人教版(2019)必修第二册Unit 4 History and traditions Reading and Thinking 课件(23张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(2019)必修第二册Unit 4 History and traditions Reading and Thinking 课件(23张ppt) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 15.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-02-06 21:58:44 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
Unit 4 History and traditions
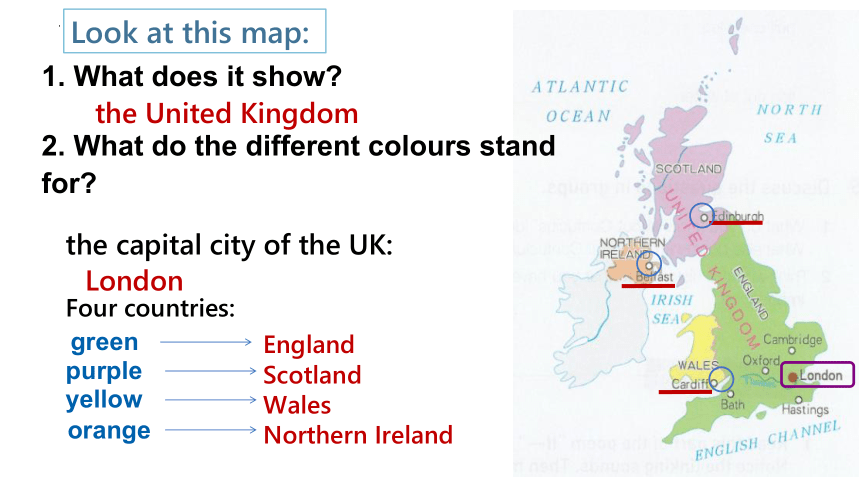
Look at this map:
the capital city of the UK:
London
Four countries:
England
Scotland
Wales
Northern Ireland
the United Kingdom
green
purple
yellow
orange
1. What does it show?
2. What do the different colours stand for?
Predicting
WHAT'S IN A NAME ?
_______________
My puzzle?
Great Britain?
the United Kingdom?
England?
Britain?
the UK?
Know more about the United Kindom.
1. What are the provinces called in England ?
A. departments
B. states
C. counties
Let’s have a competition.
√
A.
B.
C.
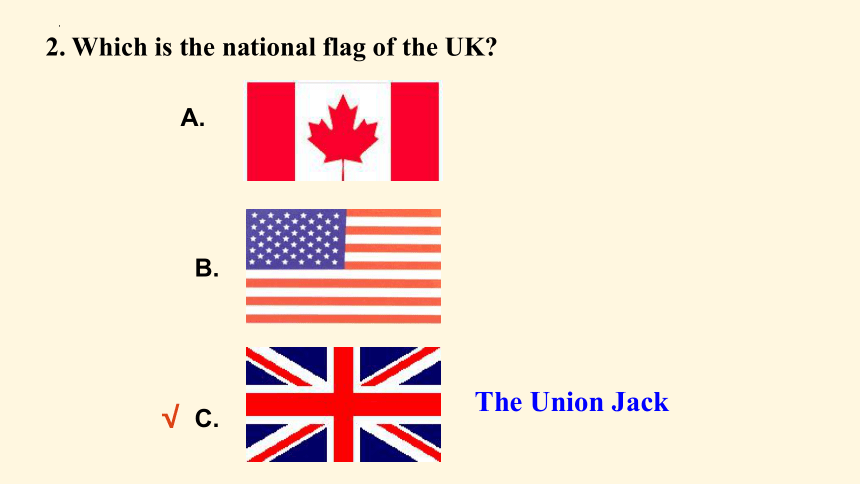
The Union Jack
√
2. Which is the national flag of the UK?
3. Who rules the country?
A. The Queen/the King
B. The Prime Minister
C. both
Rishi Sunak
里希·苏纳克
The king—the head of state, but in name only. The most powerful one is the Prime Minister, who controls everything in the UK.
Charles III
√
4. Which is the bank note of the UK ?
A.
U.S. Dollar
$
B. Euros
?
C. Pounds
?
√
5. Which is the longest river in England?
B.
the River Avon the River Thames
C.
the River Severn
√
England
Wales
Scotland
Let’s have a quiz
Northern Ireland
Southern Ireland
The United Kingdom—It actually includes four countries:England,Scotland,Wales and Northern Ireland.
6. How many countries belong to the UK?
A. two
B. three
C. four
D. five
√
What is the full name of the UK?
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and North Ireland
大不列颠及北爱尔兰联合王国
How many names are used to refer to the UK and what are they?
