人教版(新课程标准)必修二Unit1 Cultural Relics Reading课件(66张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(新课程标准)必修二Unit1 Cultural Relics Reading课件(66张ppt) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.6MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-11-03 21:25:01 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共66张PPT)
The Mystical Glamour of Tulou
The Mystical Glamour of Tulou
Tulou buildings, first built in the Song and Yuan dynasties, are exclusive large-scale earthen residential buildings in any of the world's mountainous areas.
They are varied in shapes among which the round and square ones are the most common.
They are built with local natural materials such as earth, wood and cobbles. As a result, they are economical, solid, defensive and beautiful.
In 2008, 46 Fujian Tulou were inscribed by UNESCO as World Cultural Heritage as exceptional examples of a building tradition and function.
UNESCO
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
联合国科教文组织
heritage
something that have continued over many years and have been passed on from one generation to another.
遗产
M2 Unit1
Cultural Relics
Period 1 Warming up
What’s the difference between cultural heritage and cultural relic
Cultural heritage includes tangible and intangible cultural heritages.
While cultural relic is a common translation for a Chinese word “wenwu”, it usually means physical things of historical and cultural value.
Relic is any object, building or item that has survived a long time and can tell us something of the way people lived at the time it was made. It includes tangible and intangible things as heritage.
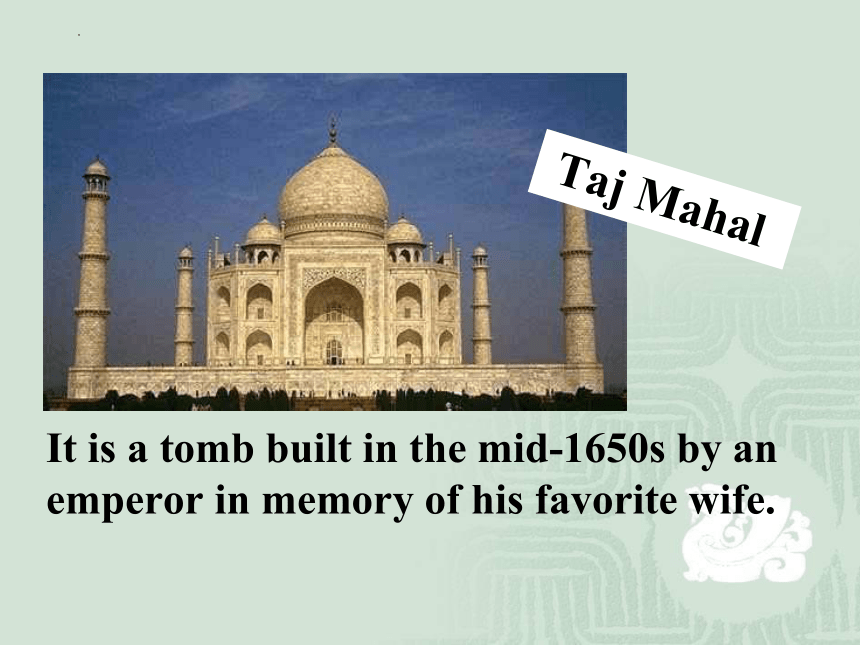
It is a tomb built in the mid-1650s by an emperor in memory of his favorite wife.
