专题04 动词---备考2023中考英语二轮高频考点剖析 课件(共30张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 专题04 动词---备考2023中考英语二轮高频考点剖析 课件(共30张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-02-02 14:10:12 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共30张PPT)
动词(短语)
备考2023中考英语二轮高频考点剖析学案
(一) 动词概说
动词是表示动作或状态的词。动词在句子中充当谓语,它是句子不可缺少的部分,用来说明主语是什么或做什么。英语中的动词有不同的形式,从这些形式可以看出句子的时态、语态和语气。例如:
The boy runs fast. 这个男孩跑得快。(runs表示主语的行为)
He is a boy. 他是个男孩。(is与后面的表语a boy表示主语的状态)
(二) 动词的分类
动词可以按照含义及它们在句中的作用分成四类,即实义动词、连系动词、助动词和情态动词。
1.实义动词
(1) 实义动词概念
实义动词是表示行为、动作或状态的词。它的词义完整,可以单独作谓语。例如:
I live in Beijing with my mother.我和我妈妈住在北京。
It has a round face. 它有一张圆脸。
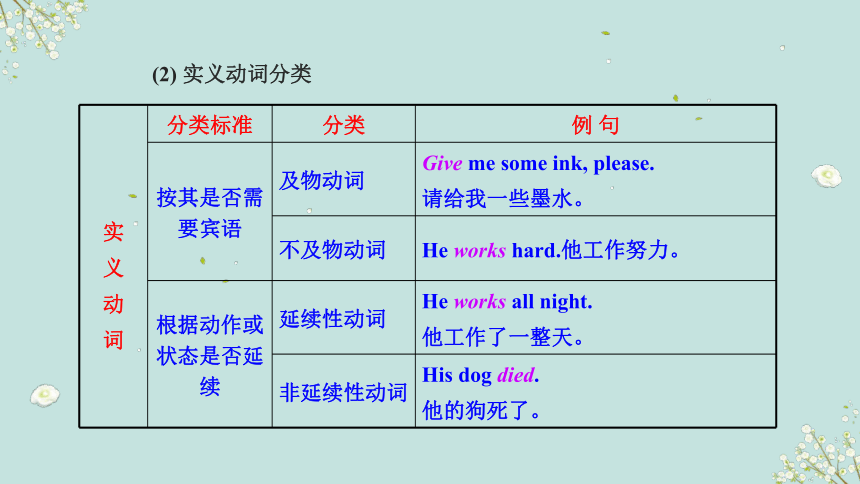
实 义 动 词 分类标准 分类 例 句
按其是否需要宾语 及物动词 Give me some ink, please.
请给我一些墨水。
不及物动词 He works hard.他工作努力。
根据动作或状态是否延续 延续性动词 He works all night.
他工作了一整天。
非延续性动词 His dog died.
他的狗死了。
(2) 实义动词分类
(3)动词的形式
英语动词有五种基本形式,即动词原形、第三人称单数、过去式、过去分词和现在分词。
①动词原形。
动词原形就是词典中所给的形式。例如:be,have,buy,sit等。
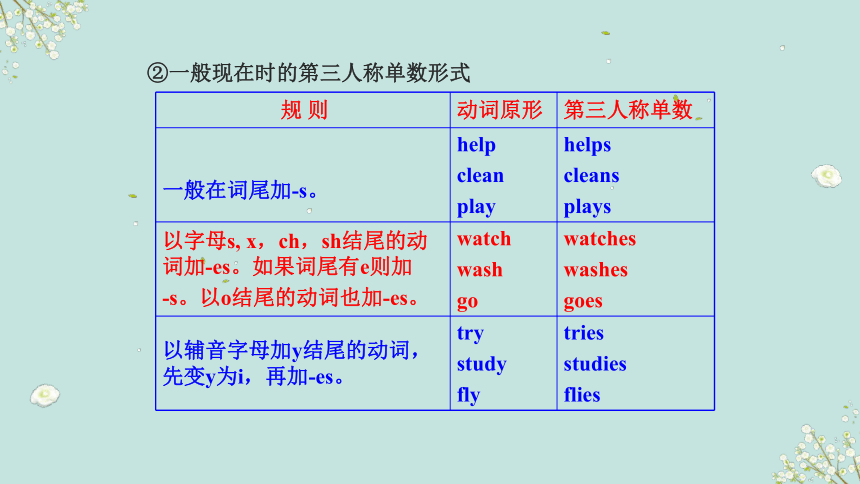
