2023届高三英语二轮复习被动语态复习课件(共33张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023届高三英语二轮复习被动语态复习课件(共33张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-11-21 21:04:28 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共33张PPT)
被动语态
1
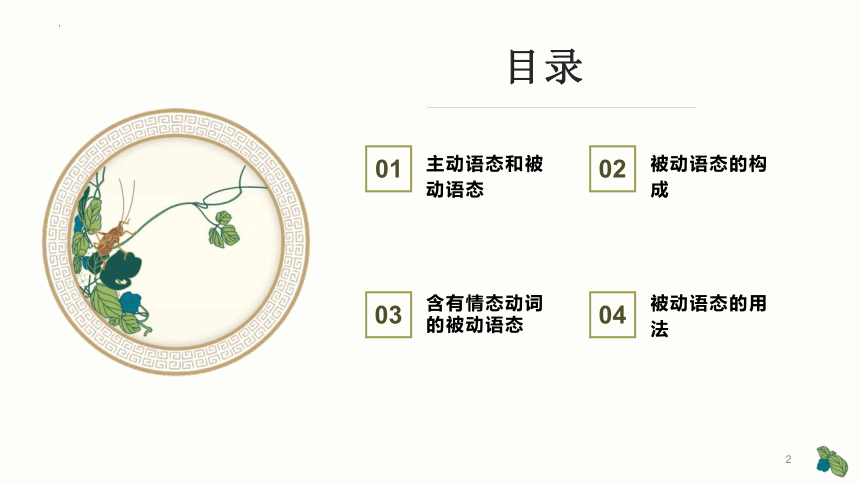
目录
含有情态动词的被动语态
03
被动语态的用法
04
主动语态和被动语态
01
被动语态的构成
02
2
主动语态和被动语态
1. 英语动词有两种语态,即主动语态和被动语态。
2. 当主语为动作的执行者时,谓语的形式为主动语态。
3. 当主语为动作的承受者时,谓语的形式为被动语态。
例如:
Many people speak English. (主动语态,句子的主语many people是动作speak的执行者。
English is spoken by many people. (被动语态,句子的主语English是动作speak的承受者)
Bell invented the telephone in 1876.(主动语态)
The telephone was invented by Bell in 1876. (被动语态)
3
被动语态的用法
1. 当不知道动作的执行者是谁时。如:
His bike has been stolen. 他的自行车被人偷了。(不知道是谁偷的)
2. 用于动作执行者泛指或者不言而明时。如:
Not a book in the library has been taken away. 图书馆里的书没有一本被拿走。(没人拿书,泛指)
3. 用于可以说出动作执行者是谁但强调的是动作的承受者时。如:
The computer was repaired by my son. 电脑被我儿子修好了。
4. 用于出于委婉、礼貌而避免提及自己或对方时。如:
Enough has been said here on this question. 这个问题已经说得够多的了。(意指不要再说下去了)
4
被动语态的用法
5. 用于文章标题、广告、新闻中(此时常会省略be的被动语态)。如:
Renmin Road blocked. 人民路堵塞了。
6. 当动作的执行者不是人时。如:
Many houses were washed away the storm. 许多房子被暴风雨冲走了。
7. 用于商务书信中书信起草人代表公司时。如:
You letter has been received. 你的来信已收到。
5
不能用于被动语态的动词
1. 不及物动词:字典里词后标有vi.的就是不及物动词.不及物动词后不能直接跟有动作的对象(即宾语).若要跟宾语,必须先在其后添加上某个介词。如:appear、come、go、get、fall、feel、keep、look等
2. 系动词:在英语中系动词的主要功能就是把表语和主语联系在一起,常见的系动词有be、look、turn、feel、get、keep、stay等。
3. 一些及物动词:
1) 部分静态动词(表感觉、情感、相互关系等)
表示拥有或者没有的动词,如:表示拥有的(have, own, possess), hold(容纳), contain(包含), belong to(属于), lack(缺少)等。
表示“适合“含义的:suit, fit, become (适合,与......相称的)
表示”相似、等同“含义的:equal, resemble, look like, mean等。
表示”继续、持续“含义的:last
表示”花费“含义的:cost
6
不能用于被动语态的动词
表示”明白“含义的,如:follow, get, catch, take等。
表示”同意、介意“含义的,如:agree with, mind等。
2)部分短暂性的动词
表示位置移动的动词:leave, arrive at/in, reach, enter, walk into, go into, jump等。这些虽然是及物动词,但是变成被动语态是讲不能的,也不能换成被动语态。比如:
I arrived at home late last night. 我昨天很晚到家。不能说成:
Home was arrived at by me late last night.
