人教版(新课程标准) 选修8Unit 4 PygmalionUnit 4 Pygmalion Reading 课件(共81张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(新课程标准) 选修8Unit 4 PygmalionUnit 4 Pygmalion Reading 课件(共81张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 4.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-01-27 21:57:55 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共81张PPT)
Period1 Reading
Unit 4 Pygmalion
The author —— George Bernard Shaw
An Irish dramatist, literary critic, a socialist spokesman, and a leading figure in the 20th century theater.
His main works:
Immaturity
Widowers’ Houses
Pygmalion
Man and Superman (1902),
Major Barbara (1905)
This play by George Bernard Shaw is an adaptation of a Greek story. Do you know this story
Warming up
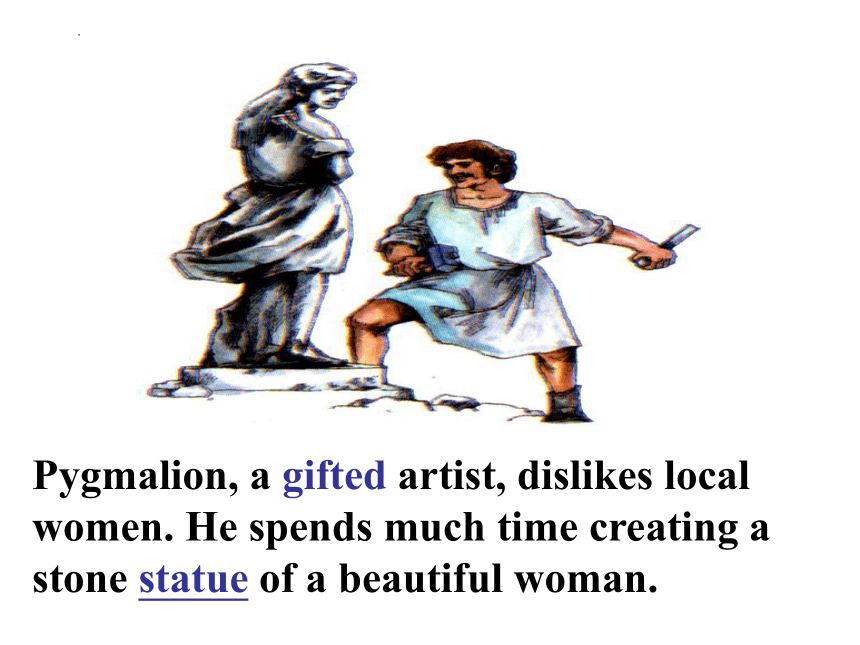
Pygmalion, a gifted artist, dislikes local women. He spends much time creating a stone statue of a beautiful woman.
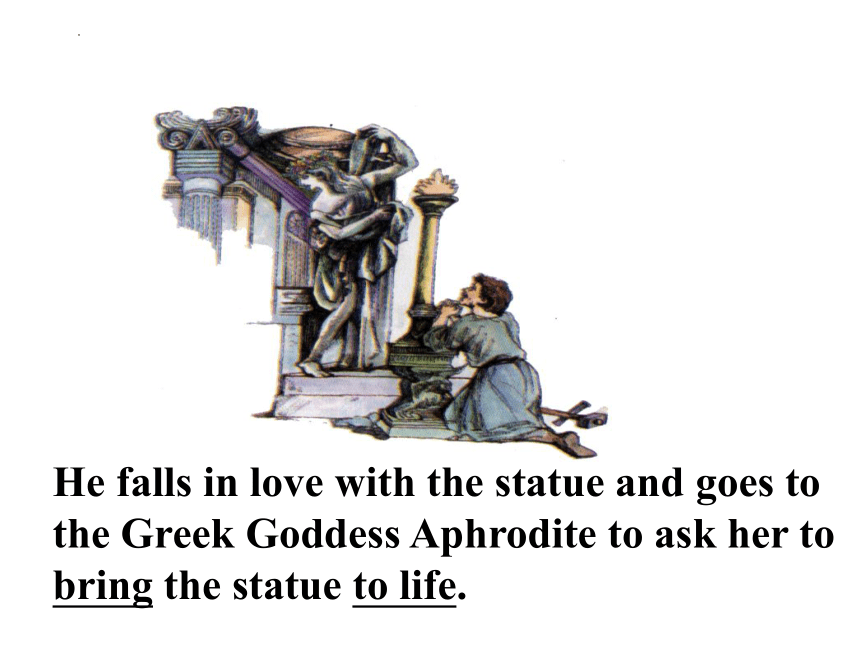
He falls in love with the statue and goes to the Greek Goddess Aphrodite to ask her to bring the statue to life.
