2023届高考英语二轮复习时态专题课件(共36张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2023届高考英语二轮复习时态专题课件(共36张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 3.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2022-12-31 21:21:09 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共36张PPT)
动词时态专题
为什么
时态很重要?
一个时态决定你是暖男还是渣男
问:How many girlfriends have you had
答:I have four girlfriends.
(渣男…)
正确回答:I have had four girlfriends.
一个时态,可以杀死一个人
问:Do you like him
答:Yeah. He was the best man I have ever known.
你是有多恨他?
一个时态,可以让我们多口语更简约、地道
你刚到底有没有听我说话啊?
你的答案:Did you listen to me just now
时态地道版:Were you listening to me
“四时” “四态”
过去时
现在时
将来时
过去将来时
一般式
进行式
完成式
完成进行式
一般表事实;进行表过程;完成表结果
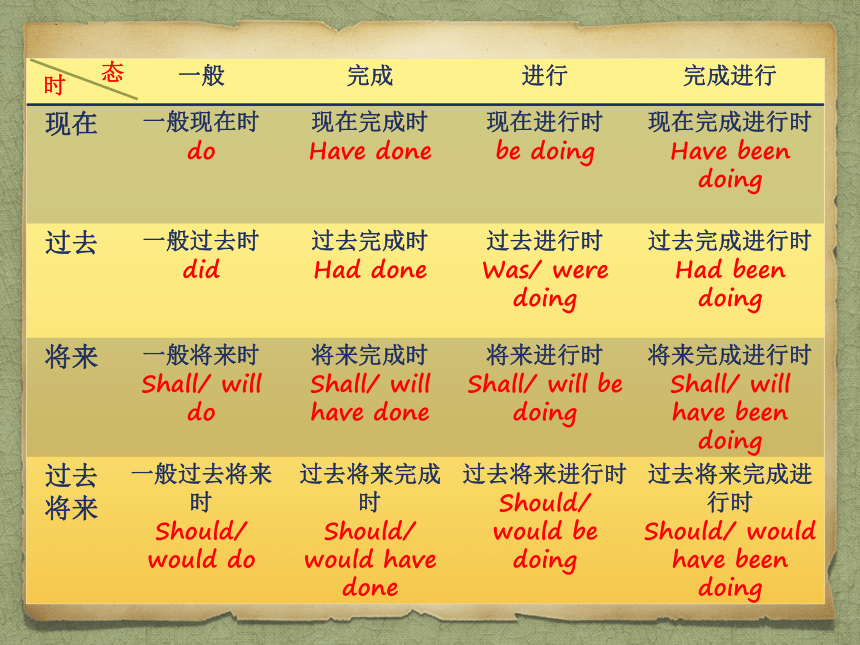
16 Different Tenses
一般 完成 进行 完成进行
现在 一般现在时 do 现在完成时 Have done 现在进行时 be doing 现在完成进行时
Have been doing
过去 一般过去时 did 过去完成时 Had done 过去进行时 Was/ were doing 过去完成进行时
Had been doing
将来 一般将来时 Shall/ will do 将来完成时 Shall/ will have done 将来进行时 Shall/ will be doing 将来完成进行时
Shall/ will have been doing
过去将来 一般过去将来时 Should/ would do 过去将来完成时 Should/ would have done 过去将来进行时 Should/ would be doing 过去将来完成进行时
Should/ would have been doing
时
态
一般现在时
时间轴
过去 现在 将来
习惯性、反复发生
经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态
表示主语目前的性格、特征、状态或能力等
客观事实、普遍真理及自然现象,或格言
按规定、计划、安排、时间表等马上要发生的事情,常与具体的时间状语连用。
主将从现(时间或条件状语从句中)
Every woman thinks she doesn’t have enough clothes to wear.
He is a man of few words.
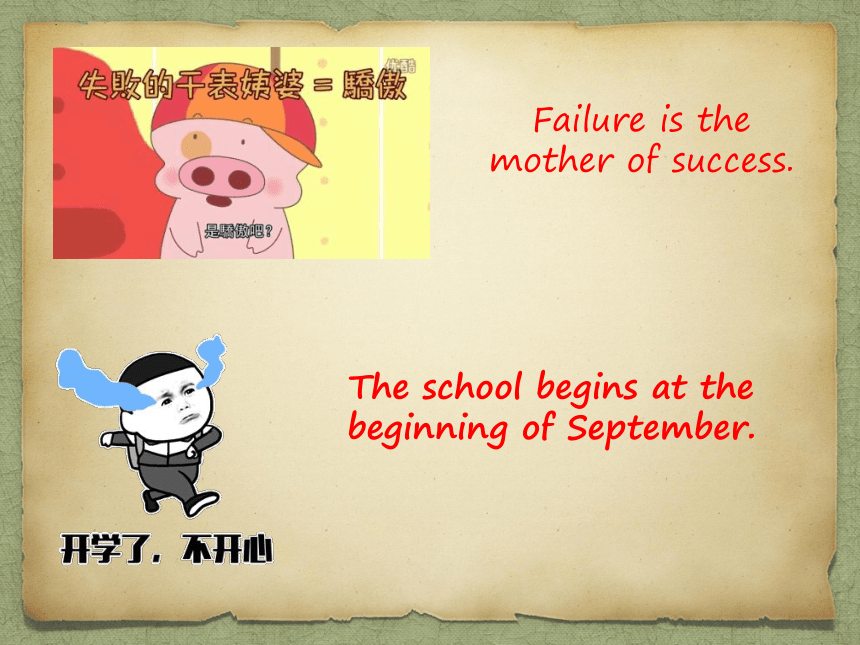
Failure is the mother of success.