What does the author suggest to solve this puzzle?
Four names are used, the United Kingdom, Great Britain, Britain and England.
Get to know a little bit about British history.
Para.1
History
1. In which order is para 2 organized?
In the 16th century
In the 18th century
In the 19th century
In the 20th century
Reading tip1:
Scanning is reading the text quickly to find specific (具体的) information,such as dates or numbers.
2. Scan para 2 to circle the words that describe time.
16th century
18th century
19th century
20th century
the Kingdom
of England
the Kingdom
of Great Britain
the United
Kingdom of
Great Britain
and Ireland
the United
Kingdom of
Great Britain
and Northern
Ireland
the United
Kingdom
the UK
different names in the history
was joined to
was joined to
was added to
broke away from
Q2: How did the UK come into being?
England +Wales
England +Wales
+Scotland
Great Britain
+Ireland
Great Britain
+ Northern Ireland
Do the four countries work together in all areas?
The UK is a country of countries.
Similarities and differences (para3)
Similarities: _____; _________;________________
Differences: ____________and ______ systems; _________________ and _____________for competitions.
currency
flag
military defence
educational
legal
their own traditions
football teams
Thinking:
How does the writer develop this paragraph?
Reading tip2:
Giving examples (for example; like) can help readers understand the point more easily & make it more convincing.
Time
Groups
Changes
1st century
Romans
towns & roads
5th century
Anglo-Saxons
English language & houses
8th century
Vikings
new vocabulary &
names of locations
11th century
Normans
castles & legal system & French words
rich culture
a long history
different groups
Four groups of people brought different cultures to the country.
What is the advantage of studying the history of the UK?
It can help you understand much more about the country and its traditions.
para.4
According to para.5, what is another advantage of studying the history of a country?
Studying the history of the country will make
your visit much more enjoyable.
para.5
Who do you think are the intended readers of this passage? Can you find supporting sentences in para5 ?
②If you keep your eyes open, you will be surprised to find that you can see both its past and its present.
①Studying the history of the country will make
your visit much more enjoyable.
Visitors to the UK
Further thinking
Passage Structure Analysis
the topic
The formation and names of
the UK
The similarities and
differences between
the UK’s 4 countries
The four groups of people in the history of the UK and the changes they brought
The significance of studying the history of a country
Para1-3
Para 4
help us understand more about the country and its traditions
Para5
make the visit more enjoyable
help us understand why the UK has many different names
The passage mainly talks about the advantages of studying British history.
Q6: What can studying the history of the UK help us?
Further thinking
Main idea:
A people without the knowledge of their past history, origin and culture is like a tree without roots.
– Marcus Garvey
Appreciate a quote
A
The capital city London is a great place to start, as it is an ancient port city that has a history dating
all the way back to Roman times. There are countless historic sites to explore, and lots of museums with ancient relics from all over the UK.
B
The capital city London is a fascinating place to start, as it is an ancient port city that has a history dating all the way back to Roman times. There are countless historic sites to explore, such as St. Paul’s Cathedral which contains statues in memory of dead poets and writers. There are also lots of museums with ancient relics from all over the UK and even the world. For example, the British Museum boasts a variety of treasures from ancient Greece, Egypt and China.
Read two versions and choose a better one.
Which city do you think is a great place for foreign visitors to enjoy in China? Please introduce it to your partner.
B
The capital city London is a fascinating place to start, as it is an ancient port city that has a history dating all the way back to Roman times. There are countless historic sites to explore, such as St. Paul’s Cathedral which contains statues in memory of dead poets and writers. There are also lots of museums with ancient relics from all over the UK and even the world. For example, the British Museum boasts a variety of treasures from ancient Greece, Egypt and China.
Thanks!
Read the text again and recite the expressions you like.
Finish your introduction to your classmates after class.
Summary & Homework
Look at this map:
the capital city of the UK:
London
Four countries:
England
Scotland
Wales
Northern Ireland
the United Kingdom
green
purple
yellow
orange
1. What does it show?
2. What do the different colours stand for?
Predicting
WHAT'S IN A NAME ?
_______________
My puzzle?
Great Britain?
the United Kingdom?
England?
Britain?
the UK?
Know more about the United Kindom.
1. What are the provinces called in England ?
A. departments
B. states
C. counties
Let’s have a competition.
√
A.
B.
C.
The Union Jack
√
2. Which is the national flag of the UK?
3. Who rules the country?
A. The Queen/the King
B. The Prime Minister
C. both
Rishi Sunak
里希·苏纳克
The king—the head of state, but in name only. The most powerful one is the Prime Minister, who controls everything in the UK.
