2023年中考英语语法:情态动词课件(共24张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023年中考英语语法:情态动词课件(共24张PPT) |
|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 6.6MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-08-03 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共24张PPT)
情态动词
Modal Verd
Changing world, dreaming of the future, the ever-changing world constantly refreshes mankind's infinite imagination the future take the dream as the cornerstone to create a new future
1
多情多义的情态动词
2
情态动词的用法
3
情态动词的否定
4
课后作业
CONTENTS
CONTENTS
01
多情多义的情态动词
CHAPTERS
CHAPTERS
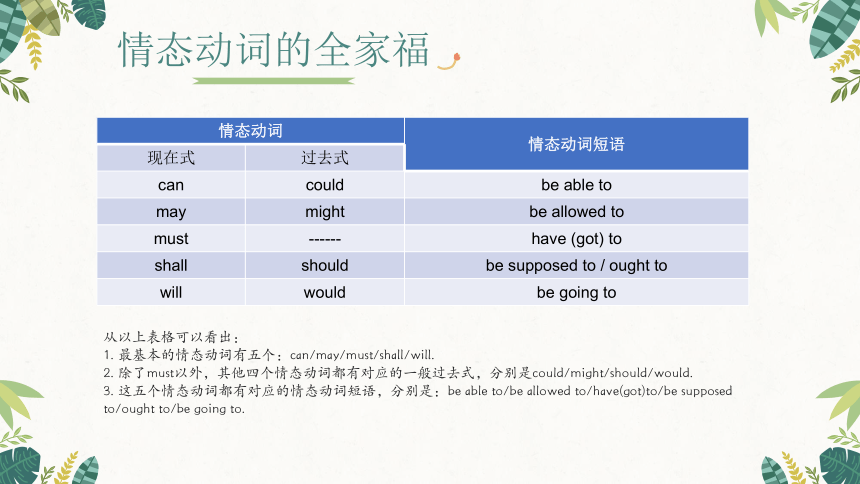
从以上表格可以看出:
1. 最基本的情态动词有五个:can/may/must/shall/will.
2. 除了must以外,其他四个情态动词都有对应的一般过去式,分别是could/might/should/would.
3. 这五个情态动词都有对应的情态动词短语,分别是:be able to/be allowed to/have(got)to/be supposed to/ought to/be going to.
情态动词的全家福
情态动词 情态动词短语
现在式 过去式 can could be able to
may might be allowed to
must ------ have (got) to
shall should be supposed to / ought to
will would be going to
请找出下列短文中的情态动词及情态动词短语。
思维训练
Would you stop complaining about things We’re supposed to do our best and we should be able to finish this work before the boss has to start screaming at us again. If you could just concentrate on getting finished, we might be allowed to leave early this afternoon. You know he’s not going to let us leave early if we can’t get the work done.
情态动词用在实义动词的前面,以添加某种意思,请比较下列句子中用与不用情态动词在意义上的差别:
情态动词的意义
① John isn’t in class. He is sick.
② John isn’t in class. He must be sick.
例句①中,没有使用情态动词,只用了一般现在时态的is, 表达的是一个客观事实。
例句②中,用了情态动词must, 则是表示说话人的主观猜测。
因此,例句②比例句①更带有主观色彩。
02
情态动词的用法
CHAPTERS
CHAPTERS
1. 对现在的肯定推测及其他含义
① must表示“推测”
e.g.: Why isn’t John in class today He must be sick.
② must表示“责任”或“义务”,译成“必须”
e.g.: You must wear a seat belt while driving.(强烈的义务)
Door must be closed when machine is in operation. (某系规章制度或规定)
I must remember to feed the cat. (用于描述说话人自身的情况)
You must come to see us one of these days. (用来谈未来的安排)
推测用法
2. 其他表推测的情态动词
①以下这些情态动词亦可表推测:如may/might/could等
e.g.: I may need the extra time to finish all this homework you gave us.
He may be sick. (50%确定,不太有把握的陈述)
He might /could be sick. (25%确定,很没有把握的陈诉,只是提供一种可能的情况。)
3. 对现在的否定推测
①A: The restaurant is always empty.