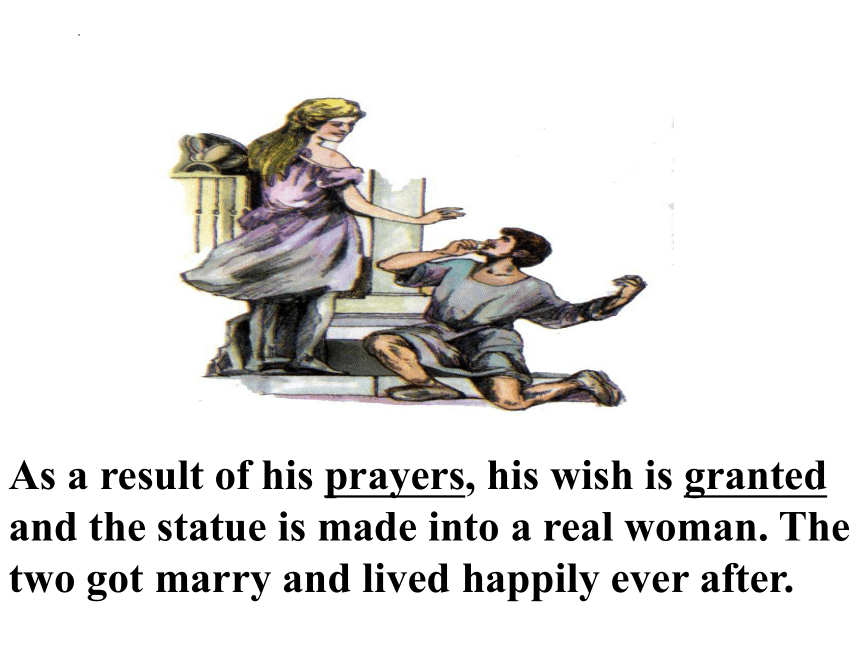
As a result of his prayers, his wish is granted and the statue is made into a real woman. The two got marry and lived happily ever after.
is that people tend to behave as you expect they will. If you expect a person to take responsibility, they probably will. If you expect them not to even try, they probably won’t.
Psychological term
The Pygmalion Effect
Have you ever heard of the “Pygmalion Effect ”
My Fair Lady
Have you seen the film
Pre-reading
This play “My fair lady” by George Bernard Shaw is an adaptation of this Greek myth.
Although there is no character called Pygmalion in the play, it is about the same theme .
the myth
the play
The play by Shaw has the same theme as the Greek story.
What is the theme of the play
Theme of the Greek story: Pygmalion, an
artist create a statue from stone and make
it have a new life .
Theme of My fair lady: Higgins, a phonetics
create a new girl Eliza from lower class to
upper class by teaching her English.
In Shaw’s play, Professor Higgins is a man who does not like women either and is very rude to them. For a bet he agrees to teach a poor young woman so that she can be passed off(充作) as a rich lady in high class society. So, like Pygmalion, Higgins creates a perfect young woman. Both the statue and Eliza depend on their creator for their new life.
Eliza
Doolittle(E):
a poor
flower girl who is
ambitious
to improve
herself.
Professor Higgins(H): an expert in phonetics, convinced that the quality of a person’s English decides his/her position in society.
Colonel Pickering(CP): an officer in the army an later a friend of Higgins’who sets him a task.
Main characters
Fateful meetings
Act One
Reading
Pygmalion
Read the text quickly and complete its main idea.
The play is mainly about a poor 1. _______ girl who is lucky to come across a professor who might help her to 2. ________ her life.
flower
improve
Skimming
Read the text carefully and fill in
the blanks.
Careful reading
Eliza Doolittle ★ She is very poor and makes a living by 1. _____________ and is 2. _________ to improve herself.
selling flowers
ambitious
Eliza Doolittle ★ When she sees Professor Higgins 3. ____________, she feels worried because she takes him for a(n) 4. ___________ in disguise who wants to catch her as a(n) 5. ______.
★ Her 6. ________ English will make her live in the 7. _______ all her life, according to Professor Higgins.
taking notes
policeman
thief
terrible
gutter
Professor Higgins ★ He is an expert in 8. _______, who thinks that the quality of a person’s English decides his / her 9. ________ in society.
★ He can know where a person is from by what he / she 10. _____.
★ He thinks if taught by him to speak properly, Eliza Doolittle
phonetics
position
says
Professor Higgins may become a(n)
11. ___________ lady.
★ He thinks Eliza Doolittle can be changed into a woman like a duchess at an ambassador’s garden party in 12. ______ months, a lady’s maid or a shop assistant.
★ He was going to 13. ______ to meet Colonel Pickering.
upper class
three
India
Colonel Pickering ★ He is a(n) 14. ______ in the army and later a friend of Higgins’.
★ He studies many Indian 15. ________ and comes to England to make Higgins’ acquaintance.
officer
dialects
1. This text is mainly about the first experience of Eliza meeting with ____.
A. Professor Higgins
B. Colonel Pickering
C. Professor Higgins and Colonel Pickering
D. a gentleman
Read through the act one and choose the best answer.
2. Which of the following can best describe Henry Higgins
A. Kind and polite.
B. Impatient and anxious.
C. Self-important and confident.
D. Unsure and generous.
3. The flower girl wanted to become ________.
A. a duchess B. a shop assistant
C. a lady D. a lady’s maid
4. The flower girl was worried when she found Higgins making notes because __.
A. she thought she did something wrong
B. she thought she didn’t have the right to sell flowers
C. she didn’t want Higgins to write down what she said
D. she thought Higgins was a policeman in disguise
5. Why Eliza began to cry Because _____.
A. she thought Professor Higgins would arrest her
B. the gentleman didn’t give her some money
C. Pickering beat and scolded her
D. there was no reason
6. From the text, we can infer that Professor Higgins is a man described below EXCEPT _________.
A. he doesn’t care about money
B. he is an expert in phonetics
C. he is proud D. he is greedy
Act one of Pygmalion tells us how the main characters of this play, Eliza Doolittle, Professor Higgins and Colonel Pickering had their _______ meetings while ________________ from a heavy rain outside a theatre in London, England in 1914.
sheltering / hiding
fateful
Eliza Doolittle was a poor flower girl. When she tried to sell her flowers to a gentleman, her _______ English caught Professor Higgins’ attention. Professor Higgins, an expert in _________, could place a person by his / her remarks. He convinced that the ______ of a person’s English decides his / her social position.
terrible
phonetics
quality
In his opinion, once educated to speak ________, Eliza Doolittle could pass herself off in three months as a ________ at an ambassador’s garden party and perhaps she could even work as ____________ or a shop assistant.
