2023届高三英语二轮复习:名词性从句、定语从句、状语从句 课件-(52张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023届高三英语二轮复习:名词性从句、定语从句、状语从句 课件-(52张ppt) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 985.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-09-16 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共52张PPT)
英语语法之从句专题 白
01
课前练习
02
名词性从句
03
定语从句
04
状语从句
具体工作措施
CONTENTS
目 录
课前练习
1. There was never any time for Kate to feel lonely, _____ she was an only child.
2. The research is so designed that once _____(begin), nothing can be done to change it .
3. When a pencil is partly in a glass of water, it looks as if it _____(break) .
4. Not until all the fish died in the river _____ (we realize) how serious the pollution was.
5. --- Did Linda see the traffic accident
--- No, no sooner ____ (she goes) than it happened.
6. Half an hour later, Lucy still couldn't get a taxi _____ the bus had dropped her.
7. Hardly had I finished my composition _____ the bell rang.
8. He did the experiment ____ he was told.
9. If we work with a strong will, we overcome any difficulty, ____ great it is.
10. They’ll stand by you _____you don’t succeed.
11. Today, we will begin ____we stopped yesterday so that no point will be left out.
12. The meaning of the word “nice” changed a few times ____ it finally came to include the sense “pleasant”.
13. You will never gain success ____ you are fully devoted to your work.
14. Parents should take seriously their children’s requests for sunglasses _____________ eye protection is necessary in sunny weather.
15. As is reported, it is 100 years ______________ Qinghua University was founded.
16. Leave your key with your neighbor ___________ you lock yourself out one day.
17. One’s life has value _______________ one brings value to the life of others.
单句填空(选择恰当的关联词或所给单词的正确形式填空, 不多于3个单词)
课前练习
1. There was never any time for Kate to feel lonely, although/though she was an only child.
2. The research is so designed that once begun(begin), nothing can be done to change it .
3. When a pencil is partly in a glass of water, it looks as if it _were broken___(break) .
4. Not until all the fish died in the river __did we realize___ (we realize) how serious the pollution was.
5. --- Did Linda see the traffic accident
--- No, no sooner _had she_gone__ (she goes) than it happened.
6. Half an hour later, Lucy still couldn't get a taxi _where__ the bus had dropped her.
7. Hardly had I finished my composition _when__ the bell rang.
8. He did the experiment _as_ he was told.
9. If we work with a strong will, we overcome any difficulty, however / no matter how great it is.
10. They’ll stand by you even_if you don’t succeed.
11. Today, we will begin where we stopped yesterday so that no point will be left out.
12. The meaning of the word “nice” changed a few times before it finally came to include the sense “pleasant”.
13. You will never gain success _unless_you are fully devoted to your work.
14. Parents should take seriously their children’s requests for sunglasses because eye protection is necessary in sunny weather.
15. As is reported, it is 100 years since Qinghua University was founded.
16. Leave your key with your neighbor in case you lock yourself out one day.
17. One’s life has value as long as/so long as one brings value to the life of others.
单句填空(选择恰当的关联词或所给单词的正确形式填空, 不多于3个单词)
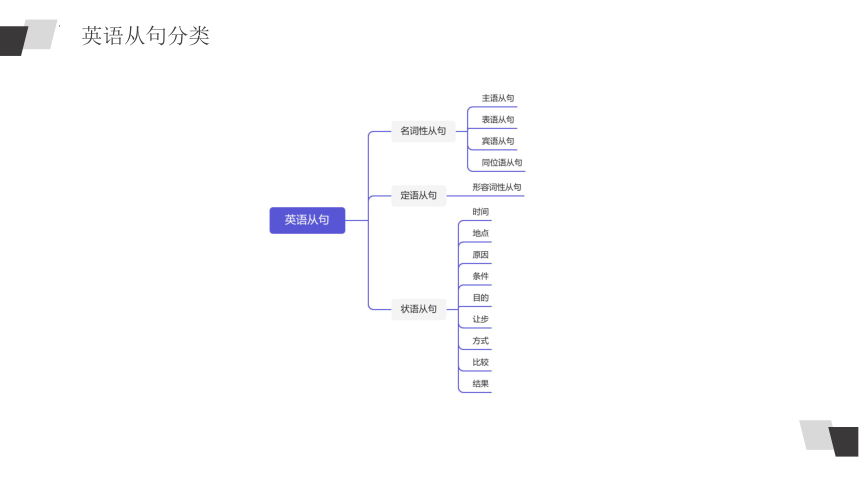
英语从句分类
01
名词性从句
名词性从句
连词:在从句中均不充当任何成分,仅起到连接作用
that(三无连接词)
whether, if(均表示“是否”表明从句内容的不确定性)
as if ,as though(均表示“好像”,“似乎”)
连接代词:what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whose, whichever, whomever
连接副词:when, where, how, why, how many, how much, how often
三类连接词
名词性从句
作句子主语的从句叫主语从句,通常放在主句谓语动词之前或由形式主语it代替,而本身放在句子末尾。that在句中无词义,只起连接作用;连接代词和连接副词在句中既保留自己的疑问含义、又起连接作用。
主语从句
例如:
What he wants to tell us is not clear.
Who will win the match is still unknown
It is known to us how he became a writer.
Where the English evening will be held has not yet been announced.
That he finished writing the composition in such a short time surprised us all.
Whether we will go for an outing tomorrow remains unknown.
Who will be our monitor hasn't been decided yet.
Whom we must study for is a question of great importance.
What caused the accident remains unknown.
Whatever you did is right.
Who the watch belongs to was lost is unknown.
What we need is time.
What we need are good doctors.
01
不可省略的连词:
1. 介词后的连词
2. that没有实际意义,但是不能省略
That she was chosen made us very happy.
3. 同位语从句的连词不可省略。
We heard the news that our team had won.
whether与if 均为“是否”的意思,但在下列情况下只可用whether:
whether引导主语从句并在句首
引导表语从句:The trouble was whether we could manage it ourselves or not. The question is whether she should have a low opinion of the test
介词后面只能用whether:
This depends upon whether we are determined to do it.
I am not interested in whether you'll come or not.
4. 从句后有"or not" ——Whether he will come is not clear. Can you tell me whether to go or to stay
名词性从句
有时为避免句子头重脚轻,常用形式主语it代替主语从句作形式主语放于句首,而把主语从句置于句末。主语从句后的谓语动词一般用单数形式。
形式主语it代替主语从句放于句首
常用句型如下:
(1) It is +名词+从句
It is a fact that … 事实是… It is an honor that …非常荣幸 It is common knowledge that …是常识
(2) it is +形容词+从句
It is natural that… 很自然… It is strange that… 奇怪的是…
(3) it +不及物动词+从句
It seems that… 似乎… It happened that… 碰巧…
(4) it is+过去分词+从句
It is reported that… 据报道… It has been proved that… 已证实…
例句:
(1)It is certain that he will win the match.
(2)It is true that he has made a very important discovery in chemistry.
(3)It is very likely that they will hold a meeting.
(4)It is strange that he should do that.
(5)It is important that we all should attend the meeting.
(6)It is strange that the man should have stuck to his silly ideas.
(7)It is a pity that we won't be able to go to the south to spend our summer vacation.
(8)It is still a mystery what caused the accident.
(9)It is said that he has gone to shanghai.(=He is said to have gone to shanghai)
(10) It is known to all that the gun powder was first invented by the Chinese.
(11)It is suggested that the work should be done with great care.
(12)It seems that he has seen the film.(=He seems to have seen the film)
(13)It happened that the two cheats were there. (=The two cheats happened to be there)
另注意在主语从句中用来表示惊奇、不相信、惋惜、理应如此等语气时,谓语动词要用虚拟语气“(should) +do”,常用的句型有:It is necessary (important, natural, strange, etc.) that … It is suggested (requested, proposed, desired, etc.) that…
That the hungry rabbit had already eaten a carrot for dinner this evening is obvious.
It is obvious that the hungry rabbit had already eaten a carrot for dinner this morning.
名词性从句
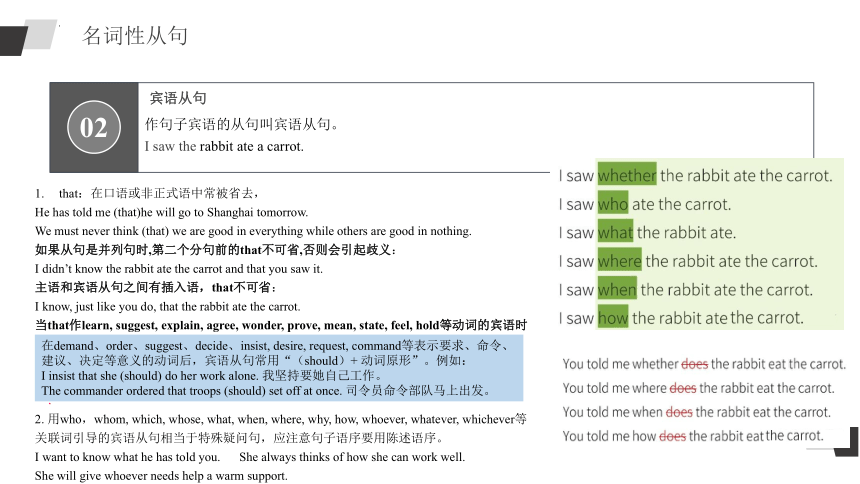
宾语从句
that:在口语或非正式语中常被省去,
He has told me (that)he will go to Shanghai tomorrow.
We must never think (that) we are good in everything while others are good in nothing.
如果从句是并列句时,第二个分句前的that不可省,否则会引起歧义:
I didn’t know the rabbit ate the carrot and that you saw it.
主语和宾语从句之间有插入语,that不可省:
I know, just like you do, that the rabbit ate the carrot.
当that作learn, suggest, explain, agree, wonder, prove, mean, state, feel, hold等动词的宾语时
2. 用who,whom, which, whose, what, when, where, why, how, whoever, whatever, whichever等
关联词引导的宾语从句相当于特殊疑问句,应注意句子语序要用陈述语序。
I want to know what he has told you. She always thinks of how she can work well.
She will give whoever needs help a warm support.
02
在demand、order、suggest、decide、insist, desire, request, command等表示要求、命令、建议、决定等意义的动词后,宾语从句常用“(should)+ 动词原形”。例如:
I insist that she (should) do her work alone. 我坚持要她自己工作。
The commander ordered that troops (should) set off at once. 司令员命令部队马上出发。
作句子宾语的从句叫宾语从句。
I saw the rabbit ate a carrot.
名词性从句
宾语从句的形式宾语it
①动词find, feel, consider, make,believe 等后面有宾语补足语的时候,则需要用it做形式宾语而将that宾语从句后置.
I think it necessary that we take plenty of hot water every day .我认为每天多喝开水是有必要的.
I feel it a pity that I haven’t been to the get-together. 我没去聚会,感觉非常遗憾.
I have made it a rule that I keep diaries. 我每天写日记成了习惯.
We all find it important that we (should) make a quick decision about this mater. 我们都认为对这件事马上做出决定很重要.
②有些动词带宾语从句时需要在宾语与从句前加it :hate, take , owe, have, see to.
I hate it when they talk with their mouths full of food.我讨厌他们满嘴食物时说话.
He will have it that our plan is really practical.他会认为我们的计划确实可行.
We take it that you will agree with us.我们认为你会同意我们的.
When you start the engine, you must see to it that car is in neutral. 开启发动机时, 一定要使汽车的离合器处于空挡位置.
③若宾语从句是wh-类,则不可用it代替
We all consider what you said to be unbelievable.我们都认为你所说的是不可信的.
We discovered what we had learned to be valuable.我们发现我们所学到的东西都是有用的.
形容词的宾语从句:sure, certain, glad,please,happy,sorry,afraid,satisfied,surprised
I am sure I will pass the exam.我确信我会通过考试.
I am sorry that I have troubled you so long.很抱歉我这么长时间在打扰你.
He is glad that Li Ming went to see him when he was ill.
他很高兴在他生病的时候李明能去看望他.
有时候except,but,besides三个介词后可见到that引导的宾语从句
I know nothing about my new neighbor except that he used to work with a company.
对于我的新邻居我只知道他曾在一家公司上班,其他一无所知.
名词性从句
宾语从句的否定转移
主句的谓语动词是think, believe, imagine, suppose, consider, espect, fancy, guess等,并且主句的主语是第一人称而且为一般现在时,从句的否定词一般要转移到主句上来
1) 将think, believe, suppose, expect, fancy, imagine等动词后面宾语从句的否定词转移到主句中,即主句的谓语动词用否定式,而从句的谓语动词用肯定式。
I don't think I know you. 我想我并不认识你。
I don' t believe he will come. 我相信他不回来。
注意:若谓语动词为hope,宾语从句中的否定词不能转移。
I hope you weren't ill. 我想你没有生病吧。
2) 将seem, appear 等后的从句的否定转移到前面。
It doesn't seem that they know where to go. 看来他们不知道往哪去。
It doesn't appear that we'll have a sunny day tomorrow. 看来我们明天不会碰上好天气。
名词性从句
宾语从句的主从时态要一致
在大多数情况下,宾语从句和主句中的时态要保持一致
当主句为现在时或将来时,宾语从句的时态一般不受主句的时态所影响.
