图说英语:新概念英语语法:三大从句结构图
文档属性
| 名称 | 图说英语:新概念英语语法:三大从句结构图 |  | |
| 格式 | doc | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 新概念英语 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-11-20 06:40:07 | ||
图片预览


文档简介
图说英语:图解名词性从句
定义:在句子中起名词作用的句子叫名词从句 (Noun Clauses). 名词性从句包括主语,宾语,表语,同位语从句.
★ 名词性从句中使用陈述句语序。
① 从属连词that; whether; if (只起引导从句的作用,在从句中不做句子成分)
② 连接代词 what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, whose, which,等.在从句
1.分类 中做主语,宾语,表语,定语等句子成分。
③ 连接副词when, where, how, why, whenever, however, wherever等在从句中做状语成分。
引导名词性 2. 名词性从句的连接词选用原则:“缺什么就补什么”
从句的连接词 I know what he is talking about. (从句中缺宾语,指物) Do you know who he is (从句中缺表语,指人)
Where he will go is unknown. (从句中缺地点状语)
I’m sure that they will come tomorrow. (从句中什么都不缺)
I don’t know which book I should choose. (从句中缺定语)
定义:充当主语功能的句子叫主语从句
That she was chosen made a great stir (轰动) in her school.
注意: ①it作形式主语的that-从句有以下四种不同的搭配关系:
It + be +形容词+ that-从句 It is necessary / important that…. …是有必要 / 重要的….
It + be + -ed 分词+ that-从句 It is universally acknowledged that../ It is known that…众所周知…
It + be +名词+ that-从句 It is common knowledge/ a fact that… ……是常识/事实
It +不及物动词+ that-分句 It happens that…碰巧.. / It occurs to sb.that… 突然想起……
名 主语从句 ②It 作形式主语和it引导强调句的比较
强调句: It is in the morning that the murder took place. (去掉该结构后,句子成分完整)
词 主语从句:It was a pity that you shouldn’t go to see the film. (在句子中作主语成分)
③whatever /whichever/ whoever引导主语从句的区别
Ⅰ Whatever 是what的强调形式表示“无论什么”相当于 anything that…
从 Whatever / Anything that she does is wrong.
Ⅱ whoever 是who的强调形式,表示‘无论谁’ 相当于anyone who….
句 ~ever Whoever / Anyone who walks around in such a heavy rain will catch a cold.
Ⅲ whichever ‘无论哪个;无论哪些’,既指人,又指物. 可修饰名词与of连用
Whichever book you borrow doesn’t matter to us.
Whichever of us fulfills his task will lend a hand to others.
定义:在复合句中充当宾语功能的句子叫宾语从句
We can learn what we didn’t know.
We find it necessary that we (should) practice English every day.
★某些作表语的形容词,如sure, happy, glad, certain等之后可带宾语从句
I am glad that you can come and help me.
注意:① wish/would rather后的宾语从句中要用虚拟语气。
I wish I had finished my homework yesterday. I’d rather you had been there yesterday
② 在表示建议,命令, 请求的词后面的宾语从句当中用should + V, should可以省略
宾语从句 His pale face suggested that he was ill so I suggested that he should go to see the doctor.
He insisted that he was innocent and insisted that he should be set free.
③ 注意it作形式宾语的结构
We all thought it a pity that we had missed the lesson. I took it for granted that they were not coming.
④ that一般不接介词宾语,偶尔可作except, in的宾语;其它介词后面需用it作形式宾语
He differs from his roommates in that he devoted his spare time to reading.
He knows nothing about Jim except that he is from London.
You can depend on it that he will help you in time of emergency.
⑤表示好恶的动词如like; hate; love;enjoy; dislike; appreciate等后面不能直接跟宾语;
I like it when the weather is sunny. I hate it when someone is later for my class.
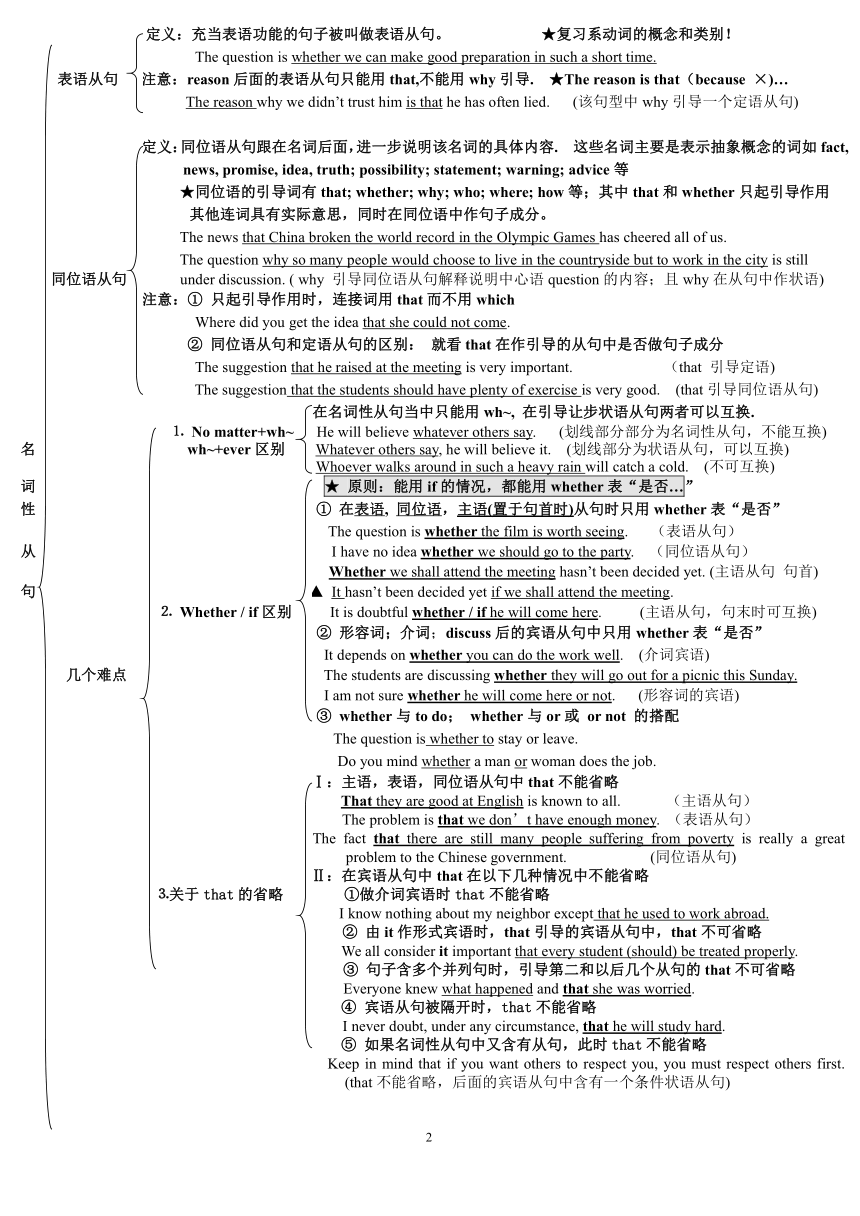
定义:充当表语功能的句子被叫做表语从句。 ★复习系动词的概念和类别!
The question is whether we can make good preparation in such a short time.
表语从句 注意:reason后面的表语从句只能用that,不能用why引导. ★The reason is that(because ×)…
The reason why we didn’t trust him is that he has often lied. (该句型中why引导一个定语从句)
定义:同位语从句跟在名词后面,进一步说明该名词的具体内容. 这些名词主要是表示抽象概念的词如fact, news, promise, idea, truth; possibility; statement; warning; advice等
★同位语的引导词有that; whether; why; who; where; how等;其中that和whether只起引导作用
其他连词具有实际意思,同时在同位语中作句子成分。
The news that China broken the world record in the Olympic Games has cheered all of us.
The question why so many people would choose to live in the countryside but to work in the city is still
同位语从句 under discussion. ( why 引导同位语从句解释说明中心语question的内容;且why在从句中作状语)
注意:① 只起引导作用时,连接词用that而不用which
Where did you get the idea that she could not come.
