Unit 3 Getting along with others_Grammar and usage 教案
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 3 Getting along with others_Grammar and usage 教案 |  | |
| 格式 | doc | ||
| 文件大小 | 48.4KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-09-23 08:43:14 | ||
图片预览

文档简介
中小学教育资源及组卷应用平台
Book 1 Unit 3 Getting along with others
Grammar and usage
Restrictive relative clauses with relative pronouns
教学目标
By the end of this section, students will be able to:
1. understand the meaning of restrictive relative clauses with relative pronouns;
2. summarize the grammatical rules of the restrictive clauses with relative pronouns;
3. apply the appropriate restrictive relative clauses with relative pronouns to describe their friends.
教学重难点
1. To understand the functions of different relative pronouns in the restrictive relative clauses;
2. To know the restrictions of different relative pronouns.
教学过程
步 骤 教学活动 设计意图 互动时间&模式
Lead-in
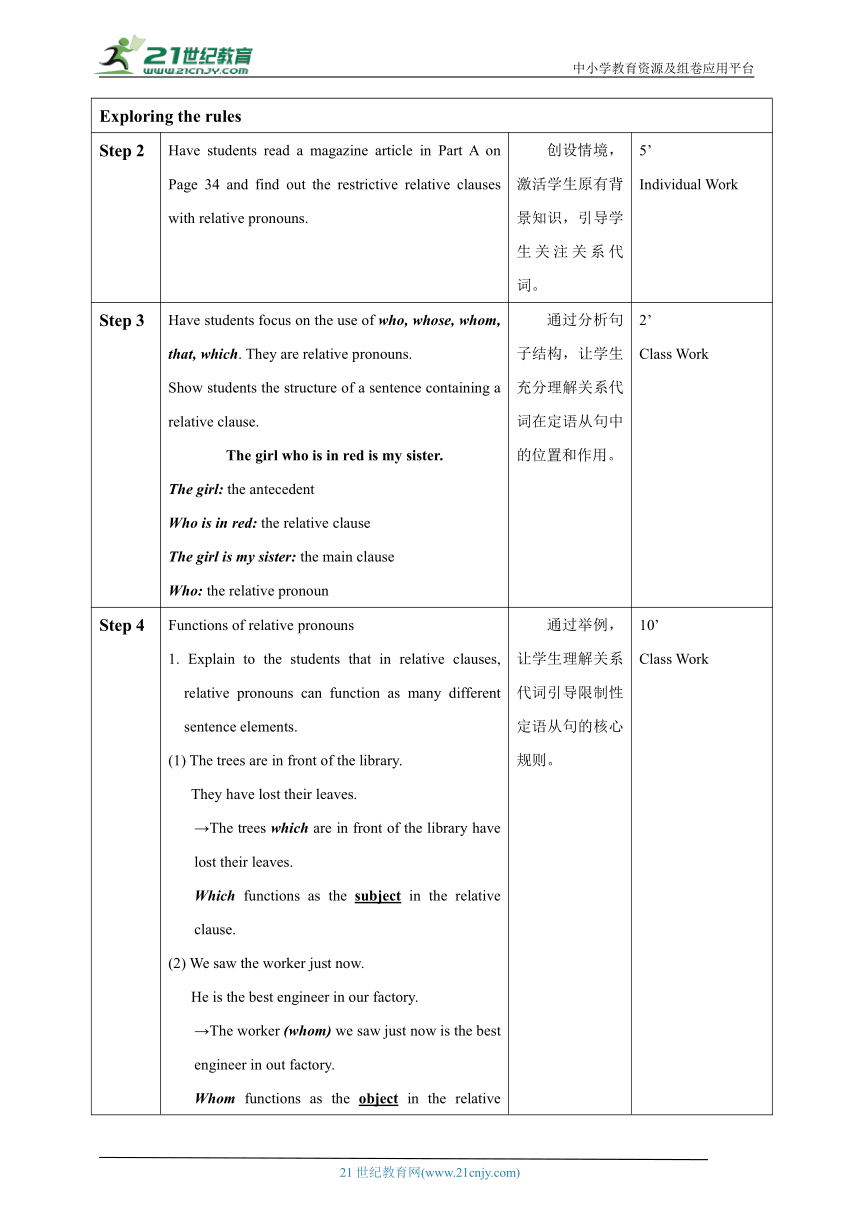
Step 1 Lead students to compare the following sentences and read them aloud. (1) People have close friends. People naturally enjoy their company. →People who have close friends naturally enjoy their company. (2) He is rich enough. He has true friends. →He is rich enough who has true friends. (3) Friendship is a precious wealth. One searches for it all his life. →Friendship is a precious wealth (that) one searches for all his life. 通过比较,引导学生关注定语从句是如何通过关系代词与主句连接的,为引入关系代词做准备。 5’ Class Work
Exploring the rules
Step 2 Have students read a magazine article in Part A on Page 34 and find out the restrictive relative clauses with relative pronouns. 创设情境,激活学生原有背景知识,引导学生关注关系代词。 5’ Individual Work
Step 3 Have students focus on the use of who, whose, whom, that, which. They are relative pronouns. Show students the structure of a sentence containing a relative clause. The girl who is in red is my sister. The girl: the antecedent Who is in red: the relative clause The girl is my sister: the main clause Who: the relative pronoun 通过分析句子结构,让学生充分理解关系代词在定语从句中的位置和作用。 2’ Class Work
Step 4 Functions of relative pronouns 1. Explain to the students that in relative clauses, relative pronouns can function as many different sentence elements. (1) The trees are in front of the library. They have lost their leaves. →The trees which are in front of the library have lost their leaves. Which functions as the subject in the relative clause. (2) We saw the worker just now. He is the best engineer in our factory. →The worker (whom) we saw just now is the best engineer in out factory. Whom functions as the object in the relative clause. (We can leave out who, whom, which and that when they are the objects in the relative clause.) (3) It used to be a farm. It is no longer a farm. →It is no longer the farm that it used to be. That functions as the predicative in the relative clause. (4) He has a sister. I can’t remember her name. →He has a sister whose name I can’t remember. Whose functions as the attributive in the relative clause. 2. Lead students to finish the table below. 人物主语that, whothat, which宾语that, who, whomthat, which定语whosewhose
