人教版 高考英语语法专项课件 动词的语态 (49张PPT 含答案)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版 高考英语语法专项课件 动词的语态 (49张PPT 含答案) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 3.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2023-02-13 10:18:44 | ||
图片预览



文档简介
(共49张PPT)
动词的语态
【备考2023】高考专项语法
目录
目 录
被动语态的各种句式
被动语态的各种时态形式
被动语态的用法
主动语态与被动语态的转换
被动语态的注意事项
课后练习
被动语态的各种句式
PART ONE
被动语态的各种句式
被动语态的各种句式
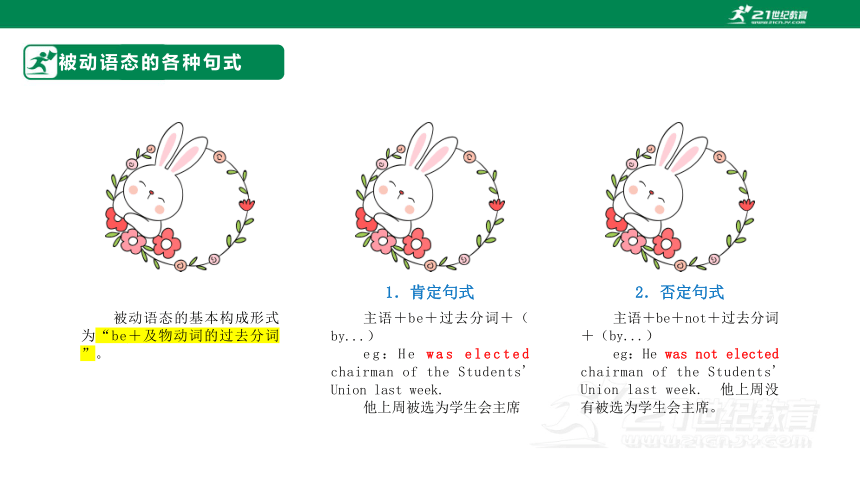
被动语态的基本构成形式为“be+及物动词的过去分词”。
1.肯定句式
主语+be+过去分词+(by...)
eg:He was elected chairman of the Students' Union last week.
他上周被选为学生会主席
2.否定句式
主语+be+not+过去分词+(by...)
eg:He was not elected chairman of the Students' Union last week. 他上周没有被选为学生会主席。
被动语态的各种句式
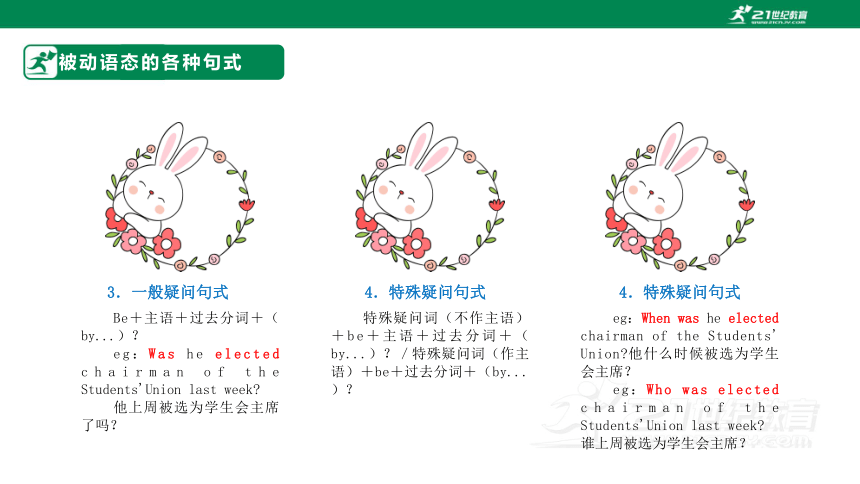
Be+主语+过去分词+(by...)?
eg:Was he elected chairman of the Students'Union last week
他上周被选为学生会主席了吗?
4.特殊疑问句式
特殊疑问词(不作主语)+be+主语+过去分词+(by...)?/特殊疑问词(作主语)+be+过去分词+(by...)?
4.特殊疑问句式
eg:When was he elected chairman of the Students' Union 他什么时候被选为学生会主席?
eg:Who was elected chairman of the Students'Union last week 谁上周被选为学生会主席?
3.一般疑问句式
被动语态的各种句式
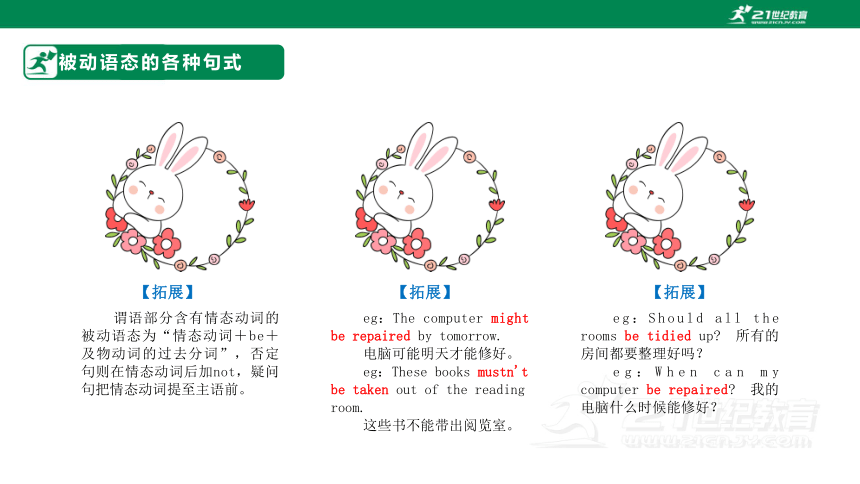
谓语部分含有情态动词的被动语态为“情态动词+be+及物动词的过去分词”,否定句则在情态动词后加not,疑问句把情态动词提至主语前。
【拓展】
eg:The computer might be repaired by tomorrow.
