中考语法专项复习(八)—— 动词和动词短语课件(共26张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 中考语法专项复习(八)—— 动词和动词短语课件(共26张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 7.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-10-02 22:35:20 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共26张PPT)
动词和动词短语
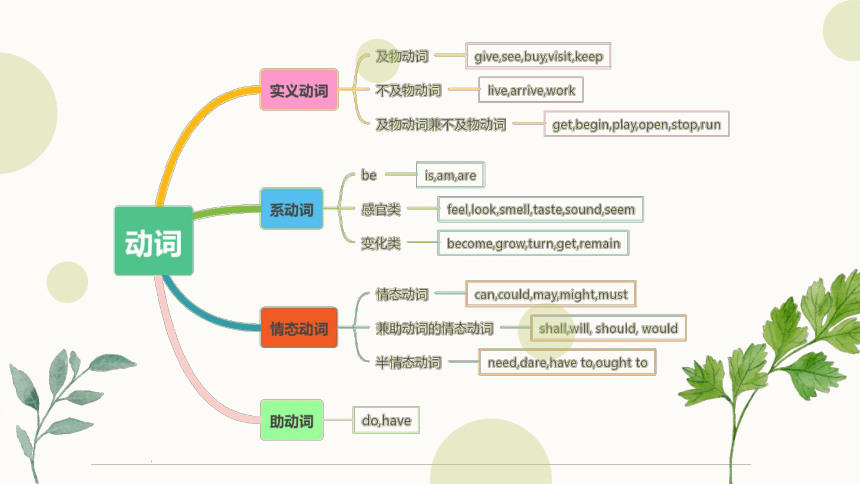
动词的分类
01
动词的用法
02
动词和动词短语
03
01 动词的分类
02 动词的用法
实义动词
一、实义动词
实义动词也叫行为动词,有完整的意义,分为及物动词(必须有宾语)和不及物动词(不需要宾语)。
实义动词有人称、时态的变化,要根据主语和句子的时间状语来定。
实义动词的用法
1. 及物动词本身意义不完整,后面需要接宾语。
如:I like this book.
我喜欢这本书。(动词+宾语)
I saw the children play in the park yesterday.
昨天我看见孩子们在公园琬。(动词+宾语+宾补)
2. 不及物动词本身意义完整,后面不用接宾语。
如:Horses run very fast.
马跑得很快。。
实义动词的用法
3. 有些动词既可作及物动词又可作不及物动词,通过看其后是否直接接宾语来区别。
如:He studies English very hard. 他学习英语非常努力。(及物动词)
He studies very hard. 他学习非常努力。(不及物动词)
系动词
二、系动词
系动词,也称连系动词,是用来辅助主语的动词。它本身有词义,但不能单独用作谓语,其后必须跟表语,构成系表结构说明主语的状况、性质、特征等情况。主要有:be,look,taste,smell,sound,feel,get,become,grow,turn,go,fall,come,keep,stay,remain,seem,appear等。
系动词的用法
1. 状态系动词(be 动词)
(1)形式一般会随人称及时态的变化而变化。
(2)后面接名词、代词、数词、介词或形容词等。
如:Tina is a teacher.
He was in Beijing yesterday.
2. 感官系统词
(1)感官系动词有:look,taste,smell,sound,feel等。
(2)后面接形容词(3)表示“看(听,闻......)起来像......”的结构:
look/sound/smell like,后面接名词或代词
如:The sky looks beautiful.
The hamburger tastes good.
That sounds interesting.
How does it smell
系动词的用法
3. 变化系动词
变化系动词有:get,become,grow,turn,go,fall,come
如:
She got mad after arguing with her husband.
The leaves turn green when spring comes.
Tom’s dream came true at last.
As time went on, he became more and more impatient.
系动词的用法
4. 持续系动词
(1)用来表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度。
(2)主要有keep, stay, remain, 后接形容词。
如:①We should keep quiet in the library.
②This matter remains a mistery.
5. 表像系动词
(1)用来表示“看起来像”这个概念。
(2)主要有look, seem, appear, 后接形容词。
如:①He looks sleepy.
