名词性从句讲解课件
图片预览










文档简介
课件32张PPT。 名词性从句*名词性从句的特点是从句都有关联词引导,从句的语序和陈述句的语序相同。名词性
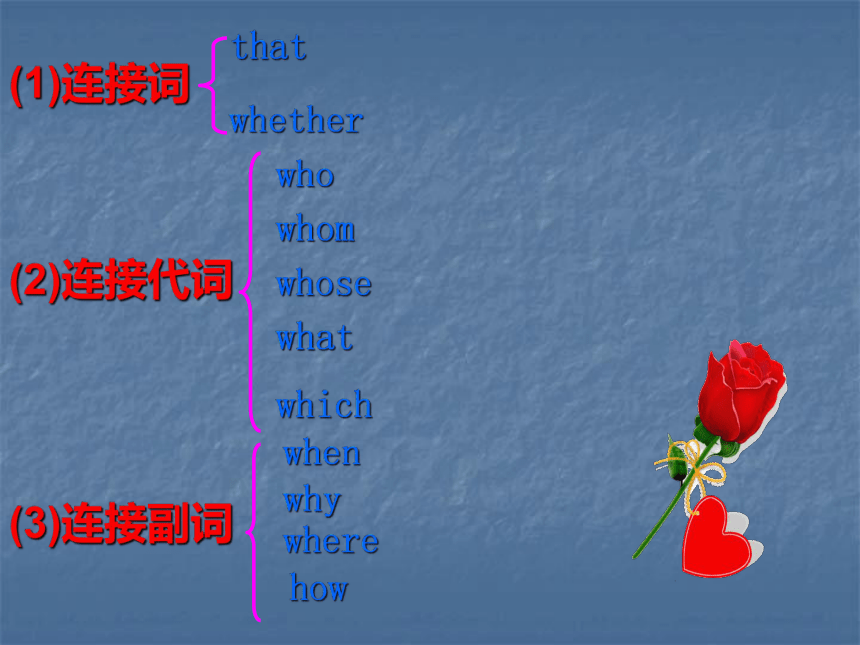
从句2.宾语从句3.表语从句4.同位语从句1.主语从句这是一本书。This is a book.陈述句这是书吗?Is this a book?疑问句(1)连接词whetherthat(2)连接代词whowhomwhosewhatwhich(3)连接副词when whywherehow1.主语从句:(subject clause)在一个完整的句子里,主语部分还含有主谓两大部分结构的句子叫主语从句。引导主语从句的关联词不能省略。例:谁去这不重要。Who will go is not important.主语例:我们需要的是更多的时间。What we need is more time.主语例:他住在哪里我们都不知道。Where he lives is unknown to us.主语例:不太清楚她为什么迟到。Why she was late is unclear.主语例:这本书怎么销售取决于它的作者。How the book will be sold depends on its writer .2.宾语从句:(object clause)用作宾语的从句叫做宾语从句。一般放在及物动词,介词后。连接代词who, whom, what,连接副词when, why, where, how,连词that, whether, if引导。 例:我希望一切都好。I hope (that) everything will be all right.动宾例:你知道他在哪里吗?Do you know where he is?动宾例:老师清楚她为什么迟到了。The teacher has found out why she was late.介宾例:对于他说的话,我感到很惊讶。I was surprised at what he said.介宾例:我认为他们知道怎样做这个练习。I thought that they knew how to do this exercise .动宾*宾语从句从句中,连词that只起连接作用,没有实际作用,可以省略,而其他的关连词却不能省略。3. 表语从句:在连系动词之后的句子叫做表语从句。例:问题是谁能去那里。The question was who could go there.表语例:那是他为什么迟到的原因。That is why he was late.表语例:问题是我们什么时候得到答案。The question is when we’ll get the answer.表语例:问题不是谁去,而是谁留下来。The problem is not who will go but who
will stay.表语4.同位语从句:同位语从句起着进一步解释或说明它前面的名词的作用,通常由that或whether引导。同位语从句常与下列先行词一起出现:fact, truth, doubt, suggestion, idea, question, problem, hope, thought, fear等。例:我不知道他什么时候回来.I have no idea when he will be back.同位语从句例:我们明天放假的消息不是真的.The news that we are having a holiday
tomorrow is not true. 同位语从句Homework:
1.他对我们说他感到不舒服。(宾语)
2.他干了什么还不清楚。(主语)
3.麻烦就是我把他的钱包丢了。(表语)
4.对你生病这件事,他们都很担心。(先行词用fact)
5.那是一个如何做了此事的问题。(用how引导)He told us that he felt ill.What he did is not yet known.The trouble is that I have lost his wallet.They were all worried about the fact you were sick.It is a question how he did it. 名词性从句(2)*引导名词性从句的引导词归纳起来
可以分为下面三类。(1)从属连词whetherthat(2)连接代词whowhomwhosewhatwhich(3)连接副词when whywherehow,if/as if
(只用于表语从句)*只起连接作用,
不充当从句
中的任何作用。*既起连接作用,
本身又做从句的
主语、宾语、
表语或定语。*既起连接作用,
本身又做从句的状语。how many,how much,*注意1.当主语从句较长时,多放在句子后部,用 it 作形式主语。It is probable that he told me everything.It is certain that she will do well in her exam.例:可以肯定的是她将会在考试中表现出色。she will do well in her exam is certain.主语例:他有可能告诉我所有东西。He told me everything is probable.主语××形式主语形式主语*以it作形式主语,把主语从句后置的常用句型有:1. It+be+形容词+that从句 certain
clear
important
necessary
probable
possible+that – clauseIt is/was+1.可以清楚的是他已经不再爱她了。It is clear that he won’t love her any more.2.重要的是我根本没有打过电话给他。It is important that I didn’t call him at all.3.必要的是我们必须努力学习。It is necessary that we must study hard.2、It + be + 名词词组 + that从句 a pity