电脑可能明天才能修好。
eg:These books mustn't be taken out of the reading room.
这些书不能带出阅览室。
【拓展】
eg:Should all the rooms be tidied up 所有的房间都要整理好吗?
eg:When can my computer be repaired 我的电脑什么时候能修好?
【拓展】
被动语态的各种时态形式
PART TWO
被动语态的各种时态形式
被动语态的各种时态形式
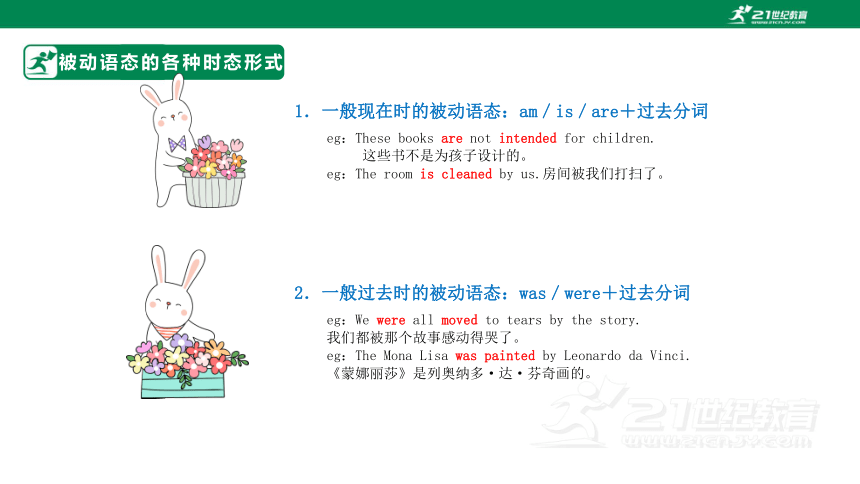
1.一般现在时的被动语态:am/is/are+过去分词
eg:These books are not intended for children.
这些书不是为孩子设计的。
eg:The room is cleaned by us.房间被我们打扫了。
2.一般过去时的被动语态:was/were+过去分词
eg:We were all moved to tears by the story.
我们都被那个故事感动得哭了。
eg:The Mona Lisa was painted by Leonardo da Vinci.
《蒙娜丽莎》是列奥纳多·达·芬奇画的。
被动语态的各种时态形式
3.一般将来时的被动语态:will/shall/be going to/be to+be+过去分词
eg:When will the work be finished 这项工作什么时候能完成?
eg:In the near future,more advances in the robot technology will be made by scientists.
在不久的将来,科学家们将会在机器人技术方面取得更大的进步。
4.现在进行时的被动语态:am/is/are+being+过去分词
eg:Is the accident now being looked into
这个事故现在正在调查吗?
eg:While she is being tortured, Liu Fan grabs a sword from a guard and kills herself.
柳凡在受折磨时,从一个卫兵的手中夺过一把剑自刎。
被动语态的各种时态形式
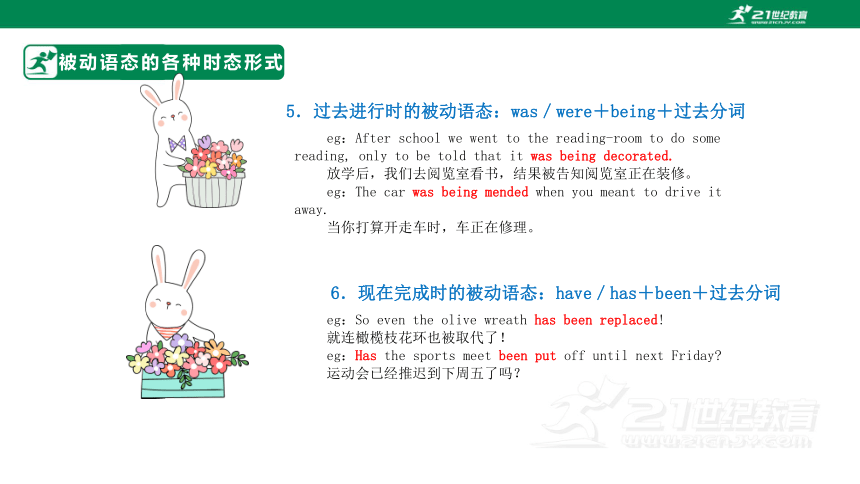
5.过去进行时的被动语态:was/were+being+过去分词
eg:After school we went to the reading-room to do some reading, only to be told that it was being decorated.
放学后,我们去阅览室看书,结果被告知阅览室正在装修。
eg:The car was being mended when you meant to drive it away.
当你打算开走车时,车正在修理。
6.现在完成时的被动语态:have/has+been+过去分词
eg:So even the olive wreath has been replaced!
就连橄榄枝花环也被取代了!
eg:Has the sports meet been put off until next Friday
运动会已经推迟到下周五了吗?
被动语态的各种时态形式
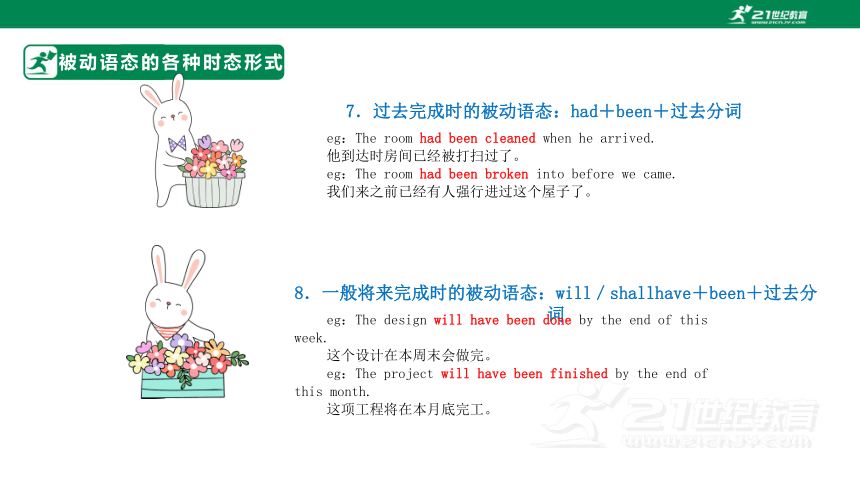
7.过去完成时的被动语态:had+been+过去分词
eg:The room had been cleaned when he arrived.
