2013年深圳市中考英语备考之时态
图片预览







文档简介
课件55张PPT。 轻松
享受时。。。时:动作发生时间1.时 与 体现在
过去
将来时体:动作完成的程度不强调动作完成的程度
动作未完结
动作已完结=一般体=进行体/ing=完成体/have
(时间点)
(时间段)一般体进行体完成体现
在过
去将
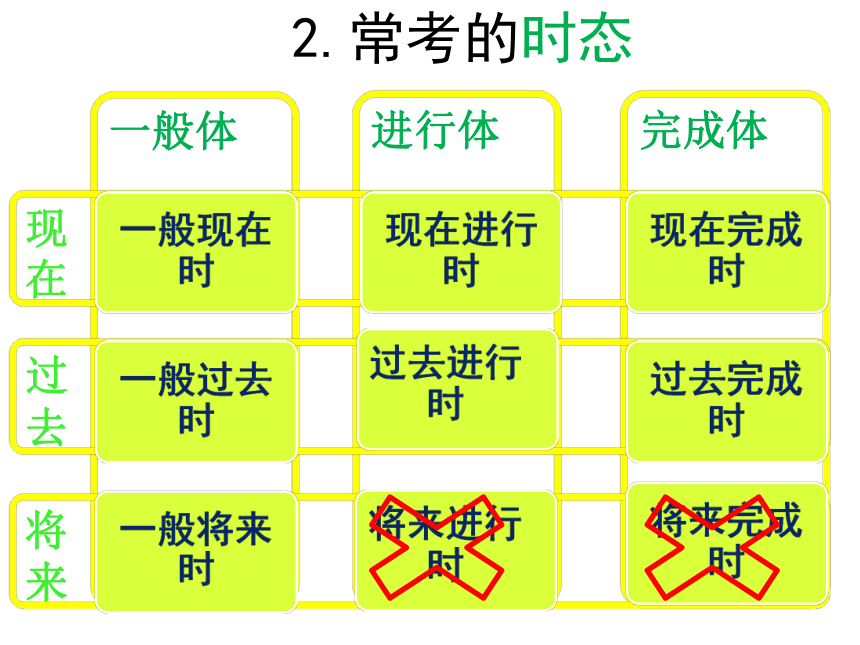
来2.常考的时态一般现在时一般过去时一般将来时将来进行时过去进行时现在进行时现在完成时过去完成时将来完成时一般体进行体完成体现
在过
去将
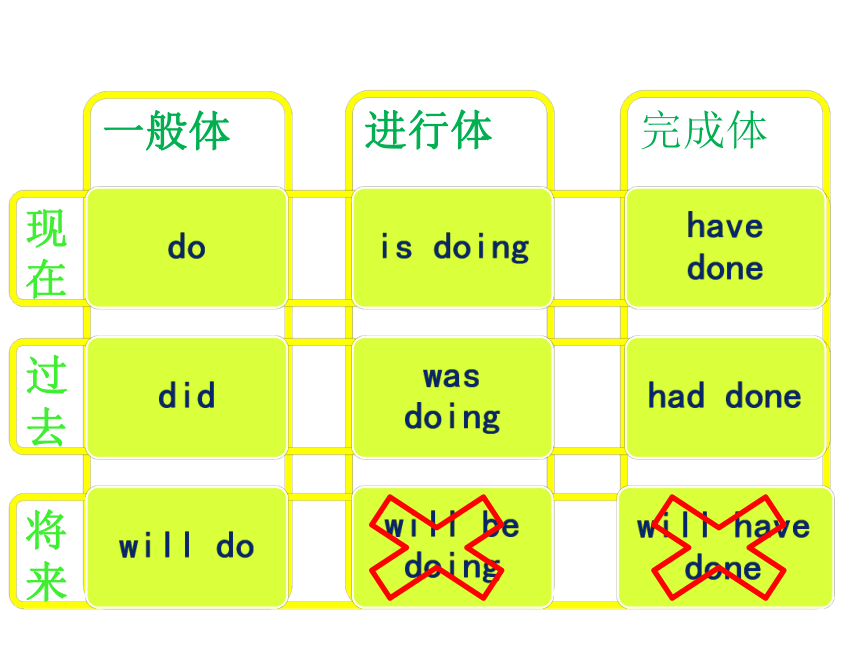
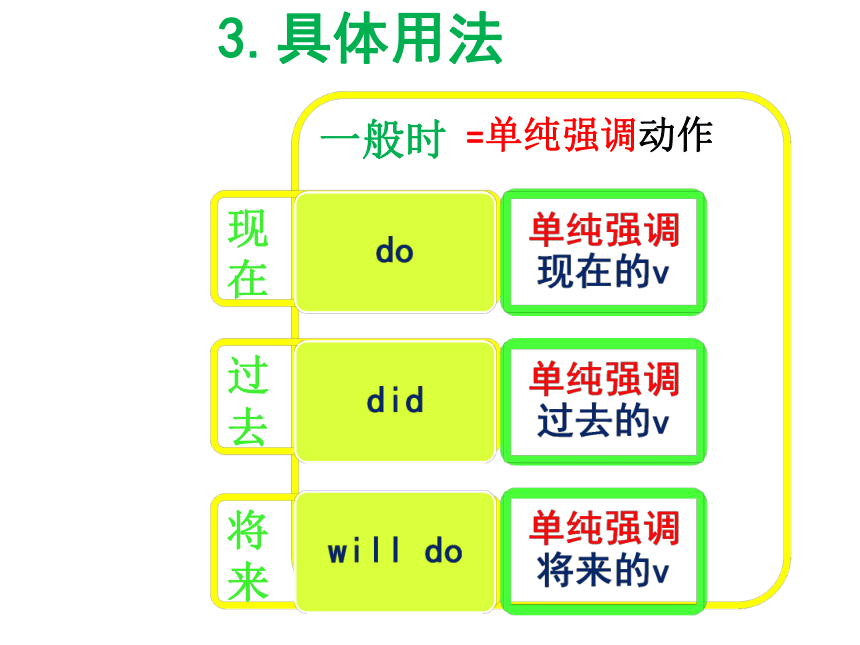
