2023届高考英语二轮复习语法专项定语从句精品课件(22张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023届高考英语二轮复习语法专项定语从句精品课件(22张ppt) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 21.7MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-10-08 17:24:42 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共22张PPT)
定语从句
2023一轮复习——语法专项
Part 1 定语从句的概述
Part 1 定语从句的概述
定语从句:在复合句中修饰名词或代词的从句。
例:He is the man who helped me.
The building which stands near the river is our school.
先行词:被修饰的名词或代词在定语从句中叫作先行词。
例:The house whose windows face south belongs to him.
关系词:把先行词和定语从句联系起来。代替先行词在定语从句中充当句子成分。
关系代词在定语从句中可以作主语、宾语、定语;关系副词在定语从句中可以作状语。
例:Do you have anything that you want to say for yourself
I still remember the day when I first came to Beijing.
限制性定语从句:对先行词起修饰、限制作用,为句中不可缺少的部分,主句和从句关
系非常紧密,不能用逗号分开。
例:The book that you were looking for was sold out.
The people who work in my office are very friendly.
非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明的作用,若将其去掉,不影响主句意思的完
整,主句和从句之间必须用逗号分开。
除了that以外,其他的关系代词和关系副词都和限制性定语从句用法相同,只是所有关系
词都必须写上,不能省略。
例:The small town, where he once worked, has turned to be a modern industry city.
Part 1 定语从句的概述
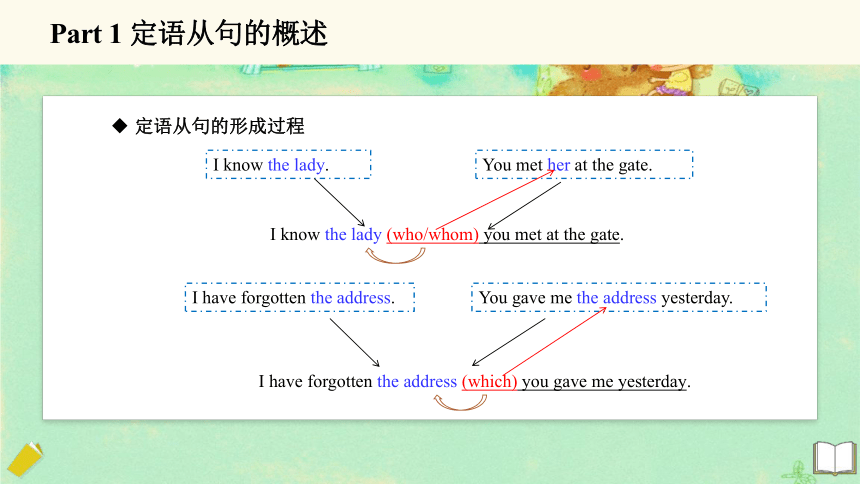
定语从句的形成过程
Part 1 定语从句的概述
I know the lady.
You met her at the gate.
I know the lady (who/whom) you met at the gate.
I have forgotten the address.
You gave me the address yesterday.
I have forgotten the address (which) you gave me yesterday.
定语从句的形成过程
Part 1 定语从句的概述
The building is a department store.
Its windows are blue.
The building whose windows are blue is a department store.
I still remember the day.
I first made an English speech on that day.
I still remember the day when I first made an English speech.
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
高考中,有关定语从句的考点常为关系词的填写,掌握关系词的用法是得分的要点。
引导定语从句的关系词
关系代词 which, that, who, whom, whose, as等
关系副词 when, where, why
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词that
仅在限制性定语从句中使用,既可以指代人又可以指代物,在定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语,作宾语时可省略,但不能作介词宾语。
下面几种情况必须用that引导定语从句:
先行词是不定代词all, few, little, much, something, nothing, anything等;
先行词被the only, the very, any, every, no, all, few, little, much等修饰;
先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰;
先行词既有人又有物;
主句的主语是疑问词who或which;
主句以here, there开头;
有两个定语从句,其中一个关系代词宜用which,另外一个宜用that。
例:She is the girl that/who lives next door.