②She seems to be sad.
情态动词
三、情态动词
情态动词,本身有一定的词义,表示语气的单词。但是情态动词不能独立作谓语,只能和动词原形一起构成谓语。
常见的有: can (could), may (might), must, need, ought to, dare (dared), shall (should), will (would)。
情态动词
can 表示能力
could 表示过去的能力(can的过去式),有礼貌的请求
may 表示允许或征求对方许可
might 表示过去的允许(may的过去式),表示可能性
must 表示必须、应该
need 表示需要,常用于疑问句、否定句和条件句中
shoud 表示应该,表示建议和推测
ought 表示应该,语气比should要强一些
shall 表示征求对方的意见,用于第一人称
will 表示意志或决心
would 表示主观一只(will的过去式)
情态动词的用法
情态动词和助动词一样,后面可直接跟否定词not
shall not-shan't
will not-won't
can not-can't
must not-mustn't
should not-shouldn't
would not-wouldn't
could not-couldn't
dare not-daren't
need not-needn't
情态动词的用法
1. 情态动词+ 行为动词原形
如:I can play the piano.
我会弹钢琴。
May I help you
我可以帮助到你吗?
We should go to bed before 10 o’clock.
我们应该在10点前睡觉。
情态动词的用法
2. 情态动词表猜测的三种句式
(1)在肯定句中一般用must(一定),could(可能),might/may(也许,或许)。
如:Miss Lin must/could/might know the answer to the question.
林老师一定/可能/或许知道这个问题的答案。
The light is on, he must be at home.
灯是亮着的,他肯定在家。
情态动词的用法
情态动词表猜测的三种句式
(1)否定句中用can’t/couldn’t(不可能),may not/might not(可能不)。
如:That can’t be Lucy. She has gone to Beijing.
那不可能是露西,她去北京了。
She might know where is the key.
她可能知道钥匙在哪里。
情态动词的用法
情态动词表猜测的三种句式
(1)疑问句中把can/could放为句首。
如:Can you give me a favor
你可以帮我一个忙吗?
Could he have finished the homework
他可能把作业完成了吗?
助动词
四、助动词
助动词本身无词义或意义不完整,不能单独作谓语,须和其他动词连用,帮助构成时态、语态、否定与和疑问句等结构。常见的助动词有:be(am/is/are), have(has/had),do(does/did),will(would)等。
助动词的用法
助动词 用法 例子
be(am, is, are,was, were) 与实义动词构成现在进行时、过去进行时(be+doing)或者被动语态(be + done) We are watching TV in the living room.
He was playing football at 7:00 last night.
English is spoken in many countries.
do, does, did 用于实义动词的否定句和疑问句中。 Do you have a mobie phone
She doesn’t like ice cream.
Did you do your homework last night
will 与实义动词构成一般将来时。 I will tell you a story this evening.
She will come back tomorrow.
Thank you!
动词和动词短语
动词的分类
01
动词的用法
02
动词和动词短语
03
01 动词的分类
02 动词的用法
实义动词
一、实义动词
实义动词也叫行为动词,有完整的意义,分为及物动词(必须有宾语)和不及物动词(不需要宾语)。
实义动词有人称、时态的变化,要根据主语和句子的时间状语来定。
实义动词的用法
1. 及物动词本身意义不完整,后面需要接宾语。
如:I like this book.
我喜欢这本书。(动词+宾语)
I saw the children play in the park yesterday.
昨天我看见孩子们在公园琬。(动词+宾语+宾补)
2. 不及物动词本身意义完整,后面不用接宾语。
如:Horses run very fast.
马跑得很快。。
实义动词的用法
3. 有些动词既可作及物动词又可作不及物动词,通过看其后是否直接接宾语来区别。
如:He studies English very hard. 他学习英语非常努力。(及物动词)
He studies very hard. 他学习非常努力。(不及物动词)
系动词
二、系动词
系动词,也称连系动词,是用来辅助主语的动词。它本身有词义,但不能单独用作谓语,其后必须跟表语,构成系表结构说明主语的状况、性质、特征等情况。主要有:be,look,taste,smell,sound,feel,get,become,grow,turn,go,fall,come,keep,stay,remain,seem,appear等。
系动词的用法
1. 状态系动词(be 动词)
(1)形式一般会随人称及时态的变化而变化。
(2)后面接名词、代词、数词、介词或形容词等。
如:Tina is a teacher.
