2023年中考英语语法复习专题课件--动词的分类(共24张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023年中考英语语法复习专题课件--动词的分类(共24张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 454.6KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-08-02 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共24张PPT)
专题八 动词的分类
考察内容
动词的分类→实义动词+助动词+情态动词+系动词
动词的基本形式→动词原形+第三人称单数+过去式+过去分词+现在分词
易混动词辨析→spend,cost,take 与pay等易混词的区别
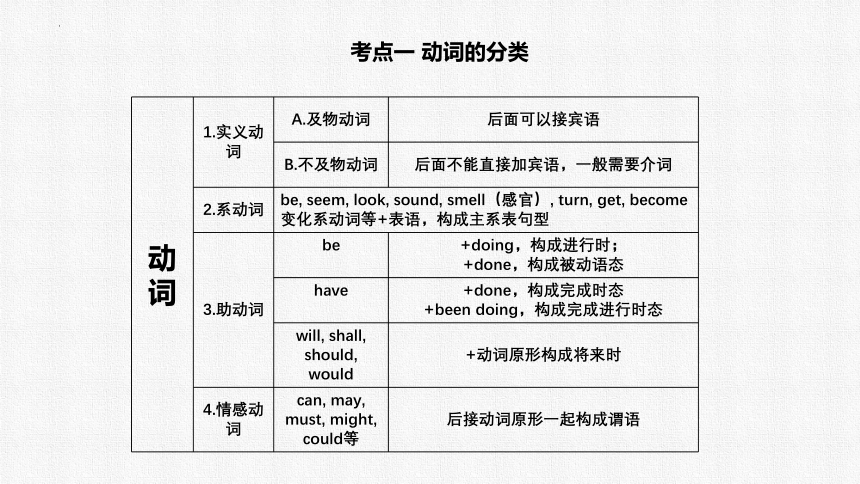
考点一 动词的分类
动词 1.实义动词 A.及物动词 后面可以接宾语
B.不及物动词 后面不能直接加宾语,一般需要介词
2.系动词 be, seem, look, sound, smell(感官), turn, get, become变化系动词等+表语,构成主系表句型
3.助动词 be +doing,构成进行时;
+done,构成被动语态
have +done,构成完成时态
+been doing,构成完成进行时态
will, shall, should, would +动词原形构成将来时
4.情感动词 can, may, must, might, could等 后接动词原形一起构成谓语
考点一 动词的分类
1.实义动词:也称行为动词,是唯一能独立作谓语的一类动词,可以分为及物动词和不及物动词两类。
<1>及物动词:身意义不够完整,需要后接宾语才能使其意思完整。
①动词+宾语,构成主谓宾句型。
eg:We learn English every day. 我们每天学习英语。
②动词+直接宾语+to/for+间接宾语 = 动词+间接宾语+直接宾语,构成主谓双宾句型。有的动词必须在后面带表示人的间接宾语和表示物的直接宾语,即两个宾语才能表达完整的意思。
例如: Please pass me the book.= Please pass the book to me.请把那本书递给我。
My mother bought (buy)me a snow globe on my birthday.= My mother bought a snow globe for me on my birthday.
