外研版(2019) 必修第一册 Unit 2 Exploring English Starting out and Understanding ideas 课件(32张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019) 必修第一册 Unit 2 Exploring English Starting out and Understanding ideas 课件(32张) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 72.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-09-13 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共32张PPT)
Unit 2 Exploring English
Starting out & understanding ideas
To have another language is to possess a second soul.
—— Charlemagne
Teaching objectives
Learning objectives:
1、Students can grasp the new words and expressions such as unique、creative、sculpture、burn up and so on.
2、Students can grasp the general idea for the whole passage.
Ability objectives:
Students will be able to use different basic reading strategies like prediction/skimming/scanning correctly in their reading process.
Emotional objectives:
Students can foster their interest in learning English and can cooperate with classmates actively and complete the tasks together.
Key points and difficult points
Key points:
1、Help students know the meaning and usage of the new words and expressions such as unique、creative、sculpture、burn up and so on.
2、Let students understand the general idea for the whole passage through reading.
Difficult points:
How to use different basic reading strategies like prediction/skimming/scanning correctly in their reading process.
Warming-up(6mins)
Watch the video and complete the tasks.
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
Where do a third of English words come from What examples are given in the video
3,Draw a thinking map of the history of English.
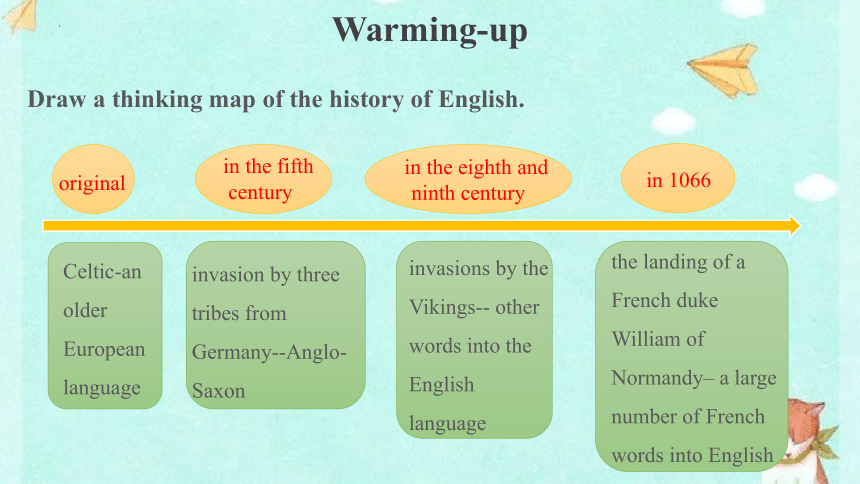
Warming-up
Draw a thinking map of the history of English.
original
in the fifth century
in the eighth and ninth century
in 1066
Warming-up
Warming-up
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
Where do a third of English words come from What examples are given in the video
The UK, Ireland, the USA, Canada, New Zealand and Australia.
More than a third of English words come from French.
For example, fruit, table, crocodile and invasion.
Warming-up
Draw a thinking map of the history of English.
original
in the fifth century
in the eighth and ninth century
in 1066
Celtic-an older European language
invasion by three tribes from Germany--Anglo-Saxon
invasions by the Vikings-- other words into the English language
the landing of a French duke William of Normandy– a large number of French words into English
Pre-reading-prediction
Look at the title of the passage and the pictures. Tick what you think the passage is about.
Neither Pine
nor Apple
in Pineapple
title
sculpt
sculpture
carsick
homesick
opposing
behavior
confusing
n. 题目,标题
v. 雕刻,雕塑
adj. 晕车的
adj. 想家的
adj. 令人困惑的
n. 雕像,雕刻品,雕塑作品
adj. (观点,意见等)相反的,相对立的
n. 举止,行为
Pre-reading-words/phrases explanation
unique
burn up
burn down
alarm
reflect
creativity
visible
wind up
adj. 独一无二的,独特的
v. 显示,反映
n. 创造性,创造力
adj. 看得见的,可见的
给(机械)上发条;使(活动、
会议等)结束
烧毁,烧尽
烧毁
n. 警报器;闹钟
Pre-reading-words/phrases explanation
Global reading-skimming
Read the passage and check your prediction.
Neither Pine
nor Apple
in Pineapple
Global reading-scanning
Read the passage again and finish the following two questions.
What is the topic sentence of this passage
Choose the author’s purpose in writing the passage.
This got me thinking how English can be a crazy language to learn.
