中考英语二轮语法专题复习---动词 课件(共67张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 中考英语二轮语法专题复习---动词 课件(共67张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 430.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津深圳版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-05-26 20:26:59 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共67张PPT)
专题六 动词
表示动作和状态的词叫做动词。根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为四类:实义动词(Notional Verb)、连系动词(Link Verb)、助动词(Auxiliary Verb)、情态动词(Modal Verb);还可以根据其后是否带有宾语分为两类:及物动词(Transitive Verb)和不及物动词(Intransitive Verb)。
考点①
连系动词
用法 例子
① be动词 He is a teacher. 他是一名教师。
② 四变:become(be) 变成,turn变色,get变温,go变质 be(become) happy, turn red,
get cool/warm/hot/dark,
go bad(变质)
连系动词把主语和说明主语性质、状态或身份等的词语(作表语的形容词或名词)联系起来,并和这些词语一起构成谓语。
用法 例子
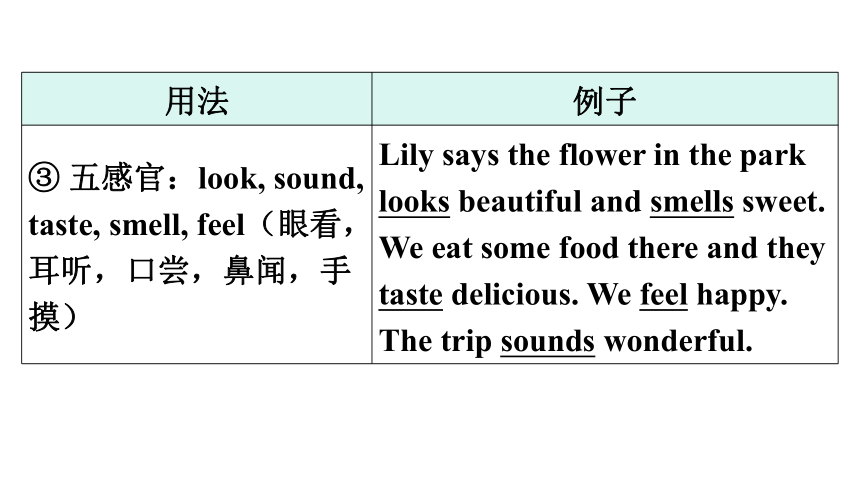
③ 五感官:look, sound, taste, smell, feel(眼看,耳听,口尝,鼻闻,手摸) Lily says the flower in the park looks beautiful and smells sweet. We eat some food there and they taste delicious. We feel happy. The trip sounds wonderful.
( ) The children all looked _____ at the broken model plane and felt quite _____ .
A. sad, sad B. sadly, sadly C. sad, sadly D. sadly, sad
注意区分
D
look只有翻译为“看起来”时才是系动词,后加形容词;
翻译成“看”是实义动词,后面用副词修饰。
用法 例子
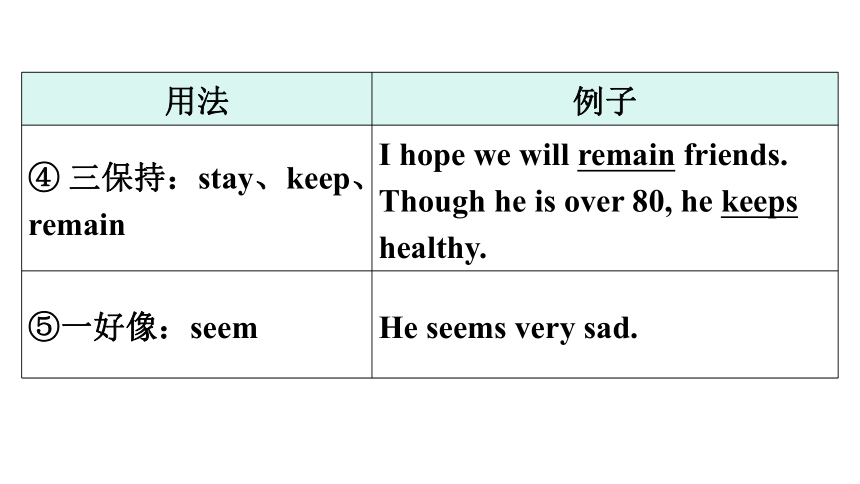
④ 三保持:stay、keep、remain I hope we will remain friends.
Though he is over 80, he keeps healthy.
⑤一好像:seem He seems very sad.
Seem的用法
①seem to do sth
Some people seem to do it as a hobby.
②It seems that……
It seems that no one knows what happens in the park.