他到达时房间已经被打扫过了。
eg:The room had been broken into before we came.
我们来之前已经有人强行进过这个屋子了。
8.一般将来完成时的被动语态:will/shallhave+been+过去分词
eg:The design will have been done by the end of this week.
这个设计在本周末会做完。
eg:The project will have been finished by the end of this month.
这项工程将在本月底完工。
被动语态的用法
PART THREE
被动语态的用法
被动语态的用法
1.当不知道动作的执行者是谁或没有必要说明动作的执行者时
eg:The boy was punished for lying.
那个男孩因说谎而受惩罚。
eg:The book was published in 1992.
这本书是1992年出版的。
被动语态的用法
2.强调动作的承受者时
当强调动作的承受者并将承受者作为谈话的中心时用被动语态。
eg:That thief was caught. 那个小偷被抓住了。
eg:The book was taken away by my teacher. 书被我的老师拿走了。
被动语态的用法
3.当动作的执行者不是人而是无生命的事物时
eg:The number of deaths from heart disease will be reduced greatly if people are persuaded to eat more fruit and vegetables.
如果人们被说服吃更多的水果和蔬菜,那么死于心脏病的人数将大大减少。
eg:The house was struck by lightning.
房子被闪电击中。
被动语态的用法
4.出于礼貌,避免说出动作的执行者时
eg:He has been told many times not to park the car here. 有人多次告知他不要把车停在这里。
eg:Everybody is expected to obey the following rules. 希望大家遵守以下规定。
被动语态的用法
5.为使句子更加合理、流畅时
有时为了使句子保持平衡或使句子更加合理,常用被动语态,从而使语句更加流畅。
eg:He appeared on the stage and was warmly applauded by the audience.
他出现在台上,受到观众热烈的鼓掌欢迎。
eg:All these advertisements were made by our company, which was set up in 1990.
所有这些广告都是我们公司做的,我们的公司是1990年成立的。
被动语态的用法
6.公告、新闻报道、报纸标题、科技文章中
eg:Millions of pounds'worth of damage has been caused by a storm which swept across the north of England last night.
昨天晚上一场席卷英格兰北部的风暴造成了上百万英镑的损失。
eg:Fifteen million trees had been blown down by the high winds. 1500万棵树被强风刮倒了。
被动语态的用法
7.习惯用法的需要
有些习惯用法常以被动语态的形式出现。
eg:Mary was born in 2002.
玛丽出生于2002年。
eg:The old man was dressed in a blue coat.
那位老人穿了一件蓝色外套。。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
PART FOUR
主动语态与被动语态的转换
主动语态与被动语态的转换
主动语态与被动语态的转换
1.“主语+谓语+宾语”结构的主、被动转换
将原来的宾语变为被动句的主语,宾语若为人称代词,要将其变成主格;原来的谓语变为“be+过去分词”形式;原来的主语在被动句中由by引出,主语若为人称代词要变为宾格,有时by...短语可省略。
eg:Jim drew a picture. →A picture was drawn by Jim.
吉姆画了一幅画。
eg:The company fired him. →He was fired by the company.
公司解雇了他。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
2.“主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语”结构的主、被动转换
可以将两个宾语中的任何一个宾语作为被动句的主语。直接宾语作被动语态的主语时,句子又有两种:一种转换为带介词to的结构,一种转换为带介词for的结构。
(1)转换为带介词to的结构
可以这样转换的动词主要有give,send,take,bring等。
eg:She passed me an English book./She passed an English book to me.→An English book was passed to me by her./I was passed an English book by her. 她递给我一本英语书。
eg:He sent me an e-mail./He sent an e-mail to me.→An e-mail was sent to me by him. /I was sent an e-mail by him.
他给我发了一封电子邮件。
(2)转换为带介词for的结构可以这样转换的动词主要有buy,make,find,get等。
eg:Jack bought me a nice gift./Jack bought a nice gift for me.→A nice gift was bought for me by Jack. 杰克给我买了一份很棒的礼物。
eg:She made me a nice cake./ She made a nice cake for me.→A nice cake was made for me by her. 她给我做了一个很好的蛋糕。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
3.“主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语”结构的主、被动转换
“主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语”结构变为被 动语态时,应将主动句中的宾语变为主语,宾语补足语形式不变但相应地成为主语补足语。
eg: We made Mr White leader of the team.→Mr White was made leader of the team.
我们选怀特先生为队长。
eg:I find this book very interesting.→This book is found very interesting.
我发现这本书很有趣。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
【拓展】
不带to的不定式作宾语补足语在句子变为被动时要加上to(let除外)。
eg:You don't have to make Peter work hard.→Peter doesn't have to be made to work hard.
你没有必要逼迫彼得努力学习。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
4.谓语为短语动词的主、被动转换
(1)“动词+介词/副词”型
要把动词短语作为整体看,介词或副词不可拆开或漏掉。
eg:We worked out a practical plan.
→A practical plan was worked out by us.
我们已制订出了一个切实可行的计划。
eg:My grandma look after my little brother.
→My little brother is looked after by my grandmother.
奶奶照看我的小弟弟。
(2)“动词+副词+介词”或“动词+名词+介词”型
有时可把结构中的名词变为被动语态的主语。
eg:I can't put up with such big noise.→Such big noise can't be put up with.