7
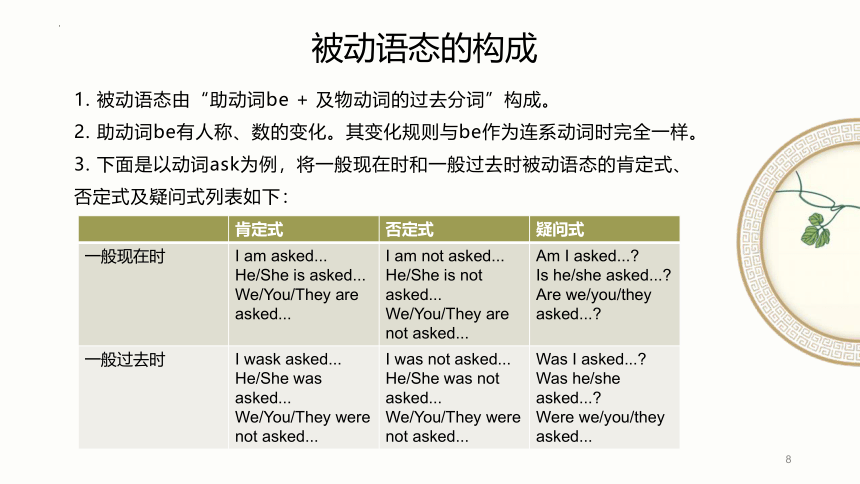
被动语态的构成
1. 被动语态由“助动词be + 及物动词的过去分词”构成。
2. 助动词be有人称、数的变化。其变化规则与be作为连系动词时完全一样。
3. 下面是以动词ask为例,将一般现在时和一般过去时被动语态的肯定式、否定式及疑问式列表如下:
肯定式 否定式 疑问式
一般现在时 I am asked... He/She is asked... We/You/They are asked... I am not asked... He/She is not asked... We/You/They are not asked... Am I asked...
Is he/she asked...
Are we/you/they asked...
一般过去时 I wask asked... He/She was asked... We/You/They were not asked... I was not asked... He/She was not asked... We/You/They were not asked... Was I asked...
Was he/she asked...
Were we/you/they asked...
8
被动语态的构成
9
8种基本时态的被动语态:
1. 一般现在时的被动语态:am(is,are) + 过去分词
2. 一般过去时的被动语态:was(were) + 过去分词
3. 一般将来时的被动语态:will be + 过去分词
4. 过去将来时的被动语态:would be + 过去分词
5. 现在进行时的被动语态:am(is,are) being + 过去分词
6. 过去进行时的被动语态:was(were) being + 过去分词
7. 现在完成时的被动语态:has(have) been + 过去分词
8. 过去完成时的被动语态:had been + 过去分词
一般现在时的被动语态
10
1. 肯定句结构: 主语+am/is/are+动词过去分词 (+by+动作执行者)
English is used by a lot of people in the world.
英语被全世界的很多人使用。
The flowers are bought by the girl. 这些花是这个女孩买的。
2. 否定句结构:主语+am not/isn’t/aren’t + 动词分词(+by+动作执行者)
The door isn’t made of wood. 这扇门不是木头做的。
The flowers aren’t bought by the girl. 这些花不是这个女孩买的。
3. 一般疑问句结构:Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Is the door made of wood 这扇门是木头做的吗?
Is the flowers are bought by the girl?这些花是这个女孩买的吗?
4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词+am/is/are + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Where is the paper used 被用在哪里?
When is the room often cleaned 房间通常是什么时候打扫的?
一般过去时的被动语态
11
1. 肯定句结构: 主语+was/were+动词过去分词 (+by+动作执行者)
He was called a hero. 他被称为是一位英雄。
We were allowed to go home early。我们被允许早早回家。
2. 否定句结构:主语+wasn’t / weren’t + 动词分词(+by+动作执行者)
He wasn’t called a hero. 他没被称为是一位英雄。
We weren’t allowed to go home early。我们不被允许早早回家。
3. 一般疑问句结构:Was / Were + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Was he called a hero 他被称为是一位英雄吗?
Were we allowed to go home early?允许我们早早回家吗?
4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词+was/were + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Who was called a hero 谁被称为英雄?
When was he called a hero? 他什么时候被称为英雄?
When were the flowers bought 这些花什么时候买的
一般将来时的被动语态
12
1. 肯定句结构: 主语+ will be +动词过去分词 (+by+动作执行者)
主语+ am/is/are +动词过去分词 (+by+动作执行者)
His homework will be finished tomorrow. 他的作业明天会完成。
The flowers will be bought tomorrow。花明天会买。
2. 否定句结构:主语+ won’t be + 动词分词(+by+动作执行者)
主语+ am not/isn’t/aren’t + 动词分词(+by+动作执行者)
The monkey won’t be put in the cage.
The monkey is not going to be put in the cage.
3. 一般疑问句结构:Was / Were + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Will the house be built next year / Is the house going to be built next year
房子将在明年建吗?
4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句,特殊疑问词第一个字母大写。
When will the house be built / When is the house going to be built
房子将于什么时候被建?
过去将来时的被动语态
13
**过去将来时:
1. 过去将来时是表示过去将要发生/打算要做某事,一般用在宾语从句,且这个宾语从句前面主句的谓语动词常为一般过去时。
2. 过去将来时是指从过去某一时刻看以后要发生的动作或状态,另外,过去将来时常可用来表示过去习惯性的动作,此时,不管是什么人称,一律用would。
被动语态是表主语是承受者。
过去将来时的被动语态常出现在英语间接引语中
2. 肯定结构:主语是第一人称时用 should be + 过去分词构成
主语是第二人称、第三人称时用 would be + 过去分词构成
was / were + going to be + 过去分词
I should be told about the thing. 应该告诉我这件事。
He would be told about the thing. 应该告诉他这件事。
He said that something would be needed to finish the work. 他说要完成这项任务,需要一些条件。
It was said that they would be selected by lottery. 据说他们将抽签选出。
过去将来时的被动语态
14
3. 否定结构:should not be / would not be + 过去分词;wasn’t / weren’t going to be + 过去分词
His brother said that the homework wouldn't be finished by him in half an hour. 他哥说这个工作他半个小时应该完成不了。
They said the building was not going to be finished the next month. 他们说大楼下个月完不了工。
He said I was not going to be wanted on the phone.他说没人会打电话给我。
4. 一般疑问结构:Would / Should + 主语 + be + 过去分词; Was / Were + 主语 + going to be + 过去分词。
Would the machine be repaired by these workers the next day
这部机器工人是第二天才修理的吗?
