2023届高考英语二轮语法复习动词时态语态 课件(28张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023届高考英语二轮语法复习动词时态语态 课件(28张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-12-17 18:09:18 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共28张PPT)
词性七—动词
动词的时态、语态
动词的分类——实义动词;系动词;助动词;情态动词
1
2
3
动词—时态
动词的词形变化——原形;过去式;过去分词
动词的语法——时态;语态;非谓语动词;虚拟语气
1. 动词的分类—1.实义动词
含实在的意义
表示动作或者状态
在句中独立做谓语
They eat a lot of potatoes.
I’m reading an English book now.
2. 连系动词
本身有一定意义
be 动词&感官动词
His father is a teacher. (be 动词 作 谓语)
Twins usually look the same.
3.助动词
本身没有词义,不能独立作谓语,只和主要动词一起构成谓语动词
表示 否定 疑问 时态 语态 等
有 人称 单复数 和 时态 的 变化
He doesn’t speak English.(辅助构成否定)
We are playing basketball.
(be 动词 作助动词 辅助构成 现在进行时)
4.情态动词
本身有意义,不能独立作谓语,和动词一起构成 谓语动词
情态动词 没有人称和单复数的变化,有些情态动词有过去式
You can keep the books for two weeks.
can—could
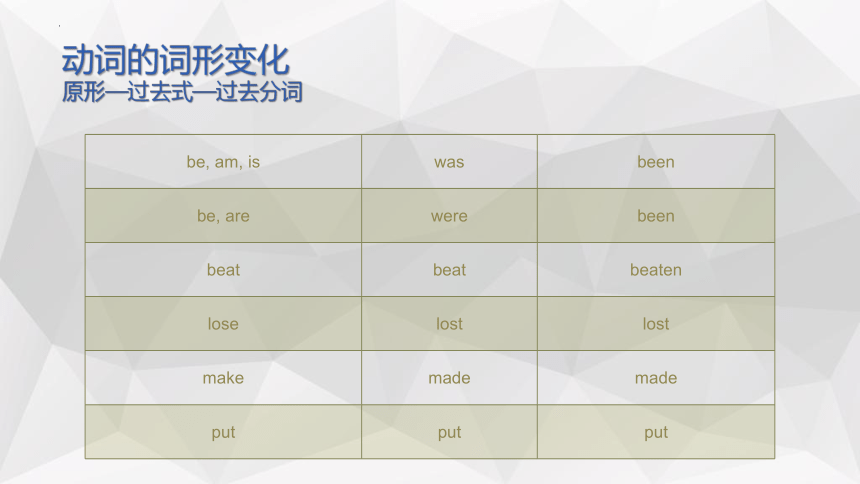
动词的词形变化
原形—过去式—过去分词
be, am, is
was
been
be, are
were
been
beat
beat
beaten
lose
lost
lost
make
made
made
put
put
put
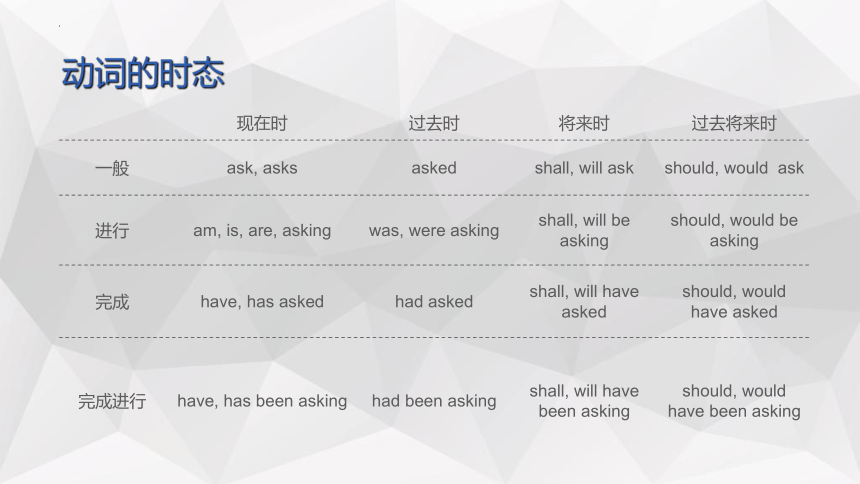
动词的时态
现在时 过去时 将来时 过去将来时
一般 ask, asks asked shall, will ask should, would ask
进行 am, is, are, asking was, were asking shall, will be asking should, would be asking
完成 have, has asked had asked shall, will have asked should, would have asked
完成进行 have, has been asking had been asking shall, will have been asking should, would have been asking
动词的时态
一般现在时(4个知识点)
一般过去时(2个知识点)
一般将来时(2个知识点)
现在进行时(3个知识点)
过去进行时(3个知识点)
现在完成时(4个知识点)
过去完成时(3个知识点)
过去将来时(4个知识点)
现在完成进行时(2个知识点)
现在
将来
过去
一般过去时
过去完成时
现在完成时
一般现在时
现在进行时
一般将来时
1.一般现在时
经常或习惯发生的动作或状态
常用的时间状语
They go to the Palace Museum once a year.
