初中英语时态复习
图片预览











文档简介
课件36张PPT。时态复习 Revision of tense一般现在时
一般过去时
现在进行时
一般将来时
现在完成时
一般现在时态 Ⅰ一般现在时态的陈述句概念:一般现在时态表示的是经常反复发生的动作或存在的状态。eg: I am a teacher .
You are a worker.
She/He is a student .
We/You/They are students.1.Be 的用法:
I用 am, you用are, is用于他(he)、她(she) 、它(it),复数(we,you,they)全部都用are1、一般动词,在词尾加 s ; 如:
work--works, live--lives, play--plays, sing-- sings.
eg: She lives in Ningbo. 她住在宁波。
2、以s/x/sh/ch/o 等字母结尾的动词,词尾加 -es ,
teach------ teaches, wash----- washes.
eg: My mother washes the coat. 我母亲洗了大衣。行为动词do一般现在时第三人称单数(he,she,it) 的构成规则:2.行为动词: DO 和DOESII 一般现在时的否定式
1.Be 动词的否定式: be + notI am a teacher.
You are a worker
She is a doctor
We are friends.I’m not a teacher
You aren’t a worker
She isn’t a doctor.
We aren’t friends.
is not=isn’t
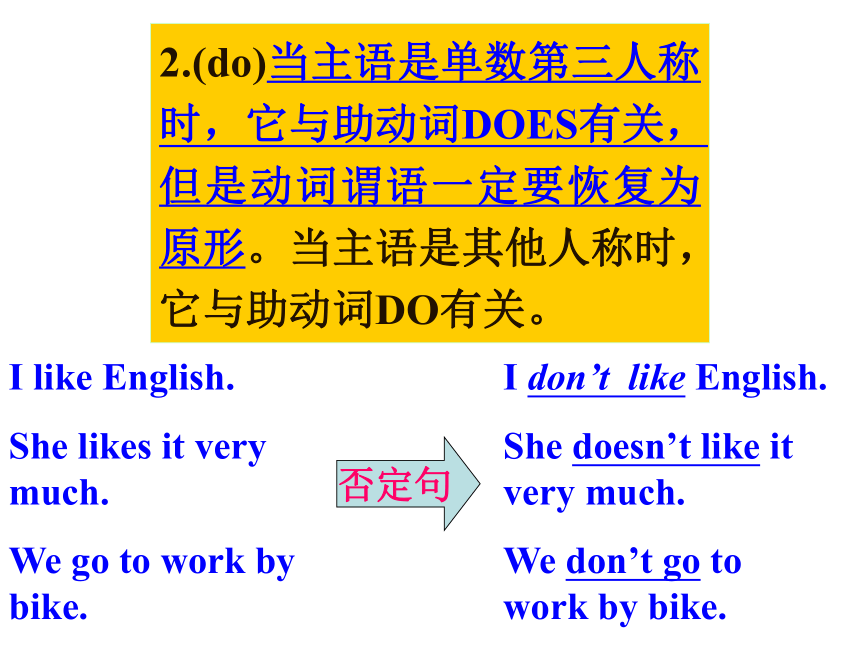
are not=aren’t 否定句2.(do)当主语是单数第三人称时,它与助动词DOES有关,但是动词谓语一定要恢复为原形。当主语是其他人称时,它与助动词DO有关。I like English.
She likes it very much.
We go to work by bike.I don’t like English.
She doesn’t like it very much.
We don’t go to work by bike.否定句概念:用 yes 或 no 来回答的疑问句叫做一般疑问句。
一般疑问句句首的第一个词一般读得比较重。
III一般疑问句I am a teacher. Are you a teacher?
You are a worker. Are you a worker?
He is a student. Is he a student?
We are friends. Are you friends?1.对于BE 动词,疑问句要求把BE 提前,第一人称的单数和复数(I/WE),第一变成第二人称。疑问句2.对于实义动词,疑问句要求是:当主语是他(he),她(she),它(it)时,句子前面加DOES,并把动词恢复原形;当主语是其他人称时,句前加DO ,第一人称(I/we)换第二人称(you)。I often go there.
You like the music.
He goes to work by bus .
We /You/They like it.Do you often go there ?
Do you like the music?
Does he go to work by bus ?
