新概念英语第一册语法总结及练习(无答案)
文档属性
| 名称 | 新概念英语第一册语法总结及练习(无答案) |
|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 100.7KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 新概念英语 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-11-12 10:09:13 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
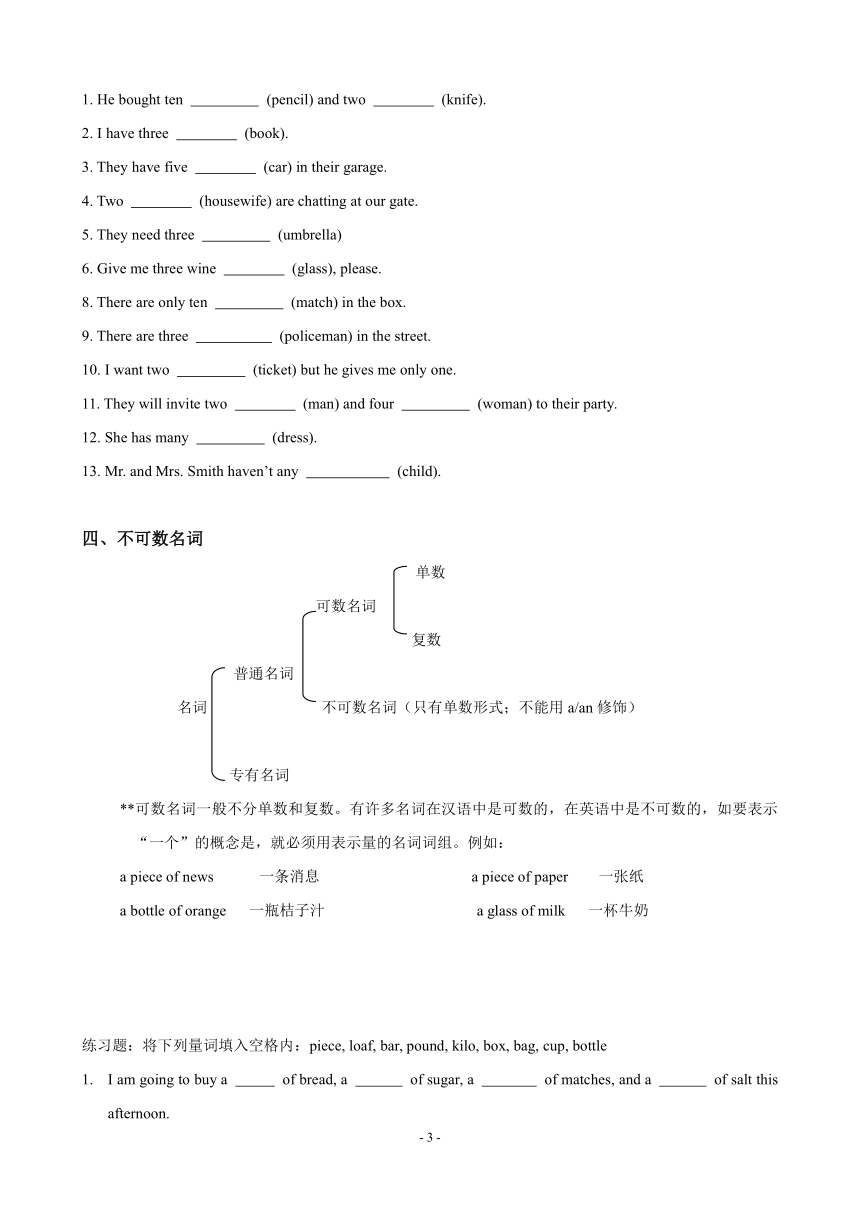
图说新概念英语第一册语法讲与练
物主代词、人称代词
人称数 单 数 复 数
第一人称 第二人称 第三人称 第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
形容词性物主代词 my your his, her, its our your their
名词性物主代词 mine yours his, hers, its ours yours theirs
主格 I you he, she, it we you they
宾格 me you him, her, it us you them
反身代词 myself yourself himself, herself, itself ourselves yourselves themselves
练习题:
( ) 1. Help to the cakes, boys and girls.
A. yourself B. your C. myself D. yourselves
( ) 2. All of come from France.
A. we B. our C. us D. ours
( ) 3. My brother will take to the park this Sunday.
A. I and my brother B. my brother and me C. me and my brother D. my brother and I
( ) 4.Whose pen is this It’s .
A. he B. his C. him D. he’s
( ) 5. It’s not classroom. It’s .
A. their; our B. theirs; our C. them; us D. their; ours
( ) 6. is a good teacher. We all like .
A. He; him B. They; them C. You; yours D. She; hers
( ) 7. Lucy wants some bananas. Give to .
A. they; she B. them; her C. them; he D. they; her
( ) 8. Let have a look. I think can.
A. me; I B. her; me C. I; I D. us; me
祈使句
表示请求、要求、命令、建议等方面意义的句子称为祈使句。祈使句以动词原形开头,省略主语you。祈使句的否定形式是在动词原形前加don’t.
