2022届高考英语二轮复习:状语从句课件(62张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2022届高考英语二轮复习:状语从句课件(62张) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-05-24 16:01:15 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共62张PPT)
状语从句
复习重点
1. 状语从句的基本用法;
2. 引导状语从句的常见连词;
3. 各种从属连词的含义及用法比较。
注意:从句是一个句子,要有“主谓(宾、宾补)”等。
01 状语从句的概念与种类
概念:在句中起状语作用的从句叫作状语从句。引导状语从句的连词被称为从属连词,状语从句需用陈述句语序,可位于复合句的句首或句末。句式为“状语从句+主句”或“主句+状语从句”。
种类:
根据状语从句在句中的不同作用可分为:时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、让步和比较状语从句,共9种。
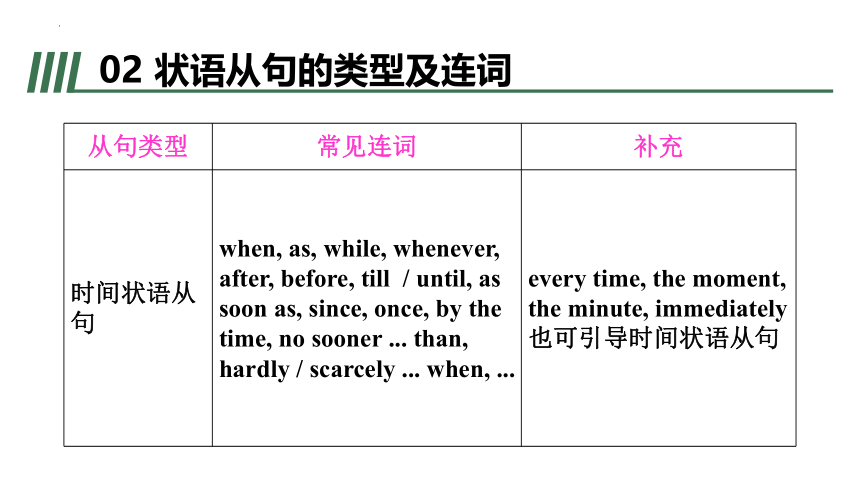
从句类型 常见连词 补充
时间状语从句 when, as, while, whenever, after, before, till / until, as soon as, since, once, by the time, no sooner ... than, hardly / scarcely ... when, ... every time, the moment, the minute, immediately也可引导时间状语从句
02 状语从句的类型及连词
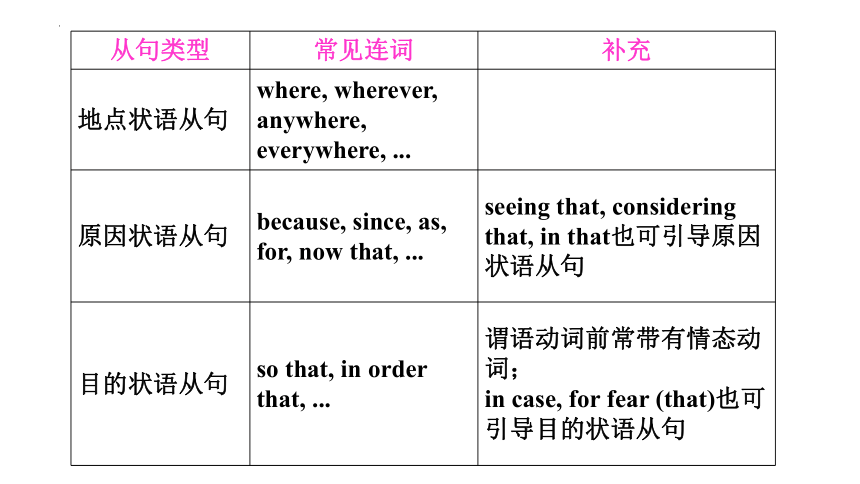
从句类型 常见连词 补充
地点状语从句 where, wherever, anywhere, everywhere, ...
原因状语从句 because, since, as, for, now that, ... seeing that, considering that, in that也可引导原因状语从句
目的状语从句 so that, in order that, ... 谓语动词前常带有情态动词;
in case, for fear (that)也可引导目的状语从句
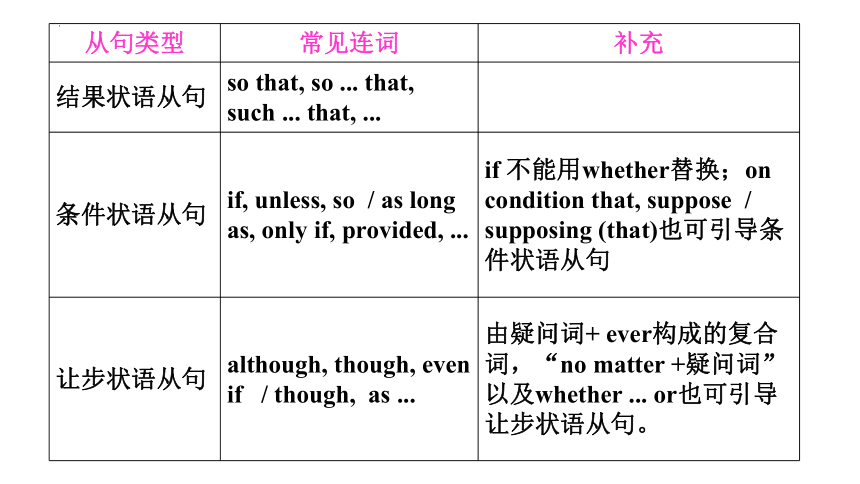
从句类型 常见连词 补充
结果状语从句 so that, so ... that, such ... that, ...
