2022届高考英语谓语动词时态与语态课件(25张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2022届高考英语谓语动词时态与语态课件(25张) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 27.6MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-07-31 14:30:46 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共25张PPT)
谓语动词时态语态
老师:Fayre
教学时间:2022/06/07
目录
Contents
时态的种类与结构
part
易混时态的区别与运用
part
常见的固定时态
part
谓语动词的语态
part
01
02
03
04
时态的种类与结构
part
01
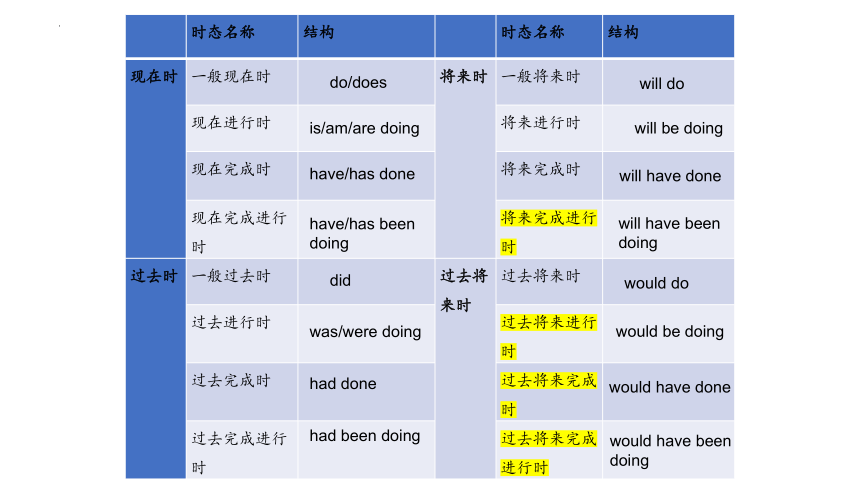
时态名称 结构 时态名称 结构
现在时 一般现在时 将来时 一般将来时
现在进行时 将来进行时
现在完成时 将来完成时
现在完成进行时 将来完成进行时
过去时 一般过去时 过去将来时 过去将来时
过去进行时 过去将来进行时
过去完成时 过去将来完成时
过去完成进行时 过去将来完成进行时
do/does
is/am/are doing
have/has done
have/has been doing
did
was/were doing
had done
had been doing
will do
will be doing
will have done
will have been doing
would do
would be doing
would have done
would have been doing
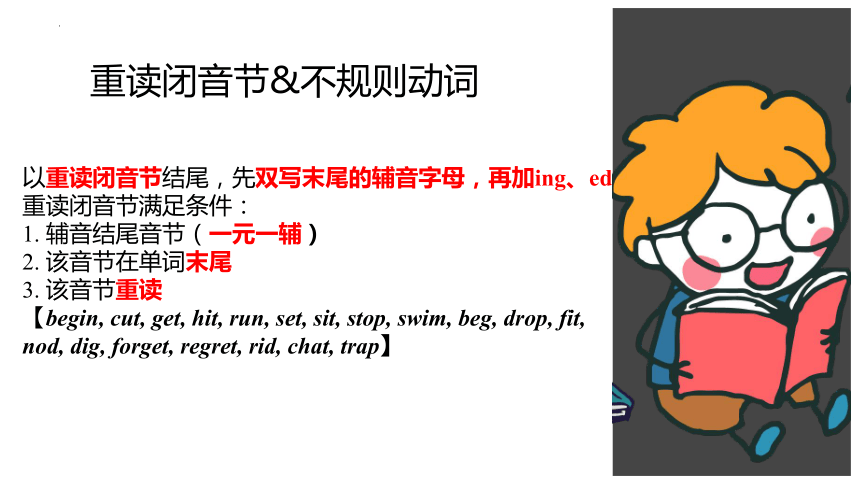
重读闭音节&不规则动词
以重读闭音节结尾,先双写末尾的辅音字母,再加ing、ed
重读闭音节满足条件:
1. 辅音结尾音节(一元一辅)
2. 该音节在单词末尾
3. 该音节重读
【begin, cut, get, hit, run, set, sit, stop, swim, beg, drop, fit,
nod, dig, forget, regret, rid, chat, trap】
易混时态区别与运用
part
02
一般现在时的用法
经常发生或反复发生的动作
现阶段的情况或状态
客观事实,普遍真理,格言警句。
在时间、条件、让步状语从句中,用一般现在时代替一般将来时(主将从现)
表示按时刻表发生的事情用一般现在时表将来
1) 在时间、条件、让步状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来 (主将从现)
a. If he comes this afternoon, we’ll have a further discussion. (come)
b. When I graduate from college, I will travel around the world. (graduate)
2) 按计划、规定要发生的动作;按时刻表发生的事情,用一般现在时表示将来
a. The shopping mall opens at 10:00 a.m.(open)
b. The train leaves at 9:20 in the morning. (leave)
现在进行时
1. 现在进行时与always, continually , constantly, 等连用,表示厌恶或赞扬的感彩
a. The lazy person is always complaining about life.
