, their Everyone knows this, doesn't he/don't they
人人都知道这一点,对吗
If anybody/anyone comes, ask him to wait. 要是有人来,让他等着。
指事物的复合不定代词若用作主语,谓语动词只能用单数,相应的人称代词也只能用it,而不用they
Everything is ready, isn't it? 一切都准备好了,是吗?
不定代词 anyone, everyone 等只能指人,不能指物,且其后一般不接
of 短语,若是指物或后接 of 短语,可用 any one, every one
any one of the boys孩子们当中的任
何一个
二、介词
1. 定义:介词表示名词、代词等与句中其他词的关系,在句中不能单独作句子成分。介词后面一般有名词、代词(如果是人称代词,则要用宾格)或相当于名词的其他词类、短语或从句作它的宾语,表示与其他成分的关系。介词和它的宾语构成介词词组,在句中作状语、表语、补语、定语或介词宾语。同时介词的用法也很灵活,同一个介词可以表达多种意义。介词可以分为时间介词、方位介词和方式介词等。
2.表示时间的介词(1)at, on, in
介词 用法 举例
at 用于具体的时刻 at seven o'clock;at half past two
on 主要用于具体的某一天或某一天的上午、下午或晚上,还用于具有某种特征的一个上午、下午或晚上 on Monday;
on Teachers' Day;
on August 8th, 2008;
on Monday morning/on the morning of Monday;
on a winter afternoon
in
用于世纪、年、季节、月 in the 21st century;
in 2010;
in spring;
in January
(2)五个表示延续时间的介词
类别 举例
by:在……之前;不迟于…… I must be at school by eight tomorrow morning. 我明天早晨八点前必须到校。
in:在……以后;在……时间内 He will be back in ten minutes. 他十分钟之后将会回来。
for:历时……之久;持续…… He has been a teacher for nine years. 他当老师已经9年了。
since:自从……以来;自……以后 I have lived here since ten years ago. 我已经在这儿住了10年了。
until:直到……才,用于否定句中,其前的谓语动词多为非延续性动词;用于肯定句中,其前的谓语动词要用延续性动词 We don't see any flowers until May. 直到五月我们才看到一些花。
You must stand here until the sun sets. 你必须站在这里直到太阳落山为止。
3.表方位、方式、运动方向的介词
(1)表示方位的介词
类别 要点
in,on,to in,on,to的后面均可加the再接方位名词
(east, south, west, north等)。用in表示“范围A在范围B之内”;用on表示“两个范围接壤并且相邻”;用to则表示“范围A在范围B的区域之外即相邻不接壤”(如中国和日本)
其他表示方位的常用介词 over:在……(垂直)的正上方
above:在……(不一定垂直)的上方
under:在……(垂直的)正下方
below:在……(不一定垂直)的下方
near:在……附近
next to:紧挨着
round/around:在……周围
by:在……旁边
(2)表示方式的介词
类别 举例
by+不带限定词的单数交通工具名词,意为“乘坐……” 海:by ship/boat/sea
陆:by bus/car/train/bike/taxi
空:by air/plane/spaceship
on/in+限定词+交通工具,意为“乘坐……” He goes to work on his bike/in his car. 他骑自行车/开车去上班。
on foot为固定短语,意为“步行” She goes to school on foot. =She walks to school. 她步行上学。
(3)表示运动方向的介词
类别 举例
across:从……表面穿过,通常表示由平面的一端到另一端(如马路、河流、桥梁等) Please be careful when you go across the road. 过马路时请小心。
through:从……内部穿过,即穿过一个空间(如洞、窗户、森林等) Look! The mosquito is trying to fly through the window. 看!蚊子正试图飞出窗户。
past和by:从旁边经过或路过 We often go past/by a bakery on our way to school. 上学路上我们经常路过一个面包店。
along和down:沿着 Walk along/down the street till the end.沿着街道直走到尽头。
4.其他重要的介词
类别 用法 举例
with 表示“和;同;与……;带着;随着” with my brother 跟我哥哥一起
with pleasure十分乐意
with best wishes致以美好的祝愿
speak with your mouth full 满嘴东西说话
a girl with sunglasses戴墨镜的女孩
表示“有着;具有” coffee with sugar and milk 加糖和牛奶的咖啡
a man with good manners一个很有礼貌的男士
表示“用;被;以” cut with a knife 用刀切开
in 表示“穿;戴”,后接衣服、颜色或鞋帽 He is in blue. 他穿着蓝色的衣服。
I know the man in a hat. 我认识那个戴帽子的男人。
表示“用”,后接语言或材料,表示手段或方法
等 How do you say that in English?那个用英语怎么说?
She wrote the letter in pencil. 她用铅笔写了这封信。
表示境况、情绪、状态等 in trouble陷入困境
in danger处于危险中
in surprise惊讶地
in good health身体健康
表示“关于……;在……方面” I'm weak in maths. 我的数学不好。
against与for against表示“反对;违反;不利于”,其反义词为for,此时for表示“支持;
赞成” We are all against his idea. 我们都反对他的想法。
Are you for or against the plan?你是支持还是反对这个计划?
except与
besides except表示“除……外”,具有排他性质 We all went to see the film except Mr Wang. 除了王先生,我们都去看电影了。(王先生没去)
besides表示“除了……以外还有……”,具有附加性质 Besides Mr Wang, we also went to see the film. 除了王先生,我们也去看电影了。(王先生也去了)
一、根据句意及首字母或中文提示完成单词
1. Their new school is as beautiful as ________.
2. The ________(铃) is ringing. Let's go to the classroom.
3. Grace was ________(缺席) from school.
4. He has travelled to _________(日本) several times.
5. I think _________(社会的) life is a great tool.
yours
bell
absent
Japan
social
课堂小测
二、根据汉语意思完成句子,词数不限
6. 你最喜欢学校的什么?