我不能容忍这么大的噪音。
eg:These children are taken good care of.
→Good care is taken of these children.
这些孩子被照顾得很好。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
4.谓语为短语动词的主、被动转换
(1)“动词+介词/副词”型
要把动词短语作为整体看,介词或副词不可拆开或漏掉。
eg:We worked out a practical plan.
→A practical plan was worked out by us.
我们已制订出了一个切实可行的计划。
eg:My grandma look after my little brother.
→My little brother is looked after by my grandmother.
奶奶照看我的小弟弟。
(2)“动词+副词+介词”或“动词+名词+介词”型
有时可把结构中的名词变为被动语态的主语。
eg:I can't put up with such big noise.→Such big noise can't be put up with.
我不能容忍这么大的噪音。
eg:These children are taken good care of.
→Good care is taken of these children.
这些孩子被照顾得很好。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
5.宾语为从句的主、被动转换
含有宾语从句的主动句在变为被动语态时,常用形式主语it替代被动句的主语,变为“It+be+过去分词+原来的宾语从句”结构或“sb./sth.+be+过去分词+to do...”结构。
eg:They say that she is very clever.
→It is said that she is very clever.或She is said to be very clever.
他们说她很聪明。
eg: People believed that the Chinese team would win.
→It was believed that the Chinese team would win. 人们相信中国队会赢。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
6.祈使句的被动语态
肯定祈使句的被动结构为“Let+宾语+be+过去分词”;否定祈使句的被动结构为“Don't+let+宾语+be+过去分词”或“Let+宾语+not be+过去分词”。
eg:Keep the book where it is.
→Let the book be kept where it is.
把书留在原来的地方。
eg: Don't release the news.
→Don't let the news be released. /Let the news not be released.
不要泄漏消息。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
7.双重被动结构
双重被动结构是指句中谓语动词和其后的非谓语 动词均为被动结构,句子的主语既是谓语动词的承受者,同时又是非谓语动词的承受者。
eg:Teachers used to require their students to do too much homework.→Too much homework used to be required to be done by the students.
老师以前经常要求学生做太多的作业。
eg: The teacher allowed the books to be taken out of the library.→The books were allowed to be taken out of the library by the teacher.
老师允许图书被带出图书馆。
被动语态的注意事项
PART FIVE
被动语态的注意事项
被动语态的注意事项
(1)英语中有一些短语常以被动形式呈现,但表示主动意义
eg:She is usually dressed in white.
她通常穿白色衣服。
eg:The boy was seated by the window.
男孩坐在窗户旁。
1.被动形式表示主动意义
被动语态的注意事项
(2)英语中有一些表示情感、态度等的过去分词的用法及意义相当于形容词,作表语时与被动语态的形式相同,但表示主动意义
eg:Told not to go with us, she was disappointed.
因为被告知不能和我们一起去,她很失望。
eg:Are you satisfied with the work
你对这项工作满意吗?
1.被动形式表示主动意义
被动语态的注意事项
2.主动形式表示被动意义
(1)某些系动词,如sound,taste,feel,look,appear, seem,prove等,可用主动形式表示被动意义
eg:The flowers smell sweet. 花儿很香。
eg:This kind of cloth feels soft.这种布料摸起来很柔软。
(2)有些不及物动词(其主语大多指物)可以表达被动意义
①某些可用来表示主语内在“品质”或“性能”的动词,如lock,shut,open,read,write,sell, wash, clean, draw, cut,translate等,在句子中常用主动形式表示被动意义。这种词后常有副词修饰。
eg:The book sells wells. 这本书卖得很好。
eg:This shirt will wear very long.这种衬衣将会很耐穿。
②某些表示“发生”的动词(短语),如break out, take place,happen, occur,burst out等没有被动语态,但其意义中包含被动概念。
eg:The war broke out in 1937. 战争爆发于1937年。
eg:The meeting takes place next Monday. 会议下周一举行。
被动语态的注意事项
2.主动形式表示被动意义
(3)有些介词短语作表语,其主动形式含有被动意义
eg:The fire was finally under control. 大火最终被控制住了。
eg:The task is in the charge of you. 这项任务由你负责。
被动语态的注意事项
3.不可转换为被动句的主动句
不可转换为被动句的主动句主要有以下几种情况:
(1)谓语动词为某些状态动词时
主动句中谓语动词是表示状态的动词,如have,own,possess,want时,不可用被动句。
eg:His father owns a local pub.
他父亲在当地有一家酒馆。
eg:His answer wants politeness.
他的回答有失礼貌。
被动语态的注意事项
3.不可转换为被动句的主动句
(2)受宾语限制的句子
当句子的宾语是反身代词、相互代词、表示地点的名词、不定式短语、动词的-ing形式及抽象名词等时,一般不能变成被动句。
eg:You can help yourself to some food. 你可以随便吃点东西。 为反身代词
eg:We live a happy life here. 我们在这儿过着幸福的生活。 为抽象名词
被动语态的注意事项
4.被动语态和系表结构的区别
此处的系表结构指“be+过去分词”结构,它与 被动语态的形式完全一样,所以在应用时要注意它们的区别。
(1)被动语态中的过去分词多是动词,强调动作;系表结构中的过去分词相当于形容词,多强调状态
eg:The house was surrounded by the police. 被动语态,表示动作
这房子被警察包围了。
eg:My pen is gone.我的钢笔不见了。
系表结构,表示状态
被动语态的注意事项
4.被动语态和系表结构的区别
(2)被动语态常由介词by引出动作的发出者,而系表结构中常用其他介词,如 about,at,in,on, with, over,to等
eg:I was interested by what you showed me. 被动语态
你给我看的东西让我很感兴趣。
eg:I'm interested in the watch.