Come in!Don’t come in! Stop talking!Don’t stop talking.
Let her in!Don’t let her in! Open the door, please!Don’t open the door!
练习题:用括号内所给动词的正确形式填空。
1. It’s an important meeting. (not, be) late.
2. (not, make) any noise! Your mother is sleeping.
3. (not, speak) with your mouth full of food and (be) polite.
4. (not, leave) your homework for tomorrow, Mary.
5. (not, talk) and (read) aloud.
复数名词
表示一个以上概念时,要用名词的复数。
名词复数形式构成的规则变化
在名词后直接加s
清辅音后读[s]。例如:book-books map-maps lake-lakes desk-desks
浊辅音后读[z]。例如:pen-pens lesson-lessons table-tables bag-bags
元 音后读[z]。例如:boy-boys ruler-rulers banana-bananas
2、以s, x, ch, sh, o结尾的名词加es,读[iz]。
bus-buses box-boxes watch-watches dish-dishes tomato-tomatoes
以f或fe结尾的名词, 把f, fe变成v加es。
knife-knives life-lives thief-thieves wife-wives leaf-leaves
以辅音加y结尾的名词,把y变成i ,再加es。
country-countries family-families factory-factories city-cities story-stories
5、特殊形式:woman-women man-men child-children tooth-teeth
练习题:
( ) 1. There are forty in our school
A. women teachers B. teacher women C. woman teachers D. women teacher
( ) 2. John is very happy to have a training(培训).
A. two week B. two-month C. two-weeks D. two-months
以正确的形式将括号内的名词填入空内
1. He bought ten (pencil) and two (knife).
2. I have three (book).
3. They have five (car) in their garage.
4. Two (housewife) are chatting at our gate.
5. They need three (umbrella)
6. Give me three wine (glass), please.
8. There are only ten (match) in the box.
9. There are three (policeman) in the street.
10. I want two (ticket) but he gives me only one.
11. They will invite two (man) and four (woman) to their party.
12. She has many (dress).
13. Mr. and Mrs. Smith haven’t any (child).
四、不可数名词
单数
可数名词
复数
普通名词
名词 不可数名词(只有单数形式;不能用a/an修饰)
专有名词
**可数名词一般不分单数和复数。有许多名词在汉语中是可数的,在英语中是不可数的,如要表示“一个”的概念是,就必须用表示量的名词词组。例如:
a piece of news 一条消息 a piece of paper 一张纸
a bottle of orange 一瓶桔子汁 a glass of milk 一杯牛奶
练习题:将下列量词填入空格内:piece, loaf, bar, pound, kilo, box, bag, cup, bottle
I am going to buy a of bread, a of sugar, a of matches, and a of salt this afternoon.
Give me a of paper and a of chalk, please.
He always has a of milk, a of chocolate.
She asks for a of wine and a of rice.
五、There be 句型:
概念:某地有某人或某物。
构成<一>:
肯定句:There is +可数名词单数/不可数名词+地点
There is a book on the desk. /There is some milk in the bottle.
可数名词 不可数名词
否定句:There is +not +可数名词单数/不可数名词+地点
There is not (isn’t) a book on the desk. /There is not (isn’t) any milk in the bottle.
疑问句:Is there +可数名词单数/不可数名词+地点
Is there a book on the desk /Is there any milk in the desk?
Yes, there is. No, there isn’t.
3. 构成<二 >:
1) 肯定句:There are +可数名词复数+地点
There are some books on the desk.
2) 否定句:There are +not+可数名词复数+地点
There are not (aren’t) any books on the desk.
3) 疑问句:Are there +可数名词复数+地点
Are there any books on the desk
Yes, there are. No, there aren’t.
**some用于肯定句,any用于否定和疑问句。
练习题:翻译下列句子。
在这个宾馆里有许多房间。
.
在那个盒子里有一些糖。
.
在那个房间里有几个(several)人吗?
.
是的,有几个人。 不,没有人。
. .
我一点钱都没有。
.
**there be与have的区别:
there be与have汉语意思都是表示“有”。Have前必须有主语,而“there be”则是一种特殊结构;have表示所有关系,意为“所有”,一般指某人“有”,there be则表示“存在”。例如:
Today we have two new students. 今天我们有两名新同学。
There are some apples over there. 在那边有一些苹果。
六、年、月、日和时刻的表达法
表示“在某年某月”:用介词in.
例如:在1999年9月:in September 1999
表示“在某日”:用介词on
例如:在1999年5月1日:on May 1st, 1999 在星期六:on Sunday
表示“在几点”:用介词at
例如:在6点钟:at six o’clock
练习题:用in,on, at填空
1、Tom arrived the office ten o’clock.
2、He is going to New York January 1st.
3、He often comes to visit us Saturday.
4、She was born(出生) 1990.
5、Tom was at school five o’clock.
