2022年牛津译林版中考英语复习专题突破之感叹句、祈使句、反义疑问句及情态动词(含思维导图)(含答案)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2022年牛津译林版中考英语复习专题突破之感叹句、祈使句、反义疑问句及情态动词(含思维导图)(含答案) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 695.0KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-08-25 17:01:29 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
感叹句
一、知识结构
二、知识点及考点分析
1.定义:感叹句是用来表达人的特殊情感的句子,可以表达人的喜、怒、哀、乐等强烈情感。感叹句可以是一个单词、一个短语,也可以是由what或how引导的句子,句末常用“!”。
2.感叹句句子结构分类:
what引导的感叹句
①What+a/an+名词单数形式+(主语+谓语)!
What a / an 常用来修饰单数可数名词,若其前面的形容词为元音开头,则用an;若其前面的形容词为辅音开头,则用a。
如:What an interesting story it is)!
What a lovely boy he is)!
②What+名词复数形式+(主语+谓语)!
如:What kind women they are!
③What+不可数名词+(主语+谓语)!
如:What nice music it is!
补充:
①what引导的感叹句主语和谓语通常可以省略;
②What常用来修饰复数可数名词和不可数名词。但有些不可数名词,如 rain, surprise, breakfast, lunch 等,当前面有形容词修饰,使抽象名词具体化时,则要用What a/an。
如:What a heavy rain it is)!
③★★★what引导的感叹句常与fun有关的句型放在一起考,属于感叹句易错点:
it's great fun to do sth.
做某事真的很有趣(这里的fun是不可数名词,表示有趣的事)
改为感叹句:What great fun it is to do sth.!
如:What great fun it is to play with dogs!
have fun doing sth. 做某事很开心
改为感叹句:What great fun we have playing with dogs!
tips:陈述句转化为感叹句只改变语序再加上对应的感叹句引导词what/how ,并不改变句子中原有的语法/句型功能。由此点我们可以很好区分两个带fun的感叹句用法。
how引导的感叹句
①How+形容词/副词+主语+谓语!
如:How hard the worker are working!
注意:
当how修饰动词时,动词不跟着感叹词提到主语之前。 如:How the runner runs!
what与how引导的感叹句,一般情况下可以相互转换,转换后意义不变。
如:What a clever girl she is!=How clever the girl is!
②How+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数形式+主语+谓语!
如:How interesting a book it is!
③How+主语+谓语!
如: How time flies!
关于感叹句引导词how和what的选择
第一步:找出句子主语和谓语
第二步:划掉主语和谓语
剩下为名词或名词词组 what
第三步:分析剩下的句子成分
剩下为形容词或副词 how
例子:________ difficult homework we had yesterday!
③ ①②
①找出主语谓语we had
②划掉主语谓语 we had
③剩余成分为名词词组difficult homework,故选择what;且homework为不可数名词,所以这个句子写为What difficult homework we had yesterday!
真题演练
一、选择填空
1. Look! ________ beautiful that take is!
A. What a B. What C. What an D. How
2. --- Hi, Mary, ________ beautiful day! – Yes, it is.
A. How B. What a C. What D. How a
3. ________ new radio it is!
A. How B. How a C. What a D. What
4. ________ nice computers!
A. What a B. What C. How a D. How
5. ________ day we’re having today!
A. What fine a B. How fine C. What a fine D. What a
6. ________ nice girl Kate is!
A. How B. What C. What an D. What a
7. --- Hi, Mary, ________ beautiful day! – Yes, it is.
A. How B. What a C. What D. How a
8. ________ time we’re having today!
A. What a good B. How good C. What good a D. What good
9. ________ surprising news it is!
A. How B. How a C. What D. What a
10. ________ nice cars!