B: It isn’t good. (100%确定,对客观事实的陈述)
It can’t / couldn’t be good. (90%确定,很有把握的陈述)
It may not be good. (50%确定,不太有把握的陈述)
It might not be good. (25%确定,很没有把握的陈诉,只是提供一种可能的情况)
② must表示“责任”或“义务”,译成“必须”
e.g.: You must wear a seat belt while driving.(强烈的义务)
Door must be closed when machine is in operation. (某系规章制度或规定)
I must remember to feed the cat. (用于描述说话人自身的情况)
You must come to see us one of these days. (用来谈未来的安排)
推测用法
2. 其他表推测的情态动词
①以下这些情态动词亦可表推测:如may/might/could等
e.g.: I may need the extra time to finish all this homework you gave us.
He may be sick. (50%确定,不太有把握的陈述)
He might /could be sick. (25%确定,很没有把握的陈诉,只是提供一种可能的情况。)
1. 表示请求和允许。might比may语气更委婉,而不是过去式。否定回答时可用can’t或mustn’t, 表示“不可以,禁止”。
① Might / May I smoke in this room
No, you mustn’t.
② May / Might I take this book out of the room
Yes, you can. ( No, you can’t / mustn’t.)
Might and May的用法
用May I...?征徇对方许可时比较正式和客气,而用Can I...?在口语中更常见。
2. 用于祈使句,表示祝愿。
May you succeed
3. 表示推测、可能性(不用于疑问句)。意为:或许,可能
① might不是过去式,它所表示的可能性比may小。
(1) He may/might be very busy now.
(2) Your mother may / might not know the truth.
1. 表示能力(体力、知识、技能)。意为:能,会。
Can you lift this heavy box (体力)
Mary can speak three languages. (知识)
Can you skate (技能)
此时可用be able to 代替。Can只能一般现在时和一般过去式;而be able to 则有更多的时态。
I’ll not be able to come this afternoon.
当表示“经过努力才得以做成功某事”时应用be able to; 不能用can. 如:
He was able to go to the party yesterday evening in spite of the heavy rain.
Can and Could的用法
2. 表示请求和允许。
---- Can I go now Yes, you can. / No, you can’t.
此时可与may互换。在疑问句中还可用could, might代替,不是过去式,只是语气更委婉,不能用于肯定句和答语中。
---- Could I come to see you tomorrow Yes, you can. / No, I’m afraid not.
Can and Could的用法
2. 表推测可能性。
肯定句中:can表示理论上的可能性;May表示事实上的可能性,如:
---- In Yuyao, sometimes it can be really cold.
Tom may go camping with us tomorrow, but he is not sure.
否定句和疑问句中,只能用can表猜测可能性。
Someone is knocking at the door, and who can it be
It can’t be Tom because he has gone to Beijing.
1. shall 用于第一人称,征求对方的意见。
What shall we do this evening
shall I clean the room for you
Shall的用法
2. shall 用于第二、三人称,表示说话人给对方的命令、警告、允诺或威胁。
1. You shall fail if you don’t work hard.(警告)
2. He shall have the book when I finish it.(允诺)
3. He shall be punished.(威胁)
1. 表示“应该”,常用来表示劝告、建议;认为“某人应该做某事”或“有义务责任做某事”。
We should obey traffic laws.
You shouldn‘t watch TV every day。
You shouldn’t have made this kind of silly mistakes.
Tom should have brought his report today.
这时它可以和 ought to, be supposed to 互换使用
Should的用法
2. Should (ought to)表示推测时,是指有一定根据的推测,意为“可能、该”
---When can I come for the photos I need them tomorrow,
---They ____ be ready by 12:00
1. 表示意志或意愿:决心,愿意。
We will do our best to save the child. 我们会尽力抢救这个孩子。
I told her to stop crying, but she just wouldn’t listen. 我叫她别哭,可她就是不愿听。
will和would的用法
2. 表示请求、建议或征求对方意见时,用Would you… 比用Will you… 更婉转。如:
Will/Would you please keep the door open 请让门开着好吗?
Will/Would you go with me 你愿意和我一起去吗
1. would like表示愿意。
would like to have a word with you. 我想同你说句话。
相关情态动词
2. would rather…than…宁愿……也不愿……
I would rather fail than cheat in the examination. 我宁愿考不及格,也不愿意考试作弊。
1. need作情态动词无人称或数的变化, 后接动词原形,多用于否定句和疑问句中。
如:You needn‘t worry.你不必担心
I needn’t have brought the raincoat with me in such a sunny day yesterday.
need的用法
2.由need引出的一般疑问句,肯定回答常用must或have to;否定答语常用needn't. 如:
—Need I answer the question 我需要回答那个问题吗?