条件状语从句 if, unless, so / as long as, only if, provided, ... if 不能用whether替换;on condition that, suppose / supposing (that)也可引导条件状语从句
让步状语从句 although, though, even if / though, as ... 由疑问词+ ever构成的复合词,“no matter +疑问词”以及whether ... or也可引导让步状语从句。
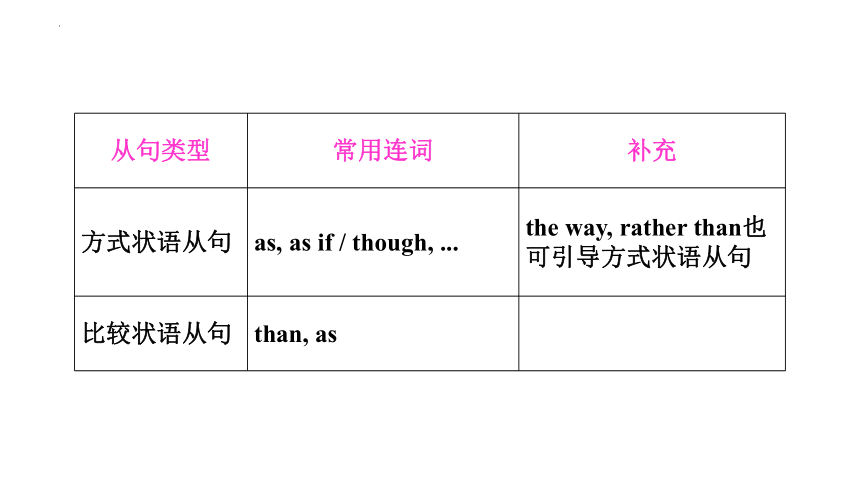
从句类型 常用连词 补充
方式状语从句 as, as if / though, ... the way, rather than也可引导方式状语从句
比较状语从句 than, as
1.1 时间状语从句
概念:在复合句中起时间状语作用的从句称为时间状语从句。引导时间状语从句的连词或词组有:when,while,as(当...时候),as soon as...(一 ...就...),since(自从),until/ till(直到),before(在...之前),after(在...之后)等。
出题点:
(1)when、while、as的用法区别;
(2)until的用法;
(3)before、after的用法。
(4)since的常用句式及用法。
03 状语从句的基本用法
1. 时间&原因状语从句
1.1.1 when、while、as引导的时间状语从句
区别一:主句谓语动词与从句谓语动词发生的先后关系---高频考点
When 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词既可以和主句谓语动词同时发生,也可有先后;
While 和 as 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词和主句的谓语动词必须是同时发生。
Eg: When he came back, his mother was cooking. 注:从句在前,逗号隔开
从句谓语动词 came 与主句谓语动词 was cooking 同时发生。
Eg: The train has been away for ten minutes when I get to the station.
从句谓语动词 get to 发生在主句谓语动词 has been away 之后
Eg: When he had finished his work, he took a rest. 注:从句在前,逗号隔开
从句谓语动词 had finished 发生在主句谓语动词 took 之前
主从句的时态要保持一致!
区别一:主句谓语动词与从句谓语动词发生的先后关系---高频考点
When 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词既可以和主句谓语动词同时发生,也可有先后;
While 和 as 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词和主句的谓语动词必须是同时发生。
Eg: I was reading a book while she was singing.
从句谓语动词 was singing 与主句谓语动词 was reading 同时发生。
Eg: As he was reading, he was shaking his head. .
从句谓语动词 was reading 与主句谓语动词 was shaking 同时发生。
总结:在主从句谓语动词发生顺序的层面上,when的使用范围要比 while 和 as更广。
区别二:从句谓语动词“延续与非延续”的区别---高频考点
When 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词既可以是延续性动词也可以是短暂性动词;
While 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词必须是延续性动词,常用于进行时态中。
Eg: I was reading a book while she was singing.
从句谓语动词 was singing 为延续性动词。
Eg: When he came back, his mother was cooking.
从句谓语动词 came 为非延续性动词
When he is reading, his mother is cooking.
从句谓语动词 is reading 为延续性动词
总结:在从句谓语动词“延续与非延续”的层面上,when的使用范围要比 while 更广。
思考:什么情况下when、while、as三者可以互换呢?
从句动作和主句动作同时发生,且从句动作为延续性动词时,when,while,as都可使用。
* Tip:as常表示“随着……”;“一边……,一边……”之意。
The atmosphere gets thinner and thinner as the height increases.随着高度的增加,大气越来越稀薄。
狙击易错点
主将从现
主祈从现
主过从过
主句是一般将来时,从句用一般现在时---主将从现
Eg:When he arrives, I will call you.
主句是祈使句,从句用一般现在时---主祈从现
Eg:Please call me when he arrives in Beijing.
主句是过去的时态,从句用过去的时态---主过从过
Eg:She was sleeping while I was reading books.
1. as soon as 意为“一……就……”,表示从句的动作一发生主句的动作随即就紧接着发生。
As soon as he finishes his classwork, he runs out of the class.
As soon as he heard the news, he jumped with joy.
2. 重点提醒:
As soon as 引导的时间状从(指未发生的动作),符合“主将从现”的时态原则。
I will tell him the news as soon as he comes back.
1.1.2 as soon as 引导的时间状语从句
表示 “一...就” 的表达:
固定句型: hardly/scarcely…when/before, as soon as
名词短语: the moment, the minute, the second, the instant
连词: immediately, directly, instantly
介词on/upon/at
构成的短语
on/upon doing sth. 一……就…… at the sight of 一看到……就……
at the sound of 一听到……就…… at the thought of 一想到……就……
1.1.3 since 引导的时间状从
Since (conj./ prep./ adv.)
1. I haven’t heard from him since I left school.
2. We have lived here since 2003/ten years ago.
3. They have never seen it ever since.
1. Since意为“自……以来”,主句常用现在完成时或一般现在时,从句常用一般过去时。
Eg:I have lived in London since I was three.
It is two years since I became a colledge student.
2. since引导的状从的谓语是短暂动词表示动作开始 ;是延续动词表示动作结束
It has been a year since he worked here.
We haven’t seen each other since we parted.
3. It + be + some time + since-clause 这个句型表示从since 从句谓语动作发生以后到现在或过去所经过的一段时间,意为“自从......以来有(多久)”
It is + some time since … ( did )
It has been + some time since ..( did )
It is ten years since I left here.
It is/ has been 5 years since we last met.
2.1.4 before & after引导的时间状语从句
1. Before 意为“在……之前”,表示主句动作发生在从句动作之前。
After 意为“在……之后”,表示主句动作发生在从句动作之后。
Eg: Pleaase turn off the lights before you leave the classroom.
I’ll call you after I’ve spoken to them.