A. What a B. What C. How a D. How
二、完成下列感叹句
________ lovely the snow looks!
________ a clever boy Jim is!
________ worried they looked!
________ hard the workers are working!
________ long hair she has!
一、1. D 2. B 3. C 4. B 5. C 6. D 7. B 8. A 9. C 10. B
二、1. How 2. What 3. How 4. How 5. What
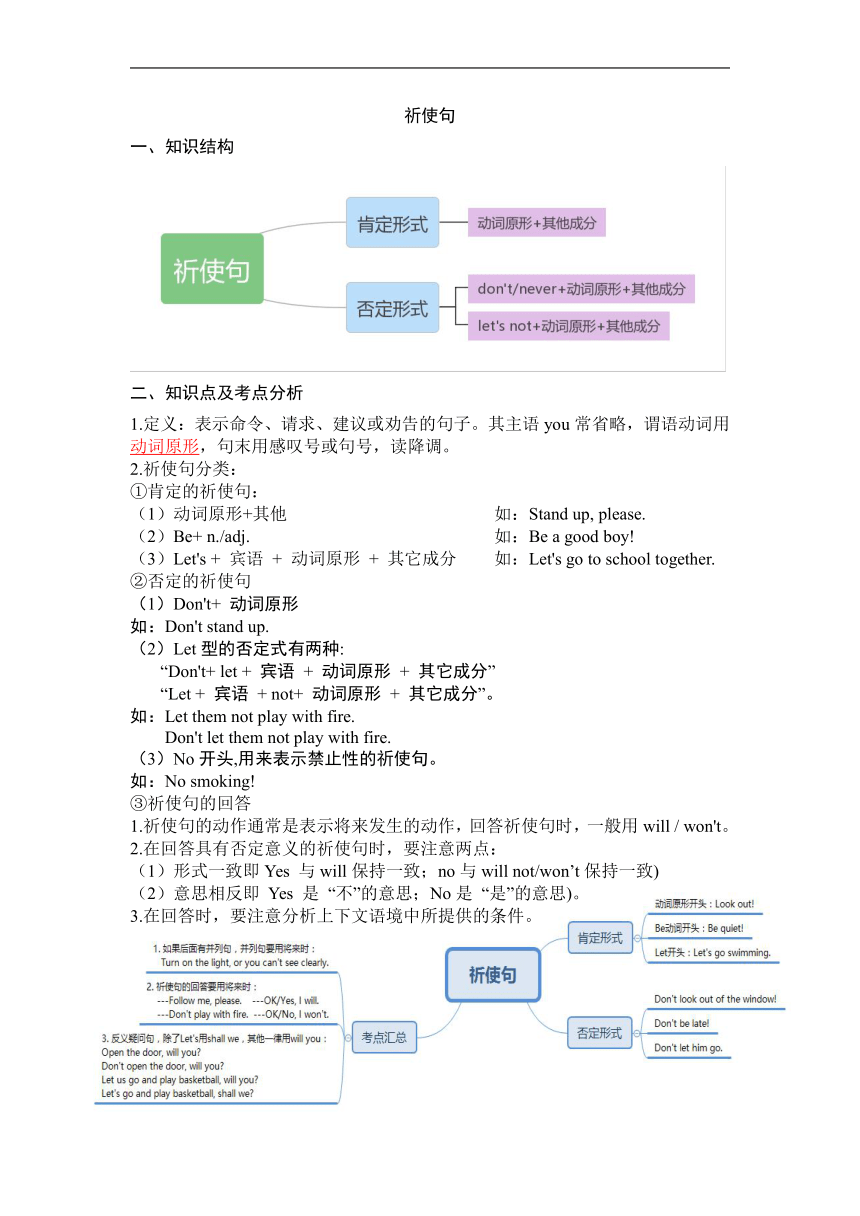
祈使句
一、知识结构
二、知识点及考点分析
1.定义:表示命令、请求、建议或劝告的句子。其主语you常省略,谓语动词用动词原形,句末用感叹号或句号,读降调。
2.祈使句分类:
①肯定的祈使句:
(1)动词原形+其他 如:Stand up, please.
(2)Be+ n./adj. 如:Be a good boy!
(3)Let's + 宾语 + 动词原形 + 其它成分 如:Let's go to school together.
②否定的祈使句
(1)Don't+ 动词原形
如:Don't stand up.
(2)Let型的否定式有两种:
“Don't+ let + 宾语 + 动词原形 + 其它成分”
“Let + 宾语 + not+ 动词原形 + 其它成分”。
如:Let them not play with fire.
Don't let them not play with fire.
(3)No开头,用来表示禁止性的祈使句。
如:No smoking!
③祈使句的回答
1.祈使句的动作通常是表示将来发生的动作,回答祈使句时,一般用will / won't。
2.在回答具有否定意义的祈使句时,要注意两点:
(1)形式一致即Yes 与will保持一致;no与will not/won’t保持一致)
(2)意思相反即 Yes 是 “不”的意思;No是 “是”的意思)。
3.在回答时,要注意分析上下文语境中所提供的条件。
真题演练
一、选择题
1. ----Don't leave the classroom with the light on.
----________.
A.Yes, I won't B.No, I won't C.Yes, I will D.No, I don't
2.My friend, Lucy, _______ afraid of snakes. She keeps a snakes a pet at home.
A.don't be B.doesn't be C.isn't D.be not
3. ----Don't forget to ask the police for help when you are in trouble.
---- _______.
A.Yes, I won't. B.No problem. C.OK, I won't D.OK, I will
4. ----Don't leave the classroom with the light on.
----________.
A. Yes, I won't B. No, I won't
C. Yes, I will D. No, I don't
5. ----Don't make so much noise, Jack. Your grandpa is sleeping now.
----___________.
A.Yes, I won't B.No, I will.
C.Yes, I will. D.Sorry, I won't
二、填空题
1.Kitty, ________________not be) afraid of snakes. Not all of them are dangerous.
2. Mike, ____________not be) afraid. I will always be with you.
3.----Martin, ____ not be) late for the visit to the museum tomorrow morning.----OK.
4. Get up early, and you ___________ not be) late.
5. Tom, ___________not be) afraid. I'll be with you all the time.
6. Mike, __________not be) afraid. I will always be with you.
7.__________share) your sadness with your friends, and you will feel better.
1.don't be
2.don't be
3.don't be
4.won't be
5.don't be
6.don't be
7.share
反义疑问句
一、知识结构
二、知识点及考点分析
1.定义:反意疑问句是提出情况或看法,问对方是否同意的句子。一般由陈述部分和反意疑问部分构成。
2.改写原则:前肯后否,前否后肯
①You can do it, can’t you
②They are not very late for the meeting, are they
3.具体考点:
反意疑问部分主语及谓语的确定
反意疑问部分主语与谓语,应根据陈述部分的主语和谓语进行选择,但是需要注意一些特殊的情况。而且,反意疑问部分的主语一般要用人称代词(一般不会用人名等),而动词若为否定形式则通常用缩写表达,且动词的形式及时态等必须保持一致。
①He has supper at home every week, doesn’t he 不能用hasn’t he )
②They have known the matter, haven’t they 不能用don’t they )
③They will go to school soon, won’t they 不能用don’t they 或 aren’t they )
④He works very hard, doesn’t he 不能用didn’t he 或won’t he )
情况分类:
①陈述部分带有little, few, never, hardly, seldom,nothing,nobody,none等否定意义的词时,问句部分用肯定式。
如:He never tells lies, does he 不用doesn’t he )
注意:当陈述部分谓语动词是含有un-, im-, in-, dis-等表否定意义的前缀的词时,陈述部分要视为肯定含义,反意疑问部分还是要用否定形式。
如:He dislikes playing football,doesn’t he
②陈述部分是there be结构时,用be there即可.