七、too和enough
too的用法:
表示“太……”,修饰形容词
She can’t move the case. It’s too heavy. 她移不动那只箱子,它太沉了。
The water is too hot and we can’t bath. 水太热了,我们没有办法洗澡。
sth+be+too+形容词+for sb to do sth 对于某人太……,以至于不能做……
The house is too expensive for me to buy. 那房子太贵了,我买不起。
sb+be+too+形容词+to do sth 某人太……,以至于不能做……
She was too busy to have a talk with me. 他太忙了,以至于不能和我说话。
They are too young to elect. 他们太小,不能参选。
enough的用法:
enough+名词
There is enough room. 有足够的空间。
There are enough books for the children to read. 有足够的书供孩子们阅读。
形容词+enough
It’s warm enough, we can wear sweaters. 天气足够暖和的, 我们可以穿毛衣了。
(3) sth+be+形容词+enough+for sb+to do sth. 某物对于(某人)足够…; 可以做…
The exam is easy enough for her to pass. 这个考试对于她来说足够简单,可以通过。
sb+be+形容词+enough to do sth。 某人很……,可以做……
He is old enough to make his own decision. 他已经长大了,可以自己做决定了。
练习题:用enough, too填空
1、The question is easy for me.
2、These exercises are difficult for him to finish in half an hour.
3、That box is heavy for him to move alone.
4、He’s rich to buy that house.
5、She’s clever to solve the difficult problem.
6、Tom is stupid to be able to do it.
7、The distance is short for us to walk.
8、The car was expensive for us to buy.
9、He’s tall to reach that top shelf.
10、It’s hot to sleep well at night.
八、形容词的比较级和最高级
形容词比较级、最高级的形式变化规则
构成法 原级 比较级 最高级
单音节词末尾加er和est cheap, tall cheaper, taller cheapest, tallest
重读闭音节,双写最后一个辅音字母,然后加er和est big, hot, thin bigger, hotter, thinner biggest, hottest, thinnest
以辅音字母+y结尾的形容词把y变i加er和est angry, happy, heavy angrier, happier, heavier angriest, happiest, heaviest
以e结尾的形容词加r和st nice nicer nicest
其他双音节词和多音节词 useful, interesting more useful, more interesting most useful, most interesting
不规则形容词比较级及最高级
原级 比较级 最高级
good better best
well better best
bad worse worst
many more most
much more most
little less least
形容词比较级的用法:比较级用于两者的比较。
其结构是:A+be+形容词的比较级+than+B.
例 如:Sam is younger than Mike. 萨姆比迈克年轻。
形容词最高级的用法:最高级用于二者以上的比较。
其结构是:主语+be+the+形容词的最高级+(n.)表示范围的短语或从句
例 如:Sam is the youngest student in my class.
练习题:用比较级和最高级填空。
1、Jane is (tall) than Tom and she is (tall) girl in the class
2、English is (important) than French and it is (useful) of all the languages(语言) in the world.
3、Betty is (pretty) girl in this town.
4、Their house is (beautiful) in the country and the garden is (large), too.
5、Mr. Smith is (busy) man in our company.
6、They have bought (expensive) car in the shop.
7、We’ll move to a house much (big) than this one.
8、Every foreigner says that Chinese is (difficult) language to learn.
9、Her husband is eleven years (old) than she is.
10、Mrs. Brown is (fat) woman I’ve ever seen.
11、He always wins a prize for the (good) garden in the town.
12、I’ll buy the one that costs (little) in the shop
九、同级比较:as…as
形容词原级用法:
1) 肯定句:A+be+as+形容词原级+as B
例 如:My cat is as old as that one. 我的猫和那只一样大。
2) 否定句:A+be+not+as(so)+形容词原级+as B
例 如:He is not as (so) tall as I. 他不如我高。
3) 疑问句:Be+A+as+形容词原级+as B?
例 如:Is she as busy as before 她还象以前那么忙吗?
十、so和neither引导的简短回答
当有人说了一句肯定意义的话,其肯定内容也适于你或另外的人或事物时,可以采用这种简略的句式。
构成:肯定句. So +be/情/助+主语
例如:Lucy is a student. So am I. / So are they. / So is her brother.
I like music. So does my brother. / So do they.
They went to the party. So did I.
当有人说了一句否定意义的话,其否定内容也适于你或另外的人或事物时,可以采用这种简略的句式。
构成:否定句. Neither+ be/情/助+主语
例如:I don’t like music. Neither does my brother.
They didn’t go to the party. Neither did I.
练习题:
1、I have read it. (John) .
2、I haven’t seen it. (Tom) .
3、You don’t know the way. (your aunt) .
4、He is a writer. (she) .
5、Tom can speak French. (his wife) .
6、He wants to help us. (she) .
7、He can’t come. (his sister) .
8、Alice couldn’t understand. (Andrew) .
9、I don’t believe him. (Ann) .
10、The pork was bad. (the beef) .
十一、反意疑问句
这种疑问句分为两部分:前一部分为陈述句,后一部分为简短问句。
前肯定后否定; 前否定后肯定
**反意疑问句的否定部分必须用缩略形式,同时它的主语必须用人称代词。
例如:You have been learned English for years, haven’t you -----前肯定后否定
He is unhappy, is he ------前否定后肯定
练习题:
1、He didn’t see it. .