________ do you like _________________ school
7. 她来中国三年了。
She ____________ China for three years.
8. 他骑自行车上学而不是乘公共汽车。
He rides to school __________________ a bus.
9. 你们玩得高兴吗?
Did you _______________________________________?
10. 我们学校的学生人数大约是600.
________________ students in our school is about 600.
What
most / best about
has been in
instead of taking
enjoy yourselves / have fun / have a good time
The number of
三、单项填空(语法专练)
( )11. I don't like _____ watch. I like _____.
A. me; your B. my; your
C. me; yours D. my; yours
( )12. —I'd like a ticket to The Sound of Music.
—Sorry, there is _____ left.
A. some B. none
C. any D. neither
( )13. The weather in London is different from _____ in Tianshui.
A. that B. one
C. it D. those
D
B
A
( )14. —When is Lang Lang's concert
—It's _____ three o'clock _____ the afternoon of December 18th.
A. at; in B. at; on
C. on; in D. in; on
( )15. —Who is your favourite singer, Mike
—TFBOYS. They are very _____ boys and girls.
A. proud of B. popular with
C. strict with D. worried about
B
B
读写综合
A. 信息归纳
请阅读下面这篇文章,根据所提供的信息,完成信息卡。
Woodlands Junior School
Hunt Road, Tonbridge, Kent, the UK
office@woodlands-junior.kent.sch.uk
Welcome to Woodlands Junior School. Our school is big and it has 380 students aged 7~11. However, it only had 108 students and four teachers when it was open on September 10th, 1964.
Main Teaching Building
As you can see, the school has a huge yard and next to it is the main teaching building. It is a two-storey building with twelve classrooms, six on each floor. In each classroom
there is a computer, an overhead projector (投影仪), and a smart whiteboard. It also has a small reading area with different kinds of books offered by the students.
Library
Our school library is used for all the reading classes weekly and at lunchtimes. The members of the reading club also meet here and do some reading after school.
School Hall
We have a fantastic school hall. It is used for gym, meetings and having lunch. It is the place where we hold many events, such as school plays, concerts, indoor games and so on.
Other Rooms
We have a well-equipped music room for music lessons, a computer room of thirty-two computers and a large staffroom for teachers to have a rest during lunchtimes.
Playgrounds
We are lucky to have two playgrounds. They are used by the students for ball games and track events(径赛项目). Our students enjoy themselves here after school every afternoon.
Information Card
The country which the school is in 1.
The opening date of the school 2.
The number of the classrooms on each floor 3.
The people who the staffroom is for 4.
The activities that the students can do on the playgrounds 5.
The UK.
September 10th, 1964.
Six / 6.
Teachers.
Ball games and track events.
B. 书面表达
当前,学生的学校生活多姿多彩,业余爱好也丰富多样。下图是我们对某所中学300名学生业余爱好的调查结果。请根据以下要求,用英语写一篇短文。
内容包括:
1. 调查结果;
2.你自己的爱好、选择的原因及带来的益处。
作文要求:
1. 不能照抄原文;不得在作文中出现学校的真实名称和学生的真实姓名。
2. 语句连贯,词数80个左右。作文的开头已经给出,不计入总词数。
【写作思路点拨】
第一步:描述某中学300名学生业余爱好的调查结果。参考句型:
1. Nearly half of ___ and a quarter of ___. A few ___.Few___.
2. _____ spend _____ doing _____.
3. _____ such as _____. As for _____.
第二步:个人选择的业余爱好,选择的原因及该爱好对本人的益处。参考句型:
_____ make sb. relaxed. _____ prefer doing_____.
第三步: 检查自己的写作。(1. 要求的2个内容都写到了吗?2. 是否有语法错误?)
Many students have hobbies. Here is the result of the survey about what 300 students usually do in their free time.
Nearly half the students like music,and a quarter of
them usually spend their time playing sports on weekends. Twenty percent enjoy reading books. A few students like collecting things they like,such as stamps,coins,and so on. Few students have other hobbies.
As for me,I prefer listening to music. Because it can give me pleasure when I'm unhappy and make me relaxed after hard study. Sometimes I listen to English songs. I can
learn English words or phrases from them. It really improves my English a lot.
同课章节目录
- Module 1 Travel
- Unit 1 We toured the city by bus and by taxi
- Unit 2 It's a long story.
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 2 Education
- Unit 1 They don't sit in rows.
- Unit 2 What do I like best about school?
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 3 Life now and then
- Unit 1 They sometimes work harder.
- Unit 2 I think life is better today.
- Unit 3 Language in use.
- Module 4 Rules and suggestions
- Unit 1 You must be careful of falling stones.
- Unit 2 we must keep the camp clean.
- Unit 3 Language in use.
- Revison A
- Module 5 Look after yourself
- Unit 1 We'd better get you to hospital.
- Unit 2 Get off the sofa!
- Unit 3 Language in use.
- Module 6 Eating togethe
- Unit 1 When is the school-leavers' party?
- Unit 2 Knives and forks are used for most Western
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 7 English for you and me
- Unit 1 Have you ever been to an English corner?
- Unit 2 We all own English.
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Module 8 My future life
- Unit 1 Here's to our friendship and the future
- Unit 2 I know that you will be better at maths.
- Unit 3 Language in use
- Revison B