1.1.4 before&after引导的时间状语从句
2. before, after若后接句子,则它们是连词;若后不接句子,则是介词,此时如果它们后接动词,则要用动名词形式。
3. 含before的常用句式有:
①It won't be+一段时间+before…用不了多久就会……(before从句用一般现在时)
②It will be+一段时间+before…要过多久之后才……(before从句用一般现在时)
③It wasn't+一段时间+before…没过多久就……(before从句用一般过去时)
④It was+一段时间+before…过了多久才……(before从句用一般过去时)
1.1.5 until/till 引导的时间状语从句
Until/ till意为“直到”。当主句为否定句时,常构成“not...until/till...”结构,意为“直到…才…”。
1. 主句是否定句时:如果主句是否定句,短暂性动词,表示该动作在until/till所表示的时间或动作之前未发生。
Eg: We didn't come back until/till midnight. 我们直到半夜才回来。
We didn't leave until/till she came. 我们直到她来了才走。
2. 主句是肯定句时:如果主句是肯定句,句子或主句的谓语动词用持续性动词,表示该动作延续到until/till所指的时间或动作为止。
Eg: We talked until/till midnight. 我们一直谈到半夜。
4. 用于句首时常用until而不用till; until 还可用于倒装句和强调句
Eg: Until you told me, I had heard nothing of what happened.
Until the manager returns, nothing can be done.
3. 若主句是一般将来时,until/till从句要用一般现在时表示将来,即主将从现。
Eg: I will wait until he comes back.
出题点: (1) because 和 since的用法。(2) as 和 for 的用法。
概念:原因状语从句通常用来表示主句中某一动作产生的原因,或说明主句内容的理由或根据。
原因状语从句可置于句首,也可置于句尾。引导原因状语从句的
从属连词主要有:because(因为),since(既然),as(由于)
1.2 原因状语从句
Because的用法:表示的因果关系最强,常用来回答why提出的问题,意为“因为”。所引出的原因往往是说话者所不知道的或最感兴趣的。Because引导的原因状语从句往往比主句显得更重要。
BecauseTom was ill, he didn’t come to school.
---Why didn’t you give Dick a call
---Because I will see him soon.
※易错点:because 与 so不能连用。
Because my mother was ill, so I didn’t go to your party. 本句错误!!
I didn’t go to your party because my mother was ill.
My mother was ill, so I didn’t go to your party.
1.2.1 because 引导的原因状语从句
1.2.2 since 引导的原因状语从句
Since表示人们已经知道的事实,不需要强调的原因,常意为“既然……”。通常放在句首。Since引导的从句是次要的,重点强调主句内容。
Since you are free tonight, why not drop in and play chess with me
Since everyone is here, let’s get started.
as 表示的原因只是对结果的附加说明,位于句首、句尾均可。
She didn’t hear us come in as she was asleep.
As you weren’t here, I left a message.
for是并列连词,可用来作附加说明,为前面的事实提供一种推断的理由,for引导的从句一般位于主句之后。
Eg:It rained last night, for the groud is wet.
We should be more careful, for it is already dark.
1.2.3 as/for引导的原因状语从句
2.1 条件状语从句
概念:在句子中作条件状语的从句称为条件状语从句。
引导词:if(如果),unless(除非,如果不),as long as(只要)等。
As long as you can keep on, you will do it.
You can’t go out unless you promise me to come back early.
If it is sunny tomorrow, we will have a picnic.
出题点:
1,if 引导条件状从和宾从的用法区别。
2,unless, as long as 引导的条件状从的用法。
3,条件状从的时态。
2. 条件&让步状语从句
2.1.1 if 引导的条件状语从句
If 意为“如果”,表示假设的情况可能发生。其主句不能用be going to 表示将来,而应该用shall或will。
If it rains tomorrow, I will stay at home.
I will stay at home if it rains tomorrow.
1,主句前后都可以,句前逗号别忘记。
2,时态:主将从现;主祈从现;主情从现。
Please call me if he comes next Sunday.
I can do it myself if I get the permission.
1,句子成分分析法:if引导的宾从位于及物动词之后,而 if引导的条件状从只能作状语,主句的结构已经完整。
Do you know if we will go to the zoo tomorrow
I will play basketball if it doesn’t rain tomorrow.
技能提升:宾语从句中的 if 和条件状语从句中 if 的区别技巧
2,时态分析法:if引导的宾从符合宾从时态:主现从不限、主过从必过、客观真理一般现。If 引导的条件状从符合“主将从现、主祈从现、主情从现”。
Do you know if we will go to the zoo tomorrow
I will play basketball if it doesn’t rain tomorrow.
Unless 意为“除非、如果不”,表示否定的含义,故其引导的从句只能是肯定形式。
Unless 在意思上相当于“if...not...”,但语气更强。
Unless 引导的条件状从也符合“主将从现、主祈从现、主情从现”原则。
We will climb the mountain tomorrow unless it rains.
= We will climb the mountain tomorrow if it doesn’t rain.
Unless you hurry up, you will be late. 主将从现
※易错点:unless引导的条件状从翻译成“除非...,否则....”时, unless 不可以和 or 连用。
Unless you hurry up, you will be late.
除非你快点,(否则) 你就会迟到。
2.1.2 unless 引导的条件状语从句
2.1.3 as long as 引导的条件状语从句
as long as 意为“只要”,符合“主将从现”的原则。
As long as you don’t give up, you will succeed.
as long as / so long as
on condition that 只要
as / so far as … “就…而论(而言)”
in case 万一
suppose/ supposing …
provided / providing that … 假定/假使
概念:表示尽管某种不利于主句动作发生的条件存在,主句中的情况依
然会出现。
引导词:though/although(尽管);even if/even though (即使)。
出题点:
1,though/ although/as的用法。
2,even if/ even though的用法。
3,no matter+疑问词 或 疑问词-ever的用法。
2.2 让步状语从句
2.2.1 although/ though/as 引导的让步状语从句
1. although 和 though 两者意思相同,意为“虽然,尽管”,一般可以互换。
注意:两个词都绝对不可以和 but 连用,但是可以和 yet 或 still 连用。
Although/ Though he worked hard, failed.
= He worked hard, but he failed.
Although/ Though it was rainning hard, yet they went on playing football.