如:There is going to be a sports meeting next Wednesday, isn’t there
③当陈述部分的主语为指物的不定代词nothing,everything,something,anything等时,反义疑问主语部分用it进行指代。
如:Something is wrong with my phone,isn’t it
④当陈述部分的主语为指人的不定代词nobody,everybody,somebody,anybody等时,反义疑问主语部分可用he或they指代,但是不能用it进行指代。
如:Somebody wants to play with you,doesn’t he/they
⑤当陈述部分的主语为指示代词this/that时,反意疑问部分的主语应用单数形式it;若主语为指示代词these/those时,反意疑问部分的主语应用复数形式they。
如:This is necessary, isn’t it
These are your classmates Tommy and Jackie, aren’t they
⑥当陈述部分的动词是has/had/have时,我们需要进行判断具体含义及用法后才能确定反义疑问句怎么改写:
has/had/have表示“有”时,反义疑问部分可以用has/had/have或者does/did/do;
如: He has a new watch,hasn’t he/doesn’t he
has/had/have to表示半情态动词“不得不”时,反义疑问部分应用does/did/do;
如: He has to finish homework,doesn’t he
has/had/have to表示实义动词“吃,喝,玩等”时,反义疑问部分应用does/did/do;
如:They have a nice dinner,don’t they
had better表示“最好”时,反义疑问部分用had;
如:They had better stop laughing,hadn’t they
has/had/have在现在完成时中,反义疑问部分应用has/had/have
如:He has been to Shanghai,hasn’t he
★★★拓展:
1.'s是is还是has的辨析:has只有表示现在完成时的助动词时,才可以缩写为's。所以,我们可以得出:'s后面如果不是过去分词,那么一定是is,而不是has。
如果's后面是过去分词,我们还要区分主被动,如果是表达主动意,那么's是has的缩写,如果表达的是被动意,那么仍然是is的缩写。
eg. He's already back to China, isn't he
He's already been back to China, hasn't he
He's always made to do a lot of housework, isn't he
2.have/has是助动词还是行为动词:如果have/has表示的是助动词,那么后面要有过去分词;如果后面没有过去分词,那么have/has就是行为动词。
eg. He has gone to Hainan, hasn't he
He has a lot of things to do, doesn't he
⑦ 当陈述部分含有need时,如果need作实义动词,则反意疑问部分应用does/did/do,如果need作情态动词,则反意疑问部分应用need。
如:We need to have a rest,don’t we
We need have a rest,needn’t we
⑧当陈述部分出现I am时,反意疑问部分应用aren'tI。
如:I am right,aren’t I
⑨反义疑问句与祈使句结合:
1)肯定祈使句的反意疑问句反问部分用will you或won't you;
2)否定祈使句的反意疑问句反问部分只用will you;
3)以let's开头的祈使句反意疑问句反问部分用shall we;
<特别注意> 只有以let's开头的祈使句的反意疑问句的反问部分才用shall we,而let us 开头的祈使句的反意疑问句的反问部分应为will you或won't you。
如:Don't be late again, will you
Let's turn on the TV, shall we
Please open the door, will/ won't you
Let us have a try,will you
⑩当陈述部分含有情态动词must时,有下列两种情况:
情态动词must表示“必须”时,疑问部分用mustn’t。
如:I must answer the question, mustn’t I
但若表推测这层含义时,不能用must,而要根据陈述部分的不定式结构(即must之后的动词)以及含义采用相应的动词形式。
如:They must have watched the movie last week, didn’t they
He must be in the library, isn’t he
陈述部分用used to +主语时,问句部分用didn’t /usedn’t +主语形式。
如:She used to live in this countryside, didn’t she /usedn’t she
当陈述部分为主从复合句,且反意疑问句的陈述部分为非第一人称主语+ thinkbelieve, suppose, consider,said,told, reported, asked) + that从句时,问句部分的动词和主语与陈述部分的主句动词和主语保持一致。
如:They all think that English is very important, don’t they 不用isn’t it )
注意:若主句的主语是第一人称I/we,其谓语动词又是 think/suppose/believe等时,反意疑问部分的主语和谓语一般应与从句一致。(特别要注意否定转移)
如: I don't think they are good parents,are they
4.反义疑问句回答原则:
①去掉句子中否定词
②将句子变为一般疑问句
③根据实际情况作答,肯定回答用yes,否定回答用no,特别注意前后形式需一致
如:Yes, he isn’t./No,he is 这样写是错的,yes后必须用肯定,no后必须用否定。
真题演练
1.— The secretary’s already on the way to the company, _________she
— _______. She was badly hurt in the accident and sent to the hospital.
A. hasn’t; Yes B. hasn’t; No C. isn’t; Yes D. isn’t; No
—He has never been to Shanghai, ______ — _______. He has been there twice.