—Yes, you must.
---Yes, you have to.是的,你必须回答。
---No, you needn't./you don’t have to不,不必了。
1. 由must引出的一般疑问句,肯定回答用must,否定答语用needn't或don't have to。如:
—Must I do the work now 我必须现在干这个活吗?
—Yes, you must /have to.
---No, you needn't /don't have to.
need的用法
2. Need 做行为动词:
Need sth
Need to do sth
Need doing=need to be done表被动
否定: don’t need
1. 注意点一:
表推测可能性:must, can, may, might, can’t, couldn’t
--I heard they went skiing in the mountains last winter.
-- it ____ true because there was little snow where.
注意
2. 表推测的用法:
1. must have done过去肯定做了某事
Since the road is wet, it must have rained last night.
不存在 mustn‘t have done 的形式。其否定或疑问形式须用 can(could) 来表示. 例如:
He can't have missed the way. I drew him a map.
“The dictionary has disappeared. Who could have taken it ”
2. may / might have done:
I can‘t find my keys. I may / might have left them at the school yesterday. 我找不到我的钥匙了。我可能昨天把他们落在学校了。
John may/might not have passed the exam; he looks very sad.约翰可能没有通过考试。他看起来很忧伤。
注意
3.can/could have done 表推测一般用在否定句和疑问句中,表示不相信或怀疑的态度。
Can/Could he have passed the exam 他可能通过了考试吗?
I think that he couldn’t/can't have gone abroad. I saw him just now.我认为他不可能出国了。我刚才还看见他了。
02
练习
CHAPTERS
CHAPTERS
练习
1. You ______________ return the library book on time.
2. I ______________ (not) find the way to the hospital. _______________ you show me the way
3. —________________ I finish the work right now
— No, you ________________ (not). You ____________ do it later.
4. He said he ________________ (not) come tonight.
5. Her mother was ill. She ________________ stay at home and look after her.
6. It’s time for class. You ________________ stop playing football or you __________be late for class.
7. We ________________ start right now, or they would get there first.
8. The cloud is lifting, so it ________________ (not) be a rainy day tomorrow.
must
can’t
Could
Can
can’t
can
couldn’t
must
must
might
need
wouldn’t
练习
1. —Must I be in hospital for a week, Doctor
—No, you . You can go back home tomorrow.
A mustn’t B. needn’t C. must
2. The desk is not dirty. You _______clean it.
mustn’t B. shouldn’t C. needn’t D . can’t
3.—May I watch TV for a while?
—No, you _______. You have to finish your homework first.
shouldn’t B. needn’t C. mustn’t D. won’t
4. —I’m a little tired. Let’s go to the zoo by taxi.
—We take a taxi. It’s not far from here.
can’t B. mustn’t C. couldn’t D. needn’t
5. . If the traffic light is red, you ________ cross the road. It’s very dangerous.
A. don’t B. mustn’t C. needn’t D. wouldn’t
A
C
A
D
B
THANKS
THANKS
情态动词
Modal Verd
Changing world, dreaming of the future, the ever-changing world constantly refreshes mankind's infinite imagination the future take the dream as the cornerstone to create a new future
1
多情多义的情态动词
2
情态动词的用法
3
情态动词的否定
4
课后作业
CONTENTS
CONTENTS
01
多情多义的情态动词
CHAPTERS
CHAPTERS
从以上表格可以看出:
1. 最基本的情态动词有五个:can/may/must/shall/will.
2. 除了must以外,其他四个情态动词都有对应的一般过去式,分别是could/might/should/would.
3. 这五个情态动词都有对应的情态动词短语,分别是:be able to/be allowed to/have(got)to/be supposed to/ought to/be going to.
情态动词的全家福
情态动词 情态动词短语
现在式 过去式 can could be able to
may might be allowed to
must ------ have (got) to
shall should be supposed to / ought to
will would be going to
请找出下列短文中的情态动词及情态动词短语。
思维训练
Would you stop complaining about things We’re supposed to do our best and we should be able to finish this work before the boss has to start screaming at us again. If you could just concentrate on getting finished, we might be allowed to leave early this afternoon. You know he’s not going to let us leave early if we can’t get the work done.
情态动词用在实义动词的前面,以添加某种意思,请比较下列句子中用与不用情态动词在意义上的差别:
情态动词的意义
① John isn’t in class. He is sick.
② John isn’t in class. He must be sick.
