高中英语高考【讲语法】07 动词及动词时态(二)语法知识点梳理课件(全国通用)(24张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 高中英语高考【讲语法】07 动词及动词时态(二)语法知识点梳理课件(全国通用)(24张ppt) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-11-19 12:59:25 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共24张PPT)
动词的分类
动词的形式
动词短语
动词及动词时态
Lesson 4
动词时态
4
China has become the first country to land a spacecraft on the far side of the moon. The unmanned Chang’e-4 probe (探测器) — the name was inspired by an ancient Chinese moon goddess — 61 (touch) down last week in the South Pole-Aitken basin. Landing on the moon’s far side is 62 (extreme) challenging. Because the moon’s body blocks direct radio communication with a probe, China first had to put a satellite in orbit above the moon in a spot 63 it could send signals to the spacecraft and to Earth. The far side of the moon is of particular 64 (interesting) to scientists because it has a lot of deep craters (环形山), more so 65 the familiar near side. Chinese researchers hope to use the instruments onboard Chang’e-4 66 (find) and study areas of the South Pole-Aitken basin. "This really excites scientists," Carle Pieters, a scientist at Brown University, says, "because it 67 (mean) we have the chance to obtain information about how the moon 68 (construct)." Data about the moon’s composition, such as how 69 ice and other treasures it contains, could help China decide whether 70 (it) plans for a future lunar (月球的) base are practical.
谓语动词
副词
连词
代词
非谓语动词
介词
名词
被动语态
where
extremely
to find
interest
means
than
is constructed
much
its
touched
新高考全国卷I
谓语动词
副词
真题重现
In recent years some Inuit people in Nunavut 65 (report) increases in bear sightings around human settlements.
While running regularly can’t make you live forever, the review says it 64 (be) more effective at lengthening life than walking, cycling or swimming.