A. has he; No, he hasn’t B. has he; No, he has
C. has he; Yes, he has D. hasn’t he; Yes, he has
3.Alice had a wonderful time yesterday,_______
A. hadn’t she B. wasn’t she C. didn’t she D. wouldn’t she
4.–She didn’t come to school yesterday, did she
–______, though she was not feeling well.
A. No, she didn’t B. Yes, she didn’t C. No, she did D. Yes,she did
5.---He hardly spent any time on his subjects,________
---________, so he does badly in his lessons.
A .didn’t he, Yes B. did he, Yes C. didn’t he, No D. did he, No
6.He’s read this book before,______
A. hasn’t he B. doesn’t he C. isn’t he D. wasn’t he
7.– Let’s go for a walk, ______
-- OK, I’m coming . Don’t forget to bring your camera, ______
A. will you; will you B. will you; shall we
C. shall we; shall we D. shall we; will you
8.John had a short walk after lunch, ________?
A. did he B. didn't he C. had he D. hadn't he
9. Nancy hardly rings you up, ___________
A. doesn’t she B. does she
C. doesn’t Nancy D. does Nancy
10.---Your brother often disagrees with you, _______ he
--- _______. We often have different opinions.
A.does; Yes B. doesn’t ;Yes
C. does; No D. doesn’t; No
情态动词
一、知识结构
二、考点及知识点分析
1.定义:情态动词是表示情态意义的动词,他表示说话人的语气和情态,它不能单独作谓语,必须与实义动词一起构成谓语,情态动词没有人称和数的变化,过去式通常表示更客气、更委婉。
2.情态动词有四个特征:
①不能单独做谓语,必须与其他动词一起构成谓语;
②没有人称和数的变化;
③情态动词后必须跟动词原形;
④具有助动词功能。
3.情态动词基本含义:
can could ) 能,会 may might) 可以,可能
will would) 将,会,愿意 must 必须
have to不得不 need 需要
should应该 had better 最好 had better not) do sth.
4.表猜测语气的情态动词
表猜测性的情态动词有:may /can’t /must 。
may表没把握的猜测;can’t 表有把握的否定猜测;must 表有把握的肯定猜测
5.情态动词开头的疑问句的答语
句型 肯定回答 否定回答
Can I… Yes, you can . No, you can’t .
May I … Yes ,you may. No, you mustn’t./No, you can’t.
Must I… Yes, you must. No, you needn’t./No you don’t have to
Need I… Yes, you must. No, you needn’t
6.情态动词的辨析
①must 与have to :
must 表主观看法,意为“必须”。
如:We must finish homework.
have to表客观需要,意为“不得不”。
如:We have to stay at home,because it’s raining outside.
②maybe与may be
may 为情态动词后接动词原形,may be一般位于句子中;
maybe为副词意思为“大概,也许”,maybe一般位于句子开头。
如:He may be tired.
Maybe he is tired.
③can与be able to
can只有现在和过去时(could),且can强调自身已具有的能力
be able to可用于任何时态中,而be able to 强调通过努力而获得的能力
如:He can speak Chinese.
I was able to swim when I was young.
④can’t 与mustn’t
can’t 表“不可能”;mustn’t表“禁止,不许”。
如:He can’t be home,I saw him go out.
You mustn’t go out.
三、情态动词具体用法分析:
1. can的用法:
①表示能力,即有某种能力,一般指与生来具来的能力,注意与be able to(强调通过努力而获得的能力) 区分。
e.g.I can smell with my nose.
②表示许可,常在口语中。常用may代替。
e.g.You can/may use my computer.
③表示推测,意为“可能”,常用于否定句和疑问句中,而can’t表示“不可能”。
e.g.Can the news be true
2.could的用法:
①can的过去形式,意思是“能、会”,表示过去拥有的能力。
e.g.She could swim when she was 11 years old.
②could在疑问句中,表示委婉请求等,此时could并不是过去式的形式。
e.g.Could you help me with my homework
3.may的用法:
①表示请求、许可,比can正式,语气更委婉。
e.g.May I use your dictionary
②表示推测,意为“可能,或许”,一般表示可能性不是很大,用于肯定句中。
e.g.It may rain next week .明天可能会下雨。
③may的过去式为might,表示推测,可能性低于may。
e.g.He drops off school. He might be sick.
④表示对某人的一种希望、祝愿,常可译为“祝愿、祝福某人...”。
句型一般为may +主语+动词原形。
e.g.May you happy!
4.must的用法:
①must表示主观要求、看法或命令,意思是“必须、一定...”。
e.g. You must finish your homework now.
②其否定形式mustn’t表示 “禁止,不准等”,不能翻译为不可能。
e.g.You mustn’t play with fire.
③must表示很有把握的推测,“肯定”,不能用于否定句中。
e.g.The light is on, so she must be at school at the moment.
④针对must提问的回答: 肯定回答为must
否定回答为needn’t 或don’t have to
e.g.—Must I finish my homework
—No, you needn’t./ No, you don’t have to.
5.need的用法:
①need表需要,用于否定句和疑问句中。
②用need提问的回答:
肯定回答为must,否定回答为needn’t或don’t have to。
e.g. —Need I finish homework today
—Yes, you must ./—No. you needn’t /don’t have to.
③need还可以作实义动词,此时有人称、数和时态的变化。
e.g. He needs to learn more about the girl.他需要多了解那个女孩。
The door needs painting. = The door needs to be painted.
6.shall的用法:shall表示征求对方意见(一般用于第一、三人称)。
e.g.Shall we go shopping 回答:Yes, please./All right./No, thank you.