② 同位语从句和定语从句的区别: 就看that在作引导的从句中是否做句子成分
The suggestion that he raised at the meeting is very important. (that 引导定语)
The suggestion that the students should have plenty of exercise is very good. (that引导同位语从句)
在名词性从句当中只能用wh~, 在引导让步状语从句两者可以互换.
⒈ No matter+wh~ He will believe whatever others say. (划线部分部分为名词性从句,不能互换)
名 wh~+ever区别 Whatever others say, he will believe it. (划线部分为状语从句,可以互换)
Whoever walks around in such a heavy rain will catch a cold. (不可互换)
词 ★ 原则:能用if的情况,都能用whether表“是否…”
性 ① 在表语, 同位语,主语(置于句首时)从句时只用whether表“是否”
The question is whether the film is worth seeing. (表语从句)
从 I have no idea whether we should go to the party. (同位语从句)
Whether we shall attend the meeting hasn’t been decided yet. (主语从句 句首)
句 ▲ It hasn’t been decided yet if we shall attend the meeting.
⒉ Whether / if区别 It is doubtful whether / if he will come here. (主语从句,句末时可互换)
② 形容词;介词;discuss后的宾语从句中只用whether表“是否”
It depends on whether you can do the work well. (介词宾语)
几个难点 The students are discussing whether they will go out for a picnic this Sunday.
I am not sure whether he will come here or not. (形容词的宾语)
③ whether与to do; whether与or或 or not 的搭配
The question is whether to stay or leave.
Do you mind whether a man or woman does the job.
Ⅰ:主语,表语,同位语从句中that不能省略
That they are good at English is known to all. (主语从句)
The problem is that we don’t have enough money. (表语从句)
The fact that there are still many people suffering from poverty is really a great problem to the Chinese government. (同位语从句)
Ⅱ:在宾语从句中that在以下几种情况中不能省略
⒊关于that的省略 ①做介词宾语时that不能省略
I know nothing about my neighbor except that he used to work abroad.
② 由it作形式宾语时,that引导的宾语从句中,that不可省略
We all consider it important that every student (should) be treated properly.
③ 句子含多个并列句时,引导第二和以后几个从句的that不可省略
Everyone knew what happened and that she was worried.
④ 宾语从句被隔开时,that不能省略
I never doubt, under any circumstance, that he will study hard.
⑤ 如果名词性从句中又含有从句,此时that不能省略
Keep in mind that if you want others to respect you, you must respect others first. (that不能省略,后面的宾语从句中含有一个条件状语从句)
图解定语从句
概念:定语可以由形容词,名词,代词,分词,不定式以及介词短语等来担任,
也可以由一个句子来充当,充当定语功能的句子称为定语从句。
①指人的先行词
⒈ 先行词: 被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词
②指物的先行词
★ 先行词还可以是前面整个句子所叙述的事情。
He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us.
先行词 (which替代前面所叙述的事情)
① 替代前面的先行词 (替代作用)
关系词的作用 ② 连接主句和定语从句 (连接作用)
③ 在定语从句中作句子成分(成分作用)
定语从句
“三要素” ⒉关系词:
引导定语的词
标准:根据关系词在从句中做的句子成分种类
关系词的分类 关系代词:在从句中做 主,宾,表,定
(that/which/who/whom/whose/as)
关系副词:在从句中作状语
(When/where/why)
⒊ 定语从句:用来做定语,修饰限定先行词的句子。
① 限制性定语从句:对先行词起限定修饰作用。
定 He is a teacher who works at our school.
定语从句 ② 非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明作用
的分类 (先行词与定语从句之间有逗号隔开)
语 Beijing, which is the capital of China, is a beautiful city with a long history.
比较: He has two sons, who work in the same company.
(He has only two sons.)
从 He has two sons who work in the same company.
(Perhaps he has two more sons)
句
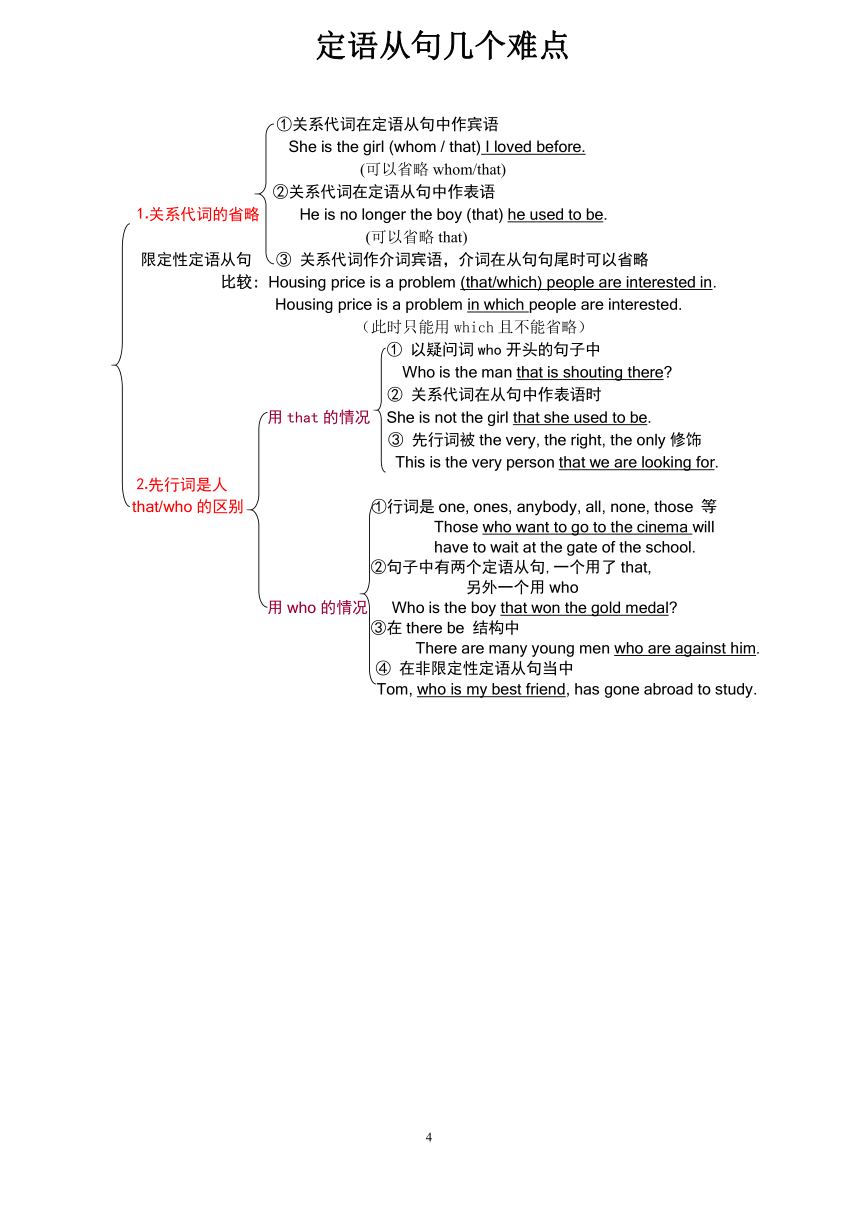
定语从句几个难点
①关系代词在定语从句中作宾语
She is the girl (whom / that) I loved before.
(可以省略whom/that)
②关系代词在定语从句中作表语
⒈关系代词的省略 He is no longer the boy (that) he used to be.
(可以省略that)
限定性定语从句 ③ 关系代词作介词宾语,介词在从句句尾时可以省略
比较: Housing price is a problem (that/which) people are interested in.
Housing price is a problem in which people are interested.
(此时只能用which且不能省略)
① 以疑问词who开头的句子中
Who is the man that is shouting there
② 关系代词在从句中作表语时
用that的情况 She is not the girl that she used to be.
③ 先行词被the very, the right, the only修饰
This is the very person that we are looking for.
⒉先行词是人
that/who的区别 ①行词是one, ones, anybody, all, none, those 等
Those who want to go to the cinema will
have to wait at the gate of the school.
②句子中有两个定语从句,一个用了that,
另外一个用who
用who的情况 Who is the boy that won the gold medal
③在there be 结构中
There are many young men who are against him.
④ 在非限定性定语从句当中
Tom, who is my best friend, has gone abroad to study.