Colonel Pickering, an officer in the army, who had studied many _______ dialects himself, came to England to make the ____________ of Professor Higgins.
properly
duchess
a lady’s maid
Indian
acquaintance
2 The social position of each character
influences the way they behave to each
other. Generally speaking, people are more
polite to those who they think are of a higher
social class (H) and less polite to those they
consider are members of a lower class (L).
Is this true of the characters in Shaw’s play
Give your evidence in the chart below.
Character Position in society Evidence in the play
Eliza
Lower class
Language: calls gentleman “sir” and “cap’in” (or captain) which is a compliment
Behaviour: respectful to people of higher class
Character Position in society Evidence in the play
Professor Higgins
Language: calls Eliza “you silly girl” and Pickering “my dear man” (an equal and friend)
Behaviour: rude (and patronizing) to lower class; polite to same or upper class
Middle class
Character Position in society Evidence in the play
Colonel Pickering
Upper class
Language: prepared to begin a conversation with Henry, whom he does not know; generous with praise to him
Behaviour: generally confident and polite; but ignores Eliza
What other things show one’s status in society apart from how one speaks
clothes you wear
Attitudes and
behavior
How many foreign
languages spoken
and countries visited
Expensive possessions
Education level
4 Choose those adjectives in the list which best describe each character in the play. In pairs discuss them and then place them in the boxes below. Some can be used more than once.
impatient kind polite rude confident anxious eager enthusiastic emotional self-important ambitious generous unsure superior dynamic
kind, polite, generous,
enthusiastic, eager, confident
impatient, rude, confident,
superior, self-important
anxious, eager, emotional,
ambitious, unsure, dynamic
5 Suppose you have a chance to help Eliza
improve her use of the English language.
Correct all these sentences in terms of
grammar, spelling, etc, so that she can use
them properly.
Come over’ere, cap’in, and buy me
flowers off a poor girl.
Come over here, captain, and buy some
flowers from a poor girl.
2. I ain’t done nothing wrong by speaking to
that gentleman.
I haven’t done anything wrong by speaking
to that gentleman.
3. I thought maybe you was a policeman in
disguise.
I thought maybe you were a policeman in
disguise.
4. How do I know whether’ ou took down
right
How do I know whether you wrote down
what I said accurately
5. A shop assistant Now that’s sommat
I want, that is!
A shop assistant Now that’s something I
would like to be!
work out 计算出, 设法弄懂, 精心制定出, 解决,
进展顺利;锻炼
You can work out the answer by adding all
the numbers.
I haven’t worked out who is going to look after
the kids tonight.
We didn’t plan our art exhibition like that but it
worked out very well.
Warming-up Explanations
Professor Higgins (H): an expert in phonetics,
convinced that the quality of a person’s English
decides his/her position in society.
希金斯教授是一位语音学专家, 他认为一个人的
英语水平决定这个人的社会地位。
convinced vt. 说服; 说动某人
convince sb. to do
我们说服了他坐火车去。
We convinced him to go by train
Language points
2) (be) convinced + of 短语/ that 从句
“坚信……”;“确信……”。例如:
我确信他有罪。
3) convince (vt.) sb + of 短语/that 从句,
“使……坚信……”; “使……确信……”。
I am convinced of his guilt.
=I am convinced that he was guilty.
我不认为她的强作欢颜能使她父亲相信她在
那个小孤岛上过得开心。
I don’t think her forced smile ______________
________________________ on that small
lonely island.
father that she lives happily
will convince her
1. Colonel Pickering (P): an officer in the army and later a friend of Higgins’ who sets him a task.
皮克林上校(简称P): 陆军军官, 后来成为希金斯的朋友。希金斯给他安排了一项任务。
officer与official
officer主要用于指军官, 也可指公司或政府机构中的高级职员;
official指政府内的文职官员, 用作形容词时指“官方的, 正式的”。
2. While watching, he makes notes.
他一边观察, 一边做笔记。
▲ while watching 为 while he was watching 省略句。在以when, while, if, unless 等引导的状语从句中,如果从句中的主语与主句主语一致且从句谓语动词含有be动词的形式,往往将从句中的主语及be动词省略,而以动词的-ing形式或过去分词形式来代替。
1) When _______ help, one often says “Thank you.” or “It’s kind of you.”
A. offering B. to offer
C. to be offered D. offered
2) While ______ the river, he saw a big crocodile.
A. to cross B. crossing
C. cross D. crossed
3. hesitate v. 犹豫, 踌躇
hesitate to do sth. 对做某事犹豫不决
hesitate about doing sth. 对做某事犹豫不决
I always hesitate _____ advising my friends
on what to read.
A. with B. to C. for D. about
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate ____
me.
A. ask B. asked C. to ask D. asking
D
C
4. hold up 1) raise; keep up 举起
Hold up your right hand.
2) show as an example 提出(作为榜样)
The teacher always holds up Tom as a model
of hard work.
3) to delay 阻滞
The building of the new road has been held
up by bad weather.
短语: hold back隐瞒;退缩;抑制
hold down压制控制hold to 遵循; 坚持
hold together 使团结; 连接在一起
5. I ain’t done nothing wrong by speaking to
that gentleman.
我跟那位先生说话, 又没做什么坏事呀。
▲ ain’t 是不规范的语言, 相当于am not,
is not, has not, have not。
① We ain’t coming. 我们不来了。
② They ain’t got it. 他们没有那玩意儿。
6. in disguise 意为“乔装”
我以为你是便衣警察。
I thought maybe ___________________________________
这位皇帝喜欢微服私访。
联想: in need of 意思是“需要”。
他需要理发了。
in need 意思是“在困难(穷困)中”。例如:
我们应该帮助贫困的人。
you was a policeman in disguise.