例句①中,没有使用情态动词,只用了一般现在时态的is, 表达的是一个客观事实。
例句②中,用了情态动词must, 则是表示说话人的主观猜测。
因此,例句②比例句①更带有主观色彩。
02
情态动词的用法
CHAPTERS
CHAPTERS
1. 对现在的肯定推测及其他含义
① must表示“推测”
e.g.: Why isn’t John in class today He must be sick.
② must表示“责任”或“义务”,译成“必须”
e.g.: You must wear a seat belt while driving.(强烈的义务)
Door must be closed when machine is in operation. (某系规章制度或规定)
I must remember to feed the cat. (用于描述说话人自身的情况)
You must come to see us one of these days. (用来谈未来的安排)
推测用法
2. 其他表推测的情态动词
①以下这些情态动词亦可表推测:如may/might/could等
e.g.: I may need the extra time to finish all this homework you gave us.
He may be sick. (50%确定,不太有把握的陈述)
He might /could be sick. (25%确定,很没有把握的陈诉,只是提供一种可能的情况。)
3. 对现在的否定推测
①A: The restaurant is always empty.
B: It isn’t good. (100%确定,对客观事实的陈述)
It can’t / couldn’t be good. (90%确定,很有把握的陈述)
It may not be good. (50%确定,不太有把握的陈述)
It might not be good. (25%确定,很没有把握的陈诉,只是提供一种可能的情况)
② must表示“责任”或“义务”,译成“必须”
e.g.: You must wear a seat belt while driving.(强烈的义务)
Door must be closed when machine is in operation. (某系规章制度或规定)
I must remember to feed the cat. (用于描述说话人自身的情况)
You must come to see us one of these days. (用来谈未来的安排)
推测用法
2. 其他表推测的情态动词
①以下这些情态动词亦可表推测:如may/might/could等
e.g.: I may need the extra time to finish all this homework you gave us.
He may be sick. (50%确定,不太有把握的陈述)
He might /could be sick. (25%确定,很没有把握的陈诉,只是提供一种可能的情况。)
1. 表示请求和允许。might比may语气更委婉,而不是过去式。否定回答时可用can’t或mustn’t, 表示“不可以,禁止”。
① Might / May I smoke in this room
No, you mustn’t.
② May / Might I take this book out of the room
Yes, you can. ( No, you can’t / mustn’t.)
Might and May的用法
用May I...?征徇对方许可时比较正式和客气,而用Can I...?在口语中更常见。
2. 用于祈使句,表示祝愿。
May you succeed
3. 表示推测、可能性(不用于疑问句)。意为:或许,可能
① might不是过去式,它所表示的可能性比may小。
(1) He may/might be very busy now.
(2) Your mother may / might not know the truth.
1. 表示能力(体力、知识、技能)。意为:能,会。
Can you lift this heavy box (体力)
Mary can speak three languages. (知识)
Can you skate (技能)
此时可用be able to 代替。Can只能一般现在时和一般过去式;而be able to 则有更多的时态。
I’ll not be able to come this afternoon.
当表示“经过努力才得以做成功某事”时应用be able to; 不能用can. 如:
He was able to go to the party yesterday evening in spite of the heavy rain.
Can and Could的用法
2. 表示请求和允许。
---- Can I go now Yes, you can. / No, you can’t.
此时可与may互换。在疑问句中还可用could, might代替,不是过去式,只是语气更委婉,不能用于肯定句和答语中。
---- Could I come to see you tomorrow Yes, you can. / No, I’m afraid not.
Can and Could的用法
2. 表推测可能性。
肯定句中:can表示理论上的可能性;May表示事实上的可能性,如:
---- In Yuyao, sometimes it can be really cold.
Tom may go camping with us tomorrow, but he is not sure.
否定句和疑问句中,只能用can表猜测可能性。
Someone is knocking at the door, and who can it be
It can’t be Tom because he has gone to Beijing.
1. shall 用于第一人称,征求对方的意见。
What shall we do this evening
shall I clean the room for you
Shall的用法
2. shall 用于第二、三人称,表示说话人给对方的命令、警告、允诺或威胁。
1. You shall fail if you don’t work hard.(警告)
2. He shall have the book when I finish it.(允诺)
3. He shall be punished.(威胁)
1. 表示“应该”,常用来表示劝告、建议;认为“某人应该做某事”或“有义务责任做某事”。
We should obey traffic laws.