Were the flowers going to be bought by the girl the next day 这些花是这个女孩第二天才买的吗?
5. 特殊疑问结构:特殊疑问词 + 一般疑问句。
When were the flowers going to be bought by the girl 这些花这个女孩什么时候去买?
现在进行时的被动语态
15
1. 定义:表示现在某个被动的动作正在进行中,表示“某人/某事此时此刻正在被...”,主语是动作或状态的承受者。
2. 肯定结构:主语 + am / is / are being +动词的过去分词
The question is being discussed at the meeting. 这个问题现在在会上被讨论。
Three new pedestrian bridegs are being built at the moment. 三条人行天桥正在兴建中。
3. 否定结构:主语 + am / is / are + not + being + 动词的过去分词
The books are not being borrowed at present. 这些书现在没有被借出。
The tiger is not being set free now. 这只老虎现在还不能被放出。
.
4. 一般疑结构:Am / Is / Are + 主语 + being + 动词的过去分词
Is a new classroom building being built in your school 你们学校正在建一幢新的教学楼吗?
Are many new cars being sold to oversea markets 很多新汽车正在销往国外市场吗?
现在进行时的被动语态
16
5. 特殊疑问结构:疑问词 + am / is / are + 主语 + being + 动词的过去分词。
What is being done to the computer 现在对这台电脑要采取什么措施?
How many houses are being built in our village 我们村现在正在建多少房子?
过去进行时的被动语态
17
1. 定义:过去的某个时间正在发生或正在进行的被动的动作。
2. 肯定结构:主语 + was / were + being + 动词的过去分词。
A new school was being built at that time. 当时正在建一所新的学校。
Some trees were being planted when she arrived. 当她到达的时候正在种着很多树。
3. 否定结构:主语 + was / were + not + being + 动词的过去分词。
A new school was not being built at that time. 当时没有在建一所新的学校。
Some trees were not being planted when she arrived. 当她到达的时候没有在种着很多树。
4. 一般疑问结构:was / were + 主语 + being + 动词的过去分词?
Was a new classroom building being put up in their school just then 他们学校当时正在建一幢新的教学楼吗?
5. 特殊疑问结构:特殊疑问词 + was / were + being + 动词的过去分词
What was being done to the machine 对这台机器采取了什么措施?
现在完成时的被动语态
18
1. 现在完成时的被动语态同它的主动语态一样,强调过去的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,通常与 already, yet, just, never, recently等副词连用。
或表示一个被动的动作或状态开始于过去,持续到现在,并可能持续下去,常与for或since等引导的时间状语连用,或用与How long… 的句型中。
2. 肯定结构:have/has+been+done
The new schools have been set up. 新学校都已经建成了。
The experiment has been done successfully. 这个实验做得很成功。
3. 否定结构:have/has+not+been+done
The books have not been borrowed by the students. 那些书还没有被学生借走。
Tom's novel has not been published. 汤姆的小说还没有被出版。
现在完成时的被动语态
19
4. 一般疑问结构:have/has + 主语+not+been+done?
—Have the letters been posted 信已经寄出去了吗? —Yes, they have. 是的,已寄出了。
—Has your bike been repaired 你的自行车修好了吗? —No, it hasn't. 不,还没有被修好。
5. 特殊疑问结构:疑问词+have/has+been+done
How long have the machines been repaired?这些机器已被修好多长时间了?
Who has been invited 谁受到了邀请?
过去完成时的被动语态
20
1. 定义:表示在过去某一时刻或某一动作之前发生的动作或状态,句中常用by,before,until,when等词引导时间状语。
We had built five new buildings by the end of last year. 直至去年年底,我们已经建了五幢新的大楼。
2. 肯定结构:主语+ had been done +其他成分
As of last September, about 20 companies have been closed due to pandemic.
直至去年九月份,已经有20家公司因为疫情的原因倒闭了。
3. 否定结构:主语+ had not been done +其他成分
Several books had not been read by his twenties. 直到他二十几岁他还有几本书没有看。
4. 一般疑问句结构:had +主语+ been done +其他成分
Had his friends been invited to his party until last night 直到昨晚他的朋友都被邀请过来参加他的舞会了吗?
过去完成时的被动语态
21
5. 特殊疑问句结构:疑问词+ had +主语+ been done +其他成分
When had his friends been invited to his party 他的朋友是什么时候被邀请去参加他的舞会的?
6. 过去完成时的被动语态常用于以下情况:
(1)表示过去某一时间以前已经完成的动作,常与by, before等引导的时间状语连用。
By the time he got to the school, the first period had been finished.
The classroom hadn't been cleaned before the teacher came.
How many buildings had been destroyed when the hurricane ended
Had the new plan been discussed before the meeting
(2)在 told, said, knew, heard, thought等动词之后的宾语从句中,若表示过去某一被动动作时,用过去完成时。
They said the production costs had been reduced.
The girl was reminded that her homework had not been handed in.
过去完成时的被动语态
22
The media reported more than 1,000 people had been killed in the storm.
(3)根据语意可以判断出动作先后的被动语态,用过去完成时。
As the assignment had been done, he went on to search the Internet.
He did what he had been told to.