He is in need of a haircut.
The emperor liked travelling in disguise.
We should help those in need.
7. Here you are (hands over the paper
covered with writing).
给你 (他把写满字的纸递过来)。
▲ hand over 移交; 让与; 交给某人照料
① The captain was unwilling to hand
over the command of his ship.
船长不愿移交军舰的指挥权。
It is certain that he will ____ his business to his son when he gets old. A. take over B. think over C. hand over D. go over
② The thief was ____(hand) over to the policeman.
hand down 传给
hand on 传递
hand up 举手
hand out 分给, 分发
covered with writing为过去分词短语作后置定语, 相当于定语从句which / that is covered with writing.
e.g. ① The concert ___(give) by him was a great success.
1) Some of the suspects ______ refused to answer and kept their mouths shut.
questioning B. being questioned
C. questioned D. to be questioned
2) You will find the word “psychology”
______ under “P” in any dictionary.
have listed B. to be listed
C. listing itself D. listed
8. mistaken adj. 错误的, 不正确的
If I’m not mistaken, we must have met before.
be mistaken about 对……持错误的见解
mistake n./v. 错误; 犯错误
make a mistake
mistake A for B 把A错当成B
9. What if I was 如果我是又怎样呢?
此句为省略句。原句为:
What if I was born in…
What if…意思为“要是……又会怎样 ”
10. Simply phonetics studied and classified from people’s own speech.
只是学了点语音学, 把人们的发音区分一下而已。
classify vt. 编排,分类,归类
e.g. Such people should be classified as
middle peasants.
这样的人应该被分类为中等农民。
归纳拓展
classify既可作及物动词, 也可作不及物动词,
作及物动词时, 表示“分为……”,常构成
be classified into “被分成……”,
be classified as “被分为……”;
classified adj. 表示“分类的, 机密的”; classification n. “分类、类”。
11. But they betray themselves every time they
open their mouths.
但每次一张嘴说话,他们就原形毕露。
betray oneself 无意中露出本性; 背叛
相当多的人面对金钱的诱惑便原形毕露。
_____________________________________
When tempted by money.
Quite a lot of people will betray themselves.
betray 1) vt. give away or make known
泄露(秘密)
他向所有的朋友透露了这个消息。
__________________________________
He betrayed the news to all his friends.
2) vt. to be disloyal or unfaithful to 出卖; 背叛
他的最好的朋友背叛了他。
___________________________
His best friend betrayed him.
他背叛祖国,向敌人投降了。
_____________________________________.
He betrayed his country to the enemy
3) to be a sign of (sth. One would like to hide)
显露; 显示
他的脸显露出他很生气。
_________________________________
betray + n. + to 出卖, 背叛
betray +n.+ (to be)/-that “无意中显示, 暴露”
名词形式 betrayal,
如: an act of betrayal 背叛的行为
His face betrayed that he was angry.
13. Now once taught by me…
一旦由我来教……
When ____(finish), the homework was
handed in.
以once, if, as, unless, when, though, although引导的状语
从句, 若从句主语与主句主语一致, 且从句中谓语动词为
be+v.-ed 形式, 或从句中主谓结构为it is (was)+ adj.时,
则从句结构可以直接由以上连词加v-ed或adj.代替。
________ (face) with so much trouble, we failed to complete the task on time.
[点拨] 固定短语sb. be faced with sth. (某人面对……) 。此处是过去分词短语作原因状语, 表状态。
Faced
14. condemn vt. 谴责
1) condemn sb. / sth. 谴责某人/某事
大部分人谴责任何形式的暴力行为。
_____________________________________
2) be condemned to death / be sentenced to
death 被判死刑
那个罪犯被判处死刑。
__________________________________
3) condemn sb. to do sth. 使…注定
他的病使他被迫一直呆在床上。
_______________________________________
___________
Most people condemn any sort of violence.
The criminal was condemned to death.
His illness condemned him to be in bed all
the time.
15. But, sir, (proudly) once educated to speak
properly, the girl could pass herself off in three
months as a duchess at an ambassador’s garden
party. 可是, 先生(自豪地), 一旦那个女孩被教会
说正确的英语, 她就能够在三个月后在一位大使
举办的舞会上冒充一位女公爵。
Pass…off…as
QQ上,骗子常常冒充好友骗钱。
The cheater often passes himself off as your
good friend to cheat you out of your money
pass away 去世
pass down/on 把……传给后世
pass out 昏过去; 失去知觉
pass …on to 把……传递给
pass through 通过; 穿过
pass by 走过; 不理会
16. acquaintance n. 相识; 了解 acquaint vt.
使某人了解
make one’s acquaintance /
make the acquaintance of sb.
结识某人
be familiar with/be acquainted with
对……熟悉
acquaint sb. with
acquaintance既可作不可数名词, 表“熟悉, 认识”, 表“某种程度的熟悉与了解”, 与with连用; 作可数名词, 表“熟识的人”。
I still keep up acquaintance _______him.
我仍然和他联系着。
I have a slight acquaintance with the language.
我懂一点这种语言。
Where did you make his acquaintance 你在哪里与他相识?
I have some acquaintance ______French, but I do not know it well. 我懂得一点法语, 但不精通。
with
with
have a nodding acquaintance with sb.
与某人为点头之交
The musician had little acquaintance
_____ modern science.
A. in B. with C. to D. of
I am delighted to _____ your acquaintance.