Taj Mahal
Mount Taishan
a natural site or a cultural site
Qing Dinasty vase
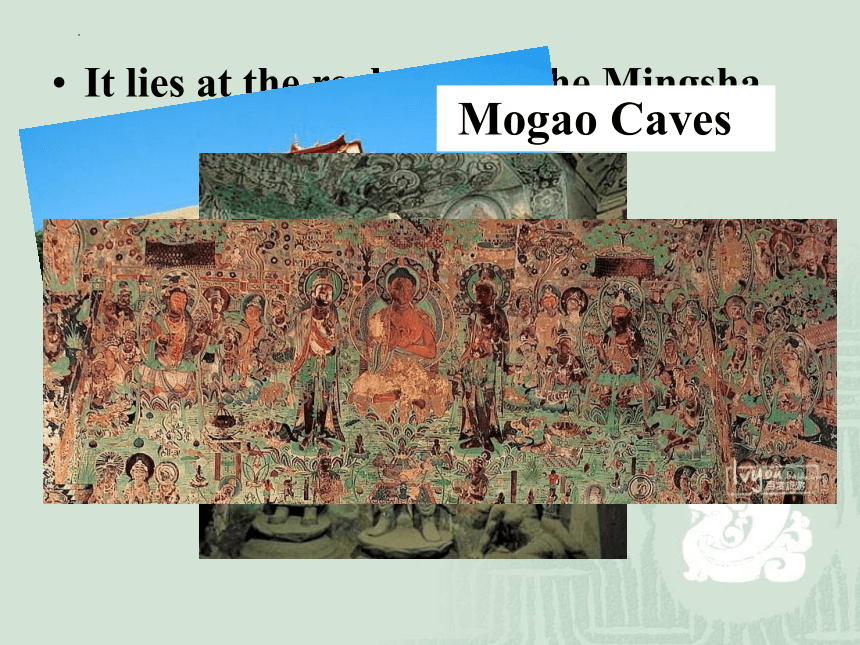
It lies at the rock side of the Mingsha Mountain in Gansu province.
It is made up of 492 caves.
It’s worth the name of art treasure house of the Chinese Nation.
Mogao Caves
Necklace
What are they made of
what amber is
Amber is the fossil form of resin from trees. It takes millions of years to form.
amber
amber
beautiful
rare/precious
Can you imagine a house made of amber
In Search of the Amber Room
In search of the Amber Room's...
culture, history, owners, functions
Task 1. Skim for structures and main ideas.
The article talks about ________________ and its _________.
the Amber Room
history
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
para. 1
para. 2-4
para. 5
description
history
rebuilding
In order of ______.
time
material
colour
design
who built it
How long was it built
A description of the Amber Room
yellow-brown, like honey
in the fancy style popular in those days
10 years
Part 1
Task 2. Detailed-reading
tons of amber, decored with gold and jewels
best artists in Prussia
1. The amber which was________ had a beautiful yellow–brown colour like ______. 2. The ______ of the room was in the ______ _____ popular in those days.
3. It was also a treasure _________ with gold and jewels, which took the country’s best _______ about ten years to make.
selected
honey
design
fancy
style
decorated
artists
selected= chose carefully
unusual
Para.2
Frederick I
Frederick William I
Peter the Great
Sent him his best soldiers in return.
a troop of
Served as
1. his in St Petersburg.
2. a small for important visitors.
winter palace
reception hall
gave to
as a gift
What happened to the Amber Room in 1716
(1716)
Para.3
pass down
Peter the Great
Catherine II
3. In 1770 the room was she wanted.
2. Told her artists to add more details to it
1. Had the Amber Room moved to a palace outside St Petersburg.
completed the way
Para.4
Time :
Event:
1941
Russia (the Russians)
Nazi Germany
(the Nazis)
at war
stole .
sent it to Konigsberg.
After that, what happened to the Amber Room .
were only able to remove furniture
and small art objects
the Amber Room
remains a mystery
Para.5
Qs:
1. Who have built a new Amber Room
2. How old is St Petersburg now
The Russians and Germans.
311 years old now.
Discussion: the process about the Amber Room itself becomes more complete.
To be ________.
To be ________.
To be ________.
To be ________.
To be ________.
To be ________.
made
given
added
stolen
searched
rebuilt
Discussion: different roles the Amber Room played in different periods.
In 1717, the Amber Room was a symbol of _______.
In 1770, the Amber Room was a symbol of _________.
In 1941, the Amber Room was a symbol of _________.
In 2003, the Amber Room was a symbol of _________.
gift
wonder
mystery
friendship/ success/ pride
The clue of the story
Peter the Great Czar
CatherineⅡ
FrederickⅠ
Frederick WilliamⅠ
pass down
given as a gift
pass down
stolen
Nazi
In groups discuss: Is it worth rebuilding lost cultural relics such as the Amber Room or Yuan Ming Yuan in Beijing Give your reasons.