另:当从句由 after,before,when或 as soon as引导时,主句和从句都可以用一般过去时。
When he arrived, he called her.
They locked the door before they left.
含有情态动词的被动语态
1. 含有情态动词的被动语态由”情态动词 + be + 及物动词的过去分词“构成。其时态及句型的变化仅由情态动词完成,“be+过去分词”部分不变。
例如:
Teenagers should be allowed to make their decisions.
Your room must be cleaned every day.
The trees may be planted behind the house.
This game can be played in the winter.
2. 含有情态动词的被动语态变为否定句时,应在情态动词后面加not;变为一般疑问句时,应将情态动词移到句首。
Waste paper should not be thrown here. 废纸不应该扔在这里。
Should it be done by Li Ming? 这件事应该是李明干吗?
23
含有情态动词的被动语态
3. 一般疑问句结构:情态动词 + 主语 + be + 动词的过去分词 + 其他成分。注意只提前情态动词,不提前be。
May she be critized by her father 她被她爸爸批评了吗?
4. 含有情态动词的主动句与被动句之间的转换:把主动句中的宾语变为被动句的宾语,主动句的谓语动词变成“情态动词+be+动词的过去分词”的形式。主动句中的主语变成被动句中的宾语(注意不同成分的代词之间的转换)。如果在不要求强调动作的执行者时,by+宾语可以省略。如:
She must clean the room on weekends.
The room must be cleaned (by her) on weekends.
she在主动句中充当主语,但在被动句中充当宾语,改为宾格的她-her
24
将主动语态变被动语态应注意几个特殊情况:
1.含双宾语的主动结构变为被动结构时,有两种方法:
①将间接宾语变为主语,直接宾语保持不变;
②将直接宾语变为主语,间接宾语用介词to或for引导。例如:
① He told us a story.(变被动语态)
→We were told a story(by him).或:A story was told to
us by him.
② Her mother gave her a new pen.(变被动语态)
A new pen was given to her by her mother.或 She was given a new pen by her mother.
2.短语动词的被动语态:在变为被动语态时,要将短语动词视为一个整体,其后的介词或副词不能省去。例如:
This dictionary mustn't be taken away from the library.
“直接宾语,是一个英语语法用语,是指谓语动词的承受者,可由名词、代词、数词、不定式充当。双宾语由直接宾语和间接宾语组成。间接宾语表示谓语动作的方向(对谁做)或动作的目标(为谁做),间接宾语紧接在谓语动词后,但它在句子中不能单独存在,并且能和直接宾语
组成双宾语。”
25
将主动语态变被动语态应注意几个特殊情况
3.含有复合宾语的主动结构变被动结构时,通常将宾语变为被动句的主语,而宾语补足语就成为主语补足语。注意:省略to的不定式作宾补时,不定式符号to必须补上。例如:
Someone saw him swim in Qianling Lake yesterday.(变被动如下)
He was seen to swim in Qianling Lake yesterday.
4.不定式的被动结构:动词不定式的被动语态为“to be +过去分词”。例如:
The radio says a wild animal zoo is to be built in our city.
5.以疑问代词开头的疑问句转换成被动句时要注意词序:应将主动句中的疑问代词改为介词by的宾语,但仍然放在句子开头。例如:
Who has broken the cup?(改为被动语态)
→By whom has the cup been broken?
26
被动语态和过去分词作表语的区别
1)含义不同:被动语态强调动作,重点说明动作由谁完成、怎样完成;而过去分词作表语通常用来描写情景,叙述人或事物的特征及所处的状态。试比较:
The window is broken.窗子破了。(系表结构)
The window is broken by him.窗子被他打破了。(被动语态)
2)用法不同:过去分词作表语时可以被 so,very,too等程度副词修饰,而被动语态则不能用so,very,too修饰,而需用much,very much,so much,too much修饰。试比较:
He was very interested in science.他对科学有极大兴趣。(系表结构)
I was so much surprised at the scene that I didn't know what to do.我被那种场面搞得大吃一惊,不知所措。(被动语态)
27
初中教材中与被动语态相关的句型
1.be covered with被……覆盖
2.be made of由……制作(发生物理变化)
be made from由……制作(发生化学变化)
be made in由(某地)制造
be made by被(某人)制造
3.be used for被用来……
be used as被当作(作为)……来使用
be used to do sth.被用来做某事
4.It is said that...据说……
It is hoped that...希望……
It is well known that...众所周知……例如:
28
几种特殊的被动语态
1.带不定式的被动语态。
The child is sure to be punished for that. 那个孩子肯定会因为那件事受罚的。
2. 带介词的动词短语的被动语态。
Such a thing has never been heard of. 这件事前所未闻。
3. 带副词的动词短语的被动语态。
The radio has just been turned off. 收音机刚刚被关上。
4. 当sell, wash, clean, run, ride, wear, write等动词若有状语well, easily, badly来修饰时,用主动形式表达被动意义。