2、The meeting won’t be long. .
3、She didn’t find it. .
4、They needn’t pay the money. .
5、She doesn’t know you. .
6、It isn’t expensive. .
7、The food wasn’t bad. .
8、You aren’t angry. .
9、You don’t like him. .
10、We shan’t go there. .
十二、no和none的用法
no:是个限定词,可以用在单数(可数及不可数)名词和复数名词前,他的意思和not a或not any几乎一样,可以代替这些词语。
**not a=no not any=no
例如:There isn’t any water left. =There is no water left.
I haven’t got any time to read the newspaper. =I have got no time to read the newspaper.
none: 在the, my, your等词和this, that等词前面要表达no的含义,应该用none of来表示no的意思。None of既可用于句子的开头也可用在句子的其他地方。
例如:None of the trains go to the small city. 没有一辆货车通过那座小城。
You’ve got many gifts, but I’ve got none. 你有许多礼物,而我一个也没有。
练习题:用not, no, none填空。
1、They had warm clothing and food.
2、 of the drivers have come.
3、I can’t get there. There’s bus.
4、I have any time to spare.
5、There are stupid students in this class.
6、 of the telephones are working.
7、Sorry I can’t stop. I’ve got time.
8、There is any food in the house.
9、I asked for two tickets but there was left.
10、There were letters for you this morning. I’m afraid.
十三、定语从句
定于从句在句子中作定语,修饰句子中的某一名词或代词。被定语从句修饰的词称为先行词。
例如:I have a sister who lives in Paris
先行词 关系代词
先行词是人,用关系代词who,在定于从句中做主语和宾语。
例如:The woman who is talking with a boy is my teacher Miss. Gao.
做主语
那位和一个男孩谈话的妇女是我的老师高小姐
The man who we met is my uncle. 我们遇见的那个男人是我的叔叔。
做宾语
先行词是人,用关系代词whom,在定于从句中只能作宾语。
例如:The little girl whom she is playing with is her daughter.
做宾语
先行词是物,用关系代词which,在定于从句中做主语和宾语。
例如:The factory which we’ll visit next week isn’t far from here.
做宾语
The car which is repairing is Tom’s.
做主语
先行词是人或物,用关系代词that,在定语从句中做主语和宾语。
例如:The policeman that is helping the old man is my brother.
先行词是人 做主语
The pen that he gave me was made in the USA.
先行词是物 做定语
**关系代词在宾语从句中做主语不可以省略,做宾语可以省略。
练习题:用who, whom, that和which将下列各组句子改写成含有一个定语从句的句子。
This is the dog. It is bit a policeman.
.
2、I spoke to the man. He couldn’t understand me.
.
We bought a loaf of bread. It had just come out of the oven.
.
4、A waitress served me with beer. It was too cold.
.
5、I didn’t recognize the tall young man. He was standing at the door.
.
十四、表示推测的情态动词
表示“一定”/不可能(must be的否定形式):
对现在的推测:must be can’t be
对过去的推测:must have done can’t have done
表示“可能”
对现在的推测:may/might be
对过去的推测:may/might have done
练习题:用must be, must have done, can’t be, can’t have done
1、Look at his face! He be very angry.
2、It be John you see. He’s in Caracas(加拉斯).
3、I saw Ann in the library yesterday. You (see) her; she is still abroad.
4、I’m feeling cold. The windows be open.
5、The carpet was made by hand. It (take) a long time.
6、The door was open when I arrived. It (be) open. I had locked it myself and the key was in my pocket.
7、There’s the milkman at the door. No, it be the milkman. It be the postman.
8、Jane be over thirty-five. Her son is only three years old now.
9、Per haps he swam across the river. No, he (do) that, he can’t swim.
10、Who’s at the door It be Susan.
十五、直接引语变间接引语
如果主句是一般现在时,则直接引语是什么时态间接引语就是什么时态。
例如:He says, “I like the film of Titanic.” 他说:“我喜欢泰坦尼克这部电影。”
He says (that) he likes the film of Titanic. 他说他喜欢泰坦尼克这部电影。
如果主句是一般过去时,则间接引语的时态要向后退一个时态
时态的变化 直接引语 间接引语
一般现在时一般过去时 She said, “I am a teacher.” She said that she was a teacher.
现在进行时过去进行时 He said, “We are having dinner.” He said they were having dinner.
现在完成时过去完成时 She said, “I have finished my homework. She said that she had finished her homework.
一般过去时过去完成时 She said, “I saw you last week.” She said she had seen me the week before.
一般将来时过去将来时 She said, “I’ll go there.” She said she would go there.
cancould; maymight She said, “I may get married next year.”They said, “We can’t afford a new house.” She said she might get married the next year.They said they couldn’t afford a new house.
客观真理的事态不发生改变 She said, “The moon travels around the earth.” She said the moon travels around the earth.