常见的带双宾语的动词有:pass, give, bring, buy, get, leave, lend, make, cook, teach, tell, write, read, return, ask, show等。
③动词+宾语+宾语补足语,构成主谓复宾句型。有的动词必须在宾语后再加上形容词、副词、名词、不定式、-ing形式、介词短语等做宾语补足语,构成复合宾语,句子意思才能够表达完整。
例如:Please keep the door open. 请让门开着。(形容词open做宾补)
考点一 动词的分类
<2>不及物动词:
①自身意思完整,无需再接宾语。
eg: Horses run fast。马儿跑得快。quickly
He sings well. 他唱得好。
②很多不及物动词也可以用作及物动词,还有的不及物动词后带上某个介词就成了带宾语的及物动词。
eg:They are reading. 他们在朗读。(read为不及物动词)
They are reading English. 他们在朗读英语。(read为及物动词)
考点一 动词的分类
2.连系动词:本身有词义,但不能单独作谓语,必须和其后面的表语一起构成合成谓语,说明主语的性质、特征、状态或身份。
常见的连系动词有be, become(变得、成为), get(变得), look(看起来),seem(似乎、好像),turn(变得),sound(听起来),smell(闻起来),taste(尝起来),feel(摸起来)等。
注:除be以外的连系动词大多数时候是实义动词,他们用作连系动词时多数没有进行时态,也没有被动语态。
例如:He is angry.他生气了。
He got angry at the news.听到这个消息他生气了。
That sounds good.那听起来不错。
Trees turn green when spring comes.春天来临,树叶转绿。
China is getting stronger and stronger.中国正变得越来越强大。
考点一 动词的分类
3.助动词:本身没有词义或意思不完整,不能单独作谓语。它们的主要作用是帮助构成时态、语态、疑问句或否定句等。
<1>助动词be(am, is, are, was, were)
① be+doing(现在分词), 构成进行时
eg:They are listening to music.他们在听音乐。(be的现在时形式帮助构成现在进行时)
They were walking down the street when the UFO landed.(be的过去时形式帮助构成过去进行时)
②be+done(及物动词的过去分词), 构成被动语态
例如:The light bulb was invented by Thomas Edison.(be的过去时形式帮助构成过去时的被动语态)
The classroom is cleaned every day.教室每天打扫。(be的现在时形式帮助构成现在时的被动语态)
The problem will be solved next week.(be的将来时形式帮助构成将来时的被动语态)
考点一 动词的分类
<2>have (has, had)
①have/has/had+done(动词的过去分词),构成完成时态。
eg:They have already done their homework.他们已经完成作业。(have+过去分词构成现在完成时)
He hasn’t come yet.他还没有回来。(has+过去分词构成现在完成时)
The bus had gone when I got to the bus stop.我到达车站时公交车已经离开。(had+过去分词构成过去完成时)
②have/has/had+been+doing(动词的现在分词),构成完成进行时态。
例如:How long have you been collecting shells 你收集贝壳有多长时间了?
<3>助动词do/ does/ did:主要帮助构成疑问句,也可用于倒装句、强调句或代替上文提到过的行为等。他们的否定式don’t/ doesn’t/ didn’t帮助构成否定句。
例如:He often plays sports after school. Does he often play。。。
We don’t speak Japanese.我们不说日语。
Did they visit the Palace Museum on their last day off 他们上个休息日参观故宫了吗?
She didn’t watch TV yesterday evening.她昨晚上没看电视。
考点一 动词的分类
<4>助动词will, shall, would, should:构成一般将来时,其中will可用于各人称,而shall一般只用于第一人称。would,should是will,shall的过去式,可以用于构成过去将来时,但很多时候被用作情态动词。
eg:There will be more trees and less pollution in the future.将来会有更多的树木,更少的污染。(帮助构成一般将来时)
考点一 动词的分类
4.情态动词:表示说话者的情感、态度和语气,但没有人称和数的变化,不能单独作谓语,须和动词一起构成句子的谓语。表示否定时在情态动词后加not (must,have to除外),表示疑问时将情态动词提至主语前即可。
<1>can 与could
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
can (could) 表示能力(= be able to) 能;会 Tom can swim.
=Tom is able to swim.
汤姆会游泳。
(疑问句中)表示请求 可以 Could you give us a hand
你可以帮我们一下吗?
(否定句、疑问句中)表示可能性 can可能 can’t不可能 The boy can’t be Jim. He’s much taller.
这个男孩不可能是吉姆。他要高很多。
区分can 与be able to
表示某种能力时,二者可通用;
can只用于现在时和过去时;be able to可用于各种时态;
遇有助动词或情态动词时只能用be able to。
tom was able to swim
tom will be able to swim
would you
考点一 动词的分类
区分maybe 与may be
maybe用于句首表示“可能;也许”,相当于perhaps;
may be中的may是情态动词,后接动词原形be,表示“可能是”,在句中作谓语。两者可互换。
eg:Maybe the boy is from Canada.
=The boy may be from Canada.
那个男孩可能来自加拿大。
<2>may与might
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
may (might) 表示可能性(可与maybe互换) 可能 Tony may know the way. =Maybe Tony knows the way.
托尼可能知道路。
表示客气请求 可以 May I come in
我可以进来吗?