2. 在although, though,as 引导的特殊让步状语从句中,as较常见。
这种让步状语从句的特点是:形容词、副词、名词(单数可数名词前不用不定冠词)、行为动词(带状语或宾语)置于句首,构成部分倒装。
注意:Though可接可不接;Although不接倒装语序。
2.2.2 even if/ even though 引导的让步状语从句
even if 和 even though均可引导让步状从,意为“即使”。两者的用法有细微区别,但通常可互换使用。
even if 引导的让步状从往往是假设性的,而even though引导的往往是真的。
Even if it rains tomorrow, we won’t change our plan.
Even though it’s hard work, I enjoy it.
2.2.3 疑问词-ever/no matter疑问词引导的让步状语从句
“疑问词-ever”可用作表示具有强烈意义的疑问词引导让步状从,此时可换成“no matter 疑问词”。
Whenever I am unhappy, it is my friend who cheers me up.
= No matter when I am unhappy, it is my friend who cheers me up.
I will wait for you however late it is.
=I will wait for you no matter how late it is.
注意: 疑问词-ever还可引导名词性从句,此时不能和no matter疑问词互换。
3.1 目的状语从句
概念:在句子中作目的状语的从句称为“目的状语从句”,常译为“为了能够……”。
引导目的状语从句的连词有:so that 和 in order that等;从句的谓语常含有“may, might, can, could, will, would”等情态动词。
so that 引导的从句只能放在主句之后,而 in order that 引导的从句既可以放在主句前,也可放在主句后。
They worked hard in order that/ so that they might succeed.
=In order that they might succeed, they worked hard .
He spoke loudly so that/ in order that others could hear him clearly.
=In order that others could hear him clearly, he spoke loudly
3. 结果&目的状语从句
※易错点---目的状语从句与不定式、介词短语的互换:
当从句主语和主句主语一致时,可用 so as to, in order to 替换目的状语从句。
He studied every day in order that he could succeed.
=He studied every day in order to succeed.
We will sit in the front of the hall so that we can hear better.
=We will sit in the front of the hall so as to hear better.
3.2 结果状语从句
概念:在句子中作结果状语的从句称为结果状语从句,一般
置于句尾。 引导结果状语从句的连词有:so(因此),“so...that...(如此...以至于...)、such...that...(如此...以至于...)、so that(因此)等。
Kathy is so lovely that we all like to play with her.
His plan was such a good one that we all agreed to accept it.
在“so...that...”结构中,so是副词,修饰形容词或副词。引导结果状语从句时常用语以下结构:
1, so+形容词/副词+that+从句.
2, so+形容词+a(n)+可数名词单数+that + 从句
3, so+many/few+(可数名词复数)+that+从句
4, so+much/little+(不可数名词)+that+从句
在“such...that...”结构中,such是形容词,修饰名词或名词短语。引导结果状语从句时常用语以下结构:
1, such+a(n)+形容词+可数名词单数+that+从句
2, such+形容词+可数名词复数+that + 从句
3, such+形容词+不可数名词+that+从句
3.2.1 so...that.../ such...that...结果状语从句
相同点:两者均可以用来引导结果状从。
不同点:such 和 so 之后修饰的词性不同:such是名词,so 是形容词或副词。
1,
Kathy is so loely that we all like to play with her.
形容词
It’s so interesting a film that we all want to see it.
形容词+a/an+可名单
He made so many mistakes that he failed the exam.
many+可名复
The little boy has so little difficulty in working out this problem
little+不可名
that I admire him very much.
so...that...引导结果状从的用法
1,
‘s
He is so young that he can’t go to school. =
He is too young to go to school. =
He is not old enough to go to school.
so...that...与 too...to...的转换
so...that...结构的否定形式可用 too...to... 或not...enough to...结构 代替。
His plan was such a good one that we all agreed to accept it.
a(an) +形容词+可名单
They’re such kindhearted teachers that we all respect them.
形容词+可名复
We had such terrible weather that we couldn’t finish the work on time. 形容词+不可名
such...that...引导结果状从的用法
1,
重点提醒:
在“so/such...that...”结构中,“so/such...”部分位于句首时,主句用 部分倒装 语序。
Eg: So excited was he that he could not fall into sleep.
(2) 有时“such+a(n)+形容词+可名单+that+从句”结构可与“so+形容词+a(n)+可名单+that + 从句”结构互换。
Eg: Mr. James is such a humorous teacher that we all like him. =
Mr. James is so humorous a teacher that we all like him.
总结:so+形容词+a(an)+可名单= such +a(an)+形容词+可名单
3.2.2 so that 引导的结果状语从句
so that 引导结果状语从句时意为“以致,以至于,因此”,从句前有时用逗号与主句分开。
He worked hard at school, so that he gained high grades in the exam.
*如何区分“so that”引导的是“目的状从”还是“结果状从呢?
so that 引导的“目的状从”中都含有“can、could”等情态动词,而 “结果状从”则没有
1. Kate got up early so that she could catch the first bus.
2. They missed the bus so that they were late for class.
4. 方式&比较状语从句
4.1 方式状语从句
概念:方式状语从句就是描述动作进行方式的状语从句,常用“和...一样”、“像/仿佛...”以及“按照...的方法”等来表达。
常见的引导词有:as, (just) as…so…, as if, as though引导。
as引导的方式状语从句通常位于主句后,但在(just) as…so…结构中位于句首,这时as从句带有比喻的含义,意思是"正如…","就像",多用于正式文体,例如:
Eg: Always do to the others as you would be done by.
As water is to fish, so air is to man.
Just as we sweep our rooms, so we should sweep backward ideas from our minds.
4.1.1 as, (just) as…so… 引导的方式状语从句
两者的意义和用法相同,引出的状语从句谓语多用虚拟语气,表示与事实相反,有时也用陈述语气,表示所说情况是事实或实现的可能性较大。汉译常作"仿佛……似的","好像……似的",例如:
They completely ignore these facts as if (as though) they never existed.
他们完全忽略了这些事实,就仿佛它不存在似的。(与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气。)
He looks as if (as though) he had been hit by lighting. 他那样子就像被雷击了似的。(与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气。)
It looks as if the weather may pick up very soon. 看来天气很快就会好起来。(实现的可能性较大,谓语用陈述语气。)
4.1.2 as if, as though 引导的方式状语从句
4.2 比较状语从句
概念:比较状语从句就是表示比较的状语从句。
常见的引导词有:as和than。
常见的句型有:
as...as...;
not so(/as)...as...;
more...than;
no more...than...;
the more...the more...