Do you/they like it?Ⅳ. 特殊疑问句特殊疑问句在考试中涉及得比较多,主要以选择和转换句型为主,首先要掌握一些常用疑问词的意思如:what(什么),when, what time(什么时间), who(谁), where(在哪里), why(为什么), how(怎样), how many+可数名词的复数(多少), how long(多长时间), how often(多久一次) 等,其次掌握它的语序,即就是特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序(Who)除外一、疑问词+ 一般疑问句句序:
Where are you from? I’m from the north.
What do you want?
I want the books on your desk.特殊疑问句的语序一般过去时态 一般过去时态的定义
动词的一般过去时态表示过去发生的动作、情况或存在的状态。行为动词(即实义动词)的过去式一般没有人称和数的变化。
谓语动词的构成形式
一般过去时的谓语动词有be动词 和行为动词两种基本形式 规则动词过去式的构成be动词和行为动词两种基本形式 be动词(或系动词be)的过去式为was和were两个。
行为动词的过去式,其变化分为规则和不规则的两种。规则动词过去式的构成 一般动词原形末尾加-ed。如:look→looked, stay→stayed ;
以e结尾的动词只加-d。如:hope→hoped, live→lived;
末尾只有一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节的动词,应先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed.如:stop→stopped, plan(计划) →planned; 规则动词过去式的构成 结尾是“辅音字母+y”的动词,先将y改为i,再加-ed. 如:study→studied, carry→carried.
–ed(或-d)的读音:在清辅音结尾的词后读[t].如:work→worked [w?? kt], help → helped [helpt]; 在浊辅音和元音后读[d]。如:call→called[k??ld], play → played [ple?d]; 在[t]和[d]音后面发[?d]。如:want→wanted[w?nt?d],need → needed [ni:d?d].一般过去时态常见的基本用法 1.表示在过去时间里发生的动作或存在的状态
Liu Jie got up at 7: 10 this morning.
He was a student three years ago.
一般过去时态常见的基本用法 2.表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。
Zhang Yaru always went to school by bike last term.
一般过去时态常见的基本用法 3.表示已故人所做的事情。
Comrade Lei Feng did good deeds all his life. (雷锋同志做了一生的好事。)
一般过去时态常见的基本用法 4.表示过去所发生的一系列的动作,而这一系列的动作是从现在的角度来考虑的,不是从动作相互之间的关系这一角度来考虑的。
Miss Liu got up at seven o’clock this morning, dressed, had breakfast, and went to work. Be was/were
Do did 一般过去时表在过去某个特定时间发生且完成的动作,或过去习惯性动作,不强调对现在的影响,只说明过去。常跟明确的过去时间连用,如:yesterday; last week; in 1945, at that time; once; during the war; before; a few days ago; when, 现在进行时定义:表示现在正在进行的动作.
结构:be (is, am, are) +doing
常见时间状语:now, 或动词look, listen
eg: We are having an English class now.
否定句:We aren’t having ……..
一般疑问句:Are you having ……?一般将来时定义:表示将要做的事或计划要做的事.
结构:be(is ,am, are) going to do
will/shall do (shall一般用于第一人称)
时间状语:tomorrow (morning, afternoon, evening),
next day (week, month, year), the day after tomorrow, in 2006 ...
Eg: They are going to have a football match next week.现在完成时的构成: Have / has +动词过去分词1. 表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果.already, ever, yet, just, before, recently, these days, up to now, in the last few years等.现在完成时的用法(2个)经常与下列词语连用2. 表示过去发生的动作持续到了现在, 可能继续发展下去,常与for或since引导的时间状语连用.总结:非延续性动词在完成时的肯定句中不可与含for, since, how long等引导的时间状语连用, 要用别的词替换.come/arrive →buy →borrow →die →leave →begin/start →join →bekeepbe deadbe away frombe onbe in/be a memberhave1.Mr. Black left China in 1990.
Mr. Black ______________________China since 1990.
2.The hero died five years ago.
The hero __________________ for five years.
3.The meeting began two minutes ago.
The meeting _________________ for two minutes.
4.We borrowed two books last week.
We _______________ the two books for a week.
5. Sally joined the League two years ago.
Sally _______________ the League for two years. 句型转换: (改为意思相同的句子)has been away from has been deadhas been onhave kepthas been in总结:have/has been to表示“到(去)过某地”,人已经回来. have/has gone to 表示“到某地去了”,人正在某地或在去某地的途中have/has been in 表示 “在某地呆多久”, 常和表示一段时间的状语连用.3. for 与since接时间状语时的区别 1. A: What a nice dog! How long have you had it? B: _______ two years.