have reported
is
by now/up to now/ so far/ recently/ in the past/last few days
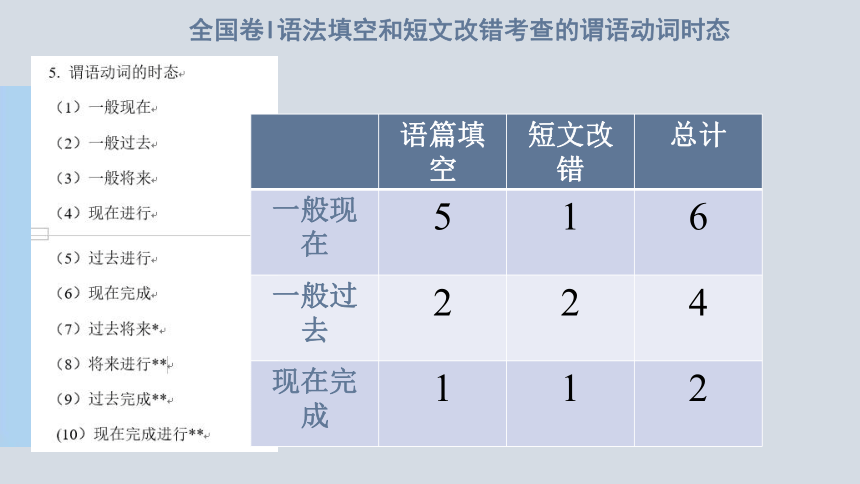
语篇填空 短文改错 总计
一般现在 5 1 6
一般过去 2 2 4
现在完成 1 1 2
全国卷I语法填空和短文改错考查的谓语动词时态
1. I wait for the bus every day.
2. I waited for the bus yesterday.
3. Maybe I will wait for the bus tomorrow.
4. I am waiting for the bus at the moment.
5. I was waiting for the bus when you called.
一般现在时
一般过去时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
6. I will be waiting for the bus this time tomorrow.
7. I have waited for the bus many times this week.
8. I have been waiting for the bus since 9 o’clock.
9. I had waited for the bus before I took a taxi.
10. I had been waiting for the bus for an hour when it finally arrived..
将来进行时
现在完成时
现在完成进行时
过去完成时
过去完成进行时
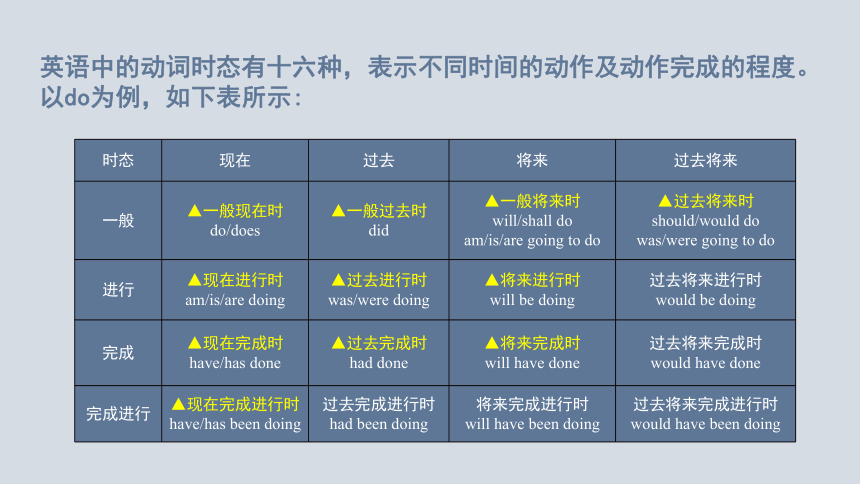
时态 现在 过去 将来 过去将来
一般 ▲一般现在时 do/does ▲一般过去时 did ▲一般将来时 will/shall do am/is/are going to do ▲过去将来时
should/would do
was/were going to do
进行 ▲现在进行时 am/is/are doing ▲过去进行时was/were doing ▲将来进行时 will be doing 过去将来进行时
would be doing
完成 ▲现在完成时 have/has done ▲过去完成时 had done ▲将来完成时 will have done 过去将来完成时
would have done
完成进行 ▲现在完成进行时 have/has been doing 过去完成进行时 had been doing 将来完成进行时 will have been doing 过去将来完成进行时would have been doing
英语中的动词时态有十六种,表示不同时间的动作及动作完成的程度。以do为例,如下表所示:
4.1 一般现在时
1. 一般现在时态表示经常性或习惯性的动作、状态或者主语目前的特征、性格或能力。
e.g. I go to school on foot every day.
Miss White speaks Chinese very well.
2. 表示客观事实、普遍真理或用在格言警句中。
e.g. Shanghai lies in the east of China.
3. 一些位移动词如:go, come, leave, start, move, arrive 等用于一般现在时可表示按规定、时间表、计划、安排将要发生的动作。通常有表示将来的时间状语。
e.g. The train leaves at five.
4. 以Here或 There开头的句子,说明正在发生的动作,常用一般现在时。
e.g. Here comes the bus!
5. 表示心理和认知类动作的常见动词,常用一般现在时,如:like, love, hate, dislike, want, need, hear, feel, see等。
e.g. The cup feels hot.
常用时间状语有 always, usually, often, sometimes, never, every week/day, once a week等。
4.2 一般过去时
1. 表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态.
e.g. Bob came across an old friend in the street the other day.
2. 表示过去习惯性或经常性的动作、行为,也可以用 used to do 来表达“过去常常”的概念。
e.g. Tony used to smoke a cigarette after dinner.
3. 表示过去连续发生的动作或平行并列的动作。
e.g. She entered the room, picked up a magazine and read it.
常用时间状语 yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week/year,
just now, an hour ago, the other day等。
My father worked there for three years.
He finished his paper during that period.
一般将来时表示将来的动作或状态,也可表示倾向和习惯性。
1. will / shall + 动词原形
e.g. I shall / will be forty years old next year.
4.3 一般将来时
2. be going to + 动词原形
(1) 表示(事先)已经决定或安排好要做的事。
e.g. I am going to do some washing tomorrow.
(2) 表示现在有迹象预示某事即将肯定或很可能发生(和个人的意志无关)。
e.g. Look at the clouds! It is going to rain.
e.g. Tomorrow will be Sunday.