The school begins at the beginning of September.
该用法常用于火车时刻表、飞机航班时刻表以及电影开演、作息、安排等时刻表上,且仅限于少数表示短暂意义的动词。例如:
Come go arrive
Leave begin start
Take off finish stop
一般过去时
时间轴
过去 现在 将来
过去发生
过去某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态,其中包括过去的习惯性动作,常与表示过去的时间状语连用。
过去常常做某事 used to do sth.
动作时间没有具体表明,需要根据语境判断。
I didn’t know …
I forgot ...
I thought/ wanted...
表示事先或说话之前不知道或不记得,但现在已经知道或记得的事情。
我原以为/原打算…
I loved you.
I thought he was an honest man.
一般将来时
时间轴
过去 现在 将来
将要发生
Will 表示事物的固有属性或必然趋势;表示将来,有时含有偶然性、临时性决定的意思。
Be going to do表示按计划、打算要做的事;还可表示“预见”,既根据某种迹象预示着要发生某事。
You will look like that guy after experiencing military training.
To avoid being like that, I will take half a month off.
I’m going to follow the latest soap opera.
Look at the wild wind, it is going to rain.
3. Be to do 表示按计划、约定或按职责、义务必须做的事或即将发生的动作。(打算/必须/一定会…)
4. Be about to do 表示立即要发生的动作,常译为“即将…,马上就…” 通常不与具体的时间状语连用。
You are to hand in your homework today.
My weight is about to break the record.
现在进行时
时间轴
过去 现在 将来
现在正在发生
表示现在或现阶段正在发生或一直进行着的动作。
表示按计划或安排将要进行的动作,这类动词主要有:go, come, leave, stay, start, arrive, land, meet, move, return等。
表示反复出现的或习惯性的动作,往往含有赞赏、厌恶、遗憾等情绪,常与always, constantly, continually, forever等连用。
It’s unbelievable that he is being lost in study these days.
I’m coming.
I am telling you all the time that whatever you said is true just because you are pretty.
The teacher is always saying that the life in the university is relaxing.
感觉类:look, smell, feel, taste, see等
情感类:like, love, admire, hate, fear, prefer等
心态类:wish, hope, want, need, believe, agree, know, remember, forget 等
存在类:appear, lie, remain, belong, have等
有些不用于进行时的词:
过去进行时
Was/ were + doing
过去的某个时间点或某段时间内正在发生的动作。
表示运动和位置移动的动词可以用过进表示将来。
I was trembling for the coldness of the dead winter while you were enjoying the sunshine of spring.
I was watching TV secretly in the room when I heard the steps of my mother, which frightened me into cooling the TV set in many ways.
现在完成时
have/ has done
过发现影
过发持现
特殊句型:It/ This/ is + the first time that sb. + have/ has done “是某人第几次做某事
情态动词+have done 虚拟语气
I didn’t notice the hole. So I fell into it.
I haven’t noticed the hole.
What annoys me is that it is my third time that I have fell into the hole without my homework.
Accompanying kids to do their homework is the hardest work that I’ve ever experienced.
I could have lived a better life and lived up to 99.
过去完成时
Had done
过去的过去
“Hardly … when ...” ; “ no sooner ... than... ” 句型中,主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时,意思为“一…就…”
By, by the end, by the time后接表示过去某一时间的短语或从句,主句用过去完成时。
表示“第几次做某事”,主句用过去时,从句用过去完成时。
I had turned off the mobile phone when my mother came in.
Hardly had the teacher turned back to write something on the blackboard when several students began to whisper.
By the time that Xuesu finished the multiple choices, Xueba had finished the whole paper and handed it in confidently.
现在完成进行时
Have/ has been doing
表示从过去某一时间开始,一直持续到现在到动作,并仍在进行。比现在完成时更强调动作到延续性,译为“一直/持续…”
Where have you been
We have been looking for you everywhere.
动词时态专题
为什么
时态很重要?
一个时态决定你是暖男还是渣男
问:How many girlfriends have you had
答:I have four girlfriends.
(渣男…)
正确回答:I have had four girlfriends.
一个时态,可以杀死一个人
问:Do you like him
答:Yeah. He was the best man I have ever known.
你是有多恨他?
一个时态,可以让我们多口语更简约、地道
你刚到底有没有听我说话啊?