A. For B. Since C. In D. From
2. Miss Gao has taught in this school ________ 1996.
A. for B. at C. in D. since
For后接时间段, since后接时间点或从句. 如: for two years; for six hours; for three days; for five minutes; since three days ago; since 1997; since three days ago; since I came to Beijing 等. 总结:1. George ______ French for ten years.
A. had learned B. has learned
C. will be learning D. learns
2. Jack has studied Chinese in the school
___ the year 2002.
A. in B. since C. on D. byBB4. 现在完成时与一般过去时的区别一般过去时的时间状语:yesterday, the day before yesterday, last year, just now, then, last week, last month, an hour ago, two days ago,in 1994等.过去完成时经常与哪些时间状语连用?与现在完成时连用表示时间的词语:
already, ever, yet, just, before, recently, these days, up to now, in the last few years等.
for+时间段
since+时间点总结:
现在完成时强调过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果, 而一般过去时表示单纯的过去的事实或状态.另外, 两种时态的时间状语不一样, 一般过去时常与具体的过去时间连用, 现在完成时不能.
一般过去时
现在进行时
一般将来时
现在完成时
一般现在时态 Ⅰ一般现在时态的陈述句概念:一般现在时态表示的是经常反复发生的动作或存在的状态。eg: I am a teacher .
You are a worker.
She/He is a student .
We/You/They are students.1.Be 的用法:
I用 am, you用are, is用于他(he)、她(she) 、它(it),复数(we,you,they)全部都用are1、一般动词,在词尾加 s ; 如:
work--works, live--lives, play--plays, sing-- sings.
eg: She lives in Ningbo. 她住在宁波。
2、以s/x/sh/ch/o 等字母结尾的动词,词尾加 -es ,
teach------ teaches, wash----- washes.
eg: My mother washes the coat. 我母亲洗了大衣。行为动词do一般现在时第三人称单数(he,she,it) 的构成规则:2.行为动词: DO 和DOESII 一般现在时的否定式
1.Be 动词的否定式: be + notI am a teacher.
You are a worker
She is a doctor
We are friends.I’m not a teacher
You aren’t a worker
She isn’t a doctor.
We aren’t friends.
is not=isn’t
are not=aren’t 否定句2.(do)当主语是单数第三人称时,它与助动词DOES有关,但是动词谓语一定要恢复为原形。当主语是其他人称时,它与助动词DO有关。I like English.
She likes it very much.
We go to work by bike.I don’t like English.
She doesn’t like it very much.
We don’t go to work by bike.否定句概念:用 yes 或 no 来回答的疑问句叫做一般疑问句。
一般疑问句句首的第一个词一般读得比较重。
III一般疑问句I am a teacher. Are you a teacher?
You are a worker. Are you a worker?
He is a student. Is he a student?
We are friends. Are you friends?1.对于BE 动词,疑问句要求把BE 提前,第一人称的单数和复数(I/WE),第一变成第二人称。疑问句2.对于实义动词,疑问句要求是:当主语是他(he),她(she),它(it)时,句子前面加DOES,并把动词恢复原形;当主语是其他人称时,句前加DO ,第一人称(I/we)换第二人称(you)。I often go there.
You like the music.
He goes to work by bus .
We /You/They like it.Do you often go there ?
Do you like the music?
Does he go to work by bus ?
Do you/they like it?Ⅳ. 特殊疑问句特殊疑问句在考试中涉及得比较多,主要以选择和转换句型为主,首先要掌握一些常用疑问词的意思如:what(什么),when, what time(什么时间), who(谁), where(在哪里), why(为什么), how(怎样), how many+可数名词的复数(多少), how long(多长时间), how often(多久一次) 等,其次掌握它的语序,即就是特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序(Who)除外一、疑问词+ 一般疑问句句序:
Where are you from? I’m from the north.
What do you want?
I want the books on your desk.特殊疑问句的语序一般过去时态 一般过去时态的定义
动词的一般过去时态表示过去发生的动作、情况或存在的状态。行为动词(即实义动词)的过去式一般没有人称和数的变化。
谓语动词的构成形式
一般过去时的谓语动词有be动词 和行为动词两种基本形式 规则动词过去式的构成be动词和行为动词两种基本形式 be动词(或系动词be)的过去式为was和were两个。
行为动词的过去式,其变化分为规则和不规则的两种。规则动词过去式的构成 一般动词原形末尾加-ed。如:look→looked, stay→stayed ;
以e结尾的动词只加-d。如:hope→hoped, live→lived;
末尾只有一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节的动词,应先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed.如:stop→stopped, plan(计划) →planned; 规则动词过去式的构成 结尾是“辅音字母+y”的动词,先将y改为i,再加-ed. 如:study→studied, carry→carried.