当主句为过去时
①从句用一般过去时或过去进行时 表示与主句谓语动词动作同时发生
I only knew he was studying in a western country, but I didn’t know what country he was in. 我只知道他当时在西方的一个国家读书,可不知道是哪个国家.
He asked me if I was reading the story The Old Man and the Sea when he was in. 他问我他进来的时候我是否正在读<<老人与海>>.
②从句过去完成时表示该动作发生在主句谓语动作之前
He told me that he had told Mary about the meeting already. 他告诉我他已经把有关会议的事情告诉的了Mary.
③从句谓语用过去将来时表示该动作发生在主句谓语动作之后
The reporter asked if the government would take necessary measures to put down the to-do. 记者问政府是否会采取必要的措施镇压骚乱.
如果从句是一个客观真理,那么从句的时态不根据主句的时态而变化
The teacher said that the moon goes around the earth yesterday.
名词性从句
表语从句的基本结构为:主语 + 系动词 + that从句,用一个句子作为表语,说明主语是什么或者怎么样系动词不光是 be动词(am、is、are),其实系动词除了be之外,还有 become(成为)、turn(变成)、go(变成)、seem(似乎)、appear(似乎、显得)、look(看起来)、feel(摸起来)、sound(听起来)、smell(闻起来)等等。
表语从句
03
连接词 例句
That(无词义,通常不省略) - The fact was that he had forgotten about it.事实上,他已经把这件事忘了。
- It seems that there is no cure.似乎没有治愈的办法。
- The trouble is that I have lost his address.麻烦是我把他的地址丢了。
whether - The question is whether such issues should be part of the agenda in the meeting.
- My first thought was whether he would visit the battlefield.
疑问副词,表示地点、时间、原因、方式等的词:where、when、how、why 等 This is where you came in.这就是你进来的地方。
That was when my sister was watching the news.那是我妹妹看新闻的时候。
The problem seemed how we could make him understand it.
That’s why he didn’t come.这就是他没有来的缘故。
疑问代词 who,whom,whose,whoever,what,whatever,which,whichever The problem is not who will go, but who will stay.问题不是谁去,而是谁留下来。
- The mountain is no longer what it used to be.这座山不再是过去的样子了。
- The best swimsuit(泳衣) for a full figure is whichever one makes you look and feel great.
特殊引导词(just) as, as if, as though, because - John looked just as he had looked twenty years before.
- It sounds as if someone is knocking at the door.听起来好像有人在敲门。
- Now it was as though she had known Millie for years.现在看来她似乎认识米莉很多年了。
- That is because I don’t like Japanese.因为我不喜欢日本人。
注意:
This is because…表示原因
He did not see the film last night. That is because he had to help his little sister with her homework.
That is why.../That is the reason why...表示原因带来的结果
He did not see the film last nigh. This is why he will see it today.
名词性从句
易错点
表语从句一定要用陈述语序
False: The question is when can he arrive at the hotel.
Right: The question is when he can arrive at the hotel.
不可以用if,而用whether 连接表语从句(as if 例外)
(除了宾语从句,主语从句、表语从句和同位语从句都用whether)
False: The question is if the enemy is marching towards us.
Right: The question is whether the enemy is marching towards us.
Right: It looked as if he had understood this question.
不像宾语从句,在有表语从句的复合句中,主句时态和从句时态
可以不一致。
Right: The question is who will travel with me to Beijing tomorrow.
Right: The question is why he cried yesterday.
that在表语从句中不可以省掉。
主句:The problem is... 疑问句:Which book do you like best 表语从句:The problem is which book you like best
主句:The problem is... 疑问句:How much does this coat cost
表语从句:The problem is how much this coat costs.
将疑问句的语序变成陈述句的语序,疑问句中主语之前有助动词 do、does、did 要先将其去掉。
主句:The question was... 疑问句:Who can answer the question?表语从句:The question was who could answer the question. (语序不变,can 变成了过去式 could)
主句:The question was ... 疑问句:What's the matter
表语从句:The question was what was the matter. 问题是发生了什么?(语序不变,is 变成了过去式 was)
疑问词在句中作主语,变为表语从句时语序不变,但时态应作相应变化。
名词性从句
表语从句中的虚拟语气:as if, as though
1、与现在事实相反,从句用过去式
-She looks as if she were angry.看她的表情,好像生气了似的。(其实没有生气)
-Ming is now in a new jacket. He looks as if he were an American boy.小明穿了一件新夹克,看起来像是个美国男孩。(实际小明还是中国男孩)
2、与过去事实相反,从句用过去完成时态had been 或 had done
- Mom appeared as if she had known nothing about it.妈妈看起来好像对这件事一无所知。(实际上妈妈早知道了,只是假装不知道)
- It looked as though I had stumbled into the meeting.看起来好像是我无意中走进了会议。(实际可能早有准备)
3、与将来事实相反,从句用would/could + 动词原形
- I am cleaning the house. It looks as if my girlfriend would come tomorrow.我正在打扫房子,就像我女朋友明天会来。(事实上女朋友可能根本不会来,更可能我连女友都没有)
- It appears as if technology would solve the problem in the future.看起来技术似乎会在未来解决这个问题。(事实上不一定,也可能根本解决不了)
as if 或 as though 引导的表语从句,有时当从句中所说的内容属于假设情况时,要用虚拟语气。而虚拟语气我们之前讲过通常从现在、过去、将来三个时间上来进行区分:
名词性从句
名词性从句中的虚拟语气总结:表示请求、命令、建议等
表示建议、请求、命令等词的虚拟语气,后面用虚拟语气(should)do。注意:经常会把 Should 省略。
名词性从句:
It is strange that he should do that.
It is important that we all should attend the meeting.
It is strange that the man should have stuck to his silly ideas.
宾语从句:
I insist that she (should) do her work alone.
The commander ordered that troops (should) set off at once.
表语从句:
-Mum's suggestion is that I (should) do my homework more carefully.
-Their plan is that they (should) build a new school in their hometown.
-The doctor's recommendation is that I (should) quit smoking. –
His advice is that your father (should) do more exercises in the morning.
名词性从句
同位语就是用不同的方式把一个概念再说一遍,用逗号隔开。
同位语从句是用一个从句充当同位语,一般在句中修饰抽象的名词
同位语从句
03
一用作同位语的从句叫同位语从句,一般跟在某些名词后面,用以说明该名词表示的具体内容。如:
I heard the news that our team had won.我听到了我们队获胜的消息。
I had no idea that you were here.我不知道你在这里。
二、可以跟同位语从句的名词通常:
I’ve come from Mr wang with a message that he won’t be able to see you this afternoon.
我从王先生那里来,他让我告诉你他今天下午不能来看你了。
三、可用于同位语从句的连词有 that(无意义),whether(是否),连接副词 how,when,where等,if,which 不能引导同位语从句
l have no idea when he will be back.
He must answer the question whether he agrees to it or not.
四、有时同位语从句可以不紧跟在说明的名词后面,而被别的词隔开。 如:
Several years later,word came that Napoleon himself was coming to inspect them. 几年以后,有消息传来说拿破仑要亲自视 察他们。
The thought came to him that maybe the enemy had fled the city. 他突然想起可能敌人已经逃出城了。
idea、plan、fact、hope、news、theory、truth、information、doubt suggestion、belief、thought、question、conclusion、knowledge、opinion、thought、message、words、possibility
课后练习
1. ________that they found an unusual plant in the forest.
A. It is said B. They are said C. It said D. It says
2. _____ caused the accident is still a complete mystery.
A. What B. That C. How D. Where
3. It worried Mary a lot _____ she would pass the college entrance examination.
A. whether B. if C. that D. how
4. Shanghai has taken on a new look. It isn’t like _____ it used to be .
A .what B. how C. that D. which
5. ____ is no possibility ______ Bob will win the first prize in the match.
A. There, that B. It, that C. There, whether D. It, whether
6. Little Tommy was reluctant to tell the schoolmaster ____ he had done the day before.
A .that B. how C .what D. where
7. The old man smiled when he saw how pretty _____ up to be during the past few years.
A. had his daughter grown B. would his daughter grow
C. his daughter would grow D. his daughter had grown
8. Have you seen Mary lately My boss wants to know _______.
A. how she is getting along B. how is she getting along
C. what she is getting along D. what is she getting along
9. ____surprised me most was _____such a little girl of seven could play the violin so well.
A. That; what B. What; that C. That; that D. What; what
10. These wild flowers are so special I would do ______ I can to save them.
A. whatever B. which C. that D. whichever
课后练习
1. ________that they found an unusual plant in the forest.
A. It is said B. They are said C. It said D. It says
2. _____ caused the accident is still a complete mystery.
A. What B. That C. How D. Where
3. It worried Mary a lot _____ she would pass the college entrance examination.
A. whether B. if C. that D. how
4. Shanghai has taken on a new look. It isn’t like _____ it used to be .
A .what B. how C. that D. which
5. ____ is no possibility ______ Bob will win the first prize in the match.
A. There, that B. It, that C. There, whether D. It, whether
6. Little Tommy was reluctant to tell the schoolmaster ____ he had done the day before.
A .that B. how C .what D. where
7. The old man smiled when he saw how pretty _____ up to be during the past few years.
A. had his daughter grown B. would his daughter grow
C. his daughter would grow D. his daughter had grown
8. Have you seen Mary lately My boss wants to know _______.
A. how she is getting along B. how is she getting along
C. what she is getting along D. what is she getting along
9. ____surprised me most was _____such a little girl of seven could play the violin so well.
A. That; what B. What; that C. That; that D. What; what
10. These wild flowers are so special I would do ______ I can to save them.
A. whatever B. which C. that D. whichever
02
定语从句
定语从句
一、关系代词引领的定语从句
1、who,whom(指人)在从句中分别作主语和宾语,如果介词放在从句后面,则whom可以省略
①The foreigner who visited our class yesterday is from Canada. (作主语)
②The boy who break the window is called Roy. (作主语)
③The person to whom you just talked is Mr Li. (作宾语)
④Mrs White is the person to whom you should write. (作宾语)
2、that(指人、指物)在从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时that 可省略
指物:①A plane is a machine that can fly. (作主语) ②The noodles (that) I cooked were delicious. (作宾语)
指人:①Who is the man that is reading the book over there? (作主语)
②The girl(that)we say yesterday was Jim’s sister. (作宾语)
3、which(指物)在从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时可省略
①The silk which is produced in Hangzhou sells well. (作主语)
②The songs (which)Liu Dehua sang were very popular. (作宾语)
定语从句
that 和which 的区别
1、先行词被all, every, no, some, any, little, much修饰时,用that而不用which。如:
①It only remains for me to pass all the money that she had to the right person.我所要做的是只是把她所有的钱交给合法的继承人。
②They go to the newspaper's own library to look up any information that they need.他们到报社自己的图书馆去查阅他们需要的资料。
③There isn't much water (that is) left in the cup.茶杯里剩下太多的水。
④Tom tried every means that he could to finish the job>为了按时完成工作,汤姆想尽了一切办法,但他还是失败了。
2、先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时,一般用that,而不用which。如:
①This is the second letter that I received from my younger sister this month.这是我这个月收到的我妹妹的第二封信。
②Gone with the Wind is one of the best films that I have ever seen.《乱世佳人》是我所看过的最好的影片之一。
定语从句
that 和which 的区别
3、先行词被修饰only, very, same, last时用that,而不用which。如:
①This is the only ticket I can find in my pocket.这是我口袋里所能找到的唯一一张票子了。
②That is the very magazine that he is looking for.那正是他要找的那本杂志。
4、如果先行词是人时,引导定语从句的关系代词用who(m)或that都可以,但不用which。如:
①The first person whom(=that) I visited there was Mr.Smith.我拜访的第一个人是史密斯先生。
②Anyone who(=that) breaks the law will be punished违反法律的人将会受到惩罚。
5、当有两或两个以上分别表示人或物的先行词时,这个定语从句要用that,而不用引导whom,who,which。He talked about the teachers and school that he had visited.他谈论他所拜访的老师和参观的学校。
6、当主句是以who或which开头的特殊疑问句时,定语从句要用that,而不用who,whom或which。如:
①Who is the person that is standing at the gate 站在门口的那个人是谁?
②Which of us that know something about physics/not know this 我们当中了解物理知识的人谁不知道这件事情。
定语从句
二、关系副词引领的定语从句
1. when引导定语从句,常用来修饰表示时间的先行词,如time,day,week,month,year等,在定语从句中充当时间状语。例如:
①I’ll never forget the days when I worked with you. 我永远不会忘记我与你共事的日子。(when用作状语)
②She dreams of the day when she will be playing the piano for a living.她梦想着有朝一日能以演奏钢琴为生。
变型:
关系副词when相当于“介词+关系代词”,when=in/on/at which。例如:
①I still remember the day when I joined the army.