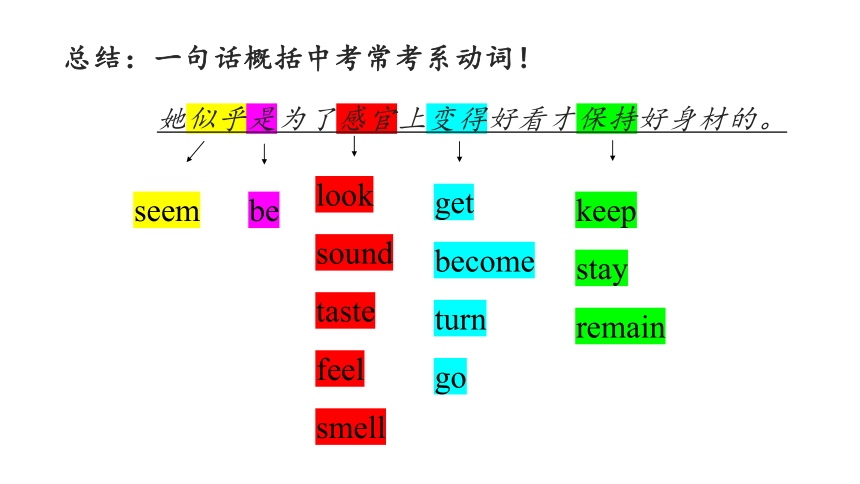
总结:一句话概括中考常考系动词!
她似乎是为了感官上变得好看才保持好身材的。
seem
be
look
sound
taste
feel
smell
get
become
turn
go
keep
stay
remain
( ) 1. —Look at the dark clouds, and the wind is blowing strongly.
—It that a big storm is coming.
A. sounds B. smells C. feels D. seems
对 点 专 练
D
( ) 2. The dish smells delicious, but it a little salty.
A. looks B. tastes C. feels D. sounds
B
( ) 3. —Good morning. I’d like a birthday gift for my mother.
—What about this scarf(围巾) It is beautiful and it soft and smooth.
A. feels B. looks C. seems D. becomes
对 点 专 练
A
( ) 4. —Three-D painting technology could be used to build a house in less than 24 hours.
—It amazing. It’s my first time that I have got to know the news.
A. looks B. smells C. sounds D. feels
C
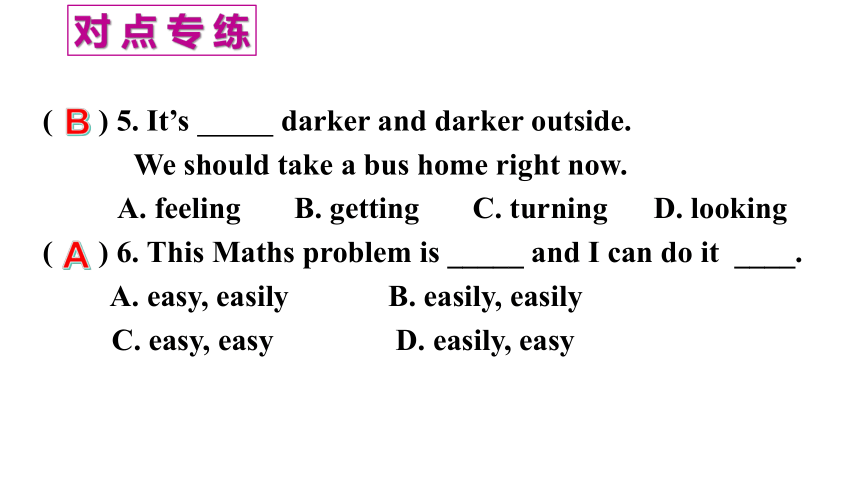
( ) 5. It’s darker and darker outside.
We should take a bus home right now.
A. feeling B. getting C. turning D. looking
( ) 6. This Maths problem is _____ and I can do it ____.
A. easy, easily B. easily, easily
C. easy, easy D. easily, easy
对 点 专 练
B
A
考点②
情态动词
情态动词本身有一定的词义,但不能单独作谓语,要与动词原形一起构成谓语。情态动词后要使用动词原形,没有人称和数的变化(have to 和be able to除外)。
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
can could 能;会;可以 I could swim at the age of seven.(肯定)
→I couldn’t swim at the age of seven.(否定)
→Could you swim at the age of seven (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
may might 可以;可能 You may take a walk after supper.(肯定)
→You may not take a walk after supper.(否定)
→May I take a walk after supper (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
must 必须;一定 We must arrive home before 10:00.(肯定)
→We needn’t (don’t have to) arrive home before 10:00.(否定)
→Must you arrive home before 10:00 (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
have/has to had to 不得不 Tom had to go home on foot last night.(肯定)
→Tom didn’t have to go home on foot last night.(否定)
→Did Tom have to go home on foot last night (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
should/ ought to 应该 We should/ought to keep the air fresh. (肯定)
→We shouldn’t/ought not (to) keep the air fresh.(否定)
→Should/Ought we (to) keep the air fresh (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
need 需要 注意:need作情态动词使用时,只用于否定句和疑问句中。
→You needn’t close all the windows.(否定)
→Need I close all the windows
(一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
had better 最好 You had better stay at home.
