外研版(2019) 必修第一册 Unit 2 Exploring English Understanding ideas 精品课件(38张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019) 必修第一册 Unit 2 Exploring English Understanding ideas 精品课件(38张ppt) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 26.1MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-10-17 21:30:06 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共37张PPT)
Unit 2 Exploring English
Understanding ideas
Look at the charts and answer the questions.
According to Chart 1, which language has the largest number of native speakers
Chinese has the largest number of native speakers.
Look at the charts and answer the questions.
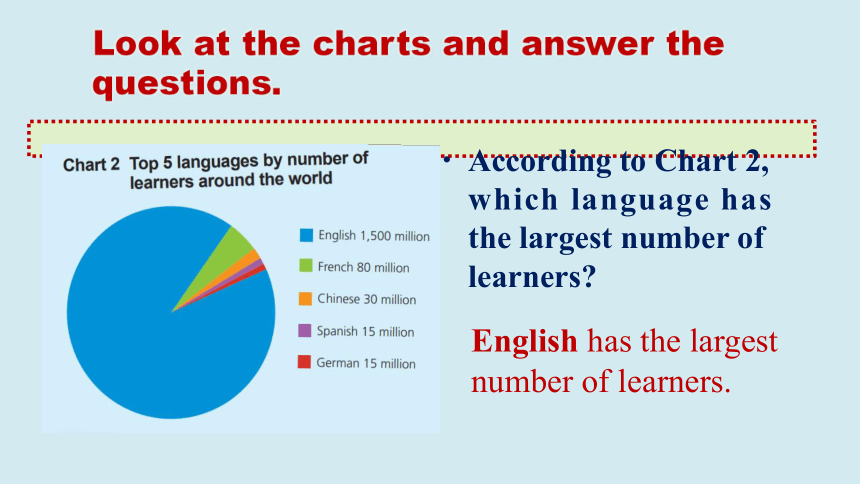
According to Chart 2, which language has the largest number of learners
English has the largest number of learners.
Look at the charts and answer the questions.
What can you learn from Chart 3
The number of English learners in China is increasing.
Why do you think many people in China learn English
Watch a video and answer the questions.
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
Where do a third of English words come from What examples are given in the video
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
Where do a third of English words come from What examples are given in the video
The UK, Ireland, the USA, Canada, New Zealand and Australia.
More than a third of English words come from French. For example, “fruit”, “table”, “crocodile” and “invasion”.
Look at the title of the passage and the pictures. Guess what the passage is about. (P14-15)
food
cooking
words
plants
fruit
Read the passage quickly and answer the questions.
What is the passage about
What is the author’s purpose in writing the passage
Tips for getting the main idea of a passage quickly
Analyze the title and the pictures carefully and predict.
Read for the topic sentence, which is usually in the first or last paragraph.
Read the first sentence of each paragraph.
Pay attention to the structure of the passage.
Read the passage quickly and answer the questions.
What is the passage about
food
cooking
words
plants
fruit
Read the passage quickly and answer the questions.
What is the author’s purpose in writing the passage
A. To tell us that English is difficult to learn.
B. To give advice on how to learn English.
C. To show that English is interesting and creative.
D. To explain how English was created.
Read the passage carefully and complete the notes with words from the passage. (P16)
In order to support his idea, the author uses many examples that show the 1__________ madness of English. no egg in eggplant no ham in 2.__________ neither pine nor apple in 3. ____________ sculpt a sculpture
paint a(n) 4.__________
BUT take a photo
unique
hamburger
pineapple
painting
We can’t always understand a compound word by adding the meanings of the words it is made up of!
The same rule doesn’t always apply to everything!
seasick → sick at sea 5__________→ sick in the air 6________ → sick in a car BUT 7 ________ → sick at home “Hard” is the opposite of “soft”.
“Hardly”and “softly” are not a(n) 8___________ pair.
airsick
carsick
homesick
opposing
“Harmless” is the opposite of “harmful”. Shameful and shameless 9_________ are the same. burn up → burn down
fill in a form→ 10 _____ a form
behaviors
fill out
Different words or phrases may have
the same meaning!
Stars are out. → They are visible. Lights are out. → They are 11 __________. I wind up my watch. →It starts.
I wind up the passage. →
It 12________.
The reason is that English was invented by people, and it 13 __________ the creativity of the human race. invisible
ends
reflects
The same words and phrases may have
different meanings in different contexts.