→I still remember the day on which I joined the army 。
②July is the month when we have a lot of rain.
→July is the month in which we have a lot of rain. 七月是我们有大量雨水月份。
③There was a time when there were no radios, telephones or TV sets here.
→There was a time during which there were no radios, telephones or TV sets here.
曾经有一段时间,这里没有收音机,电视机,电话。
如果关系词在定语从句中充当主语或宾语(而不是状语)时,定语从句须用关系代词that/which引导(做宾语时可以省略)。如:
①I was busy learning the computer science that summer that/which was rather hot.我忙着学习计算机科学的这个夏天相当热。(作主语)
② Don’t forget the time (that) I’ve told you. 不要忘记我告诉你的时间。(that用作told的宾语)
定语从句
二、关系副词引领的定语从句
2.where引导定语从句,一般用来修饰表示地点的先行词,在定语从句中充当地点状语。例如:
①Returning to a city where one used to live can be a saddening experience.重归故地有时会给人带来几许惆怅。
②I went off in search of a garage where I could buy some petro1.我跑去寻找加油站买汽油。
③The tourists sought out a shady spot where they sat down and rested.旅游者找到一块阴凉的地方坐下休息。
【变形规则】
关系副词where相当于“介词+关系代词”,where=in/on/at which。例如:
①Beijing is the place where I was born.
→Beijing is the place in which I was born. 北京是我的出生地。
②The school where his sister works is a key school in JiangShu Province.
→The school at which his sister works is a key school in JiangShu Province.
他姐姐工作的这所学校是江苏省重点学校。
③Have you ever been to the house where Lu Xun once lived.
→Have you ever been to the house in which Lu Xun once lived 你去过鲁迅曾经住过的房子吗?
如果关系词在定语从句中充当主语或宾语(而不是状语)时,定语从句须用关系代词that/which引导(做宾语时可以省略)。如:
①Tomorrow we'll visit the school that/which is said to be the largest in town.我们明天将去参观一下据说将是镇上最大的学校(作主语)
②This is the house which (that) I visited two years ago.这是两年前我曾经参观过的房子。(作宾语)
定语从句
二、关系副词引领的定语从句
3.关系副词why引导定语从句,修饰先行词reason,在定语从句中充当原因状语。例如:
①The reason why she didn't get the job was that her English was not very good.
她没得到这个工作的原因是她的英语不是很好。
②The reason why he is late is that his car went wrong.他迟到的原因是他的汽车坏了。
③That is the reason why we must go now.这就是我们现在必须走的理由。
This is one of the basic reasons why some of our work can't be done well.这是我们有些工作做不好的一个基本原因。
【变形规则】
关系副词why相当于“介词+关系代词”,why=for which。例如:
①Is this the reason why he refused our offer
→Is this the reason for which he refused our offer
这就是他拒绝我们帮助他的理由吗?
②The reason why he didn't attend the meeting was that he was ill.
→The reason for which he didn't attend the meeting was that he was ill. 他之所以没有出席会议是因为他病了。
如果关系词在定语从句中充当主语或宾语(而不是状语)时,定语从句须用关系代词that/which引导(做宾语时可以省略)。如:
①The reason that /which sounded unbelievable proved to be true.这听起来令人难以置信的事实证明是正确的。(做主语)
②The reason that he explained for his being late was that he had missed the early bus.他所解释的迟到的原因是他误了头班汽车。(explain是及物动词,that在从句中作其宾语)
定语从句
二、关系副词引领的定语从句
4. how可引导定语从句,表示方法。常用在先行词way后面。例如:
当先行词为way时,定语从句常用that, in which,或how引导,that常可以省略。例如:
①This is the way how he always treats me.他一贯就是这样对待我的。
②That's the way how I learn English.那就是我学英语的方法。
way后的定语从句的引导词不用时较多。但如果关系词在句中作主语或宾语时,则用which或that 引导。例如:
This is the way (that) /in which I do such things.
比较: Please do the experiment in the way (that/which)I have shown you.
定语从句
三、限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
相同点:都属于定语从句
不同点:① 形式上:限制性定从无逗号;非限制性定从有逗号。
② 意义上:限制性定从对先行词起修饰限制作用;非限制性定从起补充说明作用。
He has found the book (that) he was looking for.
Yesterday I met Li Ping, who seemed to be very busy.
He told me a story yesterday,which I think is very interesting. (which指a story)
Tom has made great progress, which makes me very happy. (which指逗号前面整句话意思)
由as引导的非限制性定语从句
as与which都可用来引导非限制性定语从句,来指代整个主句的内容。当非限制性定语从句位于句末且as或which在从句中作主语、宾语或表语时,两者常可互换。
He married her,which/as was natural.(作主语)
他和她结婚了,这是很自然的事。
He is an old kind farmer,which/as anybody can see.(作宾语)
任何人都能看得出来,他是一位善良的老农民。
She is a little poor in English.which makes her parents a little worried.
He failed in the experiment,which was unexpected.
As is known to all Diaoyu Island belongs to China.
As is expected,he has been admitted to Beijing University.
定语从句
as用于定语从句:such+名词+as… 像…一样的,像…之类的;the same+名词+as… 和…同样的
其中as可作为关系代词在从句中充当主语、宾语或表语。
1.We have found such materials as are used in their factory.
我们已经找到了像他们工厂里用的那种材料。(as作主语)
2.These houses are sold at such a low price as people expected.
这些房子以人们预料的那样的低价出售。(as作宾语)
3.He is not the same man as he was.
他和过去不同了。(as作表语)
注意 such…as…引导的定语从句与such…that…引导的状语从句的区别:
He is such a clever boy as everyone likes.(定语从句-缺少成分him)
他是一个人人都喜爱的聪明孩子。
He is such a clever boy that everyone likes him. (状语从句-不缺少成分)
他是一个如此聪明的孩子,以至于人人都喜爱他。
在the same...as结构中,有时也可用the same...that,但两者句意不同。as表示“相似性”,that表示“同一性”,试比较:
This is the same pen as I lost yesterday.
这支钢笔和我昨天丢失的那支是一样的。(两者相似,但不是同一个)
This is the same pen that I lost yesterday.
这正是我昨天丢失的那支钢笔。(即是同一个)
This is the same(kind of)bag as I lost yesterday.
这个包与我昨天丢的是同样的。
This is the same bag(=the very bag)that I lost yesterday.
这正是我昨天丢的那个包。
定语从句
四、定语从句中的主谓一致
1、one of the + 复数名词:从句谓语动词通常用复数形式,跟定语从句所靠近的那个复数名词在数上保持一致。如:
That is one of the books that are required for study at school. 那是学校里要求学生学习的书籍之一。
This is one of the most wonderful novels that have been published since 1990. 这是自1990年以来出版的最精彩的小说之一。
She is one of the few persons who know Spanish. 她是懂得西班牙语的少数几个人中的一位。
This is one of the most famous plays that were written in the thirties. 这是30年代写的最著名的剧本之一。
2、如果one of the + 复数名词这一结构前面带有定冠词或the only之类的限定语,后面定语从句中的谓语动词则要用单数形式,这是因为定语从句在意义上修饰的是the one或the only one,而不是那个复数名词。如:
He is the one of the teachers who knows French in our school. 他是我校教师中惟一懂法语的人。(修饰the one) He is one of the teachers who know French in our school.
他是我校懂法语的教师之一。(修饰the teachers)
This is the only one of the rooms that is free now. 这是这些房间中惟一没人住的一间。(修饰the only one) This is one of the rooms that are free now.
这是目前没人住的房间之一。(修饰rooms)
定语从句
定语从句的其他补充
当先行词指事或人时,定语从句中关系代词用which不用that的情况:
①在非限制性定语从句中,只用which,不用that
He broke my cup, which made me angry.他打破了我的杯子,这使我很生气。
②当动词短语中的介词提前时,只用which, 不用that.
This is a house in which Lu Xun once lived. 这是鲁迅曾住过的房子。
注意:在一些固定搭配的动词短语中,由于动词和介词不可分割,因此不能把介词置于关系代词之前。
This is the pen(which/that) I’m looking for.
这是我正在寻找的那只钢笔。
只用who而不用that引导定语从句的情况
①先行词是指人的不定代词,如one, ones, anyone, no one,those, all, nobody, anybody,none等时,用who不用that.
People all like those who have good manners.人们都喜欢那些有礼貌的人。
②在there be 结构中,先行词指人时,多用who
There are some people who want to have holidays in Hainan.有一些想去海南度假的人。
③在非限制定语从句中,指人且作主语时,用who 不用that
Professor Wang, who is over sixty, still works hard day and night.
课后练习
1.This is the best factory ____we visited last year .
A. where B. which C. in which D. that
2.Is this the factory ____computers are built
A. that B. which C. in which D. in that
3.please pass me the dictionary ____cover is red .
A. whose B.its C. which D. which of
4.The man ____has arrived .
A. whom I told you B. that I told you
C. whom I told you about him D. I told you about
5. Do you know the comrade ____we are talking
A. to whom B. to who C. whom D. to that
6. They visited the house ___the great writer was born .
A. from where B. in which C. which D. in where
7. The comrade ___is speaking at the meeting is my teacher .
A. whom B. which C. who D. whose
8. He asked us to watch carefully everything ___he did in class .
A. who B. that C. what D. where
9. I’ll visit the professor tomorrow ,___he will be back from Shanghai .
A. who B. that C. when D. which
10.The school ___I study is a new one .
A. on which B. at where C. on that D. at which
课后练习
1.His parents wouldn’t let him marry anyone ______ family was poor.
A.of whom B.whom C.of whose D.whose
2.She heard a terrible noise, _______ brought her heart into her mouth.
A.it B.which C.this D.that
3.In the dark street , there wasn’t a single person _____ she could turn for help.
A.that B.who C.from whom D.to whom
4.The weather turned out to be very good , ____ was more than we could expect.
A.what B.which C.that D.it
5.After living in Pairs for fifty years he returned to the small town ____ he grew up as a child.
A.which B.where C.that D.when
6.Carol said the work would be done by October,______personally I doubt very much.
A. it B.that C.when D.which
7.Dorothy was always speaking highly of her role in the play, ________,of course , made the others unhappy.
A.who B.which C.this D.what
8.Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase , _____ was very reasonable.
A.which price C.the price of which
C.its price D.the price of whose
9._____ has already been pointed out , grammar is not a set of dead rules.
A.As B.It C.That D.Which
10.He lived in London for 3 months , during ____ time he learned some English.
A.this B.which C.that D.same
课后练习
1.His parents wouldn’t let him marry anyone ______ family was poor.
A.of whom B.whom C.of whose D.whose
2.She heard a terrible noise, _______ brought her heart into her mouth.
A.it B.which C.this D.that
3.In the dark street , there wasn’t a single person _____ she could turn for help.
A.that B.who C.from whom D.to whom
4.The weather turned out to be very good , ____ was more than we could expect.
A.what B.which C.that D.it
5.After living in Pairs for fifty years he returned to the small town ____ he grew up as a child.
A.which B.where C.that D.when
6.Carol said the work would be done by October,______personally I doubt very much.
A. it B.that C.when D.which
7.Dorothy was always speaking highly of her role in the play, ________,of course , made the others unhappy.
A.who B.which C.this D.what
8.Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase , _____ was very reasonable.
A.which price C.the price of which
C.its price D.the price of whose
9._____ has already been pointed out , grammar is not a set of dead rules.
A.As B.It C.That D.Which
10.He lived in London for 3 months , during ____ time he learned some English.
A.this B.which C.that D.same
03
状语从句
状语从句
地点状语从句
01
连接词:where, wherever, everywhere, anywhere
例句:
When you read the book, you’d better make a mark where you have any questions.
Wherever you are, whatever you do, I will be right here waiting for you.
Wherever you work, you will gain much valuable experience as long as you are willing to work.
Everywhere they went, they were warmly received.
独特用法:Where—不能翻译成“在……地方”时,通常翻译成“如果”,表示在……条件下。
例如:有志者,事竞成-Where you are confident, you will succeed.
1.You’d better not leave the medicine_____ kids can get at it. A.even if B.which C.where D.so that
2._____you go,don’t forget your people. A.Whenever B.However C.Wherever D.Whichever
状语从句
原因状语从句
02
连接词:because, since, as, for, now that, in that, seeing that, considering that, given that, considering that
较:because, since,as和for
(1)because语势最强,用来说明人所不知道的原因,回答why提出的问题。当原因是显而易见的或已为人们所知,就用since或as
Mr. Zhang disliked me because I’m handsome and rich.
Since/As the weather is so bad, we have to delay our journey.
(2)由because引导的从句如果放在句末,且前面有逗号,则可用for代替。但如果不是说明直接原因,而是多种情况加以判断,就只能用for.
He is absent today, because/for he is ill. He must be ill, for he is absent today.
now that:“既然” in that:“因为”,通常只能放于句中,强调重要的、唯一的原因。
Now that everybody has come,let’s begin our conference.