That is one of the things (that/which) I will never forget.
指代人,可与who互换
指代物,可与which互换,作宾语时可省略
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词which
指代物或一句话,在定语从句中作主语、宾语或介词的宾语。
“介词+which”引导定语从句的用法
例:He has visited the school many times, in which he has many friends.
He lived in a big house, in front of which stood a big tall tree.
例:They sold pants which/that were made from tent material.
These are oranges (which/that) I picked myself.
This is the company with which we signed the agreement.
He was late again, which made the teacher very unhappy.
指代物,可与that互换
指代物,可与that互换,作宾语时可省略
指代物,作介词宾语,不可省略
指代一句话,作从句中主语,不可与that替换
该结构能和关系副词where替换,其中介词不能放在定语从句句末
“复合介词短语+which”引导的定语从句常用倒装语序
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词who和whom
who指代人,在定语从句中作主语、宾语,但介词提到关系代词前,不能用who。在限制性定语从句中who可用that代替。
whom指代人,在定语从句中作宾语,介词提到关系代词前,只能用whom。在限制性定语从句中可用who或that代替。
例:She is the girl who/that lives next door.
I discussed it with my brother, who is a lawyer.
That’s the girl (whom/who/that) I teach.
This is the scientist, of whom the achievements are well known.
指代人,可与that互换,作主语
指代人,作介词宾语,不可以替换为who或that,
不可省略
指代人,作主语,不可以替换为whom或that
指代人,作宾语,可以替换为whom或that或者省略
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词whose
指人或者物,在定语从句中作定语。当从句中含有与先行词有所属关系的词的时候,我们就用whose引导定语从句,相当于of whom 或of which。
例:This is the scientist whose achievements are well known.
This is the house whose window broke last night.
whose指代人
whose指代物
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词的基本用法总结
that 既指人也可以指物 只用于限制性定语从句;
关系代词作宾语且介词提到前面时,不用that;
在定语从句中作主语、宾语或表语。
which 指物或一句话 用于限制性或非限制性定语从句;
在定语从句中作主语、宾语。
who 指人 用于限制性或非限制性定语从句;
在定语从句中作主语、宾语。
whom 指人 用于限制性或非限制性定语从句;
在定语从句中作宾语。
whose 既可以指人也可以指物 用于限制性或非限制性定语从句;
在定语从句中作定语,相当于of whom或of which。
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系副词when, where, why
when指时间,在定语从句中作时间状语,相当于“表时间的介词(如:in, at, on, during等)+which”。
where指地点,在定语从句中作地点状语,相当于“表地点的介词(如:in, at, on, under等)+which”。
why指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语,相当于“表原因的介词(如:for)+which”
例:I still remember the day when I first came to Beijing. (when=on which)
例:Can you tell me the office where he works (where=in which)
例:Do you know the reason why he is absent (why=for which)
当先行词为situation, case, stage, point等, 且关系词在定语从句中作状语时,也要用关系副词where引导。
有时为表达清楚,还可以在关系副词where/when前加介词from/to等。
关系副词when, where可用于非限制性定语从句,而关系副词why不可以。
注意:
关系代词和关系副词的判别
这是学习定语从句的学生经常遇到的困难,出现问题的原因有两个,一是不会划分句子结构,二是只根据先行词的词义推测,但正确的做法只有一条:回归补缺定成分。“回归”是把先行词移到从句中,“补缺”是看看放在什么位置上才通顺,“定成分”是看这个词在句中的作用,这样就能做出相应正确的的选择了。一般选择顺序是先看关系代词再看关系副词。具体的操作方法将在例句中说明。
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
(1) I’ll never forget the days _____ I stayed in your country.
我永远不会忘记我待在你们国家的那些日子。
(2) I’ll never forget the days _____ I spent in your country.