1. as + ...形容词/副词... + as + 从句
He knows as much as I do.
You can have as many dreams as you want.
2. not so(/as) + ...形容词/副词... + as + 从句
She doesn't work so hard as you do.
The task is not as easy as we thought.
3. ...形容词比较级/副词比较级... + than + 从句
The situation was more complicated than it sounded on the phone.
You look much better than you did weeks ago.
4. no + 形容词比较级/副词比较级...+ than + 从句
There is no prettier girl than Helen is. 没有比海伦更漂亮的女孩了。
5. the 形容词比较级/副词比较级 + 从句... the 形容词比较级/副词比较级+ 从句
The warmer it gets, the faster the ice melts.
天气越暖和,冰融化得越快。
补充:英语中倍数的表达
1. 倍数+as+形容词或副词的原级+as+其它。
这种结构又常演变成下列两类:
①倍数+as+many+可数名词复数+as;
②倍数+as+much+不可数名词+as。如:
e.g. There are seven times as many people as I expected.是我预料的人数的七倍。
2. 倍数+形容词(或副词)的比较级+ than+其它。
e.g. The hall is five times bigger than our classroom.这个大厅的面积比我们教室大五倍。
3. 倍数+the+名词(size,height,weight,length,width等)+of+其它。
e.g. The earth is 49 times the size of the moon.地球的体积是月球的49倍。
4. 倍数+what从句。
e.g. The production is now three times what it was ten years ago.现在的产量是十年前的三倍。
where在地点状语从句中,除了指地点外,还可指处境等。
* 由where引导的地点状语从句与定语从句的区别:
5. 地点状语从句
You’d better make a mark where you have some questions.
You’d better make a mark at the place where you have some questions.
1. 句子结构不同
where引导定语从句时,从句前应有一个表示(抽象)地点或处所的名词作先行词,而状语从句前没有先行词。
2. where的作用不同
where引导定语从句时,指代地点名词,在定语从句中做状语。
where引导状语从句时,修饰的是主句的谓语。
状语从句的倒装问题
1、So difficult _____ it to live in an English-speaking country
that I determined to learn English.
A. I have felt B. have I felt C. I did feel D. did I feel
2、Not until all the fish died in the river _____ how serious the
pollution was.
A. did the villagers realize B. the villagers realized
C. the villagers did realize D. didn’t the villagers realize
状语从句的倒装一般有下面几种情况:① 否定词开头;
② so 加 adj. 开头;③ as / though引导的让步状语从句。
D
A
特别注意:
Hardly … when …
No sooner … than …
Child as he is, …
Hardly had he got to the station when the train left.
No sooner had he got to the station than the train left.
Child as he is, he can speak seven foreign languages.
真 题 演 练
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
THANK YOU !
状语从句
复习重点
1. 状语从句的基本用法;
2. 引导状语从句的常见连词;
3. 各种从属连词的含义及用法比较。
注意:从句是一个句子,要有“主谓(宾、宾补)”等。
01 状语从句的概念与种类
概念:在句中起状语作用的从句叫作状语从句。引导状语从句的连词被称为从属连词,状语从句需用陈述句语序,可位于复合句的句首或句末。句式为“状语从句+主句”或“主句+状语从句”。
种类:
根据状语从句在句中的不同作用可分为:时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、让步和比较状语从句,共9种。
从句类型 常见连词 补充
时间状语从句 when, as, while, whenever, after, before, till / until, as soon as, since, once, by the time, no sooner ... than, hardly / scarcely ... when, ... every time, the moment, the minute, immediately也可引导时间状语从句
02 状语从句的类型及连词
从句类型 常见连词 补充
地点状语从句 where, wherever, anywhere, everywhere, ...
原因状语从句 because, since, as, for, now that, ... seeing that, considering that, in that也可引导原因状语从句
目的状语从句 so that, in order that, ... 谓语动词前常带有情态动词;
in case, for fear (that)也可引导目的状语从句
从句类型 常见连词 补充
结果状语从句 so that, so ... that, such ... that, ...
条件状语从句 if, unless, so / as long as, only if, provided, ... if 不能用whether替换;on condition that, suppose / supposing (that)也可引导条件状语从句
让步状语从句 although, though, even if / though, as ... 由疑问词+ ever构成的复合词,“no matter +疑问词”以及whether ... or也可引导让步状语从句。
从句类型 常用连词 补充
方式状语从句 as, as if / though, ... the way, rather than也可引导方式状语从句
比较状语从句 than, as
1.1 时间状语从句
概念:在复合句中起时间状语作用的从句称为时间状语从句。引导时间状语从句的连词或词组有:when,while,as(当...时候),as soon as...(一 ...就...),since(自从),until/ till(直到),before(在...之前),after(在...之后)等。
出题点:
(1)when、while、as的用法区别;
(2)until的用法;
(3)before、after的用法。
(4)since的常用句式及用法。
03 状语从句的基本用法
1. 时间&原因状语从句
1.1.1 when、while、as引导的时间状语从句
区别一:主句谓语动词与从句谓语动词发生的先后关系---高频考点
When 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词既可以和主句谓语动词同时发生,也可有先后;
While 和 as 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词和主句的谓语动词必须是同时发生。
Eg: When he came back, his mother was cooking. 注:从句在前,逗号隔开
从句谓语动词 came 与主句谓语动词 was cooking 同时发生。
Eg: The train has been away for ten minutes when I get to the station.
从句谓语动词 get to 发生在主句谓语动词 has been away 之后
Eg: When he had finished his work, he took a rest. 注:从句在前,逗号隔开
从句谓语动词 had finished 发生在主句谓语动词 took 之前
主从句的时态要保持一致!
区别一:主句谓语动词与从句谓语动词发生的先后关系---高频考点
When 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词既可以和主句谓语动词同时发生,也可有先后;
While 和 as 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词和主句的谓语动词必须是同时发生。
Eg: I was reading a book while she was singing.
从句谓语动词 was singing 与主句谓语动词 was reading 同时发生。
Eg: As he was reading, he was shaking his head. .