How does the author give examples Can you find the sentence patterns the author uses to give examples
The author gives examples mainly by comparing. He uses the following sentence patterns.
For example, we ..., but we ...
If... are..., why are... not...
When we..., we can. But when we..., we can’t....
Can you think of similar examples in Chinese
There isn’t fish in “Yu-Shiang Shredded Pork”.
There isn’t a wife in a “Laopobing”.
Read the following information and answer the questions. (P16)
How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
Does the information above give you a better understanding of the passage Give your reasons.
Eggplants got the name because they used to look
like eggs.
How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
The name of “pineapple” developed from the spanish word “pina”, with “apple” added to show it’s a kind of fruit.
The name of hamburger came from the idea of “Hamburg steak”, and later people reinvented it and called it “hamburger”.
2. Does the information above give you a better understanding of the passage Give your reasons.
Do you agree with the author’s opinion about the English language Give your reasons.
What do you find most challenging about learning English How do you deal with this
Think share
1. What is the opposite of white ( )
2. The post office is opposite the station. ( )
3. “True” and “false” have opposite meanings. ( )
1. opposite
Important words
① adj. 对面的;相反的
② n. 对立的人或物;对立面;反义词
③ prep. 与……相对;在……对面
①
②
③
Water is the opposing force to fire. 水火不相容。
The opposing team won the game. 对方赢得了比赛。
2. opposing
Important words
adj. 对立的;对抗的;对手的;相反的
Important lexical chunks
1 have trouble (in) doing...
2 get sb doing
3 sculpt a sculpture
4 paint a painting
5 take a photo
6 speak of
have difficulty (in) doing
to make someone do something
雕刻雕塑
画油画
照相
提及
Important lexical chunks
7 burn up / burn down
8 fill in / out a form
9 go off
10 wind up the watch
11 wind up the passage
to be completely destroyed by fire
填表
离开;(闹铃)响;爆炸
to make the watch work
to bring the passage to an end
“neither ... nor ... ”句型,意为:既不……,也不……,可以连接两个并列结构。neither和nor均为否定副词,位于句首时,后接部分倒装句,即neither / nor + 情态动词 / 助动词 / be动词 + 主语,如:Neither does she like tea or coffee. 其他否定意义的副词(如little, hardly, nowhere, scarcely, rarely, seldom, never 等)置于句首时,其后的句子也要用部分倒装的形式。
1. Neither is there pine nor apple in pinapple.
Important sentences
凤梨里面既没有松树也没有苹果。
Exercise
Complete the following sentences.
1. Little ___________ whether we live or die.
他才不会在乎我们的死活。
2. Never before __________ such a strange person.
以前我从未见过这样古怪的人。
3. Seldom __________________ .
她上学很少迟到。
did he care
have I met
is she late for school
2. Read the following sentences and decide what
they have in common.
Important sentences
①Have you ever asked yourself why people often have
trouble learning English
②This made me realise that there’s no egg in eggplant either.
③This got me thinking how English can be a crazy language
to learn.
这三个句子均含有宾语从句
第一句中why引导宾语从句,在从句中作原因状语,
第二句中that引导宾语从句,在从句中不充当成分,
第三句中how引导宾语从句,在从句中充当方式状语。
Nobody knows whether Tom can complete the project.
Could you please tell me how to use the new cellphone
I wonder why he hasn’t come.
Exercise
1.没有人知道汤姆能否完成这个项目。
Translate the following sentences.
2. 我想知道他为什么还没来。
3. 你能告诉我如何使用这部新手机吗?
“in which”引导限定性定语从句,修饰先行词language。关系代词which指代先行词language。本句话中,in which意为“在这门语言中”。 “介词 + 关系代词”在从句中作状语。
3. You also have to wonder at the unique madness
of a language in which a house can burn up as
it burns down.
Important sentences
你也不得不惊叹一门语言独特的疯狂。在这门语言中一间房子既可以被“burn up”, 也可以被“burn down”。
1. 根据与定语从句中动词的搭配来确定介词。如:
Water is the natural medium in which fish live.
水是鱼类赖以生存的自然环境。(live in)
2. 根据与定语从句中形容词的搭配来确定介词。如:
He referred me to some reference books with which I
am not very familiar.
他我要去参考一些我不熟悉的参考书。(be familiar
with)
Important sentences
对于“介词+关系代词”结构的使用,重点是要弄清其中的介词如何确定和判断。
3. 根据与先行词的搭配来确定介词。如:
I’ll never forget the day on which she said
goodbye to me.