我对这块手表很感兴趣。 系表结构
(3)被动语态常用greatly,much等词修饰,系表结构常由very,quite, rather, too, so, more, most等词修饰
eg:I'm quite satisfied with your work. 系表结构
我对你的工作相当满意。
eg:We were greatly moved by what the little boy did. 被动语态
我们被那个小男孩的作为深深地感动了。
被动语态的注意事项
4.被动语态和系表结构的区别
(4)谓语动词带有时间、地点或方式状语时,一般是被动语态
eg:The door has already been locked. 门已经被锁上了。
被动语态
eg:The door is locked.
门锁上了。 系表结构
(5)被动语态一般由“助动词be+过去分词”构成。系表结构中be为系动词,而且除了be之外,还可用 become,get,keep,remain 等系动词
eg:She became interested in maths. 系表结构
她开始对数学感兴趣。
eg:The work remained unfinished.
这项工作依然未完成。 系表结构
被动语态的注意事项
4.被动语态和系表结构的区别
(6)被动语态可用于各种时一般时态和完成时态
eg:The machine is being repaired.
被动语态用于进行时态
正在修理机器。
eg:A new school will be built here.被动语态用于将来时态
将在这里建一所新学校。
【拓展】
在口语和非正式语体中,常用“get+过去分词”表示被动语态。这种结构一般只表示动作,用来谈论突然发生的事件。
eg:Be careful not to get burnt in the sun. 小心不要被太阳晒伤。
eg:I got caught in a heavy rain last night. 昨晚我淋了大雨。
practice
PART SIX
practice
语法填空
1. I had a strong desire to reach in and play with the toy,but _____ (hold) back thankfully by the shop window.
2. More expressways _____ (build) in Sichuan soon to promote the local economy.
3. Unless some extra money _____(find), the theatre will close.
4. The students have been working hard on their lessons and their efforts _____ (reward) with success in the end.
5. More efforts,as reported,_____ (make) in the years ahead to accelerate the supply-side structural reform.
语法填空
6. Despite the previous rounds of talks,no agreement _____ (reach) so far by the two sides.
7. -Did you enjoy the party?
-Yes.We _____ (treat) well by our hosts.
8. It is reported that a space station _____ (build) on the moon in years to come.
9. To my delight,I _____ (choose)from hundreds of applicants to attend the opening ceremony.
10. Shortly after he borrowedthis book,he _____ (call) to London to continue his research.
语法填空---答案
1.was held
【解析】根据题干中的 had a strong desire(一般过去时)可推知设空处需用一般过去时;主语1与hold back之间为被动关系,故用被动语态。综上所述答案为 was held。
2.will he built
【解析】根据题干中的soon可知设空处用一般将来时;expressways与build为被动关系,故用一般将来时的被动语态。
3.is found
【解析】由主句中的will可知unless引导的从句应用一般现在时态表将来,且 money和find之间是被动关系,故答案为is found。
语法填空---答案
4.will be rewarded
【解析】根据语境可知设空处需用一般将来时;their efforts与reward之间为被动关系,故用被动语态。综上所述,答案应为一般将来时的被动语态。
5.will be made
【解析】根据 in the years ahead并结合句意可知,动作发生在将来,故用一般将来时;主语more efforts与make为被动关系,故用被动语态。综上所述,答案为 will be made。
6.has been reached
【解析】考查动词的时态和语态。根据题干中的时间状语so far可知此处应该用现在完成时,而agreement与谓语动词之间为被动关系,所以要用现在完成时的被动语态。
语法填空---答案
7.were treated
【解析】本题考查动词的时态和语态。根据 对话内容可知所谈事情发生在过去,且主语we与 动词 treat之间为被动关系,故用一般过去时态的 被动语态。
8.will be built
【解析】本题考查动词的时态和语态。根据语境中的时间状语 in years to come 及 space station和build之间为被动关系可知这里用一般将来时态 的被动语态。
9.was chosen
【解析】本题考查时态和语态。主语I与choose为被动关系,设空处需用被动语态;又因为本题介绍的是过去的一种情况,应用一般过去时,故用一般过去时态的被动语态。
语法填空---答案
10.was called
【解析】根据 borrowed 可推知设空处需用一 般过去时,主语he与call为被动关系,故设空处需用一般过去时的被动语态。
谢谢
21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
中小学教育资源网站
兼职招聘:
https://www.21cnjy.com/recruitment/home/admin
动词的语态
【备考2023】高考专项语法
目录
目 录
被动语态的各种句式
被动语态的各种时态形式
被动语态的用法
主动语态与被动语态的转换
被动语态的注意事项
课后练习
被动语态的各种句式
PART ONE
被动语态的各种句式
被动语态的各种句式
被动语态的基本构成形式为“be+及物动词的过去分词”。
1.肯定句式
主语+be+过去分词+(by...)
eg:He was elected chairman of the Students' Union last week.
他上周被选为学生会主席
2.否定句式
主语+be+not+过去分词+(by...)
eg:He was not elected chairman of the Students' Union last week. 他上周没有被选为学生会主席。
被动语态的各种句式
Be+主语+过去分词+(by...)?
eg:Was he elected chairman of the Students'Union last week
他上周被选为学生会主席了吗?
4.特殊疑问句式
特殊疑问词(不作主语)+be+主语+过去分词+(by...)?/特殊疑问词(作主语)+be+过去分词+(by...)?
4.特殊疑问句式
eg:When was he elected chairman of the Students' Union 他什么时候被选为学生会主席?
eg:Who was elected chairman of the Students'Union last week 谁上周被选为学生会主席?
3.一般疑问句式
被动语态的各种句式
谓语部分含有情态动词的被动语态为“情态动词+be+及物动词的过去分词”,否定句则在情态动词后加not,疑问句把情态动词提至主语前。
【拓展】
eg:The computer might be repaired by tomorrow.
电脑可能明天才能修好。
eg:These books mustn't be taken out of the reading room.