(肯定)
→You had better not stay at home.(否定)
Had I better stay at home
(一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
注意:情态动词在一般疑问句中的回答。
① —May I smoke here 我可以在这里抽烟吗?
—Yes, you may/can. 是的,你可以。/
—No, you mustn’t/can’t. 不,你不可以。
② —Can you come to see me tomorrow
你明天能来看我吗?
—Yes, I can. 是的,我可以。/
—No, I can’t. 不,我不能。
1
情态动词一览表
③ —Must he go now 他一定要现在走吗?
—Yes, he must. 是的,他必须走。/
—No, he needn’t (doesn’t have to). 不,他不需要。
④ —Need I finish my homework today
我需要今天完成作业吗?
—Yes, you must. 是的,你必须。/
—No, you needn’t (don’t have to). 不,你不需要。
2
情态动词的常见用法
情态动词 用法 例子
can/could 表示“能;会” 表示能力 I can speak English well.
我能说一口流利的英语。
2
情态动词的常见用法
情态动词 用法 例子
can, may表示“可以”,在疑问句中表示有礼貌地提出请求 表示请求和允许 —May I close the window
我能关窗吗?
—Yes, you can. 是的,你可以。
—Can I come in
我能进来吗?
—No,you can’t. 不,你不能。
2
情态动词的常见用法
情态动词 用法 例子
can’t 表示“不能” 表示不允许 We can’t speak loudly in public.
我们不能在公共场合大声说话。
You mustn’t break the rules.
你不能违反规则。
mustn’t 表示“禁止”,态度比can’t强硬
3
情态动词的特殊用法
情态动词 用法 例子
be able to 与can一样都可表示能力(can为现在时,could为过去时),但可用于各种时态,有人称和数的变化 She is able to/can sing English songs well.
她能把英语歌唱得很好。
He will be able to finish the work in an hour.
他将能在一小时内完成工作。
3
情态动词的特殊用法
情态动词 用法 例子
have/has to 客观条件,用have/has to; 主观因素,用must (have/has to 可用于多种时态) She had to look after her little sister when her mother was out.
当妈妈外出时,她不得不照看妹妹。
As a student, you must study hard.
作为一名学生,你必须好好学习。
3
情态动词的特殊用法
情态动词 用法 例子
will/would/ shall 表示请求或劝说 Shall we begin now
我们现在就开始好吗?
Will you go there with me
你愿意和我一起去那儿吗?
对 点 专 练
( ) 1. You walk too close to the edge 边缘 of the path because you might fall and hurt yourself.
A. mustn’t B. needn’t C. may not D. might not
A
( ) 2. —Why not stay a little longer
—I’d love to, but it’s getting late. I really go now, for my daughter is home alone.
A. can B. can’t C. must D. mustn’t
C
( ) 3. —Could I borrow your dictionary
—Yes, of course, you .
A. might B. will C. can D. could
对 点 专 练
( ) 4. —Where is Mom now
—I’m not sure. She be in the kitchen.
A. shall B. may C. need D. must
C
B
( ) 5. The designer has tried every possible way to make the robot light, so you worry about its weight.
A. must B. may C. can’t D. needn’t
对 点 专 练
D
考点③
助动词
1
助动词的语法特征(be, have, has, had, do, does, did, shall, will)
(1)一般没有词义;
(2)不能单独作谓语,与其他动词一起构成谓语,使用
不同的时态或语态,或使用疑问、否定句式;
(3)有人称、数和时态的变化。
2
常见助动词的用法
助动词 用法 例子
do(does) did 构成一般现在时和一般过去时的否定句或疑问句 You don’t like eatingdumplings.
你不喜欢吃饺子。
Did you watch the volleyball match last night
你昨晚看排球比赛了吗?
2
常见助动词的用法
助动词 用法 例子
do(does) did 构成祈使句的否定 Don’t be late again!
不要再迟到!
用于so, neither, nor引导的倒装句 They don’t know the exact time to set off. Neither do I.
他们不知道出发的准确时间, 我也不知道。
2
常见助动词的用法
助动词 用法 例子
have (has) had “have(has)+过去分词”构成现在完成时 He has been to Hong Kong twice.
他到过香港两次。
“had+过去分词”构成过去完成时 He had already finished his homework when his father came back.