从句谓语动词 was reading 与主句谓语动词 was shaking 同时发生。
总结:在主从句谓语动词发生顺序的层面上,when的使用范围要比 while 和 as更广。
区别二:从句谓语动词“延续与非延续”的区别---高频考点
When 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词既可以是延续性动词也可以是短暂性动词;
While 引导的时间状语从句其谓语动词必须是延续性动词,常用于进行时态中。
Eg: I was reading a book while she was singing.
从句谓语动词 was singing 为延续性动词。
Eg: When he came back, his mother was cooking.
从句谓语动词 came 为非延续性动词
When he is reading, his mother is cooking.
从句谓语动词 is reading 为延续性动词
总结:在从句谓语动词“延续与非延续”的层面上,when的使用范围要比 while 更广。
思考:什么情况下when、while、as三者可以互换呢?
从句动作和主句动作同时发生,且从句动作为延续性动词时,when,while,as都可使用。
* Tip:as常表示“随着……”;“一边……,一边……”之意。
The atmosphere gets thinner and thinner as the height increases.随着高度的增加,大气越来越稀薄。
狙击易错点
主将从现
主祈从现
主过从过
主句是一般将来时,从句用一般现在时---主将从现
Eg:When he arrives, I will call you.
主句是祈使句,从句用一般现在时---主祈从现
Eg:Please call me when he arrives in Beijing.
主句是过去的时态,从句用过去的时态---主过从过
Eg:She was sleeping while I was reading books.
1. as soon as 意为“一……就……”,表示从句的动作一发生主句的动作随即就紧接着发生。
As soon as he finishes his classwork, he runs out of the class.
As soon as he heard the news, he jumped with joy.
2. 重点提醒:
As soon as 引导的时间状从(指未发生的动作),符合“主将从现”的时态原则。
I will tell him the news as soon as he comes back.
1.1.2 as soon as 引导的时间状语从句
表示 “一...就” 的表达:
固定句型: hardly/scarcely…when/before, as soon as
名词短语: the moment, the minute, the second, the instant
连词: immediately, directly, instantly
介词on/upon/at
构成的短语
on/upon doing sth. 一……就…… at the sight of 一看到……就……
at the sound of 一听到……就…… at the thought of 一想到……就……
1.1.3 since 引导的时间状从
Since (conj./ prep./ adv.)
1. I haven’t heard from him since I left school.
2. We have lived here since 2003/ten years ago.
3. They have never seen it ever since.
1. Since意为“自……以来”,主句常用现在完成时或一般现在时,从句常用一般过去时。
Eg:I have lived in London since I was three.
It is two years since I became a colledge student.
2. since引导的状从的谓语是短暂动词表示动作开始 ;是延续动词表示动作结束
It has been a year since he worked here.
We haven’t seen each other since we parted.
3. It + be + some time + since-clause 这个句型表示从since 从句谓语动作发生以后到现在或过去所经过的一段时间,意为“自从......以来有(多久)”
It is + some time since … ( did )
It has been + some time since ..( did )
It is ten years since I left here.
It is/ has been 5 years since we last met.
2.1.4 before & after引导的时间状语从句
1. Before 意为“在……之前”,表示主句动作发生在从句动作之前。
After 意为“在……之后”,表示主句动作发生在从句动作之后。
Eg: Pleaase turn off the lights before you leave the classroom.
I’ll call you after I’ve spoken to them.
1.1.4 before&after引导的时间状语从句
2. before, after若后接句子,则它们是连词;若后不接句子,则是介词,此时如果它们后接动词,则要用动名词形式。
3. 含before的常用句式有:
①It won't be+一段时间+before…用不了多久就会……(before从句用一般现在时)
②It will be+一段时间+before…要过多久之后才……(before从句用一般现在时)
③It wasn't+一段时间+before…没过多久就……(before从句用一般过去时)
④It was+一段时间+before…过了多久才……(before从句用一般过去时)
1.1.5 until/till 引导的时间状语从句
Until/ till意为“直到”。当主句为否定句时,常构成“not...until/till...”结构,意为“直到…才…”。
1. 主句是否定句时:如果主句是否定句,短暂性动词,表示该动作在until/till所表示的时间或动作之前未发生。
Eg: We didn't come back until/till midnight. 我们直到半夜才回来。
We didn't leave until/till she came. 我们直到她来了才走。
2. 主句是肯定句时:如果主句是肯定句,句子或主句的谓语动词用持续性动词,表示该动作延续到until/till所指的时间或动作为止。
Eg: We talked until/till midnight. 我们一直谈到半夜。
4. 用于句首时常用until而不用till; until 还可用于倒装句和强调句
Eg: Until you told me, I had heard nothing of what happened.
Until the manager returns, nothing can be done.
3. 若主句是一般将来时,until/till从句要用一般现在时表示将来,即主将从现。
Eg: I will wait until he comes back.
出题点: (1) because 和 since的用法。(2) as 和 for 的用法。
概念:原因状语从句通常用来表示主句中某一动作产生的原因,或说明主句内容的理由或根据。
原因状语从句可置于句首,也可置于句尾。引导原因状语从句的
从属连词主要有:because(因为),since(既然),as(由于)
1.2 原因状语从句
Because的用法:表示的因果关系最强,常用来回答why提出的问题,意为“因为”。所引出的原因往往是说话者所不知道的或最感兴趣的。Because引导的原因状语从句往往比主句显得更重要。
BecauseTom was ill, he didn’t come to school.
---Why didn’t you give Dick a call
---Because I will see him soon.
※易错点:because 与 so不能连用。
Because my mother was ill, so I didn’t go to your party. 本句错误!!
I didn’t go to your party because my mother was ill.
My mother was ill, so I didn’t go to your party.
1.2.1 because 引导的原因状语从句
1.2.2 since 引导的原因状语从句
Since表示人们已经知道的事实,不需要强调的原因,常意为“既然……”。通常放在句首。Since引导的从句是次要的,重点强调主句内容。
Since you are free tonight, why not drop in and play chess with me
Since everyone is here, let’s get started.
as 表示的原因只是对结果的附加说明,位于句首、句尾均可。
She didn’t hear us come in as she was asleep.
As you weren’t here, I left a message.
for是并列连词,可用来作附加说明,为前面的事实提供一种推断的理由,for引导的从句一般位于主句之后。
Eg:It rained last night, for the groud is wet.