The pen writes well. 这枝钢笔写字流畅。
The book sells well. 这本书很畅销
29
练习
1. One or two man-made satellites in our country every year.
A. have been sent up B.will be sent up C.is sent up D.are sent up
2. Our TV set yesterday.
A. is repaire B.was repaired C.had been reparied D.would be reparied
3. A new building in our school next year.
A. will be built B. is built C. is being built D. has been built
4. Many books on science since I went to college.
A. were bought B.have been bought C. will be bought D.are bought
5. A wonderful English talk by Mr Liu tomorrow.
A. has been given B. is given C. is being given D. will be given
6. How the Great Pyramid(金字塔) many years ago without modern machines.
A. is,built B.would,be built C.have,been built D.was, built
7. Jack often does things foolishly, so he sometimes by others.
A.is,laughed B.is,laughed at C.was,laughed D.has, been laughed at
8. Such films by children like you.
A. must be not seen B.must not be see C.must not seen D.must not be seen
30
练习
9. Trees in winter but in spring.
A.not can be planted B.can be not planted C.can’t be planted D.can not be plant
10. In the past ten years, a lot of new buildings in our city.
A. are put up B. have put up C. have been put D. have been put up
11. The streets many times every day.
A. clean B.cleans C.cleaned D.are cleaned
12. The 30th Olympic Games in London in 2012.
A. held B. is hold C. will hold D. will be held
13. --The pizza by my mum just now. Would you like to have some
--Yes, please. A will be served B.served C. will serve D. was served
14. These photos on the Great Wall last week.
A. were taken B.took C.take D.are taken
15. --Can you read this letter for me --Sorry. It in French. I can’t read it.
A. writes B.wrote C.is written D.is writting
16. It is true that knowledge instead of being taught.
A. learns B. learned C. is learned D. was learned
31
练习题答案
1. D
2. B
3. A
4. B
5. D
6. D
7. B
8. D
9. D
10. D
11. D
12. D
13. D
14. A
15. C
16. C
32
Thank you!
33
被动语态
1
目录
含有情态动词的被动语态
03
被动语态的用法
04
主动语态和被动语态
01
被动语态的构成
02
2
主动语态和被动语态
1. 英语动词有两种语态,即主动语态和被动语态。
2. 当主语为动作的执行者时,谓语的形式为主动语态。
3. 当主语为动作的承受者时,谓语的形式为被动语态。
例如:
Many people speak English. (主动语态,句子的主语many people是动作speak的执行者。
English is spoken by many people. (被动语态,句子的主语English是动作speak的承受者)
Bell invented the telephone in 1876.(主动语态)
The telephone was invented by Bell in 1876. (被动语态)
3
被动语态的用法
1. 当不知道动作的执行者是谁时。如:
His bike has been stolen. 他的自行车被人偷了。(不知道是谁偷的)
2. 用于动作执行者泛指或者不言而明时。如:
Not a book in the library has been taken away. 图书馆里的书没有一本被拿走。(没人拿书,泛指)
3. 用于可以说出动作执行者是谁但强调的是动作的承受者时。如:
The computer was repaired by my son. 电脑被我儿子修好了。
4. 用于出于委婉、礼貌而避免提及自己或对方时。如:
Enough has been said here on this question. 这个问题已经说得够多的了。(意指不要再说下去了)
4
被动语态的用法
5. 用于文章标题、广告、新闻中(此时常会省略be的被动语态)。如:
Renmin Road blocked. 人民路堵塞了。
6. 当动作的执行者不是人时。如:
Many houses were washed away the storm. 许多房子被暴风雨冲走了。
7. 用于商务书信中书信起草人代表公司时。如:
You letter has been received. 你的来信已收到。
5
不能用于被动语态的动词
1. 不及物动词:字典里词后标有vi.的就是不及物动词.不及物动词后不能直接跟有动作的对象(即宾语).若要跟宾语,必须先在其后添加上某个介词。如:appear、come、go、get、fall、feel、keep、look等
2. 系动词:在英语中系动词的主要功能就是把表语和主语联系在一起,常见的系动词有be、look、turn、feel、get、keep、stay等。
3. 一些及物动词:
1) 部分静态动词(表感觉、情感、相互关系等)
表示拥有或者没有的动词,如:表示拥有的(have, own, possess), hold(容纳), contain(包含), belong to(属于), lack(缺少)等。
表示“适合“含义的:suit, fit, become (适合,与......相称的)
表示”相似、等同“含义的:equal, resemble, look like, mean等。
表示”继续、持续“含义的:last
表示”花费“含义的:cost
6
不能用于被动语态的动词
表示”明白“含义的,如:follow, get, catch, take等。
表示”同意、介意“含义的,如:agree with, mind等。
2)部分短暂性的动词
表示位置移动的动词:leave, arrive at/in, reach, enter, walk into, go into, jump等。这些虽然是及物动词,但是变成被动语态是讲不能的,也不能换成被动语态。比如:
I arrived at home late last night. 我昨天很晚到家。不能说成:
Home was arrived at by me late last night.
7
被动语态的构成
1. 被动语态由“助动词be + 及物动词的过去分词”构成。
2. 助动词be有人称、数的变化。其变化规则与be作为连系动词时完全一样。
3. 下面是以动词ask为例,将一般现在时和一般过去时被动语态的肯定式、否定式及疑问式列表如下:
肯定式 否定式 疑问式
一般现在时 I am asked... He/She is asked... We/You/They are asked... I am not asked... He/She is not asked... We/You/They are not asked... Am I asked...
Is he/she asked...
Are we/you/they asked...
一般过去时 I wask asked... He/She was asked... We/You/They were not asked... I was not asked... He/She was not asked... We/You/They were not asked... Was I asked...
Was he/she asked...
Were we/you/they asked...
