最新中考英语语法专题复习 动词 课件(共30张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 最新中考英语语法专题复习 动词 课件(共30张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-10-16 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共30张PPT)
1.系动词
2.实义动词(及物和不及物)
3.助动词
4.情态动词
系动词:连系表语的词。
系动词有词义,不能独立做谓语。
He is wrong.(系词+表语做谓语)
一、系动词
be(am,is,are,was,were)
感官动词
(look,smell,taste,sound,feel,seem)
表示发展变化的词
(turn,get,keep,become)
系动词
他是强壮的。
He is strong.
你必须保持健康。
You must keep healthy.
树叶变绿了。
The leaves turn green.
莉莉似乎很生气。
Lily seems very angry.
1.Autumn is coming,the leaves ______yellow.
2.The girl _______beautiful.
3.The food_______delicious.
4.Autumn is coming,it______colder and colder.
5.That song ________ well.
turn
looks
tastes
gets
sounds
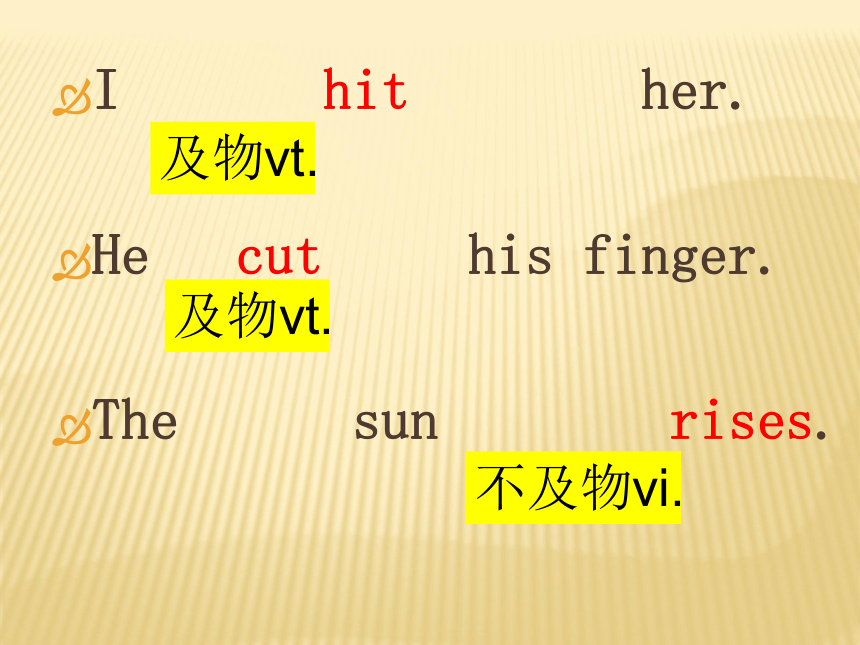
能独立做谓语的词,按句法作用分
为及物和不及物动词。
I hit her.
He cut his finger.
The sun rises.
及物vt.
不及物vi.
及物vt.
hurt-hurt-hurt(受伤、伤害)
say-said-said
stand-stood-stood
spend-spent-spent
think-thought-thought
buy-bought-bought
bring-brought-brought
catch-caught-caught
teach-taught-taught
hold-held-held
lend-lent-lent
send-sent-sent
leave-left-left
meet-met-met
sweep-swept-swept
sleep-slept-slept
keep-kept-kept
Orise-rose-risen
write-wrote-written
speak-spoke-spoken
steal-stole-stolen
Oride-rode-ridden
Odrive-drove-driven
√sing-sang-sung
Otake-took-taken
Ogive-gave-given
fly-flew-flown
Oknow-knew-known
Othrow-threw-thrown
eat-ate-eaten
forget-forgot-forgotten
I like it.
其中like是实意动词,如何变否定疑问.
用do来帮助它,我们把do、does、did等称为助动词。
I don’t like it.
Do you like it
助动词,无词义,不能独立做谓语,
帮助构成时(态),语(态),否(定句)和疑(问句)。
常见助动词有五个,be,do,have,shall,will.
be构成被动与进行,do构成疑问和否定
have构成现在完成时,shall,will表示将来时
1.I am watering the flowers.
帮助构成(现在/过去)进行时。
2.Tom was hit by his father yesterday.
帮助构成被动语态。
小测试:
She is Lily.(is 是助动词吗?)
答案:NO.
I have a book.其中have是助动词吗?
答案:NO.
have/had+V.过去分词
现在完成时/过去完成时
其中have是助动词吗?
答案:YES.
用于一般将来时态。
will用于所有人称,shall只用于第一人称。
She will finish her homework in ten minutes.
Shall I take an umbrella
She can speak French and I can’t.
什么叫情态动词?
表示说话人对所述动作的看法,如需要、可能、意愿或怀疑等情感或状态。
He can speak English well,but I can’t.
We must stay here.
情态动词有词义,不能单独做谓语,无人称和数的变化,后面必须接动词原形。
1.三个都表“能力”could 是can的过去式。
eg: I couldn’t speak English.
I can speak English now.
将来能力使用shall/will/be able to.
eg: I will be able to speak French.
2. can/could 表“请求、允许”
could 比can 更委婉。
eg:Could I borrow your book
3. can/could 表“怀疑、推测”
可能性 can‘t be
eg:It can’t be Lily’s bag.
1.表“请求、许可” might 比may更委婉、客气。
eg:May I come in
Might I come in
2. “可能”,表推测。
可能性 may be >might be
eg:He may come tomorrow.
He might come tomorrow.
必须
不得不
1.must表个人意志和主观上的必要,意为“必须”“应该”用于一般现在时;
I must go now.