A. pull B. take C. have D. make
B
D
2. I have _____ slight acquaintance ____ English. A. a; to B. a; with C. /;with D. /; to
1. He is not a ____, only a (an) ____. A. friend; acquaintances B. acquaintance; friend C. friend; acquaintance D. acquaintances; friend
单项填空
17. a handful of 一把,少数的 (人)
我们邀请了12人, 但只有几个人来。
We invited 12, but only a handful of
them came.
a basketful of
a bagful of
a mouthful of
a pocketful of
一篮子
一书包
一口
一袋
18. Well, I never! A whole pound! A
fortune! 啊, 我从没有! 一英镑! 一笔财富!
Fortune smiled on him. 他事事顺利.
1)[U] success; good luck 成功; 好运, 幸运
Fortune smiled on him. 他事事顺利.
2) [C] 未来的命运; 运道; 运气
What will be our fortune
One day good fortune befell him.
3) [C] 财富
He received a large fortune when his father died.
拓展:
fortunate adj. 幸运的
fortunately adv. 幸运地
make a fortune 发财
seek one’s fortune 外出找出路
try one’s fortune 碰运气
be fortunate to do sth. / in doing sth. 幸运地做某事
19. superior 作为形容词有两大用法:
1) 作为普通形容词, 意为“傲慢的”。例如:
我讨厌他那傲慢的态度。
I hate his superior manner.
2) 作为暗含比较级的形容词, 意为“较高级”、
“较好的”、“较……为优秀的”。
由于superior本身隐含着比较意义, 因此不能
在前面再加more。在与另一事物进行比较时,
与之搭配的介词要用to, 不能用than。如:
Johnson is superior to Mr. Wang in mathematics.
与superior用法相同的词还有inferior,
senior, junior, prior(在…之前)等。
比……优越, 不屈服于 be superior to
低于 be inferior to
比……年长 be senior to
比……年轻 be junior to
他比我小很多岁。He is junior to me by many
years.
20. in terms of 就……来说, 从……角度
In terms of money we’re quite rich, but not in
terms of happiness.
in the long/ short term
从长期/短期而言
(Passage A)
1…方面的专家 an expert in
2. 给某人派任务 set sb a task
3. 避雨 shelter/hide from rain
4. 做记录 make\take notes
5. 举起hold up
6. 对某人有用be of use to sb
7. 化装in disguise
8. 记下take down
9. 交出,移交 hand over
10. 要是…怎么办 what if…
11. 透露身份,显露(本来面目) betray oneself
12. 注定使某人… condemn sb to sth.
13. 冒充某人pass off as sb.
14. 结识,与…相见 make sb’s acquaintance
15. 一把,几个 a handful of
16. 惊奇地 in amazement
17.以…的声音 in a …voice
8. 再一次 once more
9. 需要 in need of
10. 处理对付 deal with
11. 声音模糊 fade out
12. 演员退场 go off stage
Thank You!
Period1 Reading
Unit 4 Pygmalion
The author —— George Bernard Shaw
An Irish dramatist, literary critic, a socialist spokesman, and a leading figure in the 20th century theater.
His main works:
Immaturity
Widowers’ Houses
Pygmalion
Man and Superman (1902),
Major Barbara (1905)
This play by George Bernard Shaw is an adaptation of a Greek story. Do you know this story
Warming up
Pygmalion, a gifted artist, dislikes local women. He spends much time creating a stone statue of a beautiful woman.
He falls in love with the statue and goes to the Greek Goddess Aphrodite to ask her to bring the statue to life.
As a result of his prayers, his wish is granted and the statue is made into a real woman. The two got marry and lived happily ever after.
is that people tend to behave as you expect they will. If you expect a person to take responsibility, they probably will. If you expect them not to even try, they probably won’t.
Psychological term
The Pygmalion Effect
Have you ever heard of the “Pygmalion Effect ”
My Fair Lady
Have you seen the film
Pre-reading
This play “My fair lady” by George Bernard Shaw is an adaptation of this Greek myth.
Although there is no character called Pygmalion in the play, it is about the same theme .
the myth
the play
The play by Shaw has the same theme as the Greek story.
What is the theme of the play
Theme of the Greek story: Pygmalion, an
artist create a statue from stone and make
it have a new life .
Theme of My fair lady: Higgins, a phonetics
create a new girl Eliza from lower class to
upper class by teaching her English.
In Shaw’s play, Professor Higgins is a man who does not like women either and is very rude to them. For a bet he agrees to teach a poor young woman so that she can be passed off(充作) as a rich lady in high class society. So, like Pygmalion, Higgins creates a perfect young woman. Both the statue and Eliza depend on their creator for their new life.
Eliza
Doolittle(E):
a poor
flower girl who is
ambitious
to improve
herself.
Professor Higgins(H): an expert in phonetics, convinced that the quality of a person’s English decides his/her position in society.
Colonel Pickering(CP): an officer in the army an later a friend of Higgins’who sets him a task.
Main characters
Fateful meetings
Act One
Reading
Pygmalion
Read the text quickly and complete its main idea.
The play is mainly about a poor 1. _______ girl who is lucky to come across a professor who might help her to 2. ________ her life.
flower
improve
Skimming
Read the text carefully and fill in
the blanks.
Careful reading
Eliza Doolittle ★ She is very poor and makes a living by 1. _____________ and is 2. _________ to improve herself.
selling flowers
ambitious
Eliza Doolittle ★ When she sees Professor Higgins 3. ____________, she feels worried because she takes him for a(n) 4. ___________ in disguise who wants to catch her as a(n) 5. ______.