当他爸爸回来的时候,他已经完成作业了。
对 点 专 练
( ) 1. —Nobody believes Tom has read 100 books so far.
—But in fact, he . You can see the news on the school website.
A. does B. has C. is D. will
B
( ) 2. My computer work. There may be something
wrong with it, but I’m not sure.
A. doesn’t B. won’t C. isn’t D. hasn’t
A
( ) 3. Mary enjoys playing the piano. So I.
A. am B. did C. do D. will
对 点 专 练
C
( ) 4. —Ann, why you like eating bitter gourd(苦瓜)
—Because I don’t like eating bitter food.
A. is B. are C. do D. don’t
D
考点④
实义动词
实义动词又称行为动词,是表示行为、动作或者状态 的词。它的词性完整,可以单独做谓语,有人称、数和时态的相应变化。
基本形式 构成规则 例子
动词原形 (do) 动词的原始形式 study, be, like, catch, depend
基本形式 构成规则 例子
第三人称单数 (does) ①以s, x, ch, sh, o结尾的+es pass—passes,
teach—teaches, go—goes
②以辅音字母加y结尾的要变y为i,再+es carry—carries,
cry—cries, fly—flies,
try—tries
③其他情况:在词尾+s read—reads, take—takes, put—puts
1
行为动词的三单构成
基本形式 构成规则 例子
现在分词(doing) ①以不发音的e结尾,去e再+ing write—writing,
have—having,
make—making
②重读闭音节,双写结尾字母再+ing swim—swimming,
run—running,
get—getting
2
行为动词的现在分词构成
基本形式 构成规则 例子
现在分词 (doing) ③以ie结尾,改ie为y,再+ing die—dying, lie—lying, tie—tying
④其他情况:在词尾+ing read—reading,
catch—catching,
do—doing
2
行为动词的现在分词构成
基本形式 构成规则 例子
过去式与 过去分词 (done) ①一般情况:在词尾+ed work—worked,
pass—passed,
depend—depended
②以e结尾,直接+d live—lived,
hope—hoped,
decide—decided
3
行为动词的过去式/过去分词构成
基本形式 构成规则 例子
过去式与 过去分词 (done) ③以辅音字母加y结尾的要变y为i,再+ed study—studied,
worry—worried,
hurry—hurried
④重读闭音节,双写结尾字母再+ed stop—stopped,
shop—shopped,
plan—planned
3
行为动词的过去式/过去分词构成
对 点 专 练
写出下列动词的相应形式。
动词原形 第三人称单数 现在分词 过去式 过去分词
be
do
stop
pass
is being was/were been
does doing did done
stops stopping stopped stopped
passes passing passed passed
对 点 专 练
写出下列动词的相应形式。
动词原形 第三人称单数 现在分词 过去式 过去分词
carry
make
die
teach
put
carries carrying carried carried
makes making made made
dies dying died died
teaches teaching taught taught
puts putting put put
考点⑤
常考的动词
短语归纳
come come back 回来
come out 出来
come from 来自
get get up 起床
get ready for 为……作好准备,
get on (well) with 与……相处(融洽)
get back 返回
get on/off 上/下车
get to 到达
give give up 放弃 give back 归还;后退,
give away 捐赠 give out 分发
give birth to 生育
look look up 查阅 look after 照看;照顾
look for 寻找 look like 看起来像……
look out 当心;小心
look around 朝四周看
look forward to 期望
put put on 穿上(衣服);上演(戏剧)
put up 建造;举起;张贴
put into 把……放进
put out 扑灭
set set up 建立
set off 出发;动身
set out 出发
take take out 提取
take place 发生
take up 开始做
take a trip 去旅行
take care of 关心;照顾
take off 脱下(衣、帽、鞋等);拿掉;(飞机)起飞
take part in 参加
对 点 专 练
1. 青少年应该学习如何照顾自己。
Teenagers should learn how to 1
themselves.
2. 很高兴收到你的来信。
It’s great to you.
3. 正如习近平所说,人类应当友好对待世界不同的文化。
As Xi Jinping said, humans should 1
different cultures of the world.
take care of
hear from
be friendly to
对 点 专 练
4. 好运总是属于有准备的人。
Good luck always somebody that has
prepared well.
5. 弗兰克想出了这个好主意。
Frank this good idea.
belongs to
came up with
语 法 巩 固
1. Nancy often goes____________ (swim) with her friends in summer
2. I want ____________ (go) to the shop.
3. The little girl likes _________________ (play) basketball. She____________ (play) on the playground now.
4. The teacher _____________ (go) to school on foot every day.
5. Let's ___________ (speak) English.
swimming
to go
教材P29 二
playing/ to play
is playing
goes
speak
语 法 巩 固
( ) 1. Dirty air and water are harmful. They kill plants, and even people.