十六、if引导的条件状语从句
由if引导的条件状语从句:主将从现
构成:If+一般现在时,主语+will/shall+动词原形
If+一般现在时,主语+情态动词+动词原形
例如:If it doesn’t rain tomorrow, we shall go and pick apples. 如果明天不下雨,我们就去摘苹果。
一般现在时 一般将来时
If my father comes home early this evening, we can go out for dinner. 如果爸爸晚上回来早,我们可以出去吃饭
一般现在时 情态动词
根据上面的两个例句我们可以看出,虽然条件状语从句的时间是表示将来的tomorrow, this evening, 但是从句还是要用一般现在时。
十七、宾语从句
我们在前面介绍了that引导的宾语从句,这里将要介绍其他类型。
由连词whether或if引导的宾语从句。例如:
I want to know whether (if) you are a teacher. 我想知道你时候是一位老师。
2、由疑问代词和疑问副词引导的宾语从句
疑问代词和疑问副词主要有what(什么), when(什么时候), how(怎么), where(在哪里), how long(多长时间)。例如:
Do you know when the film will be on
I want to know what you are doing.
She wants to know how you are.
He tells us where he is.
I want to know how long you have been in Beijing.
**特殊疑问词+陈述句语序
十八、被动语态
英语语态是动词的一种形式,用以表示主语和谓语之间的关系。语态分为主动语态和被动语态。主动语态是表示主语是动作的执行者,被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者或动作的目标。
一般现在时:主语+am/is/are+过去分词
The window is cleaned regularly. 定期擦窗户。
They are loved by people. 他们被人民所爱戴。
一般过去时:主语+was/were+过去分词
The meeting was held last week. 会议上周举行。
These bottles were made in China. 这些瓶子在中国制造。
现在完成时:主语+has/have+been+过去分词
The window has been cleaned. 窗户已被擦干净了。
They have been sent to hospital. 他们已经被派到医院去了。
一般将来时:主语+will/shall+be+过去分词
The work will be finished tomorrow.
PAGE
- 13 -
物主代词、人称代词
人称数 单 数 复 数
第一人称 第二人称 第三人称 第一人称 第二人称 第三人称
形容词性物主代词 my your his, her, its our your their
名词性物主代词 mine yours his, hers, its ours yours theirs
主格 I you he, she, it we you they
宾格 me you him, her, it us you them
反身代词 myself yourself himself, herself, itself ourselves yourselves themselves
练习题:
( ) 1. Help to the cakes, boys and girls.
A. yourself B. your C. myself D. yourselves
( ) 2. All of come from France.
A. we B. our C. us D. ours
( ) 3. My brother will take to the park this Sunday.
A. I and my brother B. my brother and me C. me and my brother D. my brother and I
( ) 4.Whose pen is this It’s .
A. he B. his C. him D. he’s
( ) 5. It’s not classroom. It’s .
A. their; our B. theirs; our C. them; us D. their; ours
( ) 6. is a good teacher. We all like .
A. He; him B. They; them C. You; yours D. She; hers
( ) 7. Lucy wants some bananas. Give to .
A. they; she B. them; her C. them; he D. they; her
( ) 8. Let have a look. I think can.
A. me; I B. her; me C. I; I D. us; me
祈使句
表示请求、要求、命令、建议等方面意义的句子称为祈使句。祈使句以动词原形开头,省略主语you。祈使句的否定形式是在动词原形前加don’t.
Come in!Don’t come in! Stop talking!Don’t stop talking.
Let her in!Don’t let her in! Open the door, please!Don’t open the door!
练习题:用括号内所给动词的正确形式填空。
1. It’s an important meeting. (not, be) late.
2. (not, make) any noise! Your mother is sleeping.
3. (not, speak) with your mouth full of food and (be) polite.
4. (not, leave) your homework for tomorrow, Mary.
5. (not, talk) and (read) aloud.
复数名词
表示一个以上概念时,要用名词的复数。
名词复数形式构成的规则变化
在名词后直接加s
清辅音后读[s]。例如:book-books map-maps lake-lakes desk-desks
浊辅音后读[z]。例如:pen-pens lesson-lessons table-tables bag-bags
元 音后读[z]。例如:boy-boys ruler-rulers banana-bananas
2、以s, x, ch, sh, o结尾的名词加es,读[iz]。
bus-buses box-boxes watch-watches dish-dishes tomato-tomatoes
以f或fe结尾的名词, 把f, fe变成v加es。
knife-knives life-lives thief-thieves wife-wives leaf-leaves
以辅音加y结尾的名词,把y变成i ,再加es。
country-countries family-families factory-factories city-cities story-stories
5、特殊形式:woman-women man-men child-children tooth-teeth
练习题:
( ) 1. There are forty in our school
A. women teachers B. teacher women C. woman teachers D. women teacher
( ) 2. John is very happy to have a training(培训).