规 则 动词原形 第三人称单数
一般在词尾加-s。 help clean play helps
cleans
plays
以字母s, x,ch,sh结尾的动词加-es。如果词尾有e则加 -s。以o结尾的动词也加-es。 watch wash go watches
washes
goes
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先变y为i,再加-es。 try study fly tries
studies
flies
②一般现在时的第三人称单数形式
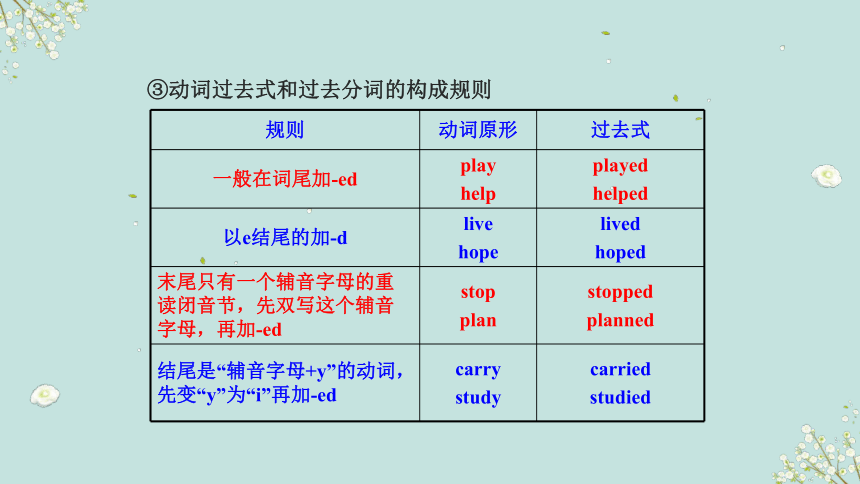
规则 动词原形 过去式
一般在词尾加-ed play help played
helped
以e结尾的加-d live hope lived
hoped
末尾只有一个辅音字母的重读闭音节,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed stop plan stopped
planned
结尾是“辅音字母+y”的动词,先变“y”为“i”再加-ed carry study carried
studied
③动词过去式和过去分词的构成规则
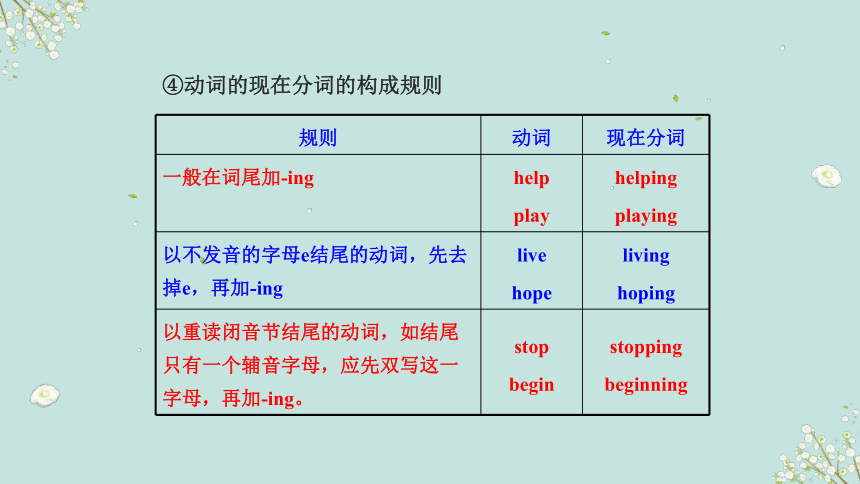
规则 动词 现在分词
一般在词尾加-ing help play helping
playing
以不发音的字母e结尾的动词,先去掉e,再加-ing live hope living
hoping
以重读闭音节结尾的动词,如结尾只有一个辅音字母,应先双写这一字母,再加-ing。 stop begin stopping
beginning
④动词的现在分词的构成规则
2. 连系动词
(1) 连系动词概念
连系动词是表示主语“是什么”或“怎么样”的词,它虽有词义,但不完整,所以不能单独作谓语,必须跟表语一起构成合成谓语,例如:
We are in Grade Two this year. 今年我们在二年级。
are 这个词的词义“是”在句子中常常不译出。
连 系 动 词 分 类 例 句
表示“是”的动词be。例如:am,is,are等。 We are in Grade Two this year.