★ Her 6. ________ English will make her live in the 7. _______ all her life, according to Professor Higgins.
taking notes
policeman
thief
terrible
gutter
Professor Higgins ★ He is an expert in 8. _______, who thinks that the quality of a person’s English decides his / her 9. ________ in society.
★ He can know where a person is from by what he / she 10. _____.
★ He thinks if taught by him to speak properly, Eliza Doolittle
phonetics
position
says
Professor Higgins may become a(n)
11. ___________ lady.
★ He thinks Eliza Doolittle can be changed into a woman like a duchess at an ambassador’s garden party in 12. ______ months, a lady’s maid or a shop assistant.
★ He was going to 13. ______ to meet Colonel Pickering.
upper class
three
India
Colonel Pickering ★ He is a(n) 14. ______ in the army and later a friend of Higgins’.
★ He studies many Indian 15. ________ and comes to England to make Higgins’ acquaintance.
officer
dialects
1. This text is mainly about the first experience of Eliza meeting with ____.
A. Professor Higgins
B. Colonel Pickering
C. Professor Higgins and Colonel Pickering
D. a gentleman
Read through the act one and choose the best answer.
2. Which of the following can best describe Henry Higgins
A. Kind and polite.
B. Impatient and anxious.
C. Self-important and confident.
D. Unsure and generous.
3. The flower girl wanted to become ________.
A. a duchess B. a shop assistant
C. a lady D. a lady’s maid
4. The flower girl was worried when she found Higgins making notes because __.
A. she thought she did something wrong
B. she thought she didn’t have the right to sell flowers
C. she didn’t want Higgins to write down what she said
D. she thought Higgins was a policeman in disguise
5. Why Eliza began to cry Because _____.
A. she thought Professor Higgins would arrest her
B. the gentleman didn’t give her some money
C. Pickering beat and scolded her
D. there was no reason
6. From the text, we can infer that Professor Higgins is a man described below EXCEPT _________.
A. he doesn’t care about money
B. he is an expert in phonetics
C. he is proud D. he is greedy
Act one of Pygmalion tells us how the main characters of this play, Eliza Doolittle, Professor Higgins and Colonel Pickering had their _______ meetings while ________________ from a heavy rain outside a theatre in London, England in 1914.
sheltering / hiding
fateful
Eliza Doolittle was a poor flower girl. When she tried to sell her flowers to a gentleman, her _______ English caught Professor Higgins’ attention. Professor Higgins, an expert in _________, could place a person by his / her remarks. He convinced that the ______ of a person’s English decides his / her social position.
terrible
phonetics
quality
In his opinion, once educated to speak ________, Eliza Doolittle could pass herself off in three months as a ________ at an ambassador’s garden party and perhaps she could even work as ____________ or a shop assistant.
Colonel Pickering, an officer in the army, who had studied many _______ dialects himself, came to England to make the ____________ of Professor Higgins.
properly
duchess
a lady’s maid
Indian
acquaintance
2 The social position of each character
influences the way they behave to each
other. Generally speaking, people are more
polite to those who they think are of a higher
social class (H) and less polite to those they
consider are members of a lower class (L).
Is this true of the characters in Shaw’s play
Give your evidence in the chart below.
Character Position in society Evidence in the play
Eliza
Lower class
Language: calls gentleman “sir” and “cap’in” (or captain) which is a compliment
Behaviour: respectful to people of higher class
Character Position in society Evidence in the play
Professor Higgins
Language: calls Eliza “you silly girl” and Pickering “my dear man” (an equal and friend)
Behaviour: rude (and patronizing) to lower class; polite to same or upper class
Middle class
Character Position in society Evidence in the play
Colonel Pickering
Upper class
Language: prepared to begin a conversation with Henry, whom he does not know; generous with praise to him
Behaviour: generally confident and polite; but ignores Eliza
What other things show one’s status in society apart from how one speaks
clothes you wear
Attitudes and
behavior
How many foreign
languages spoken
and countries visited
Expensive possessions
Education level
4 Choose those adjectives in the list which best describe each character in the play. In pairs discuss them and then place them in the boxes below. Some can be used more than once.
impatient kind polite rude confident anxious eager enthusiastic emotional self-important ambitious generous unsure superior dynamic
kind, polite, generous,
enthusiastic, eager, confident
impatient, rude, confident,
superior, self-important
anxious, eager, emotional,
ambitious, unsure, dynamic
5 Suppose you have a chance to help Eliza
improve her use of the English language.
Correct all these sentences in terms of
grammar, spelling, etc, so that she can use
them properly.
Come over’ere, cap’in, and buy me
flowers off a poor girl.
Come over here, captain, and buy some
flowers from a poor girl.
2. I ain’t done nothing wrong by speaking to
that gentleman.
I haven’t done anything wrong by speaking
to that gentleman.
3. I thought maybe you was a policeman in
disguise.
I thought maybe you were a policeman in
disguise.
4. How do I know whether’ ou took down
right
How do I know whether you wrote down
what I said accurately
5. A shop assistant Now that’s sommat
I want, that is!
A shop assistant Now that’s something I
would like to be!
work out 计算出, 设法弄懂, 精心制定出, 解决,
进展顺利;锻炼
You can work out the answer by adding all
the numbers.
I haven’t worked out who is going to look after
the kids tonight.
We didn’t plan our art exhibition like that but it
worked out very well.
Warming-up Explanations
Professor Higgins (H): an expert in phonetics,
convinced that the quality of a person’s English
decides his/her position in society.