Fish will die without water.
4. be about to + 动词原形
表示即将发生,正要做某事。常和 when引导的句子连用.
e.g. We were about to leave when it began to rain.
4.3 一般将来时
3. be to + 动词原形
(1) 表示按计划、安排要做的事。
e.g. She is to be married next month.
(2) 表示义务、责任等,应该做某事,必须做某事。
e.g. You are to be back by 9 o’clock ( = must / have to ).
You are to report to the police ( = should / ought to ).
常用时间状语 soon, tomorrow, next week, in a few minutes, the day after tomorrow 等。
表示从过去的某时间看将要发生的事情,通常用于宾语从句中。
e.g. He told me he would go to Beijing the next day.
4.4 过去将来时
2. 表示过去习惯性的动作.
e.g. Whenever he had time, he would help his mother with the housework.
过去将来时必须以过去作为参照物, 站在过去描述将来。常用时间状语有the next day/morning, the following month/week等。
1. would + 动词原形
2. was going to + 动词原形
e.g. He was going to leave when I came in.
4.5 现在进行时
1. 表示说话时正在进行的动作。
e.g. They are playing table tennis now.
2. 表示现阶段正在进行的动作(但说话时未必在进行)
e.g. I hear Mr. Green is writing a novel these days.
3. 现在进行时与always, constantly, continually, forever等频度副词连用,表示赞扬、责备、厌恶等感彩。
e.g. Tom is always throwing things about.
4. 一些位移动词如:go, come, leave, start, move, arrive 等用于现在进行时可表示按计划、安排将要发生的动作。通常有表示将来的时间状语。
e.g. He is leaving tomorrow.
常用时间状语有now, at this time,
at this moment, at present, these days等。
1. 表示过去某一时间点或一段时间正在进行的动作。
如:He was reading a novel at 9 o’clock yesterday morning.
2. 表示过去的某个动作发生的背景。
如:My brother fell while he was riding his bicycle and hurt himself.
3. 与always, constantly, continually, forever等频度副词连用,表示赞扬、责备、厌恶等感彩。
e.g. Tom was always losing his keys.
4.6 过去进行时
常用时间状语有then, at this time yesterday, at that time等。
进行时使用的注意事项:
1. be动词后跟表示活动、行为类的形容词作表语时,如果用于进行时,表示“短暂的行为或状态”。
I wasn’t sure if he was really interested or if he was just being polite. (出于礼貌假装感兴趣)
2. 英语中通常有五类动词不适宜用进行时态:
(1) 表示心理状态、情感的动词。如:love, hate, like, care, prefer等。
(2) 表示存在的状态的动词或短语。如:appear, exist, stand, seem, belong to等。
(3) 某些非延续性动词。如:accept, allow, complete, decide, receive等。
(4) 感官动词。如:see, hear, notice, feel, sound等。
(5) 表示占有与从属类动词。如:belong, contain, have, own, form等。
1. 表示过去的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。(强调“现在”的情况,表示已完成,因此不能和表示过去的时间状语连用)
e.g. They have arrived.
2. 表示从过去一直延续到现在的动作或状态。
e.g. He has lived here for ten years.
3. 用于时间和条件状语从句中,表示将来某时会完成的动作。
e.g. I’ll go home when I have finished my homework.
4.7 现在完成时
常用时间状语有 since+时间点, for+时间段, just, already, yet, before, never, ever
recently, lately, so far, in/over/during the past few years, up to now等。
My father worked there for three years. (for+时间段也可用于过去时)
He finished his paper during that period.
在完成时中,终止性动词不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,此时需要将终止性动词改为延续性动词或者状态动词。
如: Jim has left Jinan for 3 years.
Jim has been away from Jinan for 3 years.
4.7 现在完成时
延续动词:能够延续的动作或状态,如live, work, study, learn, sleep等,
可以和表示一段时间的状语连用, 比如for+时间段,since+过去的时间点等。
如:I have worked in this company for more than twenty years.