A. can B. can’t C. should D. shouldn’t
A
( ) 2. —Must we wear the school uniforms tomorrow, Mr. Wang
—No, you . Only on Mondays. Tomorrow is Tuesday.
A. shouldn’t B. needn’t C. can’t D. mustn’t
B
语 法 巩 固
( ) 3. Don’t the waste paper and bottles. They can be recycled.
A. throw away B. take out C. get away D. put out
A
( ) 4. —I don’t know how to the old books.
—Why not give them away to poor children
A. hand out B. give up C. deal with D. take up
C
语 法 巩 固
( ) 5. —Have you chemistry for the coming exam
—Yes. I’m quite ready for it.
A. repeated B. copied C. marked D. reviewed
D
( )6. —Whose cap is this Is it Cindy’s
—It be hers. Don’t you remember she even didn’t come to the party
A. can’t B. might C. may not D. must
A
( ) 7. —The driver be hurt badly in the accident.
—That’s true. Let’s send him to the hospital as soon as possible.
A. need B. can’t C. must D. may not
语 法 巩 固
C
( )8. All members decided to the money from the book sale to homeless people.
A. give up B. give away C. take up D. take away
B
( ) 9. —The summer vacation is coming. Have you made a plan for it
—Not yet. I go to Guilin.
A. may B. can C. should D. must
语 法 巩 固
A
( )10. —Why were you shouting at Tom
—I told him to be quiet, but he talking.
A. joined in B. ended up C. kept on D. put off
C
单 词 拼 写
1. He fell off the bike yesterday, but luckily, he didn’t
h himself.
2. It is difficult for most of the students to s this
physics problem.
3. After watching the video, the thief had to a his
crime(罪行) of stealing the money.
urt
olve
dmit
单 词 拼 写
4. The two dresses are so beautiful. She can’t d which
one to buy.
5. I need another 3 days to f writing the article. I’ve
only done half of it.
6. They have to c the sports meeting because of the
bad weather.
ecide
inish
ancel
完 成 句 子
1. 王俊凯擅长唱歌和打篮球。
Wang Junkai singing and playing
basketball.
2. 正如专家所说:“学习效能的好坏取决于你的学习习
惯。”
As the experts said, “Whether or not you can study well
your learning habits.”
is good at
depends on
完 成 句 子
3. 知识源于质疑。
Knowledge questioning.
4. 我能通过查字典找到生词的意思。
I can find the meaning of the new words by them
in a dictionary.
5. 离开房间之前,请将你的电脑关闭。
Please your computer before leaving the
room.
comes from
looking
up
turn off
完 成 句 子
6. 现在人们可以通过微信与他们的朋友保持联系。
People can their friends
by WeChat now.
7. 成功的关键在于从错误中学习,并且永不放弃。
The key to success is to learn from your mistakes and
never .
keep in touch with
give up
专题六 动词
表示动作和状态的词叫做动词。根据其在句中的功能,动词可分为四类:实义动词(Notional Verb)、连系动词(Link Verb)、助动词(Auxiliary Verb)、情态动词(Modal Verb);还可以根据其后是否带有宾语分为两类:及物动词(Transitive Verb)和不及物动词(Intransitive Verb)。
考点①
连系动词
用法 例子
① be动词 He is a teacher. 他是一名教师。
② 四变:become(be) 变成,turn变色,get变温,go变质 be(become) happy, turn red,
get cool/warm/hot/dark,
go bad(变质)
连系动词把主语和说明主语性质、状态或身份等的词语(作表语的形容词或名词)联系起来,并和这些词语一起构成谓语。
用法 例子
③ 五感官:look, sound, taste, smell, feel(眼看,耳听,口尝,鼻闻,手摸) Lily says the flower in the park looks beautiful and smells sweet. We eat some food there and they taste delicious. We feel happy. The trip sounds wonderful.
( ) The children all looked _____ at the broken model plane and felt quite _____ .
A. sad, sad B. sadly, sadly C. sad, sadly D. sadly, sad
注意区分
D
look只有翻译为“看起来”时才是系动词,后加形容词;
翻译成“看”是实义动词,后面用副词修饰。
用法 例子
④ 三保持:stay、keep、remain I hope we will remain friends.
Though he is over 80, he keeps healthy.
⑤一好像:seem He seems very sad.
Seem的用法
①seem to do sth
Some people seem to do it as a hobby.
②It seems that……
It seems that no one knows what happens in the park.
总结:一句话概括中考常考系动词!
她似乎是为了感官上变得好看才保持好身材的。
seem
be
look
sound
taste
feel
smell
get
become
turn
go
keep
stay
remain
( ) 1. —Look at the dark clouds, and the wind is blowing strongly.