Human beings are different from animals in that humans can speak and think.
Considering that he is no more than 12 years old, his height of 1.80 m is quite remarkable.
owing to,due to,thanks to,as a result of属于连词短语,后面只能接词或短语,不能接从句。
练习:We’d better hurry_____it is getting dark. A.and B.but C.as D.unless
He found it increasingly difficult to read,_____his eyesight was beginning to fail. A.and B.for C.but D.or
Hydrogen(氢元素) is the fundamental element of the universe_____it provides the building blocks from which the other elements are produced.
A.so that B.but that C.in that D.provided that
状语从句
条件状语从句
03
连接词:if, unless, as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, suppose that, in case that, on condition that
1、if意为“如果”。
例句:If you cheat in the exam you’ll never get away with it. 考试作弊必予追究。
2、unless的意思是“如果不”“除非”。
例句:Unless you go at once you will be late. 如果你不马上走,就会迟到的。
3、as [so] long as的意思是“如果”“只要”。
例句:I’ll remember that day as long as I live. 只要我活着,我就不会忘记那个日子。
4、in case用连词引导条件状语从句时,其意为“如果”“万一”。
例句:In case I forget, please remind me about it. 万一我忘记,请提醒我一下。
5、条件状语从句的时态:当主句为将来时态或含有将来意义时,①条件状语用一般现在时(主将从现);②如果引导的条件和事实相反,则用虚拟语气
例句:I don’t know if it will rain tomorrow. But if it rains tomorrow, I’ll stay at home.不知道明天是否会下雨,但要是下雨的话,我就呆在家里
She will sing a song if she is asked. As long as it doesn’t rain, we can play.
If I were a bird, I would fly.
The mother promises to the son to buy him a toy airplane on condition that he passes his English test.
Suppose (that) he does not come, what shall we do
You will miss the train unless you hurry up.=You’ll miss the train if you don’t hurry up.
if only:只要 He will succeed if only he does his best.
only if:只有 Only if you are here, we have confidence.
状语从句
时间状语从句
04
连接词:when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since , till, until,the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely … when
(1)当……时候:when, while, as
I’ll tell her the good news when he comes back.
While my husband is cooking I am watching TV.
As time went by, the days became shorter and shorter.
(2)一……就……:as soon as, directly, immediately, instantly连接两个句子;一些名词如the minute, the moment, the instant也可表示;
1.I’ll let you know as soon as he comes back.
2.I’ll write to you the moment/minute I arrive in Paris.
注意:scarcely...when 表示当……时候;no sooner ...than, hardly ...when一…就,主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时(否定词在句首,后面的句子需要部分倒装)
1.Hardly had he seen me when he ran away. 他一看见我就跑了。
2.No sooner had they reached home than it rained more and more heavily.他们一到家,雨就越下越大起来。
3.Scarcely was George Washington in his teens when his father died.
He had no sooner started out than he felt homesick.他刚出发就想起家来。
No sooner had he started out than he felt homesick.他刚出发就想起家来。
状语从句
时间状语从句
04
连接词:when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since , till, until,the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely … when
(3)直到...... :till/until
①肯定形式表示的意思是“做某事直至某时”,动词必须是延续性动词;
否定形式表达的意思是“直至某时才做某事”,一般用until,动词为延续性或非延续性动词都可以。
1.I’ll stay here until everyone else comes back.
2.Wait till I call you.
3.I didn’t manage it until you had explained how.
②until可用于句首和句中,而till通常不用于句首。
Until you told me, I had heard nothing of what happened. =I had heard nothing of what happened until you told me.
注意:not...until的四种不同句式—
a.正常句式:We didn’t go home until we finished our work./ I didn’t realize she was a famous film star until she took off her dark glasses
b.until在句首: Until he came home, we knew the news.在他到家之前,我们不知道这消息
c.倒装句式:Not until I began to work did I realize how much time I had wasted直到我开始工作,我才认识到了我已蹉跎了几多岁月
d.强调句式:It is(was)...that... It is not until 8 oclock that he didn’t do homework他直到8点才写作业
状语从句
结果状语从句
05
连接词:so... that,such...that.
So+形容词/副词+that+从句
So+many/few(+可数名词的复数)+that+从句。
So+much/little(+不可数名词)+that+从句。
(当名词前有表示数量多少的many, much, few, little等词修饰时,通常用so ... that句型)
So+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数+that+从句。
Tom is so kind that they all like to make friends with him.
汤姆人很好,他们都愿和他交朋友。
There are so many people on the bus that I can’t find a seat.
The piano costs so much money that Linda can’t afford it.
There‘s so little time left that we have to speed up。几乎没时间了,我们只好加快速度。
Kathy is so lovely a girl that we all like to play with her.凯茜是个很可爱的女孩,我们都愿意和她玩。
So...that...引导结果状语从句时,从句结果是否定句,可与too...to...结构进行转换。
They were so tired that they couldn't go any father
They were too tired to go any farther. 他们累得不能再走了。
状语从句
结果状语从句
05
连接词:so... that,such...that.
such+a/an+形容词+可数名词单数+that+从句。
such+形容词+可数名词复数+that+从句。
such+形容词+不可数名词+that+从句。
Kathy is such a lovely girl that we all like to play with her.
凯茜是个很可爱的女孩,我们都愿意和她玩。
These were such difficult questions that none of us could answer them.
这些问题如此难,以至于我们之中没有一个人能回答上来。
We had such terrible weather that we couldn't finish the work on time.
天气这么糟以至于我们没能按时完成工作。
so/such..that...引导结果状语从句时可把so/such置于句首,主句用倒装语序。
Such was his worry that he couldn't go on with his work.
他如此担忧,以至于不能继续上班了。
So carelessly did he drive that he was nearly killed
他开车如此粗心,差点儿丧命。
状语从句
让步状语从句,表尽管、即使
06
though,although,as, while; even if,even though; whether...or...; no matter+疑问词,疑问词+ever
1、though vs although,不可和but连用,可互换使用,区别如下:
(1)although更正式
(2)although在句前较多,though在句中较多(只是频率,两者句前句后都可以用)
She passed the examination ,though she had not studied very hard
My will remains firm though I must lower my physical sights.
Although/Though he was exhausted,(still) he kept on working.
(3)though可用于倒装,although不可以
Object as you may,I’ll go.(=Though/Although you may object,I’ll go.)
Hard as/ though he works,he makes little progress. (=Though he works hard,he makes little progress.)
Child as/though he was,he knew what was the right thing to do.(=Though he was a child,he knew what was the right thing to do.)
表语的名词、形容词,或修饰谓语动词的副词放在从句谓语之前。当作表语的单数可数名词位于句首时,名词前的不定冠词要省略
状语从句
让步状语从句,表尽管、即使
06
though,although,as, while; even if,even though; whether...or...; no matter+疑问词,疑问词+ever
2、While
① 表示尽管,虽然,用法与although类似
While (he is) respected, the mayor is not liked.
He made a comment that, while well-intentioned, still hurt my feelings.
While I think some parts of the plan are good, I don't think it's practical.
② 表示主从句信息不同点对比
While some people think his comedy is funny, others find him offensive.
③ 表示当...时候 ,引导时间状语从句,从句中的动词必须是延续性动词
Someone called while you were out.
You can get the photos developed while you wait.
3、even if vs even though
even if指的是很少做或想象的事情,even though是真实的事情,表示已经发生了的事。例如:
We’ll make a trip even if/though the weather is bad.
即使天气不好,我们也要作一次旅行。
Even if he is poor,she loves him. (=He may be poor, yet she loves him.)
即使他很穷,但她还是爱他。
They’ll stand by you even if you don’t succeed. 即使你不成功,他们也会支持你。
Even if I have to walk all the way I’ll get there. 即使我得一路走着去,我也要走到那里。
Even though he is poor, she loves him. (=He is poor, yet she loves him.)
尽管他很穷,但她还是爱他。
He seemed youthful even though he was an old man. 尽管他已经是老年人,但看上去仍然是朝气蓬勃的。
状语从句
让步状语从句,表尽管、即使
06
though,although,as, while; even if,even though; whether...or...; no matter+疑问词,疑问词+ever
4、“no matter+疑问词”vs“疑问词-ever”的含义为“……都……;不管……都……”
它们引导的让步状语从句可以互换。例如:
No matter what happened, he would not mind. (=Whatever happened, he would not mind.)
无论发生了什么事情,他都不会介意的。
No matter who you are, you must keep the law.(=Whoever you are, you must keep the law.)
不管你是谁,你都需要遵纪守法。
When anyone does something for you, no matter how small and no matter whether he's a superior or servant, it's proper to say“Thank you”.
只要任何人替你做了一件事,不管事情多么微不足道,也不管他是你的上司还是你的仆人,你都应该说声“谢谢”。
但“no matter+疑问词”结构只能引导让步状语从句,而“疑问词-ever”还可以引导名词性从句。例如:
Whatever (=No matter what) you say,I won’t believe you. (Whatever 引导让步状语句)
无论你说什么,我都不会相信你。
I'll eat whatever(≠no matter what) you give me. (whatever引导宾语从句)
你给我吃什么,我就吃什么。
Whoever comes will be welcome. (Whoever引导主语从句) 不管谁来都受到欢迎。
状语从句
让步状语从句,表尽管、即使
06
though,although,as, while; even if,even though; whether...or...; no matter+疑问词,疑问词+ever
5、表示让步关系的介词短语:regardless of, despite=in spite of +名词短语/同位语从句。
He runs every day regardless of the weather. [=he runs every day no matter what the weather is like]
Regardless of [=despite] our request, he would not alter his plans.
Despite [=in spite of] our objections, he insisted on driving.
She ran the race despite an injury.
The law has yet to be passed, despite the fact that most people are in favor of it.
6、whether...or...表示“不论是否……”,“不管是……还是……”之意。
旨在说明正反两方面的可能性都不会影响主句的意向或结果,所以它的语气是比较强烈的,从而也更加坚定了主句的内容。例如:
You'll have to attend the ceremony whether you're free or busy.
不管你忙不忙,都要参加这个典礼。
Whether you believe it or not, it's true. 无论你是否相信,这都是真的。
Whether or not they win this battle, they won't win the war.
不管他们是否能赢得这次战役,他们绝不会赢得这场战争。
状语从句
方式状语从句
07
连接词:as, as if, as though, the way,就像,好像…似的
1、方式状语从句通常由as, (just) as…so…, as if, as though引导。
1) as, (just) as…so…引导的方式状语从句通常位于主句后,但在(just) as…so…结构中位于句首,这时as从句带有比喻的含义,意思是"正如…","就像",多用于正式文体。
例如:Always do to the others as you would be done by. 你希望人家怎样待你,你就要怎样待人。
When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
2) as if, as though:两者的意义和用法相同,引出的状语从句谓语多用虚拟语气( be动词则只能是were ),表示与事实相反,有时也用陈述语气,表示所说情况是事实或实现的可能性较大。汉译常作"仿佛……似的","好像……似的"。
They completely ignore these facts as if (as though) they never existed. 他们完全忽略了这些事实,就仿佛它不存在似的。(与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气。)
The old lady treats the boy as if he were her own son. He talks as if(as though)he knew all about it.
2、其他的引导词
1)the way:Please pronounce the word the way I do.请照我这样,读这个单词.
2)口语常用的like:He sit there smiling like it was his birthday.他面带微笑坐在那儿,像是过生日似的. (这里用了虚拟语气,值得注意的是be动词用的was。)
状语从句
目的状语从句
08
连接词:so that, in order that,为了,以便
1.in order that引导的从句可置于句首,也可置于句尾,而so that引导的从句往往只置于句尾。
在目的状语从句中常常用情态动词may/might/will/would/shall/should/can/could等。
I hurried through my work in order that I could be in time for the wonderful TV programs.
Speak louder so that the people in the hall can all hear you.
Take this medicine so that you can recover soon.
She spoke very slowly in order that we could follow her.
2.in case的用法:in case 意为“目的是”,“以防,以免”。
Take a hat with you in case the weather is very hot.
I stayed all day at home in case you called.
当主从句主语一致时,目的状语从句可与不定式或in order to 可以和so as to短语转换。
He worked day and night in order that /so that he could make more money.
He worked day and night to/in order to/so as to make more money.
状语从句
比较状语从句
08
连接词:as(同级比较),than(不同程度的比较);特殊引导词:the more … the more … 越…越…; no … more than;not A so much as B引导的.
结构 例句 结构 例句
as/so + 原级 + as 和…一样 My clothes is as/so beautiful as yours. 我的衣服和你的一样美。 not so + 原级 + as 不如,不及 The story is not so interesting than the one .
这个故事不如那个故事有意思.
比较级 + than 比...优上 Our school is bigger than yours. 我们学校的规模比你们的大. less + 原级 + than 不如,比...较差 This kind of coat is less expensive than that one。这款大衣不如那一款贵
no + 比较级 + than 最多和......一样,只不过 I have no more than two dollars left in my pocket. 我口袋里只剩下两元钱了.(有钱少的含义) not more than,不多于 I have not more than two dollars left in my pocket.