今年我们在二年级。
表示“感觉”的词。例如:look,feel,smell,sound,taste等。 The story sounds interesting.
这个故事听起来很有趣。
表示“变”、“变成”的意思的词。例如:become,get,grow,turn等。 He feels sick. His face turns white.
他感到不舒服,他的脸色变苍白了。
(2) 连系动词分类
3.助动词
助动词是帮助实义动词完成某些功能(如表示时态、语
态、构成否定句、疑问句、简略答语等)的动词。助动词
本身无词义,不能单独作谓语。
(1) be作为助动词的用法:
①be后跟动词的现在分词可以构成各种进行时态。例如:
—What are you doing 你们在干什么?
—We are watching TV. 我们在看电视。
②be后跟动词的过去分词可以构成被动语态。例如:
The bridge was built last year. 这座桥是去年建造的。
(2) do(does, did)
do的过去式为did,do(did)作为助动词,有以下用法:
① do(does, did)构成一般现在时和一般过去时的疑问
句和否定句。例如:
—Do you like basketball 你喜欢篮球吗?
—Yes, I do. 是的,我喜欢。
②do构成否定祈使句。例如:
Don’t smoke here. 别在这儿吸烟。
(3) have(had)
have的过去式为had, have(had)作为助动词和过去分词一
起构成各种完成时态。例如:
Have you been to Japan 你去过日本吗?
We haven’t finished the work yet. 我们还没有完成这项工作。
(4) will(would),shall(should)
助动词will(would)用于构成一般将来时,shall(should)
用于构成过去将来时。shall(should)主语用于第一人称,
will(would)常用于一切人称。例如:
I will (shall) help her with her English.
我将在英语方面帮助她。
The weather report said that it would rain the next day.
天气预报说明天将有雨。
4.情态动词
情态动词本身有词义,表示说话人的语气和情态,但是词义
不完全,不能单独作谓语动词,只能和不带to的动词不定式
(ought除外)一起构成谓语动词。情态动词没有人称和数
的变化,第三人称的现在时也无变化。
(1) can 和could
①can 和could表示一般的能力,指过去、现在无论什么
时候想做就能做到的能力。can指现在的能力,could指过去的能力。
Birds can fly. 鸟会飞。
I could play the piano when I was five years old.
当我五岁的时候我会弹钢琴。
②can 和could用于否定句和疑问句中表示说话人的
“怀疑”、“猜测”或“不肯定”,could的语气要比can语气更轻些。
Can the news be true 这个消息是真的吗?
The man can’t be my father, because my father has gone to America.
那个人不可能是我爸爸,因为我爸爸去美国了。
③can 可以代替may表示“允许” 。
Can/May I use your dictionary 我可以用你的字典吗?
④could可以表示现在的动作,但语气较为委婉。
Could you help me 你可以帮助我吗?
(2) may 和might
①表示许可。比can和could更正式。might含有试探和犹豫不决的意思。表示给予、许可时,用may,不用might;may not用来表示拒绝或禁止。
May/Might I have a few words with your manager, please
我可以和你的经理谈一谈吗?
You may drive my car, but be careful。
你可以开我的车,但是必须小心。
Student may not smoke. 学生不准吸烟。
②表示将要发生或可能正在发生的可能性。might不是may的过去式,它所表示的可能性比may所表示的可能性要小些。may 不用于表示是否可能的疑问句。例如:
The man may be Tom’s father. 那个人可能是汤姆的爸爸。
Tom might come here. If he comes, I will phone you.
汤姆可能来这儿。如果他来,我将给你打电话。
注意:may not指“可能不”, 而can not指“不可能”。
He may come or may not come. I’m not sure.
他可能来,也可能不来,我拿不准。
(3) have to 和must
①have to主要表示客观需要,意为“不得不”。有人称和时态
的变化(has to; had to; will have to);
②must强调说话人的主观看法,意为“必须,应该”;
The boy had to stay at home alone because his parents
both went to work.
那个男孩不得不独自呆在家里,因为他的父母都去上班了。
We must go to school on time. 我们必须按时上学。
(4) can & be able to
①can只用于现在时和过去时(could), be able to可用于各种
时态。
②遇有助动词或情态动词时只能用be able to。
a. Jack could (was able to) swim at the age of five.