我永远不会忘记我在你们国家度过的那些日子。
分析:两句话的主句都一样,但这并不决定关系词的选择。再来看从句:
(1) 我们把先行词the days移到从句中:I stayed the days,讲不通!因为stayed是不及物动词,不能有宾语,这样就排除了关系代词的选择,因为关系代词在从句中只能作主语和宾语。先行词days为时间概念,所以只能用when。
(2) spent是谓语动词,我们把先行词the days移到从句中:I spent the days讲得通,spent是及物动词,从句中少宾语,所以要选用which或that。
关系代词和关系副词的判别
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
(3) September 18, 1931 is the day _____ we’ll never forget.
1931年9月18日是我们不能忘记的日子。
(4) September 18, 1931 is the day _____ Japanese started an incident in China.
1931年9月18日是日本人在中国挑起事端的日子。
分析:
(3) 我们把先行词the day移到从句中:we’ll never forget the day讲得通!因为forget是及物动词,从句中少宾语,因此要选用which或that。
(4) 从句中的主语、宾语都有了,所以只能用关系副词when。
关系代词和关系副词的判别
Part 3 定语从句的特殊用法
Part 3 定语从句的特殊用法
关系代词as
用于限制性定语从句。指人或物且在限制性定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语。
常用句型为:① such(+名词)+as...(像……一样的,像……之类的)
② the same+名词+as...(和……同样的)
用于非限制性定语从句。指代整个主句或主句中的一部分,意为:正如……,像……
例:We have found such materials as are used in their factory.
This book is not such as I expect.
I have the same book as he has.
例:As is known to us all, China is in the east of Asia.
Part 3 定语从句的特殊用法
as和which都可以引导非限制性定语从句,先行词为整个主句或主句中的一部分内容,关系词在定语从句中作主语、宾语或表语,as与which均不可省略,有时两者可以互换。
下列情况通常只用as而不用which:
当定语从句置于主句前面时
关系词作主语且定语从句为被动语态形式时,从句谓语通常为:be known, be said, be reported, be announced, be mentioned等
在下列习惯用语中: as (it) seems likely, as (it) often happens, as (it) was said earlier,
as I remember (it), as (it) appears, as is often the case, as anybody can see, as we have expected
例:As you see, the Chinese people are hard-working.
例:She has been absent again, as is expected.
例:Jack has won first prize, as it often happens.
Part 3 定语从句的特殊用法
下列情况通常只用which而不用as:
当关系代词代表前面主句中的宾语从句或定语从句的谓语带有一个复合宾语结构时
当主句和从句存在逻辑上的因果关系时
当非限制性定语从句是否定句或表示否定时
非限制性定语从句中的be动词不能省略时, 用which,反之用as
例:I don’t think that he will come to see me, which makes me sad.
例:Tom was late for school again and again, which made his teacher very angry.
例:He came here very late, which was unexpected.
例:Jane told me that she won the match, which was a lie.
As (was) planned, we met at the airport.
Thank you
定语从句
2023一轮复习——语法专项
Part 1 定语从句的概述
Part 1 定语从句的概述
定语从句:在复合句中修饰名词或代词的从句。
例:He is the man who helped me.
The building which stands near the river is our school.
先行词:被修饰的名词或代词在定语从句中叫作先行词。
例:The house whose windows face south belongs to him.
关系词:把先行词和定语从句联系起来。代替先行词在定语从句中充当句子成分。
关系代词在定语从句中可以作主语、宾语、定语;关系副词在定语从句中可以作状语。
例:Do you have anything that you want to say for yourself
I still remember the day when I first came to Beijing.
限制性定语从句:对先行词起修饰、限制作用,为句中不可缺少的部分,主句和从句关
系非常紧密,不能用逗号分开。
例:The book that you were looking for was sold out.
The people who work in my office are very friendly.
非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明的作用,若将其去掉,不影响主句意思的完
整,主句和从句之间必须用逗号分开。
除了that以外,其他的关系代词和关系副词都和限制性定语从句用法相同,只是所有关系
词都必须写上,不能省略。
例:The small town, where he once worked, has turned to be a modern industry city.
Part 1 定语从句的概述
定语从句的形成过程
Part 1 定语从句的概述
I know the lady.