We should be more careful, for it is already dark.
1.2.3 as/for引导的原因状语从句
2.1 条件状语从句
概念:在句子中作条件状语的从句称为条件状语从句。
引导词:if(如果),unless(除非,如果不),as long as(只要)等。
As long as you can keep on, you will do it.
You can’t go out unless you promise me to come back early.
If it is sunny tomorrow, we will have a picnic.
出题点:
1,if 引导条件状从和宾从的用法区别。
2,unless, as long as 引导的条件状从的用法。
3,条件状从的时态。
2. 条件&让步状语从句
2.1.1 if 引导的条件状语从句
If 意为“如果”,表示假设的情况可能发生。其主句不能用be going to 表示将来,而应该用shall或will。
If it rains tomorrow, I will stay at home.
I will stay at home if it rains tomorrow.
1,主句前后都可以,句前逗号别忘记。
2,时态:主将从现;主祈从现;主情从现。
Please call me if he comes next Sunday.
I can do it myself if I get the permission.
1,句子成分分析法:if引导的宾从位于及物动词之后,而 if引导的条件状从只能作状语,主句的结构已经完整。
Do you know if we will go to the zoo tomorrow
I will play basketball if it doesn’t rain tomorrow.
技能提升:宾语从句中的 if 和条件状语从句中 if 的区别技巧
2,时态分析法:if引导的宾从符合宾从时态:主现从不限、主过从必过、客观真理一般现。If 引导的条件状从符合“主将从现、主祈从现、主情从现”。
Do you know if we will go to the zoo tomorrow
I will play basketball if it doesn’t rain tomorrow.
Unless 意为“除非、如果不”,表示否定的含义,故其引导的从句只能是肯定形式。
Unless 在意思上相当于“if...not...”,但语气更强。
Unless 引导的条件状从也符合“主将从现、主祈从现、主情从现”原则。
We will climb the mountain tomorrow unless it rains.
= We will climb the mountain tomorrow if it doesn’t rain.
Unless you hurry up, you will be late. 主将从现
※易错点:unless引导的条件状从翻译成“除非...,否则....”时, unless 不可以和 or 连用。
Unless you hurry up, you will be late.
除非你快点,(否则) 你就会迟到。
2.1.2 unless 引导的条件状语从句
2.1.3 as long as 引导的条件状语从句
as long as 意为“只要”,符合“主将从现”的原则。
As long as you don’t give up, you will succeed.
as long as / so long as
on condition that 只要
as / so far as … “就…而论(而言)”
in case 万一
suppose/ supposing …
provided / providing that … 假定/假使
概念:表示尽管某种不利于主句动作发生的条件存在,主句中的情况依
然会出现。
引导词:though/although(尽管);even if/even though (即使)。
出题点:
1,though/ although/as的用法。
2,even if/ even though的用法。
3,no matter+疑问词 或 疑问词-ever的用法。
2.2 让步状语从句
2.2.1 although/ though/as 引导的让步状语从句
1. although 和 though 两者意思相同,意为“虽然,尽管”,一般可以互换。
注意:两个词都绝对不可以和 but 连用,但是可以和 yet 或 still 连用。
Although/ Though he worked hard, failed.
= He worked hard, but he failed.
Although/ Though it was rainning hard, yet they went on playing football.
2. 在although, though,as 引导的特殊让步状语从句中,as较常见。
这种让步状语从句的特点是:形容词、副词、名词(单数可数名词前不用不定冠词)、行为动词(带状语或宾语)置于句首,构成部分倒装。
注意:Though可接可不接;Although不接倒装语序。
2.2.2 even if/ even though 引导的让步状语从句
even if 和 even though均可引导让步状从,意为“即使”。两者的用法有细微区别,但通常可互换使用。
even if 引导的让步状从往往是假设性的,而even though引导的往往是真的。
Even if it rains tomorrow, we won’t change our plan.
Even though it’s hard work, I enjoy it.
2.2.3 疑问词-ever/no matter疑问词引导的让步状语从句
“疑问词-ever”可用作表示具有强烈意义的疑问词引导让步状从,此时可换成“no matter 疑问词”。
Whenever I am unhappy, it is my friend who cheers me up.
= No matter when I am unhappy, it is my friend who cheers me up.
I will wait for you however late it is.
=I will wait for you no matter how late it is.
注意: 疑问词-ever还可引导名词性从句,此时不能和no matter疑问词互换。
3.1 目的状语从句
概念:在句子中作目的状语的从句称为“目的状语从句”,常译为“为了能够……”。
引导目的状语从句的连词有:so that 和 in order that等;从句的谓语常含有“may, might, can, could, will, would”等情态动词。
so that 引导的从句只能放在主句之后,而 in order that 引导的从句既可以放在主句前,也可放在主句后。
They worked hard in order that/ so that they might succeed.
=In order that they might succeed, they worked hard .
He spoke loudly so that/ in order that others could hear him clearly.
=In order that others could hear him clearly, he spoke loudly
3. 结果&目的状语从句
※易错点---目的状语从句与不定式、介词短语的互换:
当从句主语和主句主语一致时,可用 so as to, in order to 替换目的状语从句。
He studied every day in order that he could succeed.
=He studied every day in order to succeed.
We will sit in the front of the hall so that we can hear better.
=We will sit in the front of the hall so as to hear better.
3.2 结果状语从句
概念:在句子中作结果状语的从句称为结果状语从句,一般
置于句尾。 引导结果状语从句的连词有:so(因此),“so...that...(如此...以至于...)、such...that...(如此...以至于...)、so that(因此)等。
Kathy is so lovely that we all like to play with her.
His plan was such a good one that we all agreed to accept it.
在“so...that...”结构中,so是副词,修饰形容词或副词。引导结果状语从句时常用语以下结构:
1, so+形容词/副词+that+从句.
2, so+形容词+a(n)+可数名词单数+that + 从句
3, so+many/few+(可数名词复数)+that+从句
4, so+much/little+(不可数名词)+that+从句
在“such...that...”结构中,such是形容词,修饰名词或名词短语。引导结果状语从句时常用语以下结构:
1, such+a(n)+形容词+可数名词单数+that+从句
2, such+形容词+可数名词复数+that + 从句
3, such+形容词+不可数名词+that+从句
3.2.1 so...that.../ such...that...结果状语从句
相同点:两者均可以用来引导结果状从。
不同点:such 和 so 之后修饰的词性不同:such是名词,so 是形容词或副词。
1,
Kathy is so loely that we all like to play with her.