希金斯教授是一位语音学专家, 他认为一个人的
英语水平决定这个人的社会地位。
convinced vt. 说服; 说动某人
convince sb. to do
我们说服了他坐火车去。
We convinced him to go by train
Language points
2) (be) convinced + of 短语/ that 从句
“坚信……”;“确信……”。例如:
我确信他有罪。
3) convince (vt.) sb + of 短语/that 从句,
“使……坚信……”; “使……确信……”。
I am convinced of his guilt.
=I am convinced that he was guilty.
我不认为她的强作欢颜能使她父亲相信她在
那个小孤岛上过得开心。
I don’t think her forced smile ______________
________________________ on that small
lonely island.
father that she lives happily
will convince her
1. Colonel Pickering (P): an officer in the army and later a friend of Higgins’ who sets him a task.
皮克林上校(简称P): 陆军军官, 后来成为希金斯的朋友。希金斯给他安排了一项任务。
officer与official
officer主要用于指军官, 也可指公司或政府机构中的高级职员;
official指政府内的文职官员, 用作形容词时指“官方的, 正式的”。
2. While watching, he makes notes.
他一边观察, 一边做笔记。
▲ while watching 为 while he was watching 省略句。在以when, while, if, unless 等引导的状语从句中,如果从句中的主语与主句主语一致且从句谓语动词含有be动词的形式,往往将从句中的主语及be动词省略,而以动词的-ing形式或过去分词形式来代替。
1) When _______ help, one often says “Thank you.” or “It’s kind of you.”
A. offering B. to offer
C. to be offered D. offered
2) While ______ the river, he saw a big crocodile.
A. to cross B. crossing
C. cross D. crossed
3. hesitate v. 犹豫, 踌躇
hesitate to do sth. 对做某事犹豫不决
hesitate about doing sth. 对做某事犹豫不决
I always hesitate _____ advising my friends
on what to read.
A. with B. to C. for D. about
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate ____
me.
A. ask B. asked C. to ask D. asking
D
C
4. hold up 1) raise; keep up 举起
Hold up your right hand.
2) show as an example 提出(作为榜样)
The teacher always holds up Tom as a model
of hard work.
3) to delay 阻滞
The building of the new road has been held
up by bad weather.
短语: hold back隐瞒;退缩;抑制
hold down压制控制hold to 遵循; 坚持
hold together 使团结; 连接在一起
5. I ain’t done nothing wrong by speaking to
that gentleman.
我跟那位先生说话, 又没做什么坏事呀。
▲ ain’t 是不规范的语言, 相当于am not,
is not, has not, have not。
① We ain’t coming. 我们不来了。
② They ain’t got it. 他们没有那玩意儿。
6. in disguise 意为“乔装”
我以为你是便衣警察。
I thought maybe ___________________________________
这位皇帝喜欢微服私访。
联想: in need of 意思是“需要”。
他需要理发了。
in need 意思是“在困难(穷困)中”。例如:
我们应该帮助贫困的人。
you was a policeman in disguise.
He is in need of a haircut.
The emperor liked travelling in disguise.
We should help those in need.
7. Here you are (hands over the paper
covered with writing).
给你 (他把写满字的纸递过来)。
▲ hand over 移交; 让与; 交给某人照料
① The captain was unwilling to hand
over the command of his ship.
船长不愿移交军舰的指挥权。
It is certain that he will ____ his business to his son when he gets old. A. take over B. think over C. hand over D. go over
② The thief was ____(hand) over to the policeman.
hand down 传给
hand on 传递
hand up 举手
hand out 分给, 分发
covered with writing为过去分词短语作后置定语, 相当于定语从句which / that is covered with writing.
e.g. ① The concert ___(give) by him was a great success.
1) Some of the suspects ______ refused to answer and kept their mouths shut.
questioning B. being questioned
C. questioned D. to be questioned
2) You will find the word “psychology”
______ under “P” in any dictionary.
have listed B. to be listed
C. listing itself D. listed
8. mistaken adj. 错误的, 不正确的
If I’m not mistaken, we must have met before.
be mistaken about 对……持错误的见解
mistake n./v. 错误; 犯错误
make a mistake
mistake A for B 把A错当成B
9. What if I was 如果我是又怎样呢?
此句为省略句。原句为:
What if I was born in…
What if…意思为“要是……又会怎样 ”
10. Simply phonetics studied and classified from people’s own speech.
只是学了点语音学, 把人们的发音区分一下而已。
classify vt. 编排,分类,归类
e.g. Such people should be classified as
middle peasants.
这样的人应该被分类为中等农民。
归纳拓展
classify既可作及物动词, 也可作不及物动词,
作及物动词时, 表示“分为……”,常构成
be classified into “被分成……”,
be classified as “被分为……”;
classified adj. 表示“分类的, 机密的”; classification n. “分类、类”。
11. But they betray themselves every time they
open their mouths.
但每次一张嘴说话,他们就原形毕露。
betray oneself 无意中露出本性; 背叛
相当多的人面对金钱的诱惑便原形毕露。
_____________________________________
When tempted by money.
Quite a lot of people will betray themselves.
betray 1) vt. give away or make known
泄露(秘密)
他向所有的朋友透露了这个消息。
__________________________________
He betrayed the news to all his friends.
2) vt. to be disloyal or unfaithful to 出卖; 背叛
他的最好的朋友背叛了他。
___________________________
His best friend betrayed him.
他背叛祖国,向敌人投降了。
_____________________________________.
He betrayed his country to the enemy
3) to be a sign of (sth. One would like to hide)
显露; 显示
他的脸显露出他很生气。
_________________________________
betray + n. + to 出卖, 背叛
betray +n.+ (to be)/-that “无意中显示, 暴露”
名词形式 betrayal,
如: an act of betrayal 背叛的行为
His face betrayed that he was angry.