—It that a big storm is coming.
A. sounds B. smells C. feels D. seems
对 点 专 练
D
( ) 2. The dish smells delicious, but it a little salty.
A. looks B. tastes C. feels D. sounds
B
( ) 3. —Good morning. I’d like a birthday gift for my mother.
—What about this scarf(围巾) It is beautiful and it soft and smooth.
A. feels B. looks C. seems D. becomes
对 点 专 练
A
( ) 4. —Three-D painting technology could be used to build a house in less than 24 hours.
—It amazing. It’s my first time that I have got to know the news.
A. looks B. smells C. sounds D. feels
C
( ) 5. It’s darker and darker outside.
We should take a bus home right now.
A. feeling B. getting C. turning D. looking
( ) 6. This Maths problem is _____ and I can do it ____.
A. easy, easily B. easily, easily
C. easy, easy D. easily, easy
对 点 专 练
B
A
考点②
情态动词
情态动词本身有一定的词义,但不能单独作谓语,要与动词原形一起构成谓语。情态动词后要使用动词原形,没有人称和数的变化(have to 和be able to除外)。
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
can could 能;会;可以 I could swim at the age of seven.(肯定)
→I couldn’t swim at the age of seven.(否定)
→Could you swim at the age of seven (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
may might 可以;可能 You may take a walk after supper.(肯定)
→You may not take a walk after supper.(否定)
→May I take a walk after supper (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
must 必须;一定 We must arrive home before 10:00.(肯定)
→We needn’t (don’t have to) arrive home before 10:00.(否定)
→Must you arrive home before 10:00 (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
have/has to had to 不得不 Tom had to go home on foot last night.(肯定)
→Tom didn’t have to go home on foot last night.(否定)
→Did Tom have to go home on foot last night (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
should/ ought to 应该 We should/ought to keep the air fresh. (肯定)
→We shouldn’t/ought not (to) keep the air fresh.(否定)
→Should/Ought we (to) keep the air fresh (一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
need 需要 注意:need作情态动词使用时,只用于否定句和疑问句中。
→You needn’t close all the windows.(否定)
→Need I close all the windows
(一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
情态动词 过去式 词义 句型变化
had better 最好 You had better stay at home.
(肯定)
→You had better not stay at home.(否定)
Had I better stay at home
(一般疑问)
1
情态动词一览表
注意:情态动词在一般疑问句中的回答。
① —May I smoke here 我可以在这里抽烟吗?
—Yes, you may/can. 是的,你可以。/
—No, you mustn’t/can’t. 不,你不可以。
② —Can you come to see me tomorrow
你明天能来看我吗?
—Yes, I can. 是的,我可以。/
—No, I can’t. 不,我不能。
1
情态动词一览表
③ —Must he go now 他一定要现在走吗?
—Yes, he must. 是的,他必须走。/
—No, he needn’t (doesn’t have to). 不,他不需要。
④ —Need I finish my homework today
我需要今天完成作业吗?
—Yes, you must. 是的,你必须。/
—No, you needn’t (don’t have to). 不,你不需要。
2
情态动词的常见用法
情态动词 用法 例子
can/could 表示“能;会” 表示能力 I can speak English well.
我能说一口流利的英语。
2
情态动词的常见用法
情态动词 用法 例子
can, may表示“可以”,在疑问句中表示有礼貌地提出请求 表示请求和允许 —May I close the window
我能关窗吗?
—Yes, you can. 是的,你可以。
—Can I come in
我能进来吗?
—No,you can’t. 不,你不能。
2
情态动词的常见用法
情态动词 用法 例子
can’t 表示“不能” 表示不允许 We can’t speak loudly in public.
我们不能在公共场合大声说话。
You mustn’t break the rules.
你不能违反规则。
mustn’t 表示“禁止”,态度比can’t强硬
3
情态动词的特殊用法
情态动词 用法 例子
be able to 与can一样都可表示能力(can为现在时,could为过去时),但可用于各种时态,有人称和数的变化 She is able to/can sing English songs well.
她能把英语歌唱得很好。
He will be able to finish the work in an hour.
他将能在一小时内完成工作。
3
情态动词的特殊用法
情态动词 用法 例子
have/has to 客观条件,用have/has to; 主观因素,用must (have/has to 可用于多种时态) She had to look after her little sister when her mother was out.
当妈妈外出时,她不得不照看妹妹。
As a student, you must study hard.
作为一名学生,你必须好好学习。
3
情态动词的特殊用法
情态动词 用法 例子
will/would/ shall 表示请求或劝说 Shall we begin now
我们现在就开始好吗?
Will you go there with me
你愿意和我一起去那儿吗?