b. You are always forgetting the important things.
2. 现在进行时表将来,短暂性动词如come, go, leave, arrive
e.g. I am leaving for New York next week.
现在完成时
常与already, so far, since, up to now, “in the last/past + 一段时间”等连用。
e.g. I have made much progress in math in the last three months.
Shelly _____ California for Texas in 1996 and ____ there ever since.
left, worked B. has left, had worked
C. left, has worked D. has left , worked
表示过去某一动作状态一直持续到现在,也可能将持续下去。
现在完成进行时
a. I have thought it over.
b. I have been thinking it over.
c. It has rained for two weeks.
d. It has been raining for two weeks.
e. Jim has painted the door.
f. He has been painting the door.
注意:现在完成时 VS 现在完成进行时:
a. I saw this movie yesterday.
b. I have seen this movie.
c. He laid the table this morning.
d. He has laid the table.
e. Eventually, he recovered from the disease.
f. He has recovered from the disease.
注意:一般过去时 VS 现在完成时:
过去完成时
表示在过去某一时刻或动作之前已经完成了的动作,即“过去的过去”。
They had got everything ready before I came. (get)
2. By the end of last week she had written two papers. (write)
By the time he got there, his friends had moved up north. (move)
表示将来时的四种形式
①will /shall +动词原形
②am/is/are going to do
③am/is/are about to do
④am/is/are to do
1. I am going to buy a new laptop this winter.
I am to take over the job.
The conference is about to begin.
一般将来时的用法
临时
计划
马上
预先安排好的;义务;命令;注定发生
1. —The telephone is ringing.
—I _____ answer it.
will B. am going to C. am to D. am about to
2. —Alice, why didn’t you come yesterday
—I _____, but I had an unexpected visitor.
A. had B. would C. was going to D. did
3. You ______________in the living room.(smoke)
4. I _____________set out when it rained.
are not to smoke
was about to
表示将来时的四种形式?
He said that he would wait for us at the bus stop.
She hoped that they would meet again someday.
过去将来时的用法
would / should do
常用的固定时态
part
03
常用的固定时态
This is the first time that I have finished through my homework on time.
This is the first time that he has finished through his homework on time.
This was the first time that I had finished through my homework on time. (finish)
it/this/that + be + the+序数词+time + that从句
常用的固定时态
1. It will be/ was + 时间段 + before...还有多长时间才...
2. It won’t/wasn’t + 时间段 + before...要不了多久就…
a. It was some time before the door opened in response to his ring.
b. It will be 2 days before the task is accomplished.
a. By the end of last week she had written two papers. (write)
b. By the time he got there, his friends had moved up north. (move)
c. By the end of 2023, the world’s population will have reached 8 billion.
d. By the time I retire, I will have taught English for 40 years.
1. By+ 时间点(现在/将来),主句用将来完成时
2. By+ 时间点(过去),主句用过去完成时
常用的固定时态
Hardly had... when... 一...就...
Scarcely had...when...
No sooner had...than...