我永远不会忘记她与我们告别的那一天。(on the
day)
4. 根据句意来确定介词的使用。如:
This is the book from which I got the story.
这就是那本书,从中我读到这个故事。(句意中含
有“从……”的意思,故用介词 from)
Important sentences
Exercise
Complete the following sentences.
1. The school __________ he once studied is very
famous.
他曾经就读的学校非常有名。
2. I know the film ___________ they are talking at
the moment.
我知道他们正在谈论的电影。
3. There are many reasons ____________ she likes
travelling.
她喜欢旅行的理由有很多。
in which
about which
for which
Homework
Work in groups, find similar examples in English language and design a poster .
THANK YOU
Unit 2 Exploring English
Understanding ideas
Look at the charts and answer the questions.
According to Chart 1, which language has the largest number of native speakers
Chinese has the largest number of native speakers.
Look at the charts and answer the questions.
According to Chart 2, which language has the largest number of learners
English has the largest number of learners.
Look at the charts and answer the questions.
What can you learn from Chart 3
The number of English learners in China is increasing.
Why do you think many people in China learn English
Watch a video and answer the questions.
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
Where do a third of English words come from What examples are given in the video
Which countries mentioned in the video have English as their first language
Where do a third of English words come from What examples are given in the video
The UK, Ireland, the USA, Canada, New Zealand and Australia.
More than a third of English words come from French. For example, “fruit”, “table”, “crocodile” and “invasion”.
Look at the title of the passage and the pictures. Guess what the passage is about. (P14-15)
food
cooking
words
plants
fruit
Read the passage quickly and answer the questions.
What is the passage about
What is the author’s purpose in writing the passage
Tips for getting the main idea of a passage quickly
Analyze the title and the pictures carefully and predict.
Read for the topic sentence, which is usually in the first or last paragraph.
Read the first sentence of each paragraph.
Pay attention to the structure of the passage.
Read the passage quickly and answer the questions.
What is the passage about
food
cooking
words
plants
fruit
Read the passage quickly and answer the questions.
What is the author’s purpose in writing the passage
A. To tell us that English is difficult to learn.
B. To give advice on how to learn English.
C. To show that English is interesting and creative.
D. To explain how English was created.
Read the passage carefully and complete the notes with words from the passage. (P16)
In order to support his idea, the author uses many examples that show the 1__________ madness of English. no egg in eggplant no ham in 2.__________ neither pine nor apple in 3. ____________ sculpt a sculpture
paint a(n) 4.__________
BUT take a photo
unique
hamburger
pineapple
painting
We can’t always understand a compound word by adding the meanings of the words it is made up of!
The same rule doesn’t always apply to everything!
seasick → sick at sea 5__________→ sick in the air 6________ → sick in a car BUT 7 ________ → sick at home “Hard” is the opposite of “soft”.
“Hardly”and “softly” are not a(n) 8___________ pair.
airsick
carsick
homesick
opposing
“Harmless” is the opposite of “harmful”. Shameful and shameless 9_________ are the same. burn up → burn down
fill in a form→ 10 _____ a form
behaviors
fill out
Different words or phrases may have
the same meaning!
Stars are out. → They are visible. Lights are out. → They are 11 __________. I wind up my watch. →It starts.
I wind up the passage. →
It 12________.
The reason is that English was invented by people, and it 13 __________ the creativity of the human race. invisible
ends
reflects
The same words and phrases may have
different meanings in different contexts.
How does the author give examples Can you find the sentence patterns the author uses to give examples
The author gives examples mainly by comparing. He uses the following sentence patterns.
For example, we ..., but we ...
If... are..., why are... not...
When we..., we can. But when we..., we can’t....
Can you think of similar examples in Chinese
There isn’t fish in “Yu-Shiang Shredded Pork”.
There isn’t a wife in a “Laopobing”.
Read the following information and answer the questions. (P16)
How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
Does the information above give you a better understanding of the passage Give your reasons.
Eggplants got the name because they used to look
like eggs.
How did pineapples, hamburgers and eggplants get their names
The name of “pineapple” developed from the spanish word “pina”, with “apple” added to show it’s a kind of fruit.
The name of hamburger came from the idea of “Hamburg steak”, and later people reinvented it and called it “hamburger”.