a shame
a duty
no surpriseIt is / was ++that – clauseIt is no surprise that our team won the game.It is a pity that we can’t go.例:我们不能去多么可惜。例:我们队赢得这场游戏是不足为奇的。3、It + be + 过去分词 + that从句 said
reported
thought
hoped
believed
known It is++that – clauseIt is thought that Joe drives badly.例:据说他是班里最好的学生。 It is said that he is the best student in the class.例:据认为Joe的车技很差。4、It + seem, happen, appear等不及物动词 + that从句。It seems that Alice won’t come to the party at all.It happened that I was out that day.例:看来Alice根本不会来这个聚会的了。例:刚好那天我外出了。引导宾语从句的连词that常可省去,特别在口语中是这样。
(1) They pretended that they were reading in the room.
(2) John made the boy sit still, promising that nothing would hurt him.注意:2.whether 和 if 引导的宾语从句:
whether 和 if 引导宾语从句时可以互换使用,但下列情况用whether不用if。(1)在whether or not结构中不可用if代替whetherI don’t know whether he’ll come or not.I wonder whether it is true or not.例:我不知道他是否会来。例:我在想这是真还是假的。(2)介词后面的宾语从句用whether,
不用ifEverything depends on whether the situation will improve.例:每样东西都取决于情况是否会改变。介词(3)引导主语从句和表语从句用whether不用if .(4) whether 可用在不定式前,if 则不能.Please tell me whether to go or not.Whether we’ll go depends on the weather.The question is whether it is worth doing.例:我们是否会去取决于天气。例:问题是它是否值得被做。主语从句表语从句不定式2、用作介词的宾语从句: He always pays attention to whatever the
teacher says.I was pleased by what he told me.例:他告诉我的事情令我很高兴。例:无论老师说什么,他总是很专注。注意:介词的宾语从句一般不用which和if来引导,而要分别用what和whether来引导。如:不可用ifwhich不可以Are you sorry for what you’ve done?Everything depends on whether we have enough
experience.例:你会对你所做的东西感到遗憾吗?例:每样事情都取决于我们是否有足够的经验.3、用作某些形容词的宾语从句:We were not surprised that he returned three days later than expected.这类形容词常见的有sure, certain, glad, pleased, happy,
afraid, surprised, satisfied等。I am sure you looked beautiful that evening.例:我肯定那天晚上你会看起来很漂亮.例:他比预期晚了三天回来,我们不感觉惊奇.例:每个人都担心有人会发现他看不见东西.Everyone was afraid that someone might find out
that he could see nothing.Mother was very pleased (that) her daughter had
passed exams.例:女儿考试及格了,妈妈非常高兴. 注意:如果宾语从句后边还有宾语补足语,则用it作形式宾语而将宾语从句后置。如:(2) He has made it clear that anyone who breaks the law is to be punished. (1) We thought it strange that Xiao Wang did
not come yesterday.宾补宾补这种句型的谓语动词有think, make, feel, find, consider.4.同位语从句:同位语从句起着进一步解释或说明它前面的名词的作用,通常由that或whether引导。同位语从句常与下列先行词一起出现:fact, truth, doubt, suggestion, idea, question, problem, hope, thought, fear等。例:我不知道他什么时候回来.I have no idea when he will be back.同位语从句例:我们明天放假的消息不是真的.The news that we are having a holiday
tomorrow is not true. 同位语从句判断以下从句是定语从句还是同位语从句:
(1)They expressed the hope that they would come over to visit China again.
