Unit 4 What time do you go to school? SectionB(1a-1e) 课件(共32张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 4 What time do you go to school? SectionB(1a-1e) 课件(共32张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 6.5MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 鲁教版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-06-19 10:36:43 | ||
图片预览



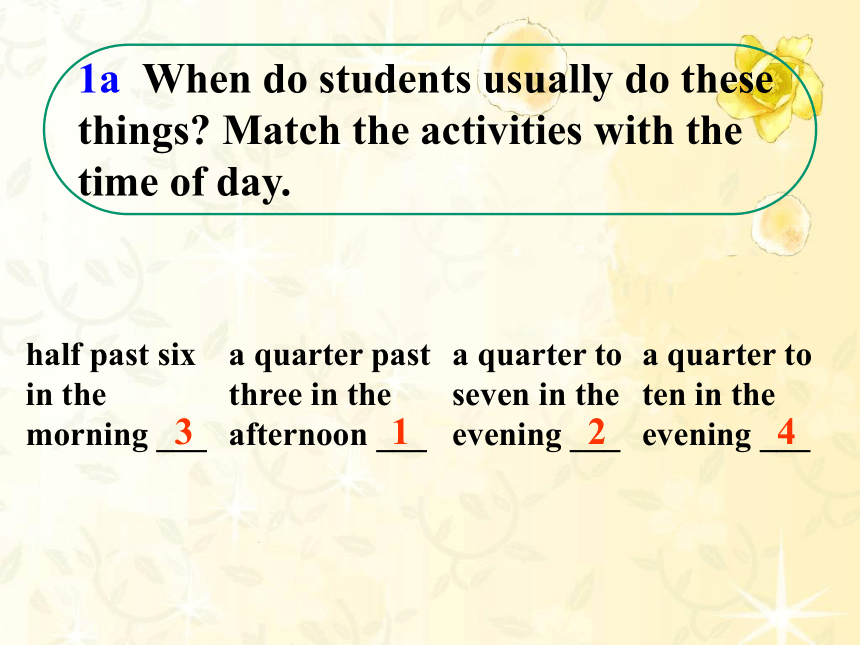