Hardly had I arrived in Beijing when I rang up my father.
Scarcely had I reached home when it began to rain.
No sooner had I got to the bus stop than the bus started.
谓语动词的语态
part
04
主动表被动的常用形式
1. 系动词look, sound, feel, smell, taste, appear, seem, go, prove, turn, stay, become, fall, get, grow, keep + 形容词/名词构成系表结构。
e.g. The cake looks tasty.
The price sounds reasonable.
2. 表示主语的某种属性特征的不及物动词,如read, write, sell, wash, clean, wear, open, cook, lock, shut等。
e.g. The novel sells very well.
The pen doesn’t write well.
3.动词want, need, require, deserve, worth后接to be done等于接doing。
want to be done = want doing,need to be done = need doing
e.g. The bicycle needs to be repaired/repairing.
主动表被动的常用形式
1. 系动词look, sound, feel, smell, taste, appear, seem, go, prove, turn, stay, become, fall, get, grow, keep + 形容词/名词构成系表结构。
e.g. The cake looks tasty.
The price sounds reasonable.
2. 表示主语的某种属性特征的不及物动词,如read, write, sell, wash, clean, wear, open, cook, lock, shut等。
e.g. The novel sells very well.
The pen doesn’t write well.
3.动词want, need, require, deserve, worth后接to be done等于接doing。
want to be done = want doing,need to be done = need doing
e.g. The bicycle needs to be repaired/repairing.
感谢大家的聆听
老师:Fayre
教学时间:2022/06/07
附赠图标
谓语动词时态语态
老师:Fayre
教学时间:2022/06/07
目录
Contents
时态的种类与结构
part
易混时态的区别与运用
part
常见的固定时态
part
谓语动词的语态
part
01
02
03
04
时态的种类与结构
part
01
时态名称 结构 时态名称 结构
现在时 一般现在时 将来时 一般将来时
现在进行时 将来进行时
现在完成时 将来完成时
现在完成进行时 将来完成进行时
过去时 一般过去时 过去将来时 过去将来时
过去进行时 过去将来进行时
过去完成时 过去将来完成时
过去完成进行时 过去将来完成进行时
do/does
is/am/are doing
have/has done
have/has been doing
did
was/were doing
had done
had been doing
will do
will be doing
will have done
will have been doing
would do
would be doing
would have done
would have been doing
重读闭音节&不规则动词
以重读闭音节结尾,先双写末尾的辅音字母,再加ing、ed
重读闭音节满足条件:
1. 辅音结尾音节(一元一辅)
2. 该音节在单词末尾
3. 该音节重读
【begin, cut, get, hit, run, set, sit, stop, swim, beg, drop, fit,
nod, dig, forget, regret, rid, chat, trap】
易混时态区别与运用
part
02
一般现在时的用法
经常发生或反复发生的动作
现阶段的情况或状态
客观事实,普遍真理,格言警句。
在时间、条件、让步状语从句中,用一般现在时代替一般将来时(主将从现)
表示按时刻表发生的事情用一般现在时表将来
1) 在时间、条件、让步状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来 (主将从现)
a. If he comes this afternoon, we’ll have a further discussion. (come)
b. When I graduate from college, I will travel around the world. (graduate)
2) 按计划、规定要发生的动作;按时刻表发生的事情,用一般现在时表示将来
a. The shopping mall opens at 10:00 a.m.(open)
b. The train leaves at 9:20 in the morning. (leave)
现在进行时
1. 现在进行时与always, continually , constantly, 等连用,表示厌恶或赞扬的感彩
a. The lazy person is always complaining about life.
b. You are always forgetting the important things.
2. 现在进行时表将来,短暂性动词如come, go, leave, arrive
e.g. I am leaving for New York next week.
现在完成时
常与already, so far, since, up to now, “in the last/past + 一段时间”等连用。
e.g. I have made much progress in math in the last three months.