杰克在五岁时就能游泳了。
b. We’ll be able to fly to the moon soon.
不久我们就能飞往月球了。
模拟演练
1. — Who’s that boy reading in the garden Is it David
— It _____ be David. I saw him in the classroom just now.
A. must B. can’t C. may D. shouldn’t
【解析】选B。根据答语“我刚才看见他在教室里了。”可以确定“不可能是大卫。”,故答案为B。
2. —Will you go to the museum with me this afternoon
—Sorry, _____ . My aunt is coming to see me.
A. I don’t B. I can’t C. I needn’t D. I mustn’t
【解析】选B。句意:——今天下午你愿意和我去博物馆吗?——对不起,我不能。我的姑姑要来看我。can’t在此作“不能”讲,故答案为B。
3. —Could you please help me with my English this weekend
—Sorry, I _____ . I have something important to do.
A. can’t B. mustn’t C. needn’t D. must
【解析】选A。句意:——这个周末你可以在英语方面帮助我吗?——对不起,我不能。我有重要的事情做。can’t在此作“不能”讲,故答案为A。
4. —Listen! Kathy is playing the piano in the next room.
—It _____ not be Kathy. She has gone to Hangzhou to visit
the Cross-sea Bridge.
A. can B. must C. need D. shall
【解析】选A。本题考查can表示推测的情况。由答语“她已经去参观杭州的跨海大桥了。”可知不可能是凯西。
5. We _____ careful when we are walking across the road. There are too many vehicles now.
A. can be B. may be C. must be D. could be
【解析】选C。句意:过马路时我们必须小心。现在有太多车辆。故选C。
6. Carol _____ be very bored with her job. She has to do the same thing every day.
A. must B. can’t C. could D. may not
【解析】选A。must在此表有把握的推测,意为“一定”。
7. —Listen, who _____ in the room
—Let’s go and see.
A. is crying B. crying C. cry D. cries
【解析】选A。Listen是现在进行时的标志,who作主语,谓语动词通常用单数。
8. —Mr. Green, _____ you _____ Three Lanes and Seven
Alleys last Sunday
—No, but I’ll visit them next week.
A. will; go to B. have; been to
C. did; go to D. have; gone to
【解析】选C。根据时间状语last Sunday可知时态为一般过去时,因谓语是实义动词,所以一般疑问句应该用助动词did引导。
9. Jane _____ . I’m waiting for her.
A. came back B. has come back
C. hasn’t come back D. didn’t come back
【解析】选C。句意:简还没有回来,我在等她。因此该题用现在完成时。
10. This toy bear _____ be Jane’s. She’s the only kid at the picnic.
A. must B. can C. need D. have to
【解析】选A。句意:这个玩具熊一定是简的。她是惟一参 加野餐的孩子。故选A。
11. In five years, I _____ a doctor.
A. will be B. was C. am D. were
【解析】选A。根据时间状语In five years可知时态应该为一般将来时,故选A。
动词(短语)
备考2023中考英语二轮高频考点剖析学案
(一) 动词概说
动词是表示动作或状态的词。动词在句子中充当谓语,它是句子不可缺少的部分,用来说明主语是什么或做什么。英语中的动词有不同的形式,从这些形式可以看出句子的时态、语态和语气。例如:
The boy runs fast. 这个男孩跑得快。(runs表示主语的行为)
He is a boy. 他是个男孩。(is与后面的表语a boy表示主语的状态)
(二) 动词的分类
动词可以按照含义及它们在句中的作用分成四类,即实义动词、连系动词、助动词和情态动词。
1.实义动词
(1) 实义动词概念
实义动词是表示行为、动作或状态的词。它的词义完整,可以单独作谓语。例如:
I live in Beijing with my mother.我和我妈妈住在北京。
It has a round face. 它有一张圆脸。
实 义 动 词 分类标准 分类 例 句
按其是否需要宾语 及物动词 Give me some ink, please.
请给我一些墨水。
不及物动词 He works hard.他工作努力。
根据动作或状态是否延续 延续性动词 He works all night.
他工作了一整天。
非延续性动词 His dog died.