这些书不能带出阅览室。
【拓展】
eg:Should all the rooms be tidied up 所有的房间都要整理好吗?
eg:When can my computer be repaired 我的电脑什么时候能修好?
【拓展】
被动语态的各种时态形式
PART TWO
被动语态的各种时态形式
被动语态的各种时态形式
1.一般现在时的被动语态:am/is/are+过去分词
eg:These books are not intended for children.
这些书不是为孩子设计的。
eg:The room is cleaned by us.房间被我们打扫了。
2.一般过去时的被动语态:was/were+过去分词
eg:We were all moved to tears by the story.
我们都被那个故事感动得哭了。
eg:The Mona Lisa was painted by Leonardo da Vinci.
《蒙娜丽莎》是列奥纳多·达·芬奇画的。
被动语态的各种时态形式
3.一般将来时的被动语态:will/shall/be going to/be to+be+过去分词
eg:When will the work be finished 这项工作什么时候能完成?
eg:In the near future,more advances in the robot technology will be made by scientists.
在不久的将来,科学家们将会在机器人技术方面取得更大的进步。
4.现在进行时的被动语态:am/is/are+being+过去分词
eg:Is the accident now being looked into
这个事故现在正在调查吗?
eg:While she is being tortured, Liu Fan grabs a sword from a guard and kills herself.
柳凡在受折磨时,从一个卫兵的手中夺过一把剑自刎。
被动语态的各种时态形式
5.过去进行时的被动语态:was/were+being+过去分词
eg:After school we went to the reading-room to do some reading, only to be told that it was being decorated.
放学后,我们去阅览室看书,结果被告知阅览室正在装修。
eg:The car was being mended when you meant to drive it away.
当你打算开走车时,车正在修理。
6.现在完成时的被动语态:have/has+been+过去分词
eg:So even the olive wreath has been replaced!
就连橄榄枝花环也被取代了!
eg:Has the sports meet been put off until next Friday
运动会已经推迟到下周五了吗?
被动语态的各种时态形式
7.过去完成时的被动语态:had+been+过去分词
eg:The room had been cleaned when he arrived.
他到达时房间已经被打扫过了。
eg:The room had been broken into before we came.
我们来之前已经有人强行进过这个屋子了。
8.一般将来完成时的被动语态:will/shallhave+been+过去分词
eg:The design will have been done by the end of this week.
这个设计在本周末会做完。
eg:The project will have been finished by the end of this month.
这项工程将在本月底完工。
被动语态的用法
PART THREE
被动语态的用法
被动语态的用法
1.当不知道动作的执行者是谁或没有必要说明动作的执行者时
eg:The boy was punished for lying.
那个男孩因说谎而受惩罚。
eg:The book was published in 1992.
这本书是1992年出版的。
被动语态的用法
2.强调动作的承受者时
当强调动作的承受者并将承受者作为谈话的中心时用被动语态。
eg:That thief was caught. 那个小偷被抓住了。
eg:The book was taken away by my teacher. 书被我的老师拿走了。
被动语态的用法
3.当动作的执行者不是人而是无生命的事物时
eg:The number of deaths from heart disease will be reduced greatly if people are persuaded to eat more fruit and vegetables.
如果人们被说服吃更多的水果和蔬菜,那么死于心脏病的人数将大大减少。
eg:The house was struck by lightning.
房子被闪电击中。
被动语态的用法
4.出于礼貌,避免说出动作的执行者时
eg:He has been told many times not to park the car here. 有人多次告知他不要把车停在这里。
eg:Everybody is expected to obey the following rules. 希望大家遵守以下规定。
被动语态的用法
5.为使句子更加合理、流畅时
有时为了使句子保持平衡或使句子更加合理,常用被动语态,从而使语句更加流畅。
eg:He appeared on the stage and was warmly applauded by the audience.
他出现在台上,受到观众热烈的鼓掌欢迎。
eg:All these advertisements were made by our company, which was set up in 1990.
所有这些广告都是我们公司做的,我们的公司是1990年成立的。
被动语态的用法
6.公告、新闻报道、报纸标题、科技文章中
eg:Millions of pounds'worth of damage has been caused by a storm which swept across the north of England last night.
昨天晚上一场席卷英格兰北部的风暴造成了上百万英镑的损失。
eg:Fifteen million trees had been blown down by the high winds. 1500万棵树被强风刮倒了。
被动语态的用法
7.习惯用法的需要
有些习惯用法常以被动语态的形式出现。
eg:Mary was born in 2002.
玛丽出生于2002年。
eg:The old man was dressed in a blue coat.
那位老人穿了一件蓝色外套。。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
PART FOUR
主动语态与被动语态的转换
主动语态与被动语态的转换
主动语态与被动语态的转换
1.“主语+谓语+宾语”结构的主、被动转换
将原来的宾语变为被动句的主语,宾语若为人称代词,要将其变成主格;原来的谓语变为“be+过去分词”形式;原来的主语在被动句中由by引出,主语若为人称代词要变为宾格,有时by...短语可省略。
eg:Jim drew a picture. →A picture was drawn by Jim.
吉姆画了一幅画。
eg:The company fired him. →He was fired by the company.
公司解雇了他。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
2.“主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语”结构的主、被动转换
可以将两个宾语中的任何一个宾语作为被动句的主语。直接宾语作被动语态的主语时,句子又有两种:一种转换为带介词to的结构,一种转换为带介词for的结构。
(1)转换为带介词to的结构
可以这样转换的动词主要有give,send,take,bring等。
eg:She passed me an English book./She passed an English book to me.→An English book was passed to me by her./I was passed an English book by her. 她递给我一本英语书。
eg:He sent me an e-mail./He sent an e-mail to me.→An e-mail was sent to me by him. /I was sent an e-mail by him.