Charles III
√
4. Which is the bank note of the UK ?
A.
U.S. Dollar
$
B. Euros
?
C. Pounds
?
√
5. Which is the longest river in England?
B.
the River Avon the River Thames
C.
the River Severn
√
England
Wales
Scotland
Let’s have a quiz
Northern Ireland
Southern Ireland
The United Kingdom—It actually includes four countries:England,Scotland,Wales and Northern Ireland.
6. How many countries belong to the UK?
A. two
B. three
C. four
D. five
√
What is the full name of the UK?
the United Kingdom of Great Britain and North Ireland
大不列颠及北爱尔兰联合王国
How many names are used to refer to the UK and what are they?
What does the author suggest to solve this puzzle?
Four names are used, the United Kingdom, Great Britain, Britain and England.
Get to know a little bit about British history.
Para.1
History
1. In which order is para 2 organized?
In the 16th century
In the 18th century
In the 19th century
In the 20th century
Reading tip1:
Scanning is reading the text quickly to find specific (具体的) information,such as dates or numbers.
2. Scan para 2 to circle the words that describe time.
16th century
18th century
19th century
20th century
the Kingdom
of England
the Kingdom
of Great Britain
the United
Kingdom of
Great Britain
and Ireland
the United
Kingdom of
Great Britain
and Northern
Ireland
the United
Kingdom
the UK
different names in the history
was joined to
was joined to
was added to
broke away from
Q2: How did the UK come into being?
England +Wales
England +Wales
+Scotland
Great Britain
+Ireland
Great Britain
+ Northern Ireland
Do the four countries work together in all areas?
The UK is a country of countries.
Similarities and differences (para3)
Similarities: _____; _________;________________
Differences: ____________and ______ systems; _________________ and _____________for competitions.
currency
flag
military defence
educational
legal
their own traditions
football teams
Thinking:
How does the writer develop this paragraph?
Reading tip2:
Giving examples (for example; like) can help readers understand the point more easily & make it more convincing.
Time
Groups
Changes
1st century
Romans
towns & roads
5th century
Anglo-Saxons
English language & houses
8th century
Vikings
new vocabulary &
names of locations
11th century
Normans
castles & legal system & French words
rich culture
a long history
different groups
Four groups of people brought different cultures to the country.
What is the advantage of studying the history of the UK?
It can help you understand much more about the country and its traditions.
para.4
According to para.5, what is another advantage of studying the history of a country?
Studying the history of the country will make
your visit much more enjoyable.
para.5
Who do you think are the intended readers of this passage? Can you find supporting sentences in para5 ?
②If you keep your eyes open, you will be surprised to find that you can see both its past and its present.
①Studying the history of the country will make
your visit much more enjoyable.
Visitors to the UK
Further thinking
Passage Structure Analysis
the topic
The formation and names of
the UK
The similarities and
differences between
the UK’s 4 countries
The four groups of people in the history of the UK and the changes they brought
The significance of studying the history of a country
Para1-3
Para 4
help us understand more about the country and its traditions
Para5
make the visit more enjoyable
help us understand why the UK has many different names
The passage mainly talks about the advantages of studying British history.
Q6: What can studying the history of the UK help us?
Further thinking
Main idea:
A people without the knowledge of their past history, origin and culture is like a tree without roots.
– Marcus Garvey
Appreciate a quote
A
The capital city London is a great place to start, as it is an ancient port city that has a history dating
all the way back to Roman times. There are countless historic sites to explore, and lots of museums with ancient relics from all over the UK.
B
The capital city London is a fascinating place to start, as it is an ancient port city that has a history dating all the way back to Roman times. There are countless historic sites to explore, such as St. Paul’s Cathedral which contains statues in memory of dead poets and writers. There are also lots of museums with ancient relics from all over the UK and even the world. For example, the British Museum boasts a variety of treasures from ancient Greece, Egypt and China.
Read two versions and choose a better one.
Which city do you think is a great place for foreign visitors to enjoy in China? Please introduce it to your partner.
B
The capital city London is a fascinating place to start, as it is an ancient port city that has a history dating all the way back to Roman times. There are countless historic sites to explore, such as St. Paul’s Cathedral which contains statues in memory of dead poets and writers. There are also lots of museums with ancient relics from all over the UK and even the world. For example, the British Museum boasts a variety of treasures from ancient Greece, Egypt and China.
Thanks!
Read the text again and recite the expressions you like.
Finish your introduction to your classmates after class.
Summary & Homework