我口袋里顶多还有两元钱.(没有钱多钱少的含义)
no less than 不亚于,至少和...一样 He has got no less dollars than he did last time. 他收到的钱不亚于他上次收到的.(有收到多的含义) not less than 不少于 He has got not less dollars than he did last time.
他收到的钱不少于他上次收到的.(不包含多或少的含义)
the 比较级 + the 比较级,越如何就越如何 The more we can do for you, the happier we will be. 为你们做得越多我们就越感到高兴. not A so much as B 与其说A不如说B He is not so much a journalist as a writer.与其说他是个新闻工作者,不如说他是个作家
课后练习
1. When visiting London, I like to travel by bus.
2. Hardly had we begun our walk when it began to rain.
3. How long is it since we visited your mother
4. We listened eagerly, for he brought news of our families.
5. Wherever she goes, there are crowds of people waiting to see her.
6. So angry was she that she couldn't speak.
7. Only if a teacher has given permission is a student allowed to enter this room.
8. Young as I am, I already know what career I want to follow.
9. As if unsure of where she was, she hesitated and looked round.
说出划线词引导的状语从句的类型
When时间状语从句
hardly…when 引导的时间状语从句
since 引导的时间状语从句
for引导的原因状语从句
Wherever 引导的地点状语从句
so…that 引导的结果状语从句
Only if 引导的条件状语从句
as 引导的让步状语从句
As if 引导的方式状语从句
再 会
英语语法之从句专题 白
01
课前练习
02
名词性从句
03
定语从句
04
状语从句
具体工作措施
CONTENTS
目 录
课前练习
1. There was never any time for Kate to feel lonely, _____ she was an only child.
2. The research is so designed that once _____(begin), nothing can be done to change it .
3. When a pencil is partly in a glass of water, it looks as if it _____(break) .
4. Not until all the fish died in the river _____ (we realize) how serious the pollution was.
5. --- Did Linda see the traffic accident
--- No, no sooner ____ (she goes) than it happened.
6. Half an hour later, Lucy still couldn't get a taxi _____ the bus had dropped her.
7. Hardly had I finished my composition _____ the bell rang.
8. He did the experiment ____ he was told.
9. If we work with a strong will, we overcome any difficulty, ____ great it is.
10. They’ll stand by you _____you don’t succeed.
11. Today, we will begin ____we stopped yesterday so that no point will be left out.
12. The meaning of the word “nice” changed a few times ____ it finally came to include the sense “pleasant”.
13. You will never gain success ____ you are fully devoted to your work.
14. Parents should take seriously their children’s requests for sunglasses _____________ eye protection is necessary in sunny weather.
15. As is reported, it is 100 years ______________ Qinghua University was founded.
16. Leave your key with your neighbor ___________ you lock yourself out one day.
17. One’s life has value _______________ one brings value to the life of others.
单句填空(选择恰当的关联词或所给单词的正确形式填空, 不多于3个单词)
课前练习
1. There was never any time for Kate to feel lonely, although/though she was an only child.
2. The research is so designed that once begun(begin), nothing can be done to change it .
3. When a pencil is partly in a glass of water, it looks as if it _were broken___(break) .
4. Not until all the fish died in the river __did we realize___ (we realize) how serious the pollution was.
5. --- Did Linda see the traffic accident
--- No, no sooner _had she_gone__ (she goes) than it happened.
6. Half an hour later, Lucy still couldn't get a taxi _where__ the bus had dropped her.
7. Hardly had I finished my composition _when__ the bell rang.
8. He did the experiment _as_ he was told.
9. If we work with a strong will, we overcome any difficulty, however / no matter how great it is.
10. They’ll stand by you even_if you don’t succeed.
11. Today, we will begin where we stopped yesterday so that no point will be left out.
12. The meaning of the word “nice” changed a few times before it finally came to include the sense “pleasant”.
13. You will never gain success _unless_you are fully devoted to your work.
14. Parents should take seriously their children’s requests for sunglasses because eye protection is necessary in sunny weather.
15. As is reported, it is 100 years since Qinghua University was founded.
16. Leave your key with your neighbor in case you lock yourself out one day.
17. One’s life has value as long as/so long as one brings value to the life of others.
单句填空(选择恰当的关联词或所给单词的正确形式填空, 不多于3个单词)
英语从句分类
01
名词性从句
名词性从句
连词:在从句中均不充当任何成分,仅起到连接作用
that(三无连接词)
whether, if(均表示“是否”表明从句内容的不确定性)
as if ,as though(均表示“好像”,“似乎”)
连接代词:what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whose, whichever, whomever
连接副词:when, where, how, why, how many, how much, how often
三类连接词
名词性从句
作句子主语的从句叫主语从句,通常放在主句谓语动词之前或由形式主语it代替,而本身放在句子末尾。that在句中无词义,只起连接作用;连接代词和连接副词在句中既保留自己的疑问含义、又起连接作用。
主语从句
例如:
What he wants to tell us is not clear.
Who will win the match is still unknown
It is known to us how he became a writer.
Where the English evening will be held has not yet been announced.
That he finished writing the composition in such a short time surprised us all.
Whether we will go for an outing tomorrow remains unknown.
Who will be our monitor hasn't been decided yet.
Whom we must study for is a question of great importance.
What caused the accident remains unknown.
Whatever you did is right.
Who the watch belongs to was lost is unknown.
What we need is time.
What we need are good doctors.
01
不可省略的连词:
1. 介词后的连词
2. that没有实际意义,但是不能省略
That she was chosen made us very happy.
3. 同位语从句的连词不可省略。
We heard the news that our team had won.
whether与if 均为“是否”的意思,但在下列情况下只可用whether:
whether引导主语从句并在句首
引导表语从句:The trouble was whether we could manage it ourselves or not. The question is whether she should have a low opinion of the test
介词后面只能用whether:
This depends upon whether we are determined to do it.
I am not interested in whether you'll come or not.
4. 从句后有"or not" ——Whether he will come is not clear. Can you tell me whether to go or to stay
名词性从句
有时为避免句子头重脚轻,常用形式主语it代替主语从句作形式主语放于句首,而把主语从句置于句末。主语从句后的谓语动词一般用单数形式。
形式主语it代替主语从句放于句首
常用句型如下:
(1) It is +名词+从句
It is a fact that … 事实是… It is an honor that …非常荣幸 It is common knowledge that …是常识
(2) it is +形容词+从句
It is natural that… 很自然… It is strange that… 奇怪的是…
(3) it +不及物动词+从句
It seems that… 似乎… It happened that… 碰巧…
(4) it is+过去分词+从句
It is reported that… 据报道… It has been proved that… 已证实…
例句:
(1)It is certain that he will win the match.
(2)It is true that he has made a very important discovery in chemistry.
(3)It is very likely that they will hold a meeting.
(4)It is strange that he should do that.
(5)It is important that we all should attend the meeting.
(6)It is strange that the man should have stuck to his silly ideas.
(7)It is a pity that we won't be able to go to the south to spend our summer vacation.
(8)It is still a mystery what caused the accident.
(9)It is said that he has gone to shanghai.(=He is said to have gone to shanghai)
(10) It is known to all that the gun powder was first invented by the Chinese.
(11)It is suggested that the work should be done with great care.
(12)It seems that he has seen the film.(=He seems to have seen the film)
(13)It happened that the two cheats were there. (=The two cheats happened to be there)
另注意在主语从句中用来表示惊奇、不相信、惋惜、理应如此等语气时,谓语动词要用虚拟语气“(should) +do”,常用的句型有:It is necessary (important, natural, strange, etc.) that … It is suggested (requested, proposed, desired, etc.) that…
That the hungry rabbit had already eaten a carrot for dinner this evening is obvious.
It is obvious that the hungry rabbit had already eaten a carrot for dinner this morning.
名词性从句
宾语从句
that:在口语或非正式语中常被省去,
He has told me (that)he will go to Shanghai tomorrow.
We must never think (that) we are good in everything while others are good in nothing.
如果从句是并列句时,第二个分句前的that不可省,否则会引起歧义:
I didn’t know the rabbit ate the carrot and that you saw it.
主语和宾语从句之间有插入语,that不可省:
I know, just like you do, that the rabbit ate the carrot.
当that作learn, suggest, explain, agree, wonder, prove, mean, state, feel, hold等动词的宾语时
2. 用who,whom, which, whose, what, when, where, why, how, whoever, whatever, whichever等
关联词引导的宾语从句相当于特殊疑问句,应注意句子语序要用陈述语序。
I want to know what he has told you. She always thinks of how she can work well.
She will give whoever needs help a warm support.
02
在demand、order、suggest、decide、insist, desire, request, command等表示要求、命令、建议、决定等意义的动词后,宾语从句常用“(should)+ 动词原形”。例如:
I insist that she (should) do her work alone. 我坚持要她自己工作。
The commander ordered that troops (should) set off at once. 司令员命令部队马上出发。
作句子宾语的从句叫宾语从句。
I saw the rabbit ate a carrot.
名词性从句
宾语从句的形式宾语it
①动词find, feel, consider, make,believe 等后面有宾语补足语的时候,则需要用it做形式宾语而将that宾语从句后置.
I think it necessary that we take plenty of hot water every day .我认为每天多喝开水是有必要的.
I feel it a pity that I haven’t been to the get-together. 我没去聚会,感觉非常遗憾.
I have made it a rule that I keep diaries. 我每天写日记成了习惯.
We all find it important that we (should) make a quick decision about this mater. 我们都认为对这件事马上做出决定很重要.
②有些动词带宾语从句时需要在宾语与从句前加it :hate, take , owe, have, see to.
I hate it when they talk with their mouths full of food.我讨厌他们满嘴食物时说话.
He will have it that our plan is really practical.他会认为我们的计划确实可行.
We take it that you will agree with us.我们认为你会同意我们的.
When you start the engine, you must see to it that car is in neutral. 开启发动机时, 一定要使汽车的离合器处于空挡位置.
③若宾语从句是wh-类,则不可用it代替
We all consider what you said to be unbelievable.我们都认为你所说的是不可信的.
We discovered what we had learned to be valuable.我们发现我们所学到的东西都是有用的.
形容词的宾语从句:sure, certain, glad,please,happy,sorry,afraid,satisfied,surprised
I am sure I will pass the exam.我确信我会通过考试.
I am sorry that I have troubled you so long.很抱歉我这么长时间在打扰你.
He is glad that Li Ming went to see him when he was ill.
他很高兴在他生病的时候李明能去看望他.
有时候except,but,besides三个介词后可见到that引导的宾语从句
I know nothing about my new neighbor except that he used to work with a company.
对于我的新邻居我只知道他曾在一家公司上班,其他一无所知.
名词性从句
宾语从句的否定转移
主句的谓语动词是think, believe, imagine, suppose, consider, espect, fancy, guess等,并且主句的主语是第一人称而且为一般现在时,从句的否定词一般要转移到主句上来
1) 将think, believe, suppose, expect, fancy, imagine等动词后面宾语从句的否定词转移到主句中,即主句的谓语动词用否定式,而从句的谓语动词用肯定式。
I don't think I know you. 我想我并不认识你。
I don' t believe he will come. 我相信他不回来。
注意:若谓语动词为hope,宾语从句中的否定词不能转移。
I hope you weren't ill. 我想你没有生病吧。
2) 将seem, appear 等后的从句的否定转移到前面。
It doesn't seem that they know where to go. 看来他们不知道往哪去。
It doesn't appear that we'll have a sunny day tomorrow. 看来我们明天不会碰上好天气。
名词性从句
宾语从句的主从时态要一致
在大多数情况下,宾语从句和主句中的时态要保持一致
当主句为现在时或将来时,宾语从句的时态一般不受主句的时态所影响.
当主句为过去时
①从句用一般过去时或过去进行时 表示与主句谓语动词动作同时发生
I only knew he was studying in a western country, but I didn’t know what country he was in. 我只知道他当时在西方的一个国家读书,可不知道是哪个国家.
He asked me if I was reading the story The Old Man and the Sea when he was in. 他问我他进来的时候我是否正在读<<老人与海>>.
②从句过去完成时表示该动作发生在主句谓语动作之前
He told me that he had told Mary about the meeting already. 他告诉我他已经把有关会议的事情告诉的了Mary.
③从句谓语用过去将来时表示该动作发生在主句谓语动作之后
The reporter asked if the government would take necessary measures to put down the to-do. 记者问政府是否会采取必要的措施镇压骚乱.
如果从句是一个客观真理,那么从句的时态不根据主句的时态而变化
The teacher said that the moon goes around the earth yesterday.
名词性从句
表语从句的基本结构为:主语 + 系动词 + that从句,用一个句子作为表语,说明主语是什么或者怎么样系动词不光是 be动词(am、is、are),其实系动词除了be之外,还有 become(成为)、turn(变成)、go(变成)、seem(似乎)、appear(似乎、显得)、look(看起来)、feel(摸起来)、sound(听起来)、smell(闻起来)等等。
表语从句
03
连接词 例句
That(无词义,通常不省略) - The fact was that he had forgotten about it.事实上,他已经把这件事忘了。
- It seems that there is no cure.似乎没有治愈的办法。
- The trouble is that I have lost his address.麻烦是我把他的地址丢了。
whether - The question is whether such issues should be part of the agenda in the meeting.
