外研版(2019)必修第一册Unit 4 Friends forever Using language -attributive clauses 课件-(29张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版(2019)必修第一册Unit 4 Friends forever Using language -attributive clauses 课件-(29张ppt) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-11-13 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共29张PPT)
Unit 4 Friends forever
Using language-
Atrributive clause(1)
To discover and summarize the function and effect of an attributive clause by discussing;
To summarize the usage of relative pronouns(that, which, who, whom, whose) in attributive clauses.
To apply attributive clauses correctly in real context.
to encourage Ss to make like-minded friends by taking part in collective activities.
Learning objectives
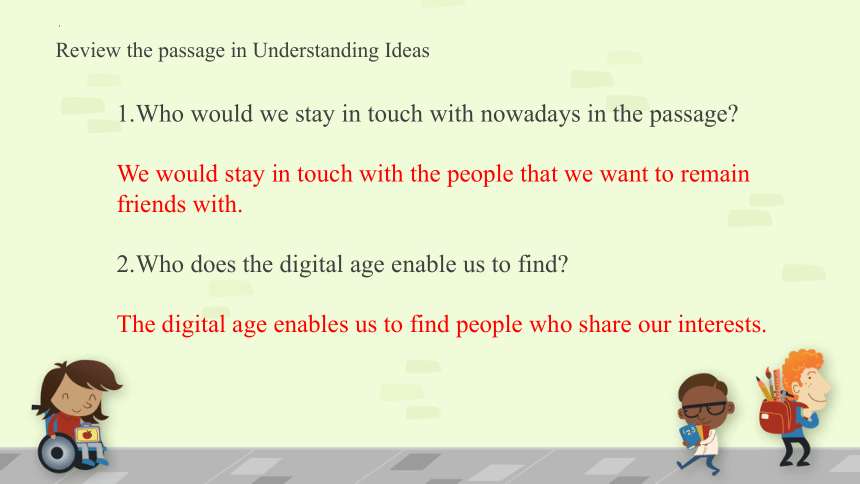
Review the passage in Understanding Ideas
1.Who would we stay in touch with nowadays in the passage
We would stay in touch with the people that we want to remain friends with.
2.Who does the digital age enable us to find
The digital age enables us to find people who share our interests.
a.We can stay in touch with the people that we want to remain friends with.
1.What does “that” refer to in sentence (a)
“That” refers to “the people”.
Analyze the sentences
b.The digital age also enables us to find people who share our
interests…
2.What does “who” refer to in sentence (b)
“Who” refers to “people”.
Analyze the sentences
Compare these following sentences.
a. We can stay in touch with the people that we want to remain friends with.
b. The digital age also enables us to find people who share our interests .
c. We can stay in touch with people. We want to remain friends with.
d. The digital age also enables us to find people. These people share our interests.
Compare sentences(a) and (b) with sentences(c) and (d),answer the questions.
3. What is the difference between the two groups of sentences
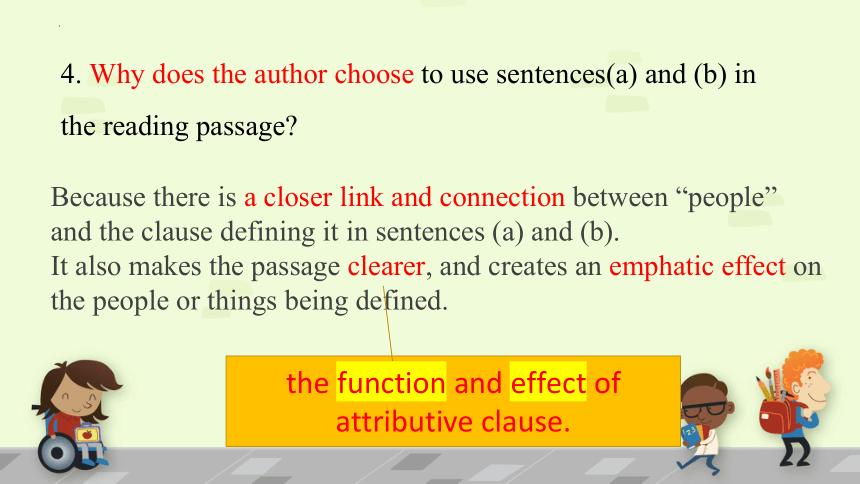
4. Why does the author choose to use sentences(a) and (b) in the
reading passage
5. What words can be used to introduce attributive clauses
Do you know other words
3. What is the difference between the two groups of sentences
Answer:
(a) and (b) both contain a clause defining a noun in each sentence.