1 To tell us that English is very difficult to learn.
2 To give advice on how to learn English.
3 To show that English is interesting and creative.
4 To explain how English was created.
Any supportive sentences
Detailed reading
Read and complete the notes with words from the passage.
unique
hamburger
pineapple
painting
airsick
carsick
homesick
opposing
behaviors
fill out
invisible
ends
reflects
Post-reading-thinking
Read the following information and answer the questions.
a. How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
b. Does the information above give you a better understanding of the passage Give your reasons.
The name of “pineapple” developed from the Spanish word “pina”, with “apple” added to show it’s a kind of fruit; the name of hamburger came from the idea of “Hamburg steak”, and later people reinvented it and called it “hamburger”; eggplants got the name because they used to look like eggs.
Group Discussion
Do you think English is a crazy language to learn Why Can you give more examples
In my opinion, English is crazily interesting. For example, the sentence “Never trouble troubles till trouble troubles you” includes two parts of speech of the word “ trouble”. The first one and the forth one are verbs; and the second and third one are nouns. Usually, it’s very important to figure out the part of speech of each word so that we can better memorize it.
Summary
Can you summarize all the examples that the author used to show the unique madness of English?
Homework
1,Retell the passage after class.
2,Find some similar language phenomena in Chinese and give some examples. Share them with your classmates in the next class.
Homework hints
Some examples:
鱼香肉丝中没有“鱼”
狮子头中没有“狮子”
老婆饼里没有“老婆”
The development of languages is closely connected with culture and if we want to learn languages well, we’d better know more culture behind them.
Goodbye!
Love you guys!
Notes
1. This got me thinking how English can be a crazy language to learn.
get sb doing=make someone do sth
The failure in the examination got me reflecting on my careless learning.
考试失利让我反思我的学习不认真。
Notes
2. Neither is there pine nor apple in pineapple.
neither...nor...意为“既不……也不……”,其含义是否定的,可连接任意两个并列的成分。
neither...nor...的用法:
(1) neither...nor...连接两个主语时,谓语动词的单复数应和临近的主语一致,遵循“就近原则”。
(2) neither可以单独作主语,表示“两者中没有一个”。
Notes
(3) 表示“一个人没有做某事,另一个人也没做同一类事”时,可用neither或nor引起的部分倒装句进行简略回答,其结构为:Neither/Nor+助动词/情态动词/be动词+主语
Neither dad nor mum is at home today. 今天父母都不在家。
Neither of them likes football. 他们俩都不喜欢足球。
They didn’t go to the park yesterday. Neither/Nor did we.
昨天他们没去公园,我们也没去。
Notes
Fill in the blanks with proper words.
a. Neither his parents nor he ____________ (like) eating meat.
b. —I have never been to New York yet.
—____________________(我也没去过).
c. The parents were not satisfied with the result and their son wasn’t either.
→______________________________________ satisfied with the result.
likes
Neither / Nor have I
Neither the parents nor their son was
Notes
3. That is why when the stars are out, they are visible, but when the lights are out, they are invisible.
That is why...意为“这就是……的原因”;why引导表语从句,表示结果。
其他相关句型:
That / It is / was because...
这/那是因为……(because引导表语从句,表示原因)
The reason why...is / was that...
……的原因是……(why引导定语从句并在从句中做状语;that引导表语从句,表示原因)
He fell off a tall tree. That was why he hurt his leg.
=He hurt his leg. That was because he fell off a tall tree.
=The reason why he hurt his leg was that he fell off a tall tree.
他从一棵很高的树上摔下来。那就是他弄伤腿的原因。
Notes
Fill in the blanks with proper words.
a. He’s more of a talker than a doer. This is ____________ he never finishes anything.
b. From space, the earth looks blue. This is ____________ about seventy-one percent of its surface is covered by water.
c. Tom came late for the meeting because he was ill.
→ Tom was ill.________ ________ ________ he came late for the meeting.
→Tom came late for the meeting.________ ________ ________ he was ill.