7.should的用法:意为“应该”,表示劝告、建议、或表达某人的义务、责任等。
e.g.We human should protect the environment.
8.had better的用法:表示“最好做某事”,无人称的变化,后面接不带to的不定式,
否定形式为:had better not。
e.g.We had better solve the problem now.
真题演练
1.______she ride a bike when she was 8 years old
A. Can B. Could C. Need D. May
2.Excuse me , ____you show me the way to the station
A. must B. could C. shall D. need
3.Computers___work out difficult maths problems very quickly.
A. can B. need C. must D. should
4.______I come in , Mr Wu Come in , please. You must come here earlier next time.
A. Shall B. Need C. Must D. May
5.Can you speak Japanese No, I ________
A. mustn’t B. can’t C .needn’t D. May not
6.May I borrow your new computer next week Sorry,you_______
A. won’t B. may not C. can’t D. didn’t
7.Could you get a glass of water for me __________
A. Good idea B. You’re welcome C. That’s all right D. No problem
8.Must I still stay here now ______
A . Yes,you do B. No, you may not C. No,you needn’t D. Yes, you are
9. John ______ go there with us tonight, but he isn’t very sure about it.
A. must B. can C. will D. may
10. Even the top students in our class can’t solve this problem. So it _be very difficult.
A. can B. may C. must D. need
11. Put on more clothes. You ______ be feeling cold with only a shirt on.
A. can B. could C. would D. must
12. A computer ______ think for itself, it must be told what to do.
A. can’t B. couldn’t C. may not D. might not
13. ______ I know your name
A. May B. Will C. Shall D. Must
14. This pen looks like mine, yet it isn’t. Whose ______ it be
A. must B. may C. would D. can
15. What kinds of homes will we live in the future
Nobody ______ be sure, but scientists are working out new ideas now.
A. will B. may C. can D. must 1-5 BBADB 6-10CDCDC 11-15DAADC
一、知识结构
二、知识点及考点分析
1.定义:感叹句是用来表达人的特殊情感的句子,可以表达人的喜、怒、哀、乐等强烈情感。感叹句可以是一个单词、一个短语,也可以是由what或how引导的句子,句末常用“!”。
2.感叹句句子结构分类:
what引导的感叹句
①What+a/an+名词单数形式+(主语+谓语)!
What a / an 常用来修饰单数可数名词,若其前面的形容词为元音开头,则用an;若其前面的形容词为辅音开头,则用a。
如:What an interesting story it is)!
What a lovely boy he is)!
②What+名词复数形式+(主语+谓语)!
如:What kind women they are!
③What+不可数名词+(主语+谓语)!
如:What nice music it is!
补充:
①what引导的感叹句主语和谓语通常可以省略;
②What常用来修饰复数可数名词和不可数名词。但有些不可数名词,如 rain, surprise, breakfast, lunch 等,当前面有形容词修饰,使抽象名词具体化时,则要用What a/an。
如:What a heavy rain it is)!
③★★★what引导的感叹句常与fun有关的句型放在一起考,属于感叹句易错点:
it's great fun to do sth.
做某事真的很有趣(这里的fun是不可数名词,表示有趣的事)
改为感叹句:What great fun it is to do sth.!
如:What great fun it is to play with dogs!
have fun doing sth. 做某事很开心
改为感叹句:What great fun we have playing with dogs!
tips:陈述句转化为感叹句只改变语序再加上对应的感叹句引导词what/how ,并不改变句子中原有的语法/句型功能。由此点我们可以很好区分两个带fun的感叹句用法。
how引导的感叹句
①How+形容词/副词+主语+谓语!
如:How hard the worker are working!
注意:
当how修饰动词时,动词不跟着感叹词提到主语之前。 如:How the runner runs!
what与how引导的感叹句,一般情况下可以相互转换,转换后意义不变。
如:What a clever girl she is!=How clever the girl is!
②How+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数形式+主语+谓语!
如:How interesting a book it is!
③How+主语+谓语!
如: How time flies!
关于感叹句引导词how和what的选择
第一步:找出句子主语和谓语
第二步:划掉主语和谓语
剩下为名词或名词词组 what
第三步:分析剩下的句子成分
剩下为形容词或副词 how
例子:________ difficult homework we had yesterday!
③ ①②
①找出主语谓语we had
②划掉主语谓语 we had
③剩余成分为名词词组difficult homework,故选择what;且homework为不可数名词,所以这个句子写为What difficult homework we had yesterday!
真题演练
一、选择填空
1. Look! ________ beautiful that take is!
A. What a B. What C. What an D. How
2. --- Hi, Mary, ________ beautiful day! – Yes, it is.
A. How B. What a C. What D. How a
3. ________ new radio it is!
A. How B. How a C. What a D. What
4. ________ nice computers!
A. What a B. What C. How a D. How
5. ________ day we’re having today!
A. What fine a B. How fine C. What a fine D. What a
6. ________ nice girl Kate is!
A. How B. What C. What an D. What a
7. --- Hi, Mary, ________ beautiful day! – Yes, it is.
A. How B. What a C. What D. How a
8. ________ time we’re having today!
A. What a good B. How good C. What good a D. What good
9. ________ surprising news it is!
A. How B. How a C. What D. What a
10. ________ nice cars!