A. two week B. two-month C. two-weeks D. two-months
以正确的形式将括号内的名词填入空内
1. He bought ten (pencil) and two (knife).
2. I have three (book).
3. They have five (car) in their garage.
4. Two (housewife) are chatting at our gate.
5. They need three (umbrella)
6. Give me three wine (glass), please.
8. There are only ten (match) in the box.
9. There are three (policeman) in the street.
10. I want two (ticket) but he gives me only one.
11. They will invite two (man) and four (woman) to their party.
12. She has many (dress).
13. Mr. and Mrs. Smith haven’t any (child).
四、不可数名词
单数
可数名词
复数
普通名词
名词 不可数名词(只有单数形式;不能用a/an修饰)
专有名词
**可数名词一般不分单数和复数。有许多名词在汉语中是可数的,在英语中是不可数的,如要表示“一个”的概念是,就必须用表示量的名词词组。例如:
a piece of news 一条消息 a piece of paper 一张纸
a bottle of orange 一瓶桔子汁 a glass of milk 一杯牛奶
练习题:将下列量词填入空格内:piece, loaf, bar, pound, kilo, box, bag, cup, bottle
I am going to buy a of bread, a of sugar, a of matches, and a of salt this afternoon.
Give me a of paper and a of chalk, please.
He always has a of milk, a of chocolate.
She asks for a of wine and a of rice.
五、There be 句型:
概念:某地有某人或某物。
构成<一>:
肯定句:There is +可数名词单数/不可数名词+地点
There is a book on the desk. /There is some milk in the bottle.
可数名词 不可数名词
否定句:There is +not +可数名词单数/不可数名词+地点
There is not (isn’t) a book on the desk. /There is not (isn’t) any milk in the bottle.
疑问句:Is there +可数名词单数/不可数名词+地点
Is there a book on the desk /Is there any milk in the desk?
Yes, there is. No, there isn’t.
3. 构成<二 >:
1) 肯定句:There are +可数名词复数+地点
There are some books on the desk.
2) 否定句:There are +not+可数名词复数+地点
There are not (aren’t) any books on the desk.
3) 疑问句:Are there +可数名词复数+地点
Are there any books on the desk
Yes, there are. No, there aren’t.
**some用于肯定句,any用于否定和疑问句。
练习题:翻译下列句子。
在这个宾馆里有许多房间。
.
在那个盒子里有一些糖。
.
在那个房间里有几个(several)人吗?
.
是的,有几个人。 不,没有人。
. .
我一点钱都没有。
.
**there be与have的区别:
there be与have汉语意思都是表示“有”。Have前必须有主语,而“there be”则是一种特殊结构;have表示所有关系,意为“所有”,一般指某人“有”,there be则表示“存在”。例如:
Today we have two new students. 今天我们有两名新同学。
There are some apples over there. 在那边有一些苹果。
六、年、月、日和时刻的表达法
表示“在某年某月”:用介词in.
例如:在1999年9月:in September 1999
表示“在某日”:用介词on
例如:在1999年5月1日:on May 1st, 1999 在星期六:on Sunday
表示“在几点”:用介词at
例如:在6点钟:at six o’clock
练习题:用in,on, at填空
1、Tom arrived the office ten o’clock.
2、He is going to New York January 1st.
3、He often comes to visit us Saturday.
4、She was born(出生) 1990.
5、Tom was at school five o’clock.
七、too和enough
too的用法:
表示“太……”,修饰形容词
She can’t move the case. It’s too heavy. 她移不动那只箱子,它太沉了。
The water is too hot and we can’t bath. 水太热了,我们没有办法洗澡。
sth+be+too+形容词+for sb to do sth 对于某人太……,以至于不能做……
The house is too expensive for me to buy. 那房子太贵了,我买不起。
sb+be+too+形容词+to do sth 某人太……,以至于不能做……
She was too busy to have a talk with me. 他太忙了,以至于不能和我说话。
They are too young to elect. 他们太小,不能参选。
enough的用法:
enough+名词
There is enough room. 有足够的空间。
There are enough books for the children to read. 有足够的书供孩子们阅读。
形容词+enough
It’s warm enough, we can wear sweaters. 天气足够暖和的, 我们可以穿毛衣了。
(3) sth+be+形容词+enough+for sb+to do sth. 某物对于(某人)足够…; 可以做…
The exam is easy enough for her to pass. 这个考试对于她来说足够简单,可以通过。
sb+be+形容词+enough to do sth。 某人很……,可以做……
He is old enough to make his own decision. 他已经长大了,可以自己做决定了。
练习题:用enough, too填空
1、The question is easy for me.
2、These exercises are difficult for him to finish in half an hour.
3、That box is heavy for him to move alone.
4、He’s rich to buy that house.
5、She’s clever to solve the difficult problem.
6、Tom is stupid to be able to do it.
7、The distance is short for us to walk.
8、The car was expensive for us to buy.
9、He’s tall to reach that top shelf.
10、It’s hot to sleep well at night.
八、形容词的比较级和最高级
形容词比较级、最高级的形式变化规则
构成法 原级 比较级 最高级
单音节词末尾加er和est cheap, tall cheaper, taller cheapest, tallest
重读闭音节,双写最后一个辅音字母,然后加er和est big, hot, thin bigger, hotter, thinner biggest, hottest, thinnest
以辅音字母+y结尾的形容词把y变i加er和est angry, happy, heavy angrier, happier, heavier angriest, happiest, heaviest
以e结尾的形容词加r和st nice nicer nicest
其他双音节词和多音节词 useful, interesting more useful, more interesting most useful, most interesting
不规则形容词比较级及最高级
原级 比较级 最高级
good better best
well better best
bad worse worst
many more most
much more most
little less least
形容词比较级的用法:比较级用于两者的比较。
其结构是:A+be+形容词的比较级+than+B.