对 点 专 练
( ) 1. You walk too close to the edge 边缘 of the path because you might fall and hurt yourself.
A. mustn’t B. needn’t C. may not D. might not
A
( ) 2. —Why not stay a little longer
—I’d love to, but it’s getting late. I really go now, for my daughter is home alone.
A. can B. can’t C. must D. mustn’t
C
( ) 3. —Could I borrow your dictionary
—Yes, of course, you .
A. might B. will C. can D. could
对 点 专 练
( ) 4. —Where is Mom now
—I’m not sure. She be in the kitchen.
A. shall B. may C. need D. must
C
B
( ) 5. The designer has tried every possible way to make the robot light, so you worry about its weight.
A. must B. may C. can’t D. needn’t
对 点 专 练
D
考点③
助动词
1
助动词的语法特征(be, have, has, had, do, does, did, shall, will)
(1)一般没有词义;
(2)不能单独作谓语,与其他动词一起构成谓语,使用
不同的时态或语态,或使用疑问、否定句式;
(3)有人称、数和时态的变化。
2
常见助动词的用法
助动词 用法 例子
do(does) did 构成一般现在时和一般过去时的否定句或疑问句 You don’t like eatingdumplings.
你不喜欢吃饺子。
Did you watch the volleyball match last night
你昨晚看排球比赛了吗?
2
常见助动词的用法
助动词 用法 例子
do(does) did 构成祈使句的否定 Don’t be late again!
不要再迟到!
用于so, neither, nor引导的倒装句 They don’t know the exact time to set off. Neither do I.
他们不知道出发的准确时间, 我也不知道。
2
常见助动词的用法
助动词 用法 例子
have (has) had “have(has)+过去分词”构成现在完成时 He has been to Hong Kong twice.
他到过香港两次。
“had+过去分词”构成过去完成时 He had already finished his homework when his father came back.
当他爸爸回来的时候,他已经完成作业了。
对 点 专 练
( ) 1. —Nobody believes Tom has read 100 books so far.
—But in fact, he . You can see the news on the school website.
A. does B. has C. is D. will
B
( ) 2. My computer work. There may be something
wrong with it, but I’m not sure.
A. doesn’t B. won’t C. isn’t D. hasn’t
A
( ) 3. Mary enjoys playing the piano. So I.
A. am B. did C. do D. will
对 点 专 练
C
( ) 4. —Ann, why you like eating bitter gourd(苦瓜)
—Because I don’t like eating bitter food.
A. is B. are C. do D. don’t
D
考点④
实义动词
实义动词又称行为动词,是表示行为、动作或者状态 的词。它的词性完整,可以单独做谓语,有人称、数和时态的相应变化。
基本形式 构成规则 例子
动词原形 (do) 动词的原始形式 study, be, like, catch, depend
基本形式 构成规则 例子
第三人称单数 (does) ①以s, x, ch, sh, o结尾的+es pass—passes,
teach—teaches, go—goes
②以辅音字母加y结尾的要变y为i,再+es carry—carries,
cry—cries, fly—flies,
try—tries
③其他情况:在词尾+s read—reads, take—takes, put—puts
1
行为动词的三单构成
基本形式 构成规则 例子
现在分词(doing) ①以不发音的e结尾,去e再+ing write—writing,
have—having,
make—making
②重读闭音节,双写结尾字母再+ing swim—swimming,
run—running,
get—getting
2
行为动词的现在分词构成
基本形式 构成规则 例子
现在分词 (doing) ③以ie结尾,改ie为y,再+ing die—dying, lie—lying, tie—tying
④其他情况:在词尾+ing read—reading,
catch—catching,
do—doing
2
行为动词的现在分词构成
基本形式 构成规则 例子
过去式与 过去分词 (done) ①一般情况:在词尾+ed work—worked,
pass—passed,
depend—depended
②以e结尾,直接+d live—lived,
hope—hoped,
decide—decided
3
行为动词的过去式/过去分词构成
基本形式 构成规则 例子
过去式与 过去分词 (done) ③以辅音字母加y结尾的要变y为i,再+ed study—studied,
worry—worried,
hurry—hurried
④重读闭音节,双写结尾字母再+ed stop—stopped,
shop—shopped,
plan—planned
3
行为动词的过去式/过去分词构成
对 点 专 练
写出下列动词的相应形式。
动词原形 第三人称单数 现在分词 过去式 过去分词
be
do
stop
pass
is being was/were been
does doing did done
stops stopping stopped stopped
passes passing passed passed
对 点 专 练
写出下列动词的相应形式。
动词原形 第三人称单数 现在分词 过去式 过去分词
carry
make
die
teach
put
carries carrying carried carried
makes making made made
dies dying died died
teaches teaching taught taught
puts putting put put
考点⑤
常考的动词
短语归纳
come come back 回来
come out 出来
come from 来自
get get up 起床
get ready for 为……作好准备,
get on (well) with 与……相处(融洽)
get back 返回
get on/off 上/下车
get to 到达
give give up 放弃 give back 归还;后退,
give away 捐赠 give out 分发
give birth to 生育
look look up 查阅 look after 照看;照顾
look for 寻找 look like 看起来像……
look out 当心;小心
look around 朝四周看
look forward to 期望
put put on 穿上(衣服);上演(戏剧)
put up 建造;举起;张贴
put into 把……放进
put out 扑灭
set set up 建立
set off 出发;动身
set out 出发
take take out 提取
take place 发生
take up 开始做
take a trip 去旅行
take care of 关心;照顾
take off 脱下(衣、帽、鞋等);拿掉;(飞机)起飞
take part in 参加
对 点 专 练
1. 青少年应该学习如何照顾自己。
Teenagers should learn how to 1
themselves.