文档简介
(共32张PPT)
Section B
Period 1 (1a – 1e)
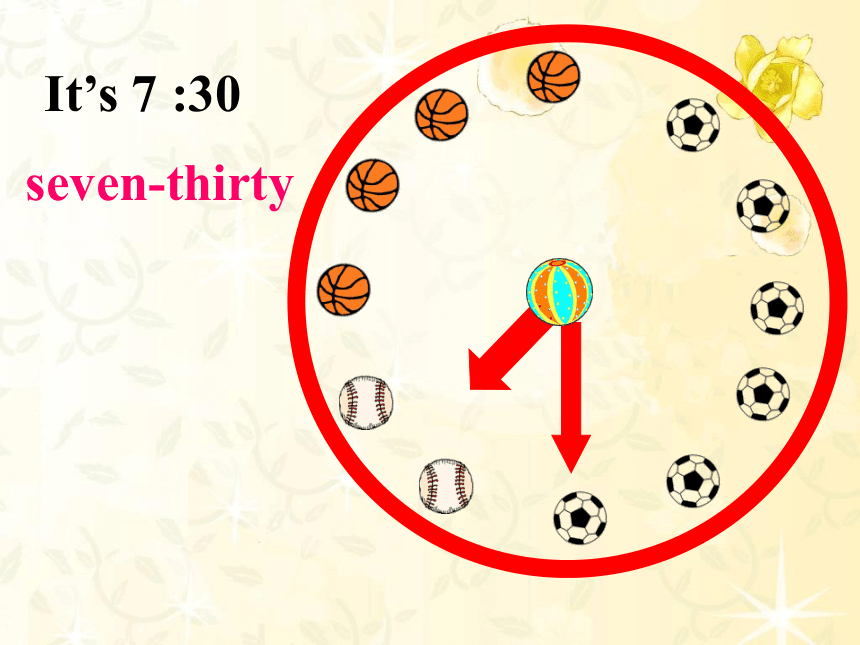
It’s 7 :30
seven-thirty
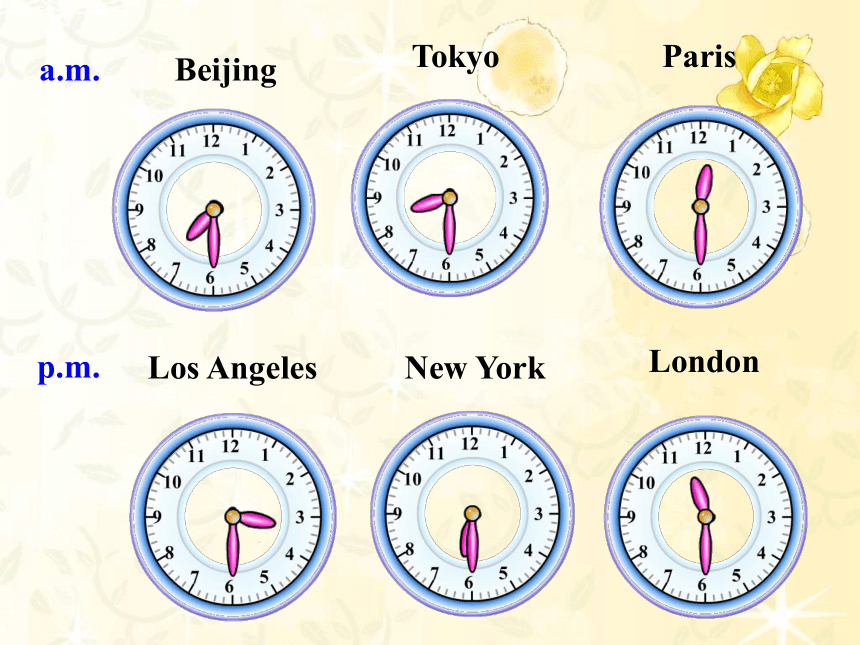
Beijing
London
Tokyo
Paris
Los Angeles
New York
p.m.
a.m.
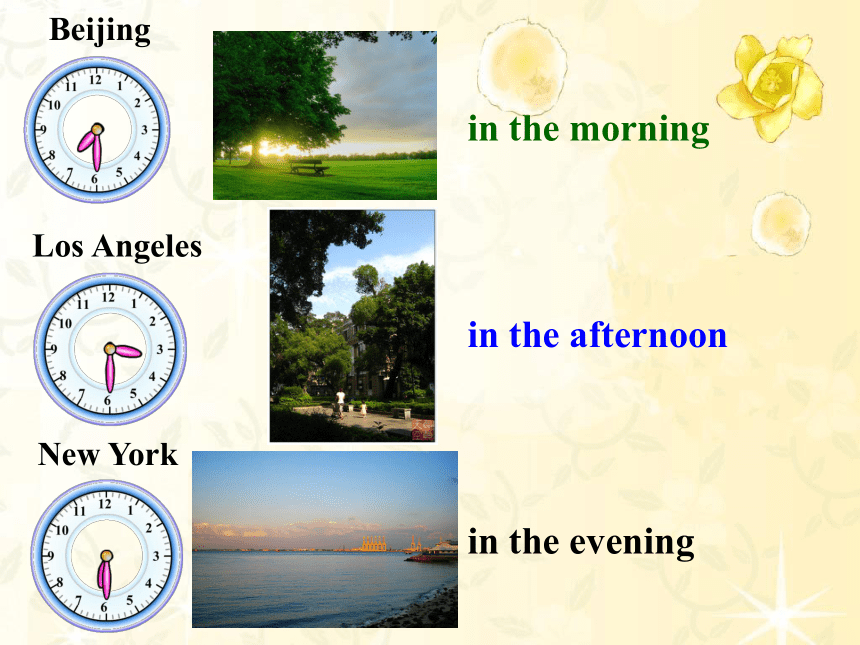
in the morning
in the afternoon
in the evening
Beijing
New York
Los Angeles
a.m.
p.m.
in the
morning
in the
in the
afternoon
evening
p.m.