例 如:Sam is younger than Mike. 萨姆比迈克年轻。
形容词最高级的用法:最高级用于二者以上的比较。
其结构是:主语+be+the+形容词的最高级+(n.)表示范围的短语或从句
例 如:Sam is the youngest student in my class.
练习题:用比较级和最高级填空。
1、Jane is (tall) than Tom and she is (tall) girl in the class
2、English is (important) than French and it is (useful) of all the languages(语言) in the world.
3、Betty is (pretty) girl in this town.
4、Their house is (beautiful) in the country and the garden is (large), too.
5、Mr. Smith is (busy) man in our company.
6、They have bought (expensive) car in the shop.
7、We’ll move to a house much (big) than this one.
8、Every foreigner says that Chinese is (difficult) language to learn.
9、Her husband is eleven years (old) than she is.
10、Mrs. Brown is (fat) woman I’ve ever seen.
11、He always wins a prize for the (good) garden in the town.
12、I’ll buy the one that costs (little) in the shop
九、同级比较:as…as
形容词原级用法:
1) 肯定句:A+be+as+形容词原级+as B
例 如:My cat is as old as that one. 我的猫和那只一样大。
2) 否定句:A+be+not+as(so)+形容词原级+as B
例 如:He is not as (so) tall as I. 他不如我高。
3) 疑问句:Be+A+as+形容词原级+as B?
例 如:Is she as busy as before 她还象以前那么忙吗?
十、so和neither引导的简短回答
当有人说了一句肯定意义的话,其肯定内容也适于你或另外的人或事物时,可以采用这种简略的句式。
构成:肯定句. So +be/情/助+主语
例如:Lucy is a student. So am I. / So are they. / So is her brother.
I like music. So does my brother. / So do they.
They went to the party. So did I.
当有人说了一句否定意义的话,其否定内容也适于你或另外的人或事物时,可以采用这种简略的句式。
构成:否定句. Neither+ be/情/助+主语
例如:I don’t like music. Neither does my brother.
They didn’t go to the party. Neither did I.
练习题:
1、I have read it. (John) .
2、I haven’t seen it. (Tom) .
3、You don’t know the way. (your aunt) .
4、He is a writer. (she) .
5、Tom can speak French. (his wife) .
6、He wants to help us. (she) .
7、He can’t come. (his sister) .
8、Alice couldn’t understand. (Andrew) .
9、I don’t believe him. (Ann) .
10、The pork was bad. (the beef) .
十一、反意疑问句
这种疑问句分为两部分:前一部分为陈述句,后一部分为简短问句。
前肯定后否定; 前否定后肯定
**反意疑问句的否定部分必须用缩略形式,同时它的主语必须用人称代词。
例如:You have been learned English for years, haven’t you -----前肯定后否定
He is unhappy, is he ------前否定后肯定
练习题:
1、He didn’t see it. .
2、The meeting won’t be long. .
3、She didn’t find it. .
4、They needn’t pay the money. .
5、She doesn’t know you. .
6、It isn’t expensive. .
7、The food wasn’t bad. .
8、You aren’t angry. .
9、You don’t like him. .
10、We shan’t go there. .
十二、no和none的用法
no:是个限定词,可以用在单数(可数及不可数)名词和复数名词前,他的意思和not a或not any几乎一样,可以代替这些词语。
**not a=no not any=no
例如:There isn’t any water left. =There is no water left.
I haven’t got any time to read the newspaper. =I have got no time to read the newspaper.
none: 在the, my, your等词和this, that等词前面要表达no的含义,应该用none of来表示no的意思。None of既可用于句子的开头也可用在句子的其他地方。
例如:None of the trains go to the small city. 没有一辆货车通过那座小城。
You’ve got many gifts, but I’ve got none. 你有许多礼物,而我一个也没有。
练习题:用not, no, none填空。
1、They had warm clothing and food.
2、 of the drivers have come.
3、I can’t get there. There’s bus.
4、I have any time to spare.
5、There are stupid students in this class.
6、 of the telephones are working.
7、Sorry I can’t stop. I’ve got time.
8、There is any food in the house.
9、I asked for two tickets but there was left.
10、There were letters for you this morning. I’m afraid.
十三、定语从句
定于从句在句子中作定语,修饰句子中的某一名词或代词。被定语从句修饰的词称为先行词。
例如:I have a sister who lives in Paris
先行词 关系代词
先行词是人,用关系代词who,在定于从句中做主语和宾语。
例如:The woman who is talking with a boy is my teacher Miss. Gao.
做主语
那位和一个男孩谈话的妇女是我的老师高小姐
The man who we met is my uncle. 我们遇见的那个男人是我的叔叔。
做宾语
先行词是人,用关系代词whom,在定于从句中只能作宾语。
例如:The little girl whom she is playing with is her daughter.