8
被动语态的构成
9
8种基本时态的被动语态:
1. 一般现在时的被动语态:am(is,are) + 过去分词
2. 一般过去时的被动语态:was(were) + 过去分词
3. 一般将来时的被动语态:will be + 过去分词
4. 过去将来时的被动语态:would be + 过去分词
5. 现在进行时的被动语态:am(is,are) being + 过去分词
6. 过去进行时的被动语态:was(were) being + 过去分词
7. 现在完成时的被动语态:has(have) been + 过去分词
8. 过去完成时的被动语态:had been + 过去分词
一般现在时的被动语态
10
1. 肯定句结构: 主语+am/is/are+动词过去分词 (+by+动作执行者)
English is used by a lot of people in the world.
英语被全世界的很多人使用。
The flowers are bought by the girl. 这些花是这个女孩买的。
2. 否定句结构:主语+am not/isn’t/aren’t + 动词分词(+by+动作执行者)
The door isn’t made of wood. 这扇门不是木头做的。
The flowers aren’t bought by the girl. 这些花不是这个女孩买的。
3. 一般疑问句结构:Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Is the door made of wood 这扇门是木头做的吗?
Is the flowers are bought by the girl?这些花是这个女孩买的吗?
4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词+am/is/are + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Where is the paper used 被用在哪里?
When is the room often cleaned 房间通常是什么时候打扫的?
一般过去时的被动语态
11
1. 肯定句结构: 主语+was/were+动词过去分词 (+by+动作执行者)
He was called a hero. 他被称为是一位英雄。
We were allowed to go home early。我们被允许早早回家。
2. 否定句结构:主语+wasn’t / weren’t + 动词分词(+by+动作执行者)
He wasn’t called a hero. 他没被称为是一位英雄。
We weren’t allowed to go home early。我们不被允许早早回家。
3. 一般疑问句结构:Was / Were + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Was he called a hero 他被称为是一位英雄吗?
Were we allowed to go home early?允许我们早早回家吗?
4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词+was/were + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Who was called a hero 谁被称为英雄?
When was he called a hero? 他什么时候被称为英雄?
When were the flowers bought 这些花什么时候买的
一般将来时的被动语态
12
1. 肯定句结构: 主语+ will be +动词过去分词 (+by+动作执行者)
主语+ am/is/are +动词过去分词 (+by+动作执行者)
His homework will be finished tomorrow. 他的作业明天会完成。
The flowers will be bought tomorrow。花明天会买。
2. 否定句结构:主语+ won’t be + 动词分词(+by+动作执行者)
主语+ am not/isn’t/aren’t + 动词分词(+by+动作执行者)
The monkey won’t be put in the cage.
The monkey is not going to be put in the cage.
3. 一般疑问句结构:Was / Were + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词过去分词(+by+动作执行者)
Will the house be built next year / Is the house going to be built next year
房子将在明年建吗?
4. 特殊疑问句结构:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句,特殊疑问词第一个字母大写。
When will the house be built / When is the house going to be built
房子将于什么时候被建?
过去将来时的被动语态
13
**过去将来时:
1. 过去将来时是表示过去将要发生/打算要做某事,一般用在宾语从句,且这个宾语从句前面主句的谓语动词常为一般过去时。
2. 过去将来时是指从过去某一时刻看以后要发生的动作或状态,另外,过去将来时常可用来表示过去习惯性的动作,此时,不管是什么人称,一律用would。
被动语态是表主语是承受者。
过去将来时的被动语态常出现在英语间接引语中
2. 肯定结构:主语是第一人称时用 should be + 过去分词构成
主语是第二人称、第三人称时用 would be + 过去分词构成
was / were + going to be + 过去分词
I should be told about the thing. 应该告诉我这件事。
He would be told about the thing. 应该告诉他这件事。
He said that something would be needed to finish the work. 他说要完成这项任务,需要一些条件。
It was said that they would be selected by lottery. 据说他们将抽签选出。
过去将来时的被动语态
14
3. 否定结构:should not be / would not be + 过去分词;wasn’t / weren’t going to be + 过去分词
His brother said that the homework wouldn't be finished by him in half an hour. 他哥说这个工作他半个小时应该完成不了。
They said the building was not going to be finished the next month. 他们说大楼下个月完不了工。
He said I was not going to be wanted on the phone.他说没人会打电话给我。
4. 一般疑问结构:Would / Should + 主语 + be + 过去分词; Was / Were + 主语 + going to be + 过去分词。
Would the machine be repaired by these workers the next day
这部机器工人是第二天才修理的吗?
Were the flowers going to be bought by the girl the next day 这些花是这个女孩第二天才买的吗?
5. 特殊疑问结构:特殊疑问词 + 一般疑问句。
When were the flowers going to be bought by the girl 这些花这个女孩什么时候去买?
现在进行时的被动语态
15
1. 定义:表示现在某个被动的动作正在进行中,表示“某人/某事此时此刻正在被...”,主语是动作或状态的承受者。
2. 肯定结构:主语 + am / is / are being +动词的过去分词
The question is being discussed at the meeting. 这个问题现在在会上被讨论。
Three new pedestrian bridegs are being built at the moment. 三条人行天桥正在兴建中。
3. 否定结构:主语 + am / is / are + not + being + 动词的过去分词
The books are not being borrowed at present. 这些书现在没有被借出。
The tiger is not being set free now. 这只老虎现在还不能被放出。
.
4. 一般疑结构:Am / Is / Are + 主语 + being + 动词的过去分词
Is a new classroom building being built in your school 你们学校正在建一幢新的教学楼吗?
Are many new cars being sold to oversea markets 很多新汽车正在销往国外市场吗?