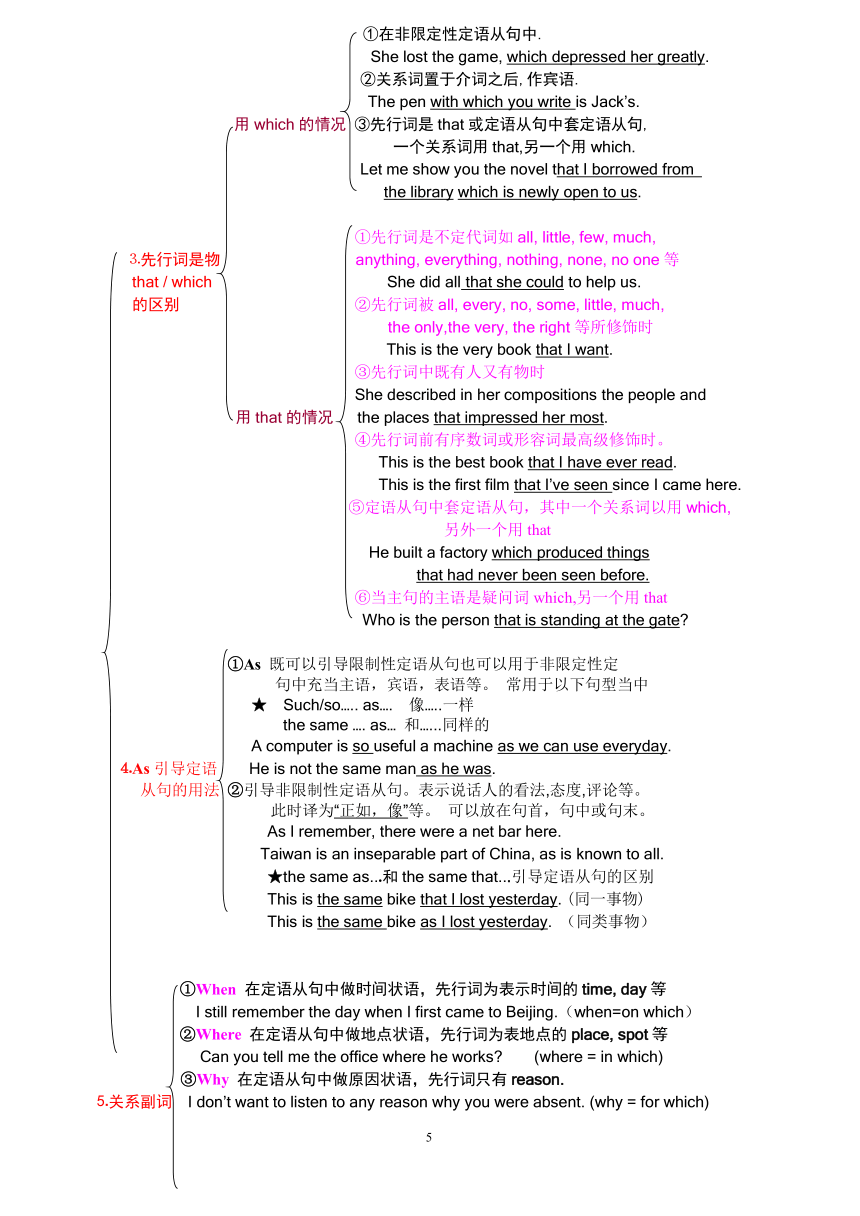
①在非限定性定语从句中.
She lost the game, which depressed her greatly.
②关系词置于介词之后,作宾语.
The pen with which you write is Jack’s.
用which的情况 ③先行词是that或定语从句中套定语从句,
一个关系词用that,另一个用which.
Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from
the library which is newly open to us.
①先行词是不定代词如all, little, few, much,
⒊先行词是物 anything, everything, nothing, none, no one等
that / which She did all that she could to help us.
的区别 ②先行词被all, every, no, some, little, much,
the only,the very, the right等所修饰时
This is the very book that I want.
③先行词中既有人又有物时
She described in her compositions the people and
用that的情况 the places that impressed her most.
④先行词前有序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。
This is the best book that I have ever read.
This is the first film that I’ve seen since I came here.
⑤定语从句中套定语从句,其中一个关系词以用which,
另外一个用that
He built a factory which produced things
that had never been seen before.
⑥当主句的主语是疑问词which,另一个用that
Who is the person that is standing at the gate
①As 既可以引导限制性定语从句也可以用于非限定性定
句中充当主语,宾语,表语等。 常用于以下句型当中
★ Such/so….. as…. 像…..一样
the same …. as… 和…...同样的
A computer is so useful a machine as we can use everyday.
⒋As引导定语 He is not the same man as he was.
从句的用法 ②引导非限制性定语从句。表示说话人的看法,态度,评论等。
此时译为“正如,像”等。 可以放在句首,句中或句末。
As I remember, there were a net bar here.
Taiwan is an inseparable part of China, as is known to all.
★the same as...和the same that...引导定语从句的区别
This is the same bike that I lost yesterday. (同一事物)
This is the same bike as I lost yesterday. (同类事物)
①When 在定语从句中做时间状语,先行词为表示时间的time, day等
I still remember the day when I first came to Beijing.(when=on which)
②Where 在定语从句中做地点状语,先行词为表地点的place, spot等
Can you tell me the office where he works (where = in which)
③Why 在定语从句中做原因状语,先行词只有reason.
⒌关系副词 I don’t want to listen to any reason why you were absent. (why = for which)
的运用 ★ 关系副词 = 相应的介词 + 关系代词
★ Where引导的定语从句还可以修饰抽象空间的名词如case(情形),
situation, position(位置),stage (阶段),point(地步)等
What are the situations where body language is the only form of communication
在哪些情况下身体语言是唯一的沟通方式(此时where = in which)
① way在定语从句中做状语时的三种引导方式 that / in which / 不填
The way in which / that / 不填 he explains the sentence to us is quite simple.
比较: The way which /that/不填 he told to us was quite simple
(★way在定语中作tell的宾语)
time表示“次数”时,用关系代词that引导定语从句
⒍几个特殊 ②先行词time This is the first time that the president has visited the country.
的先行词 time作“一段时间” 讲时,应用关系副词when
This was the time when there were no radios,
no telephones or no TV sets.
(★此时when = during which 在..期间)
③先行词reason当在定语从句中作状语时,定语从句的4种引导方式
why/for which/that/不填
This is the reason why/for which/that/不填 he can not come here.
比较:Is this the reason that/which/不填
he explained to us for his absence from the conference.
(★reason 在定语从句中做explain的宾语)
★该结构的关系代词只有两种即 介词+which(指物) 介词+whom(指人)
★该结构介词的选用原则:
① 根据定语从句中谓语动词的习惯搭配
This is the book on which I spent $ 8.
This is the book for which I paid $ 8.
② 根据现行词的搭配习惯
I remember the days during which I lived there.
I remember the day on which I graduated from university.
⒎介词+关系代词 ③ 根据整个句子所表达的意思来决定
The colorless gas without which we can’t live is called oxygen.
④ 英语中为了强调某一名词,不定式前面也可以加上关系代词。
Here is the money with which to buy the piano.
She is the right person on whom to depend.
注意:Ⅰ如果介词后移,关系代词可以省略
The person (whom/who/that) you will write to is Todd.
Ⅱ有些含有介词的动词短语介词不能提前如
look for/after; take care of; send for; hear from/of/about deal with等
This is the baby that you will look after.
①当先行词是 one of + 复数名词,定语从句的位于动词要用复数形式
The Great Wall is one of the world-famous buildings that draw lots of visitor every year.
⒏定语从句
的主谓一致 ②当先行词是 the only + one of +复数名词,从句谓语用单数形式
The Great Wall is the only one of the buildings on the earth that is seen from the moon.
③ 先行词如果是整个句子,定语从句的谓语动词用单数
Great changes have taken place in China, as is known to all.
He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us.
定语从句可以转换为 –ing或-ed形式
⒐定语从句的 The girl (who is) dancing now just returned from Taiwang.
转化 I love the stories (which were) written by Hemingway.
The man (who stands) standing there is my friend.