他的狗死了。
(2) 实义动词分类
(3)动词的形式
英语动词有五种基本形式,即动词原形、第三人称单数、过去式、过去分词和现在分词。
①动词原形。
动词原形就是词典中所给的形式。例如:be,have,buy,sit等。
规 则 动词原形 第三人称单数
一般在词尾加-s。 help clean play helps
cleans
plays
以字母s, x,ch,sh结尾的动词加-es。如果词尾有e则加 -s。以o结尾的动词也加-es。 watch wash go watches
washes
goes
以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先变y为i,再加-es。 try study fly tries
studies
flies
②一般现在时的第三人称单数形式
规则 动词原形 过去式
一般在词尾加-ed play help played
helped
以e结尾的加-d live hope lived
hoped
末尾只有一个辅音字母的重读闭音节,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed stop plan stopped
planned
结尾是“辅音字母+y”的动词,先变“y”为“i”再加-ed carry study carried
studied
③动词过去式和过去分词的构成规则
规则 动词 现在分词
一般在词尾加-ing help play helping
playing
以不发音的字母e结尾的动词,先去掉e,再加-ing live hope living
hoping
以重读闭音节结尾的动词,如结尾只有一个辅音字母,应先双写这一字母,再加-ing。 stop begin stopping
beginning
④动词的现在分词的构成规则
2. 连系动词
(1) 连系动词概念
连系动词是表示主语“是什么”或“怎么样”的词,它虽有词义,但不完整,所以不能单独作谓语,必须跟表语一起构成合成谓语,例如:
We are in Grade Two this year. 今年我们在二年级。
are 这个词的词义“是”在句子中常常不译出。
连 系 动 词 分 类 例 句
表示“是”的动词be。例如:am,is,are等。 We are in Grade Two this year.
今年我们在二年级。
表示“感觉”的词。例如:look,feel,smell,sound,taste等。 The story sounds interesting.
这个故事听起来很有趣。
表示“变”、“变成”的意思的词。例如:become,get,grow,turn等。 He feels sick. His face turns white.
他感到不舒服,他的脸色变苍白了。
(2) 连系动词分类
3.助动词
助动词是帮助实义动词完成某些功能(如表示时态、语
态、构成否定句、疑问句、简略答语等)的动词。助动词
本身无词义,不能单独作谓语。
(1) be作为助动词的用法:
①be后跟动词的现在分词可以构成各种进行时态。例如:
—What are you doing 你们在干什么?
—We are watching TV. 我们在看电视。
②be后跟动词的过去分词可以构成被动语态。例如:
The bridge was built last year. 这座桥是去年建造的。
(2) do(does, did)
do的过去式为did,do(did)作为助动词,有以下用法:
① do(does, did)构成一般现在时和一般过去时的疑问
句和否定句。例如:
—Do you like basketball 你喜欢篮球吗?
—Yes, I do. 是的,我喜欢。
②do构成否定祈使句。例如:
Don’t smoke here. 别在这儿吸烟。
(3) have(had)
have的过去式为had, have(had)作为助动词和过去分词一
起构成各种完成时态。例如:
Have you been to Japan 你去过日本吗?
We haven’t finished the work yet. 我们还没有完成这项工作。
(4) will(would),shall(should)
助动词will(would)用于构成一般将来时,shall(should)
用于构成过去将来时。shall(should)主语用于第一人称,
will(would)常用于一切人称。例如:
I will (shall) help her with her English.
我将在英语方面帮助她。
The weather report said that it would rain the next day.
天气预报说明天将有雨。
4.情态动词
情态动词本身有词义,表示说话人的语气和情态,但是词义
不完全,不能单独作谓语动词,只能和不带to的动词不定式
(ought除外)一起构成谓语动词。情态动词没有人称和数
的变化,第三人称的现在时也无变化。
(1) can 和could
①can 和could表示一般的能力,指过去、现在无论什么
时候想做就能做到的能力。can指现在的能力,could指过去的能力。
Birds can fly. 鸟会飞。
I could play the piano when I was five years old.
当我五岁的时候我会弹钢琴。
②can 和could用于否定句和疑问句中表示说话人的
“怀疑”、“猜测”或“不肯定”,could的语气要比can语气更轻些。
Can the news be true 这个消息是真的吗?
The man can’t be my father, because my father has gone to America.
那个人不可能是我爸爸,因为我爸爸去美国了。
③can 可以代替may表示“允许” 。
Can/May I use your dictionary 我可以用你的字典吗?
④could可以表示现在的动作,但语气较为委婉。
Could you help me 你可以帮助我吗?