He was in Beijing yesterday.
2. 感官系统词
(1)感官系动词有:look,taste,smell,sound,feel等。
(2)后面接形容词(3)表示“看(听,闻......)起来像......”的结构:
look/sound/smell like,后面接名词或代词
如:The sky looks beautiful.
The hamburger tastes good.
That sounds interesting.
How does it smell
系动词的用法
3. 变化系动词
变化系动词有:get,become,grow,turn,go,fall,come
如:
She got mad after arguing with her husband.
The leaves turn green when spring comes.
Tom’s dream came true at last.
As time went on, he became more and more impatient.
系动词的用法
4. 持续系动词
(1)用来表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度。
(2)主要有keep, stay, remain, 后接形容词。
如:①We should keep quiet in the library.
②This matter remains a mistery.
5. 表像系动词
(1)用来表示“看起来像”这个概念。
(2)主要有look, seem, appear, 后接形容词。
如:①He looks sleepy.
②She seems to be sad.
情态动词
三、情态动词
情态动词,本身有一定的词义,表示语气的单词。但是情态动词不能独立作谓语,只能和动词原形一起构成谓语。
常见的有: can (could), may (might), must, need, ought to, dare (dared), shall (should), will (would)。
情态动词
can 表示能力
could 表示过去的能力(can的过去式),有礼貌的请求
may 表示允许或征求对方许可
might 表示过去的允许(may的过去式),表示可能性
must 表示必须、应该
need 表示需要,常用于疑问句、否定句和条件句中
shoud 表示应该,表示建议和推测
ought 表示应该,语气比should要强一些
shall 表示征求对方的意见,用于第一人称
will 表示意志或决心
would 表示主观一只(will的过去式)
情态动词的用法
情态动词和助动词一样,后面可直接跟否定词not
shall not-shan't
will not-won't
can not-can't
must not-mustn't
should not-shouldn't
would not-wouldn't
could not-couldn't
dare not-daren't
need not-needn't
情态动词的用法
1. 情态动词+ 行为动词原形
如:I can play the piano.
我会弹钢琴。
May I help you
我可以帮助到你吗?
We should go to bed before 10 o’clock.
我们应该在10点前睡觉。
情态动词的用法
2. 情态动词表猜测的三种句式
(1)在肯定句中一般用must(一定),could(可能),might/may(也许,或许)。
如:Miss Lin must/could/might know the answer to the question.
林老师一定/可能/或许知道这个问题的答案。
The light is on, he must be at home.
灯是亮着的,他肯定在家。
情态动词的用法
情态动词表猜测的三种句式
(1)否定句中用can’t/couldn’t(不可能),may not/might not(可能不)。
如:That can’t be Lucy. She has gone to Beijing.
那不可能是露西,她去北京了。
She might know where is the key.
她可能知道钥匙在哪里。
情态动词的用法
情态动词表猜测的三种句式
(1)疑问句中把can/could放为句首。
如:Can you give me a favor
你可以帮我一个忙吗?
Could he have finished the homework
他可能把作业完成了吗?
助动词
四、助动词
助动词本身无词义或意义不完整,不能单独作谓语,须和其他动词连用,帮助构成时态、语态、否定与和疑问句等结构。常见的助动词有:be(am/is/are), have(has/had),do(does/did),will(would)等。
助动词的用法
助动词 用法 例子
be(am, is, are,was, were) 与实义动词构成现在进行时、过去进行时(be+doing)或者被动语态(be + done) We are watching TV in the living room.
He was playing football at 7:00 last night.
English is spoken in many countries.
do, does, did 用于实义动词的否定句和疑问句中。 Do you have a mobie phone
She doesn’t like ice cream.
Did you do your homework last night
will 与实义动词构成一般将来时。 I will tell you a story this evening.
She will come back tomorrow.
Thank you!
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