他给我发了一封电子邮件。
(2)转换为带介词for的结构可以这样转换的动词主要有buy,make,find,get等。
eg:Jack bought me a nice gift./Jack bought a nice gift for me.→A nice gift was bought for me by Jack. 杰克给我买了一份很棒的礼物。
eg:She made me a nice cake./ She made a nice cake for me.→A nice cake was made for me by her. 她给我做了一个很好的蛋糕。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
3.“主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语”结构的主、被动转换
“主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语”结构变为被 动语态时,应将主动句中的宾语变为主语,宾语补足语形式不变但相应地成为主语补足语。
eg: We made Mr White leader of the team.→Mr White was made leader of the team.
我们选怀特先生为队长。
eg:I find this book very interesting.→This book is found very interesting.
我发现这本书很有趣。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
【拓展】
不带to的不定式作宾语补足语在句子变为被动时要加上to(let除外)。
eg:You don't have to make Peter work hard.→Peter doesn't have to be made to work hard.
你没有必要逼迫彼得努力学习。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
4.谓语为短语动词的主、被动转换
(1)“动词+介词/副词”型
要把动词短语作为整体看,介词或副词不可拆开或漏掉。
eg:We worked out a practical plan.
→A practical plan was worked out by us.
我们已制订出了一个切实可行的计划。
eg:My grandma look after my little brother.
→My little brother is looked after by my grandmother.
奶奶照看我的小弟弟。
(2)“动词+副词+介词”或“动词+名词+介词”型
有时可把结构中的名词变为被动语态的主语。
eg:I can't put up with such big noise.→Such big noise can't be put up with.
我不能容忍这么大的噪音。
eg:These children are taken good care of.
→Good care is taken of these children.
这些孩子被照顾得很好。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
4.谓语为短语动词的主、被动转换
(1)“动词+介词/副词”型
要把动词短语作为整体看,介词或副词不可拆开或漏掉。
eg:We worked out a practical plan.
→A practical plan was worked out by us.
我们已制订出了一个切实可行的计划。
eg:My grandma look after my little brother.
→My little brother is looked after by my grandmother.
奶奶照看我的小弟弟。
(2)“动词+副词+介词”或“动词+名词+介词”型
有时可把结构中的名词变为被动语态的主语。
eg:I can't put up with such big noise.→Such big noise can't be put up with.
我不能容忍这么大的噪音。
eg:These children are taken good care of.
→Good care is taken of these children.
这些孩子被照顾得很好。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
5.宾语为从句的主、被动转换
含有宾语从句的主动句在变为被动语态时,常用形式主语it替代被动句的主语,变为“It+be+过去分词+原来的宾语从句”结构或“sb./sth.+be+过去分词+to do...”结构。
eg:They say that she is very clever.
→It is said that she is very clever.或She is said to be very clever.
他们说她很聪明。
eg: People believed that the Chinese team would win.
→It was believed that the Chinese team would win. 人们相信中国队会赢。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
6.祈使句的被动语态
肯定祈使句的被动结构为“Let+宾语+be+过去分词”;否定祈使句的被动结构为“Don't+let+宾语+be+过去分词”或“Let+宾语+not be+过去分词”。
eg:Keep the book where it is.
→Let the book be kept where it is.
把书留在原来的地方。
eg: Don't release the news.
→Don't let the news be released. /Let the news not be released.
不要泄漏消息。
主动语态与被动语态的转换
7.双重被动结构
双重被动结构是指句中谓语动词和其后的非谓语 动词均为被动结构,句子的主语既是谓语动词的承受者,同时又是非谓语动词的承受者。
eg:Teachers used to require their students to do too much homework.→Too much homework used to be required to be done by the students.
老师以前经常要求学生做太多的作业。
eg: The teacher allowed the books to be taken out of the library.→The books were allowed to be taken out of the library by the teacher.
老师允许图书被带出图书馆。
被动语态的注意事项
PART FIVE
被动语态的注意事项
被动语态的注意事项
(1)英语中有一些短语常以被动形式呈现,但表示主动意义
eg:She is usually dressed in white.
她通常穿白色衣服。
eg:The boy was seated by the window.
男孩坐在窗户旁。
1.被动形式表示主动意义
被动语态的注意事项
(2)英语中有一些表示情感、态度等的过去分词的用法及意义相当于形容词,作表语时与被动语态的形式相同,但表示主动意义
eg:Told not to go with us, she was disappointed.
因为被告知不能和我们一起去,她很失望。
eg:Are you satisfied with the work
你对这项工作满意吗?
1.被动形式表示主动意义
被动语态的注意事项
2.主动形式表示被动意义
(1)某些系动词,如sound,taste,feel,look,appear, seem,prove等,可用主动形式表示被动意义
eg:The flowers smell sweet. 花儿很香。
eg:This kind of cloth feels soft.这种布料摸起来很柔软。
(2)有些不及物动词(其主语大多指物)可以表达被动意义
①某些可用来表示主语内在“品质”或“性能”的动词,如lock,shut,open,read,write,sell, wash, clean, draw, cut,translate等,在句子中常用主动形式表示被动意义。这种词后常有副词修饰。
eg:The book sells wells. 这本书卖得很好。
eg:This shirt will wear very long.这种衬衣将会很耐穿。
②某些表示“发生”的动词(短语),如break out, take place,happen, occur,burst out等没有被动语态,但其意义中包含被动概念。
eg:The war broke out in 1937. 战争爆发于1937年。
eg:The meeting takes place next Monday. 会议下周一举行。
被动语态的注意事项
2.主动形式表示被动意义
(3)有些介词短语作表语,其主动形式含有被动意义
eg:The fire was finally under control. 大火最终被控制住了。
eg:The task is in the charge of you. 这项任务由你负责。
被动语态的注意事项
3.不可转换为被动句的主动句
不可转换为被动句的主动句主要有以下几种情况:
(1)谓语动词为某些状态动词时
主动句中谓语动词是表示状态的动词,如have,own,possess,want时,不可用被动句。
eg:His father owns a local pub.