(You can use the expressions on page 6.)
for
against
形容词短语作后置定语修饰
They have a house larger than yours.
= a house which is larger than yours.
The boys easiest to teach are in my class.
= the boys who are easiest to teach.
The design of the room was in the fancy style
popular in those days.
屋子的设计是当时流行的极富艺术表现力的
建筑式样.
It was also a treasure decorated with gold and jewels, which took the country’s best artists about ten years to make.
[点拨] 本句是一个主从复合句。 逗号前为主句,其中“decorated with gold and jewels”为过去分词短语作treasure的后置定语;逗号后为which 引导的非限制性定语从句,修饰先行词treasure。
1) 我的单车坏了,需要修理.
2) 昨晚我的钱包被人偷了.
My bike is broken, I will have it repaired.
I had my wallet stolen last night.
Later, CatherineⅡ had the Amber Room moved to the palace…
12. have sth. done结构表示两种意义:
①、让别人做某事,使某事被做
②、遭遇某种不幸。
Using Language
A Fact or an Opinion
Reading and listening
Reading this passage and think about the difference between a fact and an opinion.
What is a fact What is an opinion
What is evidence
What is a fact
What is an opinion
What is evidence
The facts given by the eyewitness is called evidence.
A fact is anything that can be proved.
An opinion is what someone believes is true but has not been proved.
prove
A fact is anything that can be proved.
vt.
It can be proved that...
link-v
sth proves (to be)+a.
The work proved to be successful.
1. An opinion is what someone believe is ture but has not been proved.
表语从句
I can't understand what he said at the meeting.
That is what he said at the meeting.
2. evidence n. 根据;证据
没有足够的证据证明他有罪。
There wasn't enough evidence to prove him guilty.
物证/人证
material evidence
testimony of a witness
in evidence
明显的,显而易见的
3. explode vi. / vt. 爆炸
The firework exploded in his hand.
Children usually like to explode firecrackers in the Spring Festival.
她冲进房间,放声大哭。
She burst into the room and burst into laugher/ burst out laughing.
...exploded into laughter.
4. entrance n. 入口
在去...的入口
at the entrance to...
禁止入内
No entrance
大学入学考试,高考
college entrance exam
1. agree with
(1).同意某人/某人的话/某人的观点/意见/看法 /决定等词 eg; sb /sb’s words/ what sb said/ opinion / view/ idea / decision
I agree with all of what you said.
(2).与… 保持一致
The verb must agree with the subject in person and number.
(3).(气候.食物等)适合某人
Bananas do not agree with me.
Language points
agree on 就… 达成一致的协议或取得一致的意见,
主语常是协商一件事的人们或单位
They agreed on the date for the meeting
agree to (to是介词) 表示同意某事,后面接建议/提/
办法/计划/安排/条件等词
eg: plan / suggestion / proposal/ arrangement
/ terms(条件/条款)…
He has agreed to our suggestion about the holiday.
agree to do sth 同意做某事
He agreed to lend his bike to me.
We agreed to start early.
(1) It is certain that Mr Black will support your proposal, for he always ___ whatever you say.
A. agrees with B. agrees on
C. agrees for D. agrees to
(2) Father didn’t ___ us to use his computer.
A.agree B. hope C. allow D. let
(3) The climate here doesn’t agree___ me.
A. to B. on C. with D. for
I __________ what he said.
After a further discussion, both sides _________
the date for the wedding.
They didn’t _________ each other on that point.
At last the teacher _________ give him another
chance.
You and I ________ this point.
They might not _________ his opinions.
She can’t _______ your demands.
agree with
agreed on
agree with
agreed to
agree on
agree with
agree to
The Restrictive and
Non- Restrictive Attributive Clause
Discovering useful structures
GRAMMAR
Can you tell the difference between Restrictive and Non-Restrictive Clause
A. In written form
B. In how close the clause is
connected with the main sentence
1. Beijing is a city that I’ve always wanted to visit.
2. Beijing, which is the capital of China, has a long history.
3. Mr. Black is the man who rescued me from the river.
4. Mr. Black, who is a doctor, rescued me from the river.
C. In Antecedent (先行词)
1. Mike sold the house which his family had lived in for 30 years.
2. Mike sold the house, which made his father very angry.
3. Mike lived in Lincoln Street, where many important people lived.
His father, who works in Beijing, came back yesterday.