- My first thought was whether he would visit the battlefield.
疑问副词,表示地点、时间、原因、方式等的词:where、when、how、why 等 This is where you came in.这就是你进来的地方。
That was when my sister was watching the news.那是我妹妹看新闻的时候。
The problem seemed how we could make him understand it.
That’s why he didn’t come.这就是他没有来的缘故。
疑问代词 who,whom,whose,whoever,what,whatever,which,whichever The problem is not who will go, but who will stay.问题不是谁去,而是谁留下来。
- The mountain is no longer what it used to be.这座山不再是过去的样子了。
- The best swimsuit(泳衣) for a full figure is whichever one makes you look and feel great.
特殊引导词(just) as, as if, as though, because - John looked just as he had looked twenty years before.
- It sounds as if someone is knocking at the door.听起来好像有人在敲门。
- Now it was as though she had known Millie for years.现在看来她似乎认识米莉很多年了。
- That is because I don’t like Japanese.因为我不喜欢日本人。
注意:
This is because…表示原因
He did not see the film last night. That is because he had to help his little sister with her homework.
That is why.../That is the reason why...表示原因带来的结果
He did not see the film last nigh. This is why he will see it today.
名词性从句
易错点
表语从句一定要用陈述语序
False: The question is when can he arrive at the hotel.
Right: The question is when he can arrive at the hotel.
不可以用if,而用whether 连接表语从句(as if 例外)
(除了宾语从句,主语从句、表语从句和同位语从句都用whether)
False: The question is if the enemy is marching towards us.
Right: The question is whether the enemy is marching towards us.
Right: It looked as if he had understood this question.
不像宾语从句,在有表语从句的复合句中,主句时态和从句时态
可以不一致。
Right: The question is who will travel with me to Beijing tomorrow.
Right: The question is why he cried yesterday.
that在表语从句中不可以省掉。
主句:The problem is... 疑问句:Which book do you like best 表语从句:The problem is which book you like best
主句:The problem is... 疑问句:How much does this coat cost
表语从句:The problem is how much this coat costs.
将疑问句的语序变成陈述句的语序,疑问句中主语之前有助动词 do、does、did 要先将其去掉。
主句:The question was... 疑问句:Who can answer the question?表语从句:The question was who could answer the question. (语序不变,can 变成了过去式 could)
主句:The question was ... 疑问句:What's the matter
表语从句:The question was what was the matter. 问题是发生了什么?(语序不变,is 变成了过去式 was)
疑问词在句中作主语,变为表语从句时语序不变,但时态应作相应变化。
名词性从句
表语从句中的虚拟语气:as if, as though
1、与现在事实相反,从句用过去式
-She looks as if she were angry.看她的表情,好像生气了似的。(其实没有生气)
-Ming is now in a new jacket. He looks as if he were an American boy.小明穿了一件新夹克,看起来像是个美国男孩。(实际小明还是中国男孩)
2、与过去事实相反,从句用过去完成时态had been 或 had done
- Mom appeared as if she had known nothing about it.妈妈看起来好像对这件事一无所知。(实际上妈妈早知道了,只是假装不知道)
- It looked as though I had stumbled into the meeting.看起来好像是我无意中走进了会议。(实际可能早有准备)
3、与将来事实相反,从句用would/could + 动词原形
- I am cleaning the house. It looks as if my girlfriend would come tomorrow.我正在打扫房子,就像我女朋友明天会来。(事实上女朋友可能根本不会来,更可能我连女友都没有)
- It appears as if technology would solve the problem in the future.看起来技术似乎会在未来解决这个问题。(事实上不一定,也可能根本解决不了)
as if 或 as though 引导的表语从句,有时当从句中所说的内容属于假设情况时,要用虚拟语气。而虚拟语气我们之前讲过通常从现在、过去、将来三个时间上来进行区分:
名词性从句
名词性从句中的虚拟语气总结:表示请求、命令、建议等
表示建议、请求、命令等词的虚拟语气,后面用虚拟语气(should)do。注意:经常会把 Should 省略。
名词性从句:
It is strange that he should do that.
It is important that we all should attend the meeting.
It is strange that the man should have stuck to his silly ideas.
宾语从句:
I insist that she (should) do her work alone.
The commander ordered that troops (should) set off at once.
表语从句:
-Mum's suggestion is that I (should) do my homework more carefully.
-Their plan is that they (should) build a new school in their hometown.
-The doctor's recommendation is that I (should) quit smoking. –
His advice is that your father (should) do more exercises in the morning.
名词性从句
同位语就是用不同的方式把一个概念再说一遍,用逗号隔开。
同位语从句是用一个从句充当同位语,一般在句中修饰抽象的名词
同位语从句
03
一用作同位语的从句叫同位语从句,一般跟在某些名词后面,用以说明该名词表示的具体内容。如:
I heard the news that our team had won.我听到了我们队获胜的消息。
I had no idea that you were here.我不知道你在这里。
二、可以跟同位语从句的名词通常:
I’ve come from Mr wang with a message that he won’t be able to see you this afternoon.
我从王先生那里来,他让我告诉你他今天下午不能来看你了。
三、可用于同位语从句的连词有 that(无意义),whether(是否),连接副词 how,when,where等,if,which 不能引导同位语从句
l have no idea when he will be back.
He must answer the question whether he agrees to it or not.
四、有时同位语从句可以不紧跟在说明的名词后面,而被别的词隔开。 如:
Several years later,word came that Napoleon himself was coming to inspect them. 几年以后,有消息传来说拿破仑要亲自视 察他们。
The thought came to him that maybe the enemy had fled the city. 他突然想起可能敌人已经逃出城了。
idea、plan、fact、hope、news、theory、truth、information、doubt suggestion、belief、thought、question、conclusion、knowledge、opinion、thought、message、words、possibility
课后练习
1. ________that they found an unusual plant in the forest.
A. It is said B. They are said C. It said D. It says
2. _____ caused the accident is still a complete mystery.
A. What B. That C. How D. Where
3. It worried Mary a lot _____ she would pass the college entrance examination.
A. whether B. if C. that D. how
4. Shanghai has taken on a new look. It isn’t like _____ it used to be .
A .what B. how C. that D. which
5. ____ is no possibility ______ Bob will win the first prize in the match.
A. There, that B. It, that C. There, whether D. It, whether
6. Little Tommy was reluctant to tell the schoolmaster ____ he had done the day before.
A .that B. how C .what D. where
7. The old man smiled when he saw how pretty _____ up to be during the past few years.
A. had his daughter grown B. would his daughter grow
C. his daughter would grow D. his daughter had grown
8. Have you seen Mary lately My boss wants to know _______.
A. how she is getting along B. how is she getting along
C. what she is getting along D. what is she getting along
9. ____surprised me most was _____such a little girl of seven could play the violin so well.
A. That; what B. What; that C. That; that D. What; what
10. These wild flowers are so special I would do ______ I can to save them.
A. whatever B. which C. that D. whichever
课后练习
1. ________that they found an unusual plant in the forest.
A. It is said B. They are said C. It said D. It says
2. _____ caused the accident is still a complete mystery.
A. What B. That C. How D. Where
3. It worried Mary a lot _____ she would pass the college entrance examination.
A. whether B. if C. that D. how
4. Shanghai has taken on a new look. It isn’t like _____ it used to be .
A .what B. how C. that D. which
5. ____ is no possibility ______ Bob will win the first prize in the match.
A. There, that B. It, that C. There, whether D. It, whether
6. Little Tommy was reluctant to tell the schoolmaster ____ he had done the day before.
A .that B. how C .what D. where
7. The old man smiled when he saw how pretty _____ up to be during the past few years.
A. had his daughter grown B. would his daughter grow
C. his daughter would grow D. his daughter had grown
8. Have you seen Mary lately My boss wants to know _______.
A. how she is getting along B. how is she getting along
C. what she is getting along D. what is she getting along
9. ____surprised me most was _____such a little girl of seven could play the violin so well.
A. That; what B. What; that C. That; that D. What; what
10. These wild flowers are so special I would do ______ I can to save them.
A. whatever B. which C. that D. whichever
02
定语从句
定语从句
一、关系代词引领的定语从句
1、who,whom(指人)在从句中分别作主语和宾语,如果介词放在从句后面,则whom可以省略
①The foreigner who visited our class yesterday is from Canada. (作主语)
②The boy who break the window is called Roy. (作主语)
③The person to whom you just talked is Mr Li. (作宾语)
④Mrs White is the person to whom you should write. (作宾语)
2、that(指人、指物)在从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时that 可省略
指物:①A plane is a machine that can fly. (作主语) ②The noodles (that) I cooked were delicious. (作宾语)
指人:①Who is the man that is reading the book over there? (作主语)
②The girl(that)we say yesterday was Jim’s sister. (作宾语)
3、which(指物)在从句中作主语或宾语,作宾语时可省略
①The silk which is produced in Hangzhou sells well. (作主语)
②The songs (which)Liu Dehua sang were very popular. (作宾语)
定语从句
that 和which 的区别
1、先行词被all, every, no, some, any, little, much修饰时,用that而不用which。如:
①It only remains for me to pass all the money that she had to the right person.我所要做的是只是把她所有的钱交给合法的继承人。
②They go to the newspaper's own library to look up any information that they need.他们到报社自己的图书馆去查阅他们需要的资料。
③There isn't much water (that is) left in the cup.茶杯里剩下太多的水。
④Tom tried every means that he could to finish the job>为了按时完成工作,汤姆想尽了一切办法,但他还是失败了。
2、先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时,一般用that,而不用which。如:
①This is the second letter that I received from my younger sister this month.这是我这个月收到的我妹妹的第二封信。
②Gone with the Wind is one of the best films that I have ever seen.《乱世佳人》是我所看过的最好的影片之一。
定语从句
that 和which 的区别
3、先行词被修饰only, very, same, last时用that,而不用which。如:
①This is the only ticket I can find in my pocket.这是我口袋里所能找到的唯一一张票子了。
②That is the very magazine that he is looking for.那正是他要找的那本杂志。
4、如果先行词是人时,引导定语从句的关系代词用who(m)或that都可以,但不用which。如:
①The first person whom(=that) I visited there was Mr.Smith.我拜访的第一个人是史密斯先生。
②Anyone who(=that) breaks the law will be punished违反法律的人将会受到惩罚。
5、当有两或两个以上分别表示人或物的先行词时,这个定语从句要用that,而不用引导whom,who,which。He talked about the teachers and school that he had visited.他谈论他所拜访的老师和参观的学校。
6、当主句是以who或which开头的特殊疑问句时,定语从句要用that,而不用who,whom或which。如:
①Who is the person that is standing at the gate 站在门口的那个人是谁?
②Which of us that know something about physics/not know this 我们当中了解物理知识的人谁不知道这件事情。
定语从句
二、关系副词引领的定语从句
1. when引导定语从句,常用来修饰表示时间的先行词,如time,day,week,month,year等,在定语从句中充当时间状语。例如:
①I’ll never forget the days when I worked with you. 我永远不会忘记我与你共事的日子。(when用作状语)
②She dreams of the day when she will be playing the piano for a living.她梦想着有朝一日能以演奏钢琴为生。
变型:
关系副词when相当于“介词+关系代词”,when=in/on/at which。例如:
①I still remember the day when I joined the army.
→I still remember the day on which I joined the army 。
②July is the month when we have a lot of rain.
→July is the month in which we have a lot of rain. 七月是我们有大量雨水月份。
③There was a time when there were no radios, telephones or TV sets here.
→There was a time during which there were no radios, telephones or TV sets here.
曾经有一段时间,这里没有收音机,电视机,电话。
如果关系词在定语从句中充当主语或宾语(而不是状语)时,定语从句须用关系代词that/which引导(做宾语时可以省略)。如:
①I was busy learning the computer science that summer that/which was rather hot.我忙着学习计算机科学的这个夏天相当热。(作主语)
② Don’t forget the time (that) I’ve told you. 不要忘记我告诉你的时间。(that用作told的宾语)
定语从句
二、关系副词引领的定语从句
2.where引导定语从句,一般用来修饰表示地点的先行词,在定语从句中充当地点状语。例如:
①Returning to a city where one used to live can be a saddening experience.重归故地有时会给人带来几许惆怅。
②I went off in search of a garage where I could buy some petro1.我跑去寻找加油站买汽油。
③The tourists sought out a shady spot where they sat down and rested.旅游者找到一块阴凉的地方坐下休息。
【变形规则】
关系副词where相当于“介词+关系代词”,where=in/on/at which。例如:
①Beijing is the place where I was born.
→Beijing is the place in which I was born. 北京是我的出生地。
②The school where his sister works is a key school in JiangShu Province.
→The school at which his sister works is a key school in JiangShu Province.