①判断从句是否为定语从句 (先行词,关系词,定语从句)
②准确判断先行词在定语从句中的成分 (主、宾、表、定、状)
10.定语从句的 从而正确选定使用关系代词或关系副词
解题方法 例:Is this the museum ___ you visited a few days ago
Is this the museum ____ the exhibition was held?
A. where B. that C. on which D. what
注意:Ⅰ.关系代词whose的用法。Whose在定语从句中做定语。
当先行词是人: whose = the + 名词 + of whom
当先行词是物:whose = the + 名词 + of which
Do you know the boy whose parents / the parents of whom are on holiday
I’d like a room whose window / the window of which faces the sea.
Ⅱ.That引导定语从句,名词性从句 和 强调句型的区别
定语从句中的that: 关系代词,在后面的定语从句中做句子成分。
名词性从句中的that: 从属连词,只起连接主从句的作用,在从句中不做句子成分。
强调句中的that, 运用于it is/was…that..结构;判断标准:去掉强调句型结构,成分仍然完整。
比较
This is the book that I am looking for.
(that 引导定语从句)
It is at Bashu middle school that I have studied for three years.
(that和前面的it is构成强调句型)
The fact that he stole the money surprised all of us.
(that 引导名词性从句--同位语从句)
That he will come to the conference has excited all of us.
(that引导名词性从句--主语从句)
We all expect that they win, for members of their team are stronger.
(that引导名词性从句--宾语从句)
The reason for your failure is that you lack confidence in yourself.
(that 引导名词性从句--表语从句)
种类 从属连词 例 句 说 明
时间状语从句 whenwhenever When I came into the room, he was writing a letter.当我进屋时,他正在写信。We shall go there whenever we are free.我们什么时间有空,我们就去那里。 when指的是“某一具体的时间”。whenever指的是“在任何一个不具体的时间”。
when I went to Beijing when I was five years old.It was foolish of you to take a taxi when you could easily walk there in five minutes.I was walking along the street when suddenly someone patted me on the shoulder from behind.I had just gone to bed when the telephone rang.We were about to start when it began to rain.We were on the point of giving up when a truck came into our sight. 当…时候when引导的从句动词短暂性,延续性皆可。when可表示原因,既然,相当于sincewhen可意为“这时”或“在那个时候”,表突然含义,可以看作是并列句,这种用法的when分句一般位于句末。when的常见句型:
was/were doing …when;
正在做某事的时候突然had done … when;
刚做完某事时突然be about to do…when;正要做某事时突然be on the point of doing…when;
正要做某事时突然
while While it was raining, they went out.天下雨的时候,他们出去了。Mum was cooking while Dad was watching TV. while指“在某一段时间里”,“在…期间”,while引导的动作必须是持续性的。
(while可以表示 而,却,表对比之意,此时为并列连词)
as He hurried home, looking behind as he went.他赶快回家,不时地一边走一边向后看。 as引导持续性动作,强调主句和从句的动作同时发生。(译成:一边…一边)
as +n. 相当于一个时间状语从句
As a boy= when he was a boy
before Be a pupil before you become a teacher. Before I could get in a word ,he had measured me.我还没来得及插话,他就给我量好了尺寸。It will be 4 years before he graduates. 他还有四年时间毕业了。We had sailed four days and four nights before we saw land. 我们航行了四天四夜才见到陆地。 We hadn’t run a mile before he felt tired.我们还没走到一英里路他就觉得累了。It wasn’t two years before he left the country. 还没到两年他们离开了那国家。
I hope to see you before long.I saw the film long before before译为在…之前, before sb can/could… 某人还没来得及…It will be +时间+ before还有多长时间……
had done … before (才……) had not done … before…不到…就…
It was not+一段时间+before 不多久就…… before long不久以后long before很久以前,
after He arrived after the game started.
比赛开始后,他到了。 在…之后
till We waited till (until)he came back .我们一直等到他回来。 如主句动词是持续性动作,常用肯定式,表示“直到…为止”
until She didn’t stop working until eleven o’clock .她到11点钟才停止工作。Until he had passed out of sight, she stood there.她站在那里看着,直到看不见他的身影。
It was not until eleven o’clock that she stopped working. 如主句动词是瞬间动词,常用否定式,表示“直…才”“在…以前不”,从句放在句首表示强调,一般用untilnot… until 用于强调句,注意否定转移It is not until… that
sinceever since Great changes have taken place in China since 1978.自从1978年以来中国发生了巨大的变化。It is 5 years since I joined the party.
(join为短暂性动词)从那时到现在 It is/ has been + 时间段 since +一般过去时.
此句型为短暂性动词可以和时间段连用的特殊句型。时间的计算一律从since从句的动作完成或状态结束时算起。
as soon as(once=directly=immediately
=instantly) As soon as I arrive in Shanghai, I’ll write to you.
我一到上海就给你写信。
Directly you feel the pains, you must go to see a doctor. 你一感觉到疼痛,就必须去看医生。 一…就…
状语从句在主句之前时一般用逗号与主句分开,如从句在主句之后则不必用标点符号。
hardly…when
=scarcely…whenno sooner…than I had hardly got home when it began to rain.我刚一到家,就下雨了。
=Hardly had I got home when it began to rain.Hardly had we begun when we were told to stop.我们刚开始就被叫停。No sooner had we got to the station than the train left. 我们刚到车站,火车就走了。 hardly…when和no sooner…than的意义相当于as soon as,但只表示过去发生的事情,主句为过去完成时,从句为过去时。
如hardly或no sooner位于句首时语气强,而且主句的谓语要用部分倒装,部分倒装提前情态动词,助动词到主语前
every time, next time, by the time,the first time, the moment,
the second,
the minute, the day,
the year, 等 Every time I travelled by boat, I got seasick.我每次乘船都晕船。Next time you come ,you’ll see him.下次你来的时候,就会见到他。The moment I heard the song, I felt cheerful.我一听到这首歌,就感到很愉快。 名词短语引导时间状语从句在时间状语从句中,不能用将来时或过去将来时,而要用现在时表将来,过去时表过去将来。
地点状语从句 wherewherever Where there is a will, there is a way.有志者,事竟成。Where there is water there is life.哪里有水,哪里就有生命。Wherever you go, you must obey the law.无论你去哪都要遵守法律。 where与wherever意义基本相同,但后者语气较强,多用于书面语。
原因状语从句 because I came back late yesterday because I was on duty.昨天我回来晚了,因为我值班。
It was because I was on duty that I came back late. because用来回答why 的问题,语气最强一般放在主句之后可与强调句相连
since Since everyone is here, let’s begin our meeting.既然大家都到了,我们开始开会。 since表示既然或全已知的理由,稍加分析即可表明的原因,多放句首
as As he didn’t know much English, he looked up the word in the dictionary .由于他英语懂得不多,他在字典中查阅这个单词。 从句常放在句首,说明原因,主句说明结果,常用于口语中。
because, since, as语气逐渐减弱
now that,seeing thatin that Now (that) the weather has cleared up, we can start our journey.鉴于天气已经晴朗,我们可以启程了。Seeing (that) he was badly ill, we sent for the doctor.鉴于他病情严重,我们派人去请医生去了。I like cities but I prefer the country in that there is fresh air. seeing (that), now that 和since, as 意义相似,他们都有“鉴于某个事实”的意思,that可以省去。由于某种原因,语气微弱
目的状语从句 so thatin order thatlest = for fear that=in case We’ll tell you the truth so that you can judge for yourself.我把真实情况告诉你,使你能自己作出判断。They worked harder than usual in order that they could finish the work ahead of time .他们比往常更加努力工作,为了能提前完成工作。Put on more clothes lest (= for fear that ) you should catch cold. 多穿点衣服,以免患感冒。 目的状语从句中常用情态动词may (might) can (could) ,should 等放在动词之前,从句往往放在主句之后,主从句之间不用任何标点符号lest, for fear that, in case 后的从句用手(should)+动词原形,虚拟
结果状语从句 so that so…that We turned up the radio, so that everyone heard the news.我们把收音机的音量放大,大家都听到了新闻。He was so excited that he couldn’t say a word.他十分激动,以致一句话都说不出来。 so that前有逗号为结果状语从句。so…that的so后面跟形容词或副词。
such…that He gave such important reasons that he was excused.他说出了这么重要的理由,得到大家的谅解。It is such an interesting novel that all of us want to read it. = It is so interesting a novel that all of us want to read it. such…that的such后面跟名词,如果名词是单数就要用such a /an…that还可以转换用so…that,语气较强
that What have we done that you should be angry with us should竟然,表惊讶含义
条件状语从句 if unlessas/so long asin case so far as Difficulties are nothing if we are not afraid of them.如果我们不怕困难,困难就算不了什么了。We shall go there tomorrow unless it rains.除非下雨,我们明天就去那里。= We shall go there tomorrow if it doesn’t rain.So/As long as you work hard, you will succeed.只要你努力工作,你就一定能成功。In case I forget, please remind me about it .万一我忘了,请提醒我一下。So far as I know, the book will be published next month.据我所知,那本书下月出版。 unless从句的谓语只能用肯定式。unless和if…not同义,unless是书面语,if…not是口语,通常二者可以换用。条件状语从句中的谓语动词的时态一般要用现在时或过去时代替一般将来时或过去将来时。
除了常见的引导词之外,还有:
假如:providing/provided that,
given that(常放于句首),
supposing that, suppose that只要,以…为条件on condition that
方式状语从句 as as if…as thoughthe way Draw a cat as I taught you .按照我教你的画一只猫。Do as you are told.按照人家告诉你做的去做。She looks as if she is ill.看上去她好象是生病了。He acted as if (though) nothing had happened.他的行动就好象什么也没有发生。They treat the black boy as if (though) he were an animal.他们对待这黑孩子仿佛他是一头牲口。She doesn’t speak the way he does. 此处as译为,按照或正如as if或as though的意义和用法基本一样。从句中可以用现在时表示可能符合事实,也可以用虚拟语气。
当as if 与感官动词连用时,可以不虚拟。若虚拟,则为退格虚拟:过去时表现在,过去完成表过去,过去将来表将来。名词短语引导方式状语从句
让步状语从句 thoughalthough Although (Though) he was over sixty, (yet) he began to learn French.虽然他六十多岁了,但仍开始学习法语 。We were not tired though (although) we had worked all day.虽然我们干了一天活,但并不累。 在句子中一般用了“虽然”就不能再用“但是”(but)但可以与yet或still连用。though / although意义相同,although更正式。
区别是:在as though, even though短语中,though和although不能互换。
though有副词词性,译成 不过,而although只是连词:
It was quiet party. I had a good time, though.