来dodidwill dowill be doingwas doingis doinghave donehad donewill have done3.具体用法一般时现
在过
去将
来dodidwill do单纯强调现在的v单纯强调过去的v单纯强调将来的v=单纯强调动作3.具体用法进行时现
在过
去将
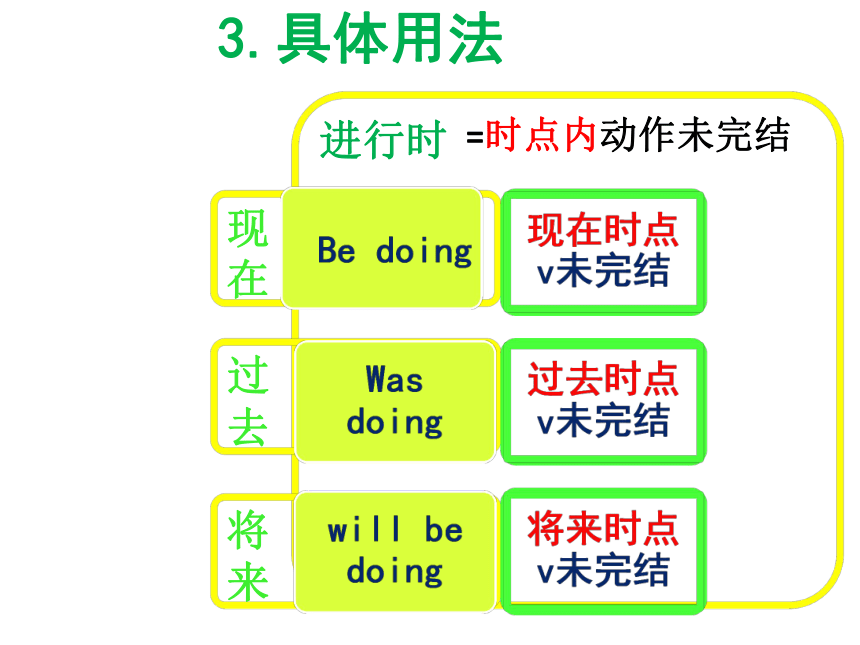
来Be doingWas doingwill be doing现在时点v未完结过去时点v未完结将来时点v未完结=时点内动作未完结3.具体用法完成时现
在过
去将
来Have doneHad doneWill have done到现在为止的时段内v已完结到过去为止的时段内v已完结到将来为止的时段内v已完结=时段内动作已完结1.一般现在时用法1)一次性的动作
2)习惯性/经常性的动作;
3)持续性的动作;
4)普遍真理
1)一次性的动作;我现在就教你。I teach you!