非延续动词:短暂性动词、瞬间动词,表示不能延续的动作,这类动词有: go, come, arrive, leave, begin, start, join, marry 等,它不能和一段时间连用。
易错点:
(× )
(√)
1. 表示将来某一时刻或某一阶段正在进行的动作。
如:Tom’s family will be enjoying their holiday this time next week.
2. 表示一种客观上要发生的情况,可以表示计划、安排或预测。
如:After you take the medicine, you will be feeling much better.
(表示预测)
Please come tomorrow afternoon. I’ll be having a meeting tomorrow morning.
(表示计划安排)
The train won’t be leaving until one o’clock.
4.8 将来进行时
将来进行时一般有明显的时间状语,如soon, at this time tomorrow 等。
1. 表示从过去到现在这段时间里一直在进行某动作,动作可能刚刚终止,也可能仍然要继续下去。
如:It has been raining all day.
→ It has rained all day. (这种情况下现在完成进行时可以和现在完成时换用。)
He has read the book. (“读书”的动作已经完成,结束了。)
He has been reading the book. (“读书”的动作还在进行着。)
4.9 现在完成进行时
不用时间状语的情况下,现在完成进行时表示动作仍在进行, 而现在完成时则表示动作已结束。
4.10 过去完成时
1. 表示过去的某个时间或动作之前已发生或完成的动作或状态。(过去的过去)
如:By the end of last term, we had learned 5,000 new words.
2. 表示动作在过去某一时间之前开始,一直延续到过去的这一时间,而且还可能继续下去的动作,常和for, since构成的短语或引导的从句连用。
By the time I left the school, he had taught the class for 3 years.
He said he had made great progress since he came here.
3. 表示原打算做但事实上并未做成某事,常见的动词有hope, want, intend, plan, expect, think等,是一种虚拟用法。
如:I had intended to see you, but I got a bad cold.
构成:助动词had+过去分词
常用时间状语有by 9 o’clock last night, by the end of ….等。
4.10 过去完成时
4.用在 “It was the first/second/third…time that…”
e.g. It was the first time we had spoken together.
5. 用于虚拟语气表示过去事实相反。
If he had seen you yesterday, he would have asked you about it.
I should have called you if I had known your telephone number.
将来完成时态表示在将来某一时间以前已经完成或一直持续的动作。
e.g. By the end of next year, we will have learned 2000 English words.
4.11 将来完成时
常用时间状语有:by 8 o’clock tomorrow morning, by the end of next week, by the time+从句(从句用一般现在时表将来)。
My cousin Ted_____ (like)watching TV very much in the past.
When Tracy’s hair was falling out after her treatment for cancer, Jenny _______ (want)to do something to help.
She knew Tracy ________ (do) not like being the only one without hair.
The computer can even help us do some shopping online, have a chat and _______ (make)friends with strengers.
Since it ________ (appear), our life has become much easier than before.
wanted
did
make
appeared
谓语动词时态的判断应该注意:
本句时间词,主从句的时态,上下句时态。
liked
6 .He always _____ (go) to school by bus.
7.The earth _____(be) round.
8.(2010 ) Jim,my close friend,moved to Beijing years ago,
and I__________ him since then.( see)
9. I ______ (make)some new friends during the holiday.
10.(2018广东)It is said that the number of forest parks in
Guangdong_______ (increase)to more than 1000 so far.
goes
is
have seen
have maken
has increased
无时间标志词
瞻前顾后找平行
语境提示定时态
主句从句相对应
并列谓语:and 、but、 or 、 both...and... 、either...or...、 neither...nor... 、
not only...but(also)...