even ifeven though I’ll go even if (though) it rains tomorrow.即使明天下雨,我也要去。 even if 和even though的意思为“即使”“纵使”有退一步设想的意味,多用于书面语中。
as Child as he is , he knows a lot .(表语)虽然他是一个孩子,但他懂得很多。Youngest as he is, he knows a lot. (表语)
(as让步状语从句中,提前作表语的名词和形容词最高级时,省冠词。)Cold as it is, (= Though it is cold,) the children play outdoors.虽然天气冷,但孩子们仍在户外玩。Much as he likes the bike, he won’t buy it.(状语)
Try as he might, he failed. (动词原形) as引出的状语从句多用于书面语,它比用though或although引导的从句,语气强,更有表现力,从句常放在句首,语序部分倒装。让步状语从句形式倒装:提前动词原形,表语,状语到主语前as, though/although,while都有虽然尽管之意,但是as必须倒装,though/although可倒可不倒,而while不能倒装。
no matter (who, what
when, where
which,how…) Do it no matter what others say.不管别人怎么说,尽管干。No matter how busy he was, he studied English every day.不管他多忙,他都每天坚持学习英语。 no matter……与 who-ever引导的让步状语从句意义基本一 样,no matter……引导的从句可是以位于主句前或主句后。
wh-ever (whatever whoever whenever whichever however) Whatever happens / may happen , we shall not lose heart.无论发生什么,我们都不要失去信心。Whoever comes, he will be welcome.无论谁来,都会受到欢迎。 wh-ever从句中的动词有时可以和may连用。判断wh-ever引导的是状语从句还是名词性从句的一点是,名词性从句,主句中一定有一个成分要在从句担任,一般从句与主句之间没有逗号。不可将no matter与wh—ever连用
比较状语从句 as…as not so/as…asthe same…assuch…as Mary is as old as my sister. 玛利和我姐姐一样大。He doesn’t run so (as) fast as Jack (does).他不如杰克跑得那样快。His book is the same as mine.他的书和我的一样。Henry is not such a good worker as Peter .享利这个工人不如彼得那样好。 连词表示同程度级的比较,
肯定句用as…as
否定句可用not as…as 或not so…asas和than引导的比较状语从句,从句主语为人称代词时可用主格或宾格。
Tom is as old as I/me.
than She has made greater progress this year than she did last year.她今年比去年进步更大。He bought fewer books than I (did).他买的书比我买的少。 表示不同程度之比较,主句中用比较级的形容词或副词。
the more …the more The more you read, the better you understand.你看的书越多,你懂得的就越多。The harder you work, the greater progress you will make.你工作越努力,你取得的进步就越大。The sooner, the better.越快越好。The warmer, the better.越暖和越好。 the more…the more 意思为越…越…,通常的语序为从句在前,主句在后,这两个the都是表示程度的副词,用在比较级的形容词或副词前面。句子意思明显,句子的主语和动词都可省略。
1
1
定义:在句子中起名词作用的句子叫名词从句 (Noun Clauses). 名词性从句包括主语,宾语,表语,同位语从句.
★ 名词性从句中使用陈述句语序。
① 从属连词that; whether; if (只起引导从句的作用,在从句中不做句子成分)
② 连接代词 what, whatever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, whose, which,等.在从句
1.分类 中做主语,宾语,表语,定语等句子成分。
③ 连接副词when, where, how, why, whenever, however, wherever等在从句中做状语成分。
引导名词性 2. 名词性从句的连接词选用原则:“缺什么就补什么”
从句的连接词 I know what he is talking about. (从句中缺宾语,指物) Do you know who he is (从句中缺表语,指人)
Where he will go is unknown. (从句中缺地点状语)
I’m sure that they will come tomorrow. (从句中什么都不缺)
I don’t know which book I should choose. (从句中缺定语)
定义:充当主语功能的句子叫主语从句
That she was chosen made a great stir (轰动) in her school.
注意: ①it作形式主语的that-从句有以下四种不同的搭配关系:
It + be +形容词+ that-从句 It is necessary / important that…. …是有必要 / 重要的….
It + be + -ed 分词+ that-从句 It is universally acknowledged that../ It is known that…众所周知…
It + be +名词+ that-从句 It is common knowledge/ a fact that… ……是常识/事实
It +不及物动词+ that-分句 It happens that…碰巧.. / It occurs to sb.that… 突然想起……
名 主语从句 ②It 作形式主语和it引导强调句的比较
强调句: It is in the morning that the murder took place. (去掉该结构后,句子成分完整)
词 主语从句:It was a pity that you shouldn’t go to see the film. (在句子中作主语成分)
③whatever /whichever/ whoever引导主语从句的区别
Ⅰ Whatever 是what的强调形式表示“无论什么”相当于 anything that…
从 Whatever / Anything that she does is wrong.
Ⅱ whoever 是who的强调形式,表示‘无论谁’ 相当于anyone who….
句 ~ever Whoever / Anyone who walks around in such a heavy rain will catch a cold.
Ⅲ whichever ‘无论哪个;无论哪些’,既指人,又指物. 可修饰名词与of连用
Whichever book you borrow doesn’t matter to us.
Whichever of us fulfills his task will lend a hand to others.
定义:在复合句中充当宾语功能的句子叫宾语从句
We can learn what we didn’t know.
We find it necessary that we (should) practice English every day.
★某些作表语的形容词,如sure, happy, glad, certain等之后可带宾语从句
I am glad that you can come and help me.
注意:① wish/would rather后的宾语从句中要用虚拟语气。
I wish I had finished my homework yesterday. I’d rather you had been there yesterday
② 在表示建议,命令, 请求的词后面的宾语从句当中用should + V, should可以省略
宾语从句 His pale face suggested that he was ill so I suggested that he should go to see the doctor.
He insisted that he was innocent and insisted that he should be set free.
③ 注意it作形式宾语的结构
We all thought it a pity that we had missed the lesson. I took it for granted that they were not coming.