They often discuss business in the evening.
表示客观真理,事实,人的技能或现在的状态时句子里一般不用时间状语
The earth turns round the sun.
Light travels faster than sound.
十分确定会发生(事先安排好的事情)或按照时间表进行的事情
用一般现在表示将来,句子中可以有将来时间
The train for Haikou leaves at 8:00 in the morning.
时间状语从句&条件状语从句,一般现在时 表示 将来
Please ring me up as soon as you arrive in Germany.
If it rains tomorrow, we will have to stay at home.
2.一般过去时
表示 过去的动作或状态
可能是 一次性, 也可能 经常发生
Little Tom broke the window at half nine this morning.
When he went into the room, he saw a stranger talking with his father.
He came to our city in the year 2000.
3. 一般将来时
表示将来某一时刻 或 经常发生的动作 或 状态
时间状语
will 动作与 人的主观愿望 无关
shall用于第一人称
will 用于所有人称
am, is, are going to +动词原形
am, is, are to +动词原形
be to +动词原形 (打算/准备 要做 的事情,主观判断即将要发生的事情)
I will graduate from this school soon.
It’s going to rain.
4. 现在进行时
be (am is are) + 现在分词
I am writing a long novel.
表示即将发生的动作,一般指近期安排好的事情
What are you doing tomorrow
频繁发生/反复进行 的动作,常与always等频度副词连用
表示赞扬,不满或者讨厌等感彩
He is always borrowing money from me and forgetting all about it some time later.
5.过去进行时
was/were +现在分词
过去进行时的时间状语
用于 宾语从句 或 时间状语从句 表示与主句动作同时进行 而且 延续时间较长;句子中通常不用状语
He was cooking supper this time yesterday.
The little girl was playing with her toy when I saw her.
She saw it happen when she was walking past.
They sang a lot of songs while they were walking in the dark forest.
6. 现在完成时
have (has) + done
时间状语
I have never seen such time pictures before.
He has just gone to England.
表示在过去开始一直延续到现在的动作或状态
I have been away from my hometown for thirty years.
Uncle Wang has worked in the factory since it opened.
在完成时中,一个瞬间动词(一次性动作)不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,此时必须将瞬间动词改为延续性动词
瞬间性动词的完成时
延续性动词或状态动词的完成时
Have (already) gone to
Have been in / at ... for (two years)
Has come to
Has been here since (1990)
7. 过去完成时
表示的时间是“过去式”
助动词had+动词的过去分词
时间状语
过去完成时时常用于宾语从句中,after引导的从句中,或者从句是before引导的主句中
They had already finished cleaning the classroom when their teacher came.
The woman had left before he realized she was a cheat.
After I had put on my shoes and hat, I walked into the darkness.
He said that he had never seen a kangaroo before.
8. 过去将来时
should或would动词原型 构成
时间状语
在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中不可以使用过去将来时,而应该使用一班过去时
表示纯粹的将来时用would或should; 表示打算或主观认为的事情用was/were going to (+动词原形)
He promised that he would pay me a lot of money if I helped him with the project.
Every time when he was free, he would sit down and read some books.
She told me she would be 18 the next month.
She told me that she was going to have a walk with her pet dog.
9. 现在完成进行时
指一个从过去就开始一直延续到现在并有可能继续下去的动作,它具有现在完成时和现在进行时双重特征
结构:have/has + been + 动词的现在分词
He has been courting her for the last three months.
动词的语态
动词的被动语态
定义
构成
用法
方法:
双宾
to
宾补
短语
定义
主语是动作的执行者(即某人做某事),叫主动语态
主语是动作的承受着(即某事被做),叫被动语态
构成
助动词be + 动词的过去分词(和主系表 不一样)
助动词be有时态、人称和数的变化
被动语态by 短语有时可省去
被动语态的用法
不知道谁是动作的执行者(即不知道所做的)时用被动语态,省略by短语
众所周知是谁做的时,用被动语态,省略by短语
强调动作的承受者,句尾加by的短语
A man was killed in the accident.
This window was broken yesterday.
(不知道谁干的)
Rice is also grown in this place.
A railroad will be built here in three years.
(众所周知)
It was written by Lu Xun.
A pet dog is never killed by its owner.