(2) We all know the truth that the earth goes round the sun.
(3) The book that I bought yesterday is worth reading.
(4) This is the question that I asked my teacher yesterday .
(5) The problem that we have not enough money has not yet been solved.同同定定同注意:同位语从句和定语从句的区别是:前者说明名词的内容,后者说明名词的性质特征;前者所用连词that不是从句的一个成分,后者所用关系代词that是从句中的一个成分。
从句2.宾语从句3.表语从句4.同位语从句1.主语从句这是一本书。This is a book.陈述句这是书吗?Is this a book?疑问句(1)连接词whetherthat(2)连接代词whowhomwhosewhatwhich(3)连接副词when whywherehow1.主语从句:(subject clause)在一个完整的句子里,主语部分还含有主谓两大部分结构的句子叫主语从句。引导主语从句的关联词不能省略。例:谁去这不重要。Who will go is not important.主语例:我们需要的是更多的时间。What we need is more time.主语例:他住在哪里我们都不知道。Where he lives is unknown to us.主语例:不太清楚她为什么迟到。Why she was late is unclear.主语例:这本书怎么销售取决于它的作者。How the book will be sold depends on its writer .2.宾语从句:(object clause)用作宾语的从句叫做宾语从句。一般放在及物动词,介词后。连接代词who, whom, what,连接副词when, why, where, how,连词that, whether, if引导。 例:我希望一切都好。I hope (that) everything will be all right.动宾例:你知道他在哪里吗?Do you know where he is?动宾例:老师清楚她为什么迟到了。The teacher has found out why she was late.介宾例:对于他说的话,我感到很惊讶。I was surprised at what he said.介宾例:我认为他们知道怎样做这个练习。I thought that they knew how to do this exercise .动宾*宾语从句从句中,连词that只起连接作用,没有实际作用,可以省略,而其他的关连词却不能省略。3. 表语从句:在连系动词之后的句子叫做表语从句。例:问题是谁能去那里。The question was who could go there.表语例:那是他为什么迟到的原因。That is why he was late.表语例:问题是我们什么时候得到答案。The question is when we’ll get the answer.表语例:问题不是谁去,而是谁留下来。The problem is not who will go but who
will stay.表语4.同位语从句:同位语从句起着进一步解释或说明它前面的名词的作用,通常由that或whether引导。同位语从句常与下列先行词一起出现:fact, truth, doubt, suggestion, idea, question, problem, hope, thought, fear等。例:我不知道他什么时候回来.I have no idea when he will be back.同位语从句例:我们明天放假的消息不是真的.The news that we are having a holiday
tomorrow is not true. 同位语从句Homework:
1.他对我们说他感到不舒服。(宾语)
2.他干了什么还不清楚。(主语)
3.麻烦就是我把他的钱包丢了。(表语)
4.对你生病这件事,他们都很担心。(先行词用fact)
5.那是一个如何做了此事的问题。(用how引导)He told us that he felt ill.What he did is not yet known.The trouble is that I have lost his wallet.They were all worried about the fact you were sick.It is a question how he did it. 名词性从句(2)*引导名词性从句的引导词归纳起来
可以分为下面三类。(1)从属连词whetherthat(2)连接代词whowhomwhosewhatwhich(3)连接副词when whywherehow,if/as if
(只用于表语从句)*只起连接作用,
不充当从句
中的任何作用。*既起连接作用,
本身又做从句的
主语、宾语、
表语或定语。*既起连接作用,
本身又做从句的状语。how many,how much,*注意1.当主语从句较长时,多放在句子后部,用 it 作形式主语。It is probable that he told me everything.It is certain that she will do well in her exam.例:可以肯定的是她将会在考试中表现出色。she will do well in her exam is certain.主语例:他有可能告诉我所有东西。He told me everything is probable.主语××形式主语形式主语*以it作形式主语,把主语从句后置的常用句型有:1. It+be+形容词+that从句 certain
clear
important
necessary
probable
possible+that – clauseIt is/was+1.可以清楚的是他已经不再爱她了。It is clear that he won’t love her any more.2.重要的是我根本没有打过电话给他。It is important that I didn’t call him at all.3.必要的是我们必须努力学习。It is necessary that we must study hard.2、It + be + 名词词组 + that从句 a pity
a shame
a duty
no surpriseIt is / was ++that – clauseIt is no surprise that our team won the game.It is a pity that we can’t go.例:我们不能去多么可惜。例:我们队赢得这场游戏是不足为奇的。3、It + be + 过去分词 + that从句 said
reported
thought
hoped
believed
known It is++that – clauseIt is thought that Joe drives badly.例:据说他是班里最好的学生。 It is said that he is the best student in the class.例:据认为Joe的车技很差。4、It + seem, happen, appear等不及物动词 + that从句。It seems that Alice won’t come to the party at all.It happened that I was out that day.例:看来Alice根本不会来这个聚会的了。例:刚好那天我外出了。引导宾语从句的连词that常可省去,特别在口语中是这样。
(1) They pretended that they were reading in the room.