④ that一般不接介词宾语,偶尔可作except, in的宾语;其它介词后面需用it作形式宾语
He differs from his roommates in that he devoted his spare time to reading.
He knows nothing about Jim except that he is from London.
You can depend on it that he will help you in time of emergency.
⑤表示好恶的动词如like; hate; love;enjoy; dislike; appreciate等后面不能直接跟宾语;
I like it when the weather is sunny. I hate it when someone is later for my class.
定义:充当表语功能的句子被叫做表语从句。 ★复习系动词的概念和类别!
The question is whether we can make good preparation in such a short time.
表语从句 注意:reason后面的表语从句只能用that,不能用why引导. ★The reason is that(because ×)…
The reason why we didn’t trust him is that he has often lied. (该句型中why引导一个定语从句)
定义:同位语从句跟在名词后面,进一步说明该名词的具体内容. 这些名词主要是表示抽象概念的词如fact, news, promise, idea, truth; possibility; statement; warning; advice等
★同位语的引导词有that; whether; why; who; where; how等;其中that和whether只起引导作用
其他连词具有实际意思,同时在同位语中作句子成分。
The news that China broken the world record in the Olympic Games has cheered all of us.
The question why so many people would choose to live in the countryside but to work in the city is still
同位语从句 under discussion. ( why 引导同位语从句解释说明中心语question的内容;且why在从句中作状语)
注意:① 只起引导作用时,连接词用that而不用which
Where did you get the idea that she could not come.
② 同位语从句和定语从句的区别: 就看that在作引导的从句中是否做句子成分
The suggestion that he raised at the meeting is very important. (that 引导定语)
The suggestion that the students should have plenty of exercise is very good. (that引导同位语从句)
在名词性从句当中只能用wh~, 在引导让步状语从句两者可以互换.
⒈ No matter+wh~ He will believe whatever others say. (划线部分部分为名词性从句,不能互换)
名 wh~+ever区别 Whatever others say, he will believe it. (划线部分为状语从句,可以互换)
Whoever walks around in such a heavy rain will catch a cold. (不可互换)
词 ★ 原则:能用if的情况,都能用whether表“是否…”
性 ① 在表语, 同位语,主语(置于句首时)从句时只用whether表“是否”
The question is whether the film is worth seeing. (表语从句)
从 I have no idea whether we should go to the party. (同位语从句)
Whether we shall attend the meeting hasn’t been decided yet. (主语从句 句首)
句 ▲ It hasn’t been decided yet if we shall attend the meeting.
⒉ Whether / if区别 It is doubtful whether / if he will come here. (主语从句,句末时可互换)
② 形容词;介词;discuss后的宾语从句中只用whether表“是否”
It depends on whether you can do the work well. (介词宾语)
几个难点 The students are discussing whether they will go out for a picnic this Sunday.
I am not sure whether he will come here or not. (形容词的宾语)
③ whether与to do; whether与or或 or not 的搭配
The question is whether to stay or leave.
Do you mind whether a man or woman does the job.
Ⅰ:主语,表语,同位语从句中that不能省略
That they are good at English is known to all. (主语从句)
The problem is that we don’t have enough money. (表语从句)
The fact that there are still many people suffering from poverty is really a great problem to the Chinese government. (同位语从句)
Ⅱ:在宾语从句中that在以下几种情况中不能省略
⒊关于that的省略 ①做介词宾语时that不能省略
I know nothing about my neighbor except that he used to work abroad.
② 由it作形式宾语时,that引导的宾语从句中,that不可省略
We all consider it important that every student (should) be treated properly.
③ 句子含多个并列句时,引导第二和以后几个从句的that不可省略
Everyone knew what happened and that she was worried.
④ 宾语从句被隔开时,that不能省略
I never doubt, under any circumstance, that he will study hard.
⑤ 如果名词性从句中又含有从句,此时that不能省略
Keep in mind that if you want others to respect you, you must respect others first. (that不能省略,后面的宾语从句中含有一个条件状语从句)
图解定语从句
概念:定语可以由形容词,名词,代词,分词,不定式以及介词短语等来担任,
也可以由一个句子来充当,充当定语功能的句子称为定语从句。
①指人的先行词
⒈ 先行词: 被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词
②指物的先行词
★ 先行词还可以是前面整个句子所叙述的事情。
He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us.
先行词 (which替代前面所叙述的事情)
① 替代前面的先行词 (替代作用)
关系词的作用 ② 连接主句和定语从句 (连接作用)
③ 在定语从句中作句子成分(成分作用)
定语从句
“三要素” ⒉关系词:
引导定语的词
标准:根据关系词在从句中做的句子成分种类
关系词的分类 关系代词:在从句中做 主,宾,表,定
(that/which/who/whom/whose/as)
关系副词:在从句中作状语
(When/where/why)
⒊ 定语从句:用来做定语,修饰限定先行词的句子。
① 限制性定语从句:对先行词起限定修饰作用。
定 He is a teacher who works at our school.
定语从句 ② 非限制性定语从句:对先行词起补充说明作用
的分类 (先行词与定语从句之间有逗号隔开)
语 Beijing, which is the capital of China, is a beautiful city with a long history.
比较: He has two sons, who work in the same company.
(He has only two sons.)
从 He has two sons who work in the same company.
(Perhaps he has two more sons)
句
定语从句几个难点
①关系代词在定语从句中作宾语
She is the girl (whom / that) I loved before.
(可以省略whom/that)
②关系代词在定语从句中作表语
⒈关系代词的省略 He is no longer the boy (that) he used to be.
(可以省略that)
限定性定语从句 ③ 关系代词作介词宾语,介词在从句句尾时可以省略
比较: Housing price is a problem (that/which) people are interested in.
Housing price is a problem in which people are interested.
(此时只能用which且不能省略)
① 以疑问词who开头的句子中
Who is the man that is shouting there
② 关系代词在从句中作表语时
用that的情况 She is not the girl that she used to be.
③ 先行词被the very, the right, the only修饰
This is the very person that we are looking for.
⒉先行词是人
that/who的区别 ①行词是one, ones, anybody, all, none, those 等
Those who want to go to the cinema will
have to wait at the gate of the school.
②句子中有两个定语从句,一个用了that,
另外一个用who
用who的情况 Who is the boy that won the gold medal
③在there be 结构中
There are many young men who are against him.
④ 在非限定性定语从句当中
Tom, who is my best friend, has gone abroad to study.
①在非限定性定语从句中.
She lost the game, which depressed her greatly.
②关系词置于介词之后,作宾语.
The pen with which you write is Jack’s.
用which的情况 ③先行词是that或定语从句中套定语从句,
一个关系词用that,另一个用which.
Let me show you the novel that I borrowed from
the library which is newly open to us.
①先行词是不定代词如all, little, few, much,
⒊先行词是物 anything, everything, nothing, none, no one等
that / which She did all that she could to help us.
的区别 ②先行词被all, every, no, some, little, much,
the only,the very, the right等所修饰时
This is the very book that I want.
③先行词中既有人又有物时
She described in her compositions the people and
用that的情况 the places that impressed her most.
④先行词前有序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。
This is the best book that I have ever read.
This is the first film that I’ve seen since I came here.
⑤定语从句中套定语从句,其中一个关系词以用which,
另外一个用that
He built a factory which produced things
that had never been seen before.
⑥当主句的主语是疑问词which,另一个用that
Who is the person that is standing at the gate
①As 既可以引导限制性定语从句也可以用于非限定性定
句中充当主语,宾语,表语等。 常用于以下句型当中
★ Such/so….. as…. 像…..一样
the same …. as… 和…...同样的
A computer is so useful a machine as we can use everyday.
⒋As引导定语 He is not the same man as he was.
从句的用法 ②引导非限制性定语从句。表示说话人的看法,态度,评论等。
此时译为“正如,像”等。 可以放在句首,句中或句末。
As I remember, there were a net bar here.
Taiwan is an inseparable part of China, as is known to all.
★the same as...和the same that...引导定语从句的区别
This is the same bike that I lost yesterday. (同一事物)
This is the same bike as I lost yesterday. (同类事物)
①When 在定语从句中做时间状语,先行词为表示时间的time, day等
I still remember the day when I first came to Beijing.(when=on which)
②Where 在定语从句中做地点状语,先行词为表地点的place, spot等
Can you tell me the office where he works (where = in which)
③Why 在定语从句中做原因状语,先行词只有reason.