–ed(或-d)的读音:在清辅音结尾的词后读[t].如:work→worked [w?? kt], help → helped [helpt]; 在浊辅音和元音后读[d]。如:call→called[k??ld], play → played [ple?d]; 在[t]和[d]音后面发[?d]。如:want→wanted[w?nt?d],need → needed [ni:d?d].一般过去时态常见的基本用法 1.表示在过去时间里发生的动作或存在的状态
Liu Jie got up at 7: 10 this morning.
He was a student three years ago.
一般过去时态常见的基本用法 2.表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。
Zhang Yaru always went to school by bike last term.
一般过去时态常见的基本用法 3.表示已故人所做的事情。
Comrade Lei Feng did good deeds all his life. (雷锋同志做了一生的好事。)
一般过去时态常见的基本用法 4.表示过去所发生的一系列的动作,而这一系列的动作是从现在的角度来考虑的,不是从动作相互之间的关系这一角度来考虑的。
Miss Liu got up at seven o’clock this morning, dressed, had breakfast, and went to work. Be was/were
Do did 一般过去时表在过去某个特定时间发生且完成的动作,或过去习惯性动作,不强调对现在的影响,只说明过去。常跟明确的过去时间连用,如:yesterday; last week; in 1945, at that time; once; during the war; before; a few days ago; when, 现在进行时定义:表示现在正在进行的动作.
结构:be (is, am, are) +doing
常见时间状语:now, 或动词look, listen
eg: We are having an English class now.
否定句:We aren’t having ……..
一般疑问句:Are you having ……?一般将来时定义:表示将要做的事或计划要做的事.
结构:be(is ,am, are) going to do
will/shall do (shall一般用于第一人称)
时间状语:tomorrow (morning, afternoon, evening),
next day (week, month, year), the day after tomorrow, in 2006 ...
Eg: They are going to have a football match next week.现在完成时的构成: Have / has +动词过去分词1. 表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果.already, ever, yet, just, before, recently, these days, up to now, in the last few years等.现在完成时的用法(2个)经常与下列词语连用2. 表示过去发生的动作持续到了现在, 可能继续发展下去,常与for或since引导的时间状语连用.总结:非延续性动词在完成时的肯定句中不可与含for, since, how long等引导的时间状语连用, 要用别的词替换.come/arrive →buy →borrow →die →leave →begin/start →join →bekeepbe deadbe away frombe onbe in/be a memberhave1.Mr. Black left China in 1990.
Mr. Black ______________________China since 1990.
2.The hero died five years ago.
The hero __________________ for five years.
3.The meeting began two minutes ago.
The meeting _________________ for two minutes.
4.We borrowed two books last week.
We _______________ the two books for a week.
5. Sally joined the League two years ago.
Sally _______________ the League for two years. 句型转换: (改为意思相同的句子)has been away from has been deadhas been onhave kepthas been in总结:have/has been to表示“到(去)过某地”,人已经回来. have/has gone to 表示“到某地去了”,人正在某地或在去某地的途中have/has been in 表示 “在某地呆多久”, 常和表示一段时间的状语连用.3. for 与since接时间状语时的区别 1. A: What a nice dog! How long have you had it? B: _______ two years.
A. For B. Since C. In D. From
2. Miss Gao has taught in this school ________ 1996.
A. for B. at C. in D. since
For后接时间段, since后接时间点或从句. 如: for two years; for six hours; for three days; for five minutes; since three days ago; since 1997; since three days ago; since I came to Beijing 等. 总结:1. George ______ French for ten years.
A. had learned B. has learned
C. will be learning D. learns
2. Jack has studied Chinese in the school
___ the year 2002.
A. in B. since C. on D. byBB4. 现在完成时与一般过去时的区别一般过去时的时间状语:yesterday, the day before yesterday, last year, just now, then, last week, last month, an hour ago, two days ago,in 1994等.过去完成时经常与哪些时间状语连用?与现在完成时连用表示时间的词语:
already, ever, yet, just, before, recently, these days, up to now, in the last few years等.
for+时间段
since+时间点总结:
现在完成时强调过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果, 而一般过去时表示单纯的过去的事实或状态.另外, 两种时态的时间状语不一样, 一般过去时常与具体的过去时间连用, 现在完成时不能.
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