表示祝愿 祝…… May you be happy!
祝你快乐!
考点一 动词的分类
<3>shall与should
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
shall (should) Shall. . . 用于第一人称,表示建议或请求 ……好 吗? Shall we ask the teacher for help
我们向老师寻求帮助好吗?
should用于各种人称,强调义务或责任 应该 Students shouldn’t have long hair.
学生们不应该留长发。
考点一 动词的分类
<4>must
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
must 表示义务、命令或要求 必须 We must tell the truth to our parents.
我们必须告诉父母真相。
表示肯定的猜测(否定猜测用can’t/mustn’t ) 一定 Lisa must be at home.
莉萨一定在家里。
(推测现在的状况)
You must be kidding!
你一定是在开玩笑!(推测现在正在发生的状况)
They must have seen the movie. 现在完成时
他们一定看过这部电影。
(推测过去的状况)
区分have to 与must
have to主要表示客观需要,意为“不得不”。有人称和时态的变化(has to; had to; will have to);
must强调说话人的主观看法,意为“必须;应该”;
(3)否定形式的不同:mustn’t表示“禁止;不应该”;not have to表示“不必”,相当于needn’t。
考点一 动词的分类
<5>will 与would
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
will (would) 用于第二人称疑问句中,表示征求意见或提建议 愿意 Will/Would you please take out the trash
你可以把垃圾拿出去吗?
will用于各种人称,表示意愿 Your parents will try their best to help you.
你的父母会尽最大努力帮助你。
考点一 动词的分类
【补】1.mustn’t表示否定意义“禁止,不允许”。可与祈使句互换。例如:
You mustn’t play football in the street.
=Don’t play football in the street.
2.have to有人称、数和时态的变化,表示受客观条件限制,意为“不得不”。例如:
She had to take the bus to work.
她不得不坐公交车去上班。
3.May. . . 句式的否定回答:No, . . . mustn’t/can’t.
Must. . . 句式的否定回答:No, . . . needn’t.
①—May I smoke here ——我可以在这儿吸烟吗?
—No, you mustn’t. ——不,你不准。/no, you can’t
②—Must I go now ——我必须现在走吗?
—No, you needn’t. /——不,你没必要。
4.must,should,may,might都可以表示“可以”,可能性程度由大到小依次为:must﹥should﹥may﹥might。
考点二 动词的五种基本形式
形式 用法 例句
原形 1.用在情态动词can, may ,must,should,would,have to 等词之后 You can borrow my bike.
2.用在助动词do,does,did,will,shall之后 What do you think of China
3.用在祈使句句首 Close the door, please.
4. 用在使役动词(make,let等)、感官动词(watch,feel等)之后 She made us laugh.
5.用在动词不定式符号to之后 My teacher asked us to clean the classroom.
第三人称单数 用在第三人称单数(形式)主语之后, 句子的时态为一般现在时 He studies English hard.
过去式 用于一般过去时 She looked at me happily.
过去分词 用于完成时态或被动语态中 He had finished his homework.
现在分词/动名词 现在分词用于进行时,动名词起名词作用 The girl is singing now.
考点三 易混词辨析
1. be used to doing sth, used to do sth和be used to do sth 区别
2.arrive,get 和rich的区别
易混词组 用法 例句
be used to doing sth 习惯做某事,to后接ing形式 I am used to getting up early.
我习惯早起。
used to do sth 过去常常做某事 I used to get up at six in the morning.
我过去常常在早上六点起床。
be used to do sth 被用来做某事 Wood is used to make paper.
木材被用来造纸。
易混词组 用法 例句
arrive in 后面接大地点 When did you arrive in Beijing?
arrive at 后面接小地点 We arrived at the village at five in the afternoon.
get to 后面跟地点名词 How do you usually get to school?
reach 是及物动词,后面直接跟地点名词 When she reached the office, the teacher was having a short rest.
考点三 易混词辨析
3. borrow,lend 与keep区别
4.die,dead,death和dying的区别
易混词 用法 例句
borrow 意为“借入”,borrow sth. from sb I borrowed a book from my friend yesterday.
昨天我从我朋友借了一本书。
lend 意为“借出”,lend sth to sb Can you lend you pen to me?