⒌关系副词 I don’t want to listen to any reason why you were absent. (why = for which)
的运用 ★ 关系副词 = 相应的介词 + 关系代词
★ Where引导的定语从句还可以修饰抽象空间的名词如case(情形),
situation, position(位置),stage (阶段),point(地步)等
What are the situations where body language is the only form of communication
在哪些情况下身体语言是唯一的沟通方式(此时where = in which)
① way在定语从句中做状语时的三种引导方式 that / in which / 不填
The way in which / that / 不填 he explains the sentence to us is quite simple.
比较: The way which /that/不填 he told to us was quite simple
(★way在定语中作tell的宾语)
time表示“次数”时,用关系代词that引导定语从句
⒍几个特殊 ②先行词time This is the first time that the president has visited the country.
的先行词 time作“一段时间” 讲时,应用关系副词when
This was the time when there were no radios,
no telephones or no TV sets.
(★此时when = during which 在..期间)
③先行词reason当在定语从句中作状语时,定语从句的4种引导方式
why/for which/that/不填
This is the reason why/for which/that/不填 he can not come here.
比较:Is this the reason that/which/不填
he explained to us for his absence from the conference.
(★reason 在定语从句中做explain的宾语)
★该结构的关系代词只有两种即 介词+which(指物) 介词+whom(指人)
★该结构介词的选用原则:
① 根据定语从句中谓语动词的习惯搭配
This is the book on which I spent $ 8.
This is the book for which I paid $ 8.
② 根据现行词的搭配习惯
I remember the days during which I lived there.
I remember the day on which I graduated from university.
⒎介词+关系代词 ③ 根据整个句子所表达的意思来决定
The colorless gas without which we can’t live is called oxygen.
④ 英语中为了强调某一名词,不定式前面也可以加上关系代词。
Here is the money with which to buy the piano.
She is the right person on whom to depend.
注意:Ⅰ如果介词后移,关系代词可以省略
The person (whom/who/that) you will write to is Todd.
Ⅱ有些含有介词的动词短语介词不能提前如
look for/after; take care of; send for; hear from/of/about deal with等
This is the baby that you will look after.
①当先行词是 one of + 复数名词,定语从句的位于动词要用复数形式
The Great Wall is one of the world-famous buildings that draw lots of visitor every year.
⒏定语从句
的主谓一致 ②当先行词是 the only + one of +复数名词,从句谓语用单数形式
The Great Wall is the only one of the buildings on the earth that is seen from the moon.
③ 先行词如果是整个句子,定语从句的谓语动词用单数
Great changes have taken place in China, as is known to all.
He has passed the driving test, which surprises all of us.
定语从句可以转换为 –ing或-ed形式
⒐定语从句的 The girl (who is) dancing now just returned from Taiwang.
转化 I love the stories (which were) written by Hemingway.
The man (who stands) standing there is my friend.
①判断从句是否为定语从句 (先行词,关系词,定语从句)
②准确判断先行词在定语从句中的成分 (主、宾、表、定、状)
10.定语从句的 从而正确选定使用关系代词或关系副词
解题方法 例:Is this the museum ___ you visited a few days ago
Is this the museum ____ the exhibition was held?
A. where B. that C. on which D. what
注意:Ⅰ.关系代词whose的用法。Whose在定语从句中做定语。
当先行词是人: whose = the + 名词 + of whom
当先行词是物:whose = the + 名词 + of which
Do you know the boy whose parents / the parents of whom are on holiday
I’d like a room whose window / the window of which faces the sea.
Ⅱ.That引导定语从句,名词性从句 和 强调句型的区别
定语从句中的that: 关系代词,在后面的定语从句中做句子成分。
名词性从句中的that: 从属连词,只起连接主从句的作用,在从句中不做句子成分。
强调句中的that, 运用于it is/was…that..结构;判断标准:去掉强调句型结构,成分仍然完整。
比较
This is the book that I am looking for.
(that 引导定语从句)
It is at Bashu middle school that I have studied for three years.
(that和前面的it is构成强调句型)
The fact that he stole the money surprised all of us.
(that 引导名词性从句--同位语从句)
That he will come to the conference has excited all of us.
(that引导名词性从句--主语从句)
We all expect that they win, for members of their team are stronger.
(that引导名词性从句--宾语从句)
The reason for your failure is that you lack confidence in yourself.
(that 引导名词性从句--表语从句)
种类 从属连词 例 句 说 明
时间状语从句 whenwhenever When I came into the room, he was writing a letter.当我进屋时,他正在写信。We shall go there whenever we are free.我们什么时间有空,我们就去那里。 when指的是“某一具体的时间”。whenever指的是“在任何一个不具体的时间”。
when I went to Beijing when I was five years old.It was foolish of you to take a taxi when you could easily walk there in five minutes.I was walking along the street when suddenly someone patted me on the shoulder from behind.I had just gone to bed when the telephone rang.We were about to start when it began to rain.We were on the point of giving up when a truck came into our sight. 当…时候when引导的从句动词短暂性,延续性皆可。when可表示原因,既然,相当于sincewhen可意为“这时”或“在那个时候”,表突然含义,可以看作是并列句,这种用法的when分句一般位于句末。when的常见句型:
was/were doing …when;
正在做某事的时候突然had done … when;
刚做完某事时突然be about to do…when;正要做某事时突然be on the point of doing…when;
正要做某事时突然
while While it was raining, they went out.天下雨的时候,他们出去了。Mum was cooking while Dad was watching TV. while指“在某一段时间里”,“在…期间”,while引导的动作必须是持续性的。
(while可以表示 而,却,表对比之意,此时为并列连词)
as He hurried home, looking behind as he went.他赶快回家,不时地一边走一边向后看。 as引导持续性动作,强调主句和从句的动作同时发生。(译成:一边…一边)
as +n. 相当于一个时间状语从句
As a boy= when he was a boy
before Be a pupil before you become a teacher. Before I could get in a word ,he had measured me.我还没来得及插话,他就给我量好了尺寸。It will be 4 years before he graduates. 他还有四年时间毕业了。We had sailed four days and four nights before we saw land. 我们航行了四天四夜才见到陆地。 We hadn’t run a mile before he felt tired.我们还没走到一英里路他就觉得累了。It wasn’t two years before he left the country. 还没到两年他们离开了那国家。
I hope to see you before long.I saw the film long before before译为在…之前, before sb can/could… 某人还没来得及…It will be +时间+ before还有多长时间……
had done … before (才……) had not done … before…不到…就…
It was not+一段时间+before 不多久就…… before long不久以后long before很久以前,
after He arrived after the game started.
比赛开始后,他到了。 在…之后
till We waited till (until)he came back .我们一直等到他回来。 如主句动词是持续性动作,常用肯定式,表示“直到…为止”
until She didn’t stop working until eleven o’clock .她到11点钟才停止工作。Until he had passed out of sight, she stood there.她站在那里看着,直到看不见他的身影。
It was not until eleven o’clock that she stopped working. 如主句动词是瞬间动词,常用否定式,表示“直…才”“在…以前不”,从句放在句首表示强调,一般用untilnot… until 用于强调句,注意否定转移It is not until… that
sinceever since Great changes have taken place in China since 1978.自从1978年以来中国发生了巨大的变化。It is 5 years since I joined the party.
(join为短暂性动词)从那时到现在 It is/ has been + 时间段 since +一般过去时.
此句型为短暂性动词可以和时间段连用的特殊句型。时间的计算一律从since从句的动作完成或状态结束时算起。
as soon as(once=directly=immediately
=instantly) As soon as I arrive in Shanghai, I’ll write to you.