Shanghai, which is in East China, is developing rapidly.
当先行词是地名人名、世界上独一无二的事物或家庭唯一成员时,通常只用非限制性定语从句。
D. In the Relative Pronouns (关系代词)
1. She married a man (that / whom /who) she met on the bus.
2. The book, which he lost yesterday, has been found.
which 在从句中作宾语,但不能省略
1. He failed in the exam, that made his mother angry.
2. He failed in the exam, which made his mother angry.
关系代词:which / who / whom /
whose / as
关系副词:when / where
(非限制性定语从句中不用关系词that;非限制性定语从句中关系词不能省略)
非限制性定语从句中通常使用下列关系代词和副词。
准关系代词as引导的定语从句
限制性定语从句
I have never seen such a clever man as he is.
He shut the window with such a force that the glass broke.
This is the same bag as I lost yesterday.
This is the same bag that I lost yesterday.
非限制性定语从句
可以放在句首、中或后,在从句中作主语或宾语
As is known to all, he is the best student in our class.
as is said above
as often happens
as mentioned above
1. I have a sister who works in a hospital.
我有一位在医院工作的姐姐。
(不只一位姐姐)
2. I have a sister, who works in a hospital.
我有一位姐姐,她在医院工作。
(只有一位姐姐)
有时同一个限制性从句变为非限制性从句会改变全句的意思。
Ex. 3 (P4)
1. Here are the farmers. They discovered the underground city last month.
Here are the farmers who discovered the underground city last month.
Attributive Clause
2. Hangzhou is a famous city in China. Many people come to buy tea in that city.
Hangzhou is a famous city in China in which/where many people come to buy tea.
3. She got so angry. I don’t know the reason.
I don’t know the reason why she got so angry.
4. The old man saw some Germans taking apart the Amber Room and removing it. You are talking to an old man.
The old man (who / whom / that ) you are talking to saw some Germans taking apart the Amber Room and removing it.
5. The woman remembered the day. She saw Nazis burying something near her home.
The woman remembered the day when she saw Nazis burying something near her home.
6. St Petersburg is a very beautiful city. It was once called Leningrad.
St Petersburg is a very beautiful city, which was once called Leningrad.
7. I remember the soldier. He told me not to tell anyone what I had seen.
I remember the soldier, who told me not to tell anyone what I had seen.
8. The soldiers moved the boxes to a mine. They wanted to hide them.
The soldiers moved the boxes to a mine, where they wanted to hide them.
9. Xi’an is one of the few cities with walls. Its walls remain as good as before.
Xi’an is one of the few cities in which/where walls remain as good as before.
10. Shanxi Province is a place with many cultural relics. Its cultural relics are well looked after.
Shanxi Province is a place where cultural relics are well looked after.
1. I’ll never forget the days _____________ we worked together.
2. I’ll never forget the days ______ ________we spent together.
3. I went to the place _______________ I worked ten years ago.
when / in which
which
where / in which
几种易混的情况
及物动词
4. I went to the place ______________ I visited ten years ago.
5. This is the reason _______________ he was late.
6. This is the reason ____________ ________ he gave.
which
why / for which
that / which
及物动词
及物动词
(1) What surprised me was not what he said but the way _______________ he said it.
(that / in which)
Practice
(2) ___ is often the case, we have worked out the production plan.
(3) This is the very house _____ he lived.
(4) Next winter, _____ you will spend in Harbin, I’m sure, will be another exciting holiday.
(5) That’s the reason ____ he was late.
As
where
which
why
(6) Robert and his songs ____ were famous in the U. S. are also popular in China.