A. What a B. What C. How a D. How
二、完成下列感叹句
________ lovely the snow looks!
________ a clever boy Jim is!
________ worried they looked!
________ hard the workers are working!
________ long hair she has!
一、1. D 2. B 3. C 4. B 5. C 6. D 7. B 8. A 9. C 10. B
二、1. How 2. What 3. How 4. How 5. What
祈使句
一、知识结构
二、知识点及考点分析
1.定义:表示命令、请求、建议或劝告的句子。其主语you常省略,谓语动词用动词原形,句末用感叹号或句号,读降调。
2.祈使句分类:
①肯定的祈使句:
(1)动词原形+其他 如:Stand up, please.
(2)Be+ n./adj. 如:Be a good boy!
(3)Let's + 宾语 + 动词原形 + 其它成分 如:Let's go to school together.
②否定的祈使句
(1)Don't+ 动词原形
如:Don't stand up.
(2)Let型的否定式有两种:
“Don't+ let + 宾语 + 动词原形 + 其它成分”
“Let + 宾语 + not+ 动词原形 + 其它成分”。
如:Let them not play with fire.
Don't let them not play with fire.
(3)No开头,用来表示禁止性的祈使句。
如:No smoking!
③祈使句的回答
1.祈使句的动作通常是表示将来发生的动作,回答祈使句时,一般用will / won't。
2.在回答具有否定意义的祈使句时,要注意两点:
(1)形式一致即Yes 与will保持一致;no与will not/won’t保持一致)
(2)意思相反即 Yes 是 “不”的意思;No是 “是”的意思)。
3.在回答时,要注意分析上下文语境中所提供的条件。
真题演练
一、选择题
1. ----Don't leave the classroom with the light on.
----________.
A.Yes, I won't B.No, I won't C.Yes, I will D.No, I don't
2.My friend, Lucy, _______ afraid of snakes. She keeps a snakes a pet at home.
A.don't be B.doesn't be C.isn't D.be not
3. ----Don't forget to ask the police for help when you are in trouble.
---- _______.
A.Yes, I won't. B.No problem. C.OK, I won't D.OK, I will
4. ----Don't leave the classroom with the light on.
----________.
A. Yes, I won't B. No, I won't
C. Yes, I will D. No, I don't
5. ----Don't make so much noise, Jack. Your grandpa is sleeping now.
----___________.
A.Yes, I won't B.No, I will.
C.Yes, I will. D.Sorry, I won't
二、填空题
1.Kitty, ________________not be) afraid of snakes. Not all of them are dangerous.
2. Mike, ____________not be) afraid. I will always be with you.
3.----Martin, ____ not be) late for the visit to the museum tomorrow morning.----OK.
4. Get up early, and you ___________ not be) late.
5. Tom, ___________not be) afraid. I'll be with you all the time.
6. Mike, __________not be) afraid. I will always be with you.
7.__________share) your sadness with your friends, and you will feel better.
1.don't be
2.don't be
3.don't be
4.won't be
5.don't be
6.don't be
7.share
反义疑问句
一、知识结构
二、知识点及考点分析
1.定义:反意疑问句是提出情况或看法,问对方是否同意的句子。一般由陈述部分和反意疑问部分构成。
2.改写原则:前肯后否,前否后肯
①You can do it, can’t you
②They are not very late for the meeting, are they
3.具体考点:
反意疑问部分主语及谓语的确定
反意疑问部分主语与谓语,应根据陈述部分的主语和谓语进行选择,但是需要注意一些特殊的情况。而且,反意疑问部分的主语一般要用人称代词(一般不会用人名等),而动词若为否定形式则通常用缩写表达,且动词的形式及时态等必须保持一致。
①He has supper at home every week, doesn’t he 不能用hasn’t he )
②They have known the matter, haven’t they 不能用don’t they )
③They will go to school soon, won’t they 不能用don’t they 或 aren’t they )
④He works very hard, doesn’t he 不能用didn’t he 或won’t he )
情况分类:
①陈述部分带有little, few, never, hardly, seldom,nothing,nobody,none等否定意义的词时,问句部分用肯定式。
如:He never tells lies, does he 不用doesn’t he )
注意:当陈述部分谓语动词是含有un-, im-, in-, dis-等表否定意义的前缀的词时,陈述部分要视为肯定含义,反意疑问部分还是要用否定形式。
如:He dislikes playing football,doesn’t he
②陈述部分是there be结构时,用be there即可.