2.have to表客观上的必要。意为“必须”“不得不”
除可用于现在时外,还可以表将来时shall/will have to和过去式had to。
1.这台电视机不能用了,我们必须买台新的。
This TV doesn’t work.We have to buy a new one.
2.那时我们必须买台新的。
We had to buy a new one.
3.我们将不得不买台新的。
We will have to buy a new one.
I _____study hard,because I want to go to Beijing University.
I _______go shopping,because the fridge is empty now.
must
have to
1.You are his mother,you_________look after him.
2.You are a student,you_______study hard.
3.She would be glad if you ______ help her.
应该
愿意
理所应当
ought to
should
would
> > >
must be
can’t be
may be
might be
既可作情态动词,又可作行为动词。
做情态动词,无人称、数变化,主要用于否定句和疑问句
1.只作情态动词的有:must,can(could),may(might)
2.可作情态动词也可作实义动词的有need,dare
3.可作情态动词也可作助动词的有will(would).shall(should)
4.具有情态动词的某些特征的有have to,ought to
1.系动词
2.实义动词(及物和不及物)
3.助动词
4.情态动词
系动词:连系表语的词。
系动词有词义,不能独立做谓语。
He is wrong.(系词+表语做谓语)
一、系动词
be(am,is,are,was,were)
感官动词
(look,smell,taste,sound,feel,seem)
表示发展变化的词
(turn,get,keep,become)
系动词
他是强壮的。
He is strong.
你必须保持健康。
You must keep healthy.
树叶变绿了。
The leaves turn green.
莉莉似乎很生气。
Lily seems very angry.
1.Autumn is coming,the leaves ______yellow.
2.The girl _______beautiful.
3.The food_______delicious.
4.Autumn is coming,it______colder and colder.
5.That song ________ well.
turn
looks
tastes
gets
sounds
能独立做谓语的词,按句法作用分
为及物和不及物动词。
I hit her.
He cut his finger.
The sun rises.
及物vt.
不及物vi.
及物vt.
hurt-hurt-hurt(受伤、伤害)
say-said-said
stand-stood-stood
spend-spent-spent
think-thought-thought
buy-bought-bought
bring-brought-brought
catch-caught-caught
teach-taught-taught
hold-held-held
lend-lent-lent
send-sent-sent
leave-left-left
meet-met-met
sweep-swept-swept
sleep-slept-slept
keep-kept-kept
Orise-rose-risen
write-wrote-written
speak-spoke-spoken
steal-stole-stolen
Oride-rode-ridden
Odrive-drove-driven
√sing-sang-sung
Otake-took-taken
Ogive-gave-given
fly-flew-flown
Oknow-knew-known
Othrow-threw-thrown
eat-ate-eaten
forget-forgot-forgotten
I like it.
其中like是实意动词,如何变否定疑问.
用do来帮助它,我们把do、does、did等称为助动词。
I don’t like it.
Do you like it
助动词,无词义,不能独立做谓语,
帮助构成时(态),语(态),否(定句)和疑(问句)。
常见助动词有五个,be,do,have,shall,will.
be构成被动与进行,do构成疑问和否定
have构成现在完成时,shall,will表示将来时
1.I am watering the flowers.
帮助构成(现在/过去)进行时。
2.Tom was hit by his father yesterday.
帮助构成被动语态。
小测试:
She is Lily.(is 是助动词吗?)
答案:NO.
I have a book.其中have是助动词吗?
答案:NO.
have/had+V.过去分词
现在完成时/过去完成时
其中have是助动词吗?
答案:YES.
用于一般将来时态。
will用于所有人称,shall只用于第一人称。
She will finish her homework in ten minutes.
Shall I take an umbrella
She can speak French and I can’t.
什么叫情态动词?
表示说话人对所述动作的看法,如需要、可能、意愿或怀疑等情感或状态。
He can speak English well,but I can’t.
We must stay here.
情态动词有词义,不能单独做谓语,无人称和数的变化,后面必须接动词原形。
1.三个都表“能力”could 是can的过去式。
eg: I couldn’t speak English.
I can speak English now.
将来能力使用shall/will/be able to.
eg: I will be able to speak French.
2. can/could 表“请求、允许”
could 比can 更委婉。
eg:Could I borrow your book
3. can/could 表“怀疑、推测”
可能性 can‘t be
eg:It can’t be Lily’s bag.
1.表“请求、许可” might 比may更委婉、客气。
eg:May I come in
Might I come in
2. “可能”,表推测。
可能性 may be >might be
eg:He may come tomorrow.
He might come tomorrow.
必须
不得不
1.must表个人意志和主观上的必要,意为“必须”“应该”用于一般现在时;
I must go now.
2.have to表客观上的必要。意为“必须”“不得不”
除可用于现在时外,还可以表将来时shall/will have to和过去式had to。
1.这台电视机不能用了,我们必须买台新的。
This TV doesn’t work.We have to buy a new one.
2.那时我们必须买台新的。
We had to buy a new one.
3.我们将不得不买台新的。
We will have to buy a new one.
I _____study hard,because I want to go to Beijing University.
I _______go shopping,because the fridge is empty now.
must
have to
1.You are his mother,you_________look after him.
2.You are a student,you_______study hard.
3.She would be glad if you ______ help her.
应该
愿意
理所应当
ought to
should
would
> > >
must be
can’t be
may be
might be
既可作情态动词,又可作行为动词。
做情态动词,无人称、数变化,主要用于否定句和疑问句
1.只作情态动词的有:must,can(could),may(might)
2.可作情态动词也可作实义动词的有need,dare
3.可作情态动词也可作助动词的有will(would).shall(should)
4.具有情态动词的某些特征的有have to,ought to
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