→________ ________ ________ Tom came late for the meeting ________ ________ he was ill.
why
because
That
was
why
That
was
because
The
reason
why
was
that
Notes
Notes
language points
做某事有麻烦/困难/问题
让某人做……
在空闲时间
雕塑
想家
提及,说到
反义词
无害的/有害的
可耻的
10. 从……往外看
11. 对……感到困惑
12. 大写的WHO
13. 好奇/想知道
14. 独一无二的
15. 烧毁
16. 填写
17. 反映了人类的创造性
18. 上发条,结束
Notes
language points
做某事有麻烦/困难/问题
让某人做……
在空闲时间
雕塑
想家
提及,说到
反义词
无害的/有害的
可耻的
have trouble / difficulty / problems doing…
get…doing
in one’s free time
sculpture
homesickness
speaking of…
opposite
harmless / harmful
shameful / shameless
Notes
language points
look out of
be confused about
capitalized WHO
wonder at
unique
burn up / burn down
fill in / fill out
reflect the creativity of human race
wind up (wind-wound-wound)
10. 从……往外看
11. 对……感到困惑
12. 大写的WHO
13. 好奇/想知道
14. 独一无二的
15. 烧毁
16. 填写
17. 反映了人类的创造性
18. 上发条,结束
Goodbye!
love you guys!
Unit 2 Exploring English
Starting out & understanding ideas
To have another language is to possess a second soul.
—— Charlemagne
Teaching objectives
Learning objectives:
1、Students can grasp the new words and expressions such as unique、creative、sculpture、burn up and so on.
2、Students can grasp the general idea for the whole passage.
Ability objectives:
Students will be able to use different basic reading strategies like prediction/skimming/scanning correctly in their reading process.
Emotional objectives:
Students can foster their interest in learning English and can cooperate with classmates actively and complete the tasks together.
Key points and difficult points
Key points:
1、Help students know the meaning and usage of the new words and expressions such as unique、creative、sculpture、burn up and so on.
2、Let students understand the general idea for the whole passage through reading.
Difficult points:
How to use different basic reading strategies like prediction/skimming/scanning correctly in their reading process.
Warming-up(6mins)
Watch the video and complete the tasks.
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
Where do a third of English words come from What examples are given in the video
3,Draw a thinking map of the history of English.
Warming-up
Draw a thinking map of the history of English.
original
in the fifth century
in the eighth and ninth century
in 1066
Warming-up
Warming-up
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
Where do a third of English words come from What examples are given in the video
The UK, Ireland, the USA, Canada, New Zealand and Australia.
More than a third of English words come from French.
For example, fruit, table, crocodile and invasion.
Warming-up
Draw a thinking map of the history of English.
original
in the fifth century
in the eighth and ninth century
in 1066
Celtic-an older European language
invasion by three tribes from Germany--Anglo-Saxon
invasions by the Vikings-- other words into the English language
the landing of a French duke William of Normandy– a large number of French words into English
Pre-reading-prediction
Look at the title of the passage and the pictures. Tick what you think the passage is about.
Neither Pine
nor Apple
in Pineapple
title
sculpt
sculpture
carsick
homesick
opposing
behavior
confusing
n. 题目,标题
v. 雕刻,雕塑
adj. 晕车的
adj. 想家的
adj. 令人困惑的
n. 雕像,雕刻品,雕塑作品
adj. (观点,意见等)相反的,相对立的
n. 举止,行为
Pre-reading-words/phrases explanation
unique
burn up
burn down
alarm
reflect
creativity
visible
wind up
adj. 独一无二的,独特的
v. 显示,反映
n. 创造性,创造力
adj. 看得见的,可见的
给(机械)上发条;使(活动、
会议等)结束
烧毁,烧尽
烧毁
n. 警报器;闹钟
Pre-reading-words/phrases explanation
Global reading-skimming
Read the passage and check your prediction.
Neither Pine
nor Apple
in Pineapple
Global reading-scanning
Read the passage again and finish the following two questions.
What is the topic sentence of this passage
Choose the author’s purpose in writing the passage.
This got me thinking how English can be a crazy language to learn.
1 To tell us that English is very difficult to learn.
2 To give advice on how to learn English.
3 To show that English is interesting and creative.
4 To explain how English was created.
Any supportive sentences
Detailed reading
Read and complete the notes with words from the passage.
unique
hamburger
pineapple
painting
airsick
carsick
homesick
opposing
behaviors
fill out
invisible
ends
reflects
Post-reading-thinking
Read the following information and answer the questions.
a. How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
b. Does the information above give you a better understanding of the passage Give your reasons.
The name of “pineapple” developed from the Spanish word “pina”, with “apple” added to show it’s a kind of fruit; the name of hamburger came from the idea of “Hamburg steak”, and later people reinvented it and called it “hamburger”; eggplants got the name because they used to look like eggs.