如:There is going to be a sports meeting next Wednesday, isn’t there
③当陈述部分的主语为指物的不定代词nothing,everything,something,anything等时,反义疑问主语部分用it进行指代。
如:Something is wrong with my phone,isn’t it
④当陈述部分的主语为指人的不定代词nobody,everybody,somebody,anybody等时,反义疑问主语部分可用he或they指代,但是不能用it进行指代。
如:Somebody wants to play with you,doesn’t he/they
⑤当陈述部分的主语为指示代词this/that时,反意疑问部分的主语应用单数形式it;若主语为指示代词these/those时,反意疑问部分的主语应用复数形式they。
如:This is necessary, isn’t it
These are your classmates Tommy and Jackie, aren’t they
⑥当陈述部分的动词是has/had/have时,我们需要进行判断具体含义及用法后才能确定反义疑问句怎么改写:
has/had/have表示“有”时,反义疑问部分可以用has/had/have或者does/did/do;
如: He has a new watch,hasn’t he/doesn’t he
has/had/have to表示半情态动词“不得不”时,反义疑问部分应用does/did/do;
如: He has to finish homework,doesn’t he
has/had/have to表示实义动词“吃,喝,玩等”时,反义疑问部分应用does/did/do;
如:They have a nice dinner,don’t they
had better表示“最好”时,反义疑问部分用had;
如:They had better stop laughing,hadn’t they
has/had/have在现在完成时中,反义疑问部分应用has/had/have
如:He has been to Shanghai,hasn’t he
★★★拓展:
1.'s是is还是has的辨析:has只有表示现在完成时的助动词时,才可以缩写为's。所以,我们可以得出:'s后面如果不是过去分词,那么一定是is,而不是has。
如果's后面是过去分词,我们还要区分主被动,如果是表达主动意,那么's是has的缩写,如果表达的是被动意,那么仍然是is的缩写。
eg. He's already back to China, isn't he
He's already been back to China, hasn't he
He's always made to do a lot of housework, isn't he
2.have/has是助动词还是行为动词:如果have/has表示的是助动词,那么后面要有过去分词;如果后面没有过去分词,那么have/has就是行为动词。
eg. He has gone to Hainan, hasn't he
He has a lot of things to do, doesn't he
⑦ 当陈述部分含有need时,如果need作实义动词,则反意疑问部分应用does/did/do,如果need作情态动词,则反意疑问部分应用need。
如:We need to have a rest,don’t we
We need have a rest,needn’t we
⑧当陈述部分出现I am时,反意疑问部分应用aren'tI。
如:I am right,aren’t I
⑨反义疑问句与祈使句结合:
1)肯定祈使句的反意疑问句反问部分用will you或won't you;
2)否定祈使句的反意疑问句反问部分只用will you;
3)以let's开头的祈使句反意疑问句反问部分用shall we;
<特别注意> 只有以let's开头的祈使句的反意疑问句的反问部分才用shall we,而let us 开头的祈使句的反意疑问句的反问部分应为will you或won't you。
如:Don't be late again, will you
Let's turn on the TV, shall we
Please open the door, will/ won't you
Let us have a try,will you
⑩当陈述部分含有情态动词must时,有下列两种情况:
情态动词must表示“必须”时,疑问部分用mustn’t。
如:I must answer the question, mustn’t I
但若表推测这层含义时,不能用must,而要根据陈述部分的不定式结构(即must之后的动词)以及含义采用相应的动词形式。
如:They must have watched the movie last week, didn’t they
He must be in the library, isn’t he
陈述部分用used to +主语时,问句部分用didn’t /usedn’t +主语形式。
如:She used to live in this countryside, didn’t she /usedn’t she
当陈述部分为主从复合句,且反意疑问句的陈述部分为非第一人称主语+ thinkbelieve, suppose, consider,said,told, reported, asked) + that从句时,问句部分的动词和主语与陈述部分的主句动词和主语保持一致。
如:They all think that English is very important, don’t they 不用isn’t it )
注意:若主句的主语是第一人称I/we,其谓语动词又是 think/suppose/believe等时,反意疑问部分的主语和谓语一般应与从句一致。(特别要注意否定转移)
如: I don't think they are good parents,are they
4.反义疑问句回答原则:
①去掉句子中否定词
②将句子变为一般疑问句
③根据实际情况作答,肯定回答用yes,否定回答用no,特别注意前后形式需一致
如:Yes, he isn’t./No,he is 这样写是错的,yes后必须用肯定,no后必须用否定。
真题演练
1.— The secretary’s already on the way to the company, _________she
— _______. She was badly hurt in the accident and sent to the hospital.
A. hasn’t; Yes B. hasn’t; No C. isn’t; Yes D. isn’t; No
—He has never been to Shanghai, ______ — _______. He has been there twice.
A. has he; No, he hasn’t B. has he; No, he has
C. has he; Yes, he has D. hasn’t he; Yes, he has
3.Alice had a wonderful time yesterday,_______
A. hadn’t she B. wasn’t she C. didn’t she D. wouldn’t she
4.–She didn’t come to school yesterday, did she
–______, though she was not feeling well.
A. No, she didn’t B. Yes, she didn’t C. No, she did D. Yes,she did
5.---He hardly spent any time on his subjects,________
---________, so he does badly in his lessons.
A .didn’t he, Yes B. did he, Yes C. didn’t he, No D. did he, No
6.He’s read this book before,______
A. hasn’t he B. doesn’t he C. isn’t he D. wasn’t he
7.– Let’s go for a walk, ______
-- OK, I’m coming . Don’t forget to bring your camera, ______
A. will you; will you B. will you; shall we
C. shall we; shall we D. shall we; will you
8.John had a short walk after lunch, ________?
A. did he B. didn't he C. had he D. hadn't he
9. Nancy hardly rings you up, ___________
A. doesn’t she B. does she
C. doesn’t Nancy D. does Nancy
10.---Your brother often disagrees with you, _______ he
--- _______. We often have different opinions.
A.does; Yes B. doesn’t ;Yes
C. does; No D. doesn’t; No
情态动词
一、知识结构
二、考点及知识点分析
1.定义:情态动词是表示情态意义的动词,他表示说话人的语气和情态,它不能单独作谓语,必须与实义动词一起构成谓语,情态动词没有人称和数的变化,过去式通常表示更客气、更委婉。
2.情态动词有四个特征:
①不能单独做谓语,必须与其他动词一起构成谓语;
②没有人称和数的变化;
③情态动词后必须跟动词原形;
④具有助动词功能。
3.情态动词基本含义:
can could ) 能,会 may might) 可以,可能
will would) 将,会,愿意 must 必须
have to不得不 need 需要
should应该 had better 最好 had better not) do sth.