(强调动作的对象)
主动语态改成被动语态的方法
将主动语态的宾语改为被动语态的主语(涉及主格和宾格)
将主动语态的谓语动词改为 be+过去分词 结构
将主动语态的主语改为介词by之后的宾语,放在谓语动词之后(有时可省略)
双宾的被动语态
把间接宾语改为被动语态的主语,直接宾语仍保留原位
把直接宾语改为主动语态的主语,简介宾语前要加介词to或for
His teacher gave him a dictionary.
He was given a dictionary by his teacher.
A dictionary was given to him by his teacher.
+ to
不带to的动词不定式作宾语补足语的主语动态,改为被动语态时不定式前要+to(使役动词 感官动词 主动无to 被动加to)
The boss made the poor man work 12 hours a day.
----The poor man was made to work 12 hours a day.
带复合宾语的动词
一般把主动语态的宾语改为主语,宾语补足语在被动语态中做助于补足语
I paint the house white.
The hose is painted white by me.
动词短语做谓语
短语动词是不可分割的整体,改为被动语态时要保持其完整性,介词或副词不可遗漏
The girl takes good care of her little brother.
The girl's little brother is taken good care of by her.
All the people laughed at him.
He was laughed at by all people.
We can repair this watch in two days.
This watch can be repaired in two days.
He made the boy work for two hours yesterday.
The boy was made to work by him for two hours yesterday.
Mother never lets me watch TV.
I am never let to watch TV (by mother).
Jack gave Peter a Christmas present just now.
A Christmas present was given to Peter by Jack.
Peter was given a Christmas present by Jack (just now).
词性七—动词
动词的时态、语态
动词的分类——实义动词;系动词;助动词;情态动词
1
2
3
动词—时态
动词的词形变化——原形;过去式;过去分词
动词的语法——时态;语态;非谓语动词;虚拟语气
1. 动词的分类—1.实义动词
含实在的意义
表示动作或者状态
在句中独立做谓语
They eat a lot of potatoes.
I’m reading an English book now.
2. 连系动词
本身有一定意义
be 动词&感官动词
His father is a teacher. (be 动词 作 谓语)
Twins usually look the same.
3.助动词
本身没有词义,不能独立作谓语,只和主要动词一起构成谓语动词
表示 否定 疑问 时态 语态 等
有 人称 单复数 和 时态 的 变化
He doesn’t speak English.(辅助构成否定)
We are playing basketball.
(be 动词 作助动词 辅助构成 现在进行时)
4.情态动词
本身有意义,不能独立作谓语,和动词一起构成 谓语动词
情态动词 没有人称和单复数的变化,有些情态动词有过去式
You can keep the books for two weeks.
can—could
动词的词形变化
原形—过去式—过去分词
be, am, is
was
been
be, are
were
been
beat
beat
beaten
lose
lost
lost
make
made
made
put
put
put
动词的时态
现在时 过去时 将来时 过去将来时
一般 ask, asks asked shall, will ask should, would ask
进行 am, is, are, asking was, were asking shall, will be asking should, would be asking
完成 have, has asked had asked shall, will have asked should, would have asked
完成进行 have, has been asking had been asking shall, will have been asking should, would have been asking
动词的时态
一般现在时(4个知识点)
一般过去时(2个知识点)
一般将来时(2个知识点)
现在进行时(3个知识点)
过去进行时(3个知识点)
现在完成时(4个知识点)
过去完成时(3个知识点)
过去将来时(4个知识点)
现在完成进行时(2个知识点)
现在
将来
过去
一般过去时
过去完成时
现在完成时
一般现在时
现在进行时
一般将来时
1.一般现在时
经常或习惯发生的动作或状态
常用的时间状语
They go to the Palace Museum once a year.
They often discuss business in the evening.
表示客观真理,事实,人的技能或现在的状态时句子里一般不用时间状语
The earth turns round the sun.
Light travels faster than sound.
十分确定会发生(事先安排好的事情)或按照时间表进行的事情
用一般现在表示将来,句子中可以有将来时间
The train for Haikou leaves at 8:00 in the morning.
时间状语从句&条件状语从句,一般现在时 表示 将来
Please ring me up as soon as you arrive in Germany.
If it rains tomorrow, we will have to stay at home.
2.一般过去时
表示 过去的动作或状态
可能是 一次性, 也可能 经常发生
Little Tom broke the window at half nine this morning.
When he went into the room, he saw a stranger talking with his father.
He came to our city in the year 2000.
3. 一般将来时
表示将来某一时刻 或 经常发生的动作 或 状态
时间状语
will 动作与 人的主观愿望 无关
shall用于第一人称
will 用于所有人称
am, is, are going to +动词原形
am, is, are to +动词原形
be to +动词原形 (打算/准备 要做 的事情,主观判断即将要发生的事情)
I will graduate from this school soon.