3. Ask students to finish “Working out the rules” on Page 34. 通过举例,让学生理解关系代词引导限制性定语从句的核心规则。 10’ Class Work
Step 5 Rules 1. Explain to students that in some cases, only “that” can be used as the relative pronouns while “which” or “who” can’t be. They are: (1) When the antecedent is an indefinite pronoun such as “all, everything, nothing, something, anything, little, much”. e.g. I’m sure she has something (that) you want. (2) When the antecedent is a noun or noun phrase with such determiners as “all, every, no, some, any, little, much”. e.g. I have read all the books (that) you wrote. (3) When the antecedent takes a premodifier in the superlative degree or an ordinal numeral. e.g. This is the best movie (that) I have ever seen. (4) When the antecedent is a noun or noun phrase modified by “the only, the very, the same, the last, the right”. e.g. This is the very book (that) I’m looking for. (5) When the antecedent includes both persons and things. e.g. Do you know the persons and things (that) they are talking about (6) When the main clause begins with “which” or “who”. Which is the dress (that) you like best Who is the girl that won the gold medal (7) When the antecedent functions as the predicative in the relative clause. e.g. My hometown is no longer the village that it used to be. 2. Show students that after a preposition, the relative pronoun can only be “which” or “whom”. The park is a place which/that I often go to. = The park is a place to which I often go. This is the woman the daughter of whom is a famous teacher. = This is the woman whose daughter is a famous teacher. 3. Show students that the relative pronoun after “the way” can be “that” “in which” or no relative pronoun. I don’t like the way (that/in which) you talk with me. 通过分析关系代词的使用限制,让学生掌握关系代词的用法。 10’ Class Work
Applying the rules
Step 6 Practice 1. Have students rewrite the sentences using restrictive relative clauses in Part B1 on Page 35. 2. Have students complete the passage in B2 with correct relative pronouns where necessary. 3. Have students work in pairs to describe a classmate of theirs, using relative clauses where necessary. Then ask them to share their descriptions in class without telling the name of the person who is described and let the other students guess who he or she is talking about. 通过句子、语篇两个层面的巩固练习,使学生学会使用关系代词引导的限制性定语从句。让学生准确、得体地使用关系代词引导的限制性定语从句来描述一位同学,与同学形成友好关系,学会珍爱友谊。 11’ Individual Work Group Work Class Work
Homework Write a short passage to describe one of your friends. 2’
21世纪教育网 www.21cnjy.com 精品试卷·第 2 页 (共 2 页)
21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
Book 1 Unit 3 Getting along with others
Grammar and usage
Restrictive relative clauses with relative pronouns
教学目标
By the end of this section, students will be able to:
1. understand the meaning of restrictive relative clauses with relative pronouns;
2. summarize the grammatical rules of the restrictive clauses with relative pronouns;
3. apply the appropriate restrictive relative clauses with relative pronouns to describe their friends.