Group Discussion
Do you think English is a crazy language to learn Why Can you give more examples
In my opinion, English is crazily interesting. For example, the sentence “Never trouble troubles till trouble troubles you” includes two parts of speech of the word “ trouble”. The first one and the forth one are verbs; and the second and third one are nouns. Usually, it’s very important to figure out the part of speech of each word so that we can better memorize it.
Summary
Can you summarize all the examples that the author used to show the unique madness of English?
Homework
1,Retell the passage after class.
2,Find some similar language phenomena in Chinese and give some examples. Share them with your classmates in the next class.
Homework hints
Some examples:
鱼香肉丝中没有“鱼”
狮子头中没有“狮子”
老婆饼里没有“老婆”
The development of languages is closely connected with culture and if we want to learn languages well, we’d better know more culture behind them.
Goodbye!
Love you guys!
Notes
1. This got me thinking how English can be a crazy language to learn.
get sb doing=make someone do sth
The failure in the examination got me reflecting on my careless learning.
考试失利让我反思我的学习不认真。
Notes
2. Neither is there pine nor apple in pineapple.
neither...nor...意为“既不……也不……”,其含义是否定的,可连接任意两个并列的成分。
neither...nor...的用法:
(1) neither...nor...连接两个主语时,谓语动词的单复数应和临近的主语一致,遵循“就近原则”。
(2) neither可以单独作主语,表示“两者中没有一个”。
Notes
(3) 表示“一个人没有做某事,另一个人也没做同一类事”时,可用neither或nor引起的部分倒装句进行简略回答,其结构为:Neither/Nor+助动词/情态动词/be动词+主语
Neither dad nor mum is at home today. 今天父母都不在家。
Neither of them likes football. 他们俩都不喜欢足球。
They didn’t go to the park yesterday. Neither/Nor did we.
昨天他们没去公园,我们也没去。
Notes
Fill in the blanks with proper words.
a. Neither his parents nor he ____________ (like) eating meat.
b. —I have never been to New York yet.
—____________________(我也没去过).
c. The parents were not satisfied with the result and their son wasn’t either.
→______________________________________ satisfied with the result.
likes
Neither / Nor have I
Neither the parents nor their son was
Notes
3. That is why when the stars are out, they are visible, but when the lights are out, they are invisible.
That is why...意为“这就是……的原因”;why引导表语从句,表示结果。
其他相关句型:
That / It is / was because...
这/那是因为……(because引导表语从句,表示原因)
The reason why...is / was that...
……的原因是……(why引导定语从句并在从句中做状语;that引导表语从句,表示原因)
He fell off a tall tree. That was why he hurt his leg.
=He hurt his leg. That was because he fell off a tall tree.
=The reason why he hurt his leg was that he fell off a tall tree.
他从一棵很高的树上摔下来。那就是他弄伤腿的原因。
Notes
Fill in the blanks with proper words.
a. He’s more of a talker than a doer. This is ____________ he never finishes anything.
b. From space, the earth looks blue. This is ____________ about seventy-one percent of its surface is covered by water.
c. Tom came late for the meeting because he was ill.
→ Tom was ill.________ ________ ________ he came late for the meeting.
→Tom came late for the meeting.________ ________ ________ he was ill.
→________ ________ ________ Tom came late for the meeting ________ ________ he was ill.
why
because
That
was
why
That
was
because
The
reason
why
was
that
Notes
Notes
language points
做某事有麻烦/困难/问题
让某人做……
在空闲时间
雕塑
想家
提及,说到
反义词
无害的/有害的
可耻的
10. 从……往外看
11. 对……感到困惑
12. 大写的WHO
13. 好奇/想知道
14. 独一无二的
15. 烧毁
16. 填写
17. 反映了人类的创造性
18. 上发条,结束
Notes
language points
做某事有麻烦/困难/问题
让某人做……
在空闲时间
雕塑
想家
提及,说到
反义词
无害的/有害的
可耻的
have trouble / difficulty / problems doing…
get…doing
in one’s free time
sculpture
homesickness
speaking of…
opposite
harmless / harmful
shameful / shameless
Notes
language points
look out of
be confused about
capitalized WHO
wonder at
unique
burn up / burn down
fill in / fill out
reflect the creativity of human race
wind up (wind-wound-wound)
10. 从……往外看
11. 对……感到困惑
12. 大写的WHO
13. 好奇/想知道
14. 独一无二的
15. 烧毁
16. 填写
17. 反映了人类的创造性
18. 上发条,结束
Goodbye!
love you guys!