What do you usually do in the
in the morning
in the afternoon
in the evening
morning
afternoon
evening
1a When do students usually do these things Match the activities with the time of day.
half past six in the morning ___
a quarter to seven in the evening ___
a quarter past three in the afternoon ___
a quarter to ten in the evening ___
1
2
3
4
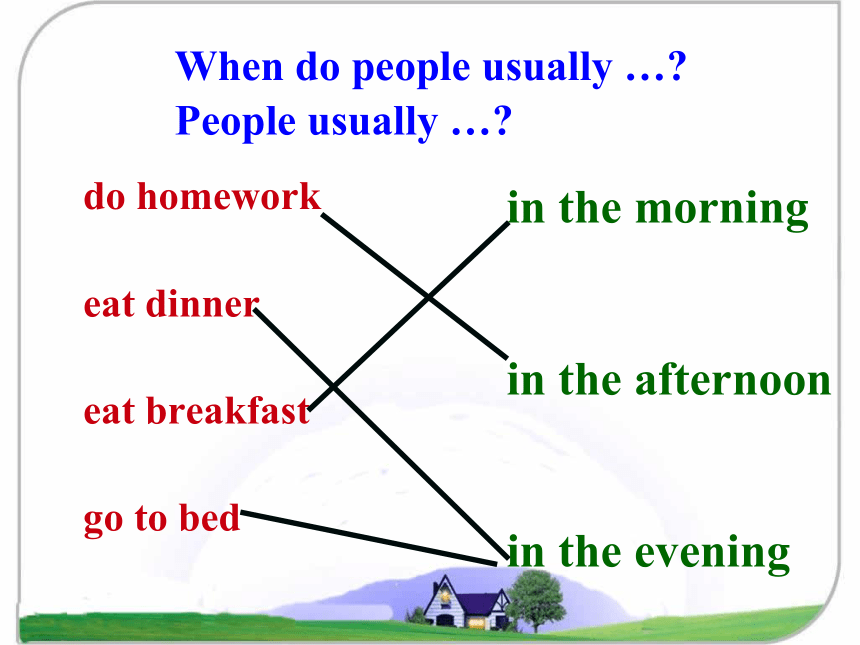
do homework
eat dinner
eat breakfast
go to bed
When do people usually …
People usually …
in the morning
in the afternoon
in the evening
1b Check your answers with your
partner.
A: When do people …
B: They …
go to work
A: When do people …
B: They …
watch TV
have lunch
A: When do students …
B: They …
A: When do students …
B: They …
do exercise
1c Listen and circle the activities you hear.
get up _____ 6. do my homework ____
2. run ____ 7. clean my room ____
3. eat breakfast ____ 8. eat dinner ____
4. go to school ____ 9. take a walk ___
5. go home _____ 10. go to bed ____
5:30
1d Listen again. Write the times next to the activities you circled in 1c.
get up _____ 6. do my homework ______
2. run ________ 7. clean my room ____
3. eat breakfast _______ 8. eat dinner ____
4. go to school _______ 9. take a walk ___
5. go home __________ 10. go to bed ________
5:30
6:00 a.m
7:00 a.m
7:45 a.m
4:15 p.m
5:30 p.m
7:15 p.m
9:00 p.m
1e Ask and answer questions about Tom.
—When does Tom usually …
— He usually …
—When does Tom usually …
— He usually …
when 和 what time 的区别
what time: 问时间,一般指具体时刻。
when: 问时间,既指具体时刻,也指大的时间。
---What time do you go to school
---I go to school at 7:00.
---When do you go to school
---I go to school at 7:00.
---I go to school in the evening.
翻译:
1.你通常几点睡觉
2.你的父亲七点钟上班吗?
3.他十二点吃午饭。
4. 请问几点钟了?
What time / When do you usually go to bed
Does your father go to work at 7:00
He has / eats lunch at 12:00.
Excuse me. What time is it, please
对下列划线部分提问, 将句子变为特殊疑问句。
(1)It’s seven o’clock.
__________ __________ is it
(2)He was born in 1992.
__________ was __________ born
What time
When he
1. In the evening, I either watch TV or play computer games.
晚上我要么看电视要么玩电脑游戏。
either … or … 表示“要么……要么……;不是……就是……;或……或……”。这个结构可用来连接两个独立的词、短语、甚至独立的句子。例如:
You can come either today or tomorrow.