(2) may 和might
①表示许可。比can和could更正式。might含有试探和犹豫不决的意思。表示给予、许可时,用may,不用might;may not用来表示拒绝或禁止。
May/Might I have a few words with your manager, please
我可以和你的经理谈一谈吗?
You may drive my car, but be careful。
你可以开我的车,但是必须小心。
Student may not smoke. 学生不准吸烟。
②表示将要发生或可能正在发生的可能性。might不是may的过去式,它所表示的可能性比may所表示的可能性要小些。may 不用于表示是否可能的疑问句。例如:
The man may be Tom’s father. 那个人可能是汤姆的爸爸。
Tom might come here. If he comes, I will phone you.
汤姆可能来这儿。如果他来,我将给你打电话。
注意:may not指“可能不”, 而can not指“不可能”。
He may come or may not come. I’m not sure.
他可能来,也可能不来,我拿不准。
(3) have to 和must
①have to主要表示客观需要,意为“不得不”。有人称和时态
的变化(has to; had to; will have to);
②must强调说话人的主观看法,意为“必须,应该”;
The boy had to stay at home alone because his parents
both went to work.
那个男孩不得不独自呆在家里,因为他的父母都去上班了。
We must go to school on time. 我们必须按时上学。
(4) can & be able to
①can只用于现在时和过去时(could), be able to可用于各种
时态。
②遇有助动词或情态动词时只能用be able to。
a. Jack could (was able to) swim at the age of five.
杰克在五岁时就能游泳了。
b. We’ll be able to fly to the moon soon.
不久我们就能飞往月球了。
模拟演练
1. — Who’s that boy reading in the garden Is it David
— It _____ be David. I saw him in the classroom just now.
A. must B. can’t C. may D. shouldn’t
【解析】选B。根据答语“我刚才看见他在教室里了。”可以确定“不可能是大卫。”,故答案为B。
2. —Will you go to the museum with me this afternoon
—Sorry, _____ . My aunt is coming to see me.
A. I don’t B. I can’t C. I needn’t D. I mustn’t
【解析】选B。句意:——今天下午你愿意和我去博物馆吗?——对不起,我不能。我的姑姑要来看我。can’t在此作“不能”讲,故答案为B。
3. —Could you please help me with my English this weekend
—Sorry, I _____ . I have something important to do.
A. can’t B. mustn’t C. needn’t D. must
【解析】选A。句意:——这个周末你可以在英语方面帮助我吗?——对不起,我不能。我有重要的事情做。can’t在此作“不能”讲,故答案为A。
4. —Listen! Kathy is playing the piano in the next room.
—It _____ not be Kathy. She has gone to Hangzhou to visit
the Cross-sea Bridge.
A. can B. must C. need D. shall
【解析】选A。本题考查can表示推测的情况。由答语“她已经去参观杭州的跨海大桥了。”可知不可能是凯西。
5. We _____ careful when we are walking across the road. There are too many vehicles now.
A. can be B. may be C. must be D. could be
【解析】选C。句意:过马路时我们必须小心。现在有太多车辆。故选C。
6. Carol _____ be very bored with her job. She has to do the same thing every day.
A. must B. can’t C. could D. may not
【解析】选A。must在此表有把握的推测,意为“一定”。
7. —Listen, who _____ in the room
—Let’s go and see.
A. is crying B. crying C. cry D. cries
【解析】选A。Listen是现在进行时的标志,who作主语,谓语动词通常用单数。
8. —Mr. Green, _____ you _____ Three Lanes and Seven
Alleys last Sunday
—No, but I’ll visit them next week.
A. will; go to B. have; been to
C. did; go to D. have; gone to
【解析】选C。根据时间状语last Sunday可知时态为一般过去时,因谓语是实义动词,所以一般疑问句应该用助动词did引导。
9. Jane _____ . I’m waiting for her.
A. came back B. has come back
C. hasn’t come back D. didn’t come back
【解析】选C。句意:简还没有回来,我在等她。因此该题用现在完成时。
10. This toy bear _____ be Jane’s. She’s the only kid at the picnic.
A. must B. can C. need D. have to
【解析】选A。句意:这个玩具熊一定是简的。她是惟一参 加野餐的孩子。故选A。
11. In five years, I _____ a doctor.
A. will be B. was C. am D. were
【解析】选A。根据时间状语In five years可知时态应该为一般将来时,故选A。
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