你能借我一支钢笔吗?
keep 意为“保存,借”,延续性动作,“长时间借” How long can we keep the book?
我们能够借这本书多久呢?
易混词 用法 例句
die 不及物动词,意为“死”,短暂性动作 Her grandfather died last year.
dead 形容词,意为“死的”,表示状态 Her grandfather has been died for two years.
death 名词,意为“死亡” His death was a great loss to China.
dying 形容词,意为“垂死的” The poor old man was dying.
考点三 易混词辨析
5.lose,forget 与leave区别
6.spend,cost,take和pay的区别
易混词 用法 例句
lose 意为“丢失,失去” I lose my watch.我的手表丢了。
forget 意为“忘记”,forget to do sth I forget your name.我忘记你的名字。
leave 意为“落在”,leave sth +地点状语 I left my watch at home. 我把我的手表落在家。
易混词 用法 例句
spend 主语为人 ① spend 时间/金钱 (in)doing sth ②spend 时间/金钱 on sth They spent two years in building this bridge.
cost 主语为 物,It costs/cost 金钱 to do sth. It costs fve thousand to buy this computer.
take 主语为物,It takes/ took 时间 to do sth. It took ten days to do this toy.
pay 与介词 for 连用 I have to pay them 20 pounds fir this room each month.
考点三 易混词辨析
5. join, take part in 与attend区别
6.wear,put on, have on 和dress的区别
易混词 用法 例句
join 一般加入党派或组织,如参军,入党 When did you brother join the army?
你哥哥什么时候参军呢?
take part in 指参加聚会或活动 We will take join in social practice during the summer vacation. 暑假期间我们期间我们将要参加社会实践。
attend 一般指出席会议 He’ ll attend an important meeting tomorrow.
他明天要参加一个重要的会议。
易混词 用法 例句
wear 强调穿的状态 He was wearing a dark suit.
put on 强调穿的动作 He put on his best clothes for the party.
have on 意为“穿着”,强调穿的状态 Mary had on her new dress.
dress 意为“某人给自己穿衣服” She dressed herself in her Sunday best.
练一练
1. You _______ stop when the traffic light turns red.
A. can B. had better +动词原形 C. need D. must
【解析】选D。must是“必须,不得不”,根据下文出现的when the traffic light turns red可知是“你必须……”。
2. —Is that girl under the tree Mary
—No, that _______ be Mary. She is in New York.
A. can B. mustn’t C. can’t
【解析】选C。由答语“她在纽约。”可知,那个女孩不可能是玛丽,故用can’t。
3. —Mr. Wang, can I finish my homework tomorrow
—Sorry, you _______.
A. can’t B. don’t C. needn’t D. won’t
【解析】选A。can’t“不能”,don’t“不”,needn’t“不需要”,won’t为will not的缩写“将不会”。根据问句“王老师,我能明天完成作业吗?”可知回答应为“对不起,你不能。”故选A。
4. —Dad, can I go to the movies tonight
—Sure, but you _______ come back home before 9 o’clock.
A. can B. must C. may D. might
【解析】选B。句意:——爸爸,今晚我可以去看电影吗?——当然,但是你必须在9点之前回家。can 表示“能;会”;must 表示“必须”;may和might表示“可以”,故选B。
5. — Mom, must I finish my homework now
— No, you _______. You may have supper first.
A. mustn’t B. needn’t C. can’t
【解析】选B。句意:——妈妈,我现在必须完成家庭作业吗?——不,你不需要。你可以先吃饭。对must引导的一般疑问句,否定回答时常用No, . . . needn’t, 故选B。
6. —Will you stay for some more days
—Sorry, I ______. My mother called to ask me to go back at once.
A. mustn’t B. may not
C. can’t D. wouldn’t
【解析】选C。句意:——你再待几天好吗?——对不起,我不能。我的母亲打电话让我马上回去。mustn’t“禁止”;may not“可能不”;wouldn’t“不愿做……,将要不……”。故选C。
7. —Shall we take a taxi
—No, we _______. It’s not far from here.
A. can’t B. mustn’t
C. shouldn’t D. needn’t
【解析】选D。由答语“它离这儿不远。”可知没必要乘出租车。故选D。
8. —Must I get up early tomorrow morning
—No, _______.