(7) They are always smoking, _____ of course, will do harm to their health.
that
which
The Mystical Glamour of Tulou
The Mystical Glamour of Tulou
Tulou buildings, first built in the Song and Yuan dynasties, are exclusive large-scale earthen residential buildings in any of the world's mountainous areas.
They are varied in shapes among which the round and square ones are the most common.
They are built with local natural materials such as earth, wood and cobbles. As a result, they are economical, solid, defensive and beautiful.
In 2008, 46 Fujian Tulou were inscribed by UNESCO as World Cultural Heritage as exceptional examples of a building tradition and function.
UNESCO
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
联合国科教文组织
heritage
something that have continued over many years and have been passed on from one generation to another.
遗产
M2 Unit1
Cultural Relics
Period 1 Warming up
What’s the difference between cultural heritage and cultural relic
Cultural heritage includes tangible and intangible cultural heritages.
While cultural relic is a common translation for a Chinese word “wenwu”, it usually means physical things of historical and cultural value.
Relic is any object, building or item that has survived a long time and can tell us something of the way people lived at the time it was made. It includes tangible and intangible things as heritage.
It is a tomb built in the mid-1650s by an emperor in memory of his favorite wife.
Taj Mahal
Mount Taishan
a natural site or a cultural site
Qing Dinasty vase
It lies at the rock side of the Mingsha Mountain in Gansu province.
It is made up of 492 caves.
It’s worth the name of art treasure house of the Chinese Nation.
Mogao Caves
Necklace
What are they made of
what amber is
Amber is the fossil form of resin from trees. It takes millions of years to form.
amber
amber
beautiful
rare/precious
Can you imagine a house made of amber
In Search of the Amber Room
In search of the Amber Room's...
culture, history, owners, functions
Task 1. Skim for structures and main ideas.
The article talks about ________________ and its _________.
the Amber Room
history
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
para. 1
para. 2-4
para. 5
description
history
rebuilding
In order of ______.
time
material
colour
design
who built it
How long was it built
A description of the Amber Room
yellow-brown, like honey
in the fancy style popular in those days
10 years
Part 1
Task 2. Detailed-reading
tons of amber, decored with gold and jewels
best artists in Prussia
1. The amber which was________ had a beautiful yellow–brown colour like ______. 2. The ______ of the room was in the ______ _____ popular in those days.
3. It was also a treasure _________ with gold and jewels, which took the country’s best _______ about ten years to make.
selected
honey
design
fancy
style
decorated
artists
selected= chose carefully
unusual
Para.2
Frederick I
Frederick William I
Peter the Great
Sent him his best soldiers in return.
a troop of
Served as
1. his in St Petersburg.
2. a small for important visitors.
winter palace
reception hall
gave to
as a gift
What happened to the Amber Room in 1716
(1716)
Para.3
pass down
Peter the Great
Catherine II
3. In 1770 the room was she wanted.
2. Told her artists to add more details to it
1. Had the Amber Room moved to a palace outside St Petersburg.
completed the way
Para.4
Time :
Event:
1941
Russia (the Russians)
Nazi Germany
(the Nazis)
at war
stole .
sent it to Konigsberg.
After that, what happened to the Amber Room .
were only able to remove furniture
and small art objects
the Amber Room
remains a mystery
Para.5
Qs:
1. Who have built a new Amber Room
2. How old is St Petersburg now
The Russians and Germans.
311 years old now.
Discussion: the process about the Amber Room itself becomes more complete.
To be ________.
To be ________.
To be ________.
To be ________.
To be ________.
To be ________.
made
given
added
stolen
searched
rebuilt
Discussion: different roles the Amber Room played in different periods.
In 1717, the Amber Room was a symbol of _______.
In 1770, the Amber Room was a symbol of _________.
In 1941, the Amber Room was a symbol of _________.
In 2003, the Amber Room was a symbol of _________.
gift
wonder
mystery
friendship/ success/ pride
The clue of the story
Peter the Great Czar
CatherineⅡ
FrederickⅠ
Frederick WilliamⅠ
pass down
given as a gift
pass down
stolen
Nazi
In groups discuss: Is it worth rebuilding lost cultural relics such as the Amber Room or Yuan Ming Yuan in Beijing Give your reasons.