It’s going to rain.
4. 现在进行时
be (am is are) + 现在分词
I am writing a long novel.
表示即将发生的动作,一般指近期安排好的事情
What are you doing tomorrow
频繁发生/反复进行 的动作,常与always等频度副词连用
表示赞扬,不满或者讨厌等感彩
He is always borrowing money from me and forgetting all about it some time later.
5.过去进行时
was/were +现在分词
过去进行时的时间状语
用于 宾语从句 或 时间状语从句 表示与主句动作同时进行 而且 延续时间较长;句子中通常不用状语
He was cooking supper this time yesterday.
The little girl was playing with her toy when I saw her.
She saw it happen when she was walking past.
They sang a lot of songs while they were walking in the dark forest.
6. 现在完成时
have (has) + done
时间状语
I have never seen such time pictures before.
He has just gone to England.
表示在过去开始一直延续到现在的动作或状态
I have been away from my hometown for thirty years.
Uncle Wang has worked in the factory since it opened.
在完成时中,一个瞬间动词(一次性动作)不能与表示一段时间的状语连用,此时必须将瞬间动词改为延续性动词
瞬间性动词的完成时
延续性动词或状态动词的完成时
Have (already) gone to
Have been in / at ... for (two years)
Has come to
Has been here since (1990)
7. 过去完成时
表示的时间是“过去式”
助动词had+动词的过去分词
时间状语
过去完成时时常用于宾语从句中,after引导的从句中,或者从句是before引导的主句中
They had already finished cleaning the classroom when their teacher came.
The woman had left before he realized she was a cheat.
After I had put on my shoes and hat, I walked into the darkness.
He said that he had never seen a kangaroo before.
8. 过去将来时
should或would动词原型 构成
时间状语
在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中不可以使用过去将来时,而应该使用一班过去时
表示纯粹的将来时用would或should; 表示打算或主观认为的事情用was/were going to (+动词原形)
He promised that he would pay me a lot of money if I helped him with the project.
Every time when he was free, he would sit down and read some books.
She told me she would be 18 the next month.
She told me that she was going to have a walk with her pet dog.
9. 现在完成进行时
指一个从过去就开始一直延续到现在并有可能继续下去的动作,它具有现在完成时和现在进行时双重特征
结构:have/has + been + 动词的现在分词
He has been courting her for the last three months.
动词的语态
动词的被动语态
定义
构成
用法
方法:
双宾
to
宾补
短语
定义
主语是动作的执行者(即某人做某事),叫主动语态
主语是动作的承受着(即某事被做),叫被动语态
构成
助动词be + 动词的过去分词(和主系表 不一样)
助动词be有时态、人称和数的变化
被动语态by 短语有时可省去
被动语态的用法
不知道谁是动作的执行者(即不知道所做的)时用被动语态,省略by短语
众所周知是谁做的时,用被动语态,省略by短语
强调动作的承受者,句尾加by的短语
A man was killed in the accident.
This window was broken yesterday.
(不知道谁干的)
Rice is also grown in this place.
A railroad will be built here in three years.
(众所周知)
It was written by Lu Xun.
A pet dog is never killed by its owner.
(强调动作的对象)
主动语态改成被动语态的方法
将主动语态的宾语改为被动语态的主语(涉及主格和宾格)
将主动语态的谓语动词改为 be+过去分词 结构
将主动语态的主语改为介词by之后的宾语,放在谓语动词之后(有时可省略)
双宾的被动语态
把间接宾语改为被动语态的主语,直接宾语仍保留原位
把直接宾语改为主动语态的主语,简介宾语前要加介词to或for
His teacher gave him a dictionary.
He was given a dictionary by his teacher.
A dictionary was given to him by his teacher.
+ to
不带to的动词不定式作宾语补足语的主语动态,改为被动语态时不定式前要+to(使役动词 感官动词 主动无to 被动加to)
The boss made the poor man work 12 hours a day.
----The poor man was made to work 12 hours a day.
带复合宾语的动词
一般把主动语态的宾语改为主语,宾语补足语在被动语态中做助于补足语
I paint the house white.
The hose is painted white by me.
动词短语做谓语
短语动词是不可分割的整体,改为被动语态时要保持其完整性,介词或副词不可遗漏
The girl takes good care of her little brother.
The girl's little brother is taken good care of by her.
All the people laughed at him.
He was laughed at by all people.
We can repair this watch in two days.
This watch can be repaired in two days.
He made the boy work for two hours yesterday.
The boy was made to work by him for two hours yesterday.
Mother never lets me watch TV.
I am never let to watch TV (by mother).
Jack gave Peter a Christmas present just now.
A Christmas present was given to Peter by Jack.
Peter was given a Christmas present by Jack (just now).