A. you mustn’t B. I don’t think you have to
C. you can’t D. you need
【解析】选B。情态动词must引导的一般疑问句的否定答语为“No, sb. needn’t. / No, sb. don’t/doesn’t have to. ”故选B。
9. It rained heavily, so we _______ stay at home watching TV or surfing the Internet all day.
A. could B. had to C. must
【解析】选B。外面下雨是待在家里的客观原因,故答案为B项。
10. —You _______ be excited that you’re going back to your hometown soon.
—Yes, I can’t wait any longer.
A. shall B. can C. need D. must
【解析】选D。由答语“是的,我不能再等待了。”可知,上一句应该是“你一定很兴奋,你不久将回到你的家乡。”must“一定”,表示有把握的肯定推测。
专题八 动词的分类
考察内容
动词的分类→实义动词+助动词+情态动词+系动词
动词的基本形式→动词原形+第三人称单数+过去式+过去分词+现在分词
易混动词辨析→spend,cost,take 与pay等易混词的区别
考点一 动词的分类
动词 1.实义动词 A.及物动词 后面可以接宾语
B.不及物动词 后面不能直接加宾语,一般需要介词
2.系动词 be, seem, look, sound, smell(感官), turn, get, become变化系动词等+表语,构成主系表句型
3.助动词 be +doing,构成进行时;
+done,构成被动语态
have +done,构成完成时态
+been doing,构成完成进行时态
will, shall, should, would +动词原形构成将来时
4.情感动词 can, may, must, might, could等 后接动词原形一起构成谓语
考点一 动词的分类
1.实义动词:也称行为动词,是唯一能独立作谓语的一类动词,可以分为及物动词和不及物动词两类。
<1>及物动词:身意义不够完整,需要后接宾语才能使其意思完整。
①动词+宾语,构成主谓宾句型。
eg:We learn English every day. 我们每天学习英语。
②动词+直接宾语+to/for+间接宾语 = 动词+间接宾语+直接宾语,构成主谓双宾句型。有的动词必须在后面带表示人的间接宾语和表示物的直接宾语,即两个宾语才能表达完整的意思。
例如: Please pass me the book.= Please pass the book to me.请把那本书递给我。
My mother bought (buy)me a snow globe on my birthday.= My mother bought a snow globe for me on my birthday.
常见的带双宾语的动词有:pass, give, bring, buy, get, leave, lend, make, cook, teach, tell, write, read, return, ask, show等。
③动词+宾语+宾语补足语,构成主谓复宾句型。有的动词必须在宾语后再加上形容词、副词、名词、不定式、-ing形式、介词短语等做宾语补足语,构成复合宾语,句子意思才能够表达完整。
例如:Please keep the door open. 请让门开着。(形容词open做宾补)
考点一 动词的分类
<2>不及物动词:
①自身意思完整,无需再接宾语。
eg: Horses run fast。马儿跑得快。quickly
He sings well. 他唱得好。
②很多不及物动词也可以用作及物动词,还有的不及物动词后带上某个介词就成了带宾语的及物动词。
eg:They are reading. 他们在朗读。(read为不及物动词)
They are reading English. 他们在朗读英语。(read为及物动词)
考点一 动词的分类
2.连系动词:本身有词义,但不能单独作谓语,必须和其后面的表语一起构成合成谓语,说明主语的性质、特征、状态或身份。
常见的连系动词有be, become(变得、成为), get(变得), look(看起来),seem(似乎、好像),turn(变得),sound(听起来),smell(闻起来),taste(尝起来),feel(摸起来)等。
注:除be以外的连系动词大多数时候是实义动词,他们用作连系动词时多数没有进行时态,也没有被动语态。
例如:He is angry.他生气了。
He got angry at the news.听到这个消息他生气了。
That sounds good.那听起来不错。
Trees turn green when spring comes.春天来临,树叶转绿。
China is getting stronger and stronger.中国正变得越来越强大。
考点一 动词的分类
3.助动词:本身没有词义或意思不完整,不能单独作谓语。它们的主要作用是帮助构成时态、语态、疑问句或否定句等。
<1>助动词be(am, is, are, was, were)
① be+doing(现在分词), 构成进行时
eg:They are listening to music.他们在听音乐。(be的现在时形式帮助构成现在进行时)
They were walking down the street when the UFO landed.(be的过去时形式帮助构成过去进行时)
②be+done(及物动词的过去分词), 构成被动语态
例如:The light bulb was invented by Thomas Edison.(be的过去时形式帮助构成过去时的被动语态)
The classroom is cleaned every day.教室每天打扫。(be的现在时形式帮助构成现在时的被动语态)
The problem will be solved next week.(be的将来时形式帮助构成将来时的被动语态)
考点一 动词的分类
<2>have (has, had)
①have/has/had+done(动词的过去分词),构成完成时态。
eg:They have already done their homework.他们已经完成作业。(have+过去分词构成现在完成时)
He hasn’t come yet.他还没有回来。(has+过去分词构成现在完成时)
The bus had gone when I got to the bus stop.我到达车站时公交车已经离开。(had+过去分词构成过去完成时)
②have/has/had+been+doing(动词的现在分词),构成完成进行时态。
例如:How long have you been collecting shells 你收集贝壳有多长时间了?