现在进行时的被动语态
16
5. 特殊疑问结构:疑问词 + am / is / are + 主语 + being + 动词的过去分词。
What is being done to the computer 现在对这台电脑要采取什么措施?
How many houses are being built in our village 我们村现在正在建多少房子?
过去进行时的被动语态
17
1. 定义:过去的某个时间正在发生或正在进行的被动的动作。
2. 肯定结构:主语 + was / were + being + 动词的过去分词。
A new school was being built at that time. 当时正在建一所新的学校。
Some trees were being planted when she arrived. 当她到达的时候正在种着很多树。
3. 否定结构:主语 + was / were + not + being + 动词的过去分词。
A new school was not being built at that time. 当时没有在建一所新的学校。
Some trees were not being planted when she arrived. 当她到达的时候没有在种着很多树。
4. 一般疑问结构:was / were + 主语 + being + 动词的过去分词?
Was a new classroom building being put up in their school just then 他们学校当时正在建一幢新的教学楼吗?
5. 特殊疑问结构:特殊疑问词 + was / were + being + 动词的过去分词
What was being done to the machine 对这台机器采取了什么措施?
现在完成时的被动语态
18
1. 现在完成时的被动语态同它的主动语态一样,强调过去的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,通常与 already, yet, just, never, recently等副词连用。
或表示一个被动的动作或状态开始于过去,持续到现在,并可能持续下去,常与for或since等引导的时间状语连用,或用与How long… 的句型中。
2. 肯定结构:have/has+been+done
The new schools have been set up. 新学校都已经建成了。
The experiment has been done successfully. 这个实验做得很成功。
3. 否定结构:have/has+not+been+done
The books have not been borrowed by the students. 那些书还没有被学生借走。
Tom's novel has not been published. 汤姆的小说还没有被出版。
现在完成时的被动语态
19
4. 一般疑问结构:have/has + 主语+not+been+done?
—Have the letters been posted 信已经寄出去了吗? —Yes, they have. 是的,已寄出了。
—Has your bike been repaired 你的自行车修好了吗? —No, it hasn't. 不,还没有被修好。
5. 特殊疑问结构:疑问词+have/has+been+done
How long have the machines been repaired?这些机器已被修好多长时间了?
Who has been invited 谁受到了邀请?
过去完成时的被动语态
20
1. 定义:表示在过去某一时刻或某一动作之前发生的动作或状态,句中常用by,before,until,when等词引导时间状语。
We had built five new buildings by the end of last year. 直至去年年底,我们已经建了五幢新的大楼。
2. 肯定结构:主语+ had been done +其他成分
As of last September, about 20 companies have been closed due to pandemic.
直至去年九月份,已经有20家公司因为疫情的原因倒闭了。
3. 否定结构:主语+ had not been done +其他成分
Several books had not been read by his twenties. 直到他二十几岁他还有几本书没有看。
4. 一般疑问句结构:had +主语+ been done +其他成分
Had his friends been invited to his party until last night 直到昨晚他的朋友都被邀请过来参加他的舞会了吗?
过去完成时的被动语态
21
5. 特殊疑问句结构:疑问词+ had +主语+ been done +其他成分
When had his friends been invited to his party 他的朋友是什么时候被邀请去参加他的舞会的?
6. 过去完成时的被动语态常用于以下情况:
(1)表示过去某一时间以前已经完成的动作,常与by, before等引导的时间状语连用。
By the time he got to the school, the first period had been finished.
The classroom hadn't been cleaned before the teacher came.
How many buildings had been destroyed when the hurricane ended
Had the new plan been discussed before the meeting
(2)在 told, said, knew, heard, thought等动词之后的宾语从句中,若表示过去某一被动动作时,用过去完成时。
They said the production costs had been reduced.
The girl was reminded that her homework had not been handed in.
过去完成时的被动语态
22
The media reported more than 1,000 people had been killed in the storm.
(3)根据语意可以判断出动作先后的被动语态,用过去完成时。
As the assignment had been done, he went on to search the Internet.
He did what he had been told to.
另:当从句由 after,before,when或 as soon as引导时,主句和从句都可以用一般过去时。
When he arrived, he called her.
They locked the door before they left.
含有情态动词的被动语态
1. 含有情态动词的被动语态由”情态动词 + be + 及物动词的过去分词“构成。其时态及句型的变化仅由情态动词完成,“be+过去分词”部分不变。
例如:
Teenagers should be allowed to make their decisions.
Your room must be cleaned every day.
The trees may be planted behind the house.
This game can be played in the winter.
2. 含有情态动词的被动语态变为否定句时,应在情态动词后面加not;变为一般疑问句时,应将情态动词移到句首。
Waste paper should not be thrown here. 废纸不应该扔在这里。
Should it be done by Li Ming? 这件事应该是李明干吗?
23
含有情态动词的被动语态
3. 一般疑问句结构:情态动词 + 主语 + be + 动词的过去分词 + 其他成分。注意只提前情态动词,不提前be。
May she be critized by her father 她被她爸爸批评了吗?
4. 含有情态动词的主动句与被动句之间的转换:把主动句中的宾语变为被动句的宾语,主动句的谓语动词变成“情态动词+be+动词的过去分词”的形式。主动句中的主语变成被动句中的宾语(注意不同成分的代词之间的转换)。如果在不要求强调动作的执行者时,by+宾语可以省略。如:
She must clean the room on weekends.