Shelly _____ California for Texas in 1996 and ____ there ever since.
left, worked B. has left, had worked
C. left, has worked D. has left , worked
表示过去某一动作状态一直持续到现在,也可能将持续下去。
现在完成进行时
a. I have thought it over.
b. I have been thinking it over.
c. It has rained for two weeks.
d. It has been raining for two weeks.
e. Jim has painted the door.
f. He has been painting the door.
注意:现在完成时 VS 现在完成进行时:
a. I saw this movie yesterday.
b. I have seen this movie.
c. He laid the table this morning.
d. He has laid the table.
e. Eventually, he recovered from the disease.
f. He has recovered from the disease.
注意:一般过去时 VS 现在完成时:
过去完成时
表示在过去某一时刻或动作之前已经完成了的动作,即“过去的过去”。
They had got everything ready before I came. (get)
2. By the end of last week she had written two papers. (write)
By the time he got there, his friends had moved up north. (move)
表示将来时的四种形式
①will /shall +动词原形
②am/is/are going to do
③am/is/are about to do
④am/is/are to do
1. I am going to buy a new laptop this winter.
I am to take over the job.
The conference is about to begin.
一般将来时的用法
临时
计划
马上
预先安排好的;义务;命令;注定发生
1. —The telephone is ringing.
—I _____ answer it.
will B. am going to C. am to D. am about to
2. —Alice, why didn’t you come yesterday
—I _____, but I had an unexpected visitor.
A. had B. would C. was going to D. did
3. You ______________in the living room.(smoke)
4. I _____________set out when it rained.
are not to smoke
was about to
表示将来时的四种形式?
He said that he would wait for us at the bus stop.
She hoped that they would meet again someday.
过去将来时的用法
would / should do
常用的固定时态
part
03
常用的固定时态
This is the first time that I have finished through my homework on time.
This is the first time that he has finished through his homework on time.
This was the first time that I had finished through my homework on time. (finish)
it/this/that + be + the+序数词+time + that从句
常用的固定时态
1. It will be/ was + 时间段 + before...还有多长时间才...
2. It won’t/wasn’t + 时间段 + before...要不了多久就…
a. It was some time before the door opened in response to his ring.
b. It will be 2 days before the task is accomplished.
a. By the end of last week she had written two papers. (write)
b. By the time he got there, his friends had moved up north. (move)
c. By the end of 2023, the world’s population will have reached 8 billion.
d. By the time I retire, I will have taught English for 40 years.
1. By+ 时间点(现在/将来),主句用将来完成时
2. By+ 时间点(过去),主句用过去完成时
常用的固定时态
Hardly had... when... 一...就...
Scarcely had...when...
No sooner had...than...
Hardly had I arrived in Beijing when I rang up my father.
Scarcely had I reached home when it began to rain.
No sooner had I got to the bus stop than the bus started.
谓语动词的语态
part
04
主动表被动的常用形式
1. 系动词look, sound, feel, smell, taste, appear, seem, go, prove, turn, stay, become, fall, get, grow, keep + 形容词/名词构成系表结构。
e.g. The cake looks tasty.
The price sounds reasonable.
2. 表示主语的某种属性特征的不及物动词,如read, write, sell, wash, clean, wear, open, cook, lock, shut等。
e.g. The novel sells very well.
The pen doesn’t write well.
3.动词want, need, require, deserve, worth后接to be done等于接doing。
want to be done = want doing,need to be done = need doing
e.g. The bicycle needs to be repaired/repairing.
主动表被动的常用形式
1. 系动词look, sound, feel, smell, taste, appear, seem, go, prove, turn, stay, become, fall, get, grow, keep + 形容词/名词构成系表结构。
e.g. The cake looks tasty.
The price sounds reasonable.
2. 表示主语的某种属性特征的不及物动词,如read, write, sell, wash, clean, wear, open, cook, lock, shut等。
e.g. The novel sells very well.
The pen doesn’t write well.
3.动词want, need, require, deserve, worth后接to be done等于接doing。
want to be done = want doing,need to be done = need doing
e.g. The bicycle needs to be repaired/repairing.
感谢大家的聆听
老师:Fayre
教学时间:2022/06/07
附赠图标