You met her at the gate.
I know the lady (who/whom) you met at the gate.
I have forgotten the address.
You gave me the address yesterday.
I have forgotten the address (which) you gave me yesterday.
定语从句的形成过程
Part 1 定语从句的概述
The building is a department store.
Its windows are blue.
The building whose windows are blue is a department store.
I still remember the day.
I first made an English speech on that day.
I still remember the day when I first made an English speech.
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
高考中,有关定语从句的考点常为关系词的填写,掌握关系词的用法是得分的要点。
引导定语从句的关系词
关系代词 which, that, who, whom, whose, as等
关系副词 when, where, why
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词that
仅在限制性定语从句中使用,既可以指代人又可以指代物,在定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语,作宾语时可省略,但不能作介词宾语。
下面几种情况必须用that引导定语从句:
先行词是不定代词all, few, little, much, something, nothing, anything等;
先行词被the only, the very, any, every, no, all, few, little, much等修饰;
先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰;
先行词既有人又有物;
主句的主语是疑问词who或which;
主句以here, there开头;
有两个定语从句,其中一个关系代词宜用which,另外一个宜用that。
例:She is the girl that/who lives next door.
That is one of the things (that/which) I will never forget.
指代人,可与who互换
指代物,可与which互换,作宾语时可省略
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词which
指代物或一句话,在定语从句中作主语、宾语或介词的宾语。
“介词+which”引导定语从句的用法
例:He has visited the school many times, in which he has many friends.
He lived in a big house, in front of which stood a big tall tree.
例:They sold pants which/that were made from tent material.
These are oranges (which/that) I picked myself.
This is the company with which we signed the agreement.
He was late again, which made the teacher very unhappy.
指代物,可与that互换
指代物,可与that互换,作宾语时可省略
指代物,作介词宾语,不可省略
指代一句话,作从句中主语,不可与that替换
该结构能和关系副词where替换,其中介词不能放在定语从句句末
“复合介词短语+which”引导的定语从句常用倒装语序
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词who和whom
who指代人,在定语从句中作主语、宾语,但介词提到关系代词前,不能用who。在限制性定语从句中who可用that代替。
whom指代人,在定语从句中作宾语,介词提到关系代词前,只能用whom。在限制性定语从句中可用who或that代替。
例:She is the girl who/that lives next door.
I discussed it with my brother, who is a lawyer.
That’s the girl (whom/who/that) I teach.
This is the scientist, of whom the achievements are well known.
指代人,可与that互换,作主语
指代人,作介词宾语,不可以替换为who或that,
不可省略
指代人,作主语,不可以替换为whom或that
指代人,作宾语,可以替换为whom或that或者省略
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词whose
指人或者物,在定语从句中作定语。当从句中含有与先行词有所属关系的词的时候,我们就用whose引导定语从句,相当于of whom 或of which。
例:This is the scientist whose achievements are well known.
This is the house whose window broke last night.
whose指代人
whose指代物
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系代词的基本用法总结
that 既指人也可以指物 只用于限制性定语从句;
关系代词作宾语且介词提到前面时,不用that;
在定语从句中作主语、宾语或表语。
which 指物或一句话 用于限制性或非限制性定语从句;
在定语从句中作主语、宾语。
who 指人 用于限制性或非限制性定语从句;
在定语从句中作主语、宾语。
whom 指人 用于限制性或非限制性定语从句;
在定语从句中作宾语。
whose 既可以指人也可以指物 用于限制性或非限制性定语从句;
在定语从句中作定语,相当于of whom或of which。
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
关系副词when, where, why
when指时间,在定语从句中作时间状语,相当于“表时间的介词(如:in, at, on, during等)+which”。
where指地点,在定语从句中作地点状语,相当于“表地点的介词(如:in, at, on, under等)+which”。
why指原因,在定语从句中作原因状语,相当于“表原因的介词(如:for)+which”
例:I still remember the day when I first came to Beijing. (when=on which)
例:Can you tell me the office where he works (where=in which)
例:Do you know the reason why he is absent (why=for which)
当先行词为situation, case, stage, point等, 且关系词在定语从句中作状语时,也要用关系副词where引导。
有时为表达清楚,还可以在关系副词where/when前加介词from/to等。
关系副词when, where可用于非限制性定语从句,而关系副词why不可以。
注意:
关系代词和关系副词的判别
这是学习定语从句的学生经常遇到的困难,出现问题的原因有两个,一是不会划分句子结构,二是只根据先行词的词义推测,但正确的做法只有一条:回归补缺定成分。“回归”是把先行词移到从句中,“补缺”是看看放在什么位置上才通顺,“定成分”是看这个词在句中的作用,这样就能做出相应正确的的选择了。一般选择顺序是先看关系代词再看关系副词。具体的操作方法将在例句中说明。
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
(1) I’ll never forget the days _____ I stayed in your country.