你的答案:Did you listen to me just now
时态地道版:Were you listening to me
“四时” “四态”
过去时
现在时
将来时
过去将来时
一般式
进行式
完成式
完成进行式
一般表事实;进行表过程;完成表结果
16 Different Tenses
一般 完成 进行 完成进行
现在 一般现在时 do 现在完成时 Have done 现在进行时 be doing 现在完成进行时
Have been doing
过去 一般过去时 did 过去完成时 Had done 过去进行时 Was/ were doing 过去完成进行时
Had been doing
将来 一般将来时 Shall/ will do 将来完成时 Shall/ will have done 将来进行时 Shall/ will be doing 将来完成进行时
Shall/ will have been doing
过去将来 一般过去将来时 Should/ would do 过去将来完成时 Should/ would have done 过去将来进行时 Should/ would be doing 过去将来完成进行时
Should/ would have been doing
时
态
一般现在时
时间轴
过去 现在 将来
习惯性、反复发生
经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态
表示主语目前的性格、特征、状态或能力等
客观事实、普遍真理及自然现象,或格言
按规定、计划、安排、时间表等马上要发生的事情,常与具体的时间状语连用。
主将从现(时间或条件状语从句中)
Every woman thinks she doesn’t have enough clothes to wear.
He is a man of few words.
Failure is the mother of success.
The school begins at the beginning of September.
该用法常用于火车时刻表、飞机航班时刻表以及电影开演、作息、安排等时刻表上,且仅限于少数表示短暂意义的动词。例如:
Come go arrive
Leave begin start
Take off finish stop
一般过去时
时间轴
过去 现在 将来
过去发生
过去某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态,其中包括过去的习惯性动作,常与表示过去的时间状语连用。
过去常常做某事 used to do sth.
动作时间没有具体表明,需要根据语境判断。
I didn’t know …
I forgot ...
I thought/ wanted...
表示事先或说话之前不知道或不记得,但现在已经知道或记得的事情。
我原以为/原打算…
I loved you.
I thought he was an honest man.
一般将来时
时间轴
过去 现在 将来
将要发生
Will 表示事物的固有属性或必然趋势;表示将来,有时含有偶然性、临时性决定的意思。
Be going to do表示按计划、打算要做的事;还可表示“预见”,既根据某种迹象预示着要发生某事。
You will look like that guy after experiencing military training.
To avoid being like that, I will take half a month off.
I’m going to follow the latest soap opera.
Look at the wild wind, it is going to rain.
3. Be to do 表示按计划、约定或按职责、义务必须做的事或即将发生的动作。(打算/必须/一定会…)
4. Be about to do 表示立即要发生的动作,常译为“即将…,马上就…” 通常不与具体的时间状语连用。
You are to hand in your homework today.
My weight is about to break the record.
现在进行时
时间轴
过去 现在 将来
现在正在发生
表示现在或现阶段正在发生或一直进行着的动作。
表示按计划或安排将要进行的动作,这类动词主要有:go, come, leave, stay, start, arrive, land, meet, move, return等。
表示反复出现的或习惯性的动作,往往含有赞赏、厌恶、遗憾等情绪,常与always, constantly, continually, forever等连用。
It’s unbelievable that he is being lost in study these days.
I’m coming.
I am telling you all the time that whatever you said is true just because you are pretty.
The teacher is always saying that the life in the university is relaxing.
感觉类:look, smell, feel, taste, see等
情感类:like, love, admire, hate, fear, prefer等
心态类:wish, hope, want, need, believe, agree, know, remember, forget 等
存在类:appear, lie, remain, belong, have等
有些不用于进行时的词:
过去进行时
Was/ were + doing
过去的某个时间点或某段时间内正在发生的动作。
表示运动和位置移动的动词可以用过进表示将来。
I was trembling for the coldness of the dead winter while you were enjoying the sunshine of spring.
I was watching TV secretly in the room when I heard the steps of my mother, which frightened me into cooling the TV set in many ways.
现在完成时
have/ has done
过发现影
过发持现
特殊句型:It/ This/ is + the first time that sb. + have/ has done “是某人第几次做某事
情态动词+have done 虚拟语气
I didn’t notice the hole. So I fell into it.
I haven’t noticed the hole.
What annoys me is that it is my third time that I have fell into the hole without my homework.
Accompanying kids to do their homework is the hardest work that I’ve ever experienced.
I could have lived a better life and lived up to 99.
过去完成时
Had done
过去的过去
“Hardly … when ...” ; “ no sooner ... than... ” 句型中,主句用过去完成时,从句用一般过去时,意思为“一…就…”
By, by the end, by the time后接表示过去某一时间的短语或从句,主句用过去完成时。
表示“第几次做某事”,主句用过去时,从句用过去完成时。
I had turned off the mobile phone when my mother came in.
Hardly had the teacher turned back to write something on the blackboard when several students began to whisper.
By the time that Xuesu finished the multiple choices, Xueba had finished the whole paper and handed it in confidently.
现在完成进行时
Have/ has been doing
表示从过去某一时间开始,一直持续到现在到动作,并仍在进行。比现在完成时更强调动作到延续性,译为“一直/持续…”
Where have you been
We have been looking for you everywhere.