<3>助动词do/ does/ did:主要帮助构成疑问句,也可用于倒装句、强调句或代替上文提到过的行为等。他们的否定式don’t/ doesn’t/ didn’t帮助构成否定句。
例如:He often plays sports after school. Does he often play。。。
We don’t speak Japanese.我们不说日语。
Did they visit the Palace Museum on their last day off 他们上个休息日参观故宫了吗?
She didn’t watch TV yesterday evening.她昨晚上没看电视。
考点一 动词的分类
<4>助动词will, shall, would, should:构成一般将来时,其中will可用于各人称,而shall一般只用于第一人称。would,should是will,shall的过去式,可以用于构成过去将来时,但很多时候被用作情态动词。
eg:There will be more trees and less pollution in the future.将来会有更多的树木,更少的污染。(帮助构成一般将来时)
考点一 动词的分类
4.情态动词:表示说话者的情感、态度和语气,但没有人称和数的变化,不能单独作谓语,须和动词一起构成句子的谓语。表示否定时在情态动词后加not (must,have to除外),表示疑问时将情态动词提至主语前即可。
<1>can 与could
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
can (could) 表示能力(= be able to) 能;会 Tom can swim.
=Tom is able to swim.
汤姆会游泳。
(疑问句中)表示请求 可以 Could you give us a hand
你可以帮我们一下吗?
(否定句、疑问句中)表示可能性 can可能 can’t不可能 The boy can’t be Jim. He’s much taller.
这个男孩不可能是吉姆。他要高很多。
区分can 与be able to
表示某种能力时,二者可通用;
can只用于现在时和过去时;be able to可用于各种时态;
遇有助动词或情态动词时只能用be able to。
tom was able to swim
tom will be able to swim
would you
考点一 动词的分类
区分maybe 与may be
maybe用于句首表示“可能;也许”,相当于perhaps;
may be中的may是情态动词,后接动词原形be,表示“可能是”,在句中作谓语。两者可互换。
eg:Maybe the boy is from Canada.
=The boy may be from Canada.
那个男孩可能来自加拿大。
<2>may与might
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
may (might) 表示可能性(可与maybe互换) 可能 Tony may know the way. =Maybe Tony knows the way.
托尼可能知道路。
表示客气请求 可以 May I come in
我可以进来吗?
表示祝愿 祝…… May you be happy!
祝你快乐!
考点一 动词的分类
<3>shall与should
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
shall (should) Shall. . . 用于第一人称,表示建议或请求 ……好 吗? Shall we ask the teacher for help
我们向老师寻求帮助好吗?
should用于各种人称,强调义务或责任 应该 Students shouldn’t have long hair.
学生们不应该留长发。
考点一 动词的分类
<4>must
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
must 表示义务、命令或要求 必须 We must tell the truth to our parents.
我们必须告诉父母真相。
表示肯定的猜测(否定猜测用can’t/mustn’t ) 一定 Lisa must be at home.
莉萨一定在家里。
(推测现在的状况)
You must be kidding!