你就这么闯进房子了。You break into my house. 时间状语:
everyday, often,sometimes, always, on Sunday, at +时间点等
2)习惯性,经常性的动作;我总是教你。I always teach you!你有时闯进你房子。Sometimes you break into my house.
3)现在持续性的动作; 标志:
延续性动词等(系动词表“保持”:be , keep ,stay, live 等)
我是男生。I am a boy!
4)客观真题 标志:根据翻译得出永恒事实/格言警句
我是男生。I am a boy!骄者必败。
Pride goes before a fall. 地球 绕着 太阳转。 The earth moves around the sun. 注意:此用法在转述中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。She told me
Pride goes before a fall.
骄者必败。1.现在进行时用法1)正在发生的一次性的动作
2)长期习惯性/经常性的动作;
3)持续性/渐变的动作;
2.现在进行时? We are waiting for you.
1)正在发生的一次性的动作
2)长期习惯性/经常性的动作;
Mr. Green is writing another novel. (说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)与always, constantly, forever 等词连用
往往带有说话人的主观色彩。
You are always changing your mind. 表示渐变的动词有:
get, grow, become, turn等。
3)持续性/渐变的动作;1)The leaves are turning red.
2)It‘s getting warmer and warmer.
1) 事实状态的动词 have, belong, possess, cost, owe, exist, include, contain(包括), matter, weigh, measure, continue等 I have two brothers. This house belongs to my sister.
不用进行时的动词? 2) 心理状态的动词 Know, realize, think , believe, suppose, imagine, agree, recognize, remember, want, need, forget, prefer, mean, understand, love, hate等 I need your help. He loves her very much. 不用进行时的动词? 3) 瞬间动词 accept, receive, complete, finish, give, allow, decide, refuse等 I accept your advice.
不用进行时的动词?
4) 系动词 seem, remain, lie, see, hear, smell, feel, taste, get, become, turn等 You seem a little tired.
不用进行时的动词?3.一般过去时用法
1)过去习惯性,经常性的动作;
2)过去的状态与特征;
Where did you go just now? When I was a child, I often played football in the street. 区别一般过去时与过去进行时4.过去进行时用法过去进行时构成:否定式: 疑问式:was/were +doingwas/were not +doingWas/Were ……doing?比较-“同时性”
Be doing when=at or during the time that
=时间点/一段时间;
while=during the time that=一段时间总结: when+ do 瞬间V=时间点
while+ be doing 瞬间动词=时间段
when 和while的用法区别 当我到达山顶时,阳光正照耀着。
When I got to the top of the mountain, the sun was shining.他们离开车站时,正在下雨。
It was raining when they left the station.I got to the top of the mountain
while the sun was shining.