联系上下文前后句 时态
主过从过 状语从句:主将从现
动词的分类
动词的形式
动词短语
动词及动词时态
Lesson 4
动词时态
4
China has become the first country to land a spacecraft on the far side of the moon. The unmanned Chang’e-4 probe (探测器) — the name was inspired by an ancient Chinese moon goddess — 61 (touch) down last week in the South Pole-Aitken basin. Landing on the moon’s far side is 62 (extreme) challenging. Because the moon’s body blocks direct radio communication with a probe, China first had to put a satellite in orbit above the moon in a spot 63 it could send signals to the spacecraft and to Earth. The far side of the moon is of particular 64 (interesting) to scientists because it has a lot of deep craters (环形山), more so 65 the familiar near side. Chinese researchers hope to use the instruments onboard Chang’e-4 66 (find) and study areas of the South Pole-Aitken basin. "This really excites scientists," Carle Pieters, a scientist at Brown University, says, "because it 67 (mean) we have the chance to obtain information about how the moon 68 (construct)." Data about the moon’s composition, such as how 69 ice and other treasures it contains, could help China decide whether 70 (it) plans for a future lunar (月球的) base are practical.
谓语动词
副词
连词
代词
非谓语动词
介词
名词
被动语态
where
extremely
to find
interest
means
than
is constructed
much
its
touched
新高考全国卷I
谓语动词
副词
真题重现
In recent years some Inuit people in Nunavut 65 (report) increases in bear sightings around human settlements.
While running regularly can’t make you live forever, the review says it 64 (be) more effective at lengthening life than walking, cycling or swimming.
have reported
is
by now/up to now/ so far/ recently/ in the past/last few days
语篇填空 短文改错 总计
一般现在 5 1 6
一般过去 2 2 4
现在完成 1 1 2
全国卷I语法填空和短文改错考查的谓语动词时态
1. I wait for the bus every day.
2. I waited for the bus yesterday.
3. Maybe I will wait for the bus tomorrow.
4. I am waiting for the bus at the moment.
5. I was waiting for the bus when you called.
一般现在时
一般过去时
一般将来时
现在进行时
过去进行时
6. I will be waiting for the bus this time tomorrow.
7. I have waited for the bus many times this week.
8. I have been waiting for the bus since 9 o’clock.
9. I had waited for the bus before I took a taxi.
10. I had been waiting for the bus for an hour when it finally arrived..
将来进行时
现在完成时
现在完成进行时
过去完成时
过去完成进行时
时态 现在 过去 将来 过去将来
一般 ▲一般现在时 do/does ▲一般过去时 did ▲一般将来时 will/shall do am/is/are going to do ▲过去将来时
should/would do
was/were going to do
进行 ▲现在进行时 am/is/are doing ▲过去进行时was/were doing ▲将来进行时 will be doing 过去将来进行时
would be doing
完成 ▲现在完成时 have/has done ▲过去完成时 had done ▲将来完成时 will have done 过去将来完成时
would have done
完成进行 ▲现在完成进行时 have/has been doing 过去完成进行时 had been doing 将来完成进行时 will have been doing 过去将来完成进行时would have been doing
英语中的动词时态有十六种,表示不同时间的动作及动作完成的程度。以do为例,如下表所示:
4.1 一般现在时
1. 一般现在时态表示经常性或习惯性的动作、状态或者主语目前的特征、性格或能力。
e.g. I go to school on foot every day.
Miss White speaks Chinese very well.
2. 表示客观事实、普遍真理或用在格言警句中。
e.g. Shanghai lies in the east of China.
3. 一些位移动词如:go, come, leave, start, move, arrive 等用于一般现在时可表示按规定、时间表、计划、安排将要发生的动作。通常有表示将来的时间状语。
e.g. The train leaves at five.
4. 以Here或 There开头的句子,说明正在发生的动作,常用一般现在时。
e.g. Here comes the bus!
5. 表示心理和认知类动作的常见动词,常用一般现在时,如:like, love, hate, dislike, want, need, hear, feel, see等。
e.g. The cup feels hot.
常用时间状语有 always, usually, often, sometimes, never, every week/day, once a week等。
4.2 一般过去时
1. 表示过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态.
e.g. Bob came across an old friend in the street the other day.
2. 表示过去习惯性或经常性的动作、行为,也可以用 used to do 来表达“过去常常”的概念。
e.g. Tony used to smoke a cigarette after dinner.
3. 表示过去连续发生的动作或平行并列的动作。
e.g. She entered the room, picked up a magazine and read it.
常用时间状语 yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week/year,
just now, an hour ago, the other day等。
My father worked there for three years.