你一定是在开玩笑!(推测现在正在发生的状况)
They must have seen the movie. 现在完成时
他们一定看过这部电影。
(推测过去的状况)
区分have to 与must
have to主要表示客观需要,意为“不得不”。有人称和时态的变化(has to; had to; will have to);
must强调说话人的主观看法,意为“必须;应该”;
(3)否定形式的不同:mustn’t表示“禁止;不应该”;not have to表示“不必”,相当于needn’t。
考点一 动词的分类
<5>will 与would
原形 (过去式) 用法 含义 例句
will (would) 用于第二人称疑问句中,表示征求意见或提建议 愿意 Will/Would you please take out the trash
你可以把垃圾拿出去吗?
will用于各种人称,表示意愿 Your parents will try their best to help you.
你的父母会尽最大努力帮助你。
考点一 动词的分类
【补】1.mustn’t表示否定意义“禁止,不允许”。可与祈使句互换。例如:
You mustn’t play football in the street.
=Don’t play football in the street.
2.have to有人称、数和时态的变化,表示受客观条件限制,意为“不得不”。例如:
She had to take the bus to work.
她不得不坐公交车去上班。
3.May. . . 句式的否定回答:No, . . . mustn’t/can’t.
Must. . . 句式的否定回答:No, . . . needn’t.
①—May I smoke here ——我可以在这儿吸烟吗?
—No, you mustn’t. ——不,你不准。/no, you can’t
②—Must I go now ——我必须现在走吗?
—No, you needn’t. /——不,你没必要。
4.must,should,may,might都可以表示“可以”,可能性程度由大到小依次为:must﹥should﹥may﹥might。
考点二 动词的五种基本形式
形式 用法 例句
原形 1.用在情态动词can, may ,must,should,would,have to 等词之后 You can borrow my bike.
2.用在助动词do,does,did,will,shall之后 What do you think of China
3.用在祈使句句首 Close the door, please.
4. 用在使役动词(make,let等)、感官动词(watch,feel等)之后 She made us laugh.
5.用在动词不定式符号to之后 My teacher asked us to clean the classroom.
第三人称单数 用在第三人称单数(形式)主语之后, 句子的时态为一般现在时 He studies English hard.
过去式 用于一般过去时 She looked at me happily.
过去分词 用于完成时态或被动语态中 He had finished his homework.
现在分词/动名词 现在分词用于进行时,动名词起名词作用 The girl is singing now.
考点三 易混词辨析
1. be used to doing sth, used to do sth和be used to do sth 区别
2.arrive,get 和rich的区别
易混词组 用法 例句
be used to doing sth 习惯做某事,to后接ing形式 I am used to getting up early.
我习惯早起。
used to do sth 过去常常做某事 I used to get up at six in the morning.
我过去常常在早上六点起床。
be used to do sth 被用来做某事 Wood is used to make paper.
木材被用来造纸。
易混词组 用法 例句
arrive in 后面接大地点 When did you arrive in Beijing?
arrive at 后面接小地点 We arrived at the village at five in the afternoon.
get to 后面跟地点名词 How do you usually get to school?
reach 是及物动词,后面直接跟地点名词 When she reached the office, the teacher was having a short rest.
考点三 易混词辨析
3. borrow,lend 与keep区别
4.die,dead,death和dying的区别
易混词 用法 例句
borrow 意为“借入”,borrow sth. from sb I borrowed a book from my friend yesterday.
昨天我从我朋友借了一本书。
lend 意为“借出”,lend sth to sb Can you lend you pen to me?
你能借我一支钢笔吗?
keep 意为“保存,借”,延续性动作,“长时间借” How long can we keep the book?
我们能够借这本书多久呢?
易混词 用法 例句
die 不及物动词,意为“死”,短暂性动作 Her grandfather died last year.
dead 形容词,意为“死的”,表示状态 Her grandfather has been died for two years.
death 名词,意为“死亡” His death was a great loss to China.
dying 形容词,意为“垂死的” The poor old man was dying.