While it was raining ,they left the station.他们离开车站时,正在下雨。
It was raining when they left the station.It was going to rain when they left the station.天正要下雨时我们就离开车站了。
或 天还来不及下起雨来他们就离开车站了。注意: 主句, when … (“be doing/表将来”)(“一般时”)“来不及/正要…就…”我们正要启程这时下雨了 。We were about to leave when it rains .她来不及离开我就阻止了她。She was leaving when I stopped her . he was in London, he studied music. 当他在伦敦时,他学习音乐。 she was typing the letter, the telephone rang. 当她在用打字机打那封信时,电话响了。WhileWhilewhenwhen when 接 时间点/时间段
as 接 时间段相同点: when+ 延续V,译为“当。。。时”
as+ 延续性V,译为“ 随着 ”
(强调进展过程)
when 和as的用法区别 he left the house, I was sitting in the garden. 当他离开家时,我正在院子里坐着。 he arrived home, it was just nine o‘clock. 当他到家时,正是九点钟。 he grew older, he became more intelligent. 随着他年龄的增长,他变得更有才智了。 WhenWhenAs注意:而 as +延续性动词=
“一边。。。一边”
(不用be doing)如:He sings as he walks.
他边散步边唱歌。相同点: 都表示两个动作同时发生。
比较:
I read a book as I sing.
I am reading a book while you are singing .
while 和as的用法区别 总结:表“同时进行”
While 动词用 “be doing”
强调“两个对象的相反动作”
As 动词用 “do” 强调“一个对象的两个动作”
1.主句(含 be doing ) +when从句(含do)
2.主句(含do)+while+ (从句含 be doing )
3. while (从句含 be doing ) ,+主句(含do)总结:在某过程中发生了某事区别一般过去时与现在完成时一般过去时-----常与具体的时间状语连用,
现在完成时-----通常与时间段的状语。一般过去时的时间状语: yesterday, last week,…ago, in1980, in October, just now, 具体的时间状语
现在完成时的时间状语
for+一段时间,
since+过去时点,
so far/by now
目前为止,
ever从来,
never从来不,
yet还,
up to now到现在为止,
in past years
在过去几年内 1)动词是延续性的,
如live, teach, learn, work, study, know.
2)动词是瞬间性的,
come, go, leave, start, die, finish, become, get married现在完成时=到现在为止动作已完结动作从过去到现在为止的时间段内已完结但会持续动作从过去到现在为止的时间段内一次性完结举例:
I saw this film yesterday. (强调看的动作发生过了。) I have seen this film. (强调对现在的影响,
电影的内容已经知道了。) She has returned from Paris. 她已从巴黎回来了。 She returned yesterday. 她是昨天回来了。 现在完成时强调“已经发生/对未来有影响”区别:现在完成时
和
过去完成时过去完成时=到过去为止的一段时间内动作已完结
即在过去时间点之前发生I have seen this film .
电影的内容已经知道了。
She has returned from Paris . 她已从巴黎回来了。 by nowby nowI had seen this film .
上周之前电影的内容已经知道了。
She had returned from Paris . 她在那之前就已从巴黎回来了。 by last weekby then牢记had done常用的时间状语!!!
by the time/the end of+过去时点 到过去为止,
如 by the time I was 10.在我十岁以前
before+过去时点 到过去为止,
如 before I was 10.在我十岁以前
up to +过去时间点 到过去为止
如 up to 10:00.在十点以前(现在不止十点)
in the past years
在过去之前的几年内
中考真题演练---Where is Sally?
---She______ to Hong Kong. She______ yesterday.(深圳卷)
A. has been , left B. has gone, left
C. has been, has left D. has left, went34. —Henry, you _ _____ on the phone.
—Oh, ________. Thank you. (深圳卷)
A. are wanted; I come B. are wanted; I'm coming
C. are being wanted; I come D. are wanting; I'm coming31. —Have you________ your ticket, sir?
—No, I’m still________it. (深圳卷)
A. found; finding B. looked for; looking for
C, found; looking for D. looked for; finding36. Please tell Lin Feng _______ to turn off the lights when he _______. (深圳卷)
A. to not forget, leaves B. don’t forget, will leave
C. not forget, leaving D. not to forget, leaves40. — Kate, have you seen Bob these days?
— Yes. I saw him yesterday. We _______ each other for a few years. (深圳卷)
haven’t seen B. didn’t see
C. hadn’t seen D. often saw42. — Where is John?
— He ________ to the teacher’s office. (深圳卷)
A.has been B. has gone
C. goes D. went 28. -----This dish tastes _______.
-----Thank you. It _____ by Mr Smith. (深圳卷)
A. good, was cooked B. well, cooks
C .bad, is cooked D. terrible, cooked15.—David, turn off the TV________no one is watching it.