你可以今天或明天来。
either…or和or的区别和用法
来看两个例子:
She will come either today or tomorrow.
她不是今天来就是明天来。
She will come today or tomorrow.
她今天或明天来。
小结:
either … or和or的区别,主要在于语气
强弱。前者强调“非此及彼”,后者仅有
“或者”的意思。此外,either … or之后
的语句应对称,也就是说,either之后用
名词,or后面也用名词,either之后是从
句,or后面也一样。所以,“他不是醉
了,就是疯了”一句,就应说成:
He is either drunk or mad.
完成句子。
1. 你可以在那里呆两天或三天。
You may spend two __________ three days
there.
2. Sorry, there is only one ticket. ________
you ________ she can have it.
A. Not; but B. Either; not
C. Both; and D. Either; or
or
D
【2012四川自贡】“You can’t have them all. You can choose _____the kite ______ the toy car,” said the mother.
A. either; or B. not only; but also
C. both; and
【答案】A
2. At twelve, she eats lots of fruit and vegetables for lunch.
lot pron. 许多;大量
lots of (= a lot of) 许多,大量
The boy has a lot of / lots of pocket money.
这男孩有许多零用钱。
There are a lot of / lots of famous movie stars in the USA.
美国有许多著名的电影明星。
lots of、 a lot of 既可以修饰不可数名词也可以修饰可数名词的复数形式,相当于many或much。a lot of, lots of 通常用于肯定句,否定句中一般用many或much。
3. She knows it’s not good for her, but it tastes good!
她知道这对她(健康)不利,但它(指冰激凌)却很好吃。
1) be good for… 表示“对……有益”;
be bad for… 表示“对……有害”。例如:
It’s good for our health to go to bed early and get up early.
早睡早起对我们的健康有好处。
It’s good for … 对……有益
It’s bad for … 对……有害
完成句子:
1. Smoking is ________ your health. (吸烟无益健康。)
2. We hope you can give up; it will ____________ your health. (我们希望你戒烟,这对你的健康有利。)
bad for
be good for
2) taste表示“吃上去;品尝”,之后要用形容词。
表示感觉的系动词还有smell(闻起来)和feel(摸上去)。例如:
This fish smells bad.
这鱼闻着坏了。
This sofa feels nice and soft.
这沙发摸上去舒服、柔软。
1. 这种布手感很软。
This kind of cloth feels very soft.
2. 这朵花闻起来很香。
This flower smells very sweet.
3. 它尝起来很甜。
It tastes sweet.
翻译下列句子。
Section B
Period 1 (1a – 1e)
It’s 7 :30
seven-thirty
Beijing
London
Tokyo
Paris
Los Angeles
New York
p.m.
a.m.
in the morning
in the afternoon
in the evening
Beijing
New York
Los Angeles
a.m.
p.m.
in the
morning
in the
in the
afternoon
evening
p.m.
What do you usually do in the
in the morning
in the afternoon
in the evening
morning
afternoon
evening
1a When do students usually do these things Match the activities with the time of day.
half past six in the morning ___
a quarter to seven in the evening ___
a quarter past three in the afternoon ___
a quarter to ten in the evening ___
1
2
3
4
do homework
eat dinner
eat breakfast
go to bed
When do people usually …
People usually …
in the morning
in the afternoon
in the evening
1b Check your answers with your
partner.
A: When do people …
B: They …
go to work
A: When do people …
B: They …
watch TV
have lunch
A: When do students …
B: They …
A: When do students …
B: They …
do exercise
1c Listen and circle the activities you hear.
get up _____ 6. do my homework ____
2. run ____ 7. clean my room ____
3. eat breakfast ____ 8. eat dinner ____
4. go to school ____ 9. take a walk ___
5. go home _____ 10. go to bed ____
5:30
1d Listen again. Write the times next to the activities you circled in 1c.
get up _____ 6. do my homework ______
2. run ________ 7. clean my room ____
3. eat breakfast _______ 8. eat dinner ____
4. go to school _______ 9. take a walk ___
5. go home __________ 10. go to bed ________
5:30
6:00 a.m
7:00 a.m
7:45 a.m
4:15 p.m
5:30 p.m
7:15 p.m
9:00 p.m
1e Ask and answer questions about Tom.