He finished his paper during that period.
一般将来时表示将来的动作或状态,也可表示倾向和习惯性。
1. will / shall + 动词原形
e.g. I shall / will be forty years old next year.
4.3 一般将来时
2. be going to + 动词原形
(1) 表示(事先)已经决定或安排好要做的事。
e.g. I am going to do some washing tomorrow.
(2) 表示现在有迹象预示某事即将肯定或很可能发生(和个人的意志无关)。
e.g. Look at the clouds! It is going to rain.
e.g. Tomorrow will be Sunday.
Fish will die without water.
4. be about to + 动词原形
表示即将发生,正要做某事。常和 when引导的句子连用.
e.g. We were about to leave when it began to rain.
4.3 一般将来时
3. be to + 动词原形
(1) 表示按计划、安排要做的事。
e.g. She is to be married next month.
(2) 表示义务、责任等,应该做某事,必须做某事。
e.g. You are to be back by 9 o’clock ( = must / have to ).
You are to report to the police ( = should / ought to ).
常用时间状语 soon, tomorrow, next week, in a few minutes, the day after tomorrow 等。
表示从过去的某时间看将要发生的事情,通常用于宾语从句中。
e.g. He told me he would go to Beijing the next day.
4.4 过去将来时
2. 表示过去习惯性的动作.
e.g. Whenever he had time, he would help his mother with the housework.
过去将来时必须以过去作为参照物, 站在过去描述将来。常用时间状语有the next day/morning, the following month/week等。
1. would + 动词原形
2. was going to + 动词原形
e.g. He was going to leave when I came in.
4.5 现在进行时
1. 表示说话时正在进行的动作。
e.g. They are playing table tennis now.
2. 表示现阶段正在进行的动作(但说话时未必在进行)
e.g. I hear Mr. Green is writing a novel these days.
3. 现在进行时与always, constantly, continually, forever等频度副词连用,表示赞扬、责备、厌恶等感彩。
e.g. Tom is always throwing things about.
4. 一些位移动词如:go, come, leave, start, move, arrive 等用于现在进行时可表示按计划、安排将要发生的动作。通常有表示将来的时间状语。
e.g. He is leaving tomorrow.
常用时间状语有now, at this time,
at this moment, at present, these days等。
1. 表示过去某一时间点或一段时间正在进行的动作。
如:He was reading a novel at 9 o’clock yesterday morning.
2. 表示过去的某个动作发生的背景。
如:My brother fell while he was riding his bicycle and hurt himself.
3. 与always, constantly, continually, forever等频度副词连用,表示赞扬、责备、厌恶等感彩。
e.g. Tom was always losing his keys.
4.6 过去进行时
常用时间状语有then, at this time yesterday, at that time等。
进行时使用的注意事项:
1. be动词后跟表示活动、行为类的形容词作表语时,如果用于进行时,表示“短暂的行为或状态”。
I wasn’t sure if he was really interested or if he was just being polite. (出于礼貌假装感兴趣)
2. 英语中通常有五类动词不适宜用进行时态:
(1) 表示心理状态、情感的动词。如:love, hate, like, care, prefer等。
(2) 表示存在的状态的动词或短语。如:appear, exist, stand, seem, belong to等。
(3) 某些非延续性动词。如:accept, allow, complete, decide, receive等。
(4) 感官动词。如:see, hear, notice, feel, sound等。
(5) 表示占有与从属类动词。如:belong, contain, have, own, form等。
1. 表示过去的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。(强调“现在”的情况,表示已完成,因此不能和表示过去的时间状语连用)
e.g. They have arrived.
2. 表示从过去一直延续到现在的动作或状态。
e.g. He has lived here for ten years.
3. 用于时间和条件状语从句中,表示将来某时会完成的动作。
e.g. I’ll go home when I have finished my homework.
4.7 现在完成时
常用时间状语有 since+时间点, for+时间段, just, already, yet, before, never, ever
recently, lately, so far, in/over/during the past few years, up to now等。
My father worked there for three years. (for+时间段也可用于过去时)
He finished his paper during that period.