他姐姐工作的这所学校是江苏省重点学校。
③Have you ever been to the house where Lu Xun once lived.
→Have you ever been to the house in which Lu Xun once lived 你去过鲁迅曾经住过的房子吗?
如果关系词在定语从句中充当主语或宾语(而不是状语)时,定语从句须用关系代词that/which引导(做宾语时可以省略)。如:
①Tomorrow we'll visit the school that/which is said to be the largest in town.我们明天将去参观一下据说将是镇上最大的学校(作主语)
②This is the house which (that) I visited two years ago.这是两年前我曾经参观过的房子。(作宾语)
定语从句
二、关系副词引领的定语从句
3.关系副词why引导定语从句,修饰先行词reason,在定语从句中充当原因状语。例如:
①The reason why she didn't get the job was that her English was not very good.
她没得到这个工作的原因是她的英语不是很好。
②The reason why he is late is that his car went wrong.他迟到的原因是他的汽车坏了。
③That is the reason why we must go now.这就是我们现在必须走的理由。
This is one of the basic reasons why some of our work can't be done well.这是我们有些工作做不好的一个基本原因。
【变形规则】
关系副词why相当于“介词+关系代词”,why=for which。例如:
①Is this the reason why he refused our offer
→Is this the reason for which he refused our offer
这就是他拒绝我们帮助他的理由吗?
②The reason why he didn't attend the meeting was that he was ill.
→The reason for which he didn't attend the meeting was that he was ill. 他之所以没有出席会议是因为他病了。
如果关系词在定语从句中充当主语或宾语(而不是状语)时,定语从句须用关系代词that/which引导(做宾语时可以省略)。如:
①The reason that /which sounded unbelievable proved to be true.这听起来令人难以置信的事实证明是正确的。(做主语)
②The reason that he explained for his being late was that he had missed the early bus.他所解释的迟到的原因是他误了头班汽车。(explain是及物动词,that在从句中作其宾语)
定语从句
二、关系副词引领的定语从句
4. how可引导定语从句,表示方法。常用在先行词way后面。例如:
当先行词为way时,定语从句常用that, in which,或how引导,that常可以省略。例如:
①This is the way how he always treats me.他一贯就是这样对待我的。
②That's the way how I learn English.那就是我学英语的方法。
way后的定语从句的引导词不用时较多。但如果关系词在句中作主语或宾语时,则用which或that 引导。例如:
This is the way (that) /in which I do such things.
比较: Please do the experiment in the way (that/which)I have shown you.
定语从句
三、限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
相同点:都属于定语从句
不同点:① 形式上:限制性定从无逗号;非限制性定从有逗号。
② 意义上:限制性定从对先行词起修饰限制作用;非限制性定从起补充说明作用。
He has found the book (that) he was looking for.
Yesterday I met Li Ping, who seemed to be very busy.
He told me a story yesterday,which I think is very interesting. (which指a story)
Tom has made great progress, which makes me very happy. (which指逗号前面整句话意思)
由as引导的非限制性定语从句
as与which都可用来引导非限制性定语从句,来指代整个主句的内容。当非限制性定语从句位于句末且as或which在从句中作主语、宾语或表语时,两者常可互换。
He married her,which/as was natural.(作主语)
他和她结婚了,这是很自然的事。
He is an old kind farmer,which/as anybody can see.(作宾语)
任何人都能看得出来,他是一位善良的老农民。
She is a little poor in English.which makes her parents a little worried.
He failed in the experiment,which was unexpected.
As is known to all Diaoyu Island belongs to China.
As is expected,he has been admitted to Beijing University.
定语从句
as用于定语从句:such+名词+as… 像…一样的,像…之类的;the same+名词+as… 和…同样的
其中as可作为关系代词在从句中充当主语、宾语或表语。
1.We have found such materials as are used in their factory.
我们已经找到了像他们工厂里用的那种材料。(as作主语)
2.These houses are sold at such a low price as people expected.
这些房子以人们预料的那样的低价出售。(as作宾语)
3.He is not the same man as he was.
他和过去不同了。(as作表语)
注意 such…as…引导的定语从句与such…that…引导的状语从句的区别:
He is such a clever boy as everyone likes.(定语从句-缺少成分him)
他是一个人人都喜爱的聪明孩子。
He is such a clever boy that everyone likes him. (状语从句-不缺少成分)
他是一个如此聪明的孩子,以至于人人都喜爱他。
在the same...as结构中,有时也可用the same...that,但两者句意不同。as表示“相似性”,that表示“同一性”,试比较:
This is the same pen as I lost yesterday.
这支钢笔和我昨天丢失的那支是一样的。(两者相似,但不是同一个)
This is the same pen that I lost yesterday.
这正是我昨天丢失的那支钢笔。(即是同一个)
This is the same(kind of)bag as I lost yesterday.
这个包与我昨天丢的是同样的。
This is the same bag(=the very bag)that I lost yesterday.
这正是我昨天丢的那个包。
定语从句
四、定语从句中的主谓一致
1、one of the + 复数名词:从句谓语动词通常用复数形式,跟定语从句所靠近的那个复数名词在数上保持一致。如:
That is one of the books that are required for study at school. 那是学校里要求学生学习的书籍之一。
This is one of the most wonderful novels that have been published since 1990. 这是自1990年以来出版的最精彩的小说之一。
She is one of the few persons who know Spanish. 她是懂得西班牙语的少数几个人中的一位。
This is one of the most famous plays that were written in the thirties. 这是30年代写的最著名的剧本之一。
2、如果one of the + 复数名词这一结构前面带有定冠词或the only之类的限定语,后面定语从句中的谓语动词则要用单数形式,这是因为定语从句在意义上修饰的是the one或the only one,而不是那个复数名词。如:
He is the one of the teachers who knows French in our school. 他是我校教师中惟一懂法语的人。(修饰the one) He is one of the teachers who know French in our school.
他是我校懂法语的教师之一。(修饰the teachers)
This is the only one of the rooms that is free now. 这是这些房间中惟一没人住的一间。(修饰the only one) This is one of the rooms that are free now.
这是目前没人住的房间之一。(修饰rooms)
定语从句
定语从句的其他补充
当先行词指事或人时,定语从句中关系代词用which不用that的情况:
①在非限制性定语从句中,只用which,不用that
He broke my cup, which made me angry.他打破了我的杯子,这使我很生气。
②当动词短语中的介词提前时,只用which, 不用that.
This is a house in which Lu Xun once lived. 这是鲁迅曾住过的房子。
注意:在一些固定搭配的动词短语中,由于动词和介词不可分割,因此不能把介词置于关系代词之前。
This is the pen(which/that) I’m looking for.
这是我正在寻找的那只钢笔。
只用who而不用that引导定语从句的情况
①先行词是指人的不定代词,如one, ones, anyone, no one,those, all, nobody, anybody,none等时,用who不用that.
People all like those who have good manners.人们都喜欢那些有礼貌的人。
②在there be 结构中,先行词指人时,多用who
There are some people who want to have holidays in Hainan.有一些想去海南度假的人。
③在非限制定语从句中,指人且作主语时,用who 不用that
Professor Wang, who is over sixty, still works hard day and night.
课后练习
1.This is the best factory ____we visited last year .
A. where B. which C. in which D. that
2.Is this the factory ____computers are built
A. that B. which C. in which D. in that
3.please pass me the dictionary ____cover is red .
A. whose B.its C. which D. which of
4.The man ____has arrived .
A. whom I told you B. that I told you
C. whom I told you about him D. I told you about
5. Do you know the comrade ____we are talking
A. to whom B. to who C. whom D. to that
6. They visited the house ___the great writer was born .
A. from where B. in which C. which D. in where
7. The comrade ___is speaking at the meeting is my teacher .
A. whom B. which C. who D. whose
8. He asked us to watch carefully everything ___he did in class .
A. who B. that C. what D. where
9. I’ll visit the professor tomorrow ,___he will be back from Shanghai .
A. who B. that C. when D. which
10.The school ___I study is a new one .
A. on which B. at where C. on that D. at which
课后练习
1.His parents wouldn’t let him marry anyone ______ family was poor.
A.of whom B.whom C.of whose D.whose
2.She heard a terrible noise, _______ brought her heart into her mouth.
A.it B.which C.this D.that
3.In the dark street , there wasn’t a single person _____ she could turn for help.
A.that B.who C.from whom D.to whom
4.The weather turned out to be very good , ____ was more than we could expect.
A.what B.which C.that D.it
5.After living in Pairs for fifty years he returned to the small town ____ he grew up as a child.
A.which B.where C.that D.when
6.Carol said the work would be done by October,______personally I doubt very much.
A. it B.that C.when D.which
7.Dorothy was always speaking highly of her role in the play, ________,of course , made the others unhappy.
A.who B.which C.this D.what
8.Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase , _____ was very reasonable.
A.which price C.the price of which
C.its price D.the price of whose
9._____ has already been pointed out , grammar is not a set of dead rules.
A.As B.It C.That D.Which
10.He lived in London for 3 months , during ____ time he learned some English.
A.this B.which C.that D.same
课后练习
1.His parents wouldn’t let him marry anyone ______ family was poor.
A.of whom B.whom C.of whose D.whose
2.She heard a terrible noise, _______ brought her heart into her mouth.
A.it B.which C.this D.that
3.In the dark street , there wasn’t a single person _____ she could turn for help.
A.that B.who C.from whom D.to whom
4.The weather turned out to be very good , ____ was more than we could expect.
A.what B.which C.that D.it
5.After living in Pairs for fifty years he returned to the small town ____ he grew up as a child.
A.which B.where C.that D.when
6.Carol said the work would be done by October,______personally I doubt very much.
A. it B.that C.when D.which
7.Dorothy was always speaking highly of her role in the play, ________,of course , made the others unhappy.
A.who B.which C.this D.what
8.Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase , _____ was very reasonable.
A.which price C.the price of which
C.its price D.the price of whose
9._____ has already been pointed out , grammar is not a set of dead rules.
A.As B.It C.That D.Which
10.He lived in London for 3 months , during ____ time he learned some English.
A.this B.which C.that D.same
03
状语从句
状语从句
地点状语从句
01
连接词:where, wherever, everywhere, anywhere
例句:
When you read the book, you’d better make a mark where you have any questions.
Wherever you are, whatever you do, I will be right here waiting for you.
Wherever you work, you will gain much valuable experience as long as you are willing to work.
Everywhere they went, they were warmly received.
独特用法:Where—不能翻译成“在……地方”时,通常翻译成“如果”,表示在……条件下。
例如:有志者,事竞成-Where you are confident, you will succeed.
1.You’d better not leave the medicine_____ kids can get at it. A.even if B.which C.where D.so that
2._____you go,don’t forget your people. A.Whenever B.However C.Wherever D.Whichever
状语从句
原因状语从句
02
连接词:because, since, as, for, now that, in that, seeing that, considering that, given that, considering that
较:because, since,as和for
(1)because语势最强,用来说明人所不知道的原因,回答why提出的问题。当原因是显而易见的或已为人们所知,就用since或as
Mr. Zhang disliked me because I’m handsome and rich.
Since/As the weather is so bad, we have to delay our journey.
(2)由because引导的从句如果放在句末,且前面有逗号,则可用for代替。但如果不是说明直接原因,而是多种情况加以判断,就只能用for.
He is absent today, because/for he is ill. He must be ill, for he is absent today.
now that:“既然” in that:“因为”,通常只能放于句中,强调重要的、唯一的原因。
Now that everybody has come,let’s begin our conference.
Human beings are different from animals in that humans can speak and think.
Considering that he is no more than 12 years old, his height of 1.80 m is quite remarkable.
owing to,due to,thanks to,as a result of属于连词短语,后面只能接词或短语,不能接从句。
练习:We’d better hurry_____it is getting dark. A.and B.but C.as D.unless
He found it increasingly difficult to read,_____his eyesight was beginning to fail. A.and B.for C.but D.or
Hydrogen(氢元素) is the fundamental element of the universe_____it provides the building blocks from which the other elements are produced.
A.so that B.but that C.in that D.provided that
状语从句
条件状语从句
03
连接词:if, unless, as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, suppose that, in case that, on condition that
1、if意为“如果”。
例句:If you cheat in the exam you’ll never get away with it. 考试作弊必予追究。
2、unless的意思是“如果不”“除非”。
例句:Unless you go at once you will be late. 如果你不马上走,就会迟到的。
3、as [so] long as的意思是“如果”“只要”。
例句:I’ll remember that day as long as I live. 只要我活着,我就不会忘记那个日子。
4、in case用连词引导条件状语从句时,其意为“如果”“万一”。
例句:In case I forget, please remind me about it. 万一我忘记,请提醒我一下。
5、条件状语从句的时态:当主句为将来时态或含有将来意义时,①条件状语用一般现在时(主将从现);②如果引导的条件和事实相反,则用虚拟语气
例句:I don’t know if it will rain tomorrow. But if it rains tomorrow, I’ll stay at home.不知道明天是否会下雨,但要是下雨的话,我就呆在家里
She will sing a song if she is asked. As long as it doesn’t rain, we can play.