The room must be cleaned (by her) on weekends.
she在主动句中充当主语,但在被动句中充当宾语,改为宾格的她-her
24
将主动语态变被动语态应注意几个特殊情况:
1.含双宾语的主动结构变为被动结构时,有两种方法:
①将间接宾语变为主语,直接宾语保持不变;
②将直接宾语变为主语,间接宾语用介词to或for引导。例如:
① He told us a story.(变被动语态)
→We were told a story(by him).或:A story was told to
us by him.
② Her mother gave her a new pen.(变被动语态)
A new pen was given to her by her mother.或 She was given a new pen by her mother.
2.短语动词的被动语态:在变为被动语态时,要将短语动词视为一个整体,其后的介词或副词不能省去。例如:
This dictionary mustn't be taken away from the library.
“直接宾语,是一个英语语法用语,是指谓语动词的承受者,可由名词、代词、数词、不定式充当。双宾语由直接宾语和间接宾语组成。间接宾语表示谓语动作的方向(对谁做)或动作的目标(为谁做),间接宾语紧接在谓语动词后,但它在句子中不能单独存在,并且能和直接宾语
组成双宾语。”
25
将主动语态变被动语态应注意几个特殊情况
3.含有复合宾语的主动结构变被动结构时,通常将宾语变为被动句的主语,而宾语补足语就成为主语补足语。注意:省略to的不定式作宾补时,不定式符号to必须补上。例如:
Someone saw him swim in Qianling Lake yesterday.(变被动如下)
He was seen to swim in Qianling Lake yesterday.
4.不定式的被动结构:动词不定式的被动语态为“to be +过去分词”。例如:
The radio says a wild animal zoo is to be built in our city.
5.以疑问代词开头的疑问句转换成被动句时要注意词序:应将主动句中的疑问代词改为介词by的宾语,但仍然放在句子开头。例如:
Who has broken the cup?(改为被动语态)
→By whom has the cup been broken?
26
被动语态和过去分词作表语的区别
1)含义不同:被动语态强调动作,重点说明动作由谁完成、怎样完成;而过去分词作表语通常用来描写情景,叙述人或事物的特征及所处的状态。试比较:
The window is broken.窗子破了。(系表结构)
The window is broken by him.窗子被他打破了。(被动语态)
2)用法不同:过去分词作表语时可以被 so,very,too等程度副词修饰,而被动语态则不能用so,very,too修饰,而需用much,very much,so much,too much修饰。试比较:
He was very interested in science.他对科学有极大兴趣。(系表结构)
I was so much surprised at the scene that I didn't know what to do.我被那种场面搞得大吃一惊,不知所措。(被动语态)
27
初中教材中与被动语态相关的句型
1.be covered with被……覆盖
2.be made of由……制作(发生物理变化)
be made from由……制作(发生化学变化)
be made in由(某地)制造
be made by被(某人)制造
3.be used for被用来……
be used as被当作(作为)……来使用
be used to do sth.被用来做某事
4.It is said that...据说……
It is hoped that...希望……
It is well known that...众所周知……例如:
28
几种特殊的被动语态
1.带不定式的被动语态。
The child is sure to be punished for that. 那个孩子肯定会因为那件事受罚的。
2. 带介词的动词短语的被动语态。
Such a thing has never been heard of. 这件事前所未闻。
3. 带副词的动词短语的被动语态。
The radio has just been turned off. 收音机刚刚被关上。
4. 当sell, wash, clean, run, ride, wear, write等动词若有状语well, easily, badly来修饰时,用主动形式表达被动意义。
The pen writes well. 这枝钢笔写字流畅。
The book sells well. 这本书很畅销
29
练习
1. One or two man-made satellites in our country every year.
A. have been sent up B.will be sent up C.is sent up D.are sent up
2. Our TV set yesterday.
A. is repaire B.was repaired C.had been reparied D.would be reparied
3. A new building in our school next year.
A. will be built B. is built C. is being built D. has been built
4. Many books on science since I went to college.
A. were bought B.have been bought C. will be bought D.are bought
5. A wonderful English talk by Mr Liu tomorrow.
A. has been given B. is given C. is being given D. will be given
6. How the Great Pyramid(金字塔) many years ago without modern machines.
A. is,built B.would,be built C.have,been built D.was, built
7. Jack often does things foolishly, so he sometimes by others.
A.is,laughed B.is,laughed at C.was,laughed D.has, been laughed at
8. Such films by children like you.
A. must be not seen B.must not be see C.must not seen D.must not be seen
30
练习
9. Trees in winter but in spring.
A.not can be planted B.can be not planted C.can’t be planted D.can not be plant
10. In the past ten years, a lot of new buildings in our city.
A. are put up B. have put up C. have been put D. have been put up
11. The streets many times every day.
A. clean B.cleans C.cleaned D.are cleaned
12. The 30th Olympic Games in London in 2012.
A. held B. is hold C. will hold D. will be held
13. --The pizza by my mum just now. Would you like to have some
--Yes, please. A will be served B.served C. will serve D. was served
14. These photos on the Great Wall last week.
A. were taken B.took C.take D.are taken
15. --Can you read this letter for me --Sorry. It in French. I can’t read it.
A. writes B.wrote C.is written D.is writting
16. It is true that knowledge instead of being taught.
A. learns B. learned C. is learned D. was learned
31
练习题答案
1. D
2. B
3. A
4. B
5. D
6. D
7. B
8. D
9. D
10. D
11. D
12. D
13. D
14. A
15. C
16. C
32
Thank you!
33