在完成时中,终止性动词不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,此时需要将终止性动词改为延续性动词或者状态动词。
如: Jim has left Jinan for 3 years.
Jim has been away from Jinan for 3 years.
4.7 现在完成时
延续动词:能够延续的动作或状态,如live, work, study, learn, sleep等,
可以和表示一段时间的状语连用, 比如for+时间段,since+过去的时间点等。
如:I have worked in this company for more than twenty years.
非延续动词:短暂性动词、瞬间动词,表示不能延续的动作,这类动词有: go, come, arrive, leave, begin, start, join, marry 等,它不能和一段时间连用。
易错点:
(× )
(√)
1. 表示将来某一时刻或某一阶段正在进行的动作。
如:Tom’s family will be enjoying their holiday this time next week.
2. 表示一种客观上要发生的情况,可以表示计划、安排或预测。
如:After you take the medicine, you will be feeling much better.
(表示预测)
Please come tomorrow afternoon. I’ll be having a meeting tomorrow morning.
(表示计划安排)
The train won’t be leaving until one o’clock.
4.8 将来进行时
将来进行时一般有明显的时间状语,如soon, at this time tomorrow 等。
1. 表示从过去到现在这段时间里一直在进行某动作,动作可能刚刚终止,也可能仍然要继续下去。
如:It has been raining all day.
→ It has rained all day. (这种情况下现在完成进行时可以和现在完成时换用。)
He has read the book. (“读书”的动作已经完成,结束了。)
He has been reading the book. (“读书”的动作还在进行着。)
4.9 现在完成进行时
不用时间状语的情况下,现在完成进行时表示动作仍在进行, 而现在完成时则表示动作已结束。
4.10 过去完成时
1. 表示过去的某个时间或动作之前已发生或完成的动作或状态。(过去的过去)
如:By the end of last term, we had learned 5,000 new words.
2. 表示动作在过去某一时间之前开始,一直延续到过去的这一时间,而且还可能继续下去的动作,常和for, since构成的短语或引导的从句连用。
By the time I left the school, he had taught the class for 3 years.
He said he had made great progress since he came here.
3. 表示原打算做但事实上并未做成某事,常见的动词有hope, want, intend, plan, expect, think等,是一种虚拟用法。
如:I had intended to see you, but I got a bad cold.
构成:助动词had+过去分词
常用时间状语有by 9 o’clock last night, by the end of ….等。
4.10 过去完成时
4.用在 “It was the first/second/third…time that…”
e.g. It was the first time we had spoken together.
5. 用于虚拟语气表示过去事实相反。
If he had seen you yesterday, he would have asked you about it.
I should have called you if I had known your telephone number.
将来完成时态表示在将来某一时间以前已经完成或一直持续的动作。
e.g. By the end of next year, we will have learned 2000 English words.
4.11 将来完成时
常用时间状语有:by 8 o’clock tomorrow morning, by the end of next week, by the time+从句(从句用一般现在时表将来)。
My cousin Ted_____ (like)watching TV very much in the past.
When Tracy’s hair was falling out after her treatment for cancer, Jenny _______ (want)to do something to help.
She knew Tracy ________ (do) not like being the only one without hair.
The computer can even help us do some shopping online, have a chat and _______ (make)friends with strengers.
Since it ________ (appear), our life has become much easier than before.
wanted
did
make
appeared
谓语动词时态的判断应该注意:
本句时间词,主从句的时态,上下句时态。
liked
6 .He always _____ (go) to school by bus.
7.The earth _____(be) round.
8.(2010 ) Jim,my close friend,moved to Beijing years ago,
and I__________ him since then.( see)
9. I ______ (make)some new friends during the holiday.
10.(2018广东)It is said that the number of forest parks in
Guangdong_______ (increase)to more than 1000 so far.
goes
is
have seen
have maken
has increased
无时间标志词
瞻前顾后找平行
语境提示定时态
主句从句相对应
并列谓语:and 、but、 or 、 both...and... 、either...or...、 neither...nor... 、
not only...but(also)...
联系上下文前后句 时态
主过从过 状语从句:主将从现