做宾语
先行词是物,用关系代词which,在定于从句中做主语和宾语。
例如:The factory which we’ll visit next week isn’t far from here.
做宾语
The car which is repairing is Tom’s.
做主语
先行词是人或物,用关系代词that,在定语从句中做主语和宾语。
例如:The policeman that is helping the old man is my brother.
先行词是人 做主语
The pen that he gave me was made in the USA.
先行词是物 做定语
**关系代词在宾语从句中做主语不可以省略,做宾语可以省略。
练习题:用who, whom, that和which将下列各组句子改写成含有一个定语从句的句子。
This is the dog. It is bit a policeman.
.
2、I spoke to the man. He couldn’t understand me.
.
We bought a loaf of bread. It had just come out of the oven.
.
4、A waitress served me with beer. It was too cold.
.
5、I didn’t recognize the tall young man. He was standing at the door.
.
十四、表示推测的情态动词
表示“一定”/不可能(must be的否定形式):
对现在的推测:must be can’t be
对过去的推测:must have done can’t have done
表示“可能”
对现在的推测:may/might be
对过去的推测:may/might have done
练习题:用must be, must have done, can’t be, can’t have done
1、Look at his face! He be very angry.
2、It be John you see. He’s in Caracas(加拉斯).
3、I saw Ann in the library yesterday. You (see) her; she is still abroad.
4、I’m feeling cold. The windows be open.
5、The carpet was made by hand. It (take) a long time.
6、The door was open when I arrived. It (be) open. I had locked it myself and the key was in my pocket.
7、There’s the milkman at the door. No, it be the milkman. It be the postman.
8、Jane be over thirty-five. Her son is only three years old now.
9、Per haps he swam across the river. No, he (do) that, he can’t swim.
10、Who’s at the door It be Susan.
十五、直接引语变间接引语
如果主句是一般现在时,则直接引语是什么时态间接引语就是什么时态。
例如:He says, “I like the film of Titanic.” 他说:“我喜欢泰坦尼克这部电影。”
He says (that) he likes the film of Titanic. 他说他喜欢泰坦尼克这部电影。
如果主句是一般过去时,则间接引语的时态要向后退一个时态
时态的变化 直接引语 间接引语
一般现在时一般过去时 She said, “I am a teacher.” She said that she was a teacher.
现在进行时过去进行时 He said, “We are having dinner.” He said they were having dinner.
现在完成时过去完成时 She said, “I have finished my homework. She said that she had finished her homework.
一般过去时过去完成时 She said, “I saw you last week.” She said she had seen me the week before.
一般将来时过去将来时 She said, “I’ll go there.” She said she would go there.
cancould; maymight She said, “I may get married next year.”They said, “We can’t afford a new house.” She said she might get married the next year.They said they couldn’t afford a new house.
客观真理的事态不发生改变 She said, “The moon travels around the earth.” She said the moon travels around the earth.
十六、if引导的条件状语从句
由if引导的条件状语从句:主将从现
构成:If+一般现在时,主语+will/shall+动词原形
If+一般现在时,主语+情态动词+动词原形
例如:If it doesn’t rain tomorrow, we shall go and pick apples. 如果明天不下雨,我们就去摘苹果。
一般现在时 一般将来时
If my father comes home early this evening, we can go out for dinner. 如果爸爸晚上回来早,我们可以出去吃饭
一般现在时 情态动词
根据上面的两个例句我们可以看出,虽然条件状语从句的时间是表示将来的tomorrow, this evening, 但是从句还是要用一般现在时。
十七、宾语从句
我们在前面介绍了that引导的宾语从句,这里将要介绍其他类型。
由连词whether或if引导的宾语从句。例如:
I want to know whether (if) you are a teacher. 我想知道你时候是一位老师。
2、由疑问代词和疑问副词引导的宾语从句
疑问代词和疑问副词主要有what(什么), when(什么时候), how(怎么), where(在哪里), how long(多长时间)。例如:
Do you know when the film will be on
I want to know what you are doing.
She wants to know how you are.
He tells us where he is.
I want to know how long you have been in Beijing.
**特殊疑问词+陈述句语序
十八、被动语态
英语语态是动词的一种形式,用以表示主语和谓语之间的关系。语态分为主动语态和被动语态。主动语态是表示主语是动作的执行者,被动语态表示主语是动作的承受者或动作的目标。
一般现在时:主语+am/is/are+过去分词
The window is cleaned regularly. 定期擦窗户。
They are loved by people. 他们被人民所爱戴。
一般过去时:主语+was/were+过去分词
The meeting was held last week. 会议上周举行。
These bottles were made in China. 这些瓶子在中国制造。
现在完成时:主语+has/have+been+过去分词
The window has been cleaned. 窗户已被擦干净了。
They have been sent to hospital. 他们已经被派到医院去了。
一般将来时:主语+will/shall+be+过去分词
The work will be finished tomorrow.
PAGE
- 13 -
同课章节目录