(You can use the expressions on page 6.)
for
against
形容词短语作后置定语修饰
They have a house larger than yours.
= a house which is larger than yours.
The boys easiest to teach are in my class.
= the boys who are easiest to teach.
The design of the room was in the fancy style
popular in those days.
屋子的设计是当时流行的极富艺术表现力的
建筑式样.
It was also a treasure decorated with gold and jewels, which took the country’s best artists about ten years to make.
[点拨] 本句是一个主从复合句。 逗号前为主句,其中“decorated with gold and jewels”为过去分词短语作treasure的后置定语;逗号后为which 引导的非限制性定语从句,修饰先行词treasure。
1) 我的单车坏了,需要修理.
2) 昨晚我的钱包被人偷了.
My bike is broken, I will have it repaired.
I had my wallet stolen last night.
Later, CatherineⅡ had the Amber Room moved to the palace…
12. have sth. done结构表示两种意义:
①、让别人做某事,使某事被做
②、遭遇某种不幸。
Using Language
A Fact or an Opinion
Reading and listening
Reading this passage and think about the difference between a fact and an opinion.
What is a fact What is an opinion
What is evidence
What is a fact
What is an opinion
What is evidence
The facts given by the eyewitness is called evidence.
A fact is anything that can be proved.
An opinion is what someone believes is true but has not been proved.
prove
A fact is anything that can be proved.
vt.
It can be proved that...
link-v
sth proves (to be)+a.
The work proved to be successful.
1. An opinion is what someone believe is ture but has not been proved.
表语从句
I can't understand what he said at the meeting.
That is what he said at the meeting.
2. evidence n. 根据;证据
没有足够的证据证明他有罪。
There wasn't enough evidence to prove him guilty.
物证/人证
material evidence
testimony of a witness
in evidence
明显的,显而易见的
3. explode vi. / vt. 爆炸
The firework exploded in his hand.
Children usually like to explode firecrackers in the Spring Festival.
她冲进房间,放声大哭。
She burst into the room and burst into laugher/ burst out laughing.
...exploded into laughter.
4. entrance n. 入口
在去...的入口
at the entrance to...
禁止入内
No entrance
大学入学考试,高考
college entrance exam
1. agree with
(1).同意某人/某人的话/某人的观点/意见/看法 /决定等词 eg; sb /sb’s words/ what sb said/ opinion / view/ idea / decision
I agree with all of what you said.
(2).与… 保持一致
The verb must agree with the subject in person and number.
(3).(气候.食物等)适合某人
Bananas do not agree with me.
Language points
agree on 就… 达成一致的协议或取得一致的意见,
主语常是协商一件事的人们或单位
They agreed on the date for the meeting
agree to (to是介词) 表示同意某事,后面接建议/提/
办法/计划/安排/条件等词
eg: plan / suggestion / proposal/ arrangement
/ terms(条件/条款)…
He has agreed to our suggestion about the holiday.
agree to do sth 同意做某事
He agreed to lend his bike to me.
We agreed to start early.
(1) It is certain that Mr Black will support your proposal, for he always ___ whatever you say.
A. agrees with B. agrees on
C. agrees for D. agrees to
(2) Father didn’t ___ us to use his computer.
A.agree B. hope C. allow D. let
(3) The climate here doesn’t agree___ me.
A. to B. on C. with D. for
I __________ what he said.
After a further discussion, both sides _________
the date for the wedding.
They didn’t _________ each other on that point.
At last the teacher _________ give him another
chance.
You and I ________ this point.
They might not _________ his opinions.
She can’t _______ your demands.
agree with
agreed on
agree with
agreed to
agree on
agree with
agree to
The Restrictive and
Non- Restrictive Attributive Clause
Discovering useful structures
GRAMMAR
Can you tell the difference between Restrictive and Non-Restrictive Clause
A. In written form
B. In how close the clause is
connected with the main sentence
1. Beijing is a city that I’ve always wanted to visit.
2. Beijing, which is the capital of China, has a long history.
3. Mr. Black is the man who rescued me from the river.
4. Mr. Black, who is a doctor, rescued me from the river.
C. In Antecedent (先行词)
1. Mike sold the house which his family had lived in for 30 years.
2. Mike sold the house, which made his father very angry.
3. Mike lived in Lincoln Street, where many important people lived.
His father, who works in Beijing, came back yesterday.