If I were a bird, I would fly.
The mother promises to the son to buy him a toy airplane on condition that he passes his English test.
Suppose (that) he does not come, what shall we do
You will miss the train unless you hurry up.=You’ll miss the train if you don’t hurry up.
if only:只要 He will succeed if only he does his best.
only if:只有 Only if you are here, we have confidence.
状语从句
时间状语从句
04
连接词:when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since , till, until,the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely … when
(1)当……时候:when, while, as
I’ll tell her the good news when he comes back.
While my husband is cooking I am watching TV.
As time went by, the days became shorter and shorter.
(2)一……就……:as soon as, directly, immediately, instantly连接两个句子;一些名词如the minute, the moment, the instant也可表示;
1.I’ll let you know as soon as he comes back.
2.I’ll write to you the moment/minute I arrive in Paris.
注意:scarcely...when 表示当……时候;no sooner ...than, hardly ...when一…就,主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时(否定词在句首,后面的句子需要部分倒装)
1.Hardly had he seen me when he ran away. 他一看见我就跑了。
2.No sooner had they reached home than it rained more and more heavily.他们一到家,雨就越下越大起来。
3.Scarcely was George Washington in his teens when his father died.
He had no sooner started out than he felt homesick.他刚出发就想起家来。
No sooner had he started out than he felt homesick.他刚出发就想起家来。
状语从句
时间状语从句
04
连接词:when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since , till, until,the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely … when
(3)直到...... :till/until
①肯定形式表示的意思是“做某事直至某时”,动词必须是延续性动词;
否定形式表达的意思是“直至某时才做某事”,一般用until,动词为延续性或非延续性动词都可以。
1.I’ll stay here until everyone else comes back.
2.Wait till I call you.
3.I didn’t manage it until you had explained how.
②until可用于句首和句中,而till通常不用于句首。
Until you told me, I had heard nothing of what happened. =I had heard nothing of what happened until you told me.
注意:not...until的四种不同句式—
a.正常句式:We didn’t go home until we finished our work./ I didn’t realize she was a famous film star until she took off her dark glasses
b.until在句首: Until he came home, we knew the news.在他到家之前,我们不知道这消息
c.倒装句式:Not until I began to work did I realize how much time I had wasted直到我开始工作,我才认识到了我已蹉跎了几多岁月
d.强调句式:It is(was)...that... It is not until 8 oclock that he didn’t do homework他直到8点才写作业
状语从句
结果状语从句
05
连接词:so... that,such...that.
So+形容词/副词+that+从句
So+many/few(+可数名词的复数)+that+从句。
So+much/little(+不可数名词)+that+从句。
(当名词前有表示数量多少的many, much, few, little等词修饰时,通常用so ... that句型)
So+形容词+a/an+可数名词单数+that+从句。
Tom is so kind that they all like to make friends with him.
汤姆人很好,他们都愿和他交朋友。
There are so many people on the bus that I can’t find a seat.
The piano costs so much money that Linda can’t afford it.
There‘s so little time left that we have to speed up。几乎没时间了,我们只好加快速度。
Kathy is so lovely a girl that we all like to play with her.凯茜是个很可爱的女孩,我们都愿意和她玩。
So...that...引导结果状语从句时,从句结果是否定句,可与too...to...结构进行转换。
They were so tired that they couldn't go any father
They were too tired to go any farther. 他们累得不能再走了。
状语从句
结果状语从句
05
连接词:so... that,such...that.
such+a/an+形容词+可数名词单数+that+从句。
such+形容词+可数名词复数+that+从句。
such+形容词+不可数名词+that+从句。
Kathy is such a lovely girl that we all like to play with her.
凯茜是个很可爱的女孩,我们都愿意和她玩。
These were such difficult questions that none of us could answer them.
这些问题如此难,以至于我们之中没有一个人能回答上来。
We had such terrible weather that we couldn't finish the work on time.
天气这么糟以至于我们没能按时完成工作。
so/such..that...引导结果状语从句时可把so/such置于句首,主句用倒装语序。
Such was his worry that he couldn't go on with his work.
他如此担忧,以至于不能继续上班了。
So carelessly did he drive that he was nearly killed
他开车如此粗心,差点儿丧命。
状语从句
让步状语从句,表尽管、即使
06
though,although,as, while; even if,even though; whether...or...; no matter+疑问词,疑问词+ever
1、though vs although,不可和but连用,可互换使用,区别如下:
(1)although更正式
(2)although在句前较多,though在句中较多(只是频率,两者句前句后都可以用)
She passed the examination ,though she had not studied very hard
My will remains firm though I must lower my physical sights.
Although/Though he was exhausted,(still) he kept on working.
(3)though可用于倒装,although不可以
Object as you may,I’ll go.(=Though/Although you may object,I’ll go.)
Hard as/ though he works,he makes little progress. (=Though he works hard,he makes little progress.)
Child as/though he was,he knew what was the right thing to do.(=Though he was a child,he knew what was the right thing to do.)
表语的名词、形容词,或修饰谓语动词的副词放在从句谓语之前。当作表语的单数可数名词位于句首时,名词前的不定冠词要省略
状语从句
让步状语从句,表尽管、即使
06
though,although,as, while; even if,even though; whether...or...; no matter+疑问词,疑问词+ever
2、While
① 表示尽管,虽然,用法与although类似
While (he is) respected, the mayor is not liked.
He made a comment that, while well-intentioned, still hurt my feelings.
While I think some parts of the plan are good, I don't think it's practical.
② 表示主从句信息不同点对比
While some people think his comedy is funny, others find him offensive.
③ 表示当...时候 ,引导时间状语从句,从句中的动词必须是延续性动词
Someone called while you were out.
You can get the photos developed while you wait.
3、even if vs even though
even if指的是很少做或想象的事情,even though是真实的事情,表示已经发生了的事。例如:
We’ll make a trip even if/though the weather is bad.
即使天气不好,我们也要作一次旅行。
Even if he is poor,she loves him. (=He may be poor, yet she loves him.)
即使他很穷,但她还是爱他。
They’ll stand by you even if you don’t succeed. 即使你不成功,他们也会支持你。
Even if I have to walk all the way I’ll get there. 即使我得一路走着去,我也要走到那里。
Even though he is poor, she loves him. (=He is poor, yet she loves him.)
尽管他很穷,但她还是爱他。
He seemed youthful even though he was an old man. 尽管他已经是老年人,但看上去仍然是朝气蓬勃的。
状语从句
让步状语从句,表尽管、即使
06
though,although,as, while; even if,even though; whether...or...; no matter+疑问词,疑问词+ever
4、“no matter+疑问词”vs“疑问词-ever”的含义为“……都……;不管……都……”
它们引导的让步状语从句可以互换。例如:
No matter what happened, he would not mind. (=Whatever happened, he would not mind.)
无论发生了什么事情,他都不会介意的。
No matter who you are, you must keep the law.(=Whoever you are, you must keep the law.)
不管你是谁,你都需要遵纪守法。
When anyone does something for you, no matter how small and no matter whether he's a superior or servant, it's proper to say“Thank you”.
只要任何人替你做了一件事,不管事情多么微不足道,也不管他是你的上司还是你的仆人,你都应该说声“谢谢”。
但“no matter+疑问词”结构只能引导让步状语从句,而“疑问词-ever”还可以引导名词性从句。例如:
Whatever (=No matter what) you say,I won’t believe you. (Whatever 引导让步状语句)
无论你说什么,我都不会相信你。
I'll eat whatever(≠no matter what) you give me. (whatever引导宾语从句)
你给我吃什么,我就吃什么。
Whoever comes will be welcome. (Whoever引导主语从句) 不管谁来都受到欢迎。
状语从句
让步状语从句,表尽管、即使
06
though,although,as, while; even if,even though; whether...or...; no matter+疑问词,疑问词+ever
5、表示让步关系的介词短语:regardless of, despite=in spite of +名词短语/同位语从句。
He runs every day regardless of the weather. [=he runs every day no matter what the weather is like]
Regardless of [=despite] our request, he would not alter his plans.
Despite [=in spite of] our objections, he insisted on driving.
She ran the race despite an injury.
The law has yet to be passed, despite the fact that most people are in favor of it.
6、whether...or...表示“不论是否……”,“不管是……还是……”之意。
旨在说明正反两方面的可能性都不会影响主句的意向或结果,所以它的语气是比较强烈的,从而也更加坚定了主句的内容。例如:
You'll have to attend the ceremony whether you're free or busy.
不管你忙不忙,都要参加这个典礼。
Whether you believe it or not, it's true. 无论你是否相信,这都是真的。
Whether or not they win this battle, they won't win the war.
不管他们是否能赢得这次战役,他们绝不会赢得这场战争。
状语从句
方式状语从句
07
连接词:as, as if, as though, the way,就像,好像…似的
1、方式状语从句通常由as, (just) as…so…, as if, as though引导。
1) as, (just) as…so…引导的方式状语从句通常位于主句后,但在(just) as…so…结构中位于句首,这时as从句带有比喻的含义,意思是"正如…","就像",多用于正式文体。
例如:Always do to the others as you would be done by. 你希望人家怎样待你,你就要怎样待人。
When in Rome, do as the Romans do.
2) as if, as though:两者的意义和用法相同,引出的状语从句谓语多用虚拟语气( be动词则只能是were ),表示与事实相反,有时也用陈述语气,表示所说情况是事实或实现的可能性较大。汉译常作"仿佛……似的","好像……似的"。
They completely ignore these facts as if (as though) they never existed. 他们完全忽略了这些事实,就仿佛它不存在似的。(与事实相反,谓语用虚拟语气。)
The old lady treats the boy as if he were her own son. He talks as if(as though)he knew all about it.
2、其他的引导词
1)the way:Please pronounce the word the way I do.请照我这样,读这个单词.
2)口语常用的like:He sit there smiling like it was his birthday.他面带微笑坐在那儿,像是过生日似的. (这里用了虚拟语气,值得注意的是be动词用的was。)
状语从句
目的状语从句
08
连接词:so that, in order that,为了,以便
1.in order that引导的从句可置于句首,也可置于句尾,而so that引导的从句往往只置于句尾。
在目的状语从句中常常用情态动词may/might/will/would/shall/should/can/could等。
I hurried through my work in order that I could be in time for the wonderful TV programs.
Speak louder so that the people in the hall can all hear you.
Take this medicine so that you can recover soon.
She spoke very slowly in order that we could follow her.
2.in case的用法:in case 意为“目的是”,“以防,以免”。
Take a hat with you in case the weather is very hot.
I stayed all day at home in case you called.
当主从句主语一致时,目的状语从句可与不定式或in order to 可以和so as to短语转换。
He worked day and night in order that /so that he could make more money.
He worked day and night to/in order to/so as to make more money.
状语从句
比较状语从句
08
连接词:as(同级比较),than(不同程度的比较);特殊引导词:the more … the more … 越…越…; no … more than;not A so much as B引导的.
结构 例句 结构 例句
as/so + 原级 + as 和…一样 My clothes is as/so beautiful as yours. 我的衣服和你的一样美。 not so + 原级 + as 不如,不及 The story is not so interesting than the one .
这个故事不如那个故事有意思.
比较级 + than 比...优上 Our school is bigger than yours. 我们学校的规模比你们的大. less + 原级 + than 不如,比...较差 This kind of coat is less expensive than that one。这款大衣不如那一款贵
no + 比较级 + than 最多和......一样,只不过 I have no more than two dollars left in my pocket. 我口袋里只剩下两元钱了.(有钱少的含义) not more than,不多于 I have not more than two dollars left in my pocket.
我口袋里顶多还有两元钱.(没有钱多钱少的含义)
no less than 不亚于,至少和...一样 He has got no less dollars than he did last time. 他收到的钱不亚于他上次收到的.(有收到多的含义) not less than 不少于 He has got not less dollars than he did last time.
他收到的钱不少于他上次收到的.(不包含多或少的含义)
the 比较级 + the 比较级,越如何就越如何 The more we can do for you, the happier we will be. 为你们做得越多我们就越感到高兴. not A so much as B 与其说A不如说B He is not so much a journalist as a writer.与其说他是个新闻工作者,不如说他是个作家
课后练习
1. When visiting London, I like to travel by bus.
2. Hardly had we begun our walk when it began to rain.
3. How long is it since we visited your mother
4. We listened eagerly, for he brought news of our families.
5. Wherever she goes, there are crowds of people waiting to see her.
6. So angry was she that she couldn't speak.
7. Only if a teacher has given permission is a student allowed to enter this room.
8. Young as I am, I already know what career I want to follow.
9. As if unsure of where she was, she hesitated and looked round.
说出划线词引导的状语从句的类型
When时间状语从句
hardly…when 引导的时间状语从句
since 引导的时间状语从句
for引导的原因状语从句
Wherever 引导的地点状语从句
so…that 引导的结果状语从句
Only if 引导的条件状语从句
as 引导的让步状语从句
As if 引导的方式状语从句
再 会