我永远不会忘记我待在你们国家的那些日子。
(2) I’ll never forget the days _____ I spent in your country.
我永远不会忘记我在你们国家度过的那些日子。
分析:两句话的主句都一样,但这并不决定关系词的选择。再来看从句:
(1) 我们把先行词the days移到从句中:I stayed the days,讲不通!因为stayed是不及物动词,不能有宾语,这样就排除了关系代词的选择,因为关系代词在从句中只能作主语和宾语。先行词days为时间概念,所以只能用when。
(2) spent是谓语动词,我们把先行词the days移到从句中:I spent the days讲得通,spent是及物动词,从句中少宾语,所以要选用which或that。
关系代词和关系副词的判别
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
Part 2 定语从句的基本用法
(3) September 18, 1931 is the day _____ we’ll never forget.
1931年9月18日是我们不能忘记的日子。
(4) September 18, 1931 is the day _____ Japanese started an incident in China.
1931年9月18日是日本人在中国挑起事端的日子。
分析:
(3) 我们把先行词the day移到从句中:we’ll never forget the day讲得通!因为forget是及物动词,从句中少宾语,因此要选用which或that。
(4) 从句中的主语、宾语都有了,所以只能用关系副词when。
关系代词和关系副词的判别
Part 3 定语从句的特殊用法
Part 3 定语从句的特殊用法
关系代词as
用于限制性定语从句。指人或物且在限制性定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语。
常用句型为:① such(+名词)+as...(像……一样的,像……之类的)
② the same+名词+as...(和……同样的)
用于非限制性定语从句。指代整个主句或主句中的一部分,意为:正如……,像……
例:We have found such materials as are used in their factory.
This book is not such as I expect.
I have the same book as he has.
例:As is known to us all, China is in the east of Asia.
Part 3 定语从句的特殊用法
as和which都可以引导非限制性定语从句,先行词为整个主句或主句中的一部分内容,关系词在定语从句中作主语、宾语或表语,as与which均不可省略,有时两者可以互换。
下列情况通常只用as而不用which:
当定语从句置于主句前面时
关系词作主语且定语从句为被动语态形式时,从句谓语通常为:be known, be said, be reported, be announced, be mentioned等
在下列习惯用语中: as (it) seems likely, as (it) often happens, as (it) was said earlier,
as I remember (it), as (it) appears, as is often the case, as anybody can see, as we have expected
例:As you see, the Chinese people are hard-working.
例:She has been absent again, as is expected.
例:Jack has won first prize, as it often happens.
Part 3 定语从句的特殊用法
下列情况通常只用which而不用as:
当关系代词代表前面主句中的宾语从句或定语从句的谓语带有一个复合宾语结构时
当主句和从句存在逻辑上的因果关系时
当非限制性定语从句是否定句或表示否定时
非限制性定语从句中的be动词不能省略时, 用which,反之用as
例:I don’t think that he will come to see me, which makes me sad.
例:Tom was late for school again and again, which made his teacher very angry.
例:He came here very late, which was unexpected.
例:Jane told me that she won the match, which was a lie.
As (was) planned, we met at the airport.
Thank you