Shanghai, which is in East China, is developing rapidly.
当先行词是地名人名、世界上独一无二的事物或家庭唯一成员时,通常只用非限制性定语从句。
D. In the Relative Pronouns (关系代词)
1. She married a man (that / whom /who) she met on the bus.
2. The book, which he lost yesterday, has been found.
which 在从句中作宾语,但不能省略
1. He failed in the exam, that made his mother angry.
2. He failed in the exam, which made his mother angry.
关系代词:which / who / whom /
whose / as
关系副词:when / where
(非限制性定语从句中不用关系词that;非限制性定语从句中关系词不能省略)
非限制性定语从句中通常使用下列关系代词和副词。
准关系代词as引导的定语从句
限制性定语从句
I have never seen such a clever man as he is.
He shut the window with such a force that the glass broke.
This is the same bag as I lost yesterday.
This is the same bag that I lost yesterday.
非限制性定语从句
可以放在句首、中或后,在从句中作主语或宾语
As is known to all, he is the best student in our class.
as is said above
as often happens
as mentioned above
1. I have a sister who works in a hospital.
我有一位在医院工作的姐姐。
(不只一位姐姐)
2. I have a sister, who works in a hospital.
我有一位姐姐,她在医院工作。
(只有一位姐姐)
有时同一个限制性从句变为非限制性从句会改变全句的意思。
Ex. 3 (P4)
1. Here are the farmers. They discovered the underground city last month.
Here are the farmers who discovered the underground city last month.
Attributive Clause
2. Hangzhou is a famous city in China. Many people come to buy tea in that city.
Hangzhou is a famous city in China in which/where many people come to buy tea.
3. She got so angry. I don’t know the reason.
I don’t know the reason why she got so angry.
4. The old man saw some Germans taking apart the Amber Room and removing it. You are talking to an old man.
The old man (who / whom / that ) you are talking to saw some Germans taking apart the Amber Room and removing it.
5. The woman remembered the day. She saw Nazis burying something near her home.
The woman remembered the day when she saw Nazis burying something near her home.
6. St Petersburg is a very beautiful city. It was once called Leningrad.
St Petersburg is a very beautiful city, which was once called Leningrad.
7. I remember the soldier. He told me not to tell anyone what I had seen.
I remember the soldier, who told me not to tell anyone what I had seen.
8. The soldiers moved the boxes to a mine. They wanted to hide them.
The soldiers moved the boxes to a mine, where they wanted to hide them.
9. Xi’an is one of the few cities with walls. Its walls remain as good as before.
Xi’an is one of the few cities in which/where walls remain as good as before.
10. Shanxi Province is a place with many cultural relics. Its cultural relics are well looked after.
Shanxi Province is a place where cultural relics are well looked after.
1. I’ll never forget the days _____________ we worked together.
2. I’ll never forget the days ______ ________we spent together.
3. I went to the place _______________ I worked ten years ago.
when / in which
which
where / in which
几种易混的情况
及物动词
4. I went to the place ______________ I visited ten years ago.
5. This is the reason _______________ he was late.
6. This is the reason ____________ ________ he gave.
which
why / for which
that / which
及物动词
及物动词
(1) What surprised me was not what he said but the way _______________ he said it.
(that / in which)
Practice
(2) ___ is often the case, we have worked out the production plan.
(3) This is the very house _____ he lived.
(4) Next winter, _____ you will spend in Harbin, I’m sure, will be another exciting holiday.
(5) That’s the reason ____ he was late.
As
where
which
why
(6) Robert and his songs ____ were famous in the U. S. are also popular in China.
(7) They are always smoking, _____ of course, will do harm to their health.
that
which