(c) and (d) are each constructed with a pair of simple sentences, with one defining a noun that appears in the other sentence in each pair.
attributive clause
tips: pay attention to the words in bold in sentences(a) and (b)
4. Why does the author choose to use sentences(a) and (b) in the reading passage
Because there is a closer link and connection between “people” and the clause defining it in sentences (a) and (b).
It also makes the passage clearer, and creates an emphatic effect on the people or things being defined.
the function and effect of
attributive clause.
Words used to introduce attributive clauses include “that”, “which”, “whom” and “whose”.
5. What words can be used to introduce attributive clauses Do you know other words
What if the only way of getting news from faraway friends was writing letters that took ages to be delivered
如果从远方朋友那里得到消息的唯一途径是写那些需要很长时间才能送达的信,那该怎么办呢
Now look for more sentences with attributive clauses in the reading passage, underline and translate them into Chinese.
All you need is a wi-fi connection.
你所需要的只是wi-fi连接。
Whatever our hobbies, the Internet can connect us with others who also enjoy doing them, even if they live on the other side of the world.
无论我们的爱好是什么,互联网可以把我们和那些同样喜欢做这些事的人联系起来,即使他们住在世界的另一端。
On social media sites, people tend to post only positive updates that make them appear happy and friendly.
在社交媒体网站上,人们倾向于只发布积极的更新,让自己看起来快乐和友好。
定语从句
定语从句是由关系词(关系代词或关系副词)引导的从句,其作用是作定语修饰主句的某个名词或代词。其功能相当于形容词,被修饰的名词或代词被称作为先行词。
关系词三功能
1. The people who / that called yesterday want to buy the house.
本句中先行词是 the people;关系代词who指人,代替 the people,关系代词在定语从句中作主语。翻译时可把定语从句译为主句的定语。
翻译: 昨天来电的那些人想买这个房子。
2. The man (whom / who / that) I have to phone lives in Canada.
本句先行词是 the man,关系代词共有四种表达。whom,who,that均可指人,在定语从句中关系代词作宾语, 因此在口语和非正式文体中可省略,故而有四种答案。
翻译:我不得不致电的那个人住在加拿大。
3. She was not in the train which / that arrived just now.
本句中先行词是the train,关系代词which / that 均可用于指物,代替the train,关系代词在定语从句中作主语。
翻译:她不在刚刚到的那列火车上。
4. This is the book (which / that) you wanted.
本句中先行词为 the book,关系代词 that / which指物,代替 the book,关系代词在定语从句中作宾语,可省略,故而本题有三种答案。
翻译:这就是你想要的那本书。
请根据以上例句,完成下页的关系代词用法表。
关系 代词 指代的 先行词 在从句中 所做成分 是否可省略
that
which
who
whom
whose
人,物
物
人
人
(人/物)的
主语,宾语
主语,宾语
主语,宾语
宾语
定语
作宾语可省略
作宾语可省略
作宾语可省略
可省略
不可省略
Lucy is my friend. She has a hearing problem. When she first came to my school, she seemed lonely, but we soon became friends. At first it was difficult to communicate with her. So I learnt a new language. It allows me to “speak” with my hands.
Read the passage on your own, try to understand the context and get the main idea.
Lucy is a smart girl. Her ideas are always inspiring. I sometimes have problems. I can’t solve them. When this happens, I always ask Lucy for help. Lucy is a good listener. I enjoy sharing moments of my life with her.