? —But it_______off already!
The music is from the radio. (深圳卷)
A.so that , has been turned??? B.when.has turned
C.if.has been turned??? D.because, has turned 30. ----How many students are there in your class? ----Fifty. Two-thirds of us______ from Guangdong. (深圳卷)
. A. is B. comes C. are D. coming
31. ----Would you like ______ some coffee? ----No, thanks. I _____ some. (深圳卷)
A. have, already have B. had, just bad
C. having, have yet had D. to have, have already had
享受时。。。时:动作发生时间1.时 与 体现在
过去
将来时体:动作完成的程度不强调动作完成的程度
动作未完结
动作已完结=一般体=进行体/ing=完成体/have
(时间点)
(时间段)一般体进行体完成体现
在过
去将
来2.常考的时态一般现在时一般过去时一般将来时将来进行时过去进行时现在进行时现在完成时过去完成时将来完成时一般体进行体完成体现
在过
去将
来dodidwill dowill be doingwas doingis doinghave donehad donewill have done3.具体用法一般时现
在过
去将
来dodidwill do单纯强调现在的v单纯强调过去的v单纯强调将来的v=单纯强调动作3.具体用法进行时现
在过
去将
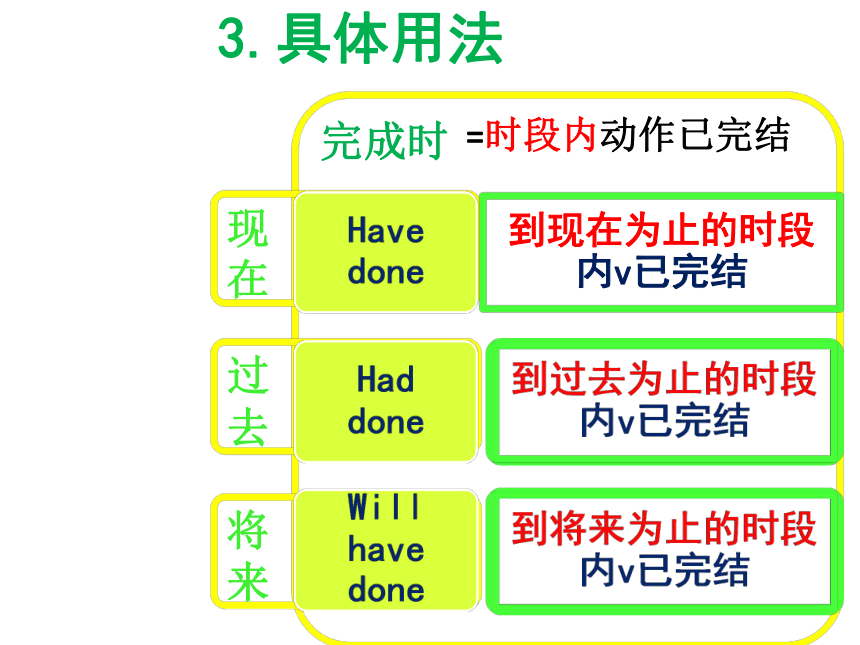
来Be doingWas doingwill be doing现在时点v未完结过去时点v未完结将来时点v未完结=时点内动作未完结3.具体用法完成时现
在过
去将
来Have doneHad doneWill have done到现在为止的时段内v已完结到过去为止的时段内v已完结到将来为止的时段内v已完结=时段内动作已完结1.一般现在时用法1)一次性的动作
2)习惯性/经常性的动作;
3)持续性的动作;
4)普遍真理
1)一次性的动作;我现在就教你。I teach you!