我一到上海就给你写信。
Directly you feel the pains, you must go to see a doctor. 你一感觉到疼痛,就必须去看医生。 一…就…
状语从句在主句之前时一般用逗号与主句分开,如从句在主句之后则不必用标点符号。
hardly…when
=scarcely…whenno sooner…than I had hardly got home when it began to rain.我刚一到家,就下雨了。
=Hardly had I got home when it began to rain.Hardly had we begun when we were told to stop.我们刚开始就被叫停。No sooner had we got to the station than the train left. 我们刚到车站,火车就走了。 hardly…when和no sooner…than的意义相当于as soon as,但只表示过去发生的事情,主句为过去完成时,从句为过去时。
如hardly或no sooner位于句首时语气强,而且主句的谓语要用部分倒装,部分倒装提前情态动词,助动词到主语前
every time, next time, by the time,the first time, the moment,
the second,
the minute, the day,
the year, 等 Every time I travelled by boat, I got seasick.我每次乘船都晕船。Next time you come ,you’ll see him.下次你来的时候,就会见到他。The moment I heard the song, I felt cheerful.我一听到这首歌,就感到很愉快。 名词短语引导时间状语从句在时间状语从句中,不能用将来时或过去将来时,而要用现在时表将来,过去时表过去将来。
地点状语从句 wherewherever Where there is a will, there is a way.有志者,事竟成。Where there is water there is life.哪里有水,哪里就有生命。Wherever you go, you must obey the law.无论你去哪都要遵守法律。 where与wherever意义基本相同,但后者语气较强,多用于书面语。
原因状语从句 because I came back late yesterday because I was on duty.昨天我回来晚了,因为我值班。
It was because I was on duty that I came back late. because用来回答why 的问题,语气最强一般放在主句之后可与强调句相连
since Since everyone is here, let’s begin our meeting.既然大家都到了,我们开始开会。 since表示既然或全已知的理由,稍加分析即可表明的原因,多放句首
as As he didn’t know much English, he looked up the word in the dictionary .由于他英语懂得不多,他在字典中查阅这个单词。 从句常放在句首,说明原因,主句说明结果,常用于口语中。
because, since, as语气逐渐减弱
now that,seeing thatin that Now (that) the weather has cleared up, we can start our journey.鉴于天气已经晴朗,我们可以启程了。Seeing (that) he was badly ill, we sent for the doctor.鉴于他病情严重,我们派人去请医生去了。I like cities but I prefer the country in that there is fresh air. seeing (that), now that 和since, as 意义相似,他们都有“鉴于某个事实”的意思,that可以省去。由于某种原因,语气微弱
目的状语从句 so thatin order thatlest = for fear that=in case We’ll tell you the truth so that you can judge for yourself.我把真实情况告诉你,使你能自己作出判断。They worked harder than usual in order that they could finish the work ahead of time .他们比往常更加努力工作,为了能提前完成工作。Put on more clothes lest (= for fear that ) you should catch cold. 多穿点衣服,以免患感冒。 目的状语从句中常用情态动词may (might) can (could) ,should 等放在动词之前,从句往往放在主句之后,主从句之间不用任何标点符号lest, for fear that, in case 后的从句用手(should)+动词原形,虚拟
结果状语从句 so that so…that We turned up the radio, so that everyone heard the news.我们把收音机的音量放大,大家都听到了新闻。He was so excited that he couldn’t say a word.他十分激动,以致一句话都说不出来。 so that前有逗号为结果状语从句。so…that的so后面跟形容词或副词。
such…that He gave such important reasons that he was excused.他说出了这么重要的理由,得到大家的谅解。It is such an interesting novel that all of us want to read it. = It is so interesting a novel that all of us want to read it. such…that的such后面跟名词,如果名词是单数就要用such a /an…that还可以转换用so…that,语气较强
that What have we done that you should be angry with us should竟然,表惊讶含义
条件状语从句 if unlessas/so long asin case so far as Difficulties are nothing if we are not afraid of them.如果我们不怕困难,困难就算不了什么了。We shall go there tomorrow unless it rains.除非下雨,我们明天就去那里。= We shall go there tomorrow if it doesn’t rain.So/As long as you work hard, you will succeed.只要你努力工作,你就一定能成功。In case I forget, please remind me about it .万一我忘了,请提醒我一下。So far as I know, the book will be published next month.据我所知,那本书下月出版。 unless从句的谓语只能用肯定式。unless和if…not同义,unless是书面语,if…not是口语,通常二者可以换用。条件状语从句中的谓语动词的时态一般要用现在时或过去时代替一般将来时或过去将来时。
除了常见的引导词之外,还有:
假如:providing/provided that,
given that(常放于句首),
supposing that, suppose that只要,以…为条件on condition that
方式状语从句 as as if…as thoughthe way Draw a cat as I taught you .按照我教你的画一只猫。Do as you are told.按照人家告诉你做的去做。She looks as if she is ill.看上去她好象是生病了。He acted as if (though) nothing had happened.他的行动就好象什么也没有发生。They treat the black boy as if (though) he were an animal.他们对待这黑孩子仿佛他是一头牲口。She doesn’t speak the way he does. 此处as译为,按照或正如as if或as though的意义和用法基本一样。从句中可以用现在时表示可能符合事实,也可以用虚拟语气。
当as if 与感官动词连用时,可以不虚拟。若虚拟,则为退格虚拟:过去时表现在,过去完成表过去,过去将来表将来。名词短语引导方式状语从句
让步状语从句 thoughalthough Although (Though) he was over sixty, (yet) he began to learn French.虽然他六十多岁了,但仍开始学习法语 。We were not tired though (although) we had worked all day.虽然我们干了一天活,但并不累。 在句子中一般用了“虽然”就不能再用“但是”(but)但可以与yet或still连用。though / although意义相同,although更正式。
区别是:在as though, even though短语中,though和although不能互换。
though有副词词性,译成 不过,而although只是连词:
It was quiet party. I had a good time, though.
even ifeven though I’ll go even if (though) it rains tomorrow.即使明天下雨,我也要去。 even if 和even though的意思为“即使”“纵使”有退一步设想的意味,多用于书面语中。
as Child as he is , he knows a lot .(表语)虽然他是一个孩子,但他懂得很多。Youngest as he is, he knows a lot. (表语)
(as让步状语从句中,提前作表语的名词和形容词最高级时,省冠词。)Cold as it is, (= Though it is cold,) the children play outdoors.虽然天气冷,但孩子们仍在户外玩。Much as he likes the bike, he won’t buy it.(状语)
Try as he might, he failed. (动词原形) as引出的状语从句多用于书面语,它比用though或although引导的从句,语气强,更有表现力,从句常放在句首,语序部分倒装。让步状语从句形式倒装:提前动词原形,表语,状语到主语前as, though/although,while都有虽然尽管之意,但是as必须倒装,though/although可倒可不倒,而while不能倒装。
no matter (who, what
when, where
which,how…) Do it no matter what others say.不管别人怎么说,尽管干。No matter how busy he was, he studied English every day.不管他多忙,他都每天坚持学习英语。 no matter……与 who-ever引导的让步状语从句意义基本一 样,no matter……引导的从句可是以位于主句前或主句后。
wh-ever (whatever whoever whenever whichever however) Whatever happens / may happen , we shall not lose heart.无论发生什么,我们都不要失去信心。Whoever comes, he will be welcome.无论谁来,都会受到欢迎。 wh-ever从句中的动词有时可以和may连用。判断wh-ever引导的是状语从句还是名词性从句的一点是,名词性从句,主句中一定有一个成分要在从句担任,一般从句与主句之间没有逗号。不可将no matter与wh—ever连用
比较状语从句 as…as not so/as…asthe same…assuch…as Mary is as old as my sister. 玛利和我姐姐一样大。He doesn’t run so (as) fast as Jack (does).他不如杰克跑得那样快。His book is the same as mine.他的书和我的一样。Henry is not such a good worker as Peter .享利这个工人不如彼得那样好。 连词表示同程度级的比较,
肯定句用as…as
否定句可用not as…as 或not so…asas和than引导的比较状语从句,从句主语为人称代词时可用主格或宾格。
Tom is as old as I/me.
than She has made greater progress this year than she did last year.她今年比去年进步更大。He bought fewer books than I (did).他买的书比我买的少。 表示不同程度之比较,主句中用比较级的形容词或副词。
the more …the more The more you read, the better you understand.你看的书越多,你懂得的就越多。The harder you work, the greater progress you will make.你工作越努力,你取得的进步就越大。The sooner, the better.越快越好。The warmer, the better.越暖和越好。 the more…the more 意思为越…越…,通常的语序为从句在前,主句在后,这两个the都是表示程度的副词,用在比较级的形容词或副词前面。句子意思明显,句子的主语和动词都可省略。
1
1
同课章节目录