2. 很高兴收到你的来信。
It’s great to you.
3. 正如习近平所说,人类应当友好对待世界不同的文化。
As Xi Jinping said, humans should 1
different cultures of the world.
take care of
hear from
be friendly to
对 点 专 练
4. 好运总是属于有准备的人。
Good luck always somebody that has
prepared well.
5. 弗兰克想出了这个好主意。
Frank this good idea.
belongs to
came up with
语 法 巩 固
1. Nancy often goes____________ (swim) with her friends in summer
2. I want ____________ (go) to the shop.
3. The little girl likes _________________ (play) basketball. She____________ (play) on the playground now.
4. The teacher _____________ (go) to school on foot every day.
5. Let's ___________ (speak) English.
swimming
to go
教材P29 二
playing/ to play
is playing
goes
speak
语 法 巩 固
( ) 1. Dirty air and water are harmful. They kill plants, and even people.
A. can B. can’t C. should D. shouldn’t
A
( ) 2. —Must we wear the school uniforms tomorrow, Mr. Wang
—No, you . Only on Mondays. Tomorrow is Tuesday.
A. shouldn’t B. needn’t C. can’t D. mustn’t
B
语 法 巩 固
( ) 3. Don’t the waste paper and bottles. They can be recycled.
A. throw away B. take out C. get away D. put out
A
( ) 4. —I don’t know how to the old books.
—Why not give them away to poor children
A. hand out B. give up C. deal with D. take up
C
语 法 巩 固
( ) 5. —Have you chemistry for the coming exam
—Yes. I’m quite ready for it.
A. repeated B. copied C. marked D. reviewed
D
( )6. —Whose cap is this Is it Cindy’s
—It be hers. Don’t you remember she even didn’t come to the party
A. can’t B. might C. may not D. must
A
( ) 7. —The driver be hurt badly in the accident.
—That’s true. Let’s send him to the hospital as soon as possible.
A. need B. can’t C. must D. may not
语 法 巩 固
C
( )8. All members decided to the money from the book sale to homeless people.
A. give up B. give away C. take up D. take away
B
( ) 9. —The summer vacation is coming. Have you made a plan for it
—Not yet. I go to Guilin.
A. may B. can C. should D. must
语 法 巩 固
A
( )10. —Why were you shouting at Tom
—I told him to be quiet, but he talking.
A. joined in B. ended up C. kept on D. put off
C
单 词 拼 写
1. He fell off the bike yesterday, but luckily, he didn’t
h himself.
2. It is difficult for most of the students to s this
physics problem.
3. After watching the video, the thief had to a his
crime(罪行) of stealing the money.
urt
olve
dmit
单 词 拼 写
4. The two dresses are so beautiful. She can’t d which
one to buy.
5. I need another 3 days to f writing the article. I’ve
only done half of it.
6. They have to c the sports meeting because of the
bad weather.
ecide
inish
ancel
完 成 句 子
1. 王俊凯擅长唱歌和打篮球。
Wang Junkai singing and playing
basketball.
2. 正如专家所说:“学习效能的好坏取决于你的学习习
惯。”
As the experts said, “Whether or not you can study well
your learning habits.”
is good at
depends on
完 成 句 子
3. 知识源于质疑。
Knowledge questioning.
4. 我能通过查字典找到生词的意思。
I can find the meaning of the new words by them
in a dictionary.
5. 离开房间之前,请将你的电脑关闭。
Please your computer before leaving the
room.
comes from
looking
up
turn off
完 成 句 子
6. 现在人们可以通过微信与他们的朋友保持联系。
People can their friends
by WeChat now.
7. 成功的关键在于从错误中学习,并且永不放弃。
The key to success is to learn from your mistakes and
never .
keep in touch with
give up
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