你就这么闯进房子了。You break into my house. 时间状语:
everyday, often,sometimes, always, on Sunday, at +时间点等
2)习惯性,经常性的动作;我总是教你。I always teach you!你有时闯进你房子。Sometimes you break into my house.
3)现在持续性的动作; 标志:
延续性动词等(系动词表“保持”:be , keep ,stay, live 等)
我是男生。I am a boy!
4)客观真题 标志:根据翻译得出永恒事实/格言警句
我是男生。I am a boy!骄者必败。
Pride goes before a fall. 地球 绕着 太阳转。 The earth moves around the sun. 注意:此用法在转述中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。She told me
Pride goes before a fall.
骄者必败。1.现在进行时用法1)正在发生的一次性的动作
2)长期习惯性/经常性的动作;
3)持续性/渐变的动作;
2.现在进行时? We are waiting for you.
1)正在发生的一次性的动作
2)长期习惯性/经常性的动作;
Mr. Green is writing another novel. (说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)与always, constantly, forever 等词连用
往往带有说话人的主观色彩。
You are always changing your mind. 表示渐变的动词有:
get, grow, become, turn等。
3)持续性/渐变的动作;1)The leaves are turning red.
2)It‘s getting warmer and warmer.
1) 事实状态的动词 have, belong, possess, cost, owe, exist, include, contain(包括), matter, weigh, measure, continue等 I have two brothers. This house belongs to my sister.
不用进行时的动词? 2) 心理状态的动词 Know, realize, think , believe, suppose, imagine, agree, recognize, remember, want, need, forget, prefer, mean, understand, love, hate等 I need your help. He loves her very much. 不用进行时的动词? 3) 瞬间动词 accept, receive, complete, finish, give, allow, decide, refuse等 I accept your advice.
不用进行时的动词?
4) 系动词 seem, remain, lie, see, hear, smell, feel, taste, get, become, turn等 You seem a little tired.
不用进行时的动词?3.一般过去时用法
1)过去习惯性,经常性的动作;
2)过去的状态与特征;
Where did you go just now? When I was a child, I often played football in the street. 区别一般过去时与过去进行时4.过去进行时用法过去进行时构成:否定式: 疑问式:was/were +doingwas/were not +doingWas/Were ……doing?比较-“同时性”
Be doing when=at or during the time that
=时间点/一段时间;
while=during the time that=一段时间总结: when+ do 瞬间V=时间点
while+ be doing 瞬间动词=时间段
when 和while的用法区别 当我到达山顶时,阳光正照耀着。
When I got to the top of the mountain, the sun was shining.他们离开车站时,正在下雨。
It was raining when they left the station.I got to the top of the mountain
while the sun was shining.
While it was raining ,they left the station.他们离开车站时,正在下雨。
It was raining when they left the station.It was going to rain when they left the station.天正要下雨时我们就离开车站了。
或 天还来不及下起雨来他们就离开车站了。注意: 主句, when … (“be doing/表将来”)(“一般时”)“来不及/正要…就…”我们正要启程这时下雨了 。We were about to leave when it rains .她来不及离开我就阻止了她。She was leaving when I stopped her . he was in London, he studied music. 当他在伦敦时,他学习音乐。 she was typing the letter, the telephone rang. 当她在用打字机打那封信时,电话响了。WhileWhilewhenwhen when 接 时间点/时间段
as 接 时间段相同点: when+ 延续V,译为“当。。。时”
as+ 延续性V,译为“ 随着 ”
(强调进展过程)
when 和as的用法区别 he left the house, I was sitting in the garden. 当他离开家时,我正在院子里坐着。 he arrived home, it was just nine o‘clock. 当他到家时,正是九点钟。 he grew older, he became more intelligent. 随着他年龄的增长,他变得更有才智了。 WhenWhenAs注意:而 as +延续性动词=
“一边。。。一边”
(不用be doing)如:He sings as he walks.
他边散步边唱歌。相同点: 都表示两个动作同时发生。
比较:
I read a book as I sing.