2. Does the information above give you a better understanding of the passage Give your reasons.
Do you agree with the author’s opinion about the English language Give your reasons.
What do you find most challenging about learning English How do you deal with this
Think share
1. What is the opposite of white ( )
2. The post office is opposite the station. ( )
3. “True” and “false” have opposite meanings. ( )
1. opposite
Important words
① adj. 对面的;相反的
② n. 对立的人或物;对立面;反义词
③ prep. 与……相对;在……对面
①
②
③
Water is the opposing force to fire. 水火不相容。
The opposing team won the game. 对方赢得了比赛。
2. opposing
Important words
adj. 对立的;对抗的;对手的;相反的
Important lexical chunks
1 have trouble (in) doing...
2 get sb doing
3 sculpt a sculpture
4 paint a painting
5 take a photo
6 speak of
have difficulty (in) doing
to make someone do something
雕刻雕塑
画油画
照相
提及
Important lexical chunks
7 burn up / burn down
8 fill in / out a form
9 go off
10 wind up the watch
11 wind up the passage
to be completely destroyed by fire
填表
离开;(闹铃)响;爆炸
to make the watch work
to bring the passage to an end
“neither ... nor ... ”句型,意为:既不……,也不……,可以连接两个并列结构。neither和nor均为否定副词,位于句首时,后接部分倒装句,即neither / nor + 情态动词 / 助动词 / be动词 + 主语,如:Neither does she like tea or coffee. 其他否定意义的副词(如little, hardly, nowhere, scarcely, rarely, seldom, never 等)置于句首时,其后的句子也要用部分倒装的形式。
1. Neither is there pine nor apple in pinapple.
Important sentences
凤梨里面既没有松树也没有苹果。
Exercise
Complete the following sentences.
1. Little ___________ whether we live or die.
他才不会在乎我们的死活。
2. Never before __________ such a strange person.
以前我从未见过这样古怪的人。
3. Seldom __________________ .
她上学很少迟到。
did he care
have I met
is she late for school
2. Read the following sentences and decide what
they have in common.
Important sentences
①Have you ever asked yourself why people often have
trouble learning English
②This made me realise that there’s no egg in eggplant either.
③This got me thinking how English can be a crazy language
to learn.
这三个句子均含有宾语从句
第一句中why引导宾语从句,在从句中作原因状语,
第二句中that引导宾语从句,在从句中不充当成分,
第三句中how引导宾语从句,在从句中充当方式状语。
Nobody knows whether Tom can complete the project.
Could you please tell me how to use the new cellphone
I wonder why he hasn’t come.
Exercise
1.没有人知道汤姆能否完成这个项目。
Translate the following sentences.
2. 我想知道他为什么还没来。
3. 你能告诉我如何使用这部新手机吗?
“in which”引导限定性定语从句,修饰先行词language。关系代词which指代先行词language。本句话中,in which意为“在这门语言中”。 “介词 + 关系代词”在从句中作状语。
3. You also have to wonder at the unique madness
of a language in which a house can burn up as
it burns down.
Important sentences
你也不得不惊叹一门语言独特的疯狂。在这门语言中一间房子既可以被“burn up”, 也可以被“burn down”。
1. 根据与定语从句中动词的搭配来确定介词。如:
Water is the natural medium in which fish live.
水是鱼类赖以生存的自然环境。(live in)
2. 根据与定语从句中形容词的搭配来确定介词。如:
He referred me to some reference books with which I
am not very familiar.
他我要去参考一些我不熟悉的参考书。(be familiar
with)
Important sentences
对于“介词+关系代词”结构的使用,重点是要弄清其中的介词如何确定和判断。
3. 根据与先行词的搭配来确定介词。如:
I’ll never forget the day on which she said
goodbye to me.
我永远不会忘记她与我们告别的那一天。(on the
day)
4. 根据句意来确定介词的使用。如:
This is the book from which I got the story.
这就是那本书,从中我读到这个故事。(句意中含
有“从……”的意思,故用介词 from)
Important sentences
Exercise
Complete the following sentences.
1. The school __________ he once studied is very
famous.
他曾经就读的学校非常有名。
2. I know the film ___________ they are talking at
the moment.
我知道他们正在谈论的电影。
3. There are many reasons ____________ she likes
travelling.
她喜欢旅行的理由有很多。
in which
about which
for which
Homework
Work in groups, find similar examples in English language and design a poster .
THANK YOU