教学重难点
1. To understand the functions of different relative pronouns in the restrictive relative clauses;
2. To know the restrictions of different relative pronouns.
教学过程
步 骤 教学活动 设计意图 互动时间&模式
Lead-in
Step 1 Lead students to compare the following sentences and read them aloud. (1) People have close friends. People naturally enjoy their company. →People who have close friends naturally enjoy their company. (2) He is rich enough. He has true friends. →He is rich enough who has true friends. (3) Friendship is a precious wealth. One searches for it all his life. →Friendship is a precious wealth (that) one searches for all his life. 通过比较,引导学生关注定语从句是如何通过关系代词与主句连接的,为引入关系代词做准备。 5’ Class Work
Exploring the rules
Step 2 Have students read a magazine article in Part A on Page 34 and find out the restrictive relative clauses with relative pronouns. 创设情境,激活学生原有背景知识,引导学生关注关系代词。 5’ Individual Work
Step 3 Have students focus on the use of who, whose, whom, that, which. They are relative pronouns. Show students the structure of a sentence containing a relative clause. The girl who is in red is my sister. The girl: the antecedent Who is in red: the relative clause The girl is my sister: the main clause Who: the relative pronoun 通过分析句子结构,让学生充分理解关系代词在定语从句中的位置和作用。 2’ Class Work
Step 4 Functions of relative pronouns 1. Explain to the students that in relative clauses, relative pronouns can function as many different sentence elements. (1) The trees are in front of the library. They have lost their leaves. →The trees which are in front of the library have lost their leaves. Which functions as the subject in the relative clause. (2) We saw the worker just now. He is the best engineer in our factory. →The worker (whom) we saw just now is the best engineer in out factory. Whom functions as the object in the relative clause. (We can leave out who, whom, which and that when they are the objects in the relative clause.) (3) It used to be a farm. It is no longer a farm. →It is no longer the farm that it used to be. That functions as the predicative in the relative clause. (4) He has a sister. I can’t remember her name. →He has a sister whose name I can’t remember. Whose functions as the attributive in the relative clause. 2. Lead students to finish the table below. 人物主语that, whothat, which宾语that, who, whomthat, which定语whosewhose
3. Ask students to finish “Working out the rules” on Page 34. 通过举例,让学生理解关系代词引导限制性定语从句的核心规则。 10’ Class Work
Step 5 Rules 1. Explain to students that in some cases, only “that” can be used as the relative pronouns while “which” or “who” can’t be. They are: (1) When the antecedent is an indefinite pronoun such as “all, everything, nothing, something, anything, little, much”. e.g. I’m sure she has something (that) you want. (2) When the antecedent is a noun or noun phrase with such determiners as “all, every, no, some, any, little, much”. e.g. I have read all the books (that) you wrote. (3) When the antecedent takes a premodifier in the superlative degree or an ordinal numeral. e.g. This is the best movie (that) I have ever seen. (4) When the antecedent is a noun or noun phrase modified by “the only, the very, the same, the last, the right”. e.g. This is the very book (that) I’m looking for. (5) When the antecedent includes both persons and things. e.g. Do you know the persons and things (that) they are talking about (6) When the main clause begins with “which” or “who”. Which is the dress (that) you like best Who is the girl that won the gold medal (7) When the antecedent functions as the predicative in the relative clause. e.g. My hometown is no longer the village that it used to be. 2. Show students that after a preposition, the relative pronoun can only be “which” or “whom”. The park is a place which/that I often go to. = The park is a place to which I often go. This is the woman the daughter of whom is a famous teacher. = This is the woman whose daughter is a famous teacher. 3. Show students that the relative pronoun after “the way” can be “that” “in which” or no relative pronoun. I don’t like the way (that/in which) you talk with me. 通过分析关系代词的使用限制,让学生掌握关系代词的用法。 10’ Class Work
Applying the rules
Step 6 Practice 1. Have students rewrite the sentences using restrictive relative clauses in Part B1 on Page 35. 2. Have students complete the passage in B2 with correct relative pronouns where necessary. 3. Have students work in pairs to describe a classmate of theirs, using relative clauses where necessary. Then ask them to share their descriptions in class without telling the name of the person who is described and let the other students guess who he or she is talking about. 通过句子、语篇两个层面的巩固练习,使学生学会使用关系代词引导的限制性定语从句。让学生准确、得体地使用关系代词引导的限制性定语从句来描述一位同学,与同学形成友好关系,学会珍爱友谊。 11’ Individual Work Group Work Class Work
Homework Write a short passage to describe one of your friends. 2’
21世纪教育网 www.21cnjy.com 精品试卷·第 2 页 (共 2 页)
21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