Lucy is my friend. She has a hearing problem. When she first came to my school, she seemed lonely, but we soon became friends. At first it was difficult to communicate with her. So I learnt a new language. It allows me to “speak” with my hands.
So I learnt a new language which / that allows me to “speak” with my hands.
Lucy is my friend who / that has a hearing problem.
Rewrite the underlined sentences with that, which, who, whom or whose.
Lucy is a smart girl. Her ideas are always inspiring. I sometimes have problems. I can’t solve them. When this happens, I always ask Lucy for help. Lucy is a good listener. I enjoy sharing moments of my life with her.
Lucy is a smart girl whose ideas are always inspiring.
I sometimes have problems (that / which) I can’t solve.
Rewrite the underlined sentences with that, which, who, whom or whose.
Lucy is a smart girl. Her ideas are always inspiring. I sometimes have problems. I can’t solve them. When this happens, I always ask Lucy for help. Lucy is a good listener. I enjoy sharing moments of my life with her.
Lucy is a good listener (whom / who / that) I enjoy sharing moments of my life with.
Can you introduce Lucy briefly by using attributive clauses
Speaking activities
Read the passage on your own, try to understand the context and get the main idea.
online forum post
Complete the online forum post with that, which, who, whom or whose.
that / which
whose
who / that
which / that
whom / who
Though taking part in collective activities,
you can make like-minded friends(志同道合的朋友). (the friends who have similar ideas and interests. )
Write sentences about your friend(s), trying to use some attributive clauses in your passage.
Preview Vocabulary and Listening.
Unit 4 Friends forever
Using language-
Atrributive clause(1)
To discover and summarize the function and effect of an attributive clause by discussing;
To summarize the usage of relative pronouns(that, which, who, whom, whose) in attributive clauses.
To apply attributive clauses correctly in real context.
to encourage Ss to make like-minded friends by taking part in collective activities.
Learning objectives
Review the passage in Understanding Ideas
1.Who would we stay in touch with nowadays in the passage
We would stay in touch with the people that we want to remain friends with.
2.Who does the digital age enable us to find
The digital age enables us to find people who share our interests.
a.We can stay in touch with the people that we want to remain friends with.
1.What does “that” refer to in sentence (a)
“That” refers to “the people”.
Analyze the sentences
b.The digital age also enables us to find people who share our
interests…
2.What does “who” refer to in sentence (b)
“Who” refers to “people”.
Analyze the sentences
Compare these following sentences.
a. We can stay in touch with the people that we want to remain friends with.
b. The digital age also enables us to find people who share our interests .
c. We can stay in touch with people. We want to remain friends with.
d. The digital age also enables us to find people. These people share our interests.
Compare sentences(a) and (b) with sentences(c) and (d),answer the questions.
3. What is the difference between the two groups of sentences
4. Why does the author choose to use sentences(a) and (b) in the
reading passage
5. What words can be used to introduce attributive clauses
Do you know other words
3. What is the difference between the two groups of sentences
Answer:
(a) and (b) both contain a clause defining a noun in each sentence.
(c) and (d) are each constructed with a pair of simple sentences, with one defining a noun that appears in the other sentence in each pair.
attributive clause
tips: pay attention to the words in bold in sentences(a) and (b)
4. Why does the author choose to use sentences(a) and (b) in the reading passage
Because there is a closer link and connection between “people” and the clause defining it in sentences (a) and (b).
It also makes the passage clearer, and creates an emphatic effect on the people or things being defined.
the function and effect of
attributive clause.
Words used to introduce attributive clauses include “that”, “which”, “whom” and “whose”.
5. What words can be used to introduce attributive clauses Do you know other words
What if the only way of getting news from faraway friends was writing letters that took ages to be delivered
如果从远方朋友那里得到消息的唯一途径是写那些需要很长时间才能送达的信,那该怎么办呢
Now look for more sentences with attributive clauses in the reading passage, underline and translate them into Chinese.
All you need is a wi-fi connection.