13. Now once taught by me…
一旦由我来教……
When ____(finish), the homework was
handed in.
以once, if, as, unless, when, though, although引导的状语
从句, 若从句主语与主句主语一致, 且从句中谓语动词为
be+v.-ed 形式, 或从句中主谓结构为it is (was)+ adj.时,
则从句结构可以直接由以上连词加v-ed或adj.代替。
________ (face) with so much trouble, we failed to complete the task on time.
[点拨] 固定短语sb. be faced with sth. (某人面对……) 。此处是过去分词短语作原因状语, 表状态。
Faced
14. condemn vt. 谴责
1) condemn sb. / sth. 谴责某人/某事
大部分人谴责任何形式的暴力行为。
_____________________________________
2) be condemned to death / be sentenced to
death 被判死刑
那个罪犯被判处死刑。
__________________________________
3) condemn sb. to do sth. 使…注定
他的病使他被迫一直呆在床上。
_______________________________________
___________
Most people condemn any sort of violence.
The criminal was condemned to death.
His illness condemned him to be in bed all
the time.
15. But, sir, (proudly) once educated to speak
properly, the girl could pass herself off in three
months as a duchess at an ambassador’s garden
party. 可是, 先生(自豪地), 一旦那个女孩被教会
说正确的英语, 她就能够在三个月后在一位大使
举办的舞会上冒充一位女公爵。
Pass…off…as
QQ上,骗子常常冒充好友骗钱。
The cheater often passes himself off as your
good friend to cheat you out of your money
pass away 去世
pass down/on 把……传给后世
pass out 昏过去; 失去知觉
pass …on to 把……传递给
pass through 通过; 穿过
pass by 走过; 不理会
16. acquaintance n. 相识; 了解 acquaint vt.
使某人了解
make one’s acquaintance /
make the acquaintance of sb.
结识某人
be familiar with/be acquainted with
对……熟悉
acquaint sb. with
acquaintance既可作不可数名词, 表“熟悉, 认识”, 表“某种程度的熟悉与了解”, 与with连用; 作可数名词, 表“熟识的人”。
I still keep up acquaintance _______him.
我仍然和他联系着。
I have a slight acquaintance with the language.
我懂一点这种语言。
Where did you make his acquaintance 你在哪里与他相识?
I have some acquaintance ______French, but I do not know it well. 我懂得一点法语, 但不精通。
with
with
have a nodding acquaintance with sb.
与某人为点头之交
The musician had little acquaintance
_____ modern science.
A. in B. with C. to D. of
I am delighted to _____ your acquaintance.
A. pull B. take C. have D. make
B
D
2. I have _____ slight acquaintance ____ English. A. a; to B. a; with C. /;with D. /; to
1. He is not a ____, only a (an) ____. A. friend; acquaintances B. acquaintance; friend C. friend; acquaintance D. acquaintances; friend
单项填空
17. a handful of 一把,少数的 (人)
我们邀请了12人, 但只有几个人来。
We invited 12, but only a handful of
them came.
a basketful of
a bagful of
a mouthful of
a pocketful of
一篮子
一书包
一口
一袋
18. Well, I never! A whole pound! A
fortune! 啊, 我从没有! 一英镑! 一笔财富!
Fortune smiled on him. 他事事顺利.
1)[U] success; good luck 成功; 好运, 幸运
Fortune smiled on him. 他事事顺利.
2) [C] 未来的命运; 运道; 运气
What will be our fortune
One day good fortune befell him.
3) [C] 财富
He received a large fortune when his father died.
拓展:
fortunate adj. 幸运的
fortunately adv. 幸运地
make a fortune 发财
seek one’s fortune 外出找出路
try one’s fortune 碰运气
be fortunate to do sth. / in doing sth. 幸运地做某事
19. superior 作为形容词有两大用法:
1) 作为普通形容词, 意为“傲慢的”。例如:
我讨厌他那傲慢的态度。
I hate his superior manner.
2) 作为暗含比较级的形容词, 意为“较高级”、
“较好的”、“较……为优秀的”。
由于superior本身隐含着比较意义, 因此不能
在前面再加more。在与另一事物进行比较时,
与之搭配的介词要用to, 不能用than。如:
Johnson is superior to Mr. Wang in mathematics.
与superior用法相同的词还有inferior,
senior, junior, prior(在…之前)等。
比……优越, 不屈服于 be superior to
低于 be inferior to
比……年长 be senior to
比……年轻 be junior to
他比我小很多岁。He is junior to me by many
years.
20. in terms of 就……来说, 从……角度
In terms of money we’re quite rich, but not in
terms of happiness.
in the long/ short term
从长期/短期而言
(Passage A)
1…方面的专家 an expert in
2. 给某人派任务 set sb a task
3. 避雨 shelter/hide from rain
4. 做记录 make\take notes
5. 举起hold up
6. 对某人有用be of use to sb
7. 化装in disguise
8. 记下take down
9. 交出,移交 hand over
10. 要是…怎么办 what if…
11. 透露身份,显露(本来面目) betray oneself
12. 注定使某人… condemn sb to sth.
13. 冒充某人pass off as sb.
14. 结识,与…相见 make sb’s acquaintance
15. 一把,几个 a handful of
16. 惊奇地 in amazement
17.以…的声音 in a …voice
8. 再一次 once more
9. 需要 in need of
10. 处理对付 deal with
11. 声音模糊 fade out
12. 演员退场 go off stage
Thank You!