You shouldn‘t watch TV every day。
You shouldn’t have made this kind of silly mistakes.
Tom should have brought his report today.
这时它可以和 ought to, be supposed to 互换使用
Should的用法
2. Should (ought to)表示推测时,是指有一定根据的推测,意为“可能、该”
---When can I come for the photos I need them tomorrow,
---They ____ be ready by 12:00
1. 表示意志或意愿:决心,愿意。
We will do our best to save the child. 我们会尽力抢救这个孩子。
I told her to stop crying, but she just wouldn’t listen. 我叫她别哭,可她就是不愿听。
will和would的用法
2. 表示请求、建议或征求对方意见时,用Would you… 比用Will you… 更婉转。如:
Will/Would you please keep the door open 请让门开着好吗?
Will/Would you go with me 你愿意和我一起去吗
1. would like表示愿意。
would like to have a word with you. 我想同你说句话。
相关情态动词
2. would rather…than…宁愿……也不愿……
I would rather fail than cheat in the examination. 我宁愿考不及格,也不愿意考试作弊。
1. need作情态动词无人称或数的变化, 后接动词原形,多用于否定句和疑问句中。
如:You needn‘t worry.你不必担心
I needn’t have brought the raincoat with me in such a sunny day yesterday.
need的用法
2.由need引出的一般疑问句,肯定回答常用must或have to;否定答语常用needn't. 如:
—Need I answer the question 我需要回答那个问题吗?
—Yes, you must.
---Yes, you have to.是的,你必须回答。
---No, you needn't./you don’t have to不,不必了。
1. 由must引出的一般疑问句,肯定回答用must,否定答语用needn't或don't have to。如:
—Must I do the work now 我必须现在干这个活吗?
—Yes, you must /have to.
---No, you needn't /don't have to.
need的用法
2. Need 做行为动词:
Need sth
Need to do sth
Need doing=need to be done表被动
否定: don’t need
1. 注意点一:
表推测可能性:must, can, may, might, can’t, couldn’t
--I heard they went skiing in the mountains last winter.
-- it ____ true because there was little snow where.
注意
2. 表推测的用法:
1. must have done过去肯定做了某事
Since the road is wet, it must have rained last night.
不存在 mustn‘t have done 的形式。其否定或疑问形式须用 can(could) 来表示. 例如:
He can't have missed the way. I drew him a map.
“The dictionary has disappeared. Who could have taken it ”
2. may / might have done:
I can‘t find my keys. I may / might have left them at the school yesterday. 我找不到我的钥匙了。我可能昨天把他们落在学校了。
John may/might not have passed the exam; he looks very sad.约翰可能没有通过考试。他看起来很忧伤。
注意
3.can/could have done 表推测一般用在否定句和疑问句中,表示不相信或怀疑的态度。
Can/Could he have passed the exam 他可能通过了考试吗?
I think that he couldn’t/can't have gone abroad. I saw him just now.我认为他不可能出国了。我刚才还看见他了。
02
练习
CHAPTERS
CHAPTERS
练习
1. You ______________ return the library book on time.
2. I ______________ (not) find the way to the hospital. _______________ you show me the way
3. —________________ I finish the work right now
— No, you ________________ (not). You ____________ do it later.
4. He said he ________________ (not) come tonight.
5. Her mother was ill. She ________________ stay at home and look after her.
6. It’s time for class. You ________________ stop playing football or you __________be late for class.
7. We ________________ start right now, or they would get there first.
8. The cloud is lifting, so it ________________ (not) be a rainy day tomorrow.
must
can’t
Could
Can
can’t
can
couldn’t
must
must
might
need
wouldn’t
练习
1. —Must I be in hospital for a week, Doctor
—No, you . You can go back home tomorrow.
A mustn’t B. needn’t C. must
2. The desk is not dirty. You _______clean it.
mustn’t B. shouldn’t C. needn’t D . can’t
3.—May I watch TV for a while?
—No, you _______. You have to finish your homework first.
shouldn’t B. needn’t C. mustn’t D. won’t
4. —I’m a little tired. Let’s go to the zoo by taxi.
—We take a taxi. It’s not far from here.
can’t B. mustn’t C. couldn’t D. needn’t
5. . If the traffic light is red, you ________ cross the road. It’s very dangerous.
A. don’t B. mustn’t C. needn’t D. wouldn’t
A
C
A
D
B
THANKS
THANKS
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