你所需要的只是wi-fi连接。
Whatever our hobbies, the Internet can connect us with others who also enjoy doing them, even if they live on the other side of the world.
无论我们的爱好是什么,互联网可以把我们和那些同样喜欢做这些事的人联系起来,即使他们住在世界的另一端。
On social media sites, people tend to post only positive updates that make them appear happy and friendly.
在社交媒体网站上,人们倾向于只发布积极的更新,让自己看起来快乐和友好。
定语从句
定语从句是由关系词(关系代词或关系副词)引导的从句,其作用是作定语修饰主句的某个名词或代词。其功能相当于形容词,被修饰的名词或代词被称作为先行词。
关系词三功能
1. The people who / that called yesterday want to buy the house.
本句中先行词是 the people;关系代词who指人,代替 the people,关系代词在定语从句中作主语。翻译时可把定语从句译为主句的定语。
翻译: 昨天来电的那些人想买这个房子。
2. The man (whom / who / that) I have to phone lives in Canada.
本句先行词是 the man,关系代词共有四种表达。whom,who,that均可指人,在定语从句中关系代词作宾语, 因此在口语和非正式文体中可省略,故而有四种答案。
翻译:我不得不致电的那个人住在加拿大。
3. She was not in the train which / that arrived just now.
本句中先行词是the train,关系代词which / that 均可用于指物,代替the train,关系代词在定语从句中作主语。
翻译:她不在刚刚到的那列火车上。
4. This is the book (which / that) you wanted.
本句中先行词为 the book,关系代词 that / which指物,代替 the book,关系代词在定语从句中作宾语,可省略,故而本题有三种答案。
翻译:这就是你想要的那本书。
请根据以上例句,完成下页的关系代词用法表。
关系 代词 指代的 先行词 在从句中 所做成分 是否可省略
that
which
who
whom
whose
人,物
物
人
人
(人/物)的
主语,宾语
主语,宾语
主语,宾语
宾语
定语
作宾语可省略
作宾语可省略
作宾语可省略
可省略
不可省略
Lucy is my friend. She has a hearing problem. When she first came to my school, she seemed lonely, but we soon became friends. At first it was difficult to communicate with her. So I learnt a new language. It allows me to “speak” with my hands.
Read the passage on your own, try to understand the context and get the main idea.
Lucy is a smart girl. Her ideas are always inspiring. I sometimes have problems. I can’t solve them. When this happens, I always ask Lucy for help. Lucy is a good listener. I enjoy sharing moments of my life with her.
Lucy is my friend. She has a hearing problem. When she first came to my school, she seemed lonely, but we soon became friends. At first it was difficult to communicate with her. So I learnt a new language. It allows me to “speak” with my hands.
So I learnt a new language which / that allows me to “speak” with my hands.
Lucy is my friend who / that has a hearing problem.
Rewrite the underlined sentences with that, which, who, whom or whose.
Lucy is a smart girl. Her ideas are always inspiring. I sometimes have problems. I can’t solve them. When this happens, I always ask Lucy for help. Lucy is a good listener. I enjoy sharing moments of my life with her.
Lucy is a smart girl whose ideas are always inspiring.
I sometimes have problems (that / which) I can’t solve.
Rewrite the underlined sentences with that, which, who, whom or whose.
Lucy is a smart girl. Her ideas are always inspiring. I sometimes have problems. I can’t solve them. When this happens, I always ask Lucy for help. Lucy is a good listener. I enjoy sharing moments of my life with her.
Lucy is a good listener (whom / who / that) I enjoy sharing moments of my life with.
Can you introduce Lucy briefly by using attributive clauses
Speaking activities
Read the passage on your own, try to understand the context and get the main idea.
online forum post
Complete the online forum post with that, which, who, whom or whose.
that / which
whose
who / that
which / that
whom / who
Though taking part in collective activities,
you can make like-minded friends(志同道合的朋友). (the friends who have similar ideas and interests. )
Write sentences about your friend(s), trying to use some attributive clauses in your passage.
Preview Vocabulary and Listening.