4.表猜测语气的情态动词
表猜测性的情态动词有:may /can’t /must 。
may表没把握的猜测;can’t 表有把握的否定猜测;must 表有把握的肯定猜测
5.情态动词开头的疑问句的答语
句型 肯定回答 否定回答
Can I… Yes, you can . No, you can’t .
May I … Yes ,you may. No, you mustn’t./No, you can’t.
Must I… Yes, you must. No, you needn’t./No you don’t have to
Need I… Yes, you must. No, you needn’t
6.情态动词的辨析
①must 与have to :
must 表主观看法,意为“必须”。
如:We must finish homework.
have to表客观需要,意为“不得不”。
如:We have to stay at home,because it’s raining outside.
②maybe与may be
may 为情态动词后接动词原形,may be一般位于句子中;
maybe为副词意思为“大概,也许”,maybe一般位于句子开头。
如:He may be tired.
Maybe he is tired.
③can与be able to
can只有现在和过去时(could),且can强调自身已具有的能力
be able to可用于任何时态中,而be able to 强调通过努力而获得的能力
如:He can speak Chinese.
I was able to swim when I was young.
④can’t 与mustn’t
can’t 表“不可能”;mustn’t表“禁止,不许”。
如:He can’t be home,I saw him go out.
You mustn’t go out.
三、情态动词具体用法分析:
1. can的用法:
①表示能力,即有某种能力,一般指与生来具来的能力,注意与be able to(强调通过努力而获得的能力) 区分。
e.g.I can smell with my nose.
②表示许可,常在口语中。常用may代替。
e.g.You can/may use my computer.
③表示推测,意为“可能”,常用于否定句和疑问句中,而can’t表示“不可能”。
e.g.Can the news be true
2.could的用法:
①can的过去形式,意思是“能、会”,表示过去拥有的能力。
e.g.She could swim when she was 11 years old.
②could在疑问句中,表示委婉请求等,此时could并不是过去式的形式。
e.g.Could you help me with my homework
3.may的用法:
①表示请求、许可,比can正式,语气更委婉。
e.g.May I use your dictionary
②表示推测,意为“可能,或许”,一般表示可能性不是很大,用于肯定句中。
e.g.It may rain next week .明天可能会下雨。
③may的过去式为might,表示推测,可能性低于may。
e.g.He drops off school. He might be sick.
④表示对某人的一种希望、祝愿,常可译为“祝愿、祝福某人...”。
句型一般为may +主语+动词原形。
e.g.May you happy!
4.must的用法:
①must表示主观要求、看法或命令,意思是“必须、一定...”。
e.g. You must finish your homework now.
②其否定形式mustn’t表示 “禁止,不准等”,不能翻译为不可能。
e.g.You mustn’t play with fire.
③must表示很有把握的推测,“肯定”,不能用于否定句中。
e.g.The light is on, so she must be at school at the moment.
④针对must提问的回答: 肯定回答为must
否定回答为needn’t 或don’t have to
e.g.—Must I finish my homework
—No, you needn’t./ No, you don’t have to.
5.need的用法:
①need表需要,用于否定句和疑问句中。
②用need提问的回答:
肯定回答为must,否定回答为needn’t或don’t have to。
e.g. —Need I finish homework today
—Yes, you must ./—No. you needn’t /don’t have to.
③need还可以作实义动词,此时有人称、数和时态的变化。
e.g. He needs to learn more about the girl.他需要多了解那个女孩。
The door needs painting. = The door needs to be painted.
6.shall的用法:shall表示征求对方意见(一般用于第一、三人称)。
e.g.Shall we go shopping 回答:Yes, please./All right./No, thank you.
7.should的用法:意为“应该”,表示劝告、建议、或表达某人的义务、责任等。
e.g.We human should protect the environment.
8.had better的用法:表示“最好做某事”,无人称的变化,后面接不带to的不定式,
否定形式为:had better not。
e.g.We had better solve the problem now.
真题演练
1.______she ride a bike when she was 8 years old
A. Can B. Could C. Need D. May
2.Excuse me , ____you show me the way to the station
A. must B. could C. shall D. need
3.Computers___work out difficult maths problems very quickly.
A. can B. need C. must D. should
4.______I come in , Mr Wu Come in , please. You must come here earlier next time.
A. Shall B. Need C. Must D. May
5.Can you speak Japanese No, I ________
A. mustn’t B. can’t C .needn’t D. May not
6.May I borrow your new computer next week Sorry,you_______
A. won’t B. may not C. can’t D. didn’t
7.Could you get a glass of water for me __________
A. Good idea B. You’re welcome C. That’s all right D. No problem
8.Must I still stay here now ______
A . Yes,you do B. No, you may not C. No,you needn’t D. Yes, you are
9. John ______ go there with us tonight, but he isn’t very sure about it.
A. must B. can C. will D. may
10. Even the top students in our class can’t solve this problem. So it _be very difficult.
A. can B. may C. must D. need
11. Put on more clothes. You ______ be feeling cold with only a shirt on.
A. can B. could C. would D. must
12. A computer ______ think for itself, it must be told what to do.
A. can’t B. couldn’t C. may not D. might not
13. ______ I know your name
A. May B. Will C. Shall D. Must
14. This pen looks like mine, yet it isn’t. Whose ______ it be
A. must B. may C. would D. can
15. What kinds of homes will we live in the future
Nobody ______ be sure, but scientists are working out new ideas now.
A. will B. may C. can D. must 1-5 BBADB 6-10CDCDC 11-15DAADC
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