(2) John made the boy sit still, promising that nothing would hurt him.注意:2.whether 和 if 引导的宾语从句:
whether 和 if 引导宾语从句时可以互换使用,但下列情况用whether不用if。(1)在whether or not结构中不可用if代替whetherI don’t know whether he’ll come or not.I wonder whether it is true or not.例:我不知道他是否会来。例:我在想这是真还是假的。(2)介词后面的宾语从句用whether,
不用ifEverything depends on whether the situation will improve.例:每样东西都取决于情况是否会改变。介词(3)引导主语从句和表语从句用whether不用if .(4) whether 可用在不定式前,if 则不能.Please tell me whether to go or not.Whether we’ll go depends on the weather.The question is whether it is worth doing.例:我们是否会去取决于天气。例:问题是它是否值得被做。主语从句表语从句不定式2、用作介词的宾语从句: He always pays attention to whatever the
teacher says.I was pleased by what he told me.例:他告诉我的事情令我很高兴。例:无论老师说什么,他总是很专注。注意:介词的宾语从句一般不用which和if来引导,而要分别用what和whether来引导。如:不可用ifwhich不可以Are you sorry for what you’ve done?Everything depends on whether we have enough
experience.例:你会对你所做的东西感到遗憾吗?例:每样事情都取决于我们是否有足够的经验.3、用作某些形容词的宾语从句:We were not surprised that he returned three days later than expected.这类形容词常见的有sure, certain, glad, pleased, happy,
afraid, surprised, satisfied等。I am sure you looked beautiful that evening.例:我肯定那天晚上你会看起来很漂亮.例:他比预期晚了三天回来,我们不感觉惊奇.例:每个人都担心有人会发现他看不见东西.Everyone was afraid that someone might find out
that he could see nothing.Mother was very pleased (that) her daughter had
passed exams.例:女儿考试及格了,妈妈非常高兴. 注意:如果宾语从句后边还有宾语补足语,则用it作形式宾语而将宾语从句后置。如:(2) He has made it clear that anyone who breaks the law is to be punished. (1) We thought it strange that Xiao Wang did
not come yesterday.宾补宾补这种句型的谓语动词有think, make, feel, find, consider.4.同位语从句:同位语从句起着进一步解释或说明它前面的名词的作用,通常由that或whether引导。同位语从句常与下列先行词一起出现:fact, truth, doubt, suggestion, idea, question, problem, hope, thought, fear等。例:我不知道他什么时候回来.I have no idea when he will be back.同位语从句例:我们明天放假的消息不是真的.The news that we are having a holiday
tomorrow is not true. 同位语从句判断以下从句是定语从句还是同位语从句:
(1)They expressed the hope that they would come over to visit China again.
(2) We all know the truth that the earth goes round the sun.
(3) The book that I bought yesterday is worth reading.
(4) This is the question that I asked my teacher yesterday .
(5) The problem that we have not enough money has not yet been solved.同同定定同注意:同位语从句和定语从句的区别是:前者说明名词的内容,后者说明名词的性质特征;前者所用连词that不是从句的一个成分,后者所用关系代词that是从句中的一个成分。
同课章节目录
- 名词
- 动词/动词短语
- 一般现在时及其被动式
- 一般过去时及其被动式
- 现在进行时及其被动式
- 过去进行时及其被动式
- 将来进行时及其被动式
- 现在完成时及其被动式
- 过去完成时及其被动式
- 一般将来时及其被动式
- 过去将来时及其被动式
- 现在完成进行时及其被动式
- 将来完成时及其被动式
- 副词
- 介词/介词短语
- 连词/连接词
- 数词/量词
- 冠词
- 形容词
- 非谓语动词
- 句型
- 简单句与并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 倒装与省略
- 强调句
- 虚拟语气
- 插入语
- 固定句型
- 祈使句/感叹句
- 疑问句/反义疑问句
- 非限制性定语从句
- 句型转换
- 定语从句
- 表语从句
- 宾语从句
- 主语从句
- 动词时态与语态
- 虚拟语气与情态动词
- 主谓一致
- 独立主格结构、with的复合结构
- 情态动词
- 状语从句
- 定语从句
- 特殊句式
- 交际用语
- 代词/不定代词
- 名词性从句
- 同位语从句
- 表语从句
- 宾语从句
- 主语从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 构词法(word formation)