—When does Tom usually …
— He usually …
—When does Tom usually …
— He usually …
when 和 what time 的区别
what time: 问时间,一般指具体时刻。
when: 问时间,既指具体时刻,也指大的时间。
---What time do you go to school
---I go to school at 7:00.
---When do you go to school
---I go to school at 7:00.
---I go to school in the evening.
翻译:
1.你通常几点睡觉
2.你的父亲七点钟上班吗?
3.他十二点吃午饭。
4. 请问几点钟了?
What time / When do you usually go to bed
Does your father go to work at 7:00
He has / eats lunch at 12:00.
Excuse me. What time is it, please
对下列划线部分提问, 将句子变为特殊疑问句。
(1)It’s seven o’clock.
__________ __________ is it
(2)He was born in 1992.
__________ was __________ born
What time
When he
1. In the evening, I either watch TV or play computer games.
晚上我要么看电视要么玩电脑游戏。
either … or … 表示“要么……要么……;不是……就是……;或……或……”。这个结构可用来连接两个独立的词、短语、甚至独立的句子。例如:
You can come either today or tomorrow.
你可以今天或明天来。
either…or和or的区别和用法
来看两个例子:
She will come either today or tomorrow.
她不是今天来就是明天来。
She will come today or tomorrow.
她今天或明天来。
小结:
either … or和or的区别,主要在于语气
强弱。前者强调“非此及彼”,后者仅有
“或者”的意思。此外,either … or之后
的语句应对称,也就是说,either之后用
名词,or后面也用名词,either之后是从
句,or后面也一样。所以,“他不是醉
了,就是疯了”一句,就应说成:
He is either drunk or mad.
完成句子。
1. 你可以在那里呆两天或三天。
You may spend two __________ three days
there.
2. Sorry, there is only one ticket. ________
you ________ she can have it.
A. Not; but B. Either; not
C. Both; and D. Either; or
or
D
【2012四川自贡】“You can’t have them all. You can choose _____the kite ______ the toy car,” said the mother.
A. either; or B. not only; but also
C. both; and
【答案】A
2. At twelve, she eats lots of fruit and vegetables for lunch.
lot pron. 许多;大量
lots of (= a lot of) 许多,大量
The boy has a lot of / lots of pocket money.
这男孩有许多零用钱。
There are a lot of / lots of famous movie stars in the USA.
美国有许多著名的电影明星。
lots of、 a lot of 既可以修饰不可数名词也可以修饰可数名词的复数形式,相当于many或much。a lot of, lots of 通常用于肯定句,否定句中一般用many或much。
3. She knows it’s not good for her, but it tastes good!
她知道这对她(健康)不利,但它(指冰激凌)却很好吃。
1) be good for… 表示“对……有益”;
be bad for… 表示“对……有害”。例如:
It’s good for our health to go to bed early and get up early.
早睡早起对我们的健康有好处。
It’s good for … 对……有益
It’s bad for … 对……有害
完成句子:
1. Smoking is ________ your health. (吸烟无益健康。)
2. We hope you can give up; it will ____________ your health. (我们希望你戒烟,这对你的健康有利。)
bad for
be good for
2) taste表示“吃上去;品尝”,之后要用形容词。
表示感觉的系动词还有smell(闻起来)和feel(摸上去)。例如:
This fish smells bad.
这鱼闻着坏了。
This sofa feels nice and soft.
这沙发摸上去舒服、柔软。
1. 这种布手感很软。
This kind of cloth feels very soft.
2. 这朵花闻起来很香。
This flower smells very sweet.
3. 它尝起来很甜。
It tastes sweet.
翻译下列句子。
同课章节目录
- Unit 1 When is your birthday?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 2 My favourite subject is science
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 3 Can you play the guitar?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 4 What time do you go to school?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 5 How do you get to school?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 6 Don't eat in class.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 7 Why do you like pandas?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 8 I'm watching TV.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 9 It's raining!
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 10 Is there a post office near here?
- Section A
- Section B