I am reading a book while you are singing .
while 和as的用法区别 总结:表“同时进行”
While 动词用 “be doing”
强调“两个对象的相反动作”
As 动词用 “do” 强调“一个对象的两个动作”
1.主句(含 be doing ) +when从句(含do)
2.主句(含do)+while+ (从句含 be doing )
3. while (从句含 be doing ) ,+主句(含do)总结:在某过程中发生了某事区别一般过去时与现在完成时一般过去时-----常与具体的时间状语连用,
现在完成时-----通常与时间段的状语。一般过去时的时间状语: yesterday, last week,…ago, in1980, in October, just now, 具体的时间状语
现在完成时的时间状语
for+一段时间,
since+过去时点,
so far/by now
目前为止,
ever从来,
never从来不,
yet还,
up to now到现在为止,
in past years
在过去几年内 1)动词是延续性的,
如live, teach, learn, work, study, know.
2)动词是瞬间性的,
come, go, leave, start, die, finish, become, get married现在完成时=到现在为止动作已完结动作从过去到现在为止的时间段内已完结但会持续动作从过去到现在为止的时间段内一次性完结举例:
I saw this film yesterday. (强调看的动作发生过了。) I have seen this film. (强调对现在的影响,
电影的内容已经知道了。) She has returned from Paris. 她已从巴黎回来了。 She returned yesterday. 她是昨天回来了。 现在完成时强调“已经发生/对未来有影响”区别:现在完成时
和
过去完成时过去完成时=到过去为止的一段时间内动作已完结
即在过去时间点之前发生I have seen this film .
电影的内容已经知道了。
She has returned from Paris . 她已从巴黎回来了。 by nowby nowI had seen this film .
上周之前电影的内容已经知道了。
She had returned from Paris . 她在那之前就已从巴黎回来了。 by last weekby then牢记had done常用的时间状语!!!
by the time/the end of+过去时点 到过去为止,
如 by the time I was 10.在我十岁以前
before+过去时点 到过去为止,
如 before I was 10.在我十岁以前
up to +过去时间点 到过去为止
如 up to 10:00.在十点以前(现在不止十点)
in the past years
在过去之前的几年内
中考真题演练---Where is Sally?
---She______ to Hong Kong. She______ yesterday.(深圳卷)
A. has been , left B. has gone, left
C. has been, has left D. has left, went34. —Henry, you _ _____ on the phone.
—Oh, ________. Thank you. (深圳卷)
A. are wanted; I come B. are wanted; I'm coming
C. are being wanted; I come D. are wanting; I'm coming31. —Have you________ your ticket, sir?
—No, I’m still________it. (深圳卷)
A. found; finding B. looked for; looking for
C, found; looking for D. looked for; finding36. Please tell Lin Feng _______ to turn off the lights when he _______. (深圳卷)
A. to not forget, leaves B. don’t forget, will leave
C. not forget, leaving D. not to forget, leaves40. — Kate, have you seen Bob these days?
— Yes. I saw him yesterday. We _______ each other for a few years. (深圳卷)
haven’t seen B. didn’t see
C. hadn’t seen D. often saw42. — Where is John?
— He ________ to the teacher’s office. (深圳卷)
A.has been B. has gone
C. goes D. went 28. -----This dish tastes _______.
-----Thank you. It _____ by Mr Smith. (深圳卷)
A. good, was cooked B. well, cooks
C .bad, is cooked D. terrible, cooked15.—David, turn off the TV________no one is watching it.
? —But it_______off already!
The music is from the radio. (深圳卷)
A.so that , has been turned??? B.when.has turned
C.if.has been turned??? D.because, has turned 30. ----How many students are there in your class? ----Fifty. Two-thirds of us______ from Guangdong. (深圳卷)
. A. is B. comes C. are D. coming
31. ----Would you like ______ some coffee? ----No, thanks. I _____ some. (深圳卷)
A. have, already have B. had, just bad
C. having, have yet had D. to have, have already had
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