考点三 易混词辨析
5.lose,forget 与leave区别
6.spend,cost,take和pay的区别
易混词 用法 例句
lose 意为“丢失,失去” I lose my watch.我的手表丢了。
forget 意为“忘记”,forget to do sth I forget your name.我忘记你的名字。
leave 意为“落在”,leave sth +地点状语 I left my watch at home. 我把我的手表落在家。
易混词 用法 例句
spend 主语为人 ① spend 时间/金钱 (in)doing sth ②spend 时间/金钱 on sth They spent two years in building this bridge.
cost 主语为 物,It costs/cost 金钱 to do sth. It costs fve thousand to buy this computer.
take 主语为物,It takes/ took 时间 to do sth. It took ten days to do this toy.
pay 与介词 for 连用 I have to pay them 20 pounds fir this room each month.
考点三 易混词辨析
5. join, take part in 与attend区别
6.wear,put on, have on 和dress的区别
易混词 用法 例句
join 一般加入党派或组织,如参军,入党 When did you brother join the army?
你哥哥什么时候参军呢?
take part in 指参加聚会或活动 We will take join in social practice during the summer vacation. 暑假期间我们期间我们将要参加社会实践。
attend 一般指出席会议 He’ ll attend an important meeting tomorrow.
他明天要参加一个重要的会议。
易混词 用法 例句
wear 强调穿的状态 He was wearing a dark suit.
put on 强调穿的动作 He put on his best clothes for the party.
have on 意为“穿着”,强调穿的状态 Mary had on her new dress.
dress 意为“某人给自己穿衣服” She dressed herself in her Sunday best.
练一练
1. You _______ stop when the traffic light turns red.
A. can B. had better +动词原形 C. need D. must
【解析】选D。must是“必须,不得不”,根据下文出现的when the traffic light turns red可知是“你必须……”。
2. —Is that girl under the tree Mary
—No, that _______ be Mary. She is in New York.
A. can B. mustn’t C. can’t
【解析】选C。由答语“她在纽约。”可知,那个女孩不可能是玛丽,故用can’t。
3. —Mr. Wang, can I finish my homework tomorrow
—Sorry, you _______.
A. can’t B. don’t C. needn’t D. won’t
【解析】选A。can’t“不能”,don’t“不”,needn’t“不需要”,won’t为will not的缩写“将不会”。根据问句“王老师,我能明天完成作业吗?”可知回答应为“对不起,你不能。”故选A。
4. —Dad, can I go to the movies tonight
—Sure, but you _______ come back home before 9 o’clock.
A. can B. must C. may D. might
【解析】选B。句意:——爸爸,今晚我可以去看电影吗?——当然,但是你必须在9点之前回家。can 表示“能;会”;must 表示“必须”;may和might表示“可以”,故选B。
5. — Mom, must I finish my homework now
— No, you _______. You may have supper first.
A. mustn’t B. needn’t C. can’t
【解析】选B。句意:——妈妈,我现在必须完成家庭作业吗?——不,你不需要。你可以先吃饭。对must引导的一般疑问句,否定回答时常用No, . . . needn’t, 故选B。
6. —Will you stay for some more days
—Sorry, I ______. My mother called to ask me to go back at once.
A. mustn’t B. may not
C. can’t D. wouldn’t
【解析】选C。句意:——你再待几天好吗?——对不起,我不能。我的母亲打电话让我马上回去。mustn’t“禁止”;may not“可能不”;wouldn’t“不愿做……,将要不……”。故选C。
7. —Shall we take a taxi
—No, we _______. It’s not far from here.
A. can’t B. mustn’t
C. shouldn’t D. needn’t
【解析】选D。由答语“它离这儿不远。”可知没必要乘出租车。故选D。
8. —Must I get up early tomorrow morning
—No, _______.
A. you mustn’t B. I don’t think you have to
C. you can’t D. you need
【解析】选B。情态动词must引导的一般疑问句的否定答语为“No, sb. needn’t. / No, sb. don’t/doesn’t have to. ”故选B。
9. It rained heavily, so we _______ stay at home watching TV or surfing the Internet all day.
A. could B. had to C. must
【解析】选B。外面下雨是待在家里的客观原因,故答案为B项。
10. —You _______ be excited that you’re going back to your hometown soon.
—Yes, I can’t wait any longer.
A. shall B. can C. need D. must
【解析】选D。由答语“是的,我不能再等待了。”可知,上一句应该是“你一定很兴奋,你不久将回到你的家乡。”must“一定”,表示有把握的肯定推测。
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