形容词
It’s so interesting a film that we all want to see it.
形容词+a/an+可名单
He made so many mistakes that he failed the exam.
many+可名复
The little boy has so little difficulty in working out this problem
little+不可名
that I admire him very much.
so...that...引导结果状从的用法
1,
‘s
He is so young that he can’t go to school. =
He is too young to go to school. =
He is not old enough to go to school.
so...that...与 too...to...的转换
so...that...结构的否定形式可用 too...to... 或not...enough to...结构 代替。
His plan was such a good one that we all agreed to accept it.
a(an) +形容词+可名单
They’re such kindhearted teachers that we all respect them.
形容词+可名复
We had such terrible weather that we couldn’t finish the work on time. 形容词+不可名
such...that...引导结果状从的用法
1,
重点提醒:
在“so/such...that...”结构中,“so/such...”部分位于句首时,主句用 部分倒装 语序。
Eg: So excited was he that he could not fall into sleep.
(2) 有时“such+a(n)+形容词+可名单+that+从句”结构可与“so+形容词+a(n)+可名单+that + 从句”结构互换。
Eg: Mr. James is such a humorous teacher that we all like him. =
Mr. James is so humorous a teacher that we all like him.
总结:so+形容词+a(an)+可名单= such +a(an)+形容词+可名单
3.2.2 so that 引导的结果状语从句
so that 引导结果状语从句时意为“以致,以至于,因此”,从句前有时用逗号与主句分开。
He worked hard at school, so that he gained high grades in the exam.
*如何区分“so that”引导的是“目的状从”还是“结果状从呢?
so that 引导的“目的状从”中都含有“can、could”等情态动词,而 “结果状从”则没有
1. Kate got up early so that she could catch the first bus.
2. They missed the bus so that they were late for class.
4. 方式&比较状语从句
4.1 方式状语从句
概念:方式状语从句就是描述动作进行方式的状语从句,常用“和...一样”、“像/仿佛...”以及“按照...的方法”等来表达。
常见的引导词有:as, (just) as…so…, as if, as though引导。
as引导的方式状语从句通常位于主句后,但在(just) as…so…结构中位于句首,这时as从句带有比喻的含义,意思是"正如…","就像",多用于正式文体,例如:
Eg: Always do to the others as you would be done by.
As water is to fish, so air is to man.
Just as we sweep our rooms, so we should sweep backward ideas from our minds.
4.1.1 as, (just) as…so… 引导的方式状语从句
两者的意义和用法相同,引出的状语从句谓语多用虚拟语气,表示与事实相反,有时也用陈述语气,表示所说情况是事实或实现的可能性较大。汉译常作"仿佛……似的","好像……似的",例如:
They completely ignore these facts as if (as though) they never existed.
他们完全忽略了这些事实,就仿佛它不存在似的。(与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气。)
He looks as if (as though) he had been hit by lighting. 他那样子就像被雷击了似的。(与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气。)
It looks as if the weather may pick up very soon. 看来天气很快就会好起来。(实现的可能性较大,谓语用陈述语气。)
4.1.2 as if, as though 引导的方式状语从句
4.2 比较状语从句
概念:比较状语从句就是表示比较的状语从句。
常见的引导词有:as和than。
常见的句型有:
as...as...;
not so(/as)...as...;
more...than;
no more...than...;
the more...the more...
1. as + ...形容词/副词... + as + 从句
He knows as much as I do.
You can have as many dreams as you want.
2. not so(/as) + ...形容词/副词... + as + 从句
She doesn't work so hard as you do.
The task is not as easy as we thought.
3. ...形容词比较级/副词比较级... + than + 从句
The situation was more complicated than it sounded on the phone.
You look much better than you did weeks ago.
4. no + 形容词比较级/副词比较级...+ than + 从句
There is no prettier girl than Helen is. 没有比海伦更漂亮的女孩了。
5. the 形容词比较级/副词比较级 + 从句... the 形容词比较级/副词比较级+ 从句
The warmer it gets, the faster the ice melts.
天气越暖和,冰融化得越快。
补充:英语中倍数的表达
1. 倍数+as+形容词或副词的原级+as+其它。
这种结构又常演变成下列两类:
①倍数+as+many+可数名词复数+as;
②倍数+as+much+不可数名词+as。如:
e.g. There are seven times as many people as I expected.是我预料的人数的七倍。
2. 倍数+形容词(或副词)的比较级+ than+其它。
e.g. The hall is five times bigger than our classroom.这个大厅的面积比我们教室大五倍。
3. 倍数+the+名词(size,height,weight,length,width等)+of+其它。
e.g. The earth is 49 times the size of the moon.地球的体积是月球的49倍。
4. 倍数+what从句。
e.g. The production is now three times what it was ten years ago.现在的产量是十年前的三倍。
where在地点状语从句中,除了指地点外,还可指处境等。
* 由where引导的地点状语从句与定语从句的区别:
5. 地点状语从句
You’d better make a mark where you have some questions.
You’d better make a mark at the place where you have some questions.
1. 句子结构不同
where引导定语从句时,从句前应有一个表示(抽象)地点或处所的名词作先行词,而状语从句前没有先行词。
2. where的作用不同
where引导定语从句时,指代地点名词,在定语从句中做状语。
where引导状语从句时,修饰的是主句的谓语。
状语从句的倒装问题
1、So difficult _____ it to live in an English-speaking country
that I determined to learn English.
A. I have felt B. have I felt C. I did feel D. did I feel
2、Not until all the fish died in the river _____ how serious the
pollution was.
A. did the villagers realize B. the villagers realized
C. the villagers did realize D. didn’t the villagers realize
状语从句的倒装一般有下面几种情况:① 否定词开头;
② so 加 adj. 开头;③ as / though引导的让步状语从句。
D
A
特别注意:
Hardly … when …
No sooner … than …
Child as he is, …
Hardly had he got to the station when the train left.
No sooner had he got to the station than the train left.
Child as he is, he can speak seven foreign languages.
真 题 演 练
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
THANK YOU !