他父亲在当地有一家酒馆。
eg:His answer wants politeness.
他的回答有失礼貌。
被动语态的注意事项
3.不可转换为被动句的主动句
(2)受宾语限制的句子
当句子的宾语是反身代词、相互代词、表示地点的名词、不定式短语、动词的-ing形式及抽象名词等时,一般不能变成被动句。
eg:You can help yourself to some food. 你可以随便吃点东西。 为反身代词
eg:We live a happy life here. 我们在这儿过着幸福的生活。 为抽象名词
被动语态的注意事项
4.被动语态和系表结构的区别
此处的系表结构指“be+过去分词”结构,它与 被动语态的形式完全一样,所以在应用时要注意它们的区别。
(1)被动语态中的过去分词多是动词,强调动作;系表结构中的过去分词相当于形容词,多强调状态
eg:The house was surrounded by the police. 被动语态,表示动作
这房子被警察包围了。
eg:My pen is gone.我的钢笔不见了。
系表结构,表示状态
被动语态的注意事项
4.被动语态和系表结构的区别
(2)被动语态常由介词by引出动作的发出者,而系表结构中常用其他介词,如 about,at,in,on, with, over,to等
eg:I was interested by what you showed me. 被动语态
你给我看的东西让我很感兴趣。
eg:I'm interested in the watch.
我对这块手表很感兴趣。 系表结构
(3)被动语态常用greatly,much等词修饰,系表结构常由very,quite, rather, too, so, more, most等词修饰
eg:I'm quite satisfied with your work. 系表结构
我对你的工作相当满意。
eg:We were greatly moved by what the little boy did. 被动语态
我们被那个小男孩的作为深深地感动了。
被动语态的注意事项
4.被动语态和系表结构的区别
(4)谓语动词带有时间、地点或方式状语时,一般是被动语态
eg:The door has already been locked. 门已经被锁上了。
被动语态
eg:The door is locked.
门锁上了。 系表结构
(5)被动语态一般由“助动词be+过去分词”构成。系表结构中be为系动词,而且除了be之外,还可用 become,get,keep,remain 等系动词
eg:She became interested in maths. 系表结构
她开始对数学感兴趣。
eg:The work remained unfinished.
这项工作依然未完成。 系表结构
被动语态的注意事项
4.被动语态和系表结构的区别
(6)被动语态可用于各种时一般时态和完成时态
eg:The machine is being repaired.
被动语态用于进行时态
正在修理机器。
eg:A new school will be built here.被动语态用于将来时态
将在这里建一所新学校。
【拓展】
在口语和非正式语体中,常用“get+过去分词”表示被动语态。这种结构一般只表示动作,用来谈论突然发生的事件。
eg:Be careful not to get burnt in the sun. 小心不要被太阳晒伤。
eg:I got caught in a heavy rain last night. 昨晚我淋了大雨。
practice
PART SIX
practice
语法填空
1. I had a strong desire to reach in and play with the toy,but _____ (hold) back thankfully by the shop window.
2. More expressways _____ (build) in Sichuan soon to promote the local economy.
3. Unless some extra money _____(find), the theatre will close.
4. The students have been working hard on their lessons and their efforts _____ (reward) with success in the end.
5. More efforts,as reported,_____ (make) in the years ahead to accelerate the supply-side structural reform.
语法填空
6. Despite the previous rounds of talks,no agreement _____ (reach) so far by the two sides.
7. -Did you enjoy the party?
-Yes.We _____ (treat) well by our hosts.
8. It is reported that a space station _____ (build) on the moon in years to come.
9. To my delight,I _____ (choose)from hundreds of applicants to attend the opening ceremony.
10. Shortly after he borrowedthis book,he _____ (call) to London to continue his research.
语法填空---答案
1.was held
【解析】根据题干中的 had a strong desire(一般过去时)可推知设空处需用一般过去时;主语1与hold back之间为被动关系,故用被动语态。综上所述答案为 was held。
2.will he built
【解析】根据题干中的soon可知设空处用一般将来时;expressways与build为被动关系,故用一般将来时的被动语态。
3.is found
【解析】由主句中的will可知unless引导的从句应用一般现在时态表将来,且 money和find之间是被动关系,故答案为is found。
语法填空---答案
4.will be rewarded
【解析】根据语境可知设空处需用一般将来时;their efforts与reward之间为被动关系,故用被动语态。综上所述,答案应为一般将来时的被动语态。
5.will be made
【解析】根据 in the years ahead并结合句意可知,动作发生在将来,故用一般将来时;主语more efforts与make为被动关系,故用被动语态。综上所述,答案为 will be made。
6.has been reached
【解析】考查动词的时态和语态。根据题干中的时间状语so far可知此处应该用现在完成时,而agreement与谓语动词之间为被动关系,所以要用现在完成时的被动语态。
语法填空---答案
7.were treated
【解析】本题考查动词的时态和语态。根据 对话内容可知所谈事情发生在过去,且主语we与 动词 treat之间为被动关系,故用一般过去时态的 被动语态。
8.will be built
【解析】本题考查动词的时态和语态。根据语境中的时间状语 in years to come 及 space station和build之间为被动关系可知这里用一般将来时态 的被动语态。
9.was chosen
【解析】本题考查时态和语态。主语I与choose为被动关系,设空处需用被动语态;又因为本题介绍的是过去的一种情况,应用一般过去时,故用一般过去时态的被动语态。
语法填空---答案
10.was called
【解析】根据 borrowed 可推知设空处需用一 般过去时,主语he与call为被动关系,故设空处需用一般过去时的被动语态。
谢谢
21世纪教育网(www.21cnjy.com)
中小学教育资源网站
兼职招聘:
https://www.21cnjy.com/recruitment/home/admin
